The Effect of Object Geometric Features on Frequency Inflection Point of Underwater Active Electrolocation System
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
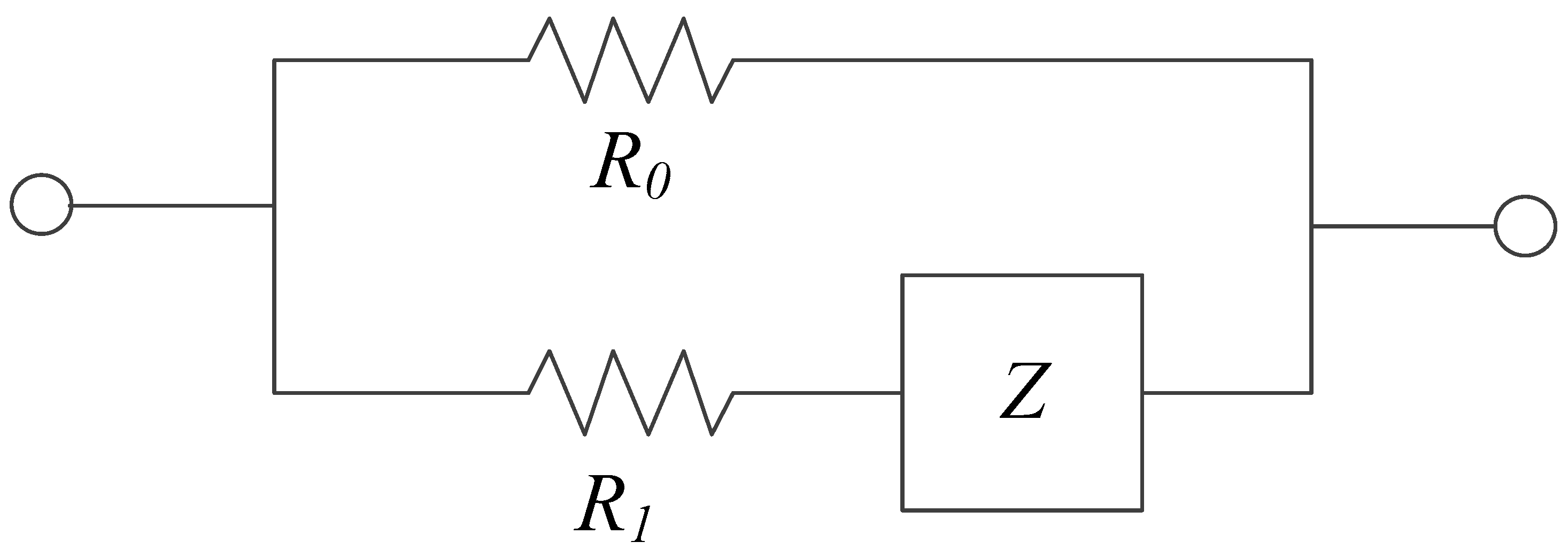
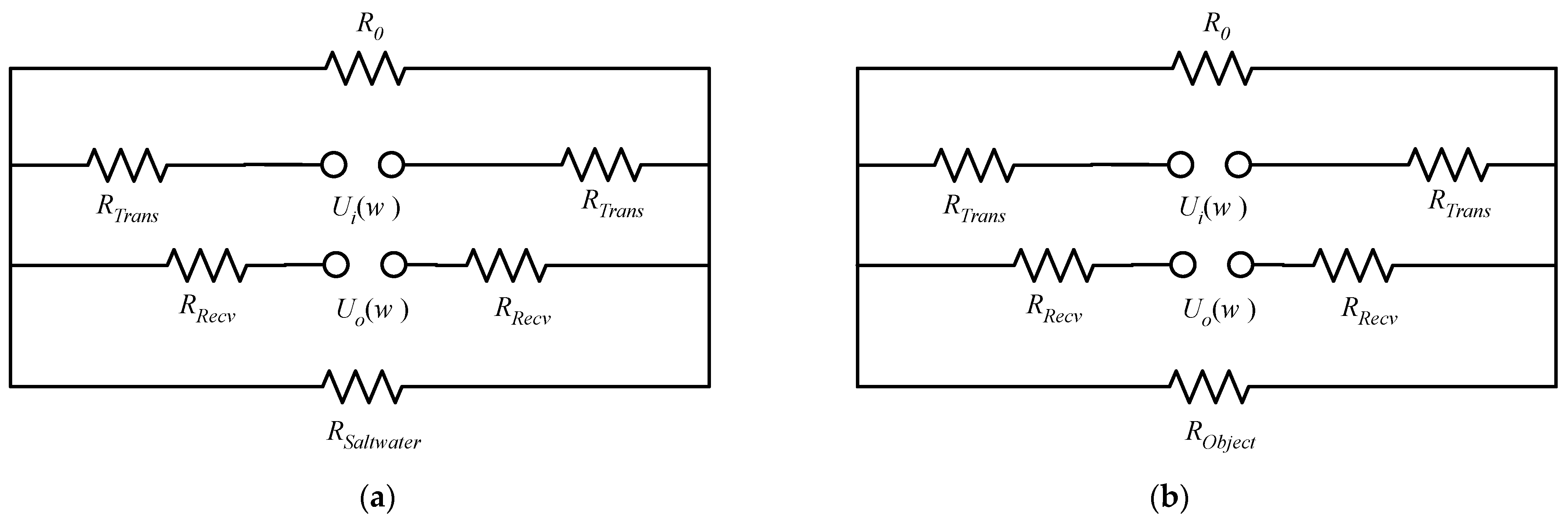
2.1. Theoretical Analysis
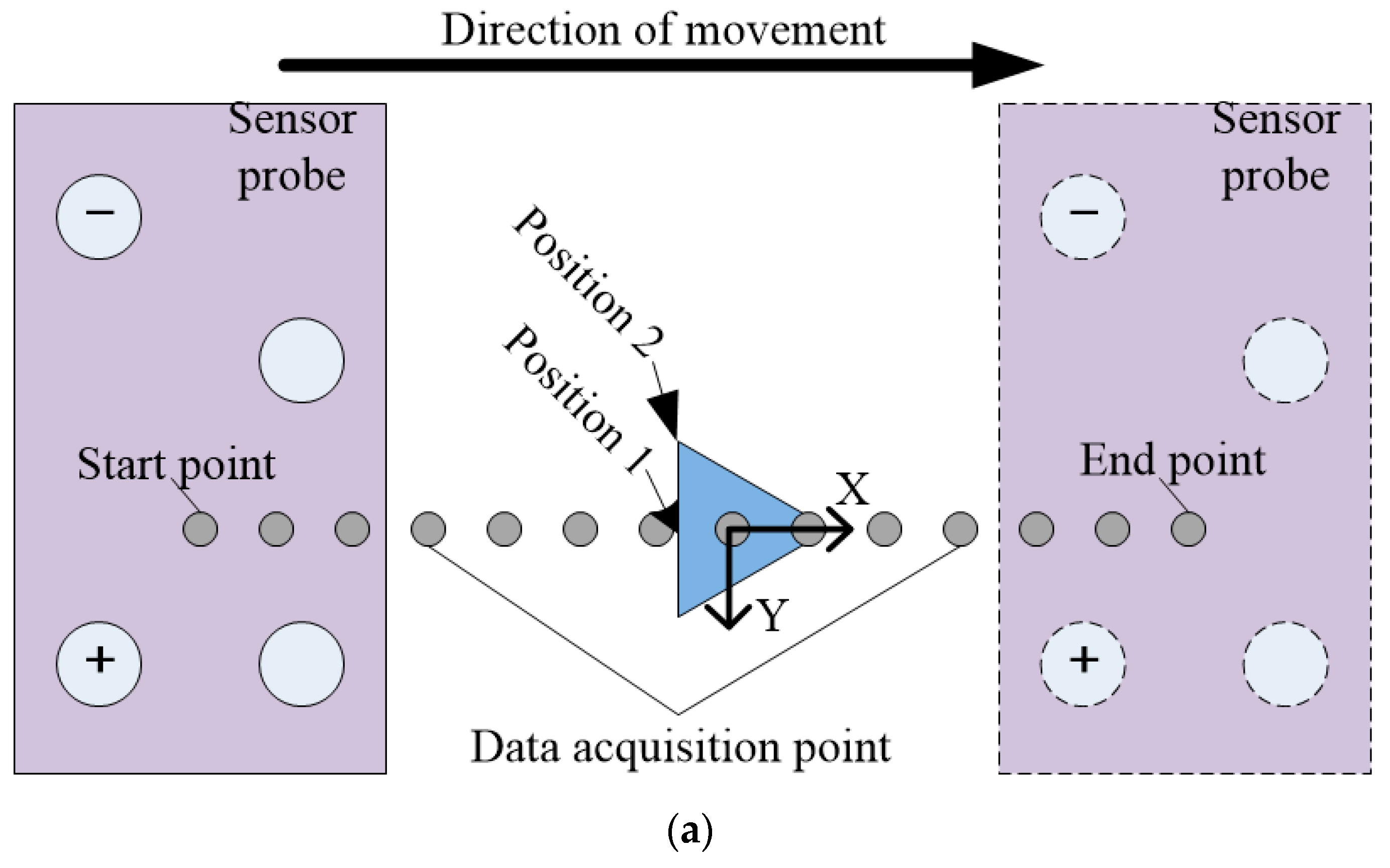
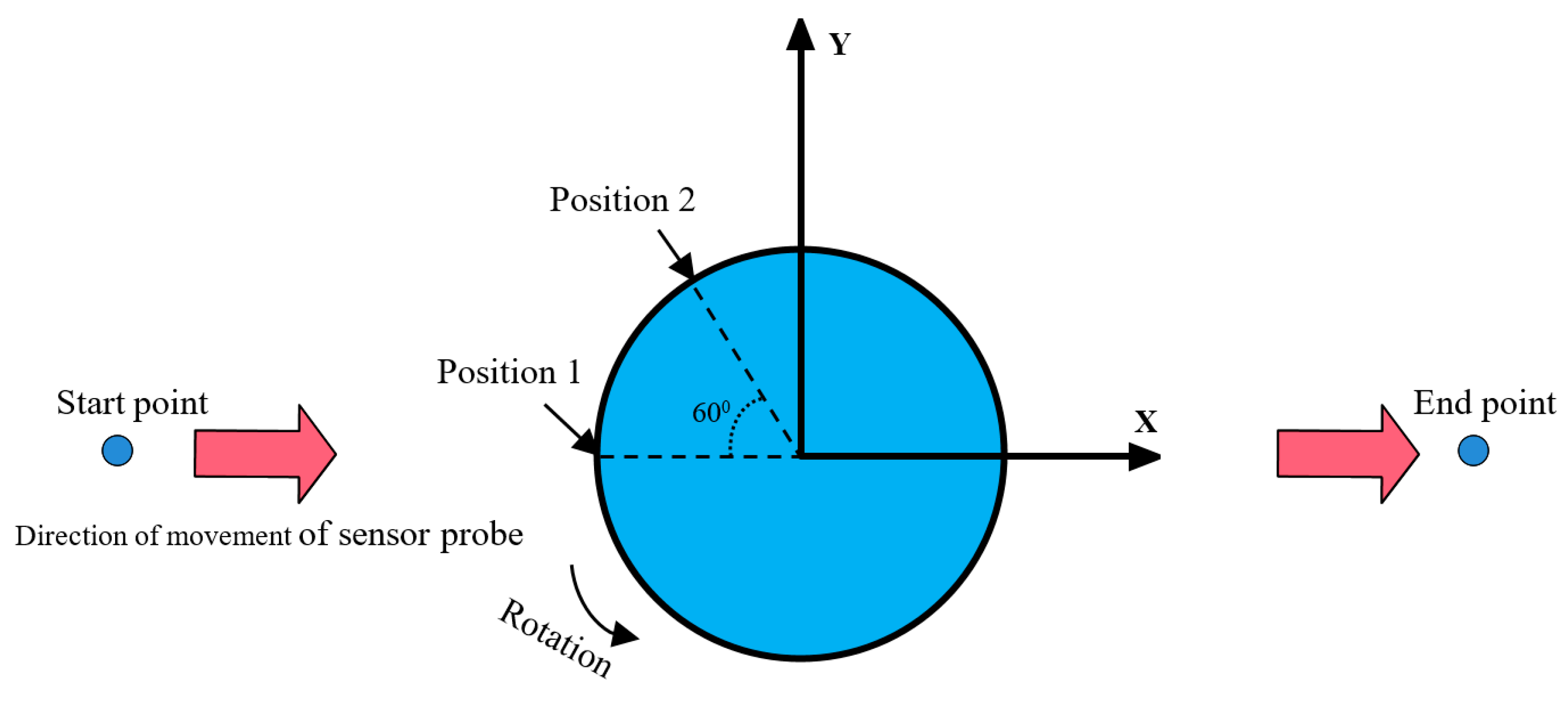
2.2. Experiment Setup
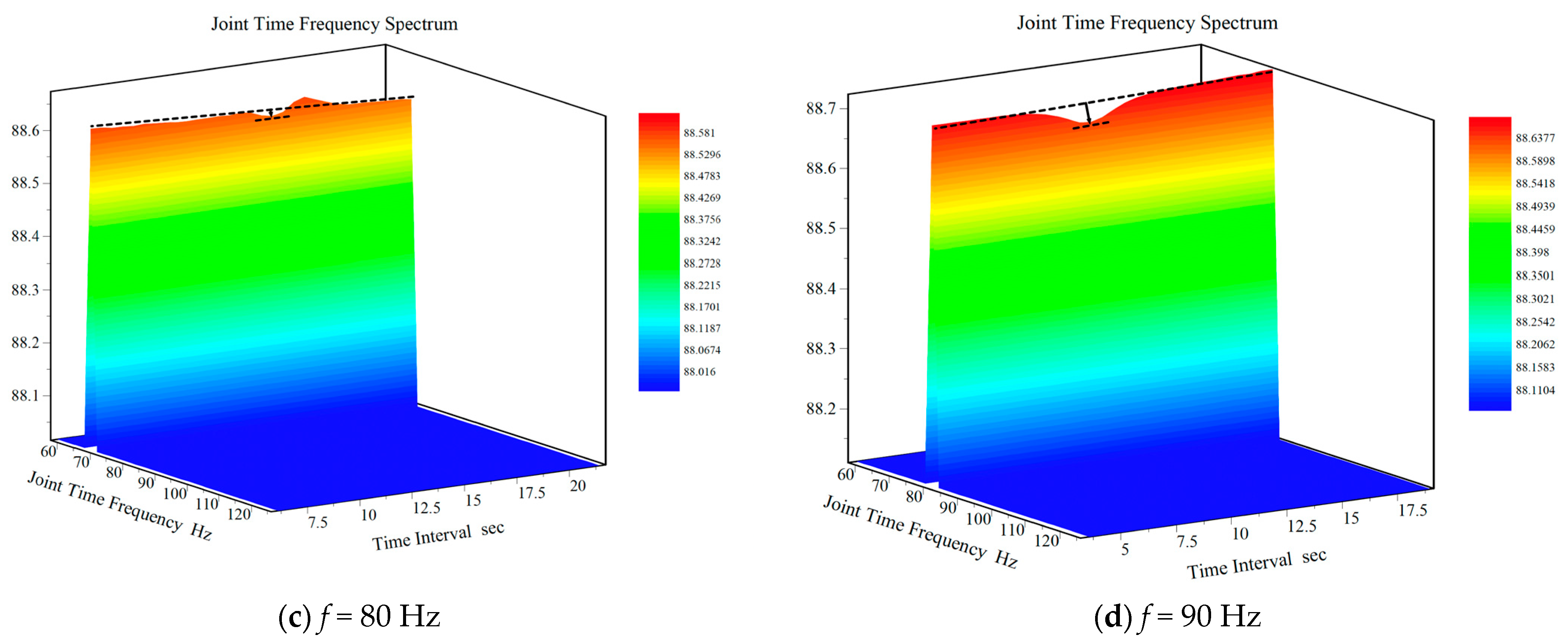
2.3. Data Processing
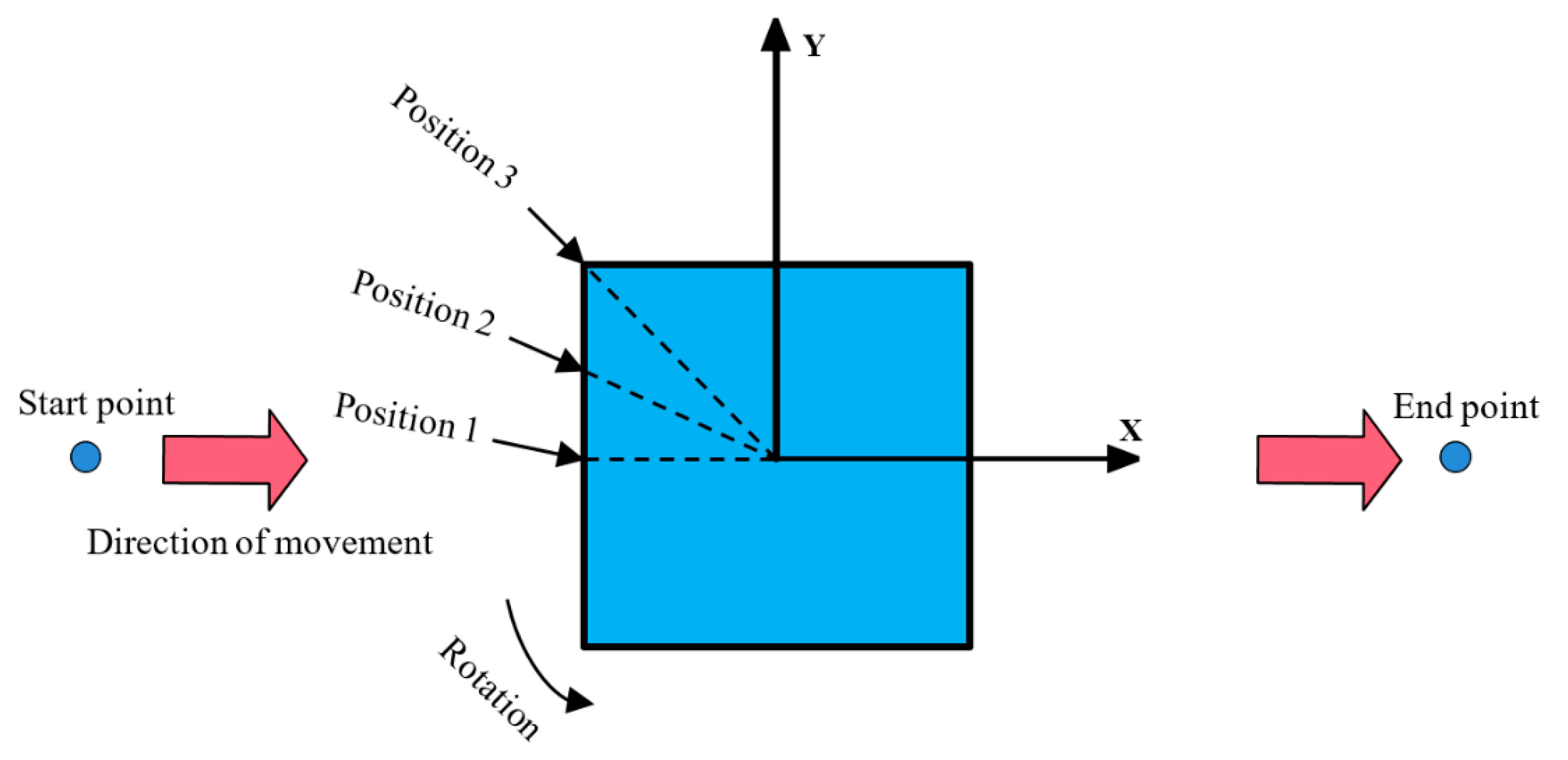
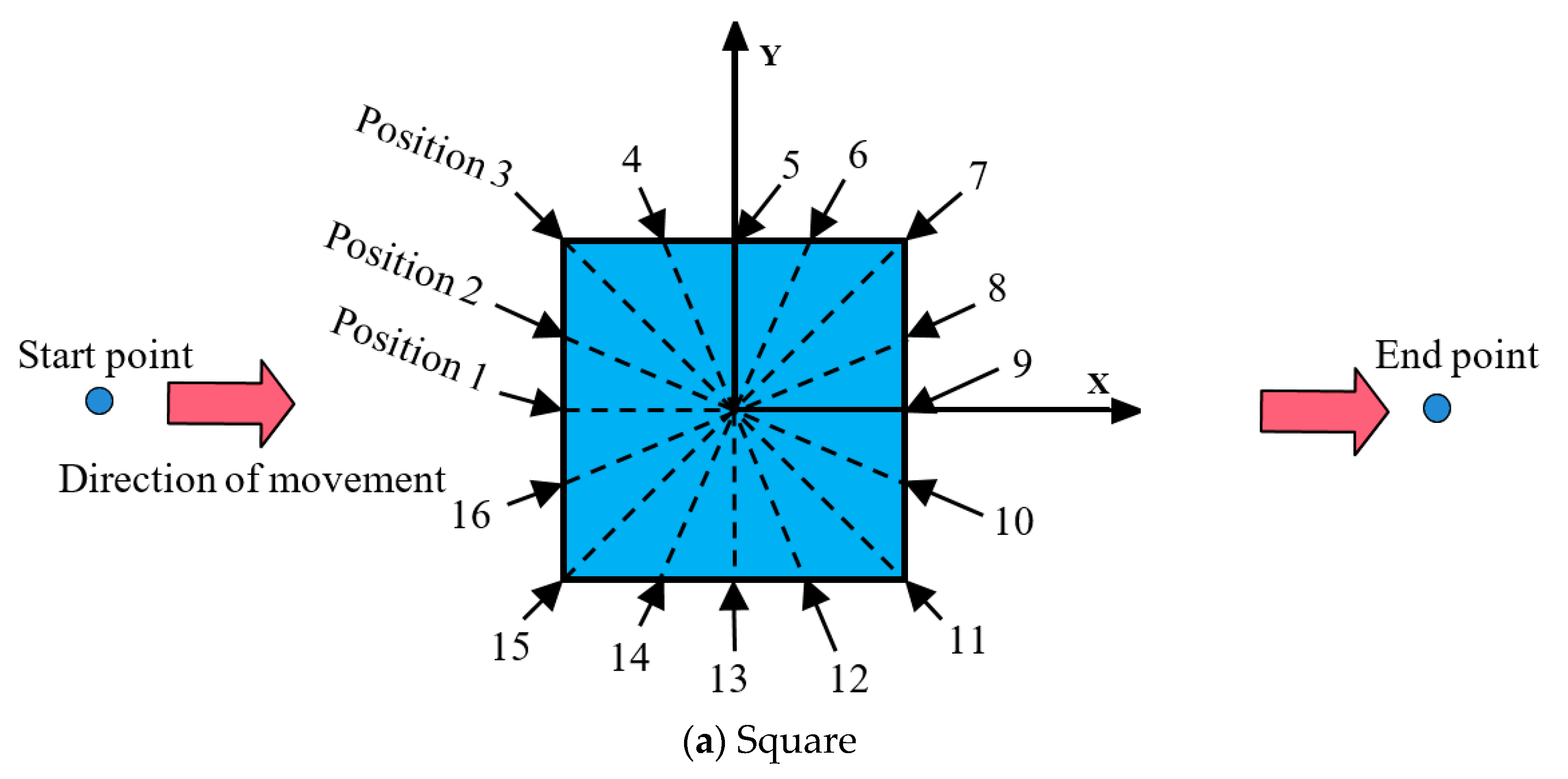
2.4. Procedures
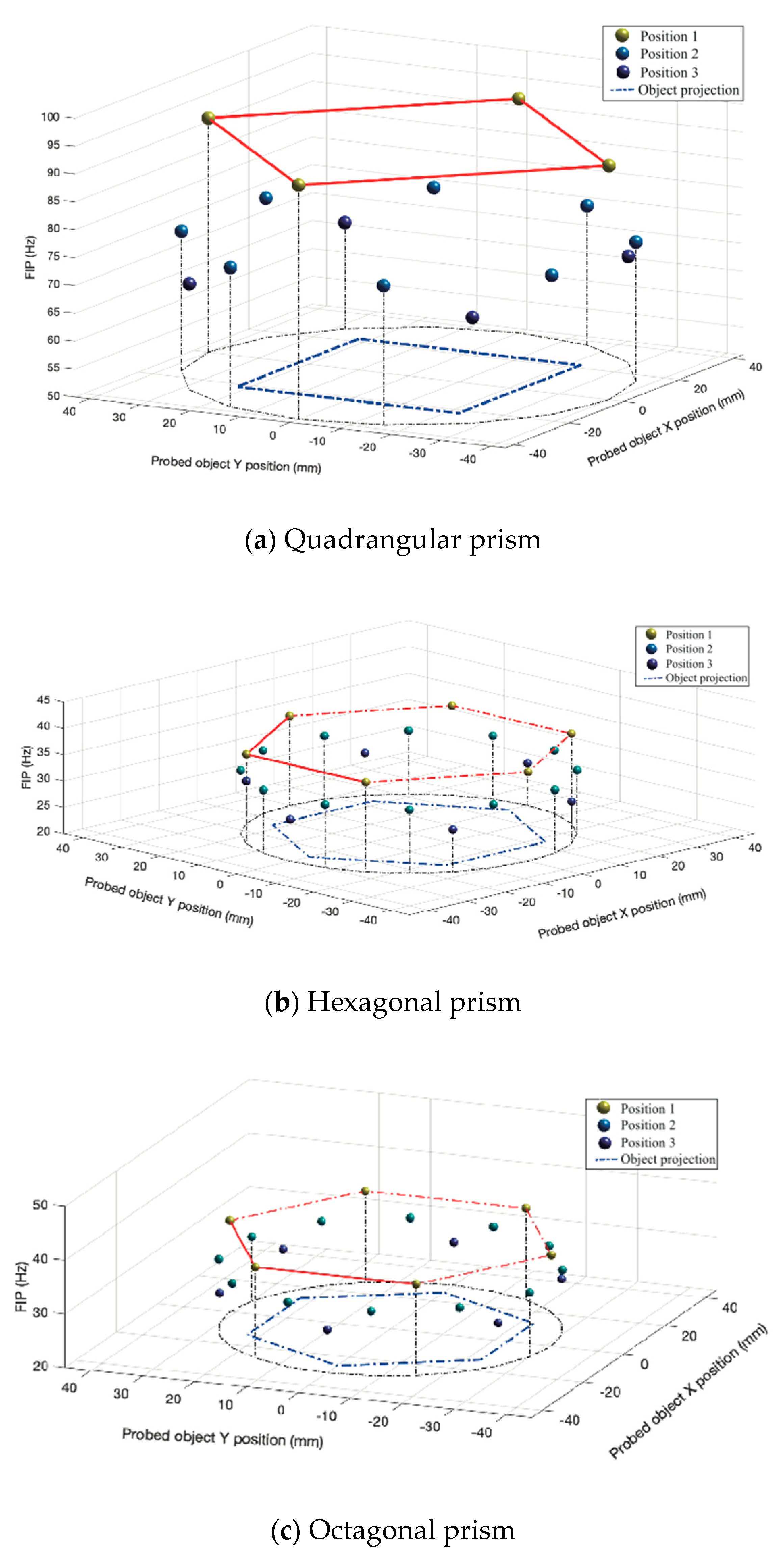
2.5. The DFDZ of Objects
3. Results
3.1. The Relationship between Surface Characteristics and FIP
3.1.1. Copper Cone
3.1.2. Copper Quadrangular Prism
3.2. Aluminum and Iron
3.2.1. FIP of Aluminum
3.2.2. FIP of Iron
4. Conclusions
5. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AIFC | Amplitude information-frequency characteristics |
| CCM | Cole–Cole model |
| FFT | Fast Fourier Transform |
| EOD | Electric organ discharge |
| IP | Induced polarization |
| FIP | Frequency inflection point |
| DFDZ | Detect frequency dead zone |
| UAES | Underwater active electrolocation system |
| JTFS | Joint time-frequency spectrogram |
| STFT | Short-time Fourier transform |
References
