Terahertz Optical Bistability in the Metal Nanoparticles-Graphene Nanodisks-Quantum Dots Hybrid Systems
Abstract
1. Introduction
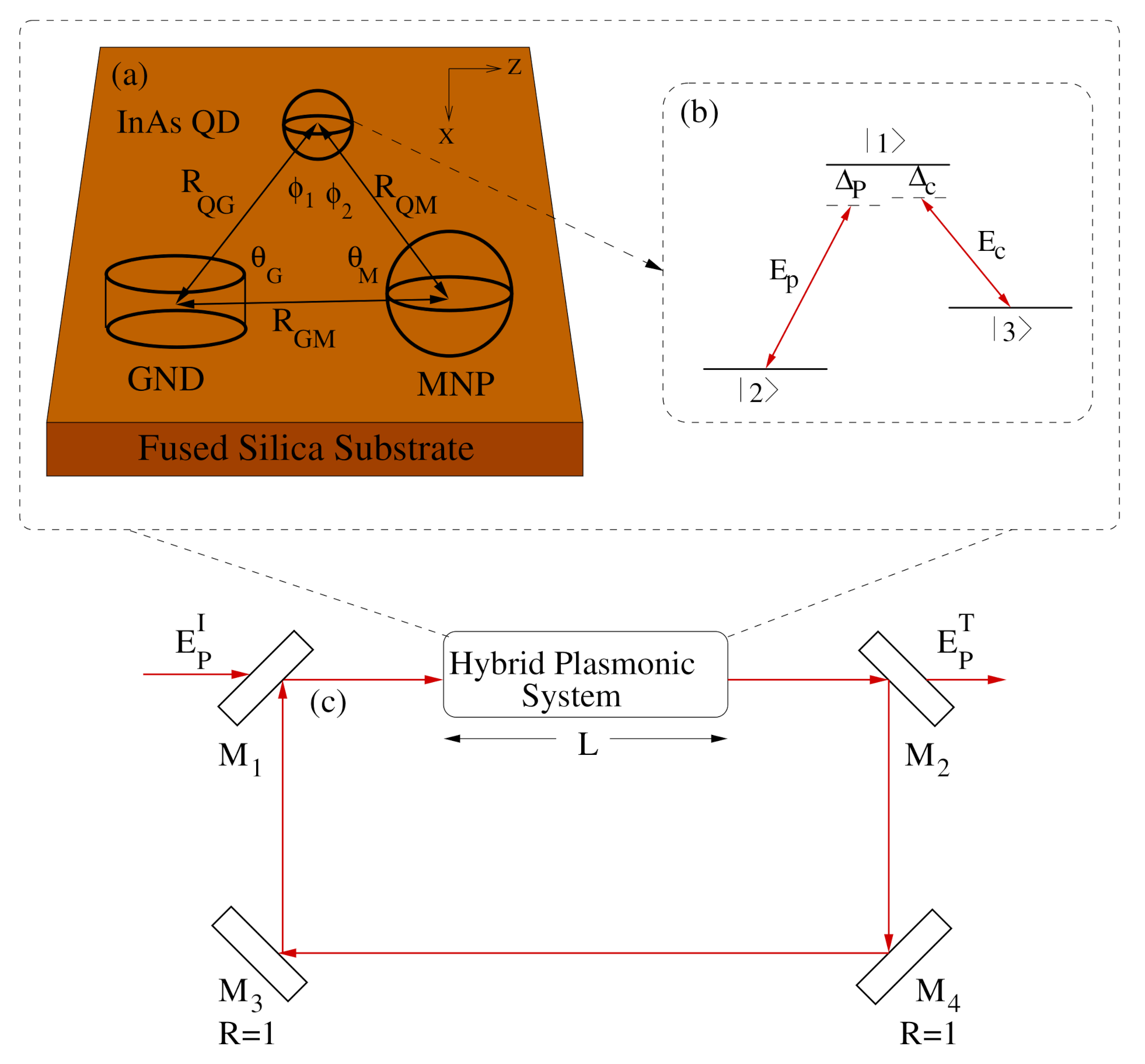
2. Theoretical Model
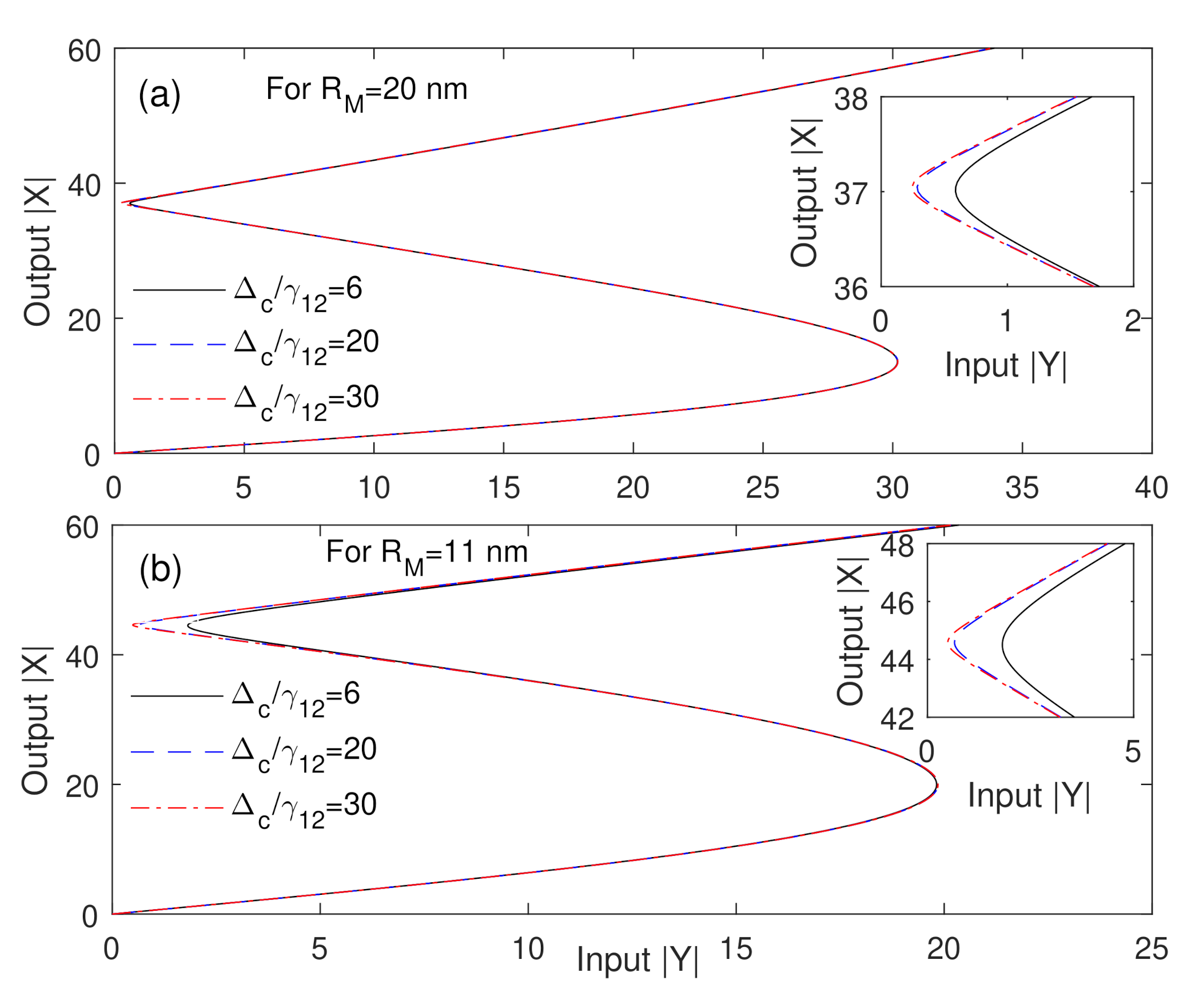
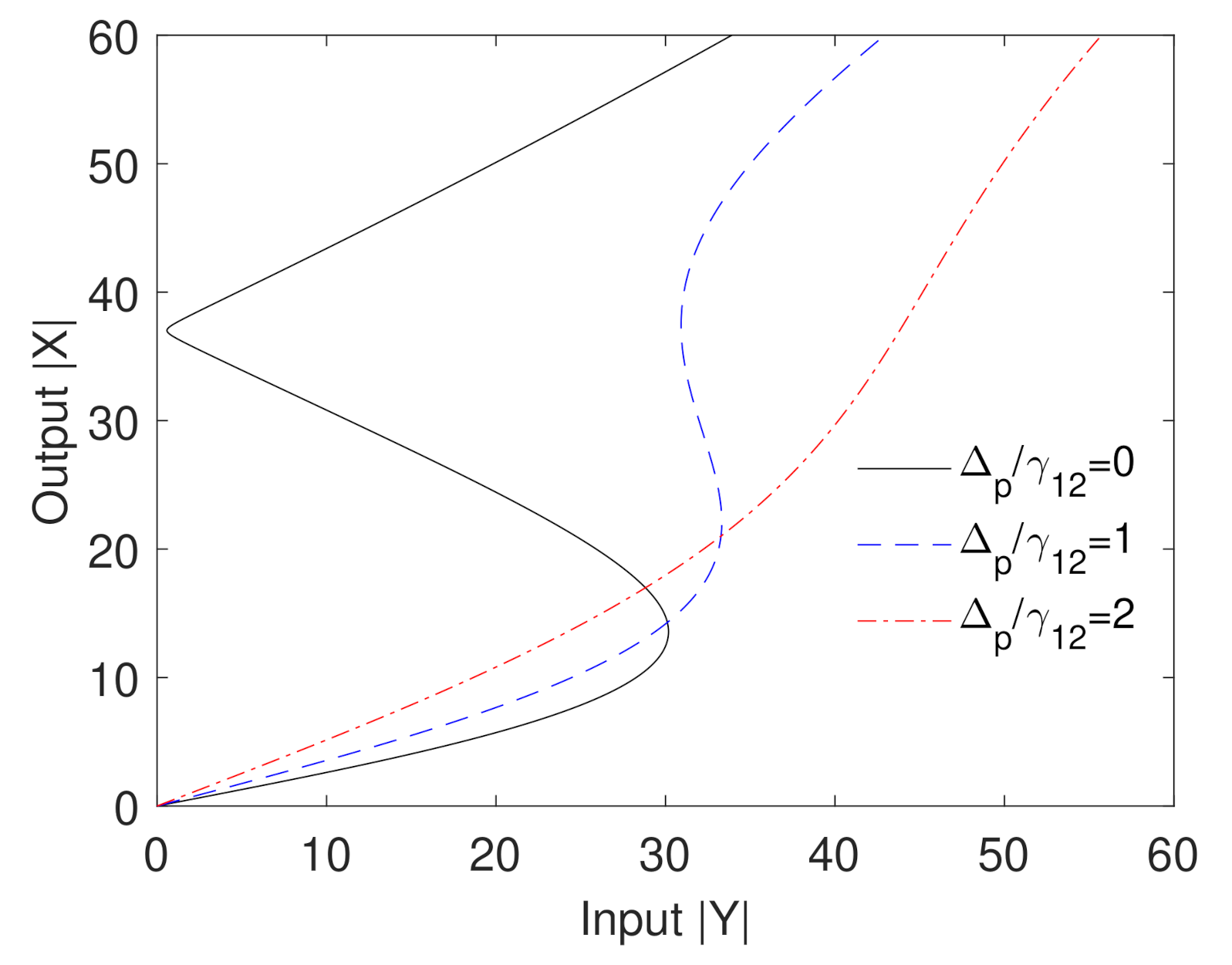
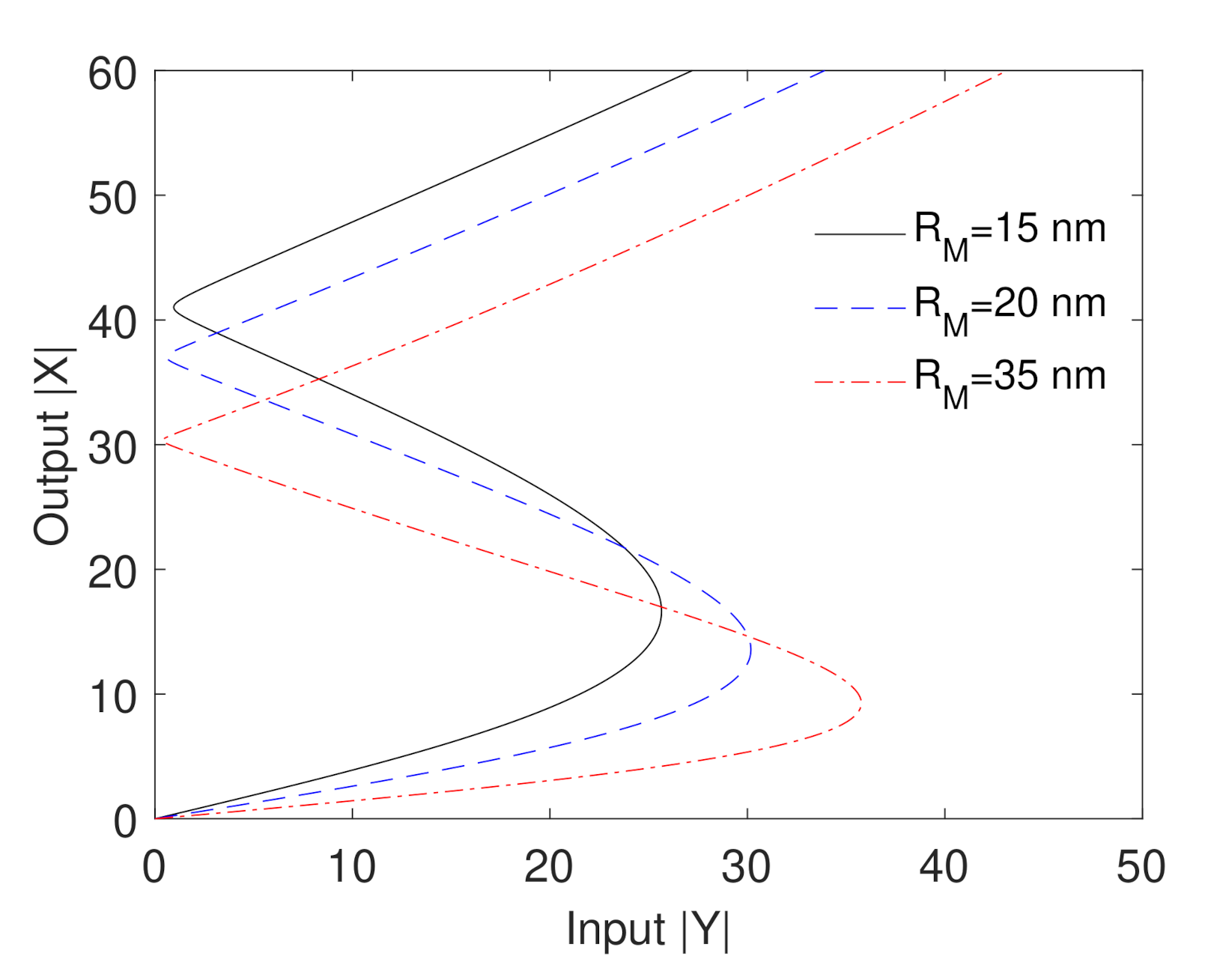
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bogue, R. Sensing with terahertz radiation: A review of recent progress. Sens. Rev. 2018, 38, 216–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, W.L.; Deibel, J.; Mittleman, D.M. Imaging with terahertz radiation. Rep. Prog. Phys. 2007, 70, 1325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hangyo, M.; Nagashima, T.; Nashima, S. Spectroscopy by pulsed terahertz radiation. Meas. Sci. Technol. 2002, 13, 1727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Son, J.H.; Oh, S.J.; Cheon, H. Potential clinical applications of terahertz radiation. J. Appl. Phys. 2019, 125, 190901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakai, K. Terahertz Optoelectronics; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2005; Volume 6. [Google Scholar]
- Boyd, R.W. Nonlinear Optics; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Gibbs Hyatt, M. Optical Bistability: Controlling Light with Light; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 1985. [Google Scholar]
- Soljacic, M.; Ibanescu, M.; Luo, C.; Johnson, S.G.; Fan, S.; Fink, Y.; Joannopoulos, J.D. All-optical switching using optical bistability in nonlinear photonic crystals. In Photonic Crystal Materials and Devices; International Society for Optics and Photonics: Bellingham, WA, USA, 2003; Volume 5000, pp. 200–214. [Google Scholar]
