Spatial Rigid-Flexible-Liquid Coupling Dynamics of Towed System Analyzed by a Hamiltonian Finite Element Method
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Dynamic Modeling of Cable Element
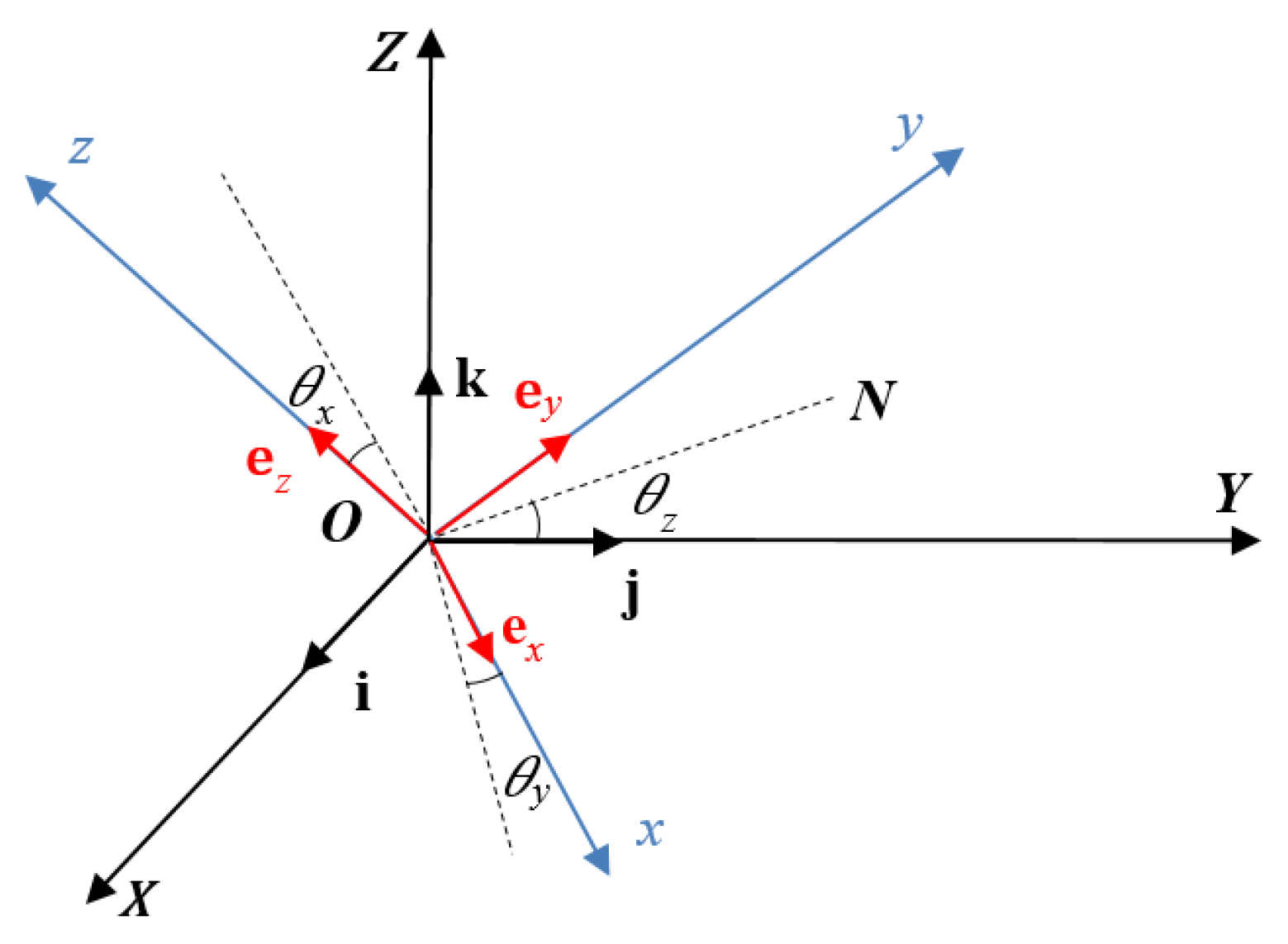
2.1. Three-Dimensional Tait-Bryan Transformation and Shape Function
- (1)
- Rotating OZ counterclockwise by an angle θz (0 ≤ θz < π) to overlap OY with ON, the new OY is perpendicular to the new OX, OZ and the local ox.
- (2)
- Rotating the new OY clockwise by an angle θy (0 ≤ θy < π) to overlap OX with the local ox.
- (3)
- Rotating the new OX counterclockwise by an angle θx (0 ≤ θx < π) to overlap OZ with the local oz and OY with the local oy.
