Fault Detection Based on Fully Convolutional Networks (FCN)
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Illustration of FCN
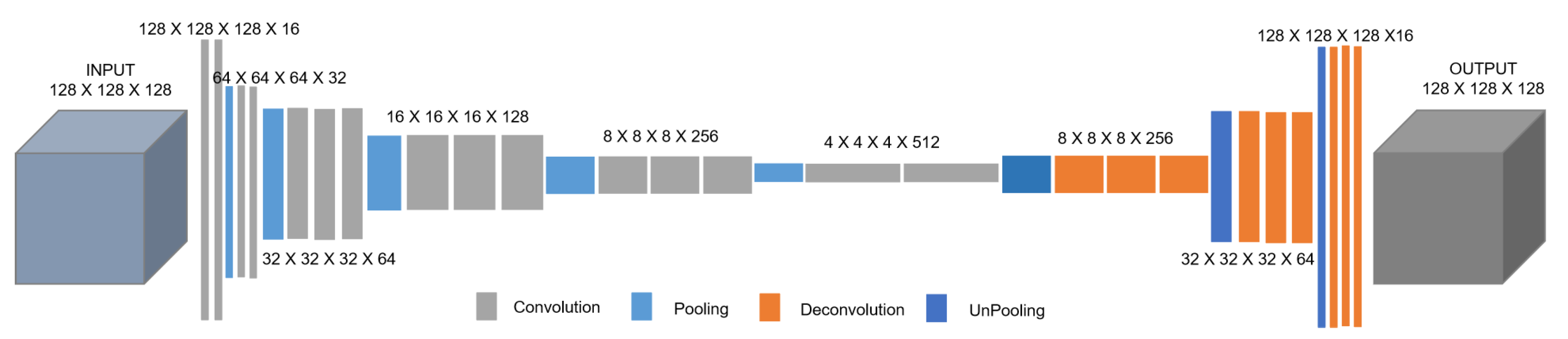
3. Architecture of Our FCN
4. Synthesizing Seismic Data Sets
- 1)
- The horizontal reflectivity model is designed as with a sequence of random values that are in the range of [−1,1].
- 2)
- Use Equation (4) to generate a fold structure.which combines with multiple 2D Gaussian functions and a linear-scale function . The combination of 2D Gaussian functions creates laterally varying folding structures, whereas the linear-scale function dampens the folding vertically from bottom to top. In this equation, each combination of the parameters generates some specific spatially varying folding str uctures in the model. By randomly choosing each of the parameters from predefined ranges, we are able to create numerous models with unique structures.
- 3)
- Substituting into leads to .
- 4)
- Planar shearing of through leads to . In the model , the parameters are randomly chosen from some predefined ranges.
- 5)
- Use Equation (5) to add planar faulting in the model and create a reflectivity model containing folds and faults.wherewhere is the vector representing the dip angle of the fault, is the vector representing the strike of the fault, and is the vector representing the normal direction perpendicular to the strike of the fault. , , and respectively represent the distribution range of the fault in the direction of , , and .
- 6)
- Convoluting the reflectivity model with a Ricker wavelet to obtain a 3D seismic image.
5. Training and Validation
6. Application
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Liu, B.; Yan, D.; Fu, X.; Lü, Y.; Gong, L.; Wang, S. Investigation of geochemical characteristics of hydrocarbon gas and its implications for Late Miocene transpressional strength—A study in the Fangzheng Basin, Northeast China. Interpretation 2018, 6, T83–T96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, B.; Zhao, X.; Fu, X.; Yuan, B.; Bai, L.; Zhang, Y.; Ostadhassan, M. Petrophysical characteristics and log identification of lacustrine shale lithofacies: A case study of the first member of Qingshankou Formation in the Songliao Basin, Northeast China. Interpretation 2020, 8, SL45–SL57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.; Sun, J.; Zhang, Y.; He, J.; Fu, X.; Yang, L.; Xing, J.; Zhao, X. Reservoir space and enrichment model of shale oil in the first member of Cretaceous Qingshankou Formation in the Changling sag, southern Songliao Basin, NE China. Pet. Explor. Dev. 2021, 48, 1–16. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, J. Similarities between Cenozoic basins of different magnitudes in East Asia continental margin. Pet. Geol. Exp. 1997, 19, 297–304. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, J.; Zhang, L. Genesis of Cenozoic basins in Northwest Pacific Ocean margin(1): Comments on basin-forming mechanism. Oil Gas Geol. 2000, 21, 93–98. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, W.-C.; Yan, J.-J. On the Evolutional Characteristics of Cenozoic Episodic rifting of Nanpu Sag. J. Jining Norm. Coll. 2020, 3, 115–119. [Google Scholar]
- Peacock, D.C.P.; Sanderson, D.J.; Rotevatn, A. Relationships between fractures. J. Struct. Geol. 2018, 106, 41–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peacock, D.C.P.; Nixon, C.W.; Sanderson, A.R.D.J.; Zuluaga, L.F. Interacting faults. J. Struct. Geol. 2017, 97, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, H.M.; Meng, L.J.; Cai, D.S.; Wu, Y.P.; Li, X.S.; Liu, M.Q. Fault formation and evolution in rift basins-sandbox modeling and cognition. Acta Geol. Sin. 2009, 83, 759–774. [Google Scholar]
- Tong, H.; Zhao, B.; Cao, Z.; Liu, G.; Dun, X.M.; Zhao, D. Structural analysis of faulting system origin in the Nanpu sag, Bohai Bay basin. Acta Geol. Sin. 2013, 87, 1647–1661. [Google Scholar]
