Effect of Temperature Fluctuation and Nutritional Status on Starry Flounder, Platichthys stellatus, Survival and Adaptive Physiological Response
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Fish and Rearing Conditions
2.2. Experimental Design
2.3. Sampling
2.4. Biochemical Analysis
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
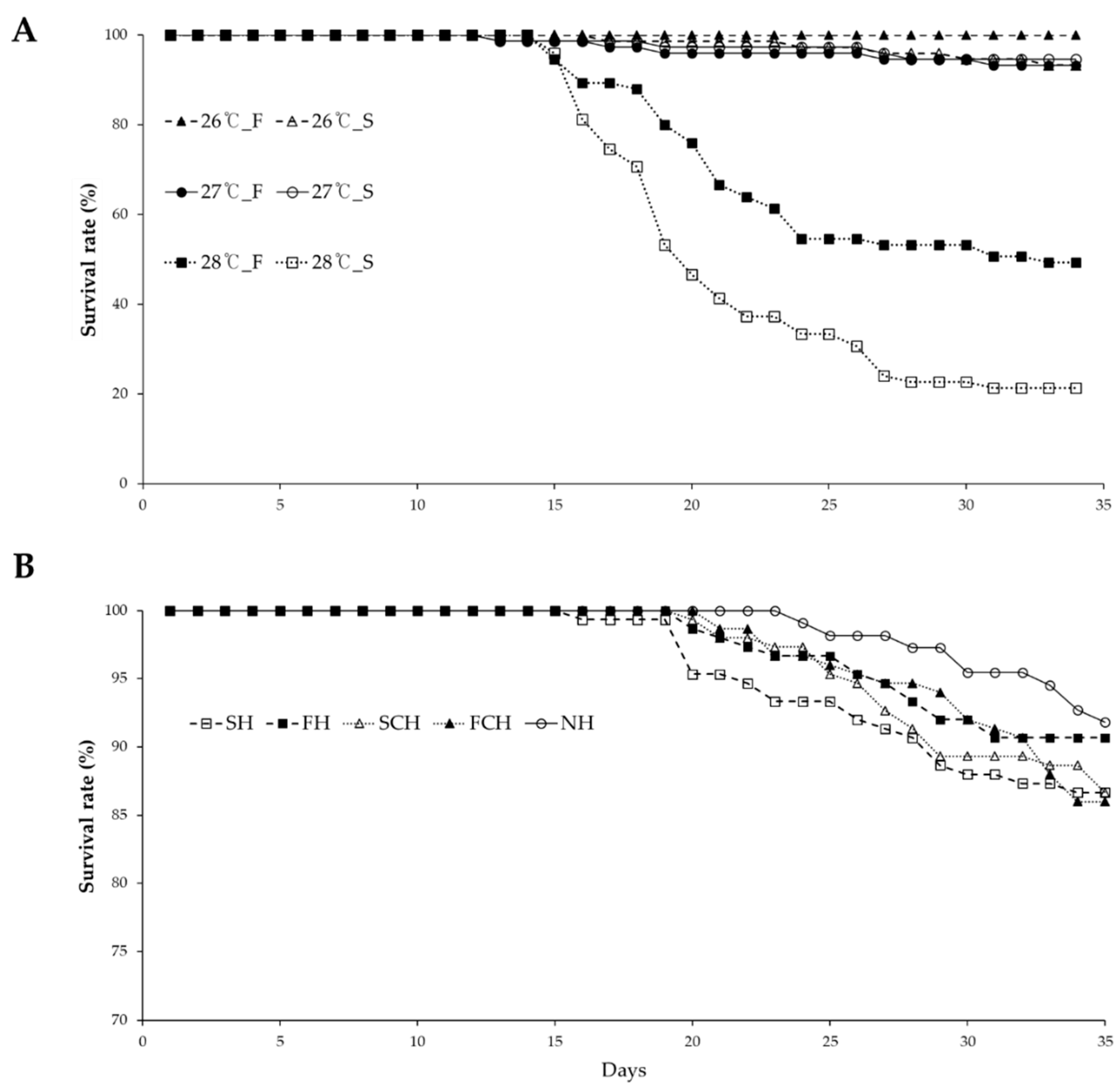
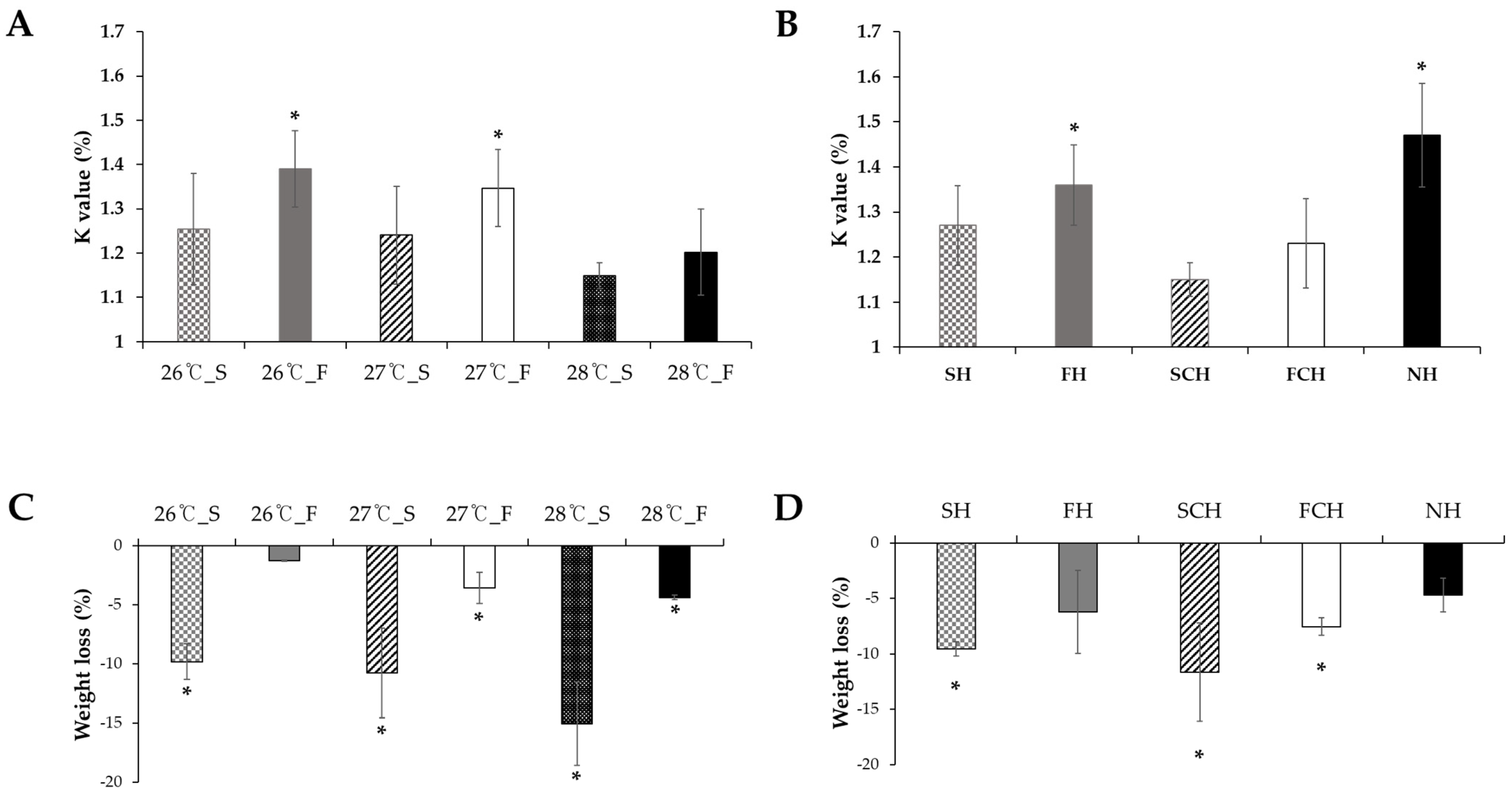
3.1. Survival Rate, Condition Factor, and Weight Loss
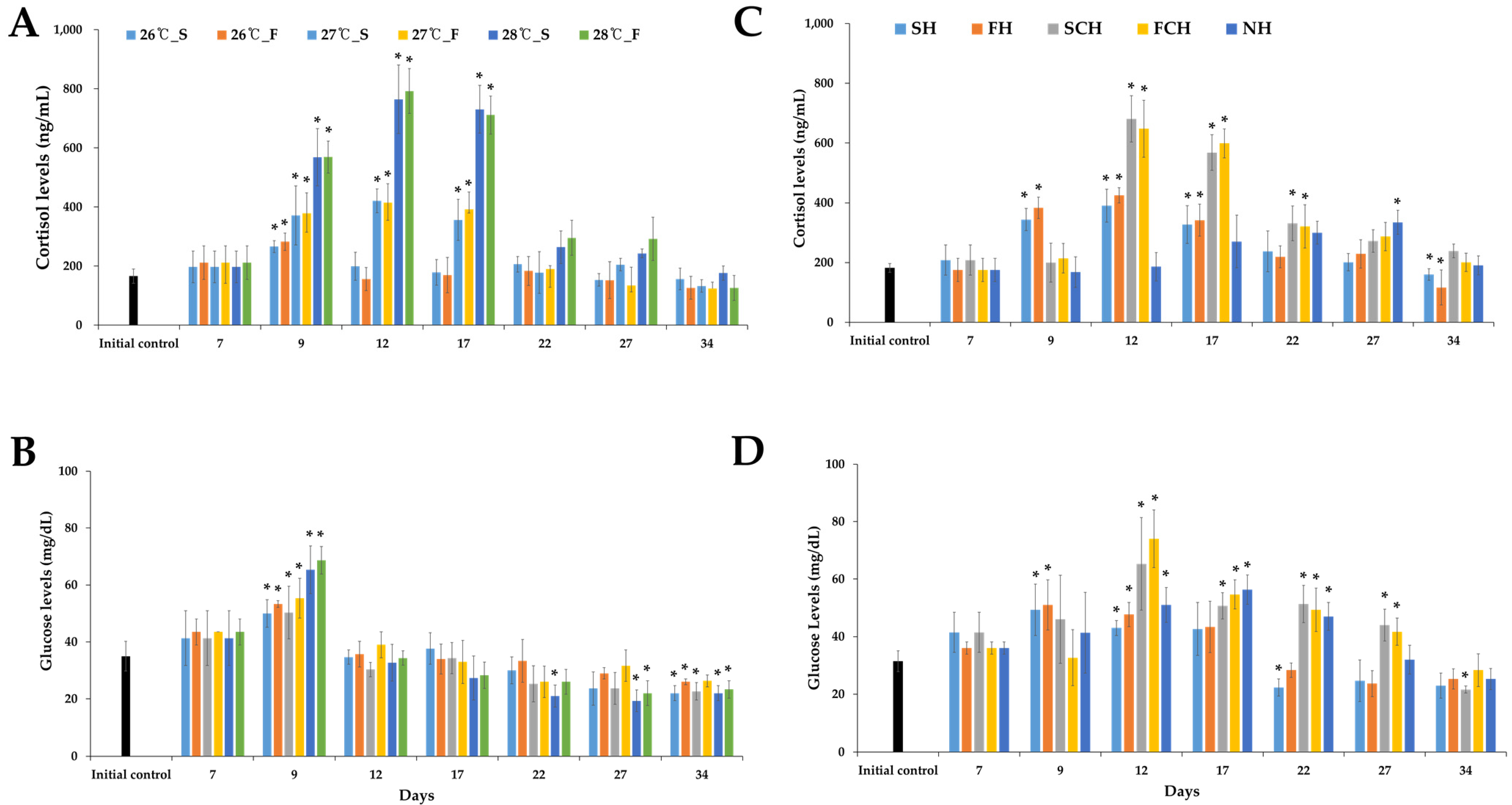
3.2. Glucose and Cortisol Level in Plasma
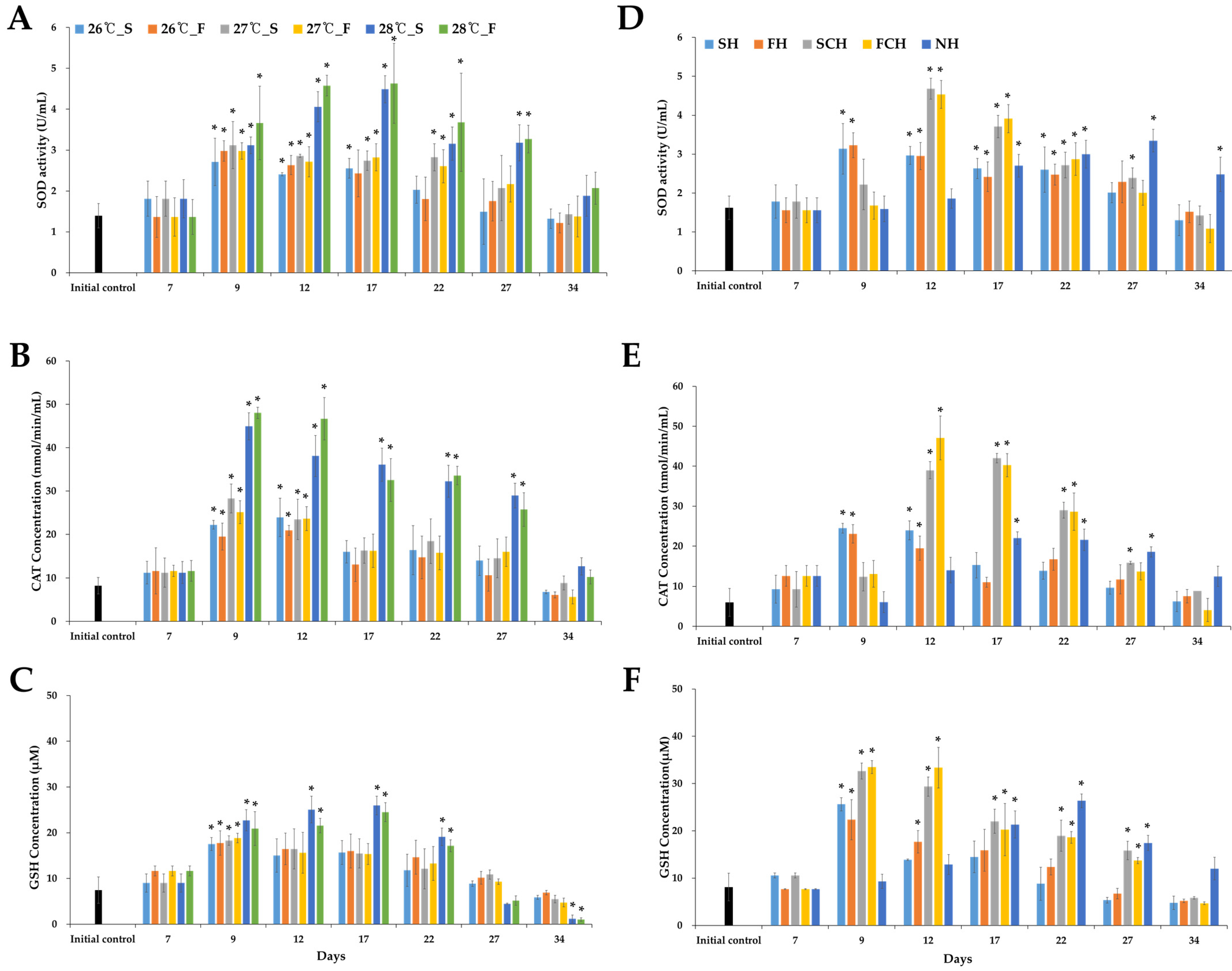
3.3. Antioxidant Activity (SOD, CAT, and GSH)
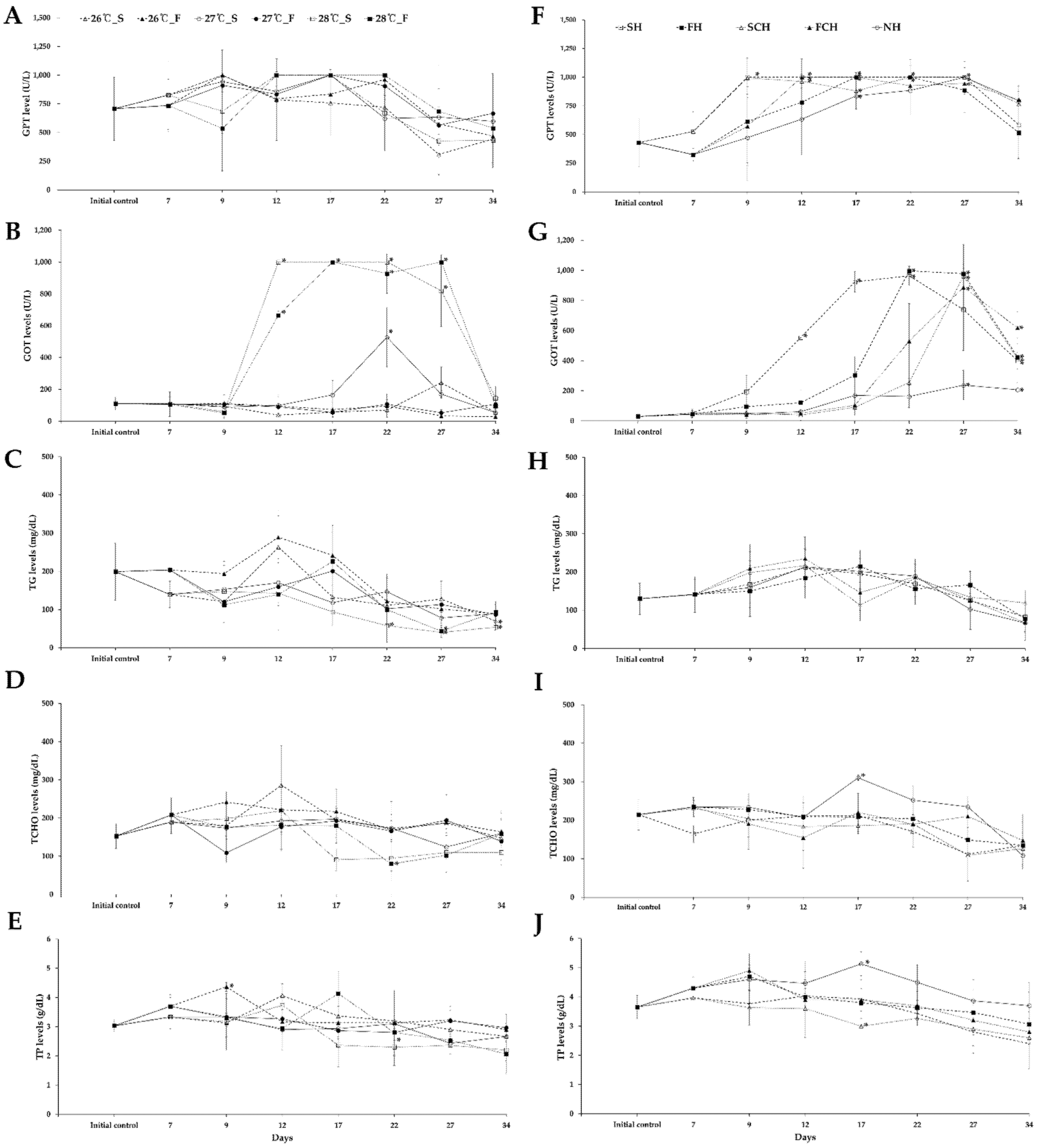
3.4. Biochemical Analysis in Plasma
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lim, H.K.; Byun, S.G.; Lee, J.H.; Park, S.U.; Kim, Y.C.; Han, H.K.; Min, B.H.; Lee, B.Y. Sexual maturity an reproductive cycle of starry flounder Platichthys stellatus cultured in indoor tank. J. Aquac. 2007, 20, 212–218. [Google Scholar]
- Lim, H.K.; Min, B.H.; Kwon, M.G.; Byun, S.-G.; Park, M.S.; Jeong, M.H.; Kim, Y.S.; Chang, Y.J. Blood physiological responses and growth of juvenile starry flounder, Platichthys stellatus exposed to different salinities. J. Environ. Biol. 2013, 34, 885–890. [Google Scholar]
- Min, B.H.; Park, M.S.; Myeong, J.-I. Stress responses of starry flounder, Platichthys stellatus (Pallas) following water temperature rise. J. Environ. Biol. 2015, 36, 1057–1062. [Google Scholar]
- Mustafa, S.; Mittal, A. Protein, RNA and DNA levels in liver and brain of starved catfish, Clarias batrachus. J. Ichthyol. 1982, 28, 396–400. [Google Scholar]
- Weatherley, A.H.; Gill, H.S. The Biology of Fish Growth, vol. Protein, Lipid and Caloric Contents; Academic Press: London, UK, 1987; pp. 139–146. [Google Scholar]
