Cyclic Behavior of Calcareous Sand from the South China Sea
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
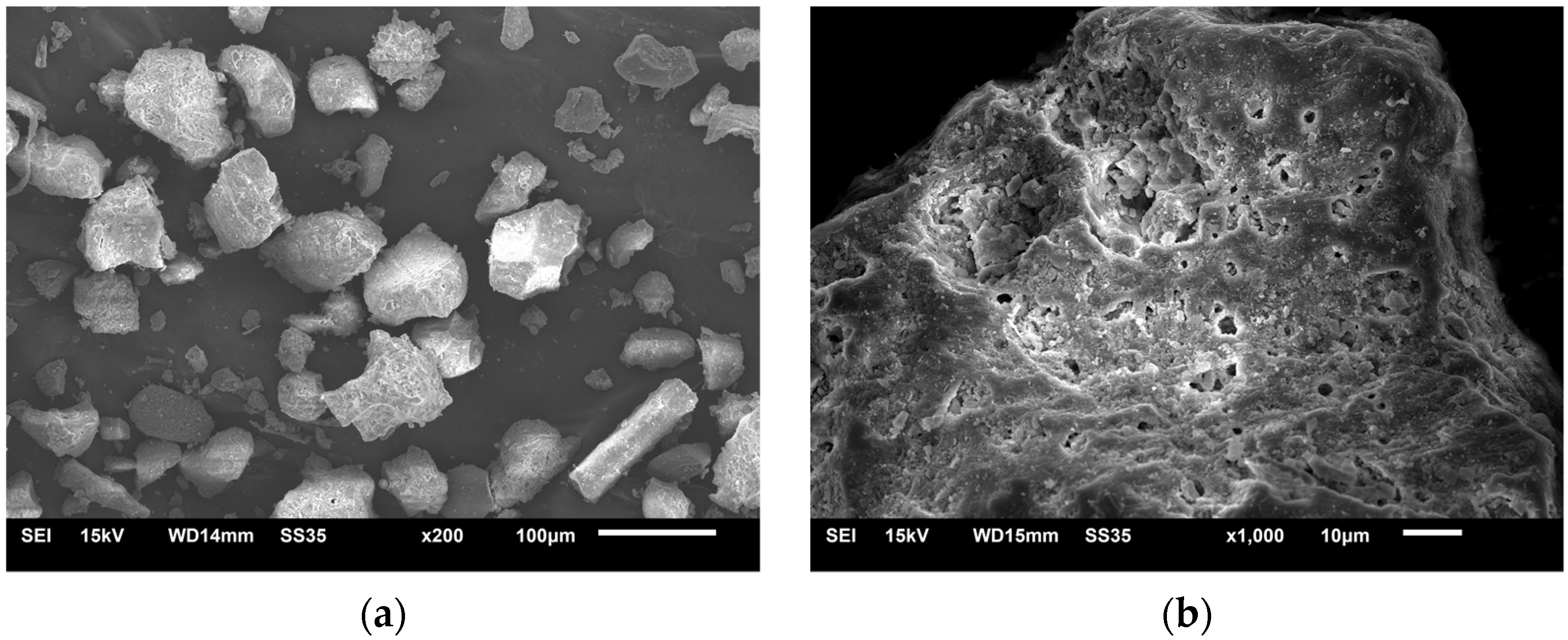
2.1. Materials
2.2. Specimen Preparation
2.3. Testing Program
