Super Hydrophilic Activated Carbon Decorated Nanopolymer Foam for Scalable, Energy Efficient Photothermal Steam Generation, as an Effective Desalination System
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Fabrication of ACM Solar Steam Generator
2.3. Solar-Driven Setup
2.4. Preparation Volatile Organic Compounds (VOCs)
2.5. Material Characterization
3. Results and Discussion
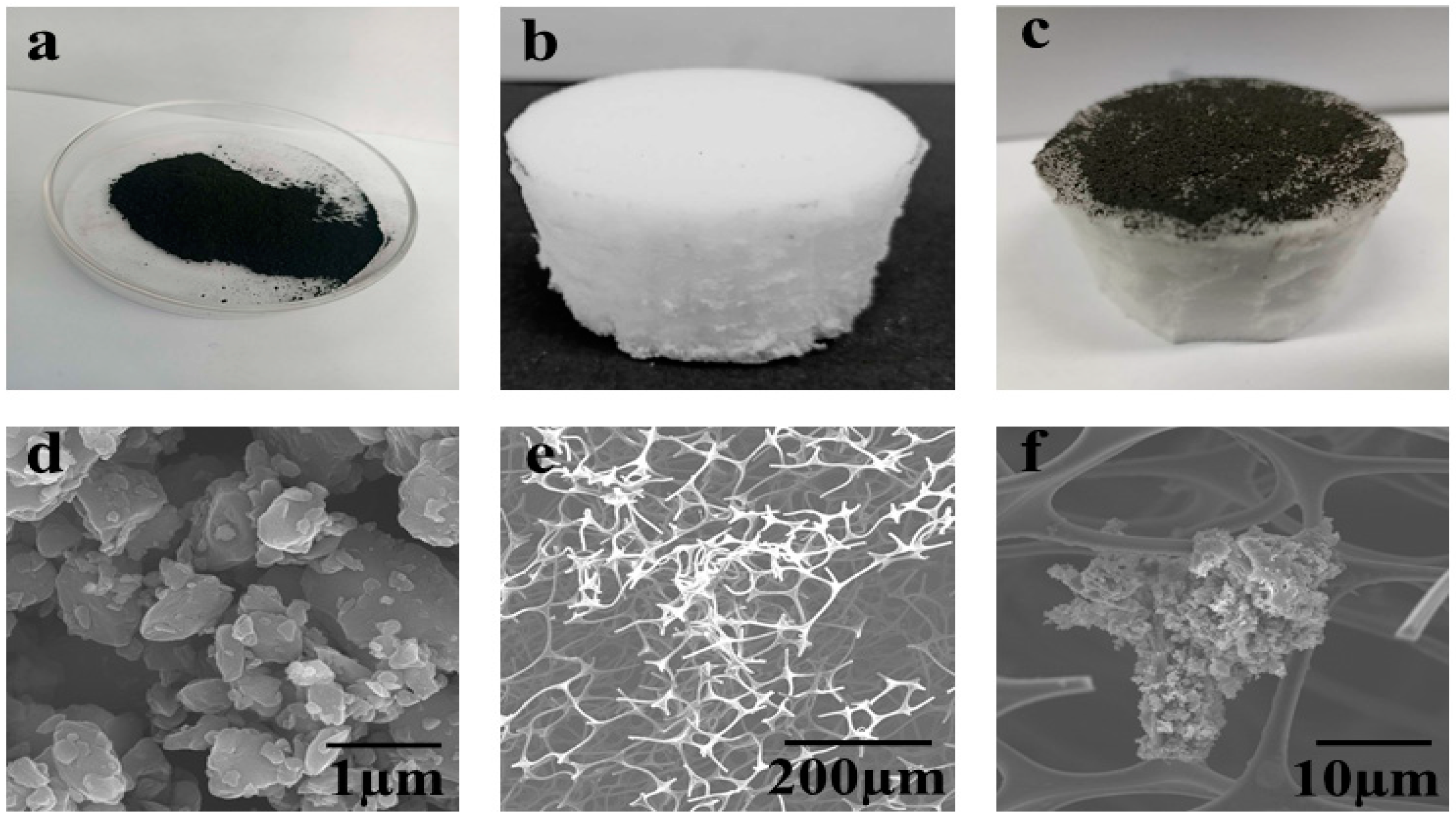
3.1. Open Porous Assembly
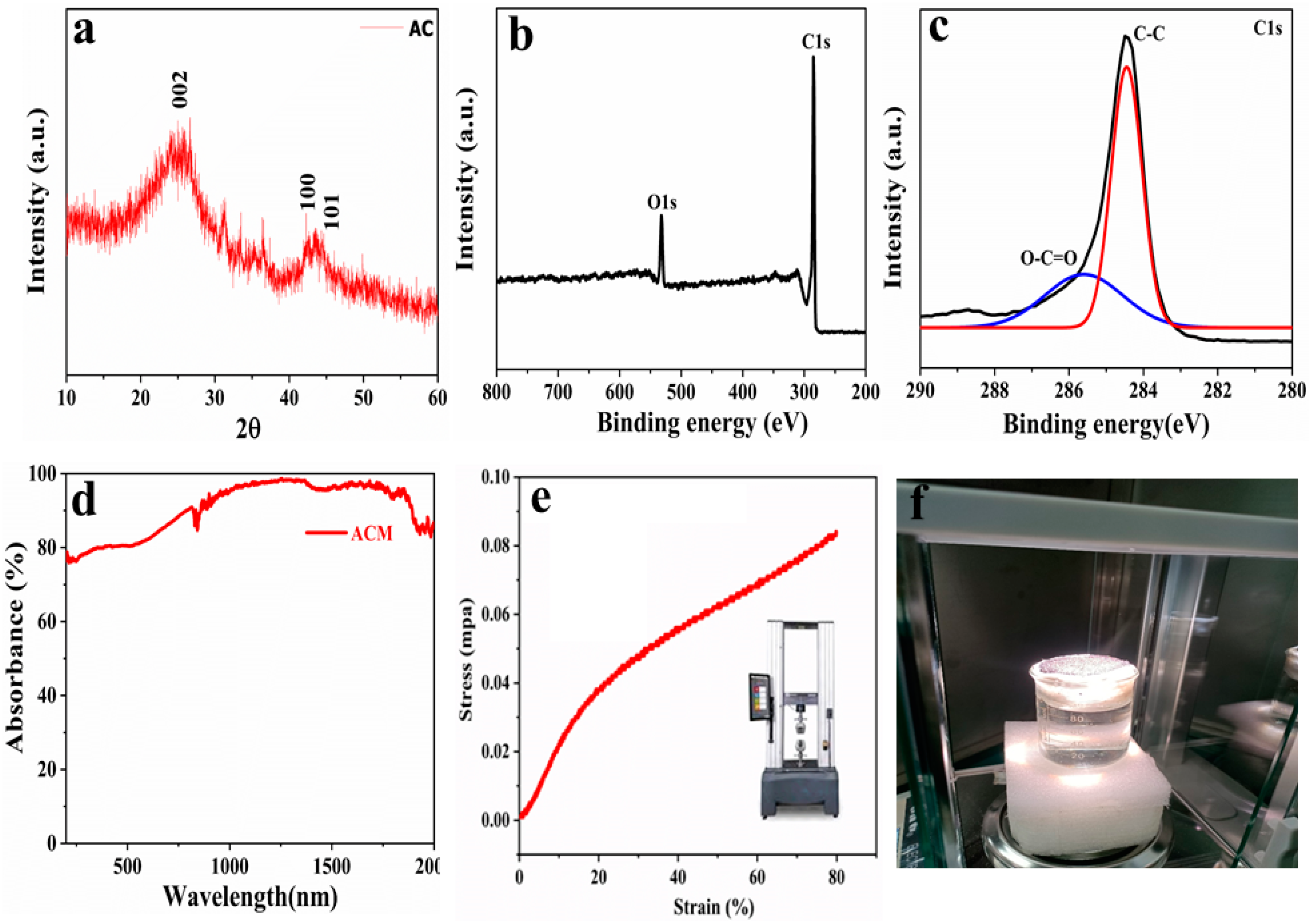
3.2. Structural and Chemical State of ACM
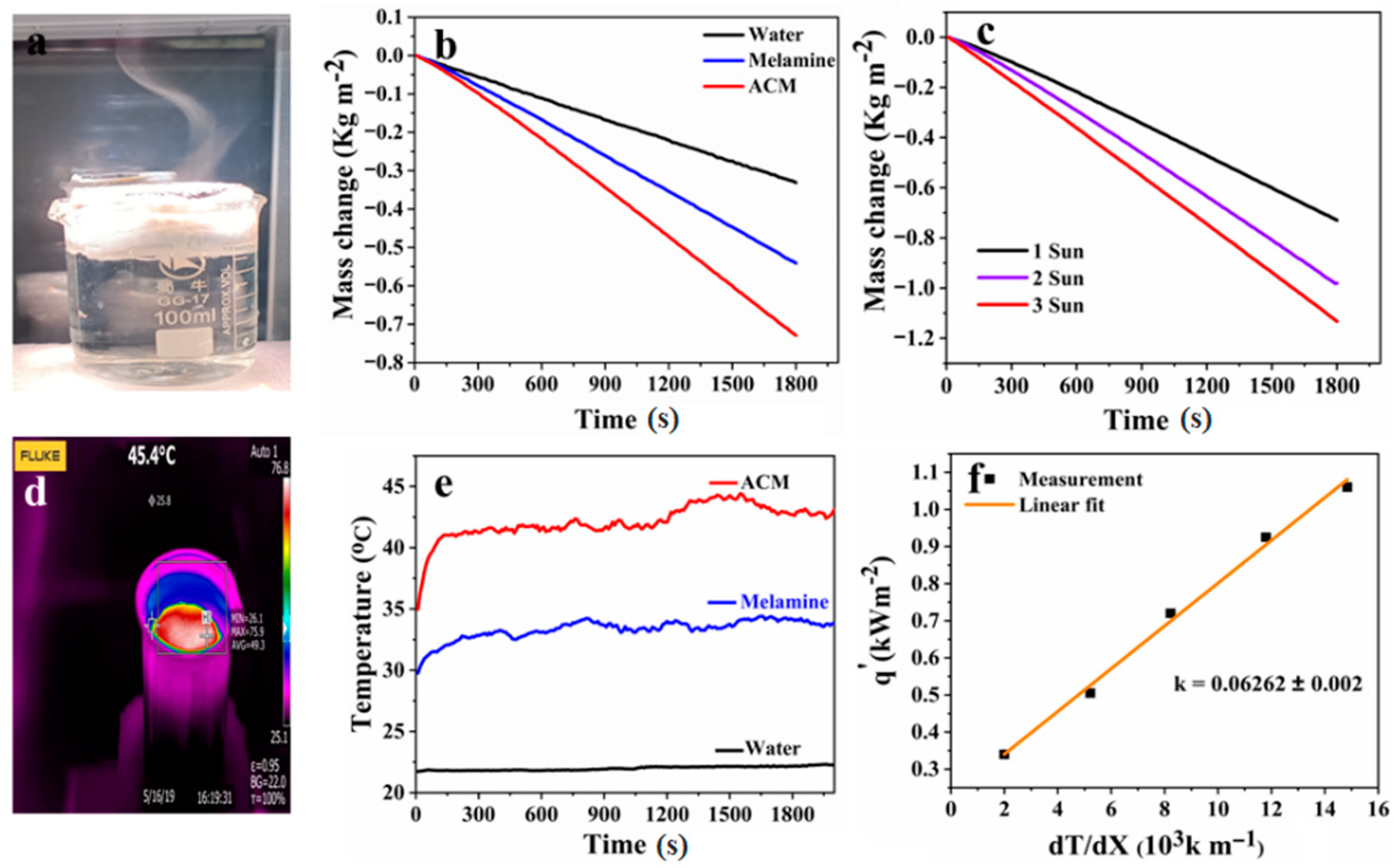
3.3. ACM Based Steam Generator
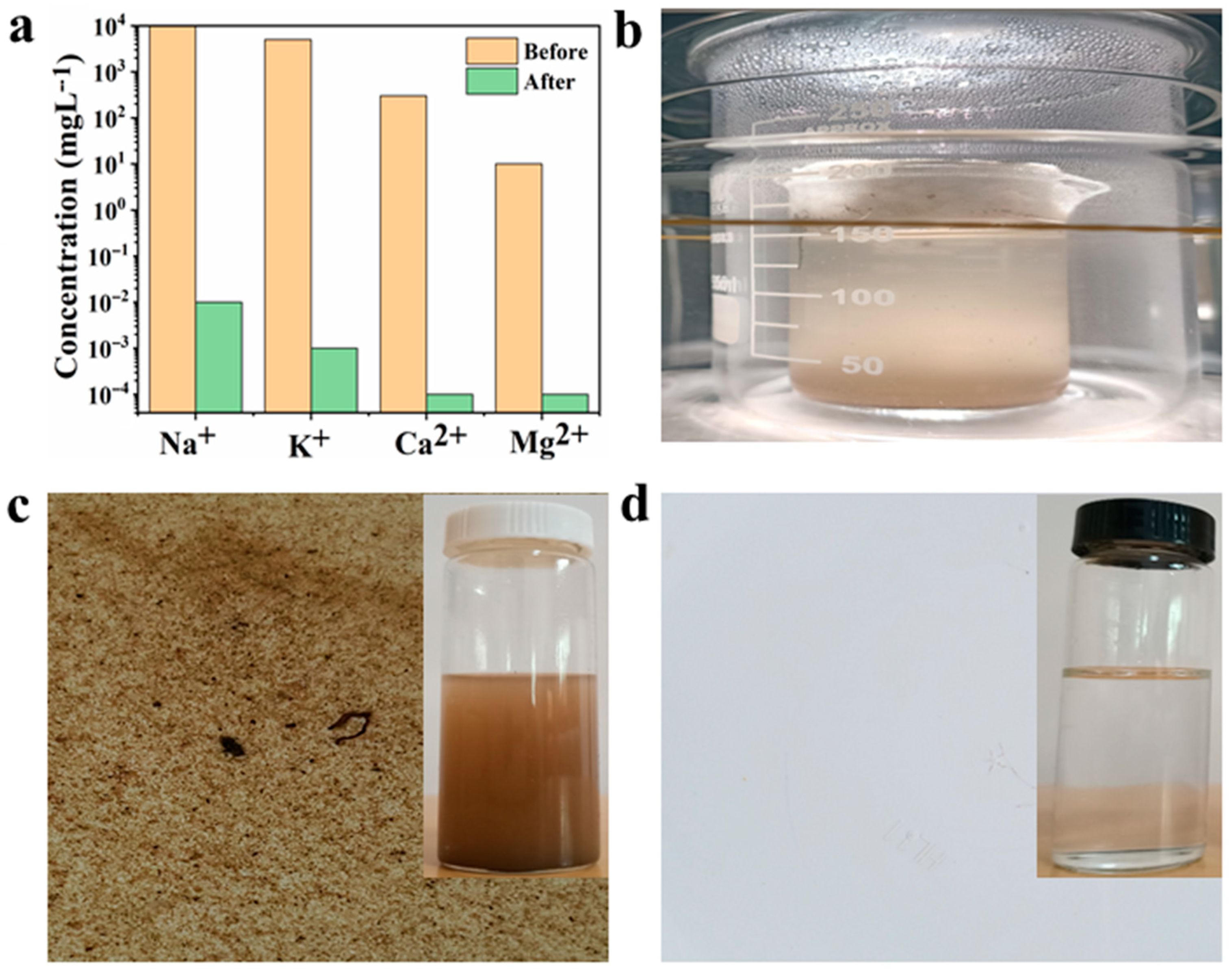
3.4. Evaporation Efficiency and VOCs Rejection
3.5. Desalination and Water Recovery
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ahmadvand, S.; Abbasi, B.; Azarfar, B.; Elhashimi, M.; Zhang, X.; Abbasi, B. Looking beyond energy efficiency: An applied review of water desalination technologies and an introduction to capillary-driven desalination. Water 2019, 11, 696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, P. Emerging investigator series: The rise of nano-enabled photothermal materials for water evaporation and clean water production by sunlight. Environ. Sci. Nano 2018, 5, 1078–1089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kuang, Y.; Chen, C.; He, S.; Hitz, E.M.; Wang, Y.; Gan, W.; Mi, R.; Hu, L. A high-performance self-regenerating solar evaporator for continuous water desalination. Adv. Mater. 2019, 31, 1900498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Irshad, M.S.; Arshad, N.; Wang, X. Nanoenabled Photothermal Materials for Clean Water Production. Glob. Chall. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, G.; Xu, J.; Wang, K. Solar water evaporation by black photothermal sheets. Nano Energy 2017, 41, 269–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, L.; Pei, J.; Jiang, H.; Hu, X. Water desalination under one sun using graphene-based material modified PTFE membrane. Desalination 2018, 442, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P.; Liao, Q.; Zhang, T.; Cheng, H.; Huang, Y.; Yang, C.; Li, C.; Jiang, L.; Qu, L. High throughput of clean water excluding ions, organic media, and bacteria from defect-abundant graphene aerogel under sunlight. Nano Energy 2018, 46, 415–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.-Y.; Xue, J.; Ma, C.; He, T.; Qian, H.; Wang, B.; Liu, J.; Lu, Y. Anti-biofouling double-layered unidirectional scaffold for long-term solar-driven water evaporation. J. Mater. Chem. A 2019, 7, 16696–16703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.; Gong, B.; Yang, H.; Tian, Y.; Xu, C.; Guo, X.; Xiong, G.; Luo, T.; Yan, J.; Cen, K.; et al. Plasma-Made Graphene Nanostructures with Molecularly Dispersed F and Na Sites for Solar Desalination of Oil-Contaminated Seawater with Complete In-Water and In-Air Oil Rejection. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2020, 12, 38512–38521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Xiao, X.; Wang, G.; Ming, X.; Liu, X.; Wang, H.; Yang, H.; Xu, W.; Wang, X. Silk-based systems for highly efficient photothermal conversion under one sun: Portability, flexibility, and durability. J. Mater. Chem. A 2018, 6, 17212–17219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Yi, G.; Fu, Z.; Yu, H.; Chen, S.; Quan, X. Vertically Aligned Janus MXene-Based Aerogels for Solar Desalination with High Efficiency and Salt Resistance. ACS Nano 2019, 13, 13196–13207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chiavazzo, E.; Morciano, M.; Viglino, F.; Fasano, M.; Asinari, P. Passive solar high-yield seawater desalination by modular and low-cost distillation. Nat. Sustain. 