Three-Dimensional Technology Applications in Maxillofacial Reconstructive Surgery: Current Surgical Implications
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Three-Dimensional (3D) Printing Techniques
2.1. Stereolithography
2.2. Laser Sintering
2.3. Extrusion Printing
3. Three-Dimensional Printing Materials
4. Clinical Examples of Additive Manufacturing (AM) Use in Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery
5. AM Process in Virtual Surgical Treatment Planning, Surgical Stimulation and Education
5.1. AM for Manufacturing of Surgical Guides for Zygomatic Implants Insertion
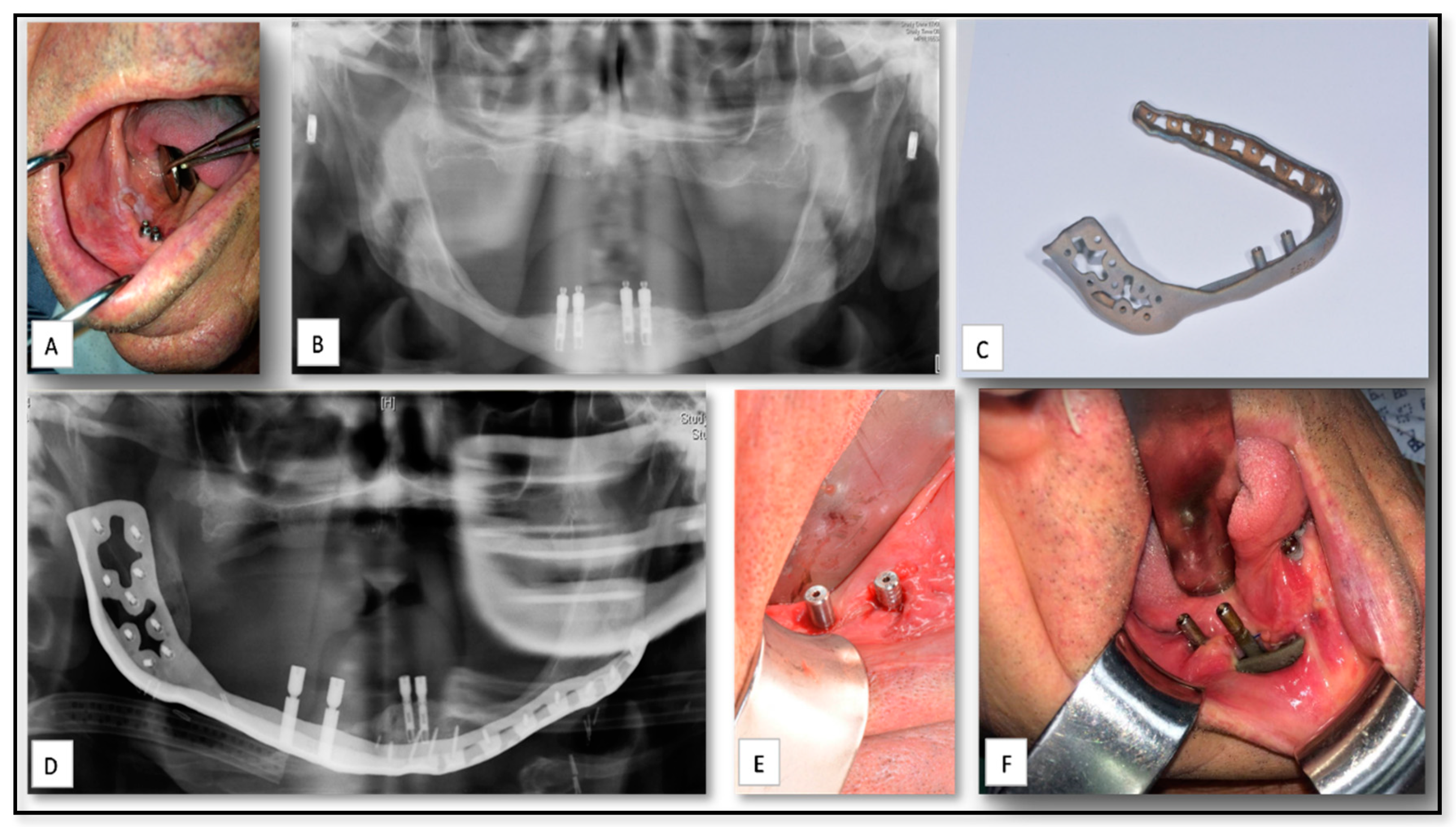
5.2. AM for of Pre-Prosthetics Patient-Specific Implant (PSI) Manufacturing
5.3. AM for PSI Manufacturing for Delayed Correction of Post-Traumatic Defects
5.4. AM for Temporomandibular Joint (TMJ) Reconstruction Surgery Due to Oncologic Rresection
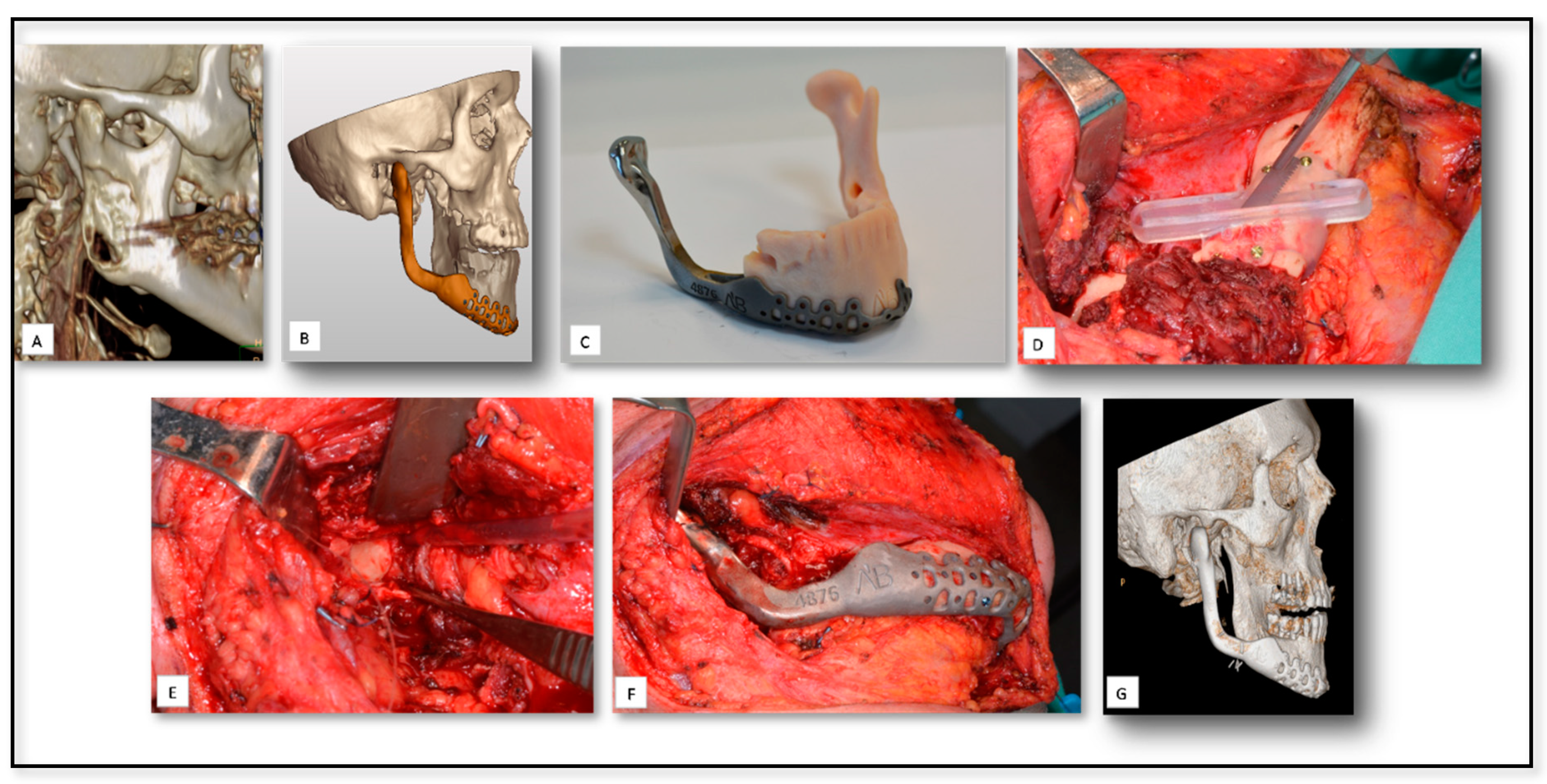
5.5. AM for Producing PSI for Reconstruction of Large Mandibular Defect after Tumor Resection
6. Current Challenges and Future Directions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Figueroa, A.A.; Gans, B.J.; Pruzansky, S. Long-term follow-up of a mandibular costochondral graft. Oral Surg. Oral Med. Oral Pathol. 1984, 58, 257–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Padwa, B.L.; Mulliken, J.B.; Maghen, A.; Kaban, L.B. Midfacial growth after costochondral graft construction of the mandibular ramus in hemifacial microsomia. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 1998, 56, 122–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naaj IAEl Leiser, Y.; Liberman, R.; Peled, M. The Use of the Temporalis Myofascial Flap in Oral Cancer Patients. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2010, 68, 578–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.-C.; Lin, P.-Y.; Chew, K.-Y.; Kuo, Y.-R. Free tissue transfers in head and neck reconstruction: Complications, outcomes and strategies for management of flap failure: Analysis of 2019 flaps in single institute. Microsurgery 2009, 504–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marx, R.E.; Morales, M. Morbidity from bone harvest in major jaw reconstruction: A randomized trial comparing the lateral anterior and posterior approaches to the ilium. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 1988, 46, 196–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spoerl, S.; Schoedel, S.; Spanier, G.; Mueller, K.; Meier, J.K.; Reichert, T.E.; Ettl, T. A decade of reconstructive surgery: Outcome and perspectives of free tissue transfer in the head and neck. Experience of a single center institution. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2020, 24, 173–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Colaco, M.; Igel, D.A.; Atala, A. The potential of 3D printing in urological research and patient care. Nat. Rev. Urol 2018, 15, 213–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murphy, S.V.; Atala, A. 3D bioprinting of tissues and organs. Nat. Biotechnol. 2014, 32, 773–785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kodama, H. Automatic method for fabricating a three- dimensional plastic model with photo- hardening polymer. Rev. Sci. Instrum. 1998, 52, 2–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, W.; Ma, X.; Gou, M.; Mei, D.; Zhang, K.; Chen, S. 3D printing of functional biomaterials for tissue engineering. Curr. Opin Biotechnol. 2016, 40, 103–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Singh, S.; Ramakrishna, S.; Singh, R. Material issues in additive manufacturing: A review. J. Manuf. Process. 2017, 25, 185–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rengier, F.; Mehndiratta, A.; Von Tengg-Kobligk, H.; Zechmann, C.M.; Unterhinninghofen, R.; Kauczor, H.U.; Giesel, F.L. 3D printing based on imaging data: Review of medical applications. Int. J. Comput. Assist. Radiol. Surg. 2010, 5, 335–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gibson, I.; Rosen, D.; Stucker, B. Additive Manufacturing Technologies: 3D Printing, Rapid Prototyping, and Direct Digital Manufacturing, 2nd ed.