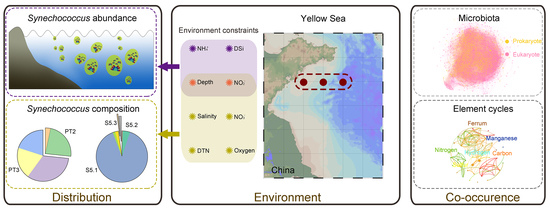
Phylogenetic and Phenogenetic Diversity of Synechococcus along a Yellow Sea Section Reveal Its Environmental Dependent Distribution and Co-Occurrence Microbial Pattern
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sampling
2.2. Cell Abundance of Synechococcus
2.3. Structures of Synechococcus Assemblages and Microbial Communities
2.3.1. DNA Extraction
2.3.2. PCR Reactions
2.3.3. Sequencing
2.3.4. Sequence Data Processing
2.4. Construction of Co-Occurrence Network
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Environmental Variables
3.2. Synechococcus Abundance and Its Environmental Constraints
3.3. Phylogenetic and Phenogenetic Diversity and Structure of Synechococcus Assemblage
3.4. Microbial Co-Occurrence with Synechococcus
4. Discussion
4.1. Distribution Features of Synechococcus Cell Abundance
4.2. Structure and Niche Occupation of Synechococcus Assemblages
4.3. Potential Ecological Functions of Synechococcus in the Coastal Ecosystem
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Scanlan, D.J.; Ostrowski, M.; Mazard, S.; Dufresne, A.; Garczarek, L.; Hess, W.R.; Post, A.F.; Hagemann, M.; Paulsen, I.; Partensky, F. Ecological genomics of marine Picocyanobacteria. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 2009, 73, 249–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ahlgren, N.A.; Rocap, G. Diversity and distribution of marine Synechococcus: Multiple gene phylogenies for consensus classification and development of qPCR assays for sensitive measurement of clades in the ocean. Front Microbiol. 2012, 3, 213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Choi, D.H.; Noh, J.H.; Shim, J. Seasonal changes in picocyanobacterial diversity as revealed by pyrosequencing in temperate waters of the East China Sea and the East Sea. Aquat. Microb. Ecol. 2013, 71, 75–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dufresne, A.; Ostrowski, M.; Scanlan, D.J.; Garczarek, L.; Mazard, S.; Palenik, B.P.; Paulsen, I.T.; De Marsac, N.T.; Wincker, P.; Dossat, C.; et al. Unravelling the genomic mosaic of a ubiquitous genus of marine cyanobacteria. Genome Biol. 2008, 9, R90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Six, C.; Thomas, J.-C.; Garczarek, L.; Ostrowski, M.; Dufresne, A.; Blot, N.; Scanlan, D.J.; Partensky, F. Diversity and evolution of phycobilisomes in marine Synechococcus spp.: A comparative genomics study. Genome Biol. 2007, 8, R259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Humily, F.; Farrant, G.; Marie, D.; Partensky, F.; Mazard, S.; Perennou, M.; Labadie, K.; Aury, J.-M.; Wincker, P.; Segui, A.N.; et al. Development of a targeted metagenomic approach to study a genomic region involved in light harvesting in marine Synechococcus. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2014, 88, 231–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Huang, S.; Wilhelm, S.; Harvey, H.R.; Taylor, K.; Jiao, N.; Chen, F. Novel lineages of Prochlorococcus and Synechococcus in the global oceans. ISME J. 2011, 6, 285–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Xia, X.; Partensky, F.; Garczarek, L.; Suzuki, K.; Guo, C.; Cheung, S.Y.; Liu, H. Phylogeography and pigment type diversity of Synechococcus cyanobacteria in surface waters of the Northwestern Pacific Ocean. Environ. Microbiol. 2016, 19, 142–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Xia, X.; Guo, W.; Tan, S.; Liu, H. Synechococcus assemblages across the salinity gradient in a salt wedge estuary. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 1254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Grébert, T.; Doré, H.; Partensky, F.; Farrant, G.K.; Boss, E.; Picheral, M.; Guidi, L.; Pesant, S.; Scanlan, D.; Wincker, P.; et al. Light color acclimation is a key process in the global ocean distribution of Synechococcus cyanobacteria. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2018, 115, E2010–E2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Paulsen, M.L.; Doré, H.; Garczarek, L.; Seuthe, L.; Müller, O.; Sandaa, R.-A.; Bratbak, G.; Larsen, A. Synechococcus in the Atlantic Gateway to the Arctic Ocean. Front. Mar. Sci. 2016, 3, 191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Saito, M.A.; Rocap, G.; Moffett, J.W. Production of cobalt binding ligands in a Synechococcus feature at the Costa Rica upwelling dome. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2005, 50, 279–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agawin, N.; Duarte, C.; Agustıí, S.; McManus, L. Abundance, biomass and growth rates of Synechococcus sp. in a tropical coastal ecosystem (Philippines, South China Sea). Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2003, 56, 493–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morozov, E.; Tang, D. Satellite Ocean colour algorithm for Prochlorococcus, Synechococcus, and Picoeukaryotes concentration retrieval in the South China Sea. Adv. Space Res. 2018, 63, 16–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiang, K.-P.; Kuo, M.-C.; Chang, J.; Wang, R.-H.; Gong, G.-C. Spatial and temporal variation of the Synechococcus population in the East China Sea and its contribution to phytoplankton biomass. Cont. Shelf Res. 2002, 22, 3–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, X.; Liu, H.; Choi, D.; Noh, J.H. Variation of Synechococcus pigment genetic diversity along two turbidity gradients in the China Seas. Microb. Ecol. 2018, 75, 10–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Song, Q.; Zheng, P.; Zhang, X.; Zou, S.; Li, Y.; Gao, X.; Zhao, Z.; Gong, J. Dynamics and distribution of marine Synechococcus abundance and genotypes during seasonal hypoxia in a Coastal Marine Ranch. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2021, 9, 549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, D.H.; Noh, J.H. Phylogenetic diversity of Synechococcus strains isolated from the East China Sea and the East Sea. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2009, 69, 439–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jing, H.; Liu, H. Phylogenetic composition of Prochlorococcus and Synechococcus in cold eddies of the South China Sea. Aquat. Microb. Ecol. 2012, 65, 207–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xia, X.; Vidyarathna, N.K.; Palenik, B.; Lee, P.; Liu, H. Comparison of the seasonal variations of Synechococcus assemblage structures in estuarine waters and coastal waters of Hong Kong. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2015, 81, 7644–7655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Huang, T.-C.; Lin, R.-F.; Chu, M.-K.; Chen, H.-M. Organization and expression of nitrogen-fixation genes in the aerobic nitrogen-fixing unicellular cyanobacterium Synechococcus sp. strain RF-1. Microbiology 1999, 145, 743–753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hung, S.-H.; Chung, C.-C.; Liao, C.-W.; Gong, G.-C.; Chang, J. Sequence diversity and expression levels of Synechococcus phosphate transporter gene in the East China Sea. J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol. 2013, 440, 90–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brzezinski, M.A.; Krause, J.W.; Baines, S.B.; Collier, J.L.; Ohnemus, D.C.; Twining, B.S. Patterns and regulation of silicon accumulation in Synechococcus spp. J. Phycol. 2017, 53, 746–761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trosvik, P.; Rudi, K.; Straetkvern, K.O.; Jakobsen, K.S.; Naes, T.; Stenseth, N.C. Web of ecological interactions in an experimental gut microbiota. Environ. Microbiol. 2010, 12, 2677–2687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berry, D.; Widder, S. Deciphering microbial interactions and detecting keystone species with co-occurrence networks. Front. Microbiol. 