2018, 1, 763–772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, X.; He, Y.; Liu, X.; Shi, L.; Zhu, J. Investigation of photothermal heating enabled by plasmonic nanofluids for direct solar steam generation. Sol. Energy 2017, 157, 35–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maleki, H. Recent advances in aerogels for environmental remediation applications: A review. Chem. Eng. J. 2016, 300, 98–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Xiong, T.; Nandakumar, D.K.; Tan, S.C. Structure Architecting for Salt-Rejecting Solar Interfacial Desalination to Achieve High-Performance Evaporation With In Situ Energy Generation. Adv. Sci. 2020, 7, 1903478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parsa, S.M.; Rahbar, A.; Koleini, M.H.; Aberoumand, S.; Afrand, M.; Amidpour, M. A renewable energy-driven thermoelectric-utilized solar still with external condenser loaded by silver/nanofluid for simultaneously water disinfection and desalination. Desalination 2020, 480, 114354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parsa, S.M.; Rahbar, A.; Koleini, M.H.; Davoud Javadi, Y.; Afrand, M.; Rostami, S.; Amidpour, M. First approach on nanofluid-based solar still in high altitude for water desalination and solar water disinfection (SODIS). Desalination 2020, 491, 114592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, L.; Gao, M.; Peh, C.K.N.; Ho, G.W. Recent progress in solar-driven interfacial water evaporation: Advanced designs and applications. Nano Energy 2019, 57, 507–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.; Xiong, G.; Yang, H.; Gong, B.; Tian, Y.; Xu, C.; Wang, Y.; Fisher, T.; Yan, J.; Cen, K.; et al. Solar Energy Conversion: Multifunctional Solar Waterways: Plasma-Enabled Self-Cleaning Nanoarchitectures for Energy-Efficient Desalination (Adv. Energy Mater. 