- Hur, J.W.; Jo, J.H.; Park, I.S. Effects of long-term starvation on hepatocyte ultrastructure of olive flounder Paralichthys olivaceus. Ichthyol. Res. 2006, 53, 306–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alderdice, D.F.; Forrester, C.R. Effects of Salinity, Temperature, and Dissolved Oxygen on Early Development of the Pacific Cod (Gadus macrocephalus). J. Fish. Res. Board Can. 1971, 28, 883–902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Y.; Zhang, G.; Liu, J.; Zang, W. Effects of temperature and salinity on oxygen consumption of tawny puffer Takifugu flavidus juvenile. Aquac. Res. 2011, 42, 301–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neubauer, P.; Andersen, K.H. Thermal performance of fish is explained by an interplay between physiology, behaviour and ecology. Conserv. Physiol. 2019, 7, coz25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Staples, J.F. Metabolic flexibility: Hibernation, torpor, and estivation. Compr. Physiol. 2016, 6, 737–771. [Google Scholar]
- Brett, J.R. Environmental Factors and Growth. In Fish Physiology; Hoar, W.S., Randall, D.J., Brett, J.R., Eds.; Academic Press: London, UK, 1979; Volume VIII, pp. 599–677. [Google Scholar]
- Gadomski, D.M.; Caddell, S.M. Effects of temperature on early-life-history stages of California halibut Paralichthys californicus. Fish. Bull. 1991, 89, 567–576. [Google Scholar]
- FAO. The State of World Fisheries and Aquaculture Sustainability in Action; FAO: Rome, Italy, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Ministry of Environment. Korean Climate Change Assessment Report 2020 (in Korea); Ministry of Environment: Sejong City, Korea, 2020.
