Aquaculture Farming Effect on Benthic Respiration and Nutrient Flux in Semi-Enclosed Coastal Waters of Korea
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Sampling and Handling
2.3. In Situ Measurement
2.4. Sediment Trap
2.5. Laboratory Analysis
2.6. Flux Calculation
2.7. Organic Carbon Budget Calculation
3. Results
3.1. Water Column and Sediment Parameters
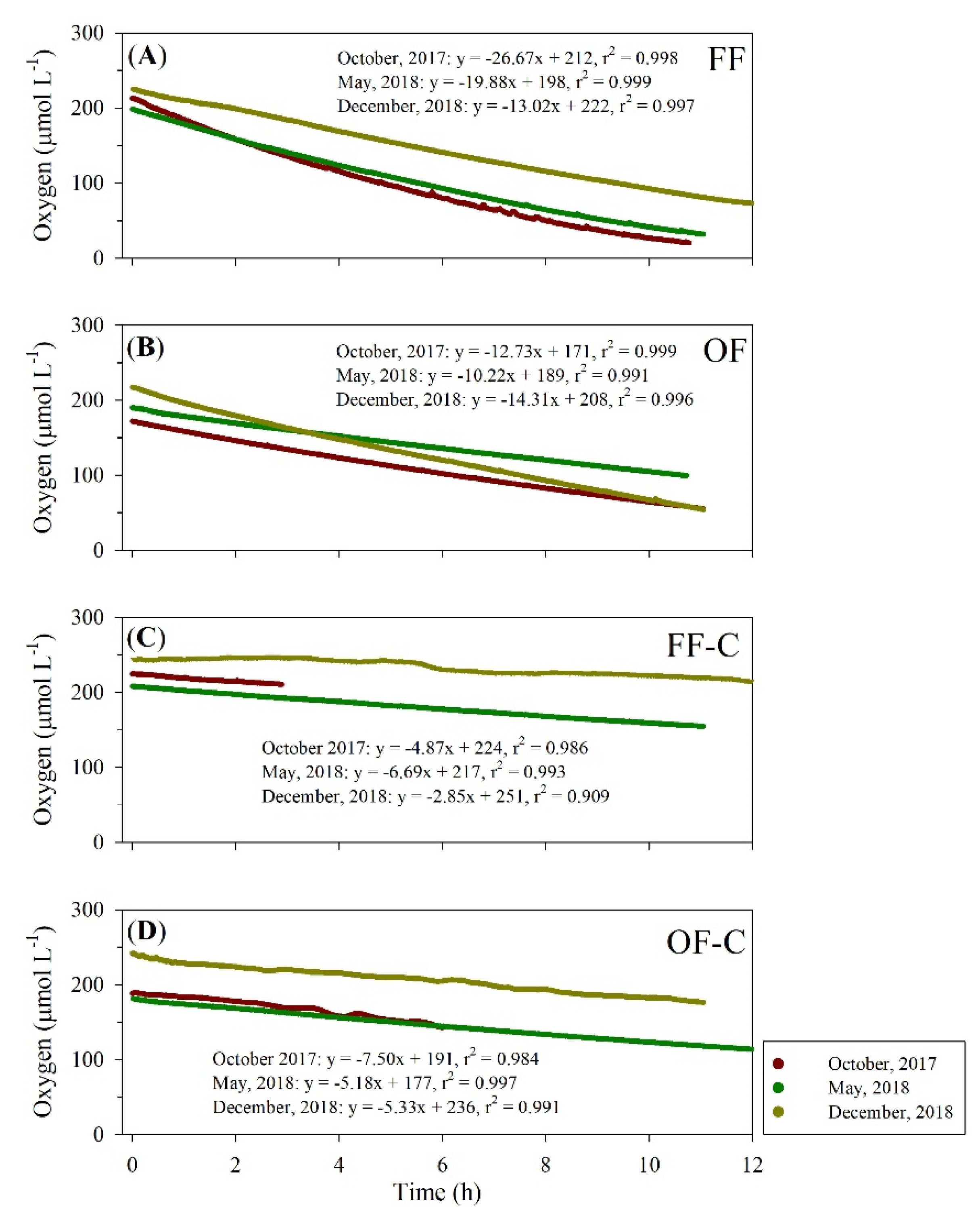
3.2. Sediment Oxygen Demand
3.3. Benthic Nutrient Flux
4. Discussion
4.1. Sediment Oxygen Demand
4.2. OC Budget
4.3. Benthic Nutrient Fluxes and Benthic–Pelagic Coupling in Aquaculture Sediment
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- FAO. Fishery and Aquaculture Statistics. Global Aquaculture and Capture Production: 1950–2017 (FishstatJ); FAO Fisheries and Aquaculture Department: Rome, Italy, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Costello, C.; Cao, L.; Gelcish, S.; Cisneros-Mata, M.Á.; Free, C.M.; Froehlich, H.E.; Golden, C.D.; Ishimura, G.; Maier, J.; Macadam-Domer, I.; et al. The future of food from the sea. Nature 2020, 588, 95–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- FAO. The State of World Fisheries and Aquaculture; Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations: Rome, Italy, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- FAO. The State of World Fisheries and Aquaculture; Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations: Rome, Italy, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- KOSIS. Korean Statistical Information Service. 2019. Available online: http://kosis.kr/eng/ (accessed on 20 May 2021).