30/2019). Adv. Energy Mater. 2019, 9, 1970119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Parsa, S.M.; Rahbar, A.; Javadi, Y.D.; Koleini, M.H.; Afrand, M.; Amidpour, M. Energy-matrices, exergy, economic, environmental, exergoeconomic, enviroeconomic, and heat transfer (6E/HT) analysis of two passive/active solar still water desalination nearly 4000m: Altitude concept. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 261, 121243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, Y.; Wang, K.; Yao, J.; Wang, H. Hollow carbon beads for significant water evaporation enhancement. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2014, 116, 704–709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dao, V.-D.; Choi, H.-S. Carbon-Based Sunlight Absorbers in Solar-Driven Steam Generation Devices. Glob. Chall. 2018, 2, 1700094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.; He, Y.; Hu, Y.; Wang, X. Commercially Available Activated Carbon Fiber Felt Enables Efficient Solar Steam Generation. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2018, 10, 9362–9368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xia, Y.; Li, Y.; Yuan, S.; Kang, Y.; Jian, M.; Hou, Q.; Gao, L.; Wang, H.; Zhang, X. A self-rotating solar evaporator for continuous and efficient desalination of hypersaline brine. J. Mater. Chem. A 2020, 8, 16212–16217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vega-Beltrán, J.C.; García-Rodríguez, L.; Martín-Mateos, I.; Blanco-Gálvez, J. Solar membrane distillation: Theoretical assessment of multi-stage concept. Desalin. Water Treat. 