2.2. Elemental Virtual Work and Elemental Matrix
2.3. Elemental Dynamic Equation in Canonical Form
3. Symplectic Integration Algorithm for Towed Cable-Payload System
3.1. Assembly of System Dynamic Equations
3.2. Symplectic Difference Algorithms
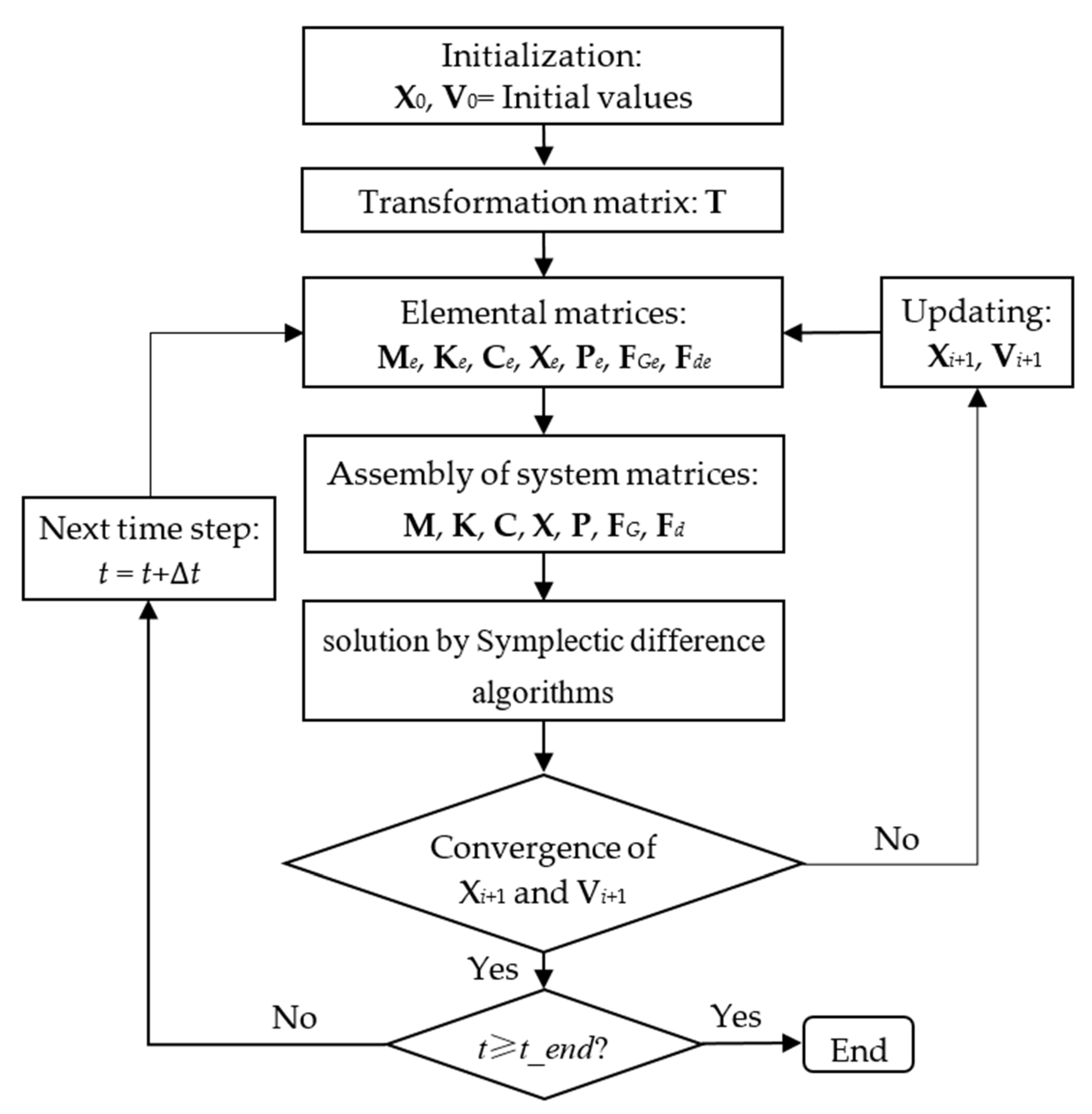
3.3. Initialization and Solution Procedure
4. Numerical and Experimental Validations
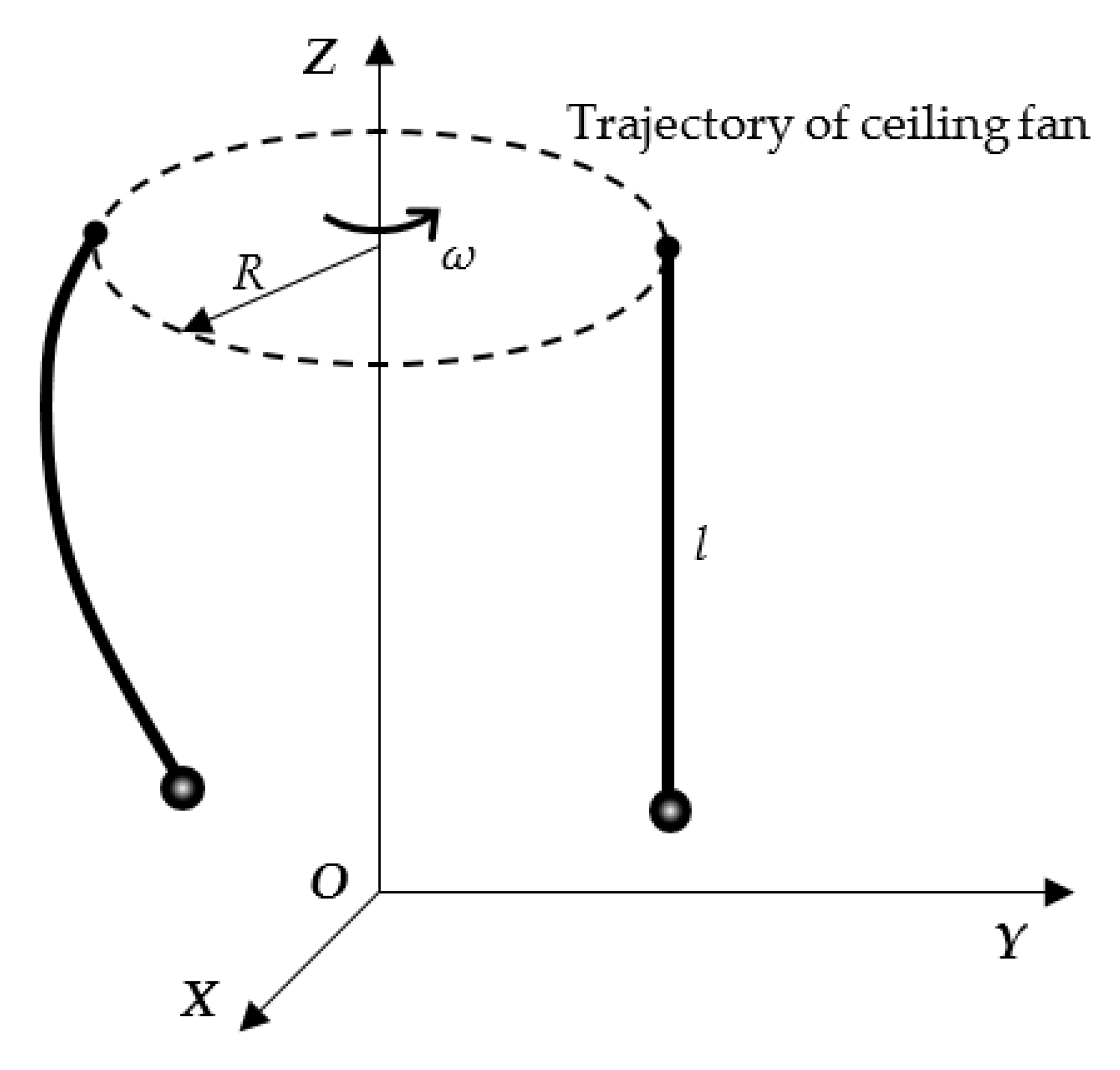
4.1. Flexible Conical Pendulum Modeling
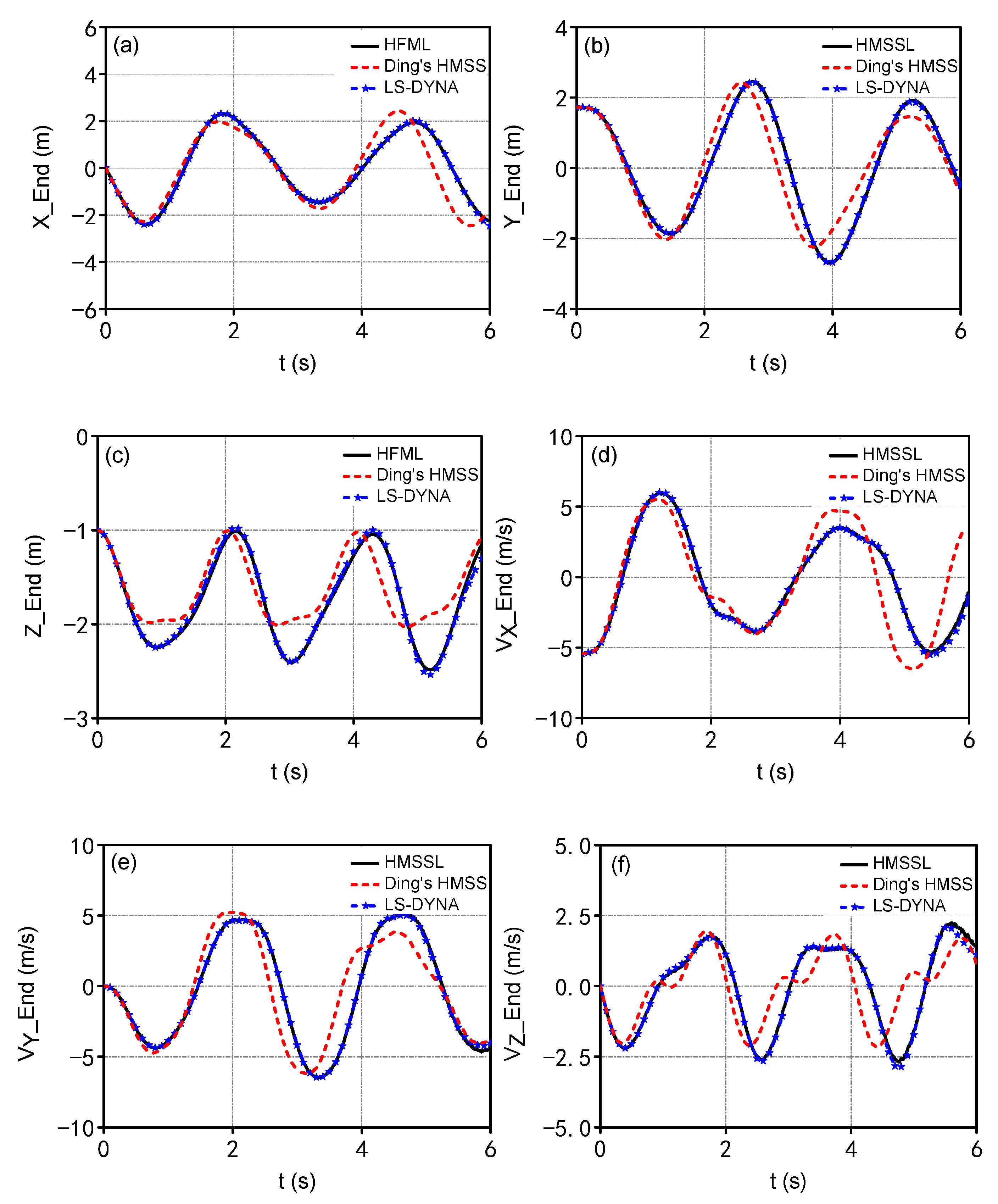
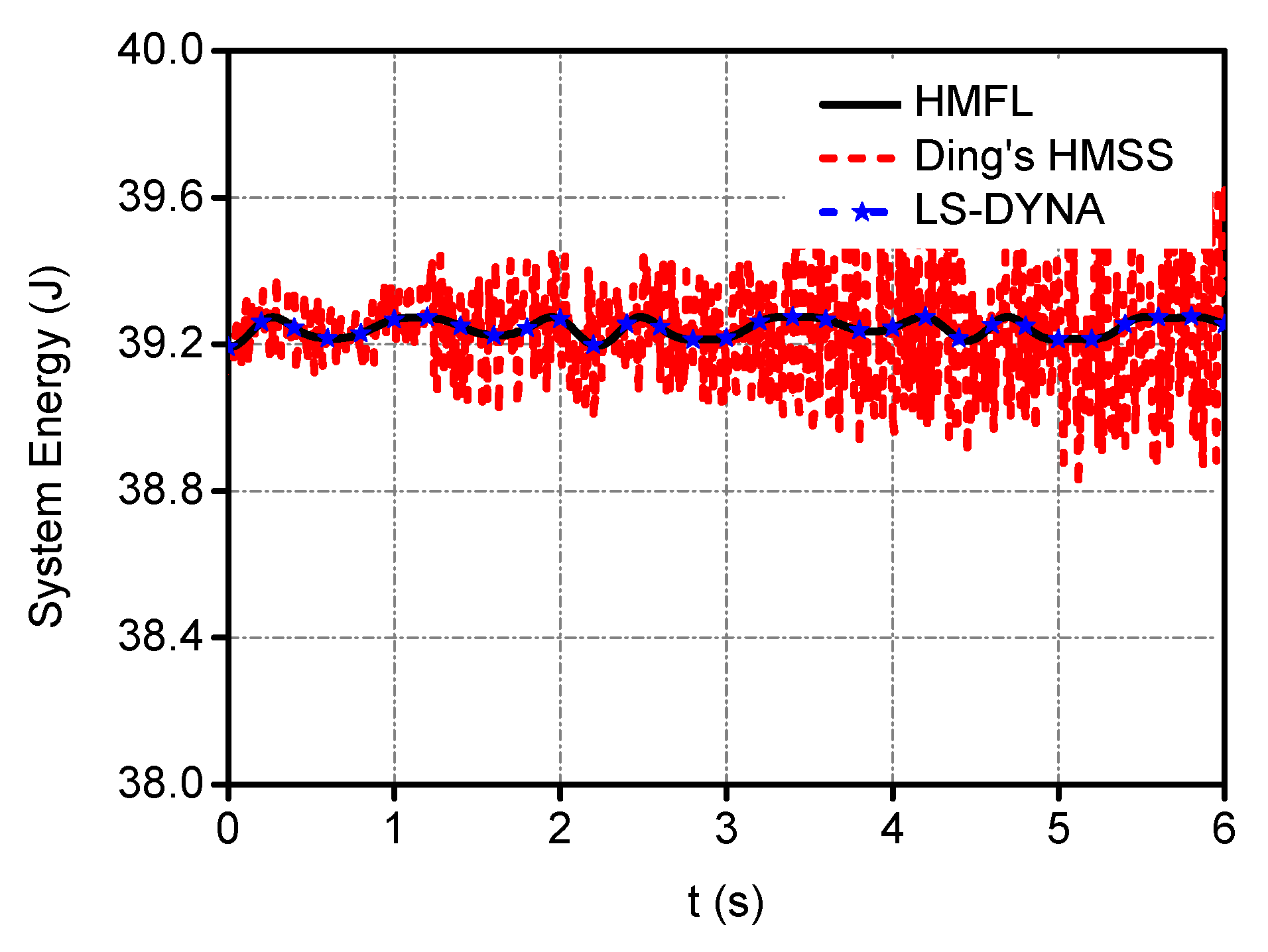
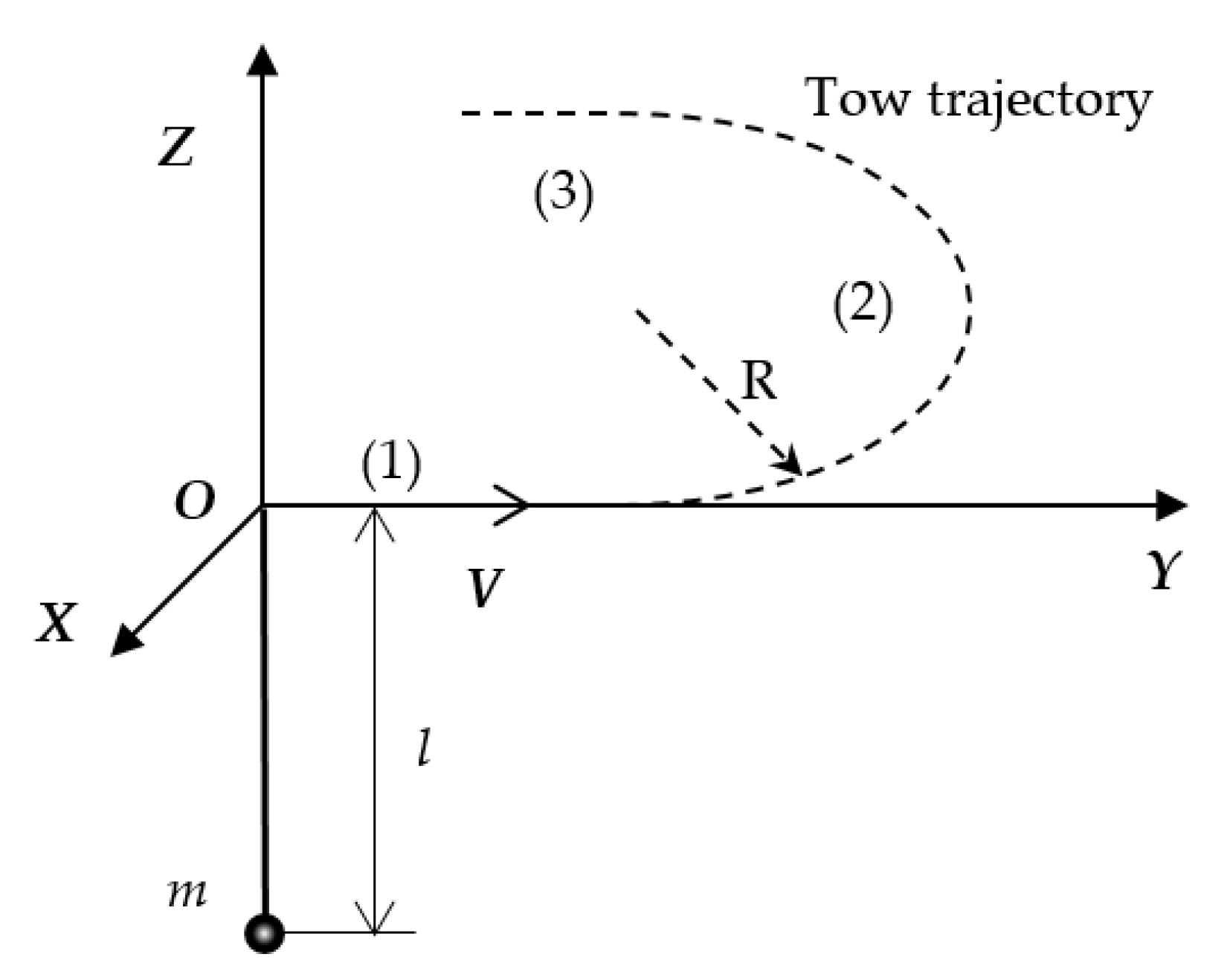
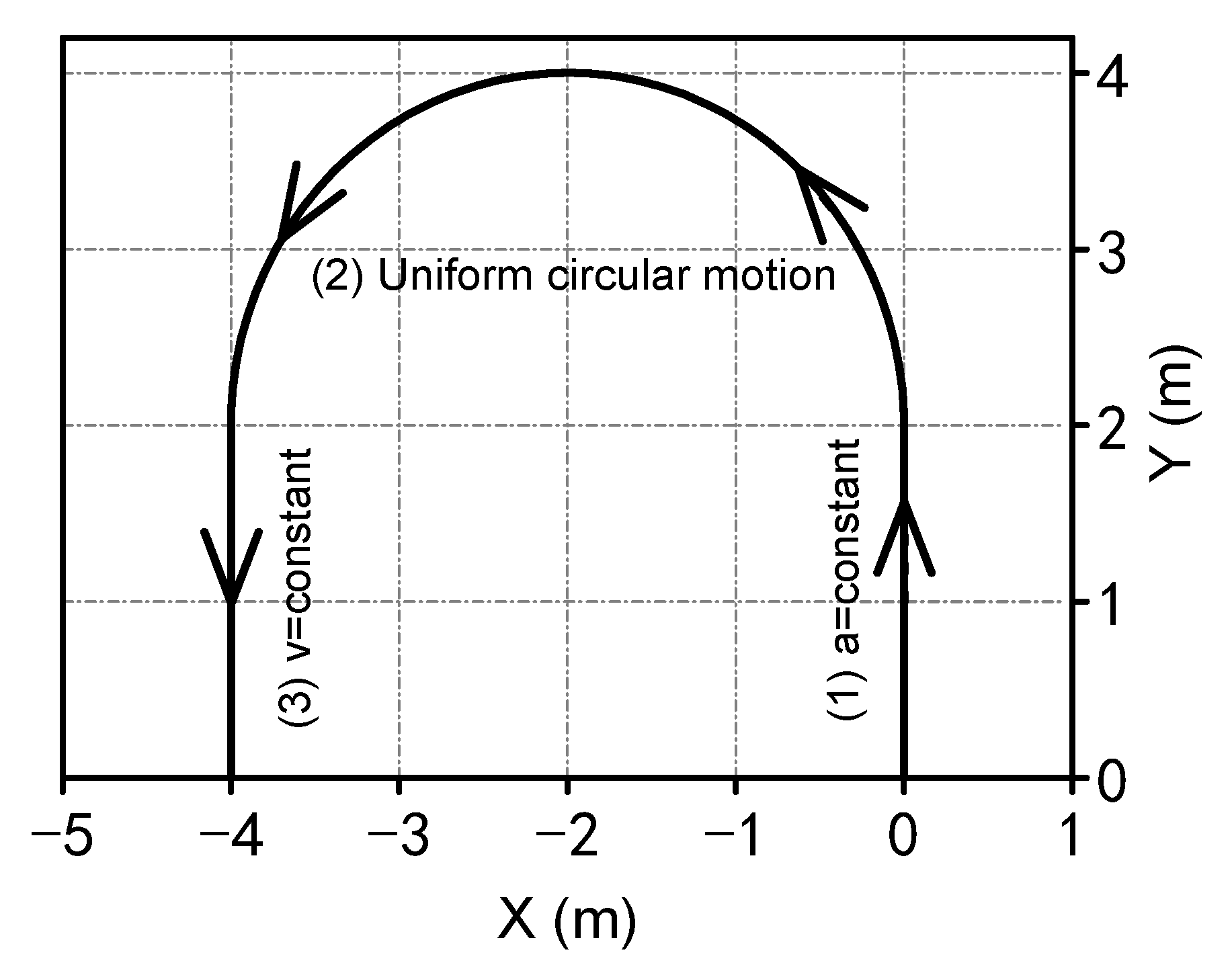
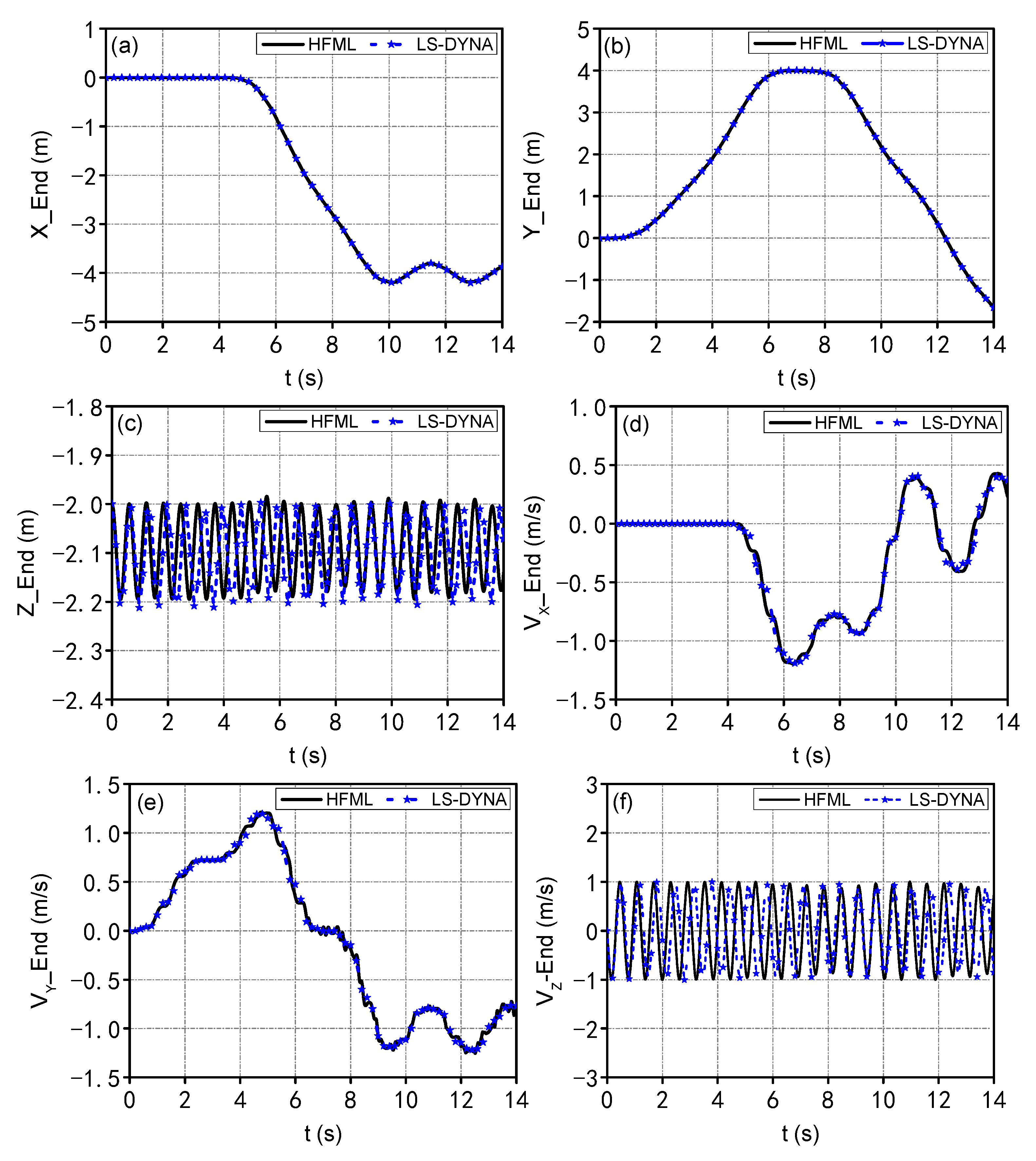
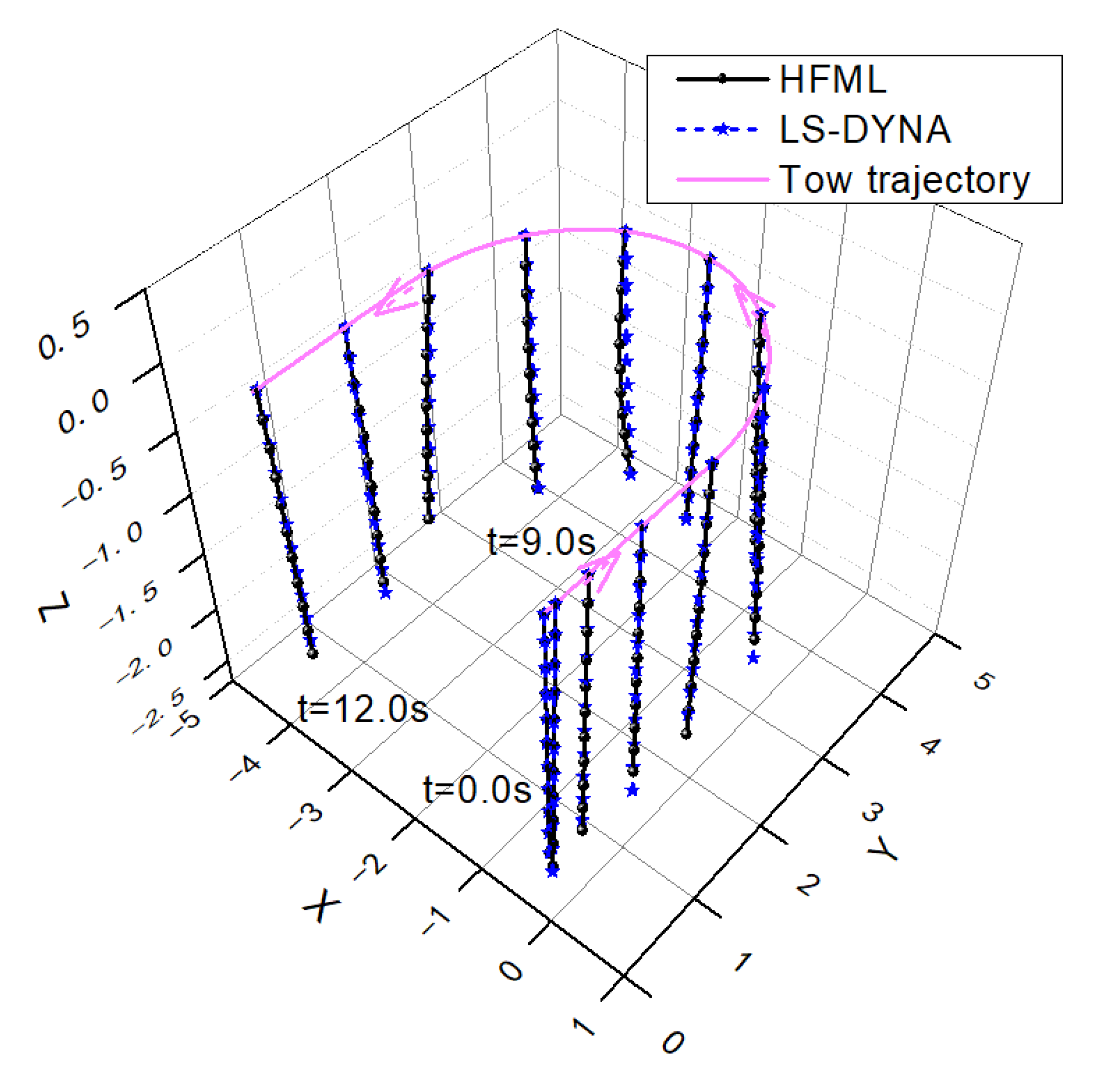
4.2. Towed Cable-Payload System in 180° U-Turn Maneuver
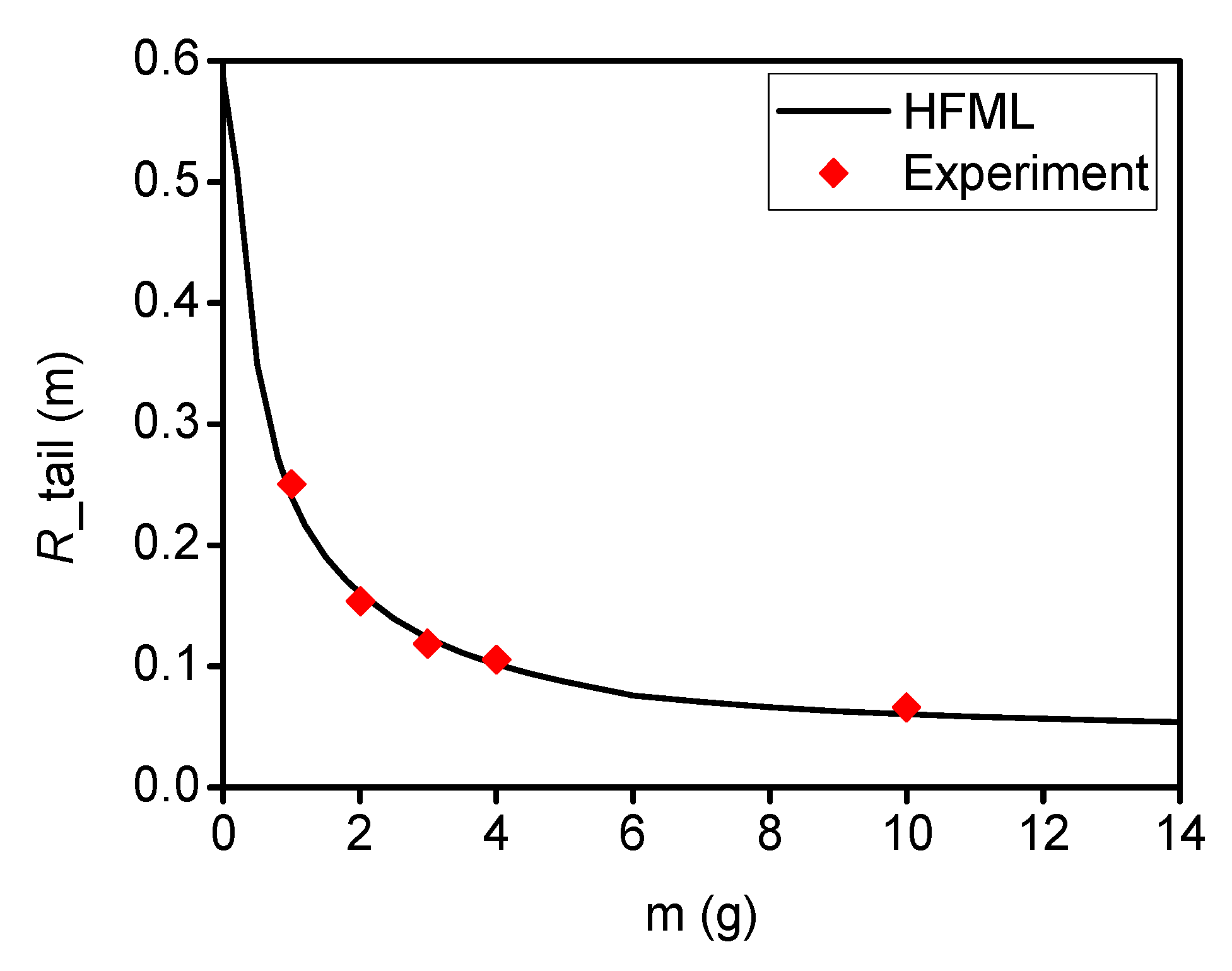
4.3. Experimental Validation of Circularly Towed System in Air
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Phillips, B.T.; Chaloux, N.; Shomberg, R.; Muoz-Soto, A.; Owens, J. The Fiber Optic Reel System: A Compact Deployment Solution for Tethered Live-Telemetry Deep-Sea Robots and Sensors. Sensors 2021, 21, 2526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.J.; He, X.Y.; Zhao, Z.J.; Ahn, C.K.; Li, H.X. Vibration Control for Spatial Aerial Refueling Hoses with Bounded Actuators. J. Mech. Eng. 2021, 68, 4209–4217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Z.; Liu, Y.; Luo, Z.; Han, X.; Wu, J.; Zhou, C. Study on the Transient Dynamic and