Impacts of Consolidation Time on the Critical Hydraulic Gradient of Newly Deposited Silty Seabed in the Yellow River Delta
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
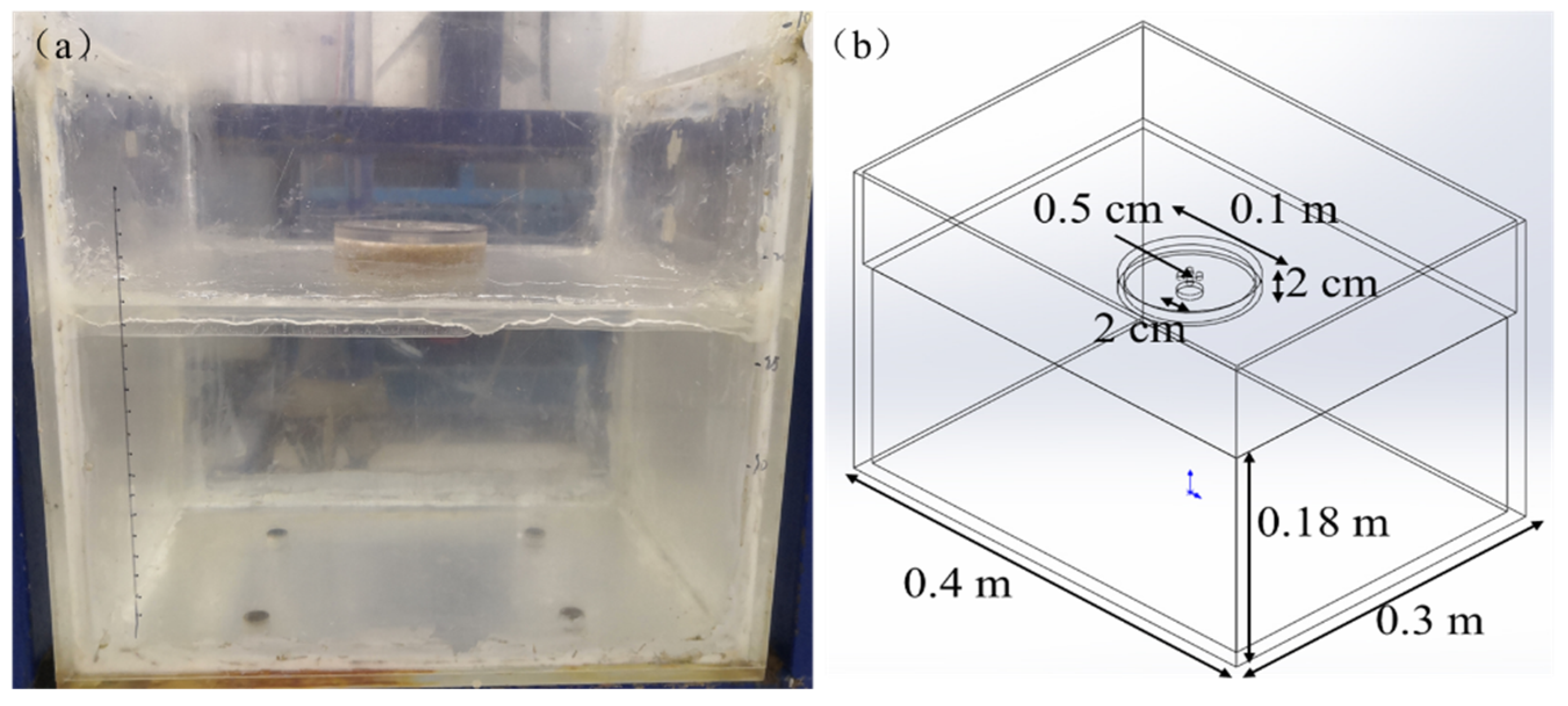
2.1. Experimental Instruments
2.2. Experimental Methods
3. Results
3.1. Sediment Consolidation Experiment
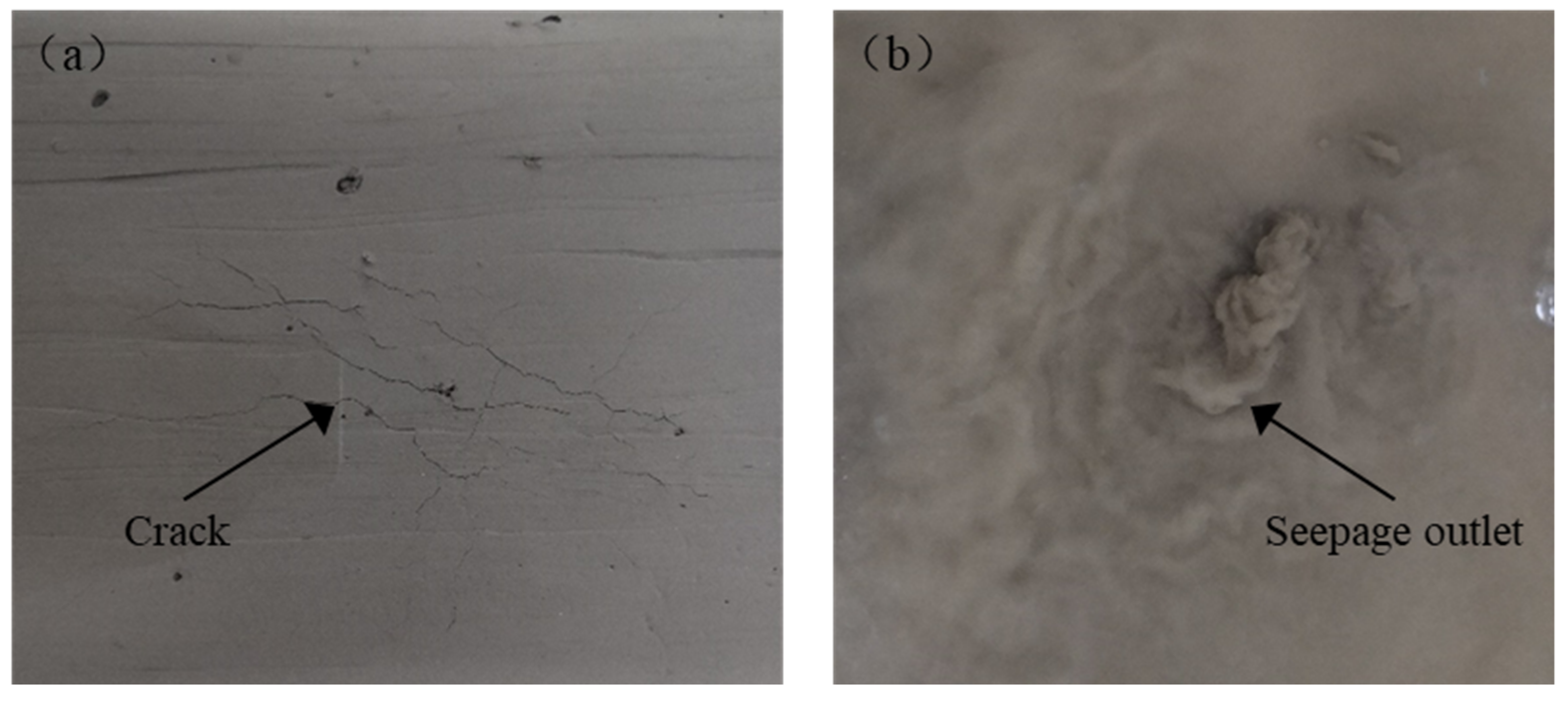
3.2. Typical Experimental Phenomenon
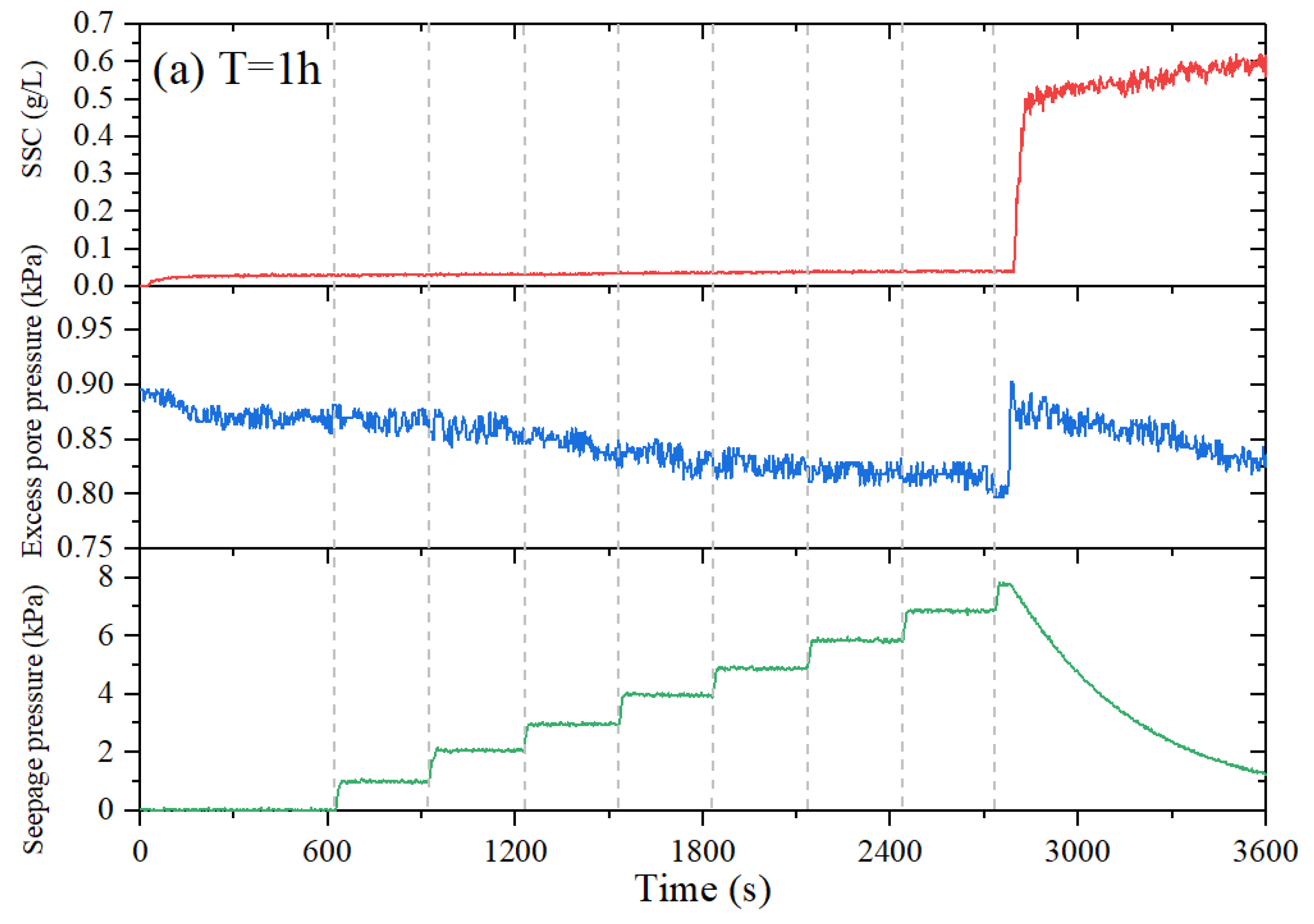
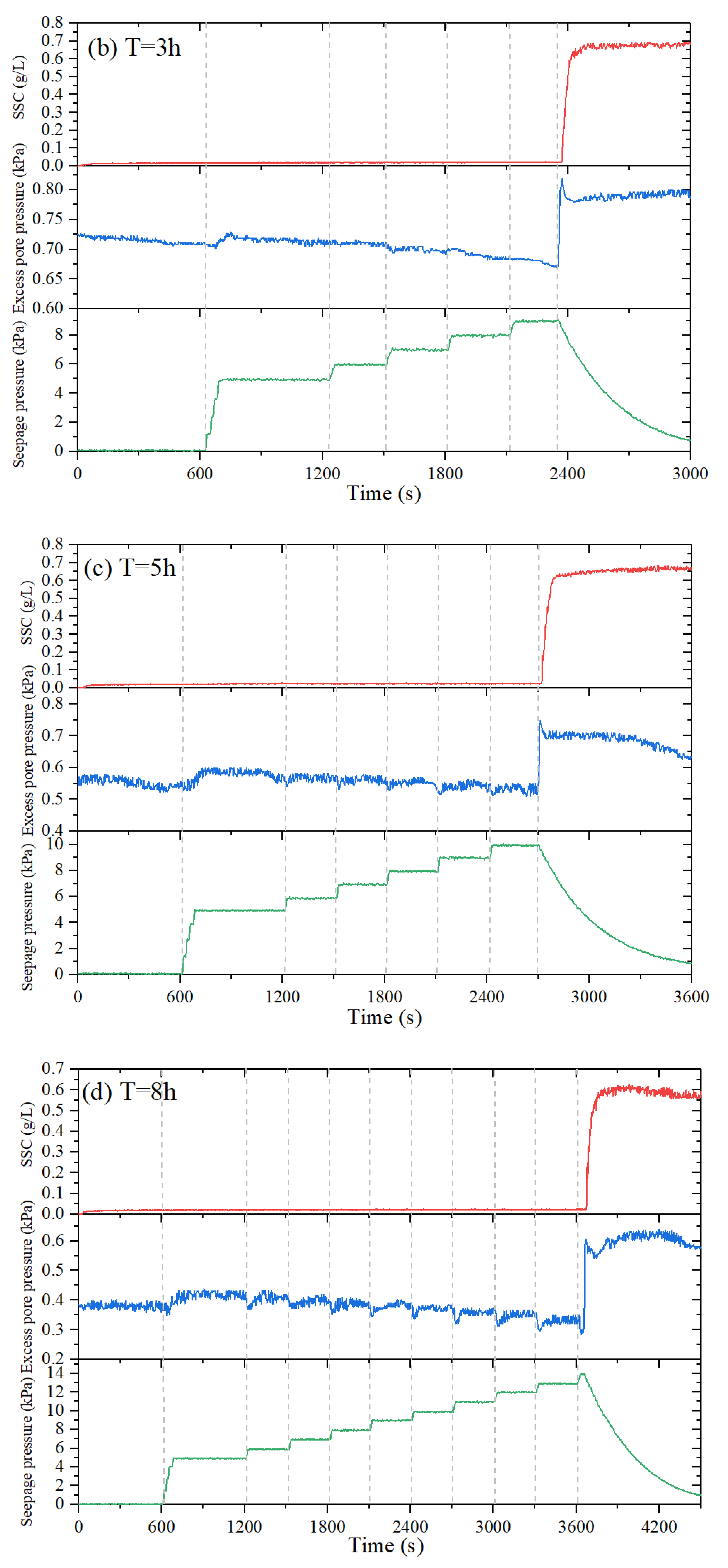
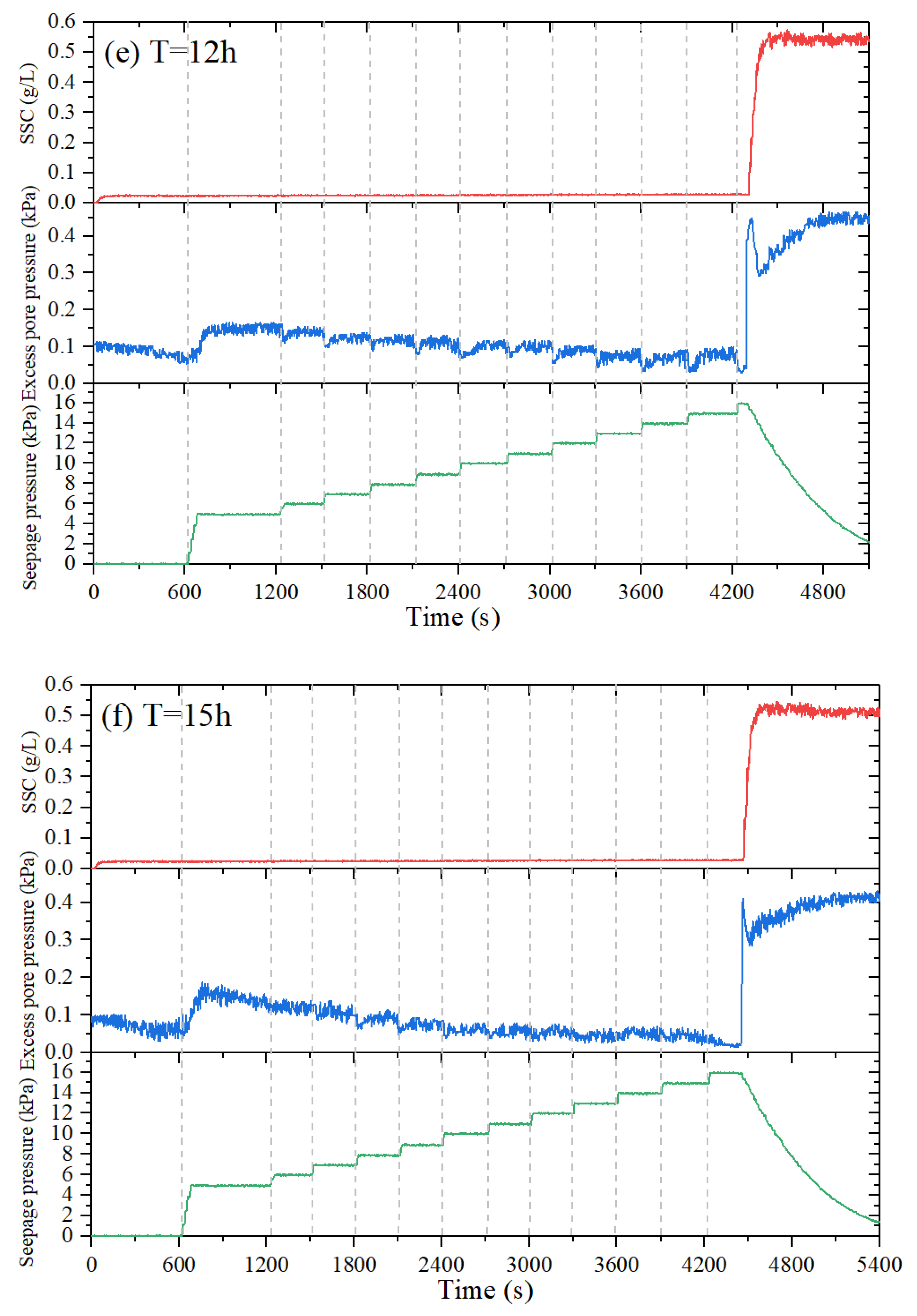
3.3. Time Evolution of Seepage Pressure, Excess Pore Pressure, and SSC in the Seabed under Different Consolidation Times
4. Discussion
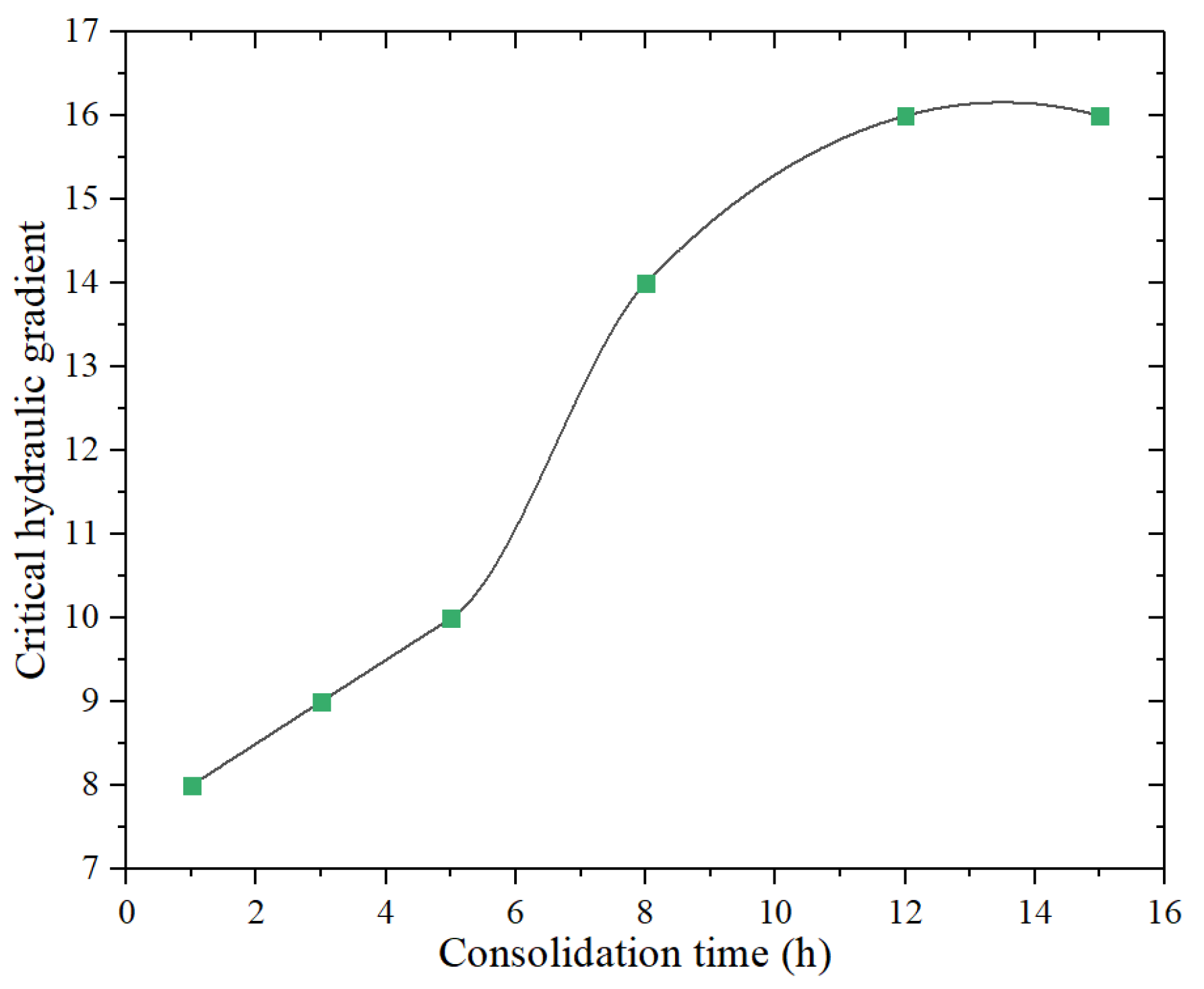
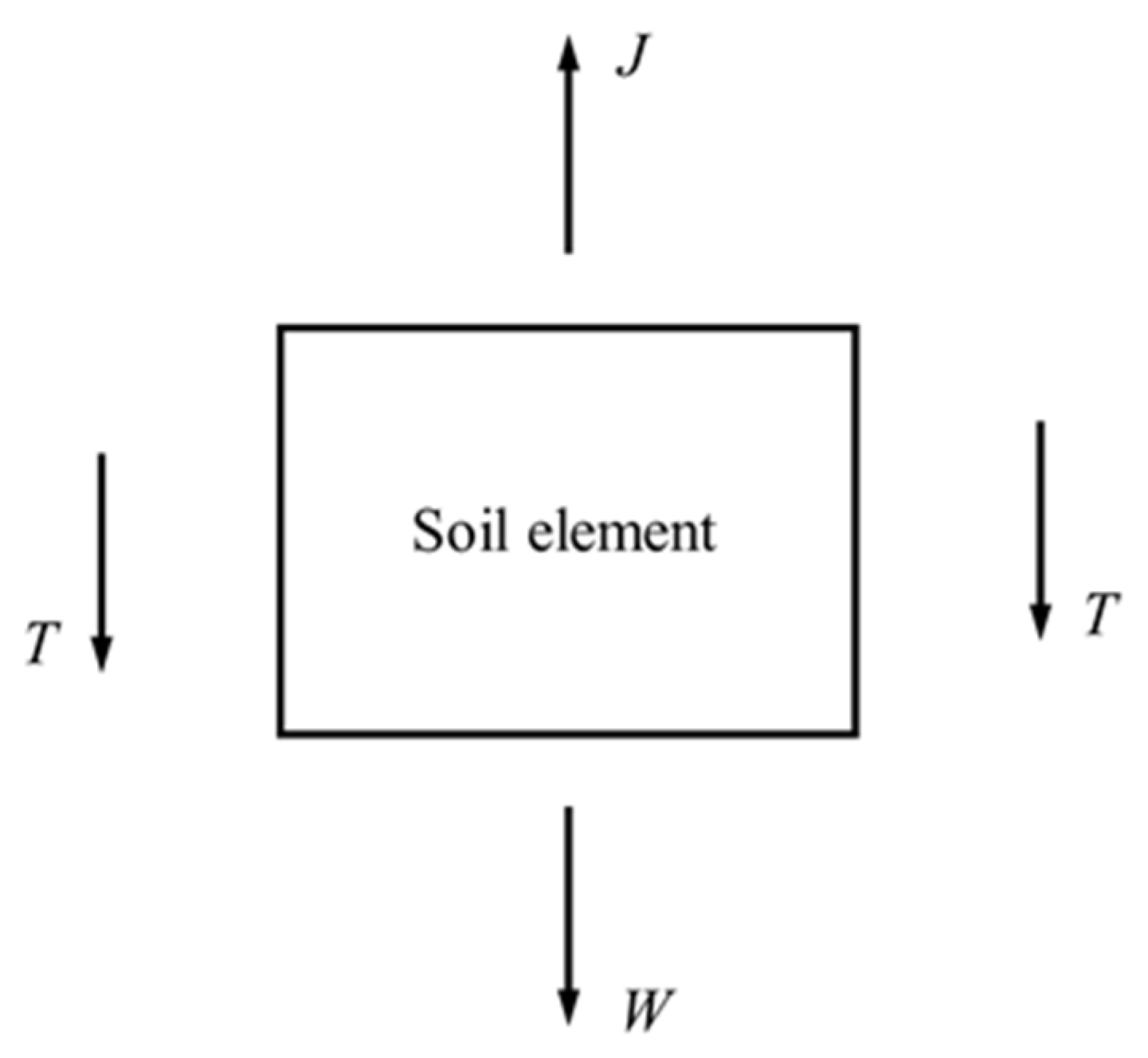
4.1. Critical Hydraulic Gradient of Silts
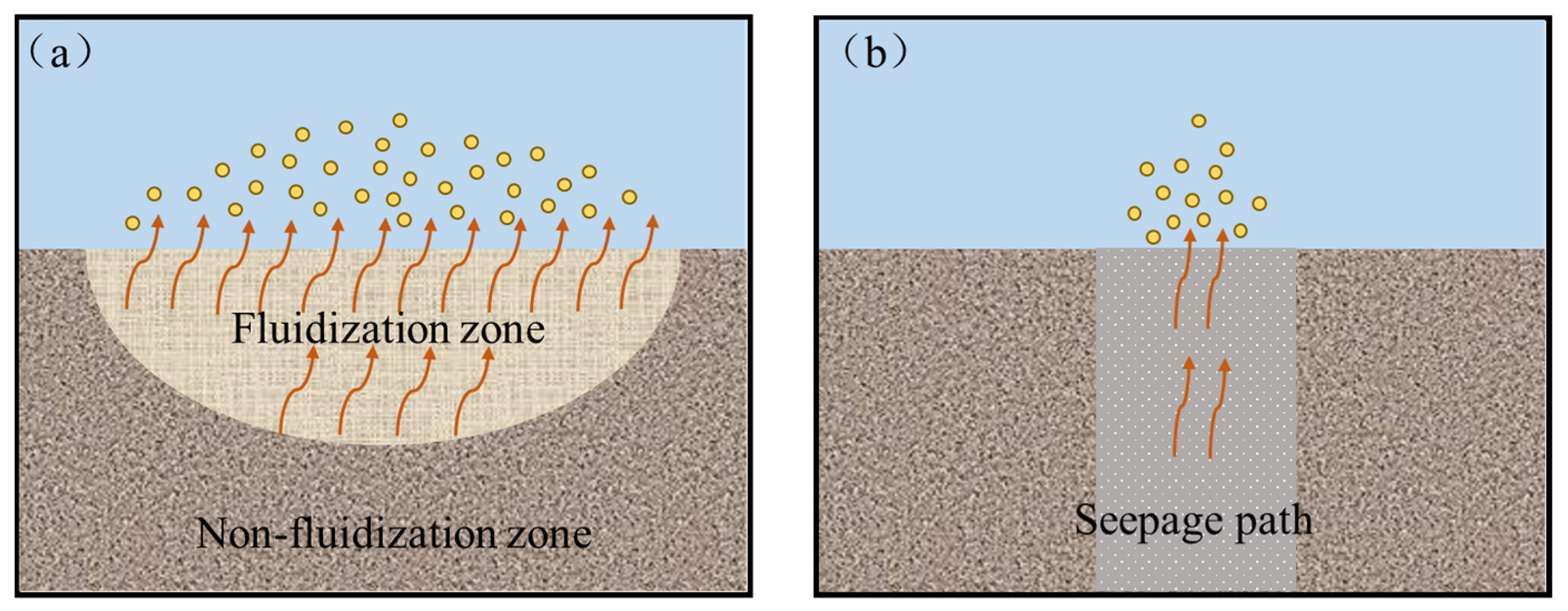
4.2. Mechanism Explanation of Silt Seepage Failure
4.3. The Contribution of Seepage Failure to Resuspension
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Jia, Y.; Liu, X.; Zhang, S.; Shan, H.; Zheng, J. Wave-Forced Sediment Erosion and Resuspension in the Modern Yellow River Delta; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Li, G.; Wei, H.; Yue, S.; Cheng, Y.; Han, Y. Sedimentation in the Yellow River delta, part II: Suspended sediment dispersal and deposition on the subaqueous delta. Mar. Geol. 1998, 149, 113–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Wei, H.; Han, Y.; Chen, Y. Sedimentation in the Yellow River delta, part I: Flow and suspended sediment structure in the upper distributary and the estuary. Mar. Geol. 1998, 149, 93–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, Y.; Zhang, L.; Zheng, J.; Liu, X.; Jeng, D.