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2015; pp. 375–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hegab, H.A. Design for additive manufacturing of composite materials and potential alloys: A review. Manuf. Rev. 2016, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bourell, D.L. Perspectives on Additive Manufacturing. Ann. Rev. Mater. Res. 2016, 46, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giannatsis, J.; Dedoussis, V. Additive fabrication technologies applied to medicine and health care: A review. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2009, 40, 116–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goffard, R.; Sforza, T.; Clarinval, A.; Dormal, T.; Boilet, L.; Hocquet, S.; Cambier, F. Additive manufacturing of biocompatible ceramics. Adv. Prod. Eng. Manag. 2013, 8, 96–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Murr, L.E.; Gaytan, S.M.; Medina, F.; Lopez, H.; Martinez, E.; MacHado, B.I.; Hernandez, D.H.; Lopez, M.I.; Wicker, R.B.; Bracke, J. Next-generation biomedical implants using additive manufacturing of complex cellular and functional mesh arrays. Philos Trans. R Soc. A Math. Phys. Eng. Sci 2010, 368, 1999–2032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Frame, M.; Huntley, J.S. Rapid prototyping in orthopaedic surgery: A user’s guide. Sci. World J. 2012, 2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cunningham, L.L.; Madsen, M.J.; Peterson, G. Stereolithographic modeling technology applied to tumor resection. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2005, 63, 873–878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frühwald, J.; Schicho, K.A.; Figl, M.; Benesch, T.; Watzinger, F.; Kainberger, F. Accuracy of craniofacial measurements: Computed tomography and three-dimensional computed tomography compared with stereolithographic models. J. Craniofac. Surg. 2008, 19, 22–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Barker, T.M.; Earwaker, W.J.S.; Lisle, D.A. Accuracy of stereolithographic models of human anatomy. Australas. Radiol. 