2014, 5, 219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Barberán, A.; Bates, S.T.; Casamayor, E.O.; Fierer, N. Using network analysis to explore co-occurrence patterns in soil microbial communities. ISME J. 2011, 6, 343–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tang, Y.; Dai, T.; Su, Z.; Hasegawa, K.; Tian, J.; Chen, L.; Wen, D. A tripartite microbial-environment network indicates how crucial microbes influence the microbial community ecology. Microb. Ecol. 2019, 79, 342–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wagg, C.; Schlaeppi, K.; Banerjee, S.; Kuramae, E.E.; Van der Heijden, M.G.A. Fungal-bacterial diversity and microbiome complexity predict ecosystem functioning. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 4841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, B.; Wang, H.; Dsouza, M.; Lou, J.; He, Y.; Dai, Z.; Brookes, P.C.; Xu, J.; Gilbert, J.A. Geographic patterns of co-occurrence network topological features for soil microbiota at continental scale in eastern China. ISME J. 2016, 10, 1891–1901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, S.; Nuccio, E.E.; Shi, Z.J.; He, Z.; Zhou, J.; Firestone, M.K. The interconnected rhizosphere: High network complexity dominates rhizosphere assemblages. Ecol. Lett. 2016, 19, 926–936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Widder, S.; Besemer, K.; Singer, G.; Ceola, S.; Bertuzzo, E.; Quince, C.; Sloan, W.T.; Rinaldo, A.; Battin, T.J. Fluvial network organization imprints on microbial co-occurrence networks. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, 12799–12804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mikhailov, I.S.; Zakharova, Y.R.; Bukin, Y.S.; Galachyants, Y.P.; Petrova, D.; Sakirko, M.V.; Likhoshway, Y.V. Co-occurrence networks among bacteria and microbial eukaryotes of Lake Baikal during a spring phytoplankton bloom. Microb. Ecol. 2019, 77, 96–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Steele, J.A.; Countway, P.D.; Xia, C.; Vigil, P.D.; Beman, J.M.; Kim, D.Y.; Chow, C.-E.T.; Sachdeva, R.; Jones, A.C.; Schwalbach, M.S.; et al. Marine bacterial, archaeal and protistan association networks reveal ecological linkages. ISME J. 2011, 5, 1414–1425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jackson, J.B.C.; Kirby, M.X.; Berger, W.H.; Bjorndal, K.A.; Botsford, L.W.; Bourque, B.J.; Bradbury, R.; Cooke, R.H.; Erlandson, J.; Estes, J.A.; et al. Historical overfishing and the recent collapse of coastal ecosystems. Science 2001, 293, 629–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Taubert, M.; Grob, C.; Howat, A.M.; Burns, O.J.; Pratscher, J.; Jehmlich, N.; Von Bergen, M.; Richnow, H.H.; Chen, Y.; Murrell, J.C. Methylamine as a nitrogen source for microorganisms from a coastal marine environment. Environ. Microbiol. 2017, 19, 2246–2257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lin, C.; Ning, X.; Su, J.; Lin, Y.; Xu, B. Environmental changes and the responses of the ecosystems of the Yellow Sea during 1976–2000. J. Mar. Syst. 2005, 55, 223–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Ran, W.; Teng, J.; Liu, Y.; Liu, H.; Yin, X.; Cao, R.; Wang, Q. Microplastic pollution in sediments from the Bohai Sea and the Yellow Sea, China. Sci. Total. Environ. 2018, 640–641, 637–645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, F.; Xuan, J.; Huang, D.; Liu, C.; Sun, J. The timing and the magnitude of spring phytoplankton blooms and their relationship with physical forcing in the central Yellow Sea in 2009. Deep. Sea Res. Part II Top. Stud. Oceanogr. 2013, 97, 4–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Chen, X.; Li, J.; Qin, S. Distribution and phenogenetic diversity of Synechococcus in the Bohai Sea. China. J. Oceanol. Limnol. 