- Islam, M.S. Nitrogen and phosphorus budget in coastal and marine cage aquaculture and impacts of effluent loading on ecosystem: Review and analysis towards model development. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2005, 50, 48–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sarà, G.; Martire, M.L.; Sanfilippo, M.; Pulicanò, G.; Cortese, G.; Mazzola, A.; Pusceddu, A. Impacts of marine aquaculture at large spatial scales: Evidences from N and P catchment loading and phytoplankton biomass. Mar. Environ. Res. 2011, 71, 317–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lee, Y.G.; Jeong, D.U.; Lee, J.S.; Choi, Y.H.; Lee, M.O. Effects of hypoxia caused by mussel farming on benthic foraminifera in semi-closed Gamak Bay, South Korea. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2016, 109, 566–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, R.S.S. The environmental impacts of marine fish culture: Towards a sustainable future. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 1995, 31, 159–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zúñiga, D.; Castro, C.G.; Aguiar, E.; Labarta, U.; Figueiras, F.G.; Fernández-Reiriz, M.J. Biodeposit contribution to natural sedimentation in a suspended Mytilus galloprovincialis Lmk mussel farm in a Galician Ría (NW Iberian Peninsula). Aquaculture 2014, 432, 311–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liao, Y.; Shou, L.; Jiang, Z.; Tang, Y.; Du, P.; Zeng, J.; Chen, Q.; Yan, X.; Chen, J. Effects of fish cage culture and suspended oyster culture on microbenthic communities in Xiangshan Bay, A semi-enclosed subtropical bay in eastern China. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2019, 142, 475–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.S.; Kim, Y.-T.; Shin, K.-H.; Hyun, J.-H.; Kim, S.-Y. Benthic nutrient fluxes at longline sea squirt and oyster aquaculture farms and their role in coastal systems. Aquacult. Int. 2011, 19, 931–944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.-H.; Kim, H.C.; Choi, S.-H.; Lee, W.-C.; Jung, R.-H.; Hyun, J.-H.; Kim, S.H.; Lee, J.S. Benthic respiration and nutrient release associated with net cage fish and longline oyster aquaculture in the Geoje-Tongyeong coastal waters in Korea. Estuar. Coasts 2020, 43, 589–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canfield, D.E.; Kristensen, E.; Thamdrup, B. Aquatic geomicrobiology. In Advances in Marine Biology; Southward, A.J., Tyler, P.A., Young, C.M., Fuiman, L.A., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2005; Volume 48, pp. 65–166. [Google Scholar]
- Canfield, D.E.; Thamdrup, B.; Hansen, J.W. The anaerobic degradation of organic matter in Danish coastal sediments: Iron reduction, manganese reduction, and sulfate reduction. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 1993, 57, 3867–3883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glud, R.N. Oxygen dynamics of marine sediments. Mar. Biol. Res. 2008, 4, 243–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berner, R.A. Early Diagenesis: A Theoretical Approach; Princeton University Press: Princeton, NY, USA, 1980. [Google Scholar]
- Leithold, E.L.; Blair, N.E.; Wegmann, K.W. Source-to-sink sedimentary systems and global carbon burial: A river runs through it. Earth-Sci. Rev. 2016, 153, 30–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hedges, J.I.; Keil, R.G.; Benner, R. What happens to terrestrial organic matter in the ocean? Org. Geochem. 1997, 27, 195–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burdige, D.J. Preservation of organic matter in marine sediments: Controls, mechanisms, and an imbalance in sediment organic carbon budgets? Chem. Rev. 2007, 107, 467–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lacoste, E.; Gaertner-Mazouni, N. Nutrient regeneration in the water column and at the sediment-water interface in pearl oyster culture (Pinctada margaritifera) in a deep atoll lagoon (Ahe, French Polynesia). Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2016, 182, 304–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.