Preliminary Study of Airfoil Design Synthesis Using a Conditional Diffusion Model and Smoothing Method
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Diffusion Model
3. Dataset and Evaluation
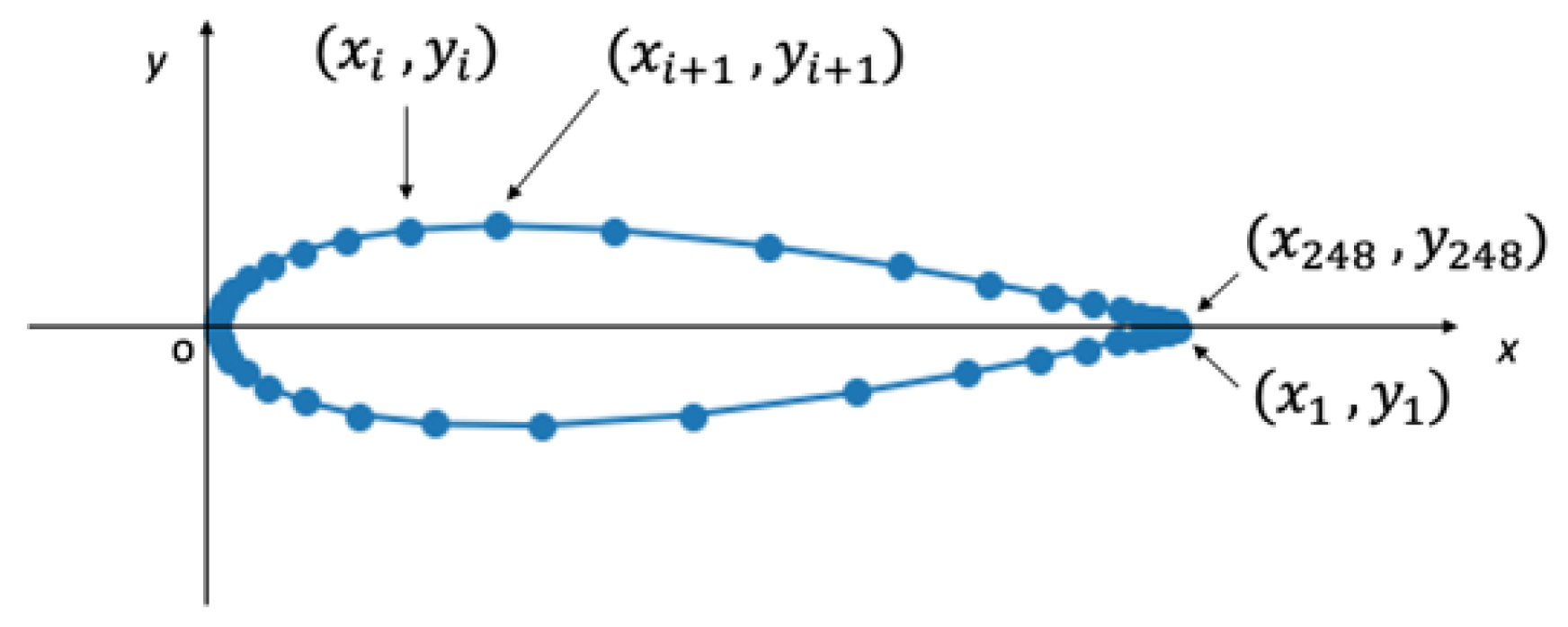
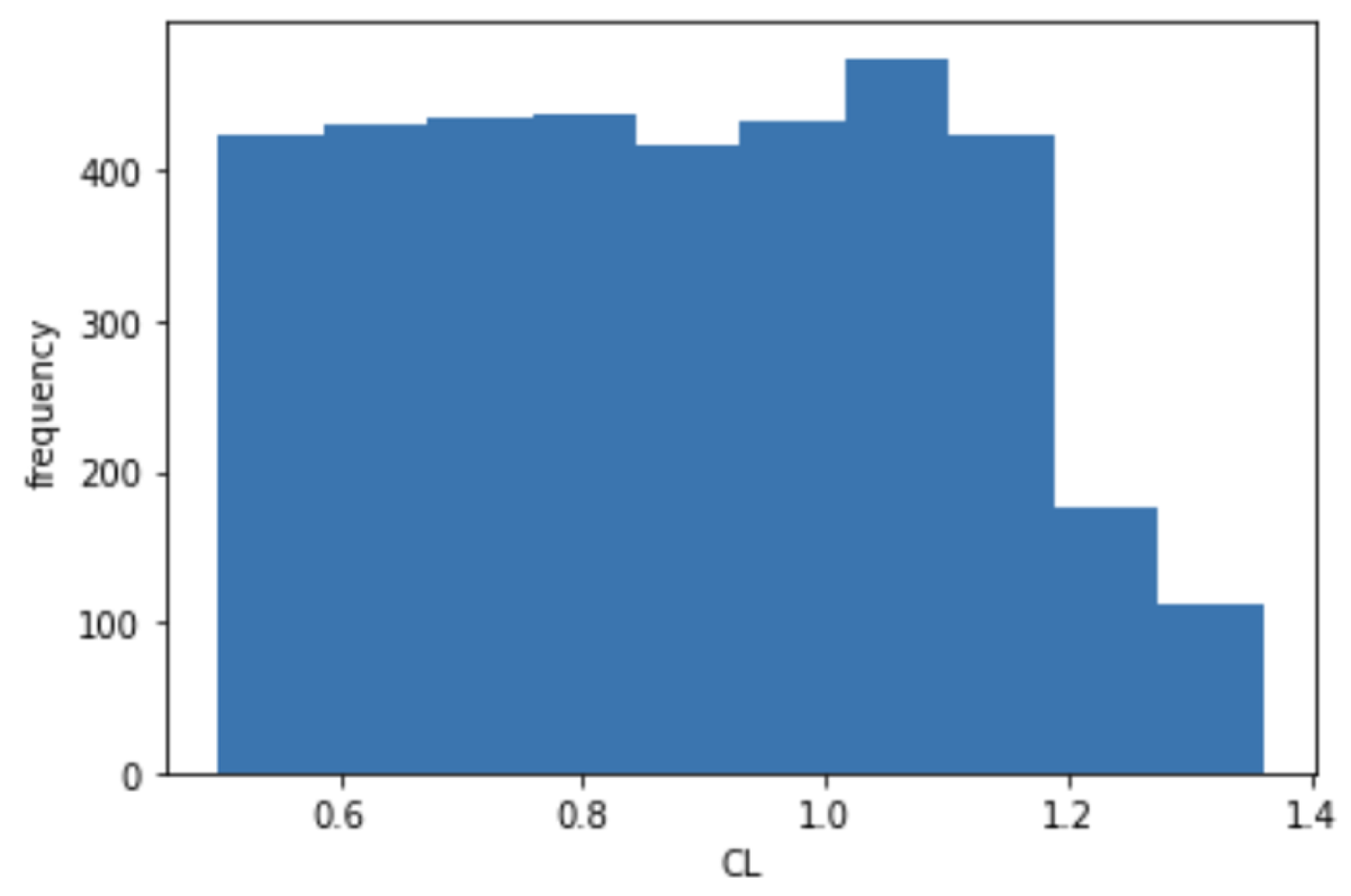
3.1. Dataset
3.2. Evaluation Method
4. Numerical Experiments
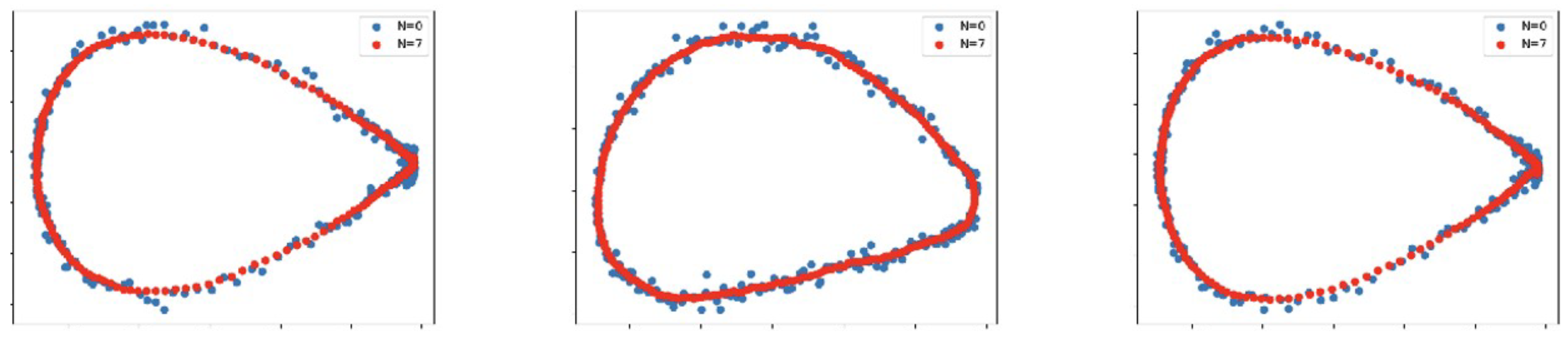
4.1. Conditional Diffusion Model with Linear Layers
4.2. Conditional Diffusion Model with Convolution Layers
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yonekura, K.; Hattori, H.; Shikada, S.; Maruyama, K. Turbine blade optimization considering smoothness of the Mach number using deep reinforcement learning. Inf. Sci. 2023, 642, 119066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Achour, G.; Sung, W.J.; Pinon-Fischer, O.J.; Mavris, D.N. Development of a Conditional Generative Adversarial Network for Airfoil Shape Optimization. In Proceedings of the AIAA Scitech 2020 Forum, Orlando, FL, USA, 6–10 January 2020; p. 2261. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Z.; Braun, J.; Paniagua, G. Three Dimensional Optimization for Subsonic Axial Turbines Operating at High Unsteady Inlet Mach Number. In Proceedings of the 2018 Joint Propulsion Conference, Cincinnati, OH, USA, 9–11 July 2018. AIAA 2018-4480. [Google Scholar]
- Nash, C.; Williams, C.K.I. The shape variational autoencoder: A deep generative model of part-segmented 3D objects. Comput. Graph. Forum 2017, 36, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Umetani, N. Exploring Generative 3D Shapes Using Autoencoder Networks. In Proceedings of the SIGGRAPH Asia 2017 Technical Briefs, Bangkok Thailand, 27–30 November 2017; SA’17. Association for Computing Machinery: New York, NY, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Yonekura, K.; Miyamoto, N.; Suzuki, K. Inverse airfoil design method for generating varieties of smooth airfoils using conditional WGAN-gp. Struct. Multidiscip. Optim. 2022, 65, 173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yonekura, K.; Tomori, Y.; Suzuki, K. Airfoil generation and feature extraction using the conditional VAE-WGAN-gp. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2311.05445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yonekura, K.; Hattori, H.; Nishizu, T. Fluid topology optimization and additive manufacturing of a liquid atomizer using extensive number of grids. Struct. Multidiscip. Optim. 