2021, in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dafner, E.V. Segmented continuous-flow analyses of nutrient in seawater: Intralaboratory comparison of technicon autoanalyzer II and bran+luebbe continuous flow autoanalyzer III. Limnol. Oceanogr. Methods 2015, 13, 511–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Wang, T.; Yu, S.; Bai, J.; Qin, S. Community characteristics and ecological roles of bacterial biofilms associated with various algal settlements on coastal reefs. J. Environ. Manag. 2019, 250, 109459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mühling, M.; Fuller, N.; Somerfield, P.; Post, A.; Wilson, W.; Scanlan, D.; Joint, I.; Mann, N. High resolution genetic diversity studies of marine Synechococcus isolates using rpoC1-based restriction fragment length polymorphism. Aquat. Microb. Ecol. 2006, 45, 263–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Walters, W.; Hyde, E.R.; Berg-Lyons, D.; Ackermann, G.; Humphrey, G.; Parada, A.; Gilbert, J.A.; Jansson, J.K.; Caporaso, J.G.; Fuhrman, J.; et al. Improved bacterial 16S rRNA Gene (V4 and V4-5) and fungal internal transcribed spacer marker gene primers for microbial community surveys. mSystems 2016, 1, e00009–e00015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhou, J.; Richlen, M.L.; Sehein, T.R.; Kulis, D.M.; Anderson, D.M.; Cai, Z. Microbial community structure and associations during a marine dinoflagellate bloom. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 1201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brown, J.W.; Pirrung, M.; McCue, L.A. FQC Dashboard: Integrates FastQC results into a web-based, interactive, and extensible FASTQ quality control tool. Bioinformatics 2017, 33, 3137–3139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Edgar, R.C.; Haas, B.J.; Clemente, J.C.; Quince, C.; Knight, R. UCHIME improves sensitivity and speed of chimera detection. Bioinformatics 2011, 27, 2194–2200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bokulich, N.A.; Subramanian, S.; Faith, J.J.; Gevers, D.; Gordon, J.I.; Knight, R.; Mills, D.A.; Caporaso, J.G. Quality-filtering vastly improves diversity estimates from Illumina amplicon sequencing. Nat. Methods 2013, 10, 57–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thompson, J.D.; Higgins, D.G.; Gibson, T.J. CLUSTAL W: Improving the sensitivity of progressive multiple sequence alignment through sequence weighting, position-specific gap penalties and weight matrix choice. Nucleic Acids Res. 1994, 22, 4673–4680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hall, T.A. BioEdit: A user-friendly biological sequence alignment editor and analysis program for Windows 95/98/NT. Nucleic Acids Symp. Ser. 1999, 41, 95–98. [Google Scholar]
- Louca, S.; Parfrey, L.W.; Doebeli, M. Decoupling function and taxonomy in the global ocean microbiome. Science 2016, 353, 1272–1277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feizi, S.; Marbach, D.; Médard, M.; Kellis, M. Network deconvolution as a general method to distinguish direct dependencies in networks. Nat. Biotechnol. 2013, 31, 726–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Deng, Y.; Jiang, Y.-H.; Yang, Y.; He, Z.; Luo, F.; Zhou, J. Molecular ecological network analyses. BMC Bioinform. 2012, 13, 113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Benjamini, Y.; Krieger, A.M.; Yekutieli, D. Adaptive linear step-up procedures that control the false discovery rate. Biometrika 2006, 93, 491–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Revelle, W.; Revelle, M.W. Package ‘psych’. 2015. Available online: https://cran.r-project.org/web/packages/psych/psych.pdf (accessed on 13 September 2021).
- Bastian, M.; Heymann, S.; Jacomy, M. Gephi: An open source software for exploring and manipulating networks. In Proceedings of the International AAAI Conference on Weblogs and Social Media, San Jose, CA, USA, 17–20 May 2009; Available online: https://gephi.org/publications/gephi-bastian-feb09.pdf (accessed on 13 September 2021).