-S.; Shan, H. Effects of wave-induced seabed liquefaction on sediment re-suspension in the Yellow River Delta. Ocean Eng. 2014, 89, 146–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Zhuang, K.; Wei, H. Sedimentation in the Yellow River delta. Part III. Seabed erosion and diapirism in the abandoned subaqueous delta lobe. Mar. Geol. 2000, 168, 129–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nichols, R.J.; Sparks, R.S.J.; Wilson, C.J.N. Experimental studies of the fluidization of layered sediments and the formation of fluid escape structures. Sedimentology 1994, 41, 233–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Liu, H.; Zhang, M. Pore pressure response of seabed in standing waves and its mechanism. Coast. Eng. 2014, 91, 213–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Zhou, J.; Wang, H. Soil Mechanics, 1st ed.; Tsinghua University Press: Beijing, China, 1994; pp. 56–64. [Google Scholar]
- Prior, D.B.; Suhayda, J.N.; Lu, N.Z.; Bornhold, B.D.; Keller, G.H.; Wiseman, W.J.; Wright, L.D.; Yang, Z.S. Storm wave reactivation of a submarine landslide. Nature 1989, 341, 47–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, G.; Sun, Y.; Wang, X.; Hu, G.; Song, Y. Wave-induced shallow slides and their features on the subaqueous Yellow River delta. Can. Geotech. J. 2009, 46, 1406–1417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeng, D.-S.; Zhang, J.; Kirca, Ö. Coastal Geohazard and Offshore Geotechnics. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2020, 8, 1011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terzaghi, K. Der Grundbruch an Stauwerken und Seine Verhutung. Wasserkraft 1922, 17, 445–449. [Google Scholar]