2023, 126, 1799–1806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radhakrishnan, S.; Bharadwaj, V.; Manjunath, V.; Srinath, R. Creative Intelligence—Automating Car Design Studio with Generative Adversarial Networks (GAN). In Machine Learning and Knowledge Extraction; Holzinger, A., Kieseberg, P., Tjoa, A.M., Weippl, E., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Swizterland, 2018; pp. 160–175. [Google Scholar]
- Shimizu, Y.; Morimoto, S.; Sanada, M.; Inoue, Y. Automatic Design System With Generative Adversarial Network and Convolutional Neural Network for Optimization Design of Interior Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motor. IEEE Trans. Energy Convers. 2023, 38, 724–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yonekura, K.; Omori, K.; Qi, X.; Suzuki, K. Designing ship hull forms using generative adversarial networks. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2311.05470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Yu, F.; Funkhouser, T. Interactive 3D Modeling with a Generative Adversarial Network. In Proceedings of the 2017 International Conference on 3D Vision (3DV), Qingdao, China, 10–12 October 2017; pp. 126–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yonekura, K.; Suzuki, K. Data-driven design exploration method using conditional variational autoencoder for airfoil design. Struct. Multidiscip. Optim. 2021, 64, 613–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wada, K.; Suzuki, K.; Yonekura, K. Physics-guided training of GAN to improve accuracy in airfoil design synthesis. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Eng. 2024, 421, 116746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, Z.; Koulieris, G.A.; Shum, H.P.H. On the Design Fundamentals of Diffusion Models: A Survey. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2306.04542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sohl-Dickstein, J.; Weiss, E.; Maheswaranathan, N.; Ganguli, S. Deep Unsupervised Learning using Nonequilibrium Thermodynamics. In Proceedings of the 32nd International Conference on Machine Learning, Lille, France, 7–9 July 2015; Volume 37, pp. 2256–2265. [Google Scholar]