- De Silva, S.S.; Soto, D. Climate change and aquaculture: Potential impacts, adaptation and mitigation. In Climate Change Implications for Fisheries and Aquaculture: Overview of Current Scientific Knowledge; FAO Fisheries and Aquaculture Technical Paper. No. 530; Cochrane, K., De Young, C., Soto, D., Bahri, T., Eds.; FAO: Rome, Italy, 2009; pp. 151–212. [Google Scholar]
- Freeman, E.O. Impact of climate change on aquaculture and fisheries in Nigeria: A review. Int. J. Multidiscipl. Res. Dev. 2017, 4, 53–59. [Google Scholar]
- Adhikari, S.; Keshav, C.A.; Barlaya, G.; Rathod, R.; Mandal, R.N.; Ikmail, S.; Saha, G.S.; De, H.K.; Sivaraman, I.; Mahapatra, A.S.; et al. Adaptation and mitigation strategies of climate change impact in freshwater aquaculture in some states of India. J. Fish. 2018, 12, 16–21. [Google Scholar]
- Barroso, J.B.; Saltuero, G.L.; Peragon, J.; de la Higuera, M.; Lupianez, J.A. Effects of long-term starvation on the NADPH production systems in several different tissues of rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss). In Fish Nutrition in Practice; Kaushik, S.J., Luquet, P., Eds.; INRA: Paris, France, 1993; pp. 333–338. [Google Scholar]
- Bastrop, R.; Jürss, K.; Wacke, R. Biochemical parameters as a measure of food availability and growth in immature rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss). Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part A Physiol. 1992, 102, 151–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Y.J.; Sun, X.J.; Ahang, S.L.; Fu, C.D.; Jiang, Z.Q. The effects of starvation and refeeding on growth and ingestion is Starry flounder, Platichthys stellatus. Fish. Sci. 2011, 30, 125–131. [Google Scholar]
- Segner, H.; Möller, H. Electron microscopical investigations on starvation-induced liver pathology in flounders Platichthys flesus. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 1984, 19, 193–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, A.; Fletcher, T.C. Serum cortisol, glucose and lipids in plaice (Pleuronectes platessa L.) exposed to starvation and aquarium stress. Comp. Bioche. Physiol. 