2010, 18, 133–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, X.; Chen, J.; Yuan, Z.; Yang, M.; Chen, G.; Yu, D.; Zhang, M.; Hong, W.; Chen, X. Integrative solar absorbers for highly efficient solar steam generation. J. Mater. Chem. A 2018, 6, 4642–4648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parsa, S.M.; Javadi Y, D.; Rahbar, A.; Majidniya, M.; Salimi, M.; Amidpour, Y.; Amidpour, M. Experimental investigation at a summit above 13,000 ft on active solar still water purification powered by photovoltaic: A comparative study. Desalination 2020, 476, 114146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Ravi, S.K.; Tan, S.C. Food-derived carbonaceous materials for solar desalination and thermo-electric power generation. Nano Energy 2019, 65, 104006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Wang, C.; Su, J.; Ling, S.; Wang, W.; An, M. Fast-Growing Field of Interfacial Solar Steam Generation: Evolutional Materials, Engineered Architectures, and Synergistic Applications. Sol. RRL 2019, 3, 1800206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, S.; Zhao, X.; Tang, C.-Y.; Yu, P.; Bao, R.-Y.; Liu, Z.-Y.; Yang, M.-B.; Yang, W. A bridge-arched and layer-structured hollow melamine foam/reduced graphene oxide composite with an enlarged evaporation area and superior thermal insulation for high-performance solar steam generation. J. Mater. Chem. A 2020, 8, 2701–2711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalagatur, N.K.; Karthick, K.; Allen, J.A.; Nirmal Ghosh, O.S.; Chandranayaka, S.; Gupta, V.K.; Krishna, K.; Mudili, V. Application of Activated Carbon Derived from Seed Shells of Jatropha curcas for Decontamination of Zearalenone Mycotoxin. Front. Pharmacol. 