- Sha, J. Research on piping in porous media. Hydro-Sci. Eng. 1981, 89–93. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J. Seepage Control of Earth-Rock Dams Theoretical Basis, Engineering Experiences and Lessons, 1st ed.; China WaterPower Press: Beijing, China, 2006; pp. 30–45. [Google Scholar]
- Davidenkoff, R.; Chang, K. Application of soil filter in hydraulic structures. Hydro-Sci. Eng. 1977, 86–105, (Translated into Chinese). [Google Scholar]
- Liu, J.; Miao, L. Research on influencing factors of impermeability strength of general cohesive soil. J. Hydraul. Eng. 1984, 11–19. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Liu, J. Seepage Stability and Seepage Control of Soil, 1st ed.; China WaterPower Press: Beijing, China, 1992; pp. 60–84. [Google Scholar]
- Song, X.; Qian, C. Analysis of hydraulic gradient of cohesive soil in water seepage. South-to-North Water Transf. Water Sci. Technol. 2010, 8, 65–67. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J. Study on seepage failure test and numerical simulation of cohesive soil. Master’s Thesis, Hefei University of Tech-nology, Hefei, China, 23 April 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, F. Discussion on Formula Derivation and Test of Critical Hydraulic Condition of Cohesive Soil. Chin. J. of Undergr. Space and Eng. 2017, 13, 1472–1476+1498. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Jeng, D.