- Lin, S.; Zou, T.; Gao, H.; Guo, X. The vertical attenuation of irradiance as a function of turbidity: A case of the Huanghai (Yellow) Sea in spring. Acta Oceanol. Sin. 2009, 28, 66–75. [Google Scholar]
- Dixon, P. VEGAN, a package of R functions for community ecology. J. Veg. Sci. 2003, 14, 927–930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blondel, V.D.; Guillaume, J.-L.; Lambiotte, R.; Lefebvre, E. Fast unfolding of communities in large networks. J. Stat. Mech. Theory Exp. 2008, 2008, P10008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, C.; Chen, H.; Zhang, Y.; Thomas, H.R.; Frank, M.H.; He, Y.; Xia, R. TBtools: An integrative toolkit developed for interactive analyses of big biological data. Mol. Plant 2020, 13, 1194–1202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flombaum, P.; Gallegos, J.L.; Gordillo, R.A.; Rincón, J.; Zabala, L.L.; Jiao, N.; Karl, D.M.; Li, W.K.W.; Lomas, M.; Veneziano, D.; et al. Present and future global distributions of the marine Cyanobacteria prochlorococcus and Synechococcus. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 9824–9829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhao, Y.; Zhao, L.; Xiao, T.; Zhao, S.; Xuan, J.; Li, C.; Ning, X. Spatial and temporal variation of picoplankton distribution in the Yellow Sea, China. Chin. J. Oceanol. Limnol. 2011, 29, 150–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Xiao, T.; Ding, T.; Lü, R. Effect of the Yellow Sea cold water mass (YSCWM) on distribution of bacterioplankton. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2006, 26, 1012–1019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mei, X.; Li, R.; Zhang, X.; Liu, Q.; Liu, J.; Wang, Z.; Lan, X.; Liu, J.; Sun, R. Evolution of the Yellow Sea warm current and the Yellow Sea cold water mass since the middle pleistocene. Palaeogeogr. Palaeoclim. Palaeoecol. 2016, 442, 48–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouman, H.A.; Ulloa, O.; Barlow, R.; Li, W.K.W.; Platt, T.; Zwirglmaier, K.; Scanlan, D.J.; Sathyendranath, S. Water-column stratification governs the community structure of subtropical marine picophytoplankton. Environ. Microbiol. Rep. 2011, 3, 473–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lohscheider, J.N.; Strittmatter, M.; Küpper, H.; Adamska, I. Vertical distribution of epibenthic freshwater Cyanobacterial Synechococcus spp. strains depends on their ability for photoprotection. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e20134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Postius, C.; Kenter, U.; Wacker, A.; Ernst, A.; Böger, P. Light causes selection among two phycoerythrin-rich Synechococcus isolates from Lake Constance. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 1998, 25, 171–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moore, L.R.; Post, A.F.; Rocap, G.; Chisholm, S.W. Utilization of different nitrogen sources by the marine cyanobacteria Prochlorococcus and Synechococcus. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2002, 47, 989–996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wyman, M.; Gregory, R.P.F.; Carr, N.G. Novel role for Phycoerythrin in a marine Cyanobacterium, Synechococcus strain DC2. Science 1985, 230, 818–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carr, N.G.; Mann, N.H. The oceanic cyanobacterial picoplankton. In The Molecular Biology of Cyanobacteria; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1994; pp. 27–48. [Google Scholar]