3. Results
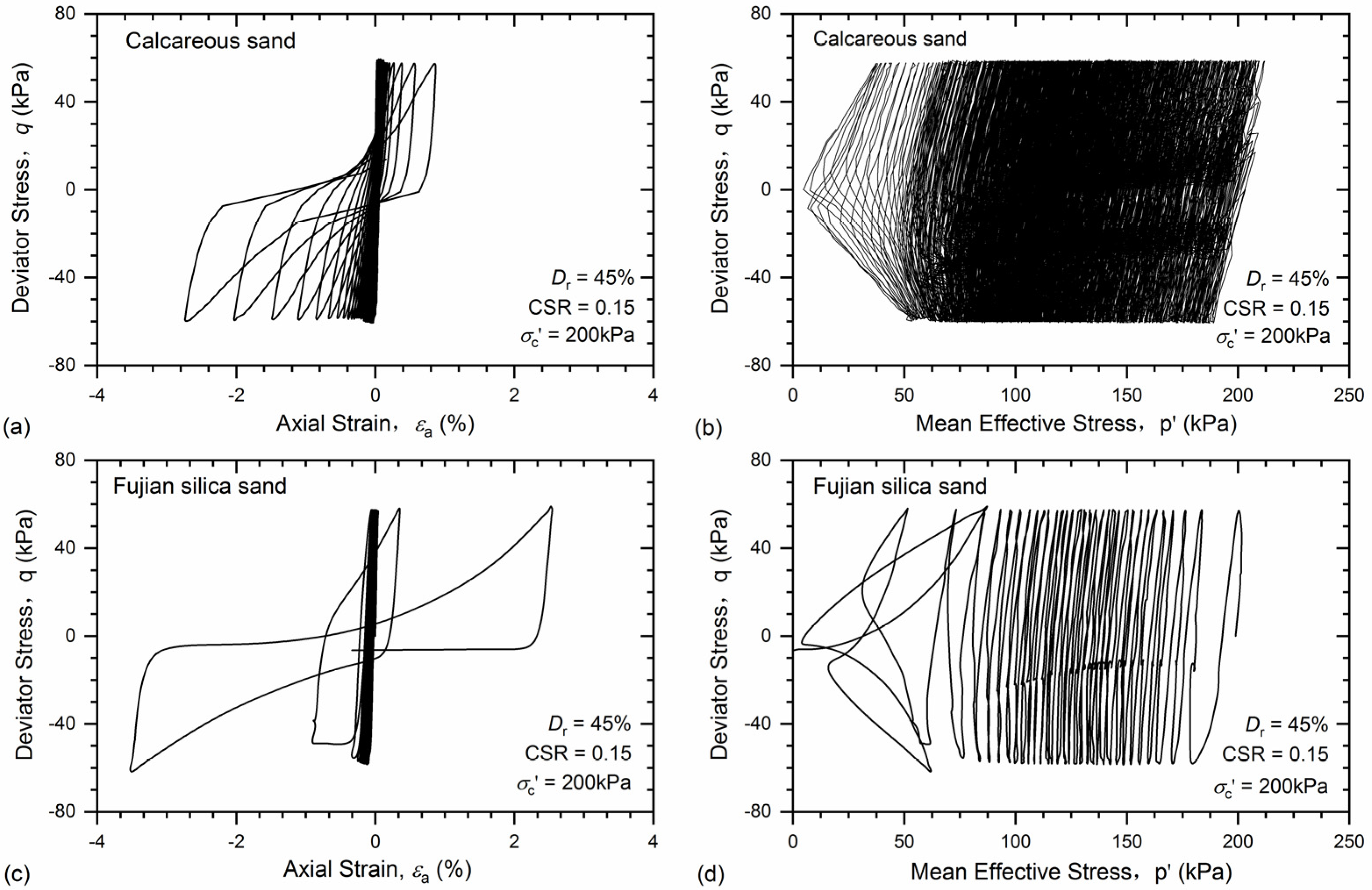
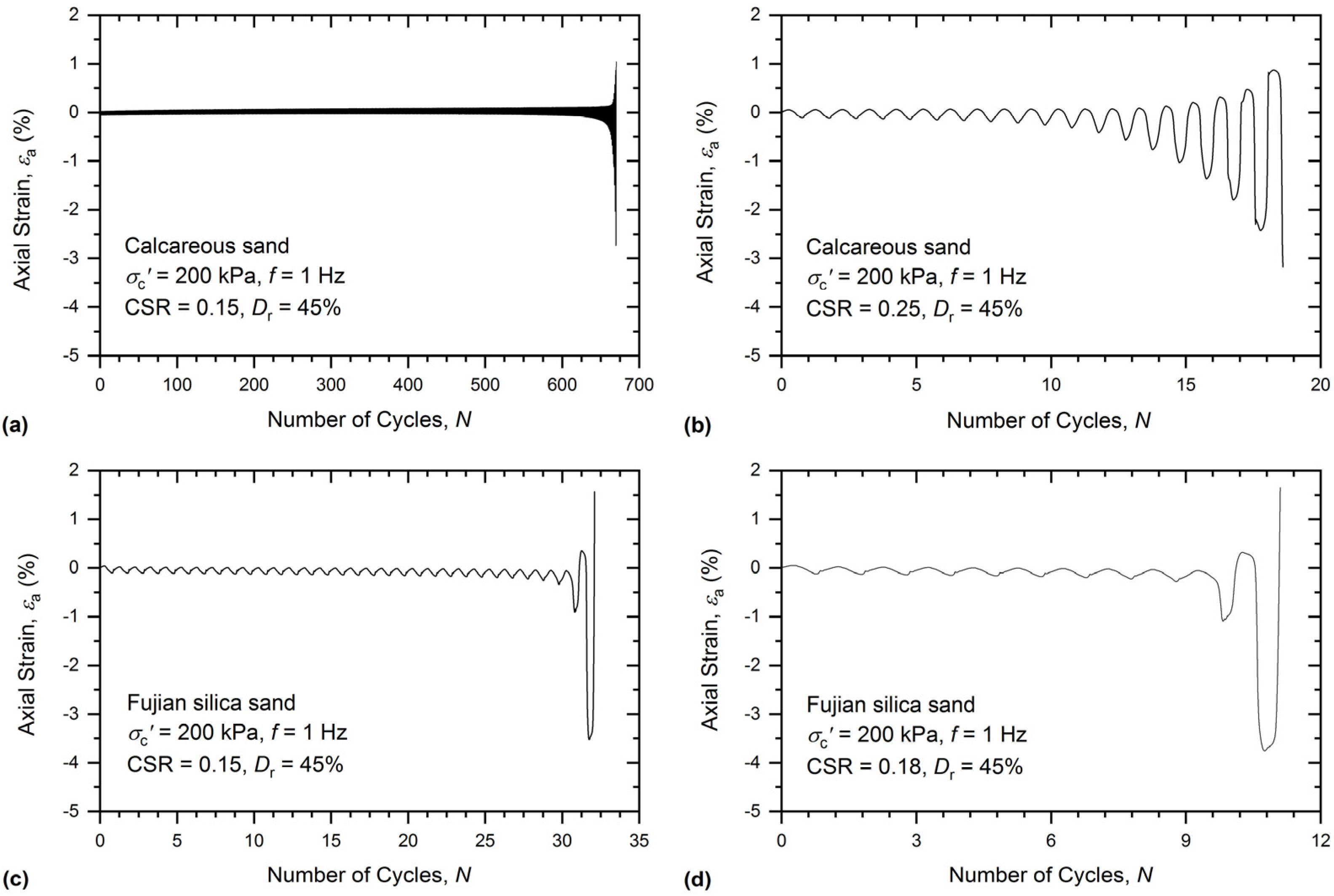
3.1. Undrained Cyclic Response
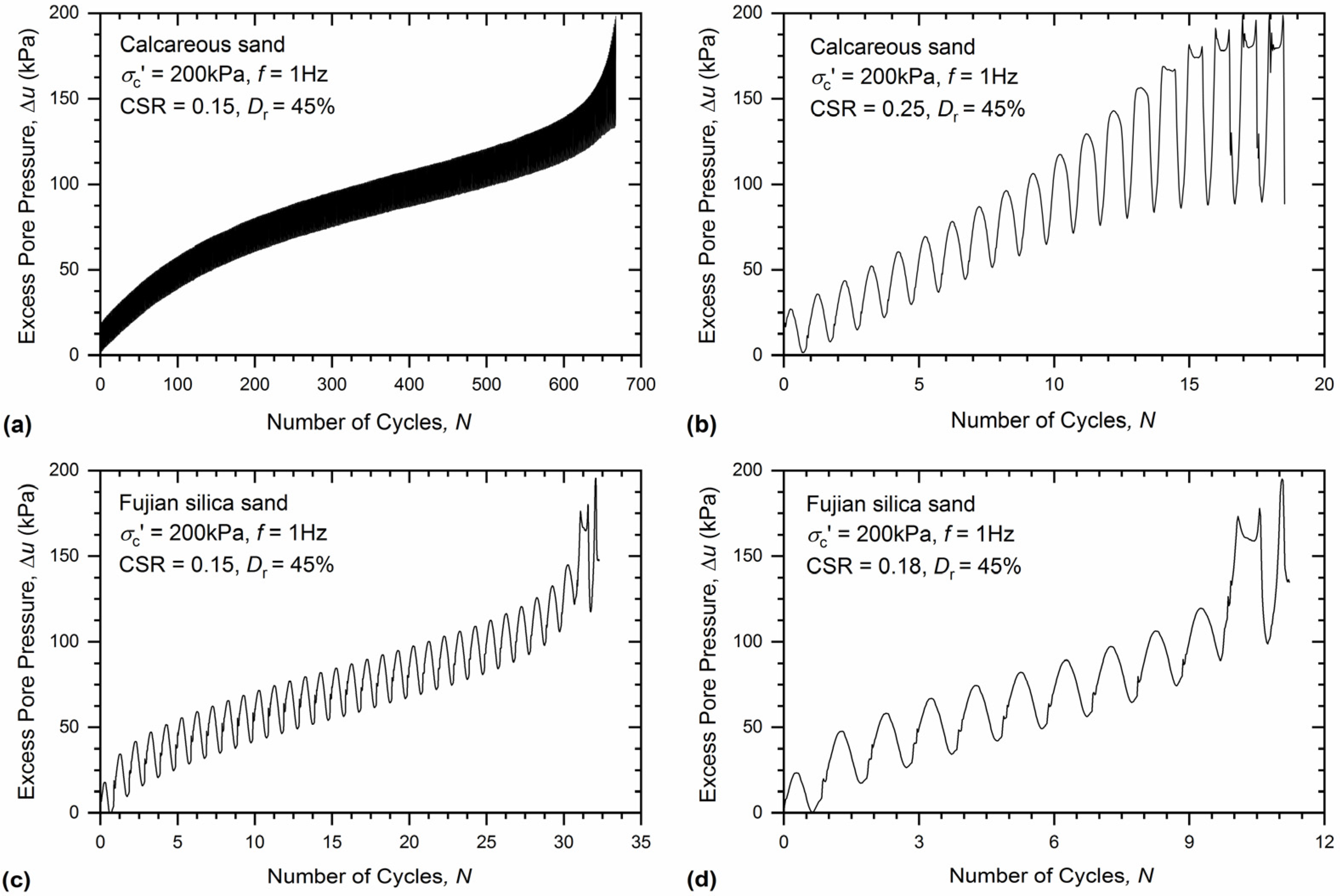
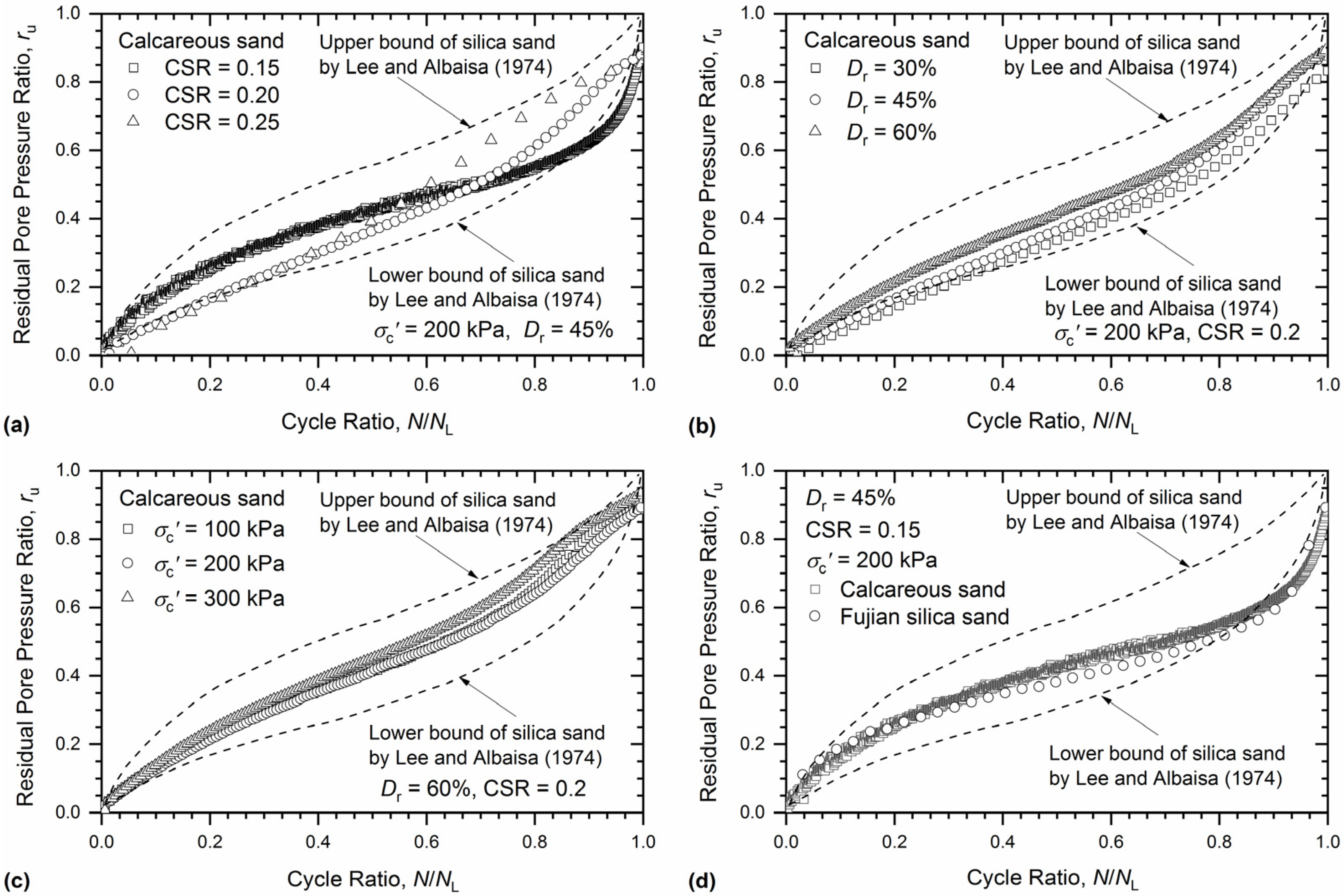