- Marfurt, K.J.; Kirlin, R.L.; Farmer, S.L.; Bahorich, M.S. 3-D seismic attributes using a semblance-based coherency algorithm. Geophysics 1998, 63, 1150–1165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Marfurt, K.J.; Sudhaker, V.; Gersztenkorn, A.; Crawford, K.D.; Nissen, S.E. Coherency calculations in the presence of structural dip. Geophysics 1999, 64, 104–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.; Lu, W. Coherence attribute at different spectral scales. Interpretation 2014, 2, SA99–SA106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wu, X. Directional structure-tensor based coherence to detect seismic faults and channels. Geophysics 2017, 82, A13–A17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Van Bemmel, P.P.; Pepper, R.E. Seismic Signal Processing Method and Apparatus for Generating a Cube of Variance Values. U.S. Patent 6,151,555, 21 November 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Randen, T.; Pedersen, S.I.; Sønneland, L. Automatic extraction of fault surfaces from three-dimensional seismic data. In Proceedings of the SEG Expanded Abstracts on 81st Annual International Meeting, Pau, France, 30 April–3 May 2001; pp. 551–554. [Google Scholar]
- Aqrawi, A.A.; Boe, T.H. Improved fault segmentation using a dip guided and modified 3D Sobel filter. In Proceedings of the SEG Expanded Abstracts on 81st Annual International Meeting, San Antonio, TX, USA, 18–23 September 2011; pp. 999–1003. [Google Scholar]
- Hale, D. Methods to compute fault images, extract fault surfaces, and estimate fault throws from 3D seismic images. Geophysics 2013, 78, 33–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Z.H.; Kavousi, P.; Di, H.B. Multi-Attributes and Neural Network-Based Fault Detection in 3D Seismic Interpretation. Adv. Mater. Res. 2014, 838, 1497–1502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Araya-Polo, M.; Dahlke, T.; Frogner, C.; Zhang, C.; Poggio, T.; Hohl, D. Automated fault detection without seismic processing. Lead. Edge 2017, 36, 208–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, L.; Dong, X.; Clee, T.E. A scalable deep learning platform for identifying geologic features from seismic attributes. Lead. Edge 2017, 36, 249–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di, H.; Shafiq, M.; AlRegib, G. Patch-level MLP classification for improved fault detection. In Proceedings of the SEG Expanded Abstracts on 88th Annual International Meeting, Anaheim, CA, USA, 14–19 October 2018; pp. 2211–2215. [Google Scholar]
- Guitton, A.; Wang, H.; Trainor-Guitton, W. Statistical imaging of faults in 3D seismic volumes using a machine learning approach. In Proceedings of the SEG Technical Program Expanded Abstracts, Beijing, China, 20–22 November 2017; pp. 2045–2049. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, B.; Li, L.; Luo, Y. A new method for automatic seismic fault detection using convolutional neural network. In Proceedings of the SEG Expanded Abstracts on 88th Annual International Meeting, Anaheim, CA, USA, 14–19 October 2018; pp. 1951–1955. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, X.; Hale, D. 3D seismic image processing for faults. Geophysics 2016, 81, IM1–IM11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xiong, W.; Ji, X.; Ma, Y.; Wang, Y.; AlBinHassan, N.M.; Ali, M.N.; Luo, Y. Seismic fault detection with convolutional neural network. Geophysics 2018, 83, 97–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, T.; Mukhopadhyay, P. A fault-detection workflow using deep learning and image processing. In Proceedings of the SEG Expanded Abstracts on 88th Annual International Meeting, Anaheim, CA, USA, 14–19 October 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, X.; Liang, L.; Shi, Y.; Fomel, S. FaultSeg3D: Using synthetic data sets to train an end-to-end convolutional neural network for 3D seismic fault segmentation. Geophysics 2019, 84, 35–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Girshick, R.; Donahue, J.; Darrell, T.; Malik, J. Rich feature hierarchies for accurate object detection and semantic segmentation. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Columbus, OH, USA, 23–28 June 2014; pp. 580–587. [Google Scholar]