-S. Wave-induced sea floor dynamics. Appl. Mech. Rev. 2003, 56, 407–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeng, D.-S. Porous Models for Wave-Seabed Interactions, 1st ed.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2012; pp. 251–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, S.; Jia, Y.; Wen, M.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Zhu, C.; Li, B.; Liu, X. Vertical migration of fine-grained sediments from interior to surface of seabed driven by seepage flows–‘sub-bottom sediment pump action’. J. Ocean Univ. China 2017, 16, 15–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lambrechts, J.; Humphrey, C.; McKinna, L.; Gourge, O.; Fabricius, K.E.; Mehta, A.J.; Lewis, S.; Wolanski, E. Importance of wave-induced bed liquefaction in the fine sediment budget of Cleveland Bay, Great Barrier Reef. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2010, 89, 154–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, D.; Liao, C.; Chen, J.; Zhang, Q. Numerical Simulation of a Sandy Seabed Response to Water Surface Waves Propagating on Current. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2018, 6, 88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, J.; Jiang, Q.; Jeng, D.; Zhang, C.; Chen, X.; Wang, L. Experimental Study on Mechanism of Wave-Induced Liquefaction of Sand-Clay Seabed. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2020, 8, 66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fox, G.A.; Wilson, G.V.; Simon, A.; Langendoen, E.J.; Akay, O.; Fuchs, J.W. Measuring streambank erosion due to ground water seepage: Correlation to bank pore water pressure, precipitation and stream stage. Earth Surface Process. Landf. 