- Rodrigues, R.M.; Williams, P.J.L.B. Inorganic nitrogen assimilation by picoplankton and whole plankton in a coastal ecosystem. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2002, 47, 1608–1616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baines, S.B.; Twining, B.; Brzezinski, M.A.; Krause, J.W.; Vogt, S.; Assael, D.; McDaniel, H. Significant silicon accumulation by marine Picocyanobacteria. Nat. Geosci. 2012, 5, 886–891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Y.; Sun, J.; Zhang, X.; Wang, J.; Huang, K. Picophytoplankton size and biomass around equatorial eastern Indian Ocean. Microbiology 2019, 8, e00629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahlgren, N.A.; Rocap, G. Culture isolation and culture-independent clone libraries reveal new marine Synechococcus ecotypes with distinctive light and N physiologies. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2006, 72, 7193–7204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zwirglmaier, K.; Jardillier, L.; Ostrowski, M.; Mazard, S.; Garczarek, L.; Vaulot, D.; Not, F.; Massana, R.; Ulloa, O.; Scanlan, D.J. Global phylogeography of marine Synechococcus and Prochlorococcus reveals a distinct partitioning of lineages among oceanic biomes. Environ. Microbiol. 2007, 10, 147–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tai, V.; Palenik, B. Temporal variation of Synechococcus clades at a coastal Pacific Ocean monitoring site. ISME J. 2009, 3, 903–915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Haverkamp, T.H.; Schouten, D.; Doeleman, M.; Wollenzien, U.; Huisman, J.; Stal, L.J. Colorful microdiversity of Synechococcus strains (Picocyanobacteria) isolated from the Baltic Sea. ISME J. 2008, 3, 397–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haverkamp, T.H.; Acinas, S.G.; Doeleman, M.; Stomp, M.; Huisman, J.; Stal, L.J. Diversity and phylogeny of Baltic Sea picocyanobacteria inferred from their ITS and phycobiliprotein operons. Environ. Microbiol. 2007, 10, 174–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Jing, H.; Wong, T.H.; Chen, B. Co-occurrence of phycocyanin-and phycoerythrin-rich Synechococcus in subtropical estuarine and coastal waters of Hong Kong. Environ. Microbiol. Rep. 2014, 6, 90–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wood, A.; Phinney, D.; Yentsch, C. Water column transparency and the distribution of spectrally distinct forms of phycoerythrin-containing organisms. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 1998, 162, 25–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Putt, M.; Glover, H.E. Diurnal patterns in photosynthetic capacity and depth-dependent photosynthesis-irradiance relationships in Synechococcus spp. and larger phytoplankton in three water masses in the Northwest Atlantic Ocean. Mar. Biol. 1986, 91, 205–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spiller, H.; Shanmugam, K.T. Physiological conditions for nitrogen fixation in a unicellular marine Cyanobacterium, Synechococcus sp. strain SF1. J. Bacteriol. 1987, 169, 5379–5384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wurster, M.; Mundt, S.; Hammer, E.; Schauer, F.; Lindequist, U. Extracellular degradation of phenol by the Cyanobacterium Synechococcus PCC 7002. Environ. Boil. Fishes 2003, 15, 171–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbier, E.B.; Hacker, S.D.; Kennedy, C.; Koch, E.W.; Stier, A.C.; Silliman, B.R. The value of estuarine and coastal ecosystem services. Ecol. Monogr. 2011, 81, 169–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Tang, K.; Zhang, L.; Zhao, Z.; Xie, X.; Chen, C.-T.A.; Wang, D.; Jiao, N.; Zhang, Y. Coupled carbon, sulfur, and nitrogen cycles mediated by microorganisms in the water column of a shallow-water hydrothermal ecosystem. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 2718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nagarkar, M.; Countway, P.D.; Du Yoo, Y.; Daniels, E.; Poulton, N.; Palenik, B. Temporal dynamics of eukaryotic microbial diversity at a coastal Pacific site. ISME J. 2018, 12, 2278–2291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