Safety Analysis of Double Aircraft-towed Cables. J. Mech. Eng. 2018, 54, 86–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Razzaghi, P.; Al Khatib, E.; Bakhtiari, S.; Hurmuzlu, Y. Real time control of tethered satellite systems to de-orbit space debris. Aerosp. Sci. Technol. 2021, 109, 106379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Li, G.; Lian, L. Numerical model of towed cable body system validation from sea trial experimental data. Ocean Eng. 2021, 226, 108859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, H.; Yin, X.; Zhu, Z.H.; Zhang, L. A high accurate hamiltonian nodal position finite element method for spatial cable structures undergoing long-term large overall motion. Commu. Nonlinear Sci. 2019, 70, 203–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minowa, A.; Toda, M. A High-Gain Observer-Based Approach to Robust Motion Control of towed Underwater Vehicles. IEEE J. Ocean. Eng. 2019, 44, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, X.; Cui, H.; Zhang, Z. A numerical method for analyzing the influence of underwater vehicle flow field on dynamic behavior of towed sonar cable array. Ocean Eng. 2019, 175, 163–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, H.B.; Chen, G.Q.; Lin, W.J. A hydrodynamic model of bridle towed system. J. Mar. Sci. Technol. 2019, 24, 200–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez Luis, A.; Antonio Armesto, J.; Guanche, R.; Barrera, C.; Vidal, C. Simulation of Marine Towing Cable Dynamics Using a Finite Elements Method. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2020, 8, 140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dehadrai, A.R.; Sharma, I.; Gupta, S.S. Three-Dimensional Dynamics of Towed Underslung Systems Using Geometrically Exact Beam Theory. AIAA J. 2021, 59, 1469–1482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Htun, T.Z.; Suzuki, H.; Garcia-Vallejo, D. Dynamic modeling of a radially multilayered tether cable for a remotely-operated underwater vehicle (ROV) based on the absolute nodal coordinate formulation (ANCF). Mech. Mach. Theory 2020, 153, 103961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Z.H. Dynamic modeling of cable system using a new nodal position finite element method. Int. J. Numer. Methods Biomed. Eng. 2010, 26, 692–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, F.J.; Zhu, Z.H.; LaRosa, M. Dynamic modeling of cable towed body using nodal position finite element method. Ocean Eng. 2011, 38, 529–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Zhu, Z. Long-term dynamic modeling of tethered spacecraft using nodal position finite element method and symplectic integration. Celest. Mech. Dyn. Astron. 2015, 123, 363–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, H.; Zhu, Z.H.; Yin, X.; Zhang, L.; Li, G.; Hu, W. Hamiltonian nodal position finite element method for cable dynamics. Int. J. Appl. Mech. 2017, 9, 1750109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Ding, H.P.; Deng, H.H.; Zhang, M. Analysis of nonlinear dynamic response of spatial flexible tether system by Symplectic difference scheme. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2019, 1324, 012048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Feng, K.; Qin, M. Symplectic Geometric Algorithms for Hamiltonian Systems; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Bazzoni, G.; Freibert, M.; Latorre, A.; Meinke, B. Complex symplectic structures on Lie algebras. J. Pure Appl. Algebra 2021, 225, 106585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leung, A.; Mao, S. A symplectic Galerkin method for non-linear vibration of beams and plates. J. Sound Vib. 1995, 183, 475–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, N.F.; Deng, Z.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, K. A symplectic Runge-Kutta method for the analysis of the tethered satellite system. Multidiscip. Model. Mater. Struct. 2017, 13, 26–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheng, F.; Zhong, Z.; Wang, K.H. Theory and model implementation for analyzing line structures subject to dynamic motions of large deformation and elongation using the absolute nodal coordinate formulation (ANCF) approach. Nonlinear Dyn. 2020, 101, 333–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chucheepsakul, S.; Monprapussorn, T.; Huang, T. Large strain formulations of extensible flexible marine pipes transporting fluid. J. Fluid Struct. 2003, 17, 185–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.S.; Yao, B.H.; Ren, P. Dynamics calculation for underwater moving slender bodies based on flexible segment model. Ocean Eng. 2013, 57, 111–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greco, M.; Ferreira, I.P. Logarithmic strain measure applied to the nonlinear positional formulation for space truss analysis. Finite Elem. Anal. Des. 2009, 45, 632–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, F.J. Elastodynamic Analysis of Towed Cable Systems by a Novel Nodal Position Finite Element Method. Master’s Thesis, York University, Toronto, ON, Canada, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Vinod, P.; Francis, R.; Prabhasuthan, P.; Nandagopan, O.R. Depth Enhancement of an Underwater Towed System using Hydrodynamic Depressor. Def. Sci. J. 2016, 66, 546–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xucheng, W. Finite Element Method; Tsinghua University Press: Beijing, China, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Xiao, L.; Liu, Q.; Lu, J. Analysis on longitudinal vibration law of deep sea stepped mining pipe. Aip Adv. 2020, 10, 125302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Leonard, J.W. Dynamics of ocean cables with local low-tension regions. Ocean Eng. 1998, 25, 443–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buckham, B.; Driscoll, F.R.; Nahon, M. Development of a finite