3.2. Development of Excess Pore Pressure
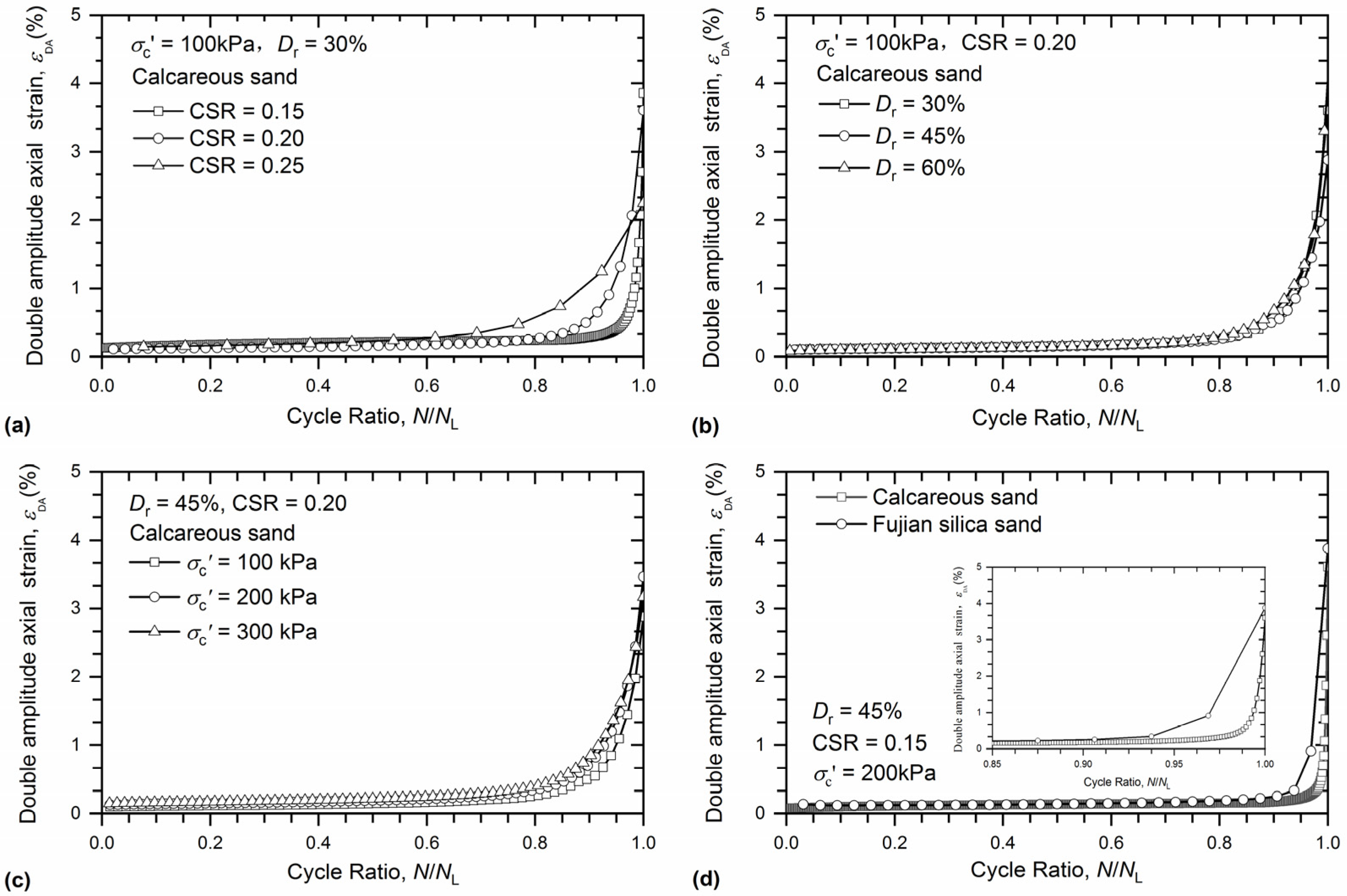
3.3. Deformation Response
3.4. Shear Modulus
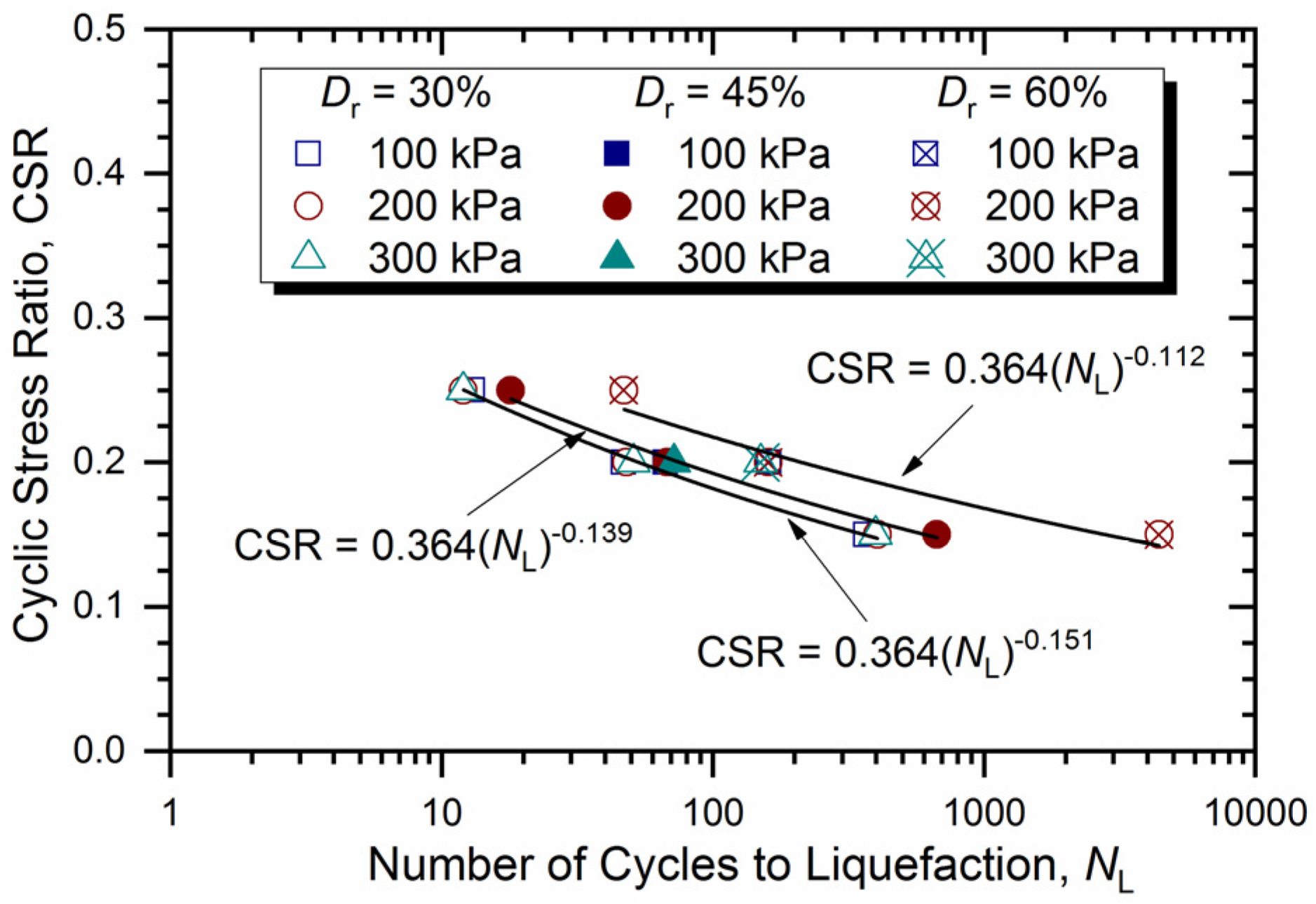
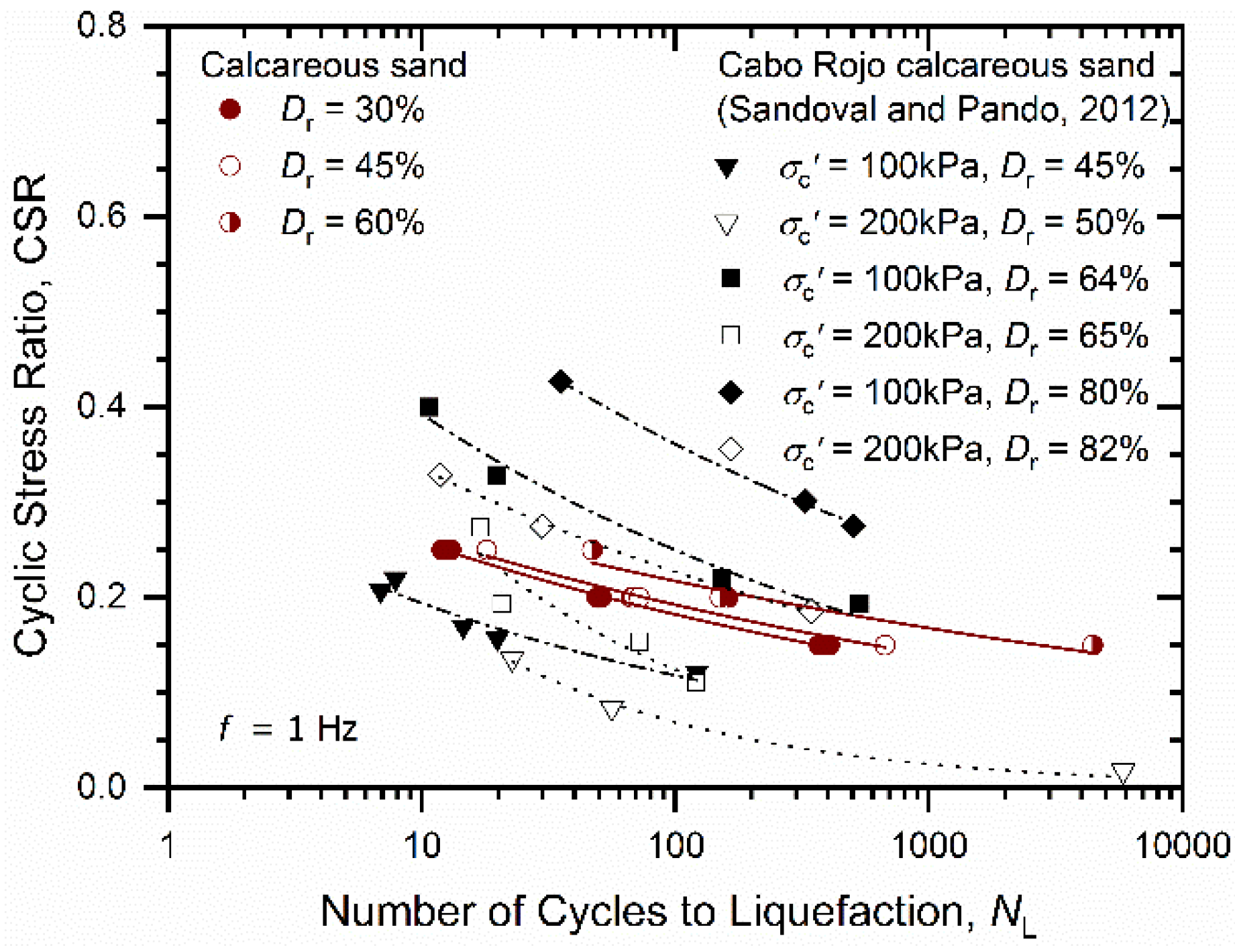
