Design of a Marine Sediments Resistivity Measurement System Based on a Circular Permutation Electrode
Abstract
:1. Introduction
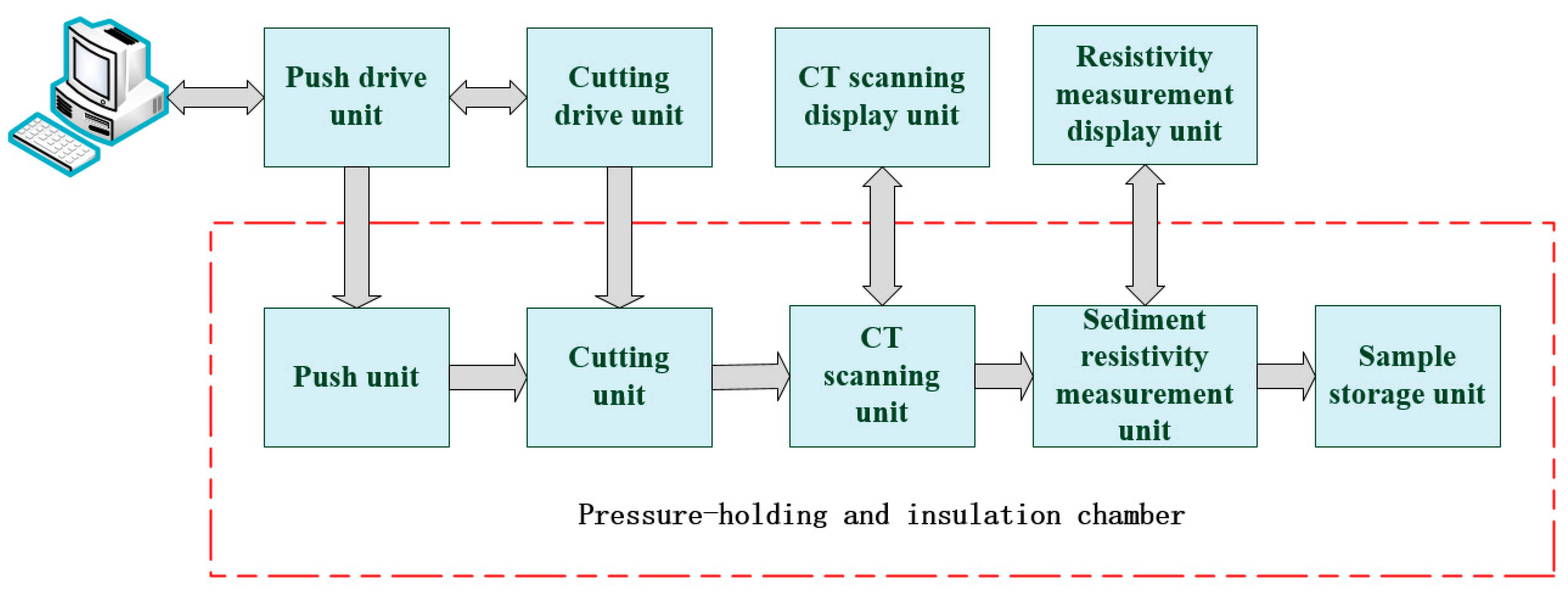
2. Overall System Design
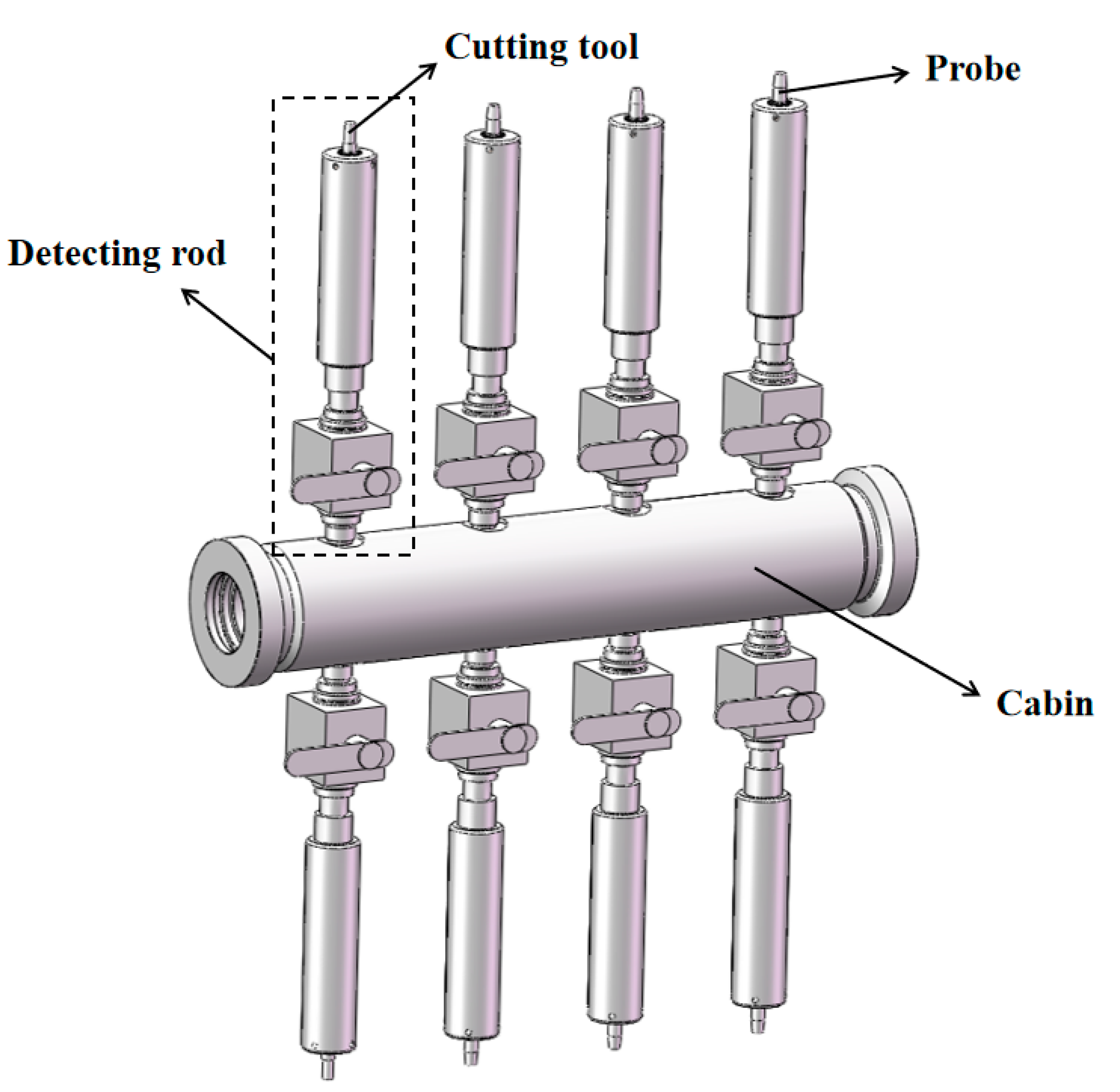
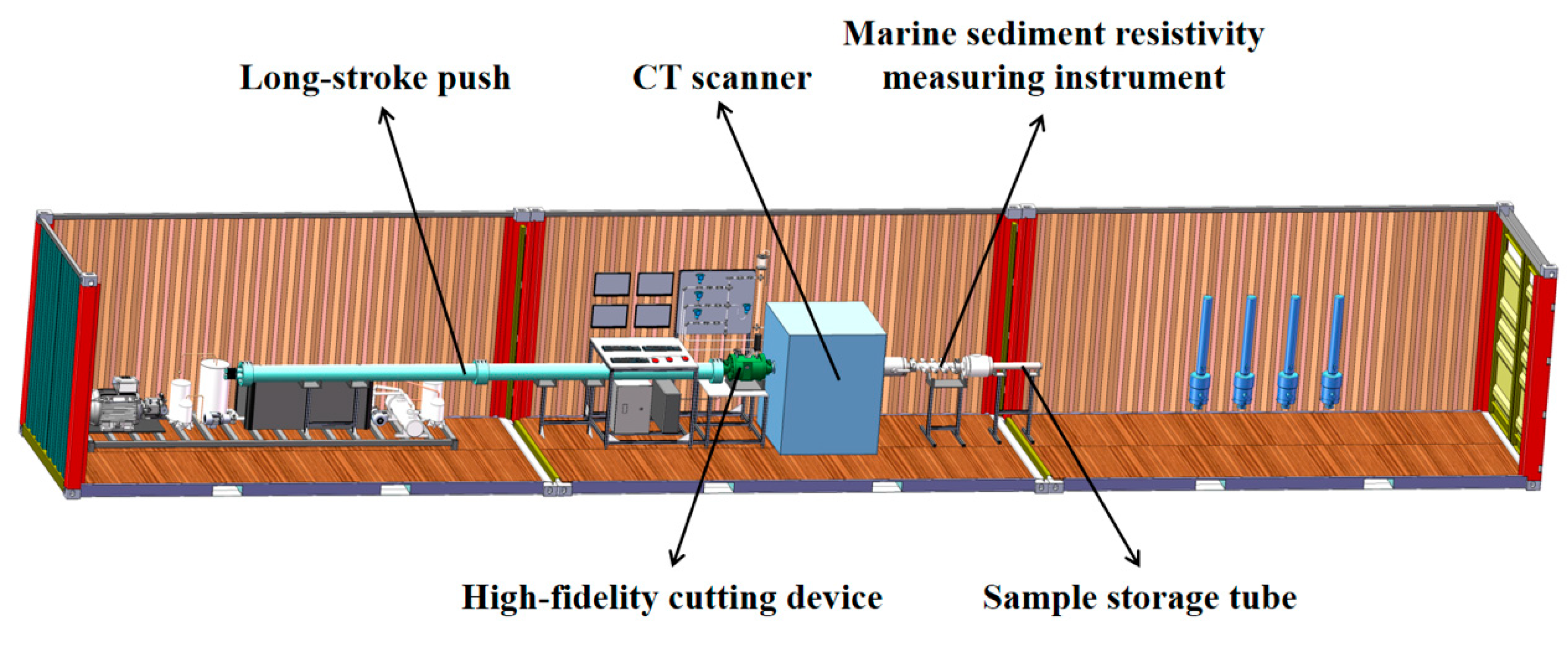
2.1. Seabed Sediment Resistivity Measuring Instrument and Marine Sediment Resistivity Measuring Instrument Pressure-Maintaining Transfer System Design
2.2. Structure Design of the Probe
2.3. Hardware Design of the Measurement System
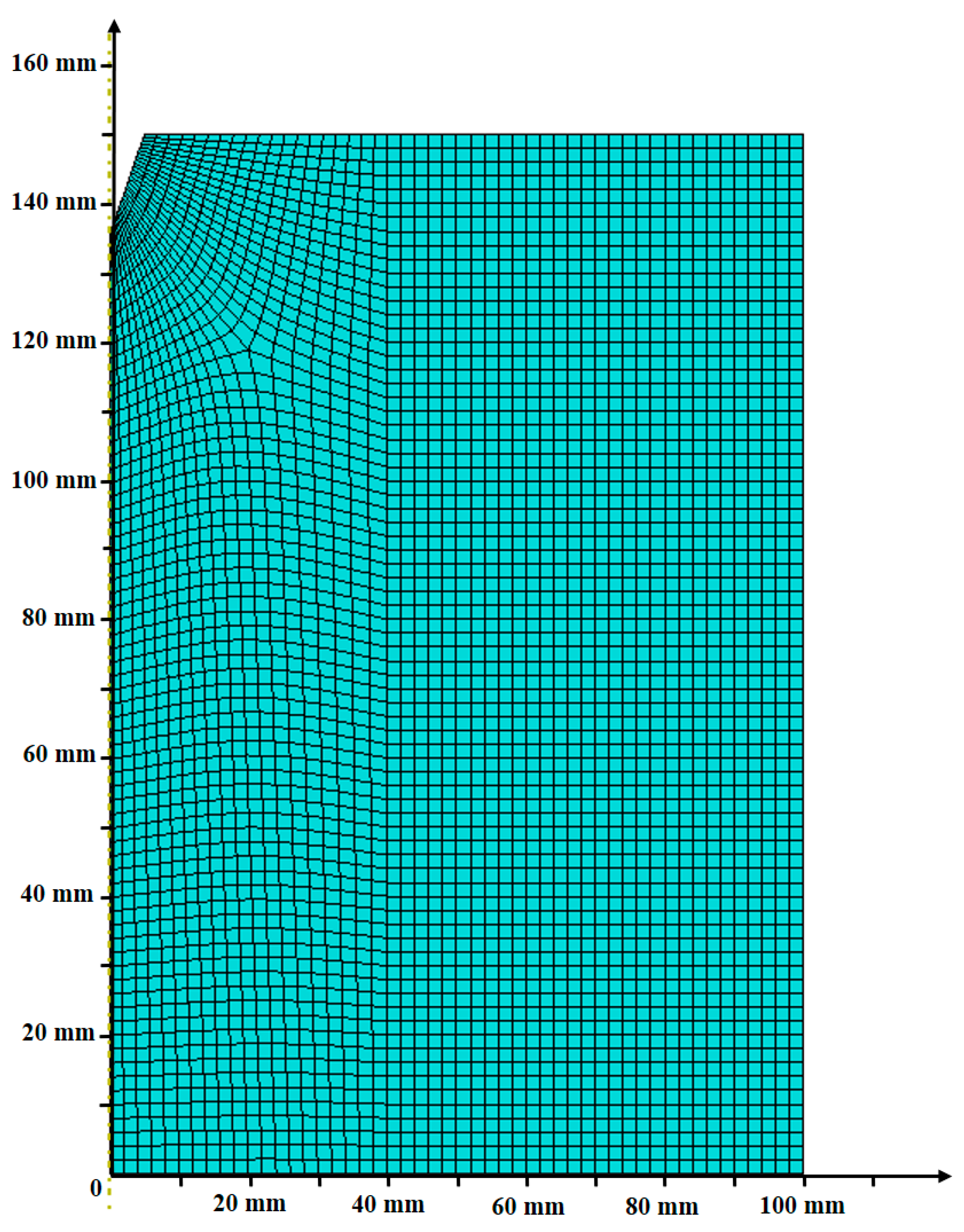
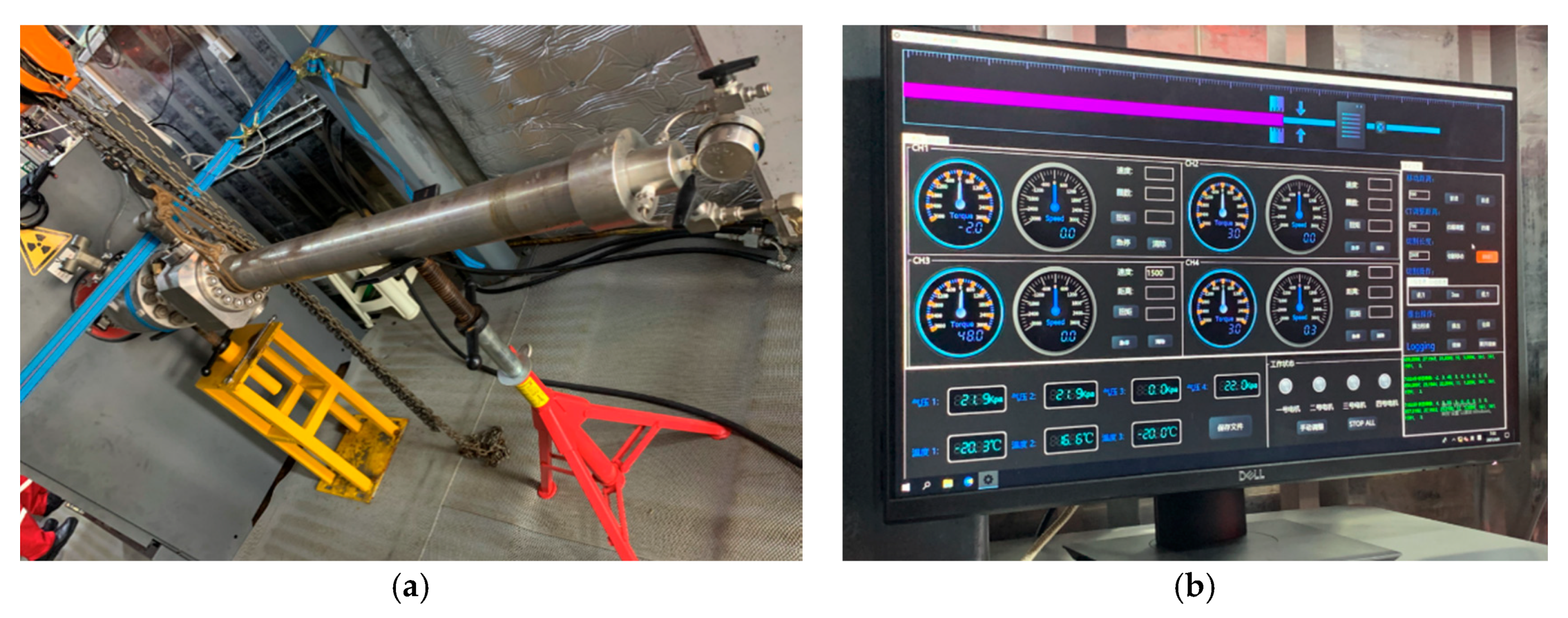
3. Mechanical Mechanism Simulation
4. Design of Resistivity Measuring Instrument
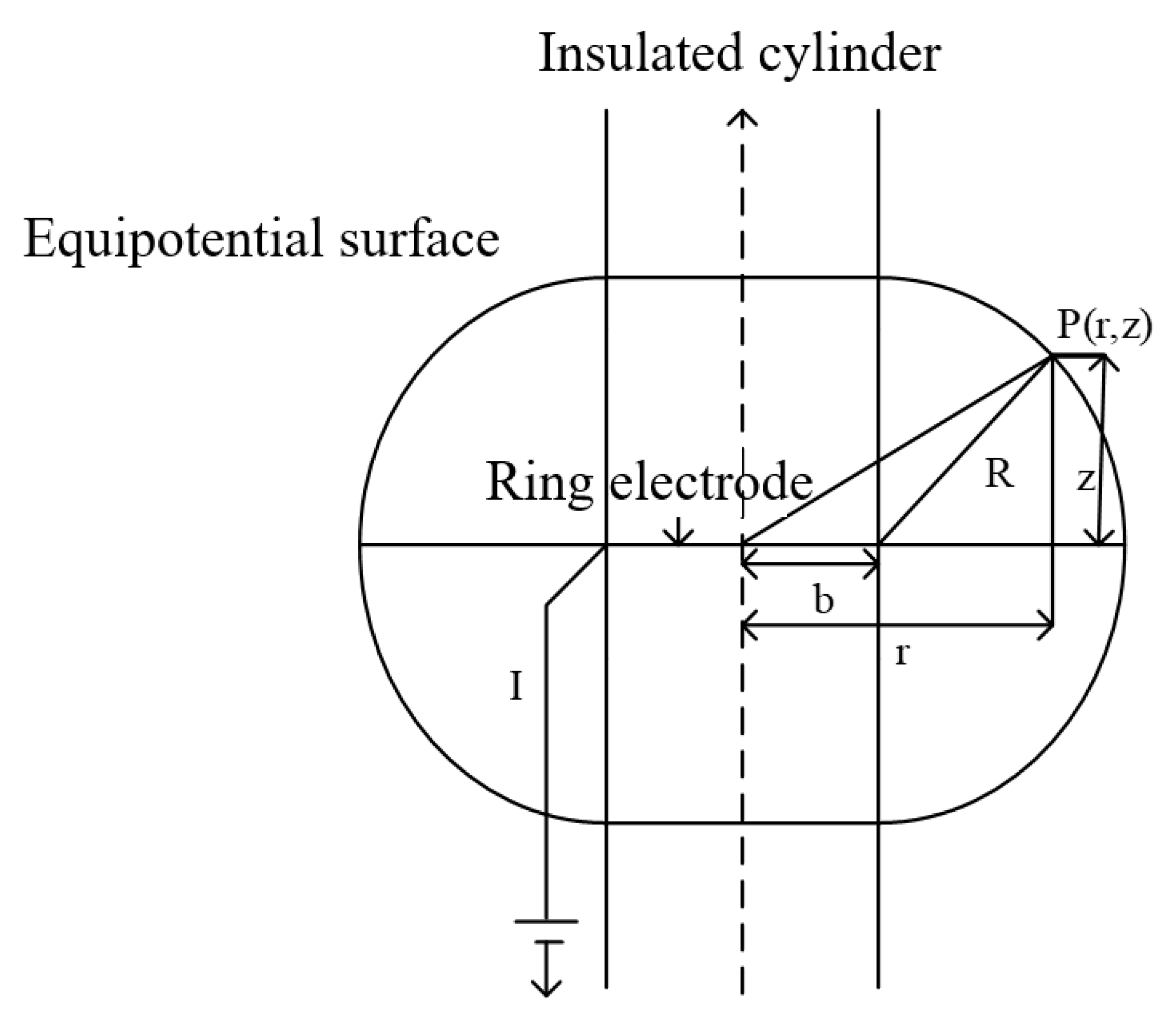
4.1. Design of Key Parameters for New Kind Circular Permutation Electrode
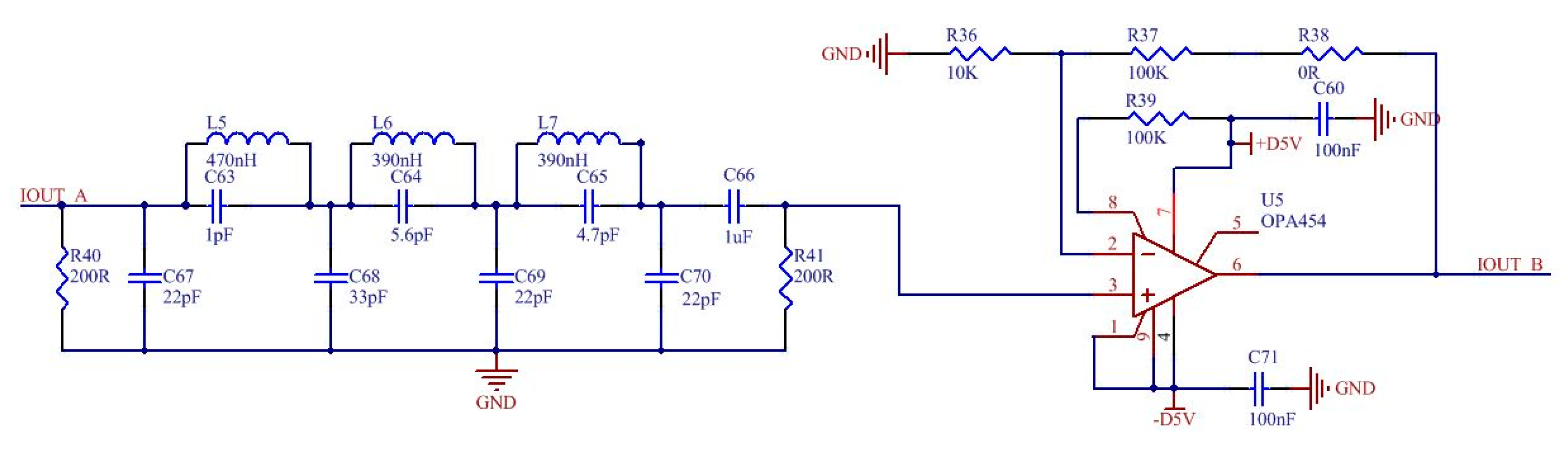
4.2. Key Parameter Design of the Filter and Amplification Module
4.3. Key Parameters Design of the Constant Current Source Module
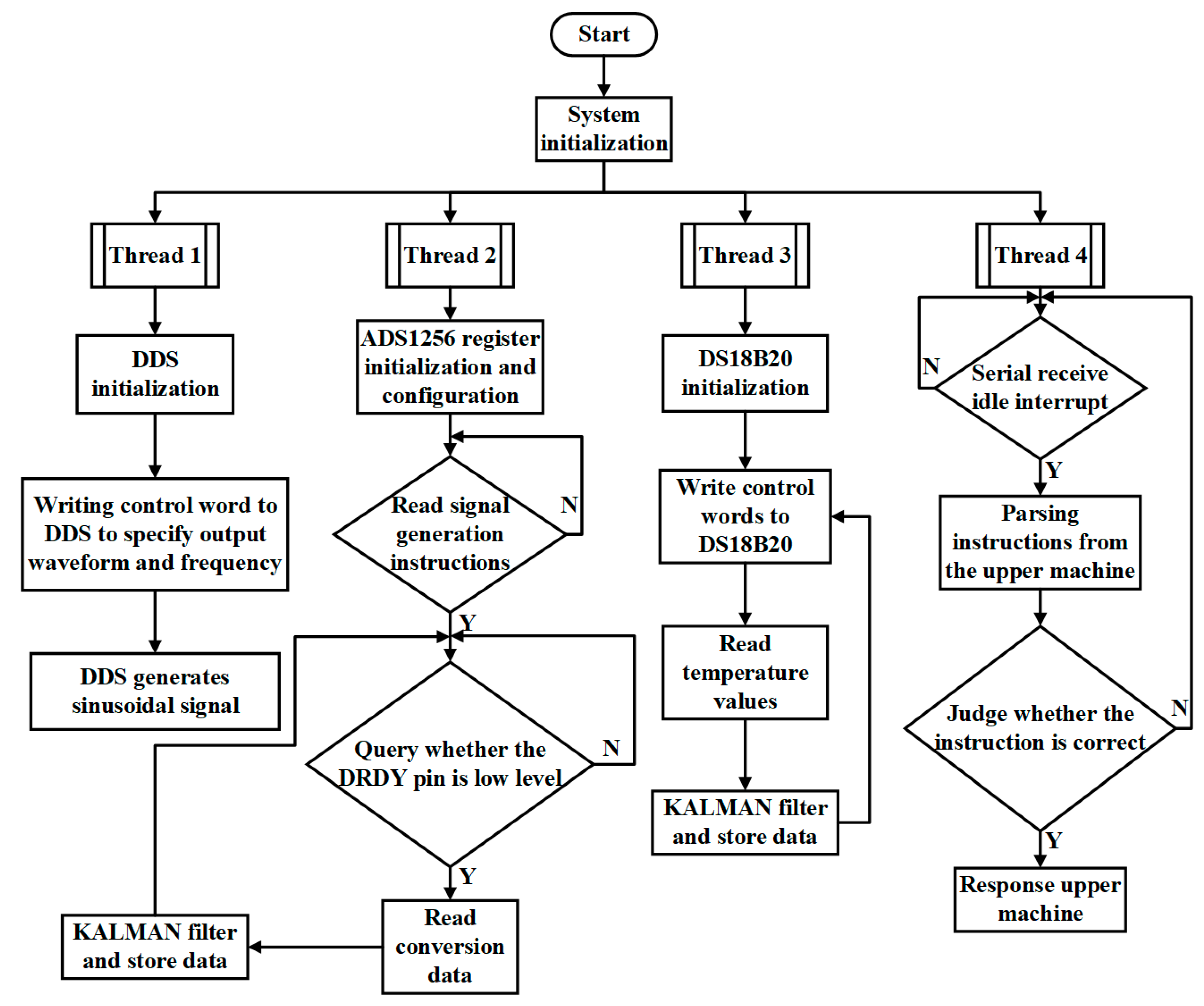
4.4. System Software Design
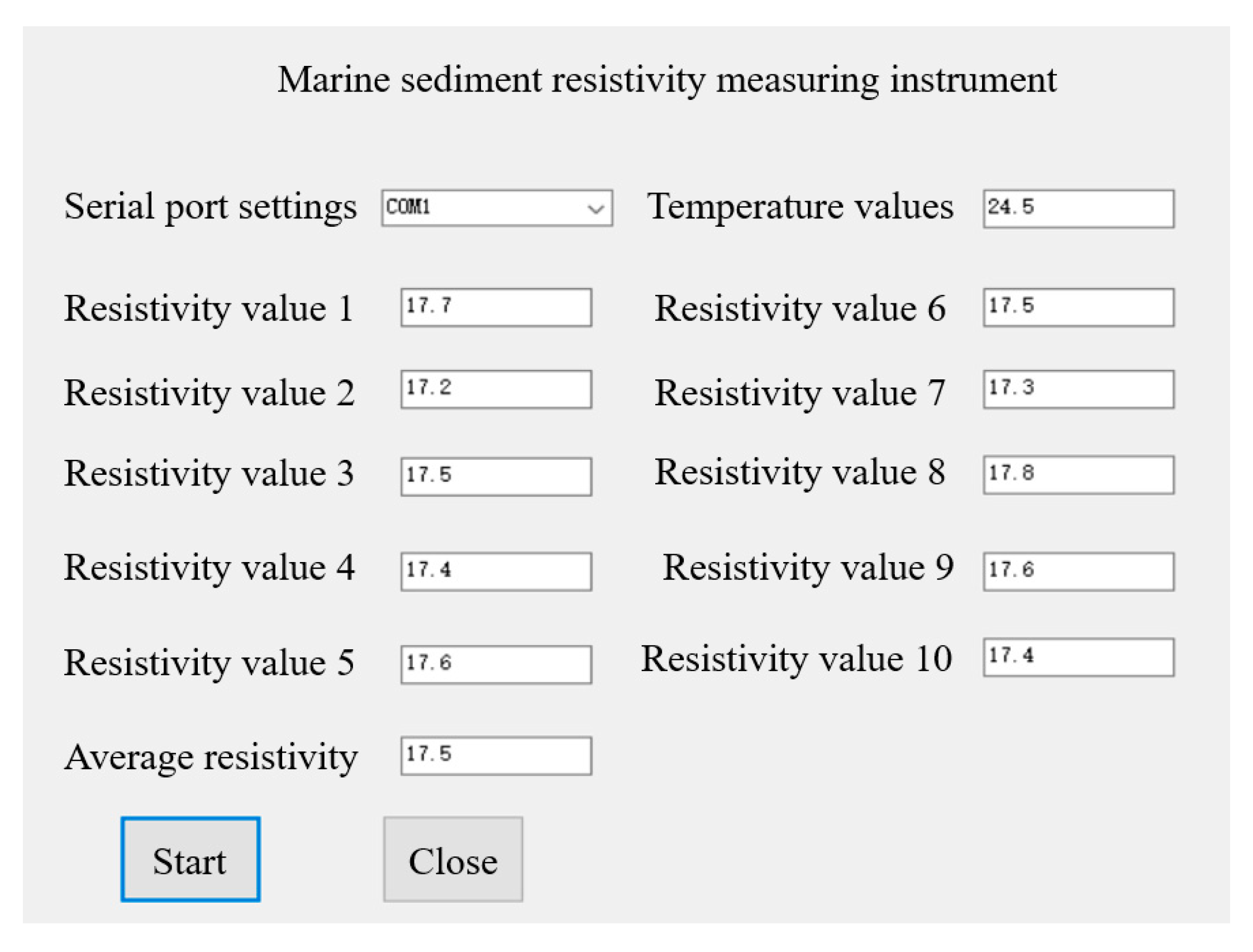
5. Resistivity Measuring Instrument Experiment
5.1. Electrical Resistivity Measurement of Distilled Water in a Laboratory