- Javaloyes, J.; Trita, A.; Mezosi, G.; Bragheri, F.; Cristiani, I.; Giuliani, G.; Sorel, M.; Scirè, A.; Balle, S. Ultrafast all-optical switching of bistable Semiconductor Ring Lasers. In The European Conference on Lasers and Electro-Optics; Optical Society of America: Washington, DC, USA, 2009; p. CB6_2. [Google Scholar]
- Chai, Z.; Hu, X.; Wang, F.; Niu, X.; Xie, J.; Gong, Q. Ultrafast all-optical switching. Adv. Opt. Mater. 2017, 5, 1600665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, M.; Holonyak, N., Jr.; Wang, C. Room temperature operation of electro-optical bistability in the edge-emitting tunneling-collector transistor laser. J. Appl. Phys. 2017, 122, 103102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C. Applications of electro-optical hybrid optical bistable devices. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Optoelectronic Science and Engineering’90, Beijing, China, 22–25 August 1990; International Society for Optics and Photonics: Bellingham, WA, USA, 2017; Volume 1230, p. 123075. [Google Scholar]
- Rahmati, A.; Amandadi, M.A. All-optical NAND/NOR logic gates using bistable switching. Pramana 2019, 93, 90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castro Neto, A.H.; Guinea, F.; Peres, N.M.R.; Novoselov, K.S.; Geim, A.K. The electronic properties of graphene. RvMP 2009, 81, 109–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Kaner, R.B. Graphene-based materials. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2008, 3, 101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Yin, Z.; Wu, S.; Qi, X.; He, Q.; Zhang, Q.; Yan, Q.; Boey, F.; Zhang, H. Graphene-based materials: Synthesis, characterization, properties, and applications. Small 2011, 7, 1876–1902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohan, V.B.; Lau, K.T.; Hui, D.; Bhattacharyya, D. Graphene-based materials and their composites: A review on production, applications and product limitations. Compos. Part B Eng. 2018, 142, 200–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonaccorso, F.; Sun, Z.; Hasan, T.; Ferrari, A. Graphene photonics and optoelectronics. Nat. Photonics 2010, 4, 611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lawal, A.T. Graphene-based nano composites and their applications. A review. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2019, 141, 111384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mikhailov, S.A. Non-linear electromagnetic response of graphene. EPL 2007, 79, 27002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mikhailov, S.A. Electromagnetic response of electrons in graphene: Non-linear effects. Phys. E Low-Dimens. Syst. Nanostruct. 2008, 40, 2626–2629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, X.; Jiang, L.; Xiang, Y. Low threshold optical bistability at terahertz frequencies with graphene surface plasmons. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, B.B.; Deng, X.H.; Yuan, J.; Liao, Q.H. Tunable THz optical bistability in graphene-based heterostructures. J. Mod. Opt. 2015, 62, 1650–1654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naseri, T.; Daneshfar, N.; Moradi-Dangi, M.; Eynipour-Malaee, F. Terahertz optical bistability of graphene-coated cylindrical core–shell nanoparticles. J. Theor. Appl. Phys. 2018, 12, 257–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahn, K.J.; Rotermund, F. Terahertz optical bistability of graphene in thin layers of dielectrics. Opt. Express 2017, 25, 8484–8490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kar, A.; Goswami, N.; Saha, A. Long-range surface plasmon-induced tunable ultralow threshold optical bistability using graphene sheets at terahertz frequency. Appl. Opt. 2017, 56, 2321–2329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Miroshnichenko, A.E.; Gao, L. Low-threshold optical bistability of graphene-wrapped dielectric composite. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 23354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, J.; Jiang, L.; Jia, Y.; Dai, X.; Xiang, Y.; Fan, D. Low threshold optical bistability in one-dimensional gratings based on graphene plasmonics. Opt. Express 2017, 25, 5972–5981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tohari, M.; Lyras, A.; AlSalhi, M. Giant self-Kerr nonlinearity in the metal nanoparticles-graphene nanodisks-quantum dots hybrid systems under low-lntensity light irradiance. Nanomaterials 2018, 8, 521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tohari, M.M.; Alqahtani, M.M.; Lyras, A. Optical multistability in the metal nanoparticle–graphene nanodisk–quantum dot