2007, 32, 1558–1573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.-L.; Jia, Y.-G.; Zheng, J.-W.; Hou, W.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, L.-P.; Shan, H.-X. Experimental evidence of wave-induced inhomogeneity in the strength of silty seabed sediments: Yellow River Delta, China. Ocean Eng. 2013, 59, 120–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Liu, H.; Zhang, M.; Wang, X. Wave-induced seepage and its possible contribution to the formation of pockmarks in the Huanghe (Yellow) River delta. Chin. J. Oceanol. Limnol. 2016, 34, 200–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Jia, Y.; Lu, F.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, S.; Peng, Z. Effects of Upward Seepage on the Resuspension of Consolidated Silty Sediments in the Yellow River Delta. J. Coast. Res. 2020, 36, 372–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, X.; Jia, Y.; Zhang, S.; Zhang, S.; Zhang, H.; Shan, H. Influence of salinity on sediment erosion-resistance: Evidence from annular flume studies. Mar. Geol. Quat. Geol. 2020, 40, 222–230. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S. Effects of Wave-Induced Silty Seabed Liquefaction on Sediment Erosion and Resuspension. Ph.D. Thesis, Ocean University of China, Qingdao, China, 8 December 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, S.; Jia, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Shan, H. Influence of Seepage Flows on the Erodibility of Fluidized Silty Sediments: Parameterization and Mechanisms. J. Geophys. Res. Ocean. 