5.2. Conductivity Measurement of Laboratory Standard Liquid
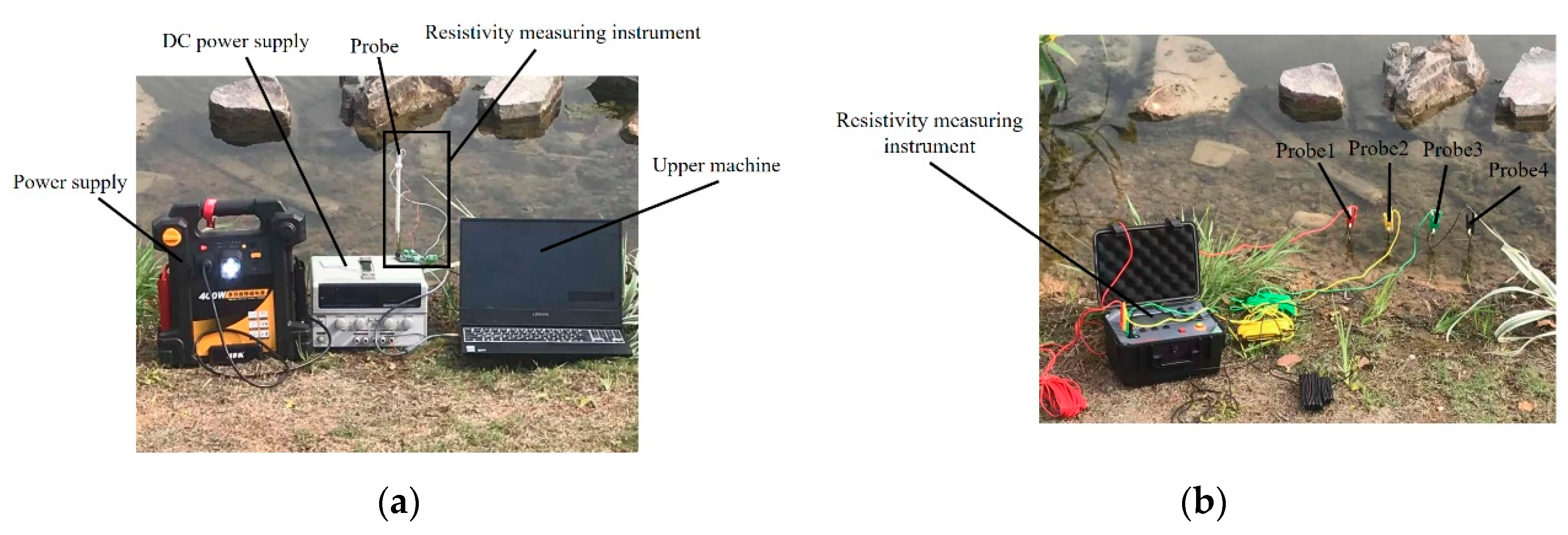
5.3. Soil Resistivity Measurement
5.4. Sediment Resistivity Measurement
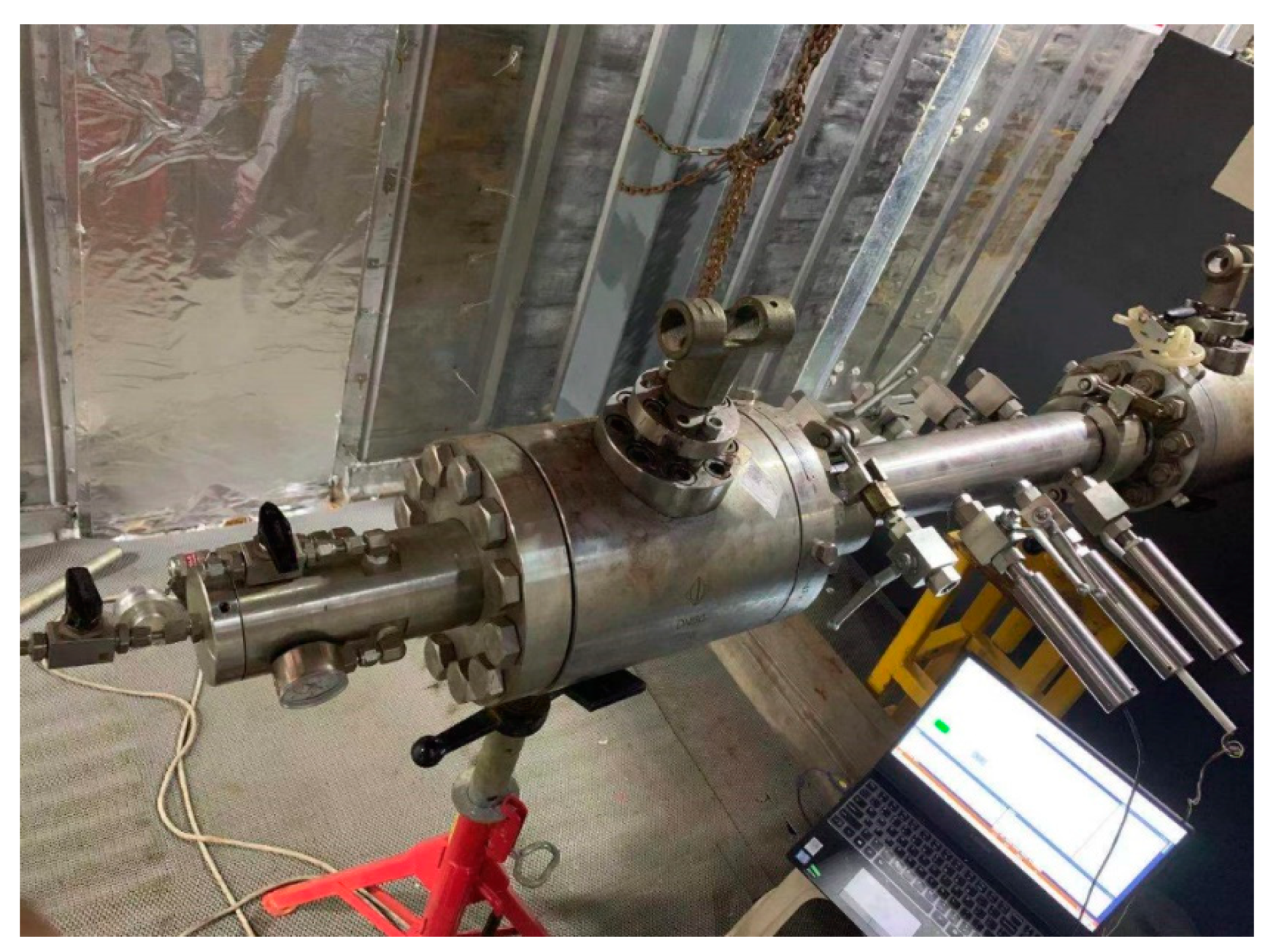
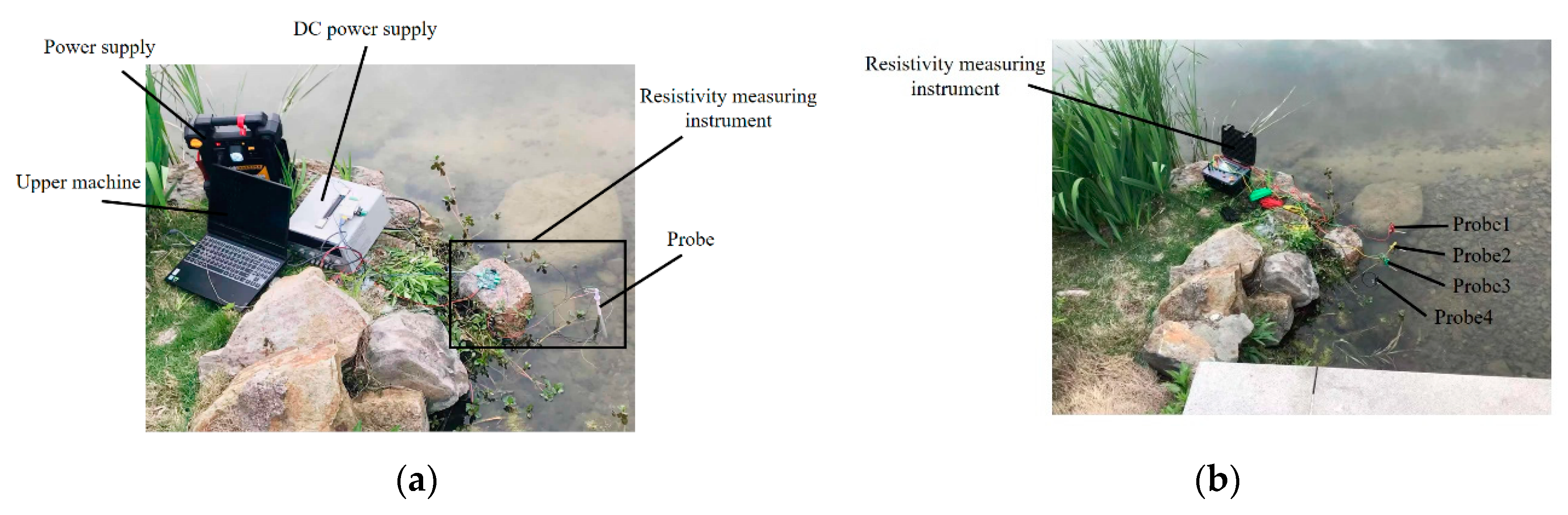
6. Overall Experiment
7. Conclusions and Foresight
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Näslund, J. The Importance of Biodiversity for Ecosystem Processes in Sediments: Experimental Examples from the Baltic Sea. Ph.D. Thesis, Department of Systems Ecology, Stockholm University, Stockholm, Sweden, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Guan, Y.; Sun, X.; Ren, Y. Mineralogy, geochemistry and genesis of the polymetallic crusts and nodules from the South China Sea. Ore Geol. Rev. 2017, 89, 206–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romoen, M.; Pfaffhuber, A.A.; Karlsrud, K.; Helle, T.E. Resistivity on Marine Sediments Retrieved from RCPTU-Soundings: A Norwegian Case Study. In Proceedings of the 2nd International Symposium on Cone Penetration Testing, Huntington Beach, CA, USA, 9–11 May 2010; Volume 2, pp. 289–296. [Google Scholar]