- Adair, R.K.; Astumian, R.D.; Weaver, J.C. Detection of weak electric fields by sharks, rays, and skates. Chaos Interdiscip. J. Nonlinear Sci. 1998, 8, 576–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Czech-Damal, N.U.; Dehnhardt, G.; Manger, P.; Hanke, W. Passive electroreception in aquatic mammals. J. Comp. Physiol. 2013, 199, 555–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Emde, G.V.D. Non-visual environmental imaging and object detection through active electrolocation in weakly electric fish. J. Comp. Physiol. 2006, 192, 601–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Emde, G.V.D.; Schwarz, S.; Gomez, L.; Budelli, R.; Grant, K. Electric fish measure distance in the dark. Nature 1998, 395, 890–894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Emde, G.V.D.; Fetz, S. Distance, shape and more: Recognition of object features during active electrolocation in a weakly electric fish. J. Exp. Biol. 2007, 210, 3082–3095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Emde, G.V.D. 3-Dimensional Scene Perception during Active Electrolocation in a Weakly Electric Pulse Fish. Front. Behav. Neurosci. 2010, 4, 26–38. [Google Scholar] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rasnow, B. The effects of simple objects on the electric field of Apteronotus. J. Comp. Physiol. 1996, 178, 397–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nelson, M.E.; Maciver, M.A. Sensory acquisition in active sensing systems. J. Comp. Physiol. 