2018, 123, 3307–3321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Gong, X.; Zhou, C.; Jin, X. Experimental study of seepage failure of Qiantang River alluvial silts. Rock Soil Mech. 2016, 37, 243–249. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, X.; Ma, Y.; Lin, L.; Xu, C. Discuss of silt critical hydraulic gradient in modern Huanghe subaqueous delta. Mar. Sci. 2002, 26, 54–57. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Green, M.O.; Coco, G. Review of wave-driven sediment resuspension and transport in estuaries. Rev. Geophys. 2014, 52, 77–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H. Mechanism and quantitative evaluation of wave-induced seabed instability in the Yellow River delta. Ph.D. Thesis, Ocean University of China, Qingdao, China, 8 June 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X.; Liu, C. New Understanding of the Regularity of Water Seepage in Cohesive Soil. Acta Geosci. Sin. 2003, 24, 91–95. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Z.; Jeng, D.S.; Zhao, H.; Guo, W.; Wang, L. Effect of seepage flow on sediment incipient motion around a free spanning pipeline. Coast. Eng. 2019, 143, 50–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, K.; Guo, Z.; Wang, L.; Jiang, H. Effect of seepage flow on shields number around a fixed and sagging pipeline. Ocean Eng. 2019, 172, 487–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Ong, M.C.; Fuhrman, D.R. CFD investigations of scour beneath a submarine pipeline with the effect of upward