- Rombach, R.; Blattmann, A.; Lorenz, D.; Esser, P.; Ommer, B. High-Resolution Image Synthesis with Latent Diffusion Models. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2112.10752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramesh, A.; Dhariwal, P.; Nichol, A.; Chu, C.; Chen, M. Hierarchical Text-Conditional Image Generation with CLIP Latents. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2204.06125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Croitoru, F.A.; Hondru, V.; Ionescu, R.T.; Shah, M. Diffusion Models in Vision: A Survey. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2023, 45, 10850–10869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, S.; Sun, P.; Song, Y.; Luo, P. DiffusionDet: Diffusion Model for Object Detection. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), Paris, France, 1–6 October 2023; pp. 19830–19843. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, Z.; Liu, J.; Wang, Y.; Chen, M.; Wang, D.; Xu, D.; Cheng, J. Diffusion models in bioinformatics and computational biolog. Nat. Rev. Bioeng. 2024, 2, 136–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Popov, V.; Vovk, I.; Gogoryan, V.; Sadekova, T.; Kudinov, M.; Wei, J. Diffusion-Based Voice Conversion with Fast Maximum Likelihood Sampling Scheme. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2109.13821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazé, F.; Ahmed, F. Diffusion Models Beat GANs on Topology Optimization. Proc. AAAI Conf. Artif. Intell. 2023, 37, 9108–9116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vlassis, N.N.; Sun, W. Denoising diffusion algorithm for inverse design of microstructures with fine-tuned nonlinear material properties. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Eng. 2023, 413, 116126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Zhang, Z.; Song, Y.; Hong, S.; Xu, R.; Zhao, Y.; Zhang, W.; Cui, B.; Yang, M.H. Diffusion Models: A Comprehensive Survey of Methods and Applications. ACM Comput. Surv. 2023, 56, 1–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Z.; Dufour, E.R.; Pelletier, C.; Fua, P.; Bauerheim, M. DiffAirfoil: An Efficient Novel Airfoil Sampler Based on Latent Space Diffusion Model for Aerodynamic Shape Optimization. In Proceedings of the AIAA Aviation Forum and Ascend 2024, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 29 July–2 August 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, J.; Jain, A.; Abbeel, P. Denoising Diffusion Probabilistic Models. In Proceedings of the Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems; Larochelle, H., Ranzato, M., Hadsell, R., Balcan, M., Lin, H., Eds.; Curran Associates, Inc.: Red Hook, NY, USA, 2020; Volume 33, pp. 6840–6851. [Google Scholar]