1986, 84, 649–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heming, T.A.; Paleczny, E.J. Compositional changes in skin mucus and blood serum during starvation of trout. Aquaculture 1987, 66, 265–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caruso, G.; Denaro, M.G.; Caruso, R.; Genovese, L.; Mancari, F.; Maricchiolo, G. Short fasting and refeeding in red porgy (Pagrus pagrus, Linnaeus 1958): Response of some haematological, biochemical and non-specific immune parameters. Mar. Environ. Res. 2012, 81, 18–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nordberg, J.; Arnér, E.S.J. Reactive oxygen species, antioxidants, and the mammalian thioredoxin system. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2001, 31, 1287–1312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez-Álvarez, R.; Morales, A.; Sanz, A. Antioxidant defences in fish: Biotic and abiotic factors. Rev. Fish Biol. Fish. 2005, 15, 75–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grim, J.M.; Miles, D.R.B.; Crockett, E.L. Temperature acclimation alters oxidative capacities and composition of membrane lipids without influencing activities of enzymatic antioxidants or susceptibility to lipid peroxidation in fish muscle. J. Exp. Biol. 2010, 213, 445–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Barton, B.A.; Iwama, G.K. Physiological changes in fish from stress in aquaculture with emphasis on the response and effects of corticosteroids. Annu. Rev. Fish Dis. 1991, 1, 3–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pacheco, M.; Santos, M.A. Biotransformation, Endocrine, and Genetic Responses of Anguilla anguilla L. to Petroleum Distillate Products and Environmentally Contaminated Waters. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2001, 49, 64–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Samaras, A.; Papandroulakis, N.; Lika, K.; Pavlidis, M. Water temperature modifies the acute stress response of European sea bass, Dicentrarchus labrax L. (1758). J. Therm. Biol. 2018, 78, 84–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, L.; Zhang, L.; Wang, J.; Ma, J.; Meng, X.; Duan, P.; Sun, L.; Sun, Y. Effect of dietary lipid level on the growth performance, feed utilization, body composition and blood chemistry of juvenile starry flounder (Platichthys stellatus). Aquac. Res. 2010, 41, 1470–1478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.; Wang, J.; Zhang, D.; Hao, T.; Sun, J.; Sun, Y.; Zhang, L. Estimation of optimum docosahexaenoic to eicosapentaenoic acid ratio (DHA/EPA) for juvenile starry flounder, Platichthys stellatus. Aquaculture 2014, 433, 105–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Li, B.; Ma, J.; Wang, S.; Huang, B.; Sun, Y.; Zhang, L. Optimum dietary protein to lipid ratio for starry flounder (Platichthys stellatus). Aquac. Res. 2017, 48, 189–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Htun-Han, M. The reproductive biology of the dab Limanda limanada (L.) in the North Sea: Gonadosomatic index, hepatosomatic index and condition factor. J. Fish. Biol. 1978, 13, 351–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Byun, S.G.; Nam, M.M.; Lee, B.I.; Lee, J.H.; Kim, Y.C. Manual of Starry Flounder Culture; National Institute Fisheries Science: Busan, Korea, 2009; pp. 1–131. [Google Scholar]
- Tang, U.M.; Muchlisin, Z.A.; Syawal, H.; Masjudi, H. Effect of water temperature on the physiological stress and growth performance of tapah (Wallago leeri) during domestication. Arch. Pol. Fish. 2017, 25, 165–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Withers, P.C. Comparative Animal Physiology; Brooks/Cole, Thompson Learning: Pacific Grove, CA, USA, 1992; p. 949. [Google Scholar]