2017, 8, 760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- World Health Organization. European Standards for Drinking-Water; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 1970. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, X.; Mishra, D.D.; Wang, X.; Peng, H.; Hu, C. Towards highly efficient solar-driven interfacial evaporation for desalination. J. Mater. Chem. A 2020, 8, 17907–17937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edition, F. Guidelines for drinking-water quality. WHO Chron. 2011, 38, 104–108. [Google Scholar]
- Schwarzenbach, R.P.; Escher, B.I.; Fenner, K.; Hofstetter, T.B.; Johnson, C.A.; Von Gunten, U.; Wehrli, B. The challenge of micropollutants in aquatic systems. Science 2006, 313, 1072–1077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Irshad, M.S.; Aziz, M.H.; Fatima, M.; Rehman, S.U.; Idrees, M.; Rana, S.; Shaheen, F.; Ahmed, A.; Javed, M.Q.; Huang, Q. Green synthesis, cytotoxicity, antioxidant and photocatalytic activity of CeO2 nanoparticles mediated via orange peel extract (OPE). Mater. Res. Express 2019, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Irshad, M.S.; Arshad, N.; Ahmed, I.; Abbasi, M.S.; Idrees, M.; Ahmad, S.; Sharaf, M.; Asghar, M.S.; Zaindin, M. Low-cost green recyclable biomaterial for energy-dependent electrical switching and intact biofilm with antibacterial properties. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 14600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Ravi, S.K.; Yang, L.; Vaghasiya, J.V.; Suresh, L.; Tan, I.; Tan, S.C. Portable Trilayer Photothermal Structure for Hybrid Energy Harvesting and Synergic Water Purification. ACS Appl. Mater Interfaces 2019, 11, 38674–38682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Xiong, T.; Qu, H.J.; Koh, J.; Nandakumar, D.K.; Wang, J.; Tan, S.C. Manipulating unidirectional fluid transportation to drive sustainable solar water extraction and brine drenching induced generation. Energy Environ. Sci. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Arshad, N.; Ahmed, I.; Irshad, M.S.; Li, H.R.; Wang, X.; Ahmad, S.; Sharaf, M.; Firdausi, M.; Zaindin, M.; Atif, M. Super Hydrophilic Activated Carbon Decorated Nanopolymer Foam for Scalable, Energy Efficient Photothermal Steam Generation, as an Effective Desalination System. Nanomaterials 2020, 10, 2510. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano10122510
Arshad N, Ahmed I, Irshad MS, Li HR, Wang X, Ahmad S, Sharaf M, Firdausi M, Zaindin M, Atif M. Super Hydrophilic Activated Carbon Decorated Nanopolymer Foam for Scalable, Energy Efficient Photothermal Steam Generation, as an Effective Desalination System. Nanomaterials. 2020; 10(12):2510. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano10122510
Chicago/Turabian StyleArshad, Naila, Iftikhar Ahmed, Muhammad Sultan Irshad, Hong Rong Li, Xianbao Wang, Shafiq Ahmad, Mohamed Sharaf, Muhammad Firdausi, Mazen Zaindin, and Muhammad Atif. 2020. "Super Hydrophilic Activated Carbon Decorated Nanopolymer Foam for Scalable, Energy Efficient Photothermal Steam Generation, as an Effective Desalination System" Nanomaterials 10, no. 12: 2510. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano10122510
APA StyleArshad, N., Ahmed, I., Irshad, M. S., Li, H. R., Wang, X., Ahmad, S., Sharaf, M., Firdausi, M., Zaindin, M., & Atif, M. (2020). Super Hydrophilic Activated Carbon Decorated Nanopolymer Foam for Scalable, Energy Efficient Photothermal Steam Generation, as an Effective Desalination System. Nanomaterials, 10(12), 2510. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano10122510