seepage. Coast. Eng. 2020, 156, 103624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhai, H.; Jeng, D.S.; Guo, Z.; Liang, Z. Impact of two-dimensional seepage flow on sediment incipient motion under waves. Appl. Ocean Res. 2021, 108, 102510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, J.; Jia, Y.; Liu, X.; Shan, H.; Zhang, M. Experimental study of the variation of sediment erodibility under wave-loading conditions. Ocean Eng. 2013, 68, 14–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Jia, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, X.; Shan, H. In situ observations of wave pumping of sediments in the Yellow River Delta with a newly developed benthic chamber. Mar. Geophys. Res. 2018, 39, 463–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



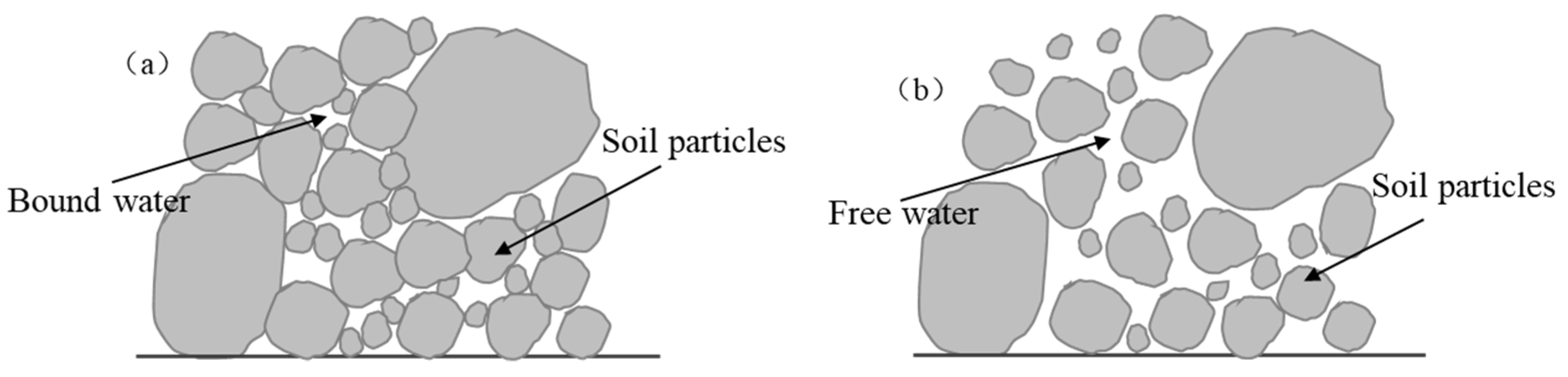
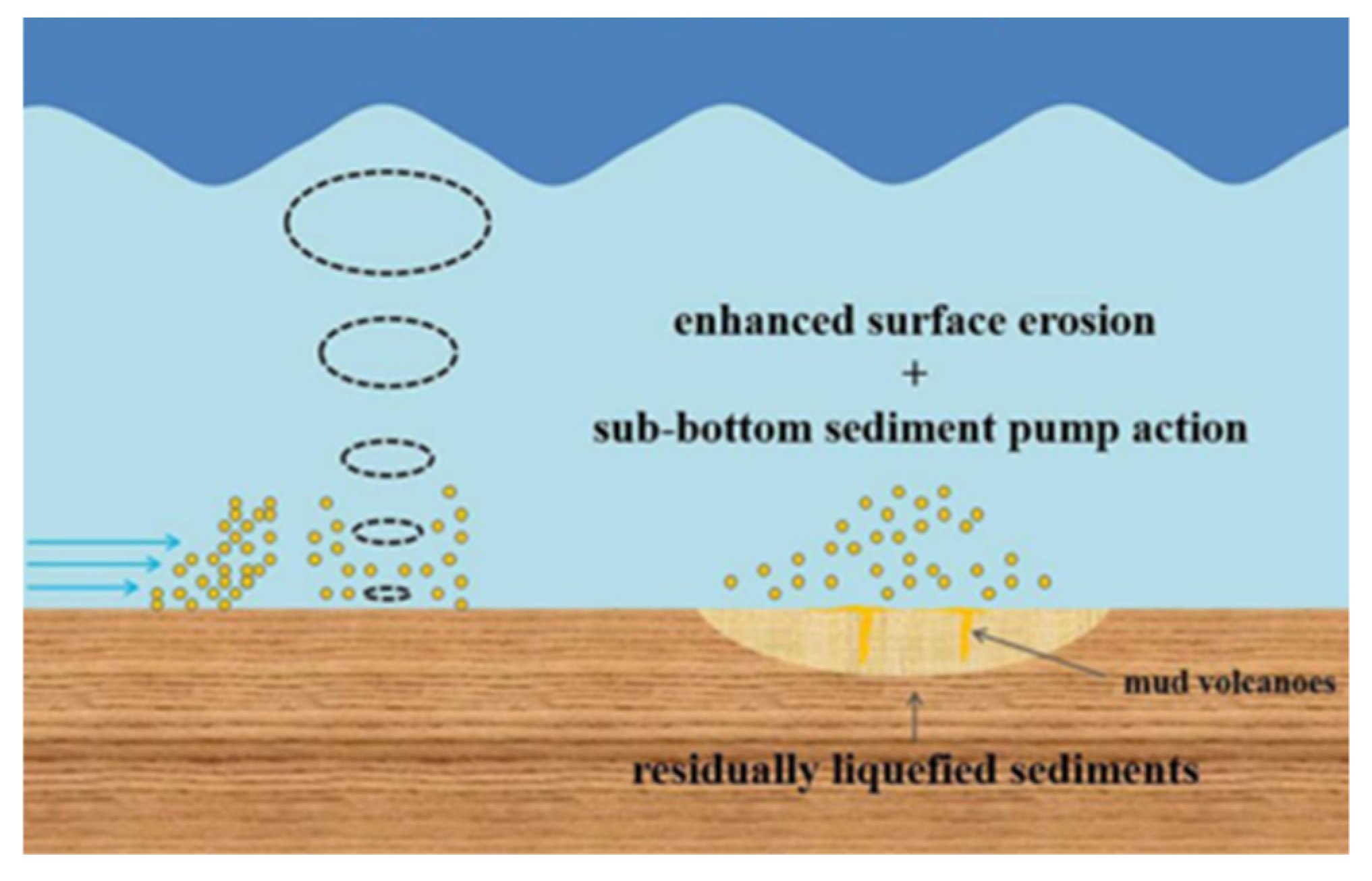
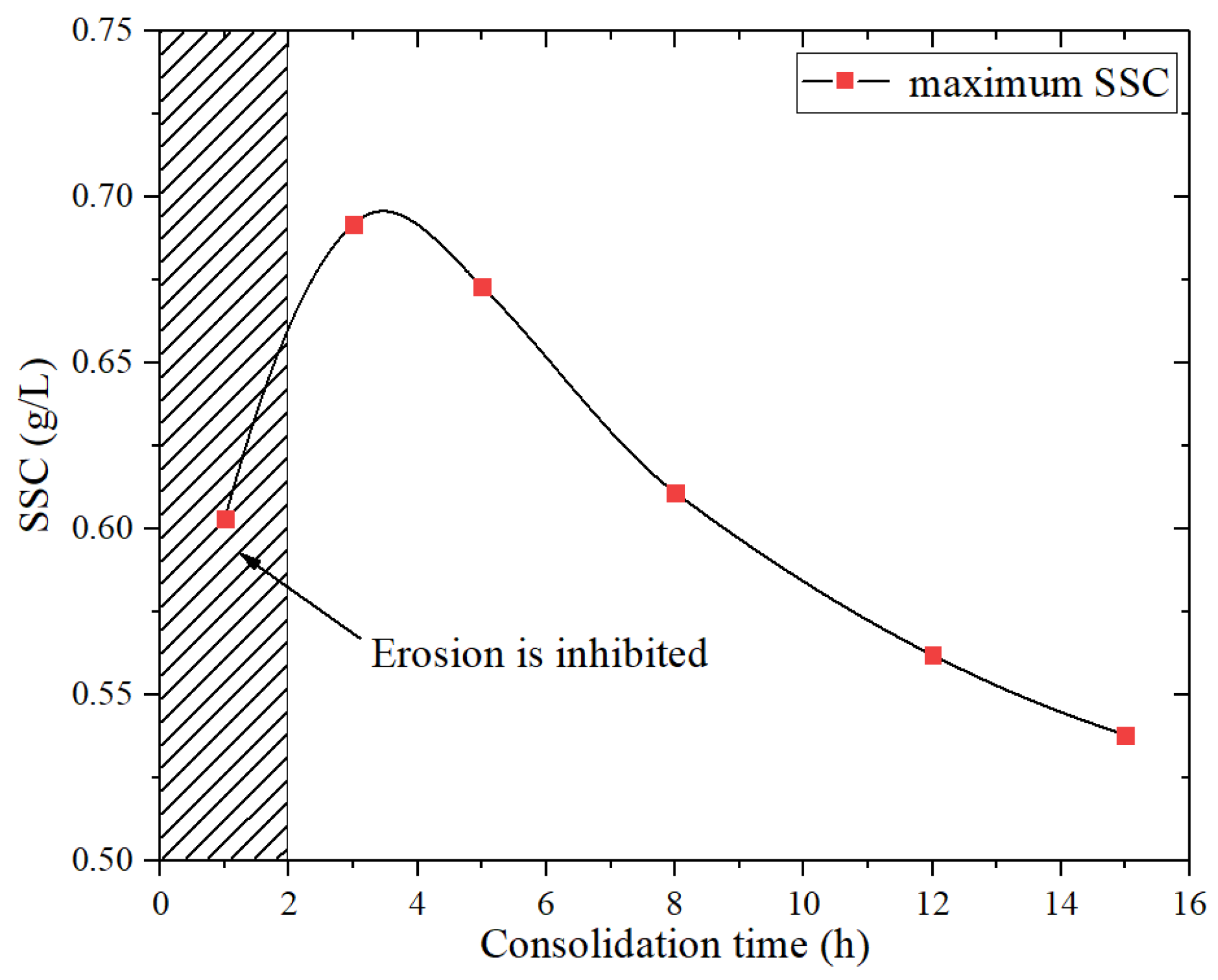
| Round No. | Consolidation Time (h) | Excess Pore Pressure (kPa) | Fluidization Degree (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 1 | 0.895 | 89.5 |
| 2 | 3 | 0.725 | 72.5 |
| 3 | 5 | 0.575 | 57.5 |
| 4 | 8 | 0.384 | 38.4 |
| 5 | 12 | 0.112 | 11.2 |
| 6 | 15 | 0.095 | 9.5 |
| Time (h) | Scouring Stage (Before Seepage) | Seepage Stage (When Seepage Failure) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Excess Pore Pressure (kPa) | SSC (g/L) | Seepage Pressure (kPa) | Excess Pore Pressure Change Range (kPa) | SSC (g/L) | |
| 1 | 0.870 | 0.030 | 8 | 0.797→0.903 | 0.515 |
| 3 | 0.704 | 0.017 | 9 | 0.670→0.819 | 0.675 |
| 5 | 0.525 | 0.022 | 10 | 0.514→0.749 | 0.631 |