element cable model for use in low-tension dynamics simulation. J. Appl. Mech. 2004, 71, 476–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krylov, V.I.; Stroud, A.H. Approximate Calculation of Integrals; Dover Publications: New York, NY, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Dash, R.; Mohanty, S.; Rout, T. Evaluation of Non Linear Response of Beams by Symplectic Integration Method. Int. J. Eng. 2010, 2, 119–134. [Google Scholar]
- Feng, K.; Qin, M. The Symplectic Methods for the Computation of Hamiltonian Equations; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1987. [Google Scholar]
- Feng, K.; Meng-Zhao, Q. Hamiltonian algorithms for Hamiltonian systems and a comparative numerical study. Comput. Phys. Commu. 1991, 65, 173–187. [Google Scholar]
- Ruth, R.D. A canonical integration technique. IEEE Trans. Nucl. Sci. 1983, 30, 2669–2671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simo, J.; Tarnow, N.; Doblare, M. Non-linear dynamics of three-dimensional rods: Exact energy and momentum conserving algorithms. Int. J. Numer. Meth. Eng. 1995, 38, 1431–1473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; He, L.; Shuai, C.; Zhou, S.-T.; Zhang, S.-K. Experimental study on U-turn maneuver of underwater towed cable system. J. Nav. Univ. Eng. 2018, 30, 26–31. [Google Scholar]
- Williams, P.; Lapthorne, P.; Trivailo, P. Circularly-towed lumped mass cable model validation from experimental data. AIAA Model. Simul. Technol. 2006, 6817, 1–29. [Google Scholar]