- Le Cren, E.D. The length-weight relationships and seasonal cycle in gonad weight and condition in the perch (Perca fluviatilis). J. Anim. Ecol. 1951, 20, 201–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Willmer, P.; Stone, J.; Johnston, I. Environmental Physiology of Animals; Wiley-Blackwell: Malden, MA, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Cowey, C.B.; Walton, M. Intermediary metabolism. In Fish Nutrition; Halver, J.E., Ed.; Academic Press: New York, NY, USA, 1989; pp. 259–329. [Google Scholar]
- Roh, H.; Kim, A.; Kim, N.; Lee, Y.; Kim, D.H. Multi-Omics Analysis Provides Novel Insight into Immuno-Physiological Pathways and Development of Thermal Resistance in Rainbow Trout Exposed to Acute Thermal Stress. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 9198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shim, K.S.; Hwang, K.T.; Sonand, M.W.; Park, G.H. Lipid Metabolism and peroxidation in broiler chicks under chronic heat stress. Asian-Australas. J. Anim. Sci. 2006, 19, 1206–1211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hooda, O.K.; Upadhyay, R.C. Physiological responses, growth rate and blood metabolites under feed restriction and thermal exposure in kids. J. Stress Physiol. Biochem. 2014, 10, 214–227. [Google Scholar]
- Peres, H.; Santos, S.; Oliva-Teles, A. Selected plasma biochemistry parameters in gilthead seabream (Sparus aurata) juveniles. J. Appl. Ichthyol. 