-H.; Lee, J.S.; Hyun, J.-H. Extremely high sulfate reduction, sediment oxygen demand and benthic nutrient flux associated with a large-scale artificial dyke and its implication to benthic-pelagic coupling in the Yeongsan River estuary, Yellow Sea. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2017, 120, 126–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.S.; Kim, S.-H.; Kim, Y.-T.; Hong, S.J.; Han, J.H.; Hyun, J.-H.; Shin, K.-H. Influence of sea squirt (Halocynthia roretzi) aquaculture on benthic-pelagic coupling in coastal waters: A study of the South Sea in Korea. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2012, 99, 10–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.S.; Kim, K.H.; Shim, J.; Han, J.H.; Choi, Y.H.; Khang, B.-J. Massive sedimentation of fine sediment with organic matter and enhanced benthic-pelagic coupling by an artificial dyke in semi-enclosed Chonsu Bay, Korea. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2012, 64, 153–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hyun, J.-H.; Kim, S.-H.; Mok, J.-S.; Lee, J.S.; An, S.-U.; Lee, W.-C. Impacts of long-line aquaculture of Pacific oyster (Crassostea gigas) on sulfate reduction and diffusive nutrient flux in the coastal sediments of Jinhae-Tongyeong, Korea. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2013, 74, 187–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, A.; Kim, B.; Mok, J.-S.; Yoo, J.; Kim, J.B.; Lee, W.-C.; Hyun, S.-H. Impact of finfish aquaculture on biogeochemical processes in coastal ecosystems and elemental sulfur as a relevant proxy for assessing farming condition. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2020, 150, 110635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chauvaud, L.; Jean, F.; Ragueneau, O.; Thouzeau, G. Long-term variation of the bay of Brest ecosystem: Benthic-pelagic coupling revisited. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2000, 200, 35–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vahtera, E.; Conley, D.J.; Gustafsson, B.G.; Kuosa, H.; Pitkänen, H.; Savchuk, O.P.; Tamminen, T.; Viitasalo, M.; Voss, M.; Wasmund, N.; et al. Internal ecosystem feedbacks enhance nitrogen-fixing cyanobacteria blooms and complicate management in the Baltic Sea. Ambio 2007, 36, 186–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, J.-W.; Kim, D.-H. An economic feasibility comparison of the extruded pellets and moist pellet on the Oliver flounder culture farm. J. Fish. Bus. Adm. 2009, 40, 189–205. [Google Scholar]
- Kang, C.-K.; Park, M.S.; Lee, P.-Y.; Choi, W.-J.; Lee, W.-C. Seasonal variations in condition, reproductive activity, and biochemical composition of the pacific oyster, Grassostrea gigas (Thunberg), in suspended culture in two coastal bays of Korea. J. Shellfish Res. 2000, 19, 771–778. [Google Scholar]
- Choi, K.S. Oyster Capture-Based Aquaculture in the Republic of Korea; In Capture-Based Aquaculture. Global Overview; Lovatelli, A., Holthus, P.F., Eds.; FAO Fisheries Technical Paper. No. 508; FAO: Rome, Italy, 2008; pp. 271–286. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, S.-H.; Lee, J.S.; Kim, K.T.; Kim, S.-L.; Yu, O.W.; Lim, D.; Kim, S.H. Low benthic mineralization and nutrient fluxes in the continental shelf sediment of the northern East China Sea. J. Sea Res. 2020, 164, 101934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansen, H.P.; Koroleff, F. Methods of Seawater Analysis; Grasshoff, K., Kremling, K., Ehrhardt, M., Eds.; Wiley-VCH: Weinhein, Germany, 1999; pp. 159–228. [Google Scholar]