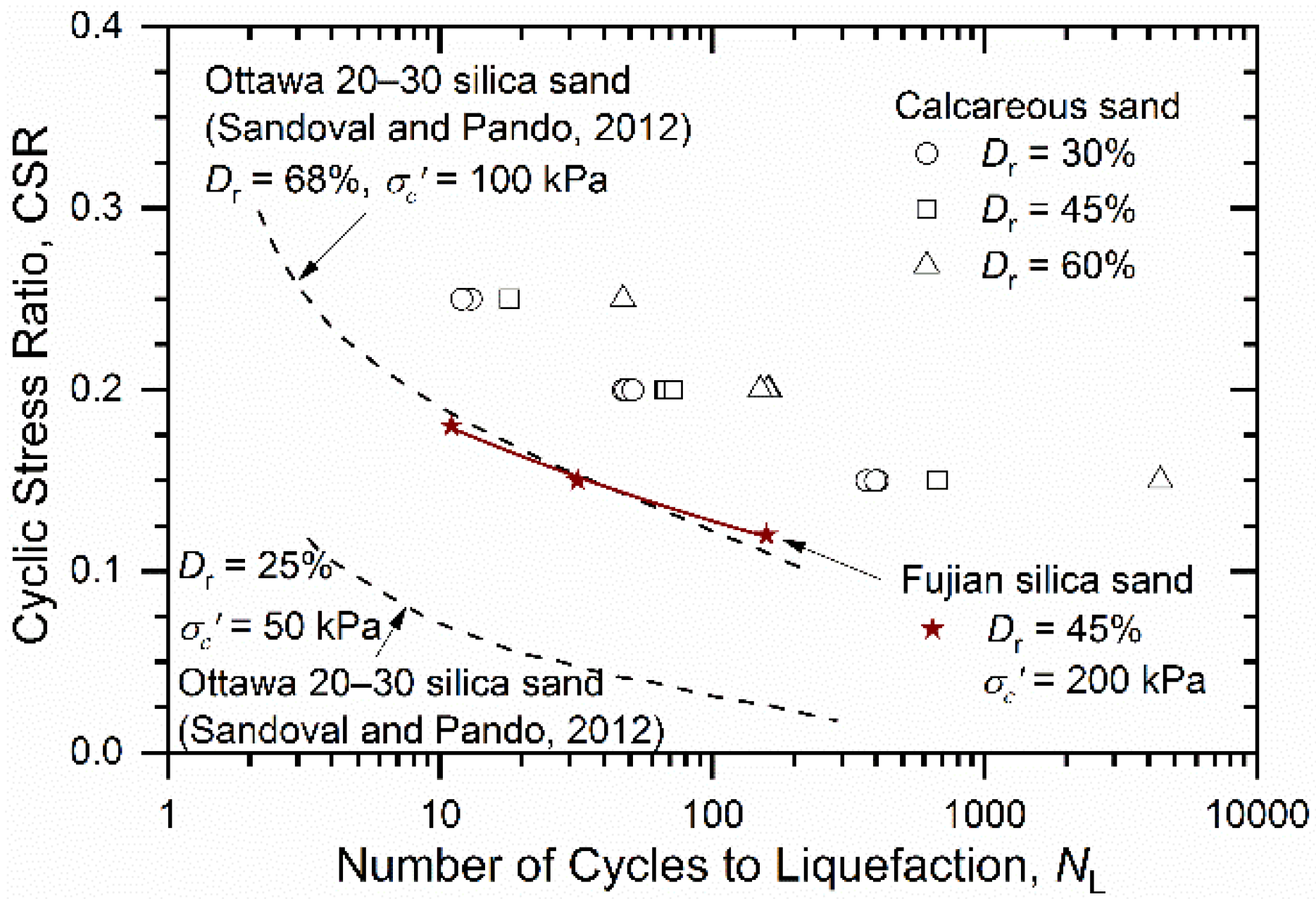
3.5. Cyclic Strength
4. Conclusions
- (1)
- During the cyclic triaxial test, both the excess pore pressure and axial strain of the calcareous sand gradually increased as it reached liquefaction, whereas for Fujian silica sand, a sudden increase in excess pore pressure and axial strain was observed when approaching liquefaction state.
- (2)
- The calcareous sand had greater liquefaction resistance than Fujian silica sand tested under same cyclic loading conditions. This may be attributed to the angular nature of calcareous sand particles providing more stable interlocking soil fabric that is resistant to liquefaction.