- Oh, M.; Kim, Y.; Park, J. Factors affecting the complex permittivity spectrum of soil at a low frequency range of 1 kHz–10 MHz. Environ. Geol. 2007, 51, 821–833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jackson, P.D. An electrical resistivity method for evaluating the in-situ porosity of clean marine sands. Mar. Georesour. Geotechnol. 1975, 1, 91–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rucker, D.F.; Noonan, G.E.; Greenwood, W.J. Electrical resistivity in support of geological mapping along the Panama Canal. Eng. Geol. 2011, 117, 121–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Won, I. The geometrical factor of a marine resistivity probe with four ring electrodes. IEEE J. Ocean. Eng. 1987, 12, 301–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosenberger, A.; Weidelt, P.; Spindeldreher, C.; Heesemann, B.; Villinger, H. Design and application of a new free fall in situ resistivity probe for marine deep water sediments. Mar. Geol. 1999, 160, 327–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, T.; Yu, H.; Jia, Y.; Xu, X.; Guo, L. Application of an In Situ Electrical Resistivity Device to Monitor Water and Salt Transport in Shandong Coastal Saline Soil. Arab. J. Sci. Eng. 2015, 40, 1907–1915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wess, J.; Bruno, Z. Lagrangian method for chiral symmetries. Phys. Rev. 1967, 163, 17–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirt, C.W.; Cook, J.L.; Butler, T.D. A Lagrangian method for calculating the dynamics of an incompressible fluid with free surface. J. Comput. Phys. 1970, 5, 103–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirt, C.W.; Amsden, A.A.; Cook, J.L. An arbitrary Lagrangian-Eulerian computing method for all flow speeds. J. Comput. Phys. 1974, 14, 227–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raptakis, A.; Oustoglou, C.; Sotiriadis, P.P. Laboratory Jitter Removal Circuit for Single-Bit All-Digital Frequency Synthesis. In Proceedings of the 2017 Panhellenic Conference on Electronics and Telecommunications (PACET), Xanthi, Greece, 17–18 November 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Podder, P.; Hasan, M.; Islam, M.; Sayeed, M. Design and implementation of Butterworth, Chebyshev-I and elliptic filter for speech signal analysis. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2002.03130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Y.K.; Suo, X.S. Design of High Precision Current Signal Source on DDS. In Proceedings of the Atlantis Press, National Conference on Electrical, Electronics and Computer Engineering, Xi’an, China, 12 December 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Strauss, D. Getting to Know Visual Studio 2019, 3rd ed.; Apress: Berkeley, CA, USA, 2020; pp. 1–60. [Google Scholar]








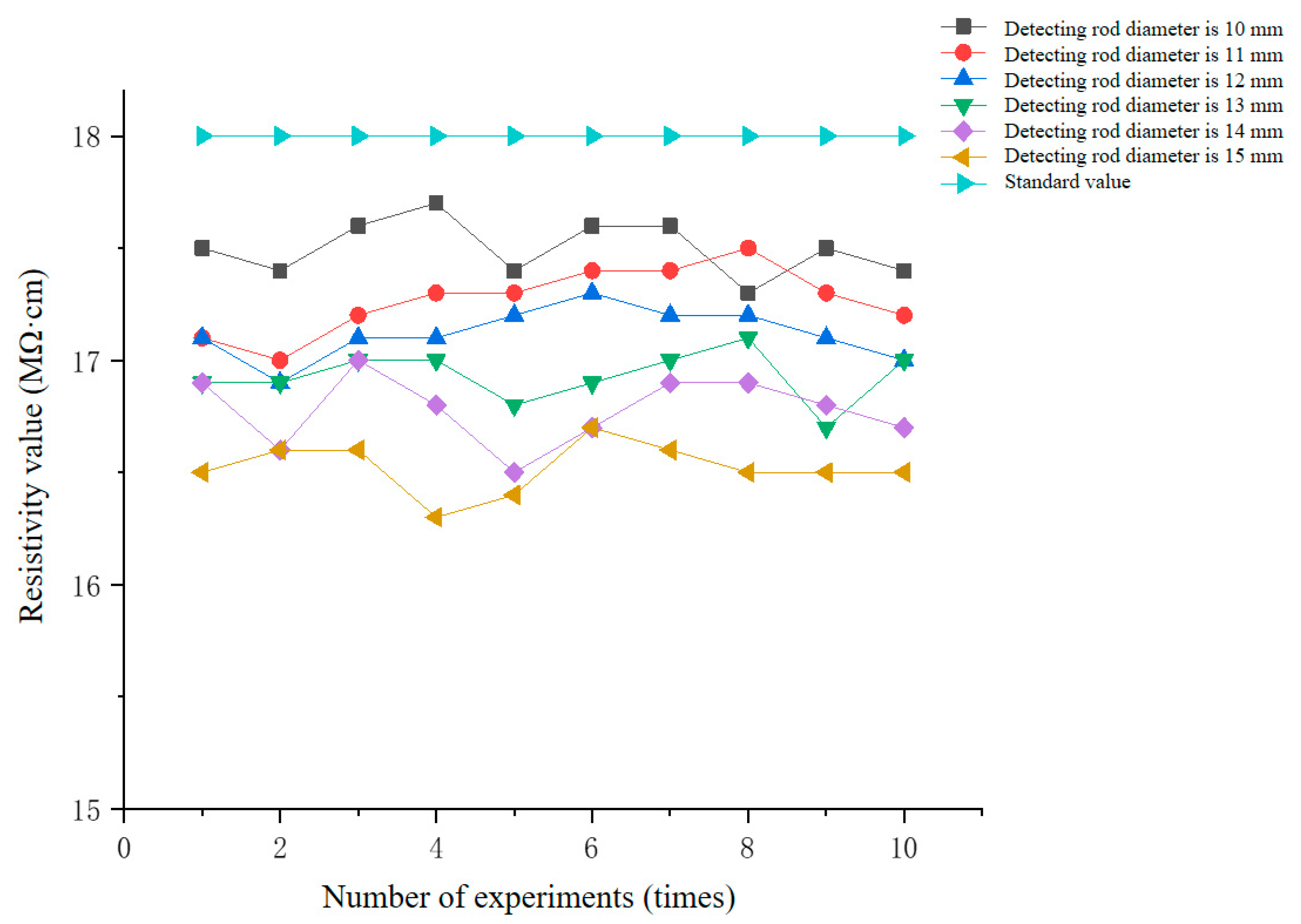



| Conductivity/Times | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | Average Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 84 us/cm | 83.1 | 82.3 | 81.6 | 80.7 | 83.2 | 83.6 | 81.3 | 82.6 | 81.2 | 83.6 | 82.32 |
| 1413 us/cm | 1365 | 1383 | 1375 | 1356 | 1398 | 1385 | 1367 | 1358 | 1396 | 1353 | 1373.6 |
| 12.88 ms/cm | 12.32 | 12.35 | 12.66 | 12.56 | 12.58 | 12.43 | 12.67 | 12.26 | 12.53 | 12.68 | 12.50 |
| Name/Times | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | Average Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| pottery clay | 23.6 | 24.3 | 23.8 | 23.9 | 23.7 | 24.3 | 24.0 | 24.2 | 24.1 | 24.2 | 23.98 |
| peat soil (pond silt) | 83.6 | 82.7 | 83.0 | 82.9 | 82.7 | 83.5 | 83.3 | 82.8 | 82.9 | 83.1 | 83.05 |