2006, 192, 573–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caputi, A.A.; Budelli, R.; Grant, K.; Bell, C.C. The electric image in weakly electric fish: Physical images of resistive objects in Gnathonemus petersii. J. Exp. Biol. 1998, 201, 2115–2128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maciver, M.A.; Fontaine, E.; Burdick, J.W. Designing future underwater vehicles: Principles and mechanisms of the weakly electric fish. IEEE J. Ocean. Eng. 2016, 29, 651–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rother, D.; Migliaro, A.; Canetti, R.; Gomez, L.; Caputi, A.; Budelli, R. Electric images of two low resistance objects in weakly electric fish. Biosystems 2003, 71, 169–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friedman, J.; Herman, H.; Truong, N.; Srivastava, M.B. A 16-electrode biomimetic electrostatic imaging system for ocean use. IEEE Sens. J. 2011, 24, 986–989. [Google Scholar]
- Emde, G.V.D.; Amey, M.; Engelmann, J.; Fetz, S.; Folde, C.; Hollmann, M.; Metzen, M.; Pusch, R. Active electrolocation in Gnathonemus petersii: Behaviour, sensory performance, and receptor systems. J. Physiol.-Paris 2008, 102, 279–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lebastard, V.; Chevallereau, C.; Girin, A.; Servagent, N.; Gossiaux, P.B.; Boyer, F. Environment reconstruction and navigation with electric sense based on a Kalman filter. Int. J. Robot. Res. 2013, 32, 172–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- MacIver, M.A.; Nelson, M.E. Towards a biorobotic electrosensory system. Auton. Robot. 2001, 11, 263–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solberg, J.R.; Lynch, K.M.; MacIver, M.A. Active electrolocation for underwater target localization. Int. J. Robot. Res. 2008, 27, 529–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Servagent, N.; Jawad, B.; Bouvier, S.; Boyer, F.; Girin, A.; Gomez, F.; Lebastard, V.; Stefanini, C.; Gossiaux, P.B. Electrolocation Sensors in Conducting Water Bio-Inspired by Electric Fish. IEEE Sens. J. 2013, 13, 1865–1882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dimble, K.D.; Ranganathan, B.N.; Keshavan, J.; Humbert, J.S. Computationally efficient underwater navigational strategy in electrically heterogeneous environments using electrolocation. In Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation(ICRA), Seattle, DC, USA, 26–30 May 2015; pp. 1172–1177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, Y.; Snyder, J.B.; Peshkin, M.; Maciver, M.A. Finding and identifying simple objects underwater with active electrosense. Int. J. Robot. Res. 2016, 34, 1255–1277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujita, K.; Kashimori, Y. Representation of object’s shape by multiple electric images in electrolocation. Biol. Cybern. 