hybrid systems. Nanomaterials 2020, 10, 1687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Low, T.; Avouris, P. Graphene plasmonics for terahertz to mid-infrared applications. ACS Nano 2014, 8, 1086–1101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nga, D.T.; Nghia, D.C.; Ha, C.V. Plasmonic properties of graphene-based nanostructures in terahertz waves. J. Sci. Adv. Mater. Devices 2017, 2, 371–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tohari, M.; Lyras, A.; Alsalhi, M. Ultrafast energy transfer in the metal nanoparticles-graphene nanodisks-quantum dots hybrid systems. Plasmonics 2019, 14, 17–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, J.; Williams, R.T. Excitonic and Photonic Processes in Materials; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Cox, J.D.; Singh, M.R.; Gumbs, G.; Anton, M.A.; Carreno, F. Dipole-dipole interaction between a quantum dot and a graphene nanodisk. Phys. Rev. B 2012, 86, 125452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jablan, M.; Buljan, H.; Soljačić, M. Plasmonics in graphene at infrared frequencies. Phys. Rev. B 2009, 80, 245435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schedin, F.; Lidorikis, E.; Lombardo, A.; Kravets, V.G.; Geim, A.K.; Grigorenko, A.N.; Novoselov, K.S.; Ferrari, A.C. Surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy of graphene. ACS Nano 2010, 4, 5617–5626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- MinovKoppensich, F.; Chang, D.; Thongrattanasiri, S.; de Abajo, F.G. Graphene plasmonics: A platform for strong light-matter interactions. Opt. Photonics News 2011, 22, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, M.R.; Schindel, D.G.; Hatef, A. Dipole-dipole interaction in a quantum dot and metallic nanorod hybrid system. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2011, 99, 181106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joshi, A.; Yang, W.; Xiao, M. Hysteresis loop with controllable shape and direction in an optical ring cavity. Phys. Rev. A 2004, 70, 041802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klimov, V. Nanoplasmonics; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]


Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tohari, M.M. Terahertz Optical Bistability in the Metal Nanoparticles-Graphene Nanodisks-Quantum Dots Hybrid Systems. Nanomaterials 2020, 10, 2173. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano10112173
Tohari MM. Terahertz Optical Bistability in the Metal Nanoparticles-Graphene Nanodisks-Quantum Dots Hybrid Systems. Nanomaterials. 2020; 10(11):2173. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano10112173
Chicago/Turabian StyleTohari, Mariam M. 2020. "Terahertz Optical Bistability in the Metal Nanoparticles-Graphene Nanodisks-Quantum Dots Hybrid Systems" Nanomaterials 10, no. 11: 2173. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano10112173
APA StyleTohari, M. M. (2020). Terahertz Optical Bistability in the Metal Nanoparticles-Graphene Nanodisks-Quantum Dots Hybrid Systems. Nanomaterials, 10(11), 2173. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano10112173