| black calcium soil (beach) | 92.1 | 93.3 | 91.5 | 92.6 | 92.5 | 92.3 | 92.8 | 94.1 | 92.5 | 93.5 | 92.72 |
| kaolinite clay (lakeside) | 72.3 | 71.4 | 73.6 | 72.8 | 71.2 | 73.3 | 75.1 | 72.5 | 73.5 | 74.2 | 72.99 |
| loess in the middle red | 223.5 | 222.3 | 225.4 | 218.3 | 219.2 | 218.5 | 216.0 | 217.5 | 213.6 | 221.6 | 220.51 |
| Name/Times | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | Average Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| pottery clay | 23.2 | 23.0 | 23.6 | 23.1 | 23.2 | 23.4 | 23.3 | 23.3 | 23.2 | 23.5 | 23.28 |
| peat soil (pond silt) | 80.8 | 81.3 | 81.2 | 81.2 | 82.0 | 81.3 | 81.0 | 81.4 | 81.5 | 81.3 | 81.30 |
| black calcium soil (beach) | 89.6 | 91.2 | 90.6 | 88.6 | 90.6 | 89.5 | 90.3 | 89.9 | 90.7 | 90.8 | 90.18 |
| kaolinite clay (lakeside) | 71.2 | 70.6 | 70.9 | 70.8 | 71.3 | 81.3 | 72.2 | 71.6 | 71.2 | 71.9 | 72.3 |
| loess in the middle red | 218.1 | 212.5 | 216.6 | 215.7 | 213.6 | 220.6 | 217.6 | 209.6 | 217.6 | 213.5 | 214.54 |
| Resistivity Value/Times | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | Average Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| developed instrument | 106.9 | 105.8 | 107.5 | 108.2 | 106.8 | 108.5 | 107.0 | 106.8 | 107.1 | 108.4 | 107.3 |