- Martens, C.S.; Klump, J.V. Biogeochemical cycling in an organic-rich coastal margin basin 4. An organic carbon budget for sediments dominated by sulfate reduction and methanogenesis. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 1984, 48, 1987–2004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hedge, J.I.; Keil, R.G. Sedimentary organic matter preservation: An assessment and speculative synthesis. Mar. Chem. 1995, 49, 81–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holby, O.; Hall, P.O.J. Chemical fluxes and mass balances in a marine fish cage farm. II. Phosphorus. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 1991, 70, 263–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hall, P.O.J.; Holby, O.; Kollberg, S.; Samuelsson, M.-O. Chemical fluxes and mass balance in a marine fish farm cage farm. IV. Nitrogen. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 1992, 89, 81–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holmer, M.; Kristensen, E. Impact of marine fish cage farming on metabolism and sulfate reduction of underlying sediments. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 1992, 80, 191–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, R.S.S.; Lam, K.S.; Mackay, D.W.; Lau, T.C.; Yam, V. Impacts of marine fish farming on water quality and bottom sediment: A case study in the subtropical environment. Mar. Environ. Res. 1994, 38, 115–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holmer, M.; Duarte, C.M.; Heliskov, A.; Olesen, B.; Terrados, J. Biogeochemical conditions in sediments enriched by organic matter from net-pen fish farms in the Bolinao area, Philippines. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2003, 46, 1470–1479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carlsson, M.S.; Enhström, P.; Lindahl, O.; Ljungqvist, L.; Petersen, J.K.; Svanberg, L.; Holmer, M. Effects of mussel farms on the benthic nitrogen cycle on the Swedish west coast. Aquac. Environ. Interact. 2012, 2, 177–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Holmer, M.; Marbá, N.; Terrados, J.; Duarte, C.M.; Fortes, M.D. Impacts of milkfish (Chanos chanos) aquaculture on carbon and nutrient fluxes in the Bolinao area, Philippines. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2002, 44, 685–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sweetman, A.K.; Norling, K.; Gunderstad, C.; Haugland, B.T.; Dale, T. Benthic ecosystem functioning beneath fish farms in different hydrodynamic environments. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2014, 59, 1139–1151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.S.; Kim, S.; Kim, S.-S.; An, S.; Kim, Y.-T.; Choi, O.-I. Sediment Oxygen Consumption in Semi-Closed Korean Coastal Bays during Summer. Ocean Sci. J. 2009, 44, 161–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hargrave, B.T.; Duplisea, D.E.; Pfeiffer, E.; Wildish, D.J. Seasonal changes in benthic fluxes of dissolved oxygen and ammonium associated with marine cultured Atlantic salmon. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 1993, 96, 249–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holmer, M.; Marba, N.; Diaz-Almela, E.; Duarte, C.M.; Tsapakis, M.; Danovaro, R. Sedimentation of organic matter from fish farms in oligotrophic Mediterranean assessed through bulk and stable isotope (13C and 15N) analyses. Aquaculture 2007, 262, 268–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Papageorgiou, N.; Kalantzi, I.; Karakassis, I. Effects of fish farming on the biological and geochemical properties of muddy and sandy sediments in the Mediterranean Sea. Mar. Environ. Res. 2010, 69, 326–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azim, M.E.; Little, D.C.; Bron, J.E. Microbial protein production in activated suspension tanks manipulating C:N ratio in feed and the implications for fish culture. Bioresour. Technol. 2008, 99, 3590–3599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lefebvre, S.; Barillé, L.; Clerc, M. Pacific oyster (Crassostrea gigas) feeding responses to a fish-farm effluent. Aquaculture 2000, 187, 185–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.-M.; Kim, K.-D. Effects of dietary carbohydrate to lipid ratios on growth and body composition of juvenile and grower rockfish, Sebastes schlegeli. Aquacult. Res. 2009, 40, 1830–1837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, S.H.; Lee, S.-M.; Lee, J.H. Effects of the extruded pellets and raw fish-based moist pellet on growth and body composition of flounder, Paralichthys olivaceus L. for 10 months. J. Aquacult. 2005, 18, 60–65. [Google Scholar]