- Ronneberger, O.; Fischer, P.; Brox, T. U-Net: Convolutional Networks for Biomedical Image Segmentation. In Proceedings of the Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention—MICCAI 2015, Munich, Germany, 5–9 October 2015; Navab, N., Hornegger, J., Wells, W.M., Frangi, A.F., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2015; pp. 234–241. [Google Scholar]
- Ho, J.; Salimans, T. Classifier-Free Diffusion Guidance. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2207.12598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drela, M. XFOIL: An Analysis and Design System for Low Reynolds Number Airfoils. In Low Reynolds Number Aerodynamics; Mueller, T.J., Ed.; Lecture Notes in Engineering; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1989; Volume 54, pp. 1–12. [Google Scholar]
- Yonekura, K.; Wada, K.; Suzuki, K. Generating various airfoils with required lift coefficients by combining NACA and Joukowski airfoils using conditional variational autoencoders. Eng. Appl. Artif. Intell. 2022, 108, 104560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Layer of U-Net | 4 | Optimizer | Adam |
| Channel of U-Net | 128 | Learning rate | 0.0001 |
| Timestep T | 400 | Batch size | 16 |
| Activation function | ReLU, GeLU |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yonekura, K.; Oshima, Y.; Aichi, M. Preliminary Study of Airfoil Design Synthesis Using a Conditional Diffusion Model and Smoothing Method. Computation 2024, 12, 227. https://doi.org/10.3390/computation12110227
Yonekura K, Oshima Y, Aichi M. Preliminary Study of Airfoil Design Synthesis Using a Conditional Diffusion Model and Smoothing Method. Computation. 2024; 12(11):227. https://doi.org/10.3390/computation12110227
Chicago/Turabian StyleYonekura, Kazuo, Yuta Oshima, and Masaatsu Aichi. 2024. "Preliminary Study of Airfoil Design Synthesis Using a Conditional Diffusion Model and Smoothing Method" Computation 12, no. 11: 227. https://doi.org/10.3390/computation12110227
APA StyleYonekura, K., Oshima, Y., & Aichi, M. (2024). Preliminary Study of Airfoil Design Synthesis Using a Conditional Diffusion Model and Smoothing Method. Computation, 12(11), 227. https://doi.org/10.3390/computation12110227