| Variables | A1 | A2 | A3 | A4 | A5 | B1 | B2 | B3 | B4 | B5 | C1 | C2 | C3 | C4 | C5 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Physical variables | |||||||||||||||
| Sampling depth (m) | 0 | 5 | 10 | 20 | 29 | 0 | 5 | 10 | 20 | 30 | 0 | 10 | 20 | 30 | 50 |
| Temperature (°C) | 27.02 | 26.96 | 26.94 | 23.27 | 20.60 | 26.53 | 26.49 | 25.04 | 20.31 | 17.56 | 25.12 | 24.66 | 23.37 | 16.09 | 8.52 |
| Salinity (PSU) | 31.32 | 31.32 | 31.32 | 31.53 | 31.76 | 31.29 | 31.28 | 31.55 | 31.86 | 31.94 | 31.61 | 31.78 | 31.88 | 31.92 | 32.47 |
| Oxygen (mg L−1) | 153.2 | 152.7 | 152.2 | 118.1 | 110.8 | 155.6 | 156.1 | 158.3 | 157.1 | 139.6 | 161.7 | 163.9 | 168.8 | 174.5 | 166.4 |
| Chemical variables | |||||||||||||||
| NO2− (μmol L−1) | 0.08 | ND | 0.10 | 0.56 | 0.82 | 0.11 | ND | 0.07 | 0.27 | 1.88 | 0.07 | 0.08 | 0.07 | 0.54 | 0.09 |
| NO3− (μmol L−1) | 0.07 | ND | 0.20 | 1.07 | 1.19 | 1.47 | ND | 0.10 | 0.93 | 1.65 | 0.25 | 0.64 | 0.02 | 0.41 | 4.46 |
| NH4+ (μmol L−1) | 0.91 | ND | 0.91 | 0.57 | 0.39 | 1.12 | ND | 0.50 | 0.39 | 0.49 | 1.09 | 1.48 | 0.78 | 0.41 | 0.60 |
| DTN (μmol L−1) | 12.30 | ND | 13.40 | 16.14 | 18.52 | 7.96 | ND | 10.07 | 8.38 | 15.80 | 13.47 | 11.23 | 10.47 | 12.92 | 16.08 |
| PO43− (μmol L−1) | 0.07 | ND | 0.07 | 0.17 | 0.25 | 0.07 | ND | 0.08 | 0.16 | 0.44 | 0.09 | 0.08 | 0.06 | 0.18 | 0.51 |
| DTP (μmol L−1) | 0.14 | ND | 0.15 | 0.29 | 0.36 | 0.12 | ND | 0.17 | 0.23 | 0.56 | 0.19 | 0.16 | 0.16 | 0.33 | 0.62 |
| DSi (μmol L−1) | 1.98 | ND | 2.30 | 5.57 | 6.50 | 2.16 | ND | 2.79 | 4.51 | 7.02 | 1.40 | 1.40 | 1.83 | 4.88 | 8.55 |
| Chl. a (ug L−1) | 1.27 | ND | 1.22 | ND | 0.57 | ND | ND | 0.72 | 0.88 | ND | 0.29 | 0.32 | 0.46 | ND | 0.14 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, T.; Chen, X.; Qin, S.; Li, J. Phylogenetic and Phenogenetic Diversity of Synechococcus along a Yellow Sea Section Reveal Its Environmental Dependent Distribution and Co-Occurrence Microbial Pattern. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2021, 9, 1018. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse9091018
Wang T, Chen X, Qin S, Li J. Phylogenetic and Phenogenetic Diversity of Synechococcus along a Yellow Sea Section Reveal Its Environmental Dependent Distribution and Co-Occurrence Microbial Pattern. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering. 2021; 9(9):1018. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse9091018
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Ting, Xi Chen, Song Qin, and Jialin Li. 2021. "Phylogenetic and Phenogenetic Diversity of Synechococcus along a Yellow Sea Section Reveal Its Environmental Dependent Distribution and Co-Occurrence Microbial Pattern" Journal of Marine Science and Engineering 9, no. 9: 1018. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse9091018
APA StyleWang, T., Chen, X., Qin, S., & Li, J. (2021). Phylogenetic and Phenogenetic Diversity of Synechococcus along a Yellow Sea Section Reveal Its Environmental Dependent Distribution and Co-Occurrence Microbial Pattern. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering, 9(9), 1018. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse9091018