- Kwon, J.N.; Jung, R.H.; Kang, Y.S.; An, K.H.; Lee, W.C. Environmental management of marine cage fish farms using numerical modelling. Sea 2005, 4, 181–195. [Google Scholar]
- Jaramillo, E.; Bertrán, C.; Bravo, A. Mussel biodeposition in an estuary in southern Chile. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 1992, 82, 85–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Andersen, K.; Handå, A.; Jensen, B.; Reitan, K.I.; Olsen, Y. Chemical composition and release rate of waste discharge from an Atlantic salmon farm with an evaluation of IMTA feasibility. Aquacult. Environ. Interact. 2013, 4, 147–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bale, A.J. Sediment trap performance in tidal waters: Comparison of cylindrical and conical collectors. Cont. Shelf Res. 1998, 18, 1401–1418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, A.-J.; Liu, J.T.; Ye, X.; Zheng, B.-X.; Li, Y.-H.; Chen, J. Settling fluxes of cohesive sediments measured by sediment traps in a semi-enclosed embayment with strong dial environment. Cont. Shelf Res. 2015, 106, 17–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hatcher, A.; Grant, J.; Schofield, B. Effects of suspended mussel culture (Mytilus spp.) on sedimentation, benthic respiration and sediment nutrient dynamics in a coastal bay. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 1994, 115, 219–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kutti, T.; Ervik, A.; Hansen, P.K. Effects of organic effluents from a salmon farm on a fjord system. I. Vertical export and disposal processes. Aquaculture 2007, 262, 367–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarà, G.; Scilipoti, D.; Mazzola, A.; Modica, A. Effects of fish farming waste to sedimentary and particulate organic matter in a southern Mediterranean area (Gulf of Castellammare, Sicily): A multiple stable isotope study (δ13C and δ15N). Aquaculture 2004, 234, 199–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tengberg, A.; Almroth, E.; Hall, P. Resuspension and its effects on organic carbon recycling and nutrient exchange in coastal sediments: In situ measurements using new experimental technology. J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol. 2003, 285–286, 119–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cromey, C.J.; Nickell, T.D.; Black, K.D.; Provost, P.G.; Griffiths, C.R. Validation of a fish farm waste resuspension model by use of a particulate tracer discharged from a point source in a coastal environment. Estuaries 2002, 25, 916–929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richard, M.; Archambault, P.; Thouzeau, G.; Mckindsey, C.W.; Desrosiers, G. 2007. Influence of suspended scallop cages and mussel lines on pelagic and benthic biogeochemical fluxes in Havre-aux Maisons Lagoon, ÎIes-de-la-Madeleine (Quebec, Canada). Can J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 2007, 63, 1198–1213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nickell, L.A.; Black, K.D.; Hughes, D.J.; Overnell, J.; Brand, T.; Nickell, T.D.; Breuer, E.; Harvey, S.M. Bioturbation sediment fluxes and benthic community structure around a salmon cage farm in Loch Creran, Scotland. J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol. 2003, 285–286, 221–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ragueneau, O.; Chauvaud, L.; Moriceau, B.; Leynaert, A.; Thouzeau, G.; Dinval, A.; Le Loc’h, F.; Jean, F. Biodeposition by an invasive suspension feeder impacts the biogeochemical cycle of Si in a coastal ecosystem (Bay of Brest, France). Biogeochemistry 2005, 75, 19–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Howarth, R.W.; Roxanne, M. Nitrogen as the limiting nutrient for eutrophication in coastal marine ecosystems: Evolving views over three decades. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2006, 51, 364–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]






| Sites | Production Cycle | Date | Operating Period (Years) | Area (km2) | Stock Density 1 (kg m−2) | Fish Feed Supply 1 (kg m−2 d−1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| FF | Intensive fish culturing | October 2017 | >30 | 0.015 | 42.8 | 1.3 |