- Ren, S.; He, K.; Girshick, R.; Sun, J. Faster R-CNN: Towards realtime object detection with region proposal networks. arXiv 2015, arXiv:1506.01497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ronneberger, O.; Fischer, P.; Brox, T. U-Net: Convolutional networks for biomedical image segmentation. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention, Munich, Germany, 5–9 October 2015; pp. 234–241. [Google Scholar]
- Xie, S.; Tu, Z. Holistically-nested edge detection. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Santiago, Chile, 7–13 December 2015; pp. 1395–1403. [Google Scholar]
- Badrinarayanan, V.; Kendall, A.; Cipolla, R. Segnet: A deep convolutional encoder-decoder architecture for image segmentation. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2017, 39, 2481–2495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, K.; Gkioxari, G.; Dollár, P.; Girshick, R. Mask R-CNN. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Venice, Italy, 22–29 October 2017; pp. 2980–2988. [Google Scholar]
- Long, J.; Shelhamer, E.; Darrell, T. Fully convolutional networks for semantic segmentation. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Boston, MA, USA, 7–12 June 2015; pp. 3431–3440. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, M.; Gong, H. Research on AlexNet Improvement and Optimization Method. CEA 2020, 56, 124–131. [Google Scholar]
- Dai, J.; Li, Y.; He, K.; Sun, J. R-FCN: Object detection via region based fully convolutional networks. In Proceedings of the Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, Barcelona, Spain, 5–10 December 2016; pp. 379–387. [Google Scholar]
- Castellano, G.; Castiello, C.; Mencar, C.; Vessio, G. Crowd detection in aerial images using spatial graphs and fully-convolutional neural networks. IEEE Access 2017, 8, 64534–64544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castellano, G.; Castiello, C.; Mencar, C.; Vessio, G. Crowd detection for drone safe landing through fully-convolutional neural networks. In International Conference on Current Trends in Theory and Practice of Informatics; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2020; pp. 301–312. [Google Scholar]
- Krizhevsky, A.; Sutskever, I.; Hinton, G.E. ImageNet classification with deep convolutional neural networks. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2012, 25, 1097–1105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidhuber, J. Deep learning. Scholarpedia 2015, 10, 32832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Guo, X.; Shi, X.; Qiu, X.; Wu, Z.; Yang, X.; Xiao, S. Cenozoic subsidence and its dynamic mechanism in Bohai Bay Basin. Geotecton. Metallog. 2007, 31, 273–280. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, Q.; Zhang, J.; Li, J.; Li, W.; Liu, G.; Feng, C. Characteristics of torsional structure and its control on hydrocarbon accumulation in Nanpu Sag. Geotecton. Metallog. 2011, 35, 183–189. [Google Scholar]
- Fan, B.; Liu, C.; Liu, G.; Zhu, J. Forming mechanism of the fault system and structural evolution history of Nanpu sag. J. Xi'an Shiyou Univ. (Nat. Sci. Ed.) 2010, 25, 13–17, 21. [Google Scholar]












Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wu, J.; Liu, B.; Zhang, H.; He, S.; Yang, Q. Fault Detection Based on Fully Convolutional Networks (FCN). J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2021, 9, 259. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse9030259
Wu J, Liu B, Zhang H, He S, Yang Q. Fault Detection Based on Fully Convolutional Networks (FCN). Journal of Marine Science and Engineering. 2021; 9(3):259. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse9030259
Chicago/Turabian StyleWu, Jizhong, Bo Liu, Hao Zhang, Shumei He, and Qianqian Yang. 2021. "Fault Detection Based on Fully Convolutional Networks (FCN)" Journal of Marine Science and Engineering 9, no. 3: 259. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse9030259
APA StyleWu, J., Liu, B., Zhang, H., He, S., & Yang, Q. (2021). Fault Detection Based on Fully Convolutional Networks (FCN). Journal of Marine Science and Engineering, 9(3), 259. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse9030259