| standard instrument | 112.8 | 109.9 | 109.6 | 112.5 | 111.3 | 113.6 | 109.8 | 112.0 | 111.8 | 112.7 | 111.6 |
| Resistivity Value/Times | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | Average Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| developed instrument | 98.3 | 100.8 | 99.0 | 99.0 | 99.8 | 99.2 | 100.1 | 99.7 | 99.0 | 99.3 | 99.4 |
| standard instrument | 104.3 | 102.1 | 102.2 | 103.5 | 102.3 | 103.7 | 103.8 | 102.6 | 102.2 | 103.3 | 103.0 |
| Resistivity Value/Times | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | Average Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sediment sample tube 1 | 7.8 | 7.6 | 8.2 | 7.9 | 7.9 | 7.8 |
| Hydrate content | *** | **** | ** | *** | *** | |
| Sediment sample tube 2 | 7.6 | 7.6 | 8.0 | 8.4 | 8.1 | 7.9 |
| Hydrate content | **** | **** | *** | none | ** | |
| Sediment sample tube 3 | 8.0 | 7.8 | 7.8 | 8.2 | 8.4 | 8.0 |
| Hydrate content | *** | **** | **** | ** | none |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhou, P.; Chen, J.; Ruan, D.; Peng, X.; Wu, X.; Ren, Z.; Gao, Q. Design of a Marine Sediments Resistivity Measurement System Based on a Circular Permutation Electrode. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2021, 9, 995. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse9090995
Zhou P, Chen J, Ruan D, Peng X, Wu X, Ren Z, Gao Q. Design of a Marine Sediments Resistivity Measurement System Based on a Circular Permutation Electrode. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering. 2021; 9(9):995. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse9090995
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhou, Peng, Jiawang Chen, Dongrui Ruan, Xiaoqing Peng, Xiaocheng Wu, Ziqiang Ren, and Qiaoling Gao. 2021. "Design of a Marine Sediments Resistivity Measurement System Based on a Circular Permutation Electrode" Journal of Marine Science and Engineering 9, no. 9: 995. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse9090995
APA StyleZhou, P., Chen, J., Ruan, D., Peng, X., Wu, X., Ren, Z., & Gao, Q. (2021). Design of a Marine Sediments Resistivity Measurement System Based on a Circular Permutation Electrode. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering, 9(9), 995. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse9090995