| Intensive fish culturing | May 2018 | 40.7 | 1.1 | |||
| After harvesting and stocking | December 2018 | 31.9 | 0.8 | |||
| OF | Intensive shellfish culturing | October 2017 | >40 | 0.091 | 16.5 | n/a |
| Stocking and shellfish culturing | May 2018 | 8.7 | n/a | |||
| Intensive shellfish culturing before harvesting | December 2018 | 21.1 | n/a |
| Season | Sites | Water Column | Sediment | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Depth | Temp. | TOC | TN | C/N | ||
| (m) | (°C) | (%, dry wt) | (mol/mol) | |||
| October 2017 | FF | 19 | 19.1 | 2.11 ± 0.12 | 0.40 ± 0.02 | 6.2 |
| OF | 11 | 18.8 | 1.46 ± 0.11 | 0.24 ± 0.01 | 7.2 | |
| FF-C | 16 | 18.7 | 1.01 ± 0.05 | 0.14 ± 0.01 | 8.4 | |
| OF-C | 10 | 18.5 | 1.13 ± 0.08 | 0.15 ± 0.01 | 8.9 | |
| May 2018 | FF | 19 | 16.1 | 1.91 ± 0.10 | 0.35 ± 0.03 | 6.4 |
| OF | 11 | 15.8 | 1.45 ± 0.04 | 0.23 ± 0.02 | 7.5 | |
| FF-C | 16 | 15.9 | 1.12 ± 0.02 | 0.14 ± 0.02 | 9.1 | |
| OF-C | 10 | 15.8 | 1.02 ± 0.12 | 0.14 ± 0.01 | 8.5 | |
| December 2018 | FF | 19 | 15.9 | 1.78 ± 0.20 | 0.31 ± 0.03 | 6.7 |
| OF | 11 | 15.3 | 1.99 ± 0.13 | 0.29 ± 0.03 | 8.0 | |
| FF-C | 16 | 15.8 | 1.11 ± 0.08 | 0.14 ± 0.02 | 9.3 | |
| OF-C | 10 | 15.0 | 1.13 ± 0.07 | 0.14 ± 0.01 | 9.4 | |
| Season | Sites | Vertical OC Flux 1 (OCin) | OC Oxidation Rate 2 (OCox) | Lateral Flux 3 (OClat) | Burial Flux 4 (OCburial) | Oxidation Efficiency 5 | Burial Efficiency 6 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (mmol C m−2 d−1) | (%) | ||||||
| May 2018 | FF | 154 ± 24 | 90 ± 1 | 55 ± 24 | 9.1 ± 1.3 | 58 | 6 |
| OF | 73 ± 6 | 46 ± 1 | 20 ± 6 | 7.3 ± 0.5 | 63 | 10 | |
| FF-C | 39 ± 5 | 30 ± 8 | 7 ± 9 | 2.1 ± 0.4 | 77 | 5 | |
| OF-C | 33 ± 2 | 23 ± 3 | 6 ± 4 | 3.7 ± 0.4 | 70 | 11 | |
| December 2018 | FF | 112 ± 13 | 59 ± 11 | 44 ± 20 | - | 53 | 8 |
| OF | 129 ± 5 | 65 ± 12 | 57 ± 13 | - | 50 | 6 | |
| FF-C | 18 ± 2 | 13 ± 3 | 3 ± 4 | - | 72 | 12 | |
| OF-C | 34 ± 4 | 24 ± 5 | 6 ± 6 | - | 71 | 11 | |
| Season | Sites | Nutrient Demand for PP 1 | Benthic Nutrient Flux | Contribution of BNFs to PP | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (mmol m−2 d−1) | (mmol m−2 d−1) | (%) | |||||
| DIN 2 | DIP | DIN 2 | DIP | DIN 2 | DIP | ||
| May | FF | 17.5 | 1.09 | 8.07 | 0.65 | 46 | 60 |
| OF | 6.53 | 0.57 | 37 | 52 | |||
| FF-C | 2.64 | 0.36 | 15 | 33 | |||
| OF-C | n.d. | n.d. | n.d. | n.d. | |||
| December | FF | 3.32 | 0.21 | 5.45 | 1.67 | 164 | 804 |
| OF | 8.95 | 0.51 | 270 | 243 | |||
| FF-C | −0.75 | 0.08 | n.d. | 40 | |||
| OF-C | 0.78 | n.d. | 23 | n.d. | |||
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kim, S.-H.; Lee, J.-S.; Kim, K.-T.; Kim, H.-C.; Lee, W.-C.; Choi, D.; Choi, S.-H.; Choi, J.-H.; Lee, H.-J.; Shin, J.-H. Aquaculture Farming Effect on Benthic Respiration and Nutrient Flux in Semi-Enclosed Coastal Waters of Korea. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2021, 9, 554. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse9050554
Kim S-H, Lee J-S, Kim K-T, Kim H-C, Lee W-C, Choi D, Choi S-H, Choi J-H, Lee H-J, Shin J-H. Aquaculture Farming Effect on Benthic Respiration and Nutrient Flux in Semi-Enclosed Coastal Waters of Korea. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering. 2021; 9(5):554. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse9050554
Chicago/Turabian StyleKim, Sung-Han, Jae-Seong Lee, Kyung-Tae Kim, Hyung-Chul Kim, Won-Chan Lee, Dongmun Choi, Sang-Hwa Choi, Jae-Hoon Choi, Hyo-Jin Lee, and Jae-Hyuk Shin. 2021. "Aquaculture Farming Effect on Benthic Respiration and Nutrient Flux in Semi-Enclosed Coastal Waters of Korea" Journal of Marine Science and Engineering 9, no. 5: 554. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse9050554
APA StyleKim, S.-H., Lee, J.-S., Kim, K.-T., Kim, H.-C., Lee, W.-C., Choi, D., Choi, S.-H., Choi, J.-H., Lee, H.-J., & Shin, J.-H. (2021). Aquaculture Farming Effect on Benthic Respiration and Nutrient Flux in Semi-Enclosed Coastal Waters of Korea. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering, 9(5), 554. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse9050554