- Lapthorne, P. Experimental Study on Circularly Towed Aerial Tethers. Master’s Thesis, Royal Melbourne Institute of Technology University, Melbourne, Australia, 2012. [Google Scholar]

Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ding, H.; Wang, Q.; Hu, W.; Yin, X. Spatial Rigid-Flexible-Liquid Coupling Dynamics of Towed System Analyzed by a Hamiltonian Finite Element Method. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2021, 9, 1157. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse9111157
Ding H, Wang Q, Hu W, Yin X. Spatial Rigid-Flexible-Liquid Coupling Dynamics of Towed System Analyzed by a Hamiltonian Finite Element Method. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering. 2021; 9(11):1157. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse9111157
Chicago/Turabian StyleDing, Huaiping, Qiao Wang, Wei Hu, and Xiaochun Yin. 2021. "Spatial Rigid-Flexible-Liquid Coupling Dynamics of Towed System Analyzed by a Hamiltonian Finite Element Method" Journal of Marine Science and Engineering 9, no. 11: 1157. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse9111157
APA StyleDing, H., Wang, Q., Hu, W., & Yin, X. (2021). Spatial Rigid-Flexible-Liquid Coupling Dynamics of Towed System Analyzed by a Hamiltonian Finite Element Method. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering, 9(11), 1157. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse9111157