| 8 | 0.366 | 0.020 | 14 | 0.284→0.607 | 0.611 |
| 12 | 0.052 | 0.023 | 16 | 0.029→0.448 | 0.562 |
| 15 | 0.038 | 0.023 | 16 | 0.016→0.410 | 0.538 |
| Critical Hydraulic Gradient Formula | |
|---|---|
| Terzaghi (1922) | 0.935 |
| Sha (1981) | 1.09 |
| Liu (2006) | 0.45 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tang, M.; Jia, Y.; Zhang, S.; Wang, C.; Liu, H. Impacts of Consolidation Time on the Critical Hydraulic Gradient of Newly Deposited Silty Seabed in the Yellow River Delta. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2021, 9, 270. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse9030270
Tang M, Jia Y, Zhang S, Wang C, Liu H. Impacts of Consolidation Time on the Critical Hydraulic Gradient of Newly Deposited Silty Seabed in the Yellow River Delta. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering. 2021; 9(3):270. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse9030270
Chicago/Turabian StyleTang, Meiyun, Yonggang Jia, Shaotong Zhang, Chenxi Wang, and Hanlu Liu. 2021. "Impacts of Consolidation Time on the Critical Hydraulic Gradient of Newly Deposited Silty Seabed in the Yellow River Delta" Journal of Marine Science and Engineering 9, no. 3: 270. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse9030270
APA StyleTang, M., Jia, Y., Zhang, S., Wang, C., & Liu, H. (2021). Impacts of Consolidation Time on the Critical Hydraulic Gradient of Newly Deposited Silty Seabed in the Yellow River Delta. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering, 9(3), 270. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse9030270