2019, 113, 239–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gottwald, M.; Herzog, H.; Emde, G.V.D. A bio-inspired electric camera for short-range object inspection in murky waters. Bioinspir. Biomim. 2019, 14, 035002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, J.G. A study of amplitude information-frequency characteristics for underwater active electrolocation system. Bioinspir. Biomim. 2015, 10, 066007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, J.G.; Wang, Y.L.; Liu, L. A Research on Effect of Probed Object Shape on Frequency Inflection Point (FIP) of Underwater Active Electrolocation System. IEEE Trans. Appl. Supercond. 2016, 26, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, Q.X.; Peng, J.G.; Chen, H.J. Amplitude information-frequency characteristics for multi-frequency excitation of underwater active electrolocation systems. Bioinspir. Biomim. 2020, 15, 016004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bazeille, S.; Lebastard, V.; Boyer, F. A Purely Model-Based Approach to Object Pose and Size Estimation with Electric Sense. IEEE Trans. Robot. 2020, 36, 1611–1618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, Y.; Neveln, I.D.; Peshkin, M.; Maciver, M.A. Enhanced detection performance in electrosense through capacitive sensing. Bioinspir. Biomim. 2016, 11, 055001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cole, K.S.; Cole, R.H. Dispersion and Absorption in Dielectrics I. Alternating Current Characteristics. J. Chem. Phys. 1941, 9, 341–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]








| Shape | Position | Position 1 | Position 2 | Position 3 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Size (mm)/Adjacent Angle | DFDZ | FIP | DFDZ | FIP | DFDZ | FIP | |
| Quadrangular prism | 20 × 20 × 40/22.5° | 80–85 | 83 | 60–70 | 65 | 40–50 | 45 |
| Projection | Square/22.5° | Regular Hexagon/15° | Regular Octagon/11.25° | Circular/15° | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Material | Prism | Pyramid | Prism | Pyramid | Prism | Pyramid | Prism | Pyramid | |
| Aluminum | Quadrangular prism | Quadrangular pyramid | Hexagonal prism | Hexagonal pyramid | Octagonal prism | Octagonal pyramid | Cylinder | Cone | |
| Iron | Quadrangular prism | Quadrangular pyramid | Hexagonal prism | Hexagonal pyramid | Octagonal prism | Octagonal pyramid | Cylinder | Cone | |
| Shape | Position | Position 1 | Position 2 | Position 3 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Size (mm)/Adjacent Angle | DFDZ | FIP | DFDZ | FIP | DFDZ | FIP | |