- (3)
- The CSR had a significant effect on the cyclic behavior of calcareous sand, including excess pore pressure development, deformation response, the degradation rate of the shear modulus, and cyclic strength. However, there was little confining-pressure effect on the cyclic behavior of calcareous sand, which is different from other calcareous sands. This may be attributed to the variations in regions and grain composition, which warrants further study.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Coop, M.R. The mechanics of uncemented carbonate sands. Géotechnique 1990, 40, 607–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miao, G.; Airey, D. Breakage and ultimate states for a carbonate sand. Géotechnique 2013, 63, 1221–1229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Liu, H.L.; Xiao, Y.; Chu, J.; Xiao, P.; Wang, Y. Biocementation of calcareous sand using soluble calcium derived from calcareous sand. Bull. Eng. Geol. Environ. 2018, 77, 1781–1791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Liu, H.L.; Stuedlein, A.W.; Evans, T.M.; Xiao, Y. Strength, Stiffness, and Microstructure Characteristics of Biocemented Calcareous Sand. Can. Geotech. J. 2019, 56, 1502–1513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Li, N.; Wang, X.; Cui, J.; Chen, Y.; Wu, Y.; Yamamoto, H. Experimental investigation on mechanical behavior and particle crushing of calcareous sand retrieved from South China Sea. Eng. Geol. 2020, 280, 105932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Wu, Y.; Cui, J.; Zhu, C.Q.; Wang, X.Z. Shape Characteristics of Coral Sand from the South China Sea. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2020, 8, 803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Airey, D.W.; Fahey, M.D. Cyclic response of calcareous soil from the North-West Shelf of Australia. Géotechnique 1991, 41, 101–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, X.; Fahey, M. Behaviour of calcareous soils in undrained cyclic simple shear. Géotechnique 2003, 53, 715–727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, S.S.; Ismail, M.A. Monotonic and cyclic behavior of two calcareous soils of different origins. J. Geotech. Geoenviron. Eng. 2006, 132, 1581–1591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hyodo, M.; Aramaki, N.; Itoh, M.; Hyde, A.F.L. Cyclic strength and deformation of crushable carbonate sand. Soil Dyn. Earthq. Eng. 1996, 15, 331–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hyodo, M.; Hyde, A.F.L.; Aramaki, N. Liquefaction of crushable soils. Géotechnique 1998, 48, 527–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qadimi, A.; Coop, M.R. The undrained cyclic behaviour of a carbonate sand. Géotechnique 2007, 57, 739–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandoval, E.A.; Pando, M.A. Experimental assessment of the liquefaction resistance of calcareous biogenous sands. Earth Sci. Res. J. 2012, 16, 55–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salem, M.; Elmamlouk, H.; Agaiby, S. Static and cyclic behavior of North Coast calcareous sand in Egypt. Soil Dyn. Earthq. Eng. 2013, 55, 83–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brandes, H.G. Simple shear behavior of calcareous and quartz sands. Geotech. Geol. Eng. 2011, 29, 113–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahnazari, H.; Rezvani, R.; Tutunchian, M.A. Post-cyclic volumetric strain of calcareous sand using hollow cylindrical torsional shear tests. Soil Dyn. Earthq. Eng. 2019, 124, 162–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, P.; Liu, H.L.; Xiao, Y.; Stuedlein, A.W.; Evans, T.M. Liquefaction resistance of bio-cemented calcareous sand. Soil. Dyn. Earthq. Eng. 2018, 107, 9–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, P.; Liu, H.L.; Stuedlein, A.W.; Evans, T.M.; Xiao, Y. Effect of relative density and biocementation on cyclic response of calcareous sand. Can. Geotech. J. 2019, 56, 1849–1862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- He, S.H.; Zhang, Q.F.; Ding, Z.; Xia, T.D.; Gan, X.L. Experimental and Estimation Studies of Resilient Modulus of Marine Coral Sand under Cyclic Loading. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2020, 8, 287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Q.; Ding, X.M.; Zhang, Y.L.; Chen, Z.X. Comparative Study on Seismic Response of Pile Group Foundation in Coral Sand and Fujian Sand. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2020, 8, 189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhou, X.Z.; Chen, Y.M.; Liu, H.L.; Zhang, X.Z. Experimental study on the cyclic behavior of loose calcareous sand under linear stress paths. Mar. Georesour. Geotec. 2020, 38, 277–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Sze, H.Y. Cyclic strength of sand under sustained shear stress. J. Geotech. Geoenviron. Eng. 2011, 137, 1275–1285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, G.X.; Wu, Q.; Zhao, K.; Shen, Z.F.; Yang, J. A Binary Packing Material–Based Procedure for Evaluating Soil Liquefaction Triggering during Earthquakes. J. Geotech. Geoenviron. Eng. 2020, 146, 4020040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seed, H.B.; Lee, K.L. Liquefaction of saturated sands during cyclic loading. J. Soil Mech. Found. Div. 1966, 92, 105–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polito, C.P.; Green, R.A.; Lee, J. Pore pressure generation models for sands and silty soils subjected to cyclic loading. J. Geotech. Geoenviron. Eng. 2008, 134, 1490–1500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, K.L.; Albaisa, A. Earthquake induced settlements in saturated sands. J. Geotech. Engng Div. 1974, 100, 387–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hardin, B.O.; Drnevich, V.P. Shear modulus and damping in soils: Design equations and curves. J. Soil Mech. Found. Div. 1972, 98, 667–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


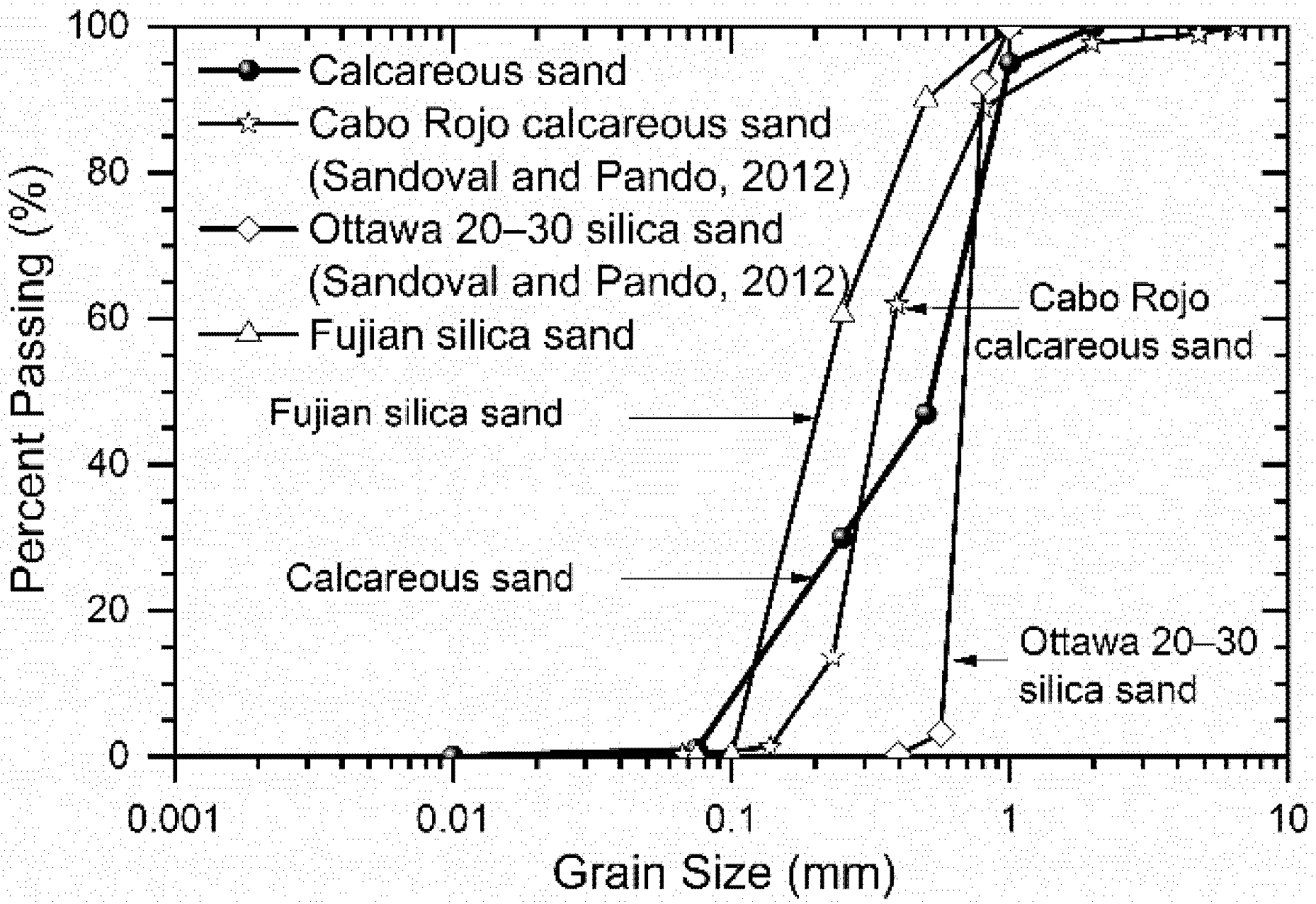

| Category of Sand | Gs | D50(mm) | Cu | Cc | emax | emin |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Calcareous sand (present study) | 2.82 | 0.53 | 4.91 | 0.76 | 1.45 | 0.81 |
| Cabo Rojo calcareous sand (Sandoval and Pando, 2012) | 2.84 | 0.37 | 1.75 | 0.94 | 2.07 | 1.51 |
| Fujian silica sand (present study) | 2.65 | 0.22 | 2.01 | 0.98 | 0.86 | 0.55 |
| Ottawa 20–30 silica sand (Sandoval and Pando, 2012) | 2.65 | 0.75 | 2.1 | 1.1 | 0.78 | 0.5 |
| Test No. | Dr (%) | CSR | NL | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CS1 | 30 | 100 | 0.15 | 368 |
| CS2 | 30 | 100 | 0.2 | 47 |
| CS3 | 30 | 100 | 0.25 | 13 |
| CS4 | 30 | 200 | 0.15 | 405 |
| CS5 | 30 | 200 | 0.2 | 48 |
| CS6 | 30 | 200 | 0.25 | 12 |
| CS7 | 30 | 300 | 0.15 | 397 |
| CS8 | 30 | 300 | 0.2 | 51 |
| CS9 | 30 | 300 | 0.25 | 12 |
| CS10 | 45 | 100 | 0.2 | 67 |
| CS11 | 45 | 200 | 0.15 | 670 |
| CS12 | 45 | 200 | 0.2 | 68 |
| CS13 | 45 | 200 | 0.25 | 18 |
| CS16 | 60 | 200 | 0.15 | 4415 |
| CS17 | 60 | 200 | 0.2 | 160 |
| CS18 | 60 | 200 | 0.25 | 47 |
| CS19 | 60 | 300 | 0.2 | 150 |
| SS1 | 45 | 200 | 0.12 | 158 |
| SS2 | 45 | 200 | 0.15 | 32 |
| SS3 | 45 | 200 | 0.18 | 11 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, L.; Yao, X.; Ji, Z.; Gao, H.; Wang, Z.; Shen, Z. Cyclic Behavior of Calcareous Sand from the South China Sea. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2021, 9, 1014. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse9091014
Liu L, Yao X, Ji Z, Gao H, Wang Z, Shen Z. Cyclic Behavior of Calcareous Sand from the South China Sea. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering. 2021; 9(9):1014. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse9091014
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Lu, Xiaofei Yao, Zhanpeng Ji, Hongmei Gao, Zhihua Wang, and Zhifu Shen. 2021. "Cyclic Behavior of Calcareous Sand from the South China Sea" Journal of Marine Science and Engineering 9, no. 9: 1014. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse9091014
APA StyleLiu, L., Yao, X., Ji, Z., Gao, H., Wang, Z., & Shen, Z. (2021). Cyclic Behavior of Calcareous Sand from the South China Sea. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering, 9(9), 1014. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse9091014