2012, 29, 630–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fazio, F.; Ferrantelli, V.; Piccione, G.; Saoca, C.; Levanti, M.; Mucciardi, M. Biochemical and hematological parameters in European sea bass (Dicentrarchus labrax Linnaeus, 1758) and Gilthead sea bream (Sparus aurata Linnaeus, 1758) in relation to temperature. Veter. Arh. 2018, 88, 397–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Echevarría, G.; Bebiá, M.M.; Zamora, S. Evolution of Biometric Indices and Plasma Metabolites during Prolonged Starvation in European Sea Bass (Dicentrarchus labrax, L.). Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part A Physiol. 1997, 118, 111–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez-Casanova, J.C.; Afonso, L.O.B.; Johnson, S.C.; Currie, S.; Gamperl, A.K. The stress and metabolic responses of juvenile Atlantic cod Gadus morhua L. to an acute thermal challenge. J. Fish Biol. 2008, 72, 899–916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- LeBlanc, S.; Middleton, S.; Gilmour, K.M.; Currie, S. Chronic social stress impairs thermal tolerance in the rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss). J. Exp. Biol. 2011, 214, 1721–1731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yeh, C.-M.; Glöck, M.; Ryu, S. An Optimized Whole-Body Cortisol Quantification Method for Assessing Stress Levels in Larval Zebrafish. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e79406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cockrem, J.F.; Bahry, M.A.; Chowdhury, V.S.; Chowdhury, V.S. Cortisol responses of goldfish (Carassius auratus) to air exposure, chasing, and increased water temperature. Gen. Comp. Endocrinol. 2019, 270, 18–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madeira, D.; Narciso, L.; Cabral, H.; Vinagre, C.; Diniz, M. Influence of temperature in thermal and oxidative stress responses in estuarine fish. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part A Mol. Integr. Physiol. 2013, 166, 237–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hermes-Lima, M. Oxygen in biology and biochemistry: Role of free radicals. In Functional Metabolism: Regulation and Adaptation; Storey, K.B., Ed.; Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2004; pp. 319–368. [Google Scholar]

Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kim, S.-S.; Han, G.-S.; Yoo, H.-K.; Kim, K.-T.; Byun, S.-G.; Jung, M.-M.; Kim, W.-J.; Hwang, S.-D. Effect of Temperature Fluctuation and Nutritional Status on Starry Flounder, Platichthys stellatus, Survival and Adaptive Physiological Response. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2021, 9, 1361. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse9121361
Kim S-S, Han G-S, Yoo H-K, Kim K-T, Byun S-G, Jung M-M, Kim W-J, Hwang S-D. Effect of Temperature Fluctuation and Nutritional Status on Starry Flounder, Platichthys stellatus, Survival and Adaptive Physiological Response. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering. 2021; 9(12):1361. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse9121361
Chicago/Turabian StyleKim, So-Sun, Gyeong-Sik Han, Hae-Kyun Yoo, Ki-Tae Kim, Soon-Gyu Byun, Min-Min Jung, Woo-Jin Kim, and Sung-Don Hwang. 2021. "Effect of Temperature Fluctuation and Nutritional Status on Starry Flounder, Platichthys stellatus, Survival and Adaptive Physiological Response" Journal of Marine Science and Engineering 9, no. 12: 1361. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse9121361
APA StyleKim, S.-S., Han, G.-S., Yoo, H.-K., Kim, K.-T., Byun, S.-G., Jung, M.-M., Kim, W.-J., & Hwang, S.-D. (2021). Effect of Temperature Fluctuation and Nutritional Status on Starry Flounder, Platichthys stellatus, Survival and Adaptive Physiological Response. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering, 9(12), 1361. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse9121361