| Quadrangular prism | 44 × 44 × 50/22.5° | 90–93 | 92 | 74–76 | 75 | 68–70 | 69 |
| Hexagonal prism | 27.5 × 55 × 48/15° | 36–38 | 37 | 30–35 | 32 | 27–30 | 28 |
| Octagonal prism | 20.1 × 52.7 × 50/11.25° | 50–60 | 55 | 40–50 | 45 | 20–30 | 25 |
| Cylinder | Φ20 × 40/15° | 106–110 | 108 | 106–110 | 108 | 106–108 | 107 |
| Quadrangular pyramid | 44.31 × 44.31 × 50/22.5° | 80–90 | 85 | 70–80 | 75 | 60–70 | 65 |
| Hexagonal pyramid | 47.62 × 55 × 50/15° | 100–120 | 110 | 90–115 | 100 | 75–95 | 85 |
| Octagonal pyramid | 48.68 × 52.7 × 50/11.25° | 120–130 | 125 | 110–120 | 115 | 100–110 | 105 |
| Cone | Φ20 × 40/15° | 30–50 | 40 | 30–50 | 40 | 30–50 | 40 |
| Shape | Position | Position 1 | Position 2 | Position 3 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Size (mm)/Adjacent Angle | DFDZ | FIP | DFDZ | FIP | DFDZ | FIP | |
| Quadrangular prism | 44 × 44 × 50/22.5° | 8–10 | 9 | 5–8 | 7 | <5 | 4 |
| Hexagonal prism | 27.5 × 55 × 48/15° | 8–10 | 9 | 5–8 | 6 | <5 | 3 |
| Octagonal prism | 20.1 × 52.7 × 50/11.25° | 16–18 | 17 | 10–12 | 11 | <5 | 3 |
| Cylinder | Φ20 × 40/15° | 10–12 | 11 | 10–12 | 11 | 10–12 | 11 |
| Quadrangular pyramid | 44.31 × 44.31 × 50/22.5° | 5–8 | 7 | 2–5 | 4 | <2 | 1 |
| Hexagonal pyramid | 47.62 × 55.5 × 50/15° | 8–10 | 9 | 8–10 | 9 | <5 | <3 |
| Octagonal pyramid | 48.68 × 52.7 × 50/11.25° | 10–15 | 12 | <5 | <2 | <2 | <1 |
| Cone | Φ20 × 40/15° | 15–18 | 17 | 15–18 | 17 | 15–18 | 17 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Han, Y.; Wu, H.; Peng, J.; Ou, B. The Effect of Object Geometric Features on Frequency Inflection Point of Underwater Active Electrolocation System. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2021, 9, 756. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse9070756
Han Y, Wu H, Peng J, Ou B. The Effect of Object Geometric Features on Frequency Inflection Point of Underwater Active Electrolocation System. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering. 2021; 9(7):756. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse9070756
Chicago/Turabian StyleHan, Yuanjian, Hailong Wu, Jiegang Peng, and Bin Ou. 2021. "The Effect of Object Geometric Features on Frequency Inflection Point of Underwater Active Electrolocation System" Journal of Marine Science and Engineering 9, no. 7: 756. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse9070756
APA StyleHan, Y., Wu, H., Peng, J., & Ou, B. (2021). The Effect of Object Geometric Features on Frequency Inflection Point of Underwater Active Electrolocation System. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering, 9(7), 756. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse9070756