1994, 38, 106–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schicho, K.; Figl, M.; Seemann, R.; Ewers, R.; Lambrecht, J.T.; Wagner, A.; Watzinger, F.; Baumann, A.; Kainberger, F.; Fruehwald, J.; et al. Accuracy of treatment planning based on stereolithography in computer assisted surgery. Med. Phys. 2006, 33, 3408–3417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mazzoli, A.; Germani, M.; Moriconi, G. Application of Optical Digitizing Techniques to Evaluate the Shape Accuracy of Anatomical Models Derived From Computed Tomography Data. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2007, 65, 1410–1418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wong, T.Y.; Fang, J.J.; Chung, C.H.; Huang, J.S.; Lee, J.W. Comparison of 2 methods of making surgical models for correction of facial asymmetry. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2005, 63, 200–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chow, L.K.; Cheung, L.K. The Usefulness of Stereomodels in Maxillofacial Surgical Management. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2007, 65, 2260–2268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mehra, P.; Miner, J.; D’Innocenzo, R.; Nadershah, M. Use of 3-D Stereolithographic Models in Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery. J. Maxillofac. Oral Surg. 2011, 10, 6–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gu, D.D.; Meiners, W.; Wissenbach, K.; Poprawe, R. Laser additive manufacturing of metallic components: Materials, processes and mechanisms. Int. Mater. Rev. 2012, 57, 133–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fischer, P.; Romano, V.; Blatter, A.; Weber, H.P. Highly precise pulsed selective laser sintering of metallic powders. Laser Phys. Lett 2005, 2, 48–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schleifenbaum, H.; Meiners, W.; Wissenbach, K.; Hinke, C. Individualized production by means of high power Selective Laser Melting. CIRP J. Manuf. Sci. Technol. 2010, 2, 161–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciocca, L.; Fantini, M.; De Crescenzio, F.; Corinaldesi, G.; Scotti, R. Direct metal laser sintering (DMLS) of a customized titanium mesh for prosthetically guided bone regeneration of atrophic maxillary arches. Med. Biol. Eng. Comput. 2011, 49, 1347–1352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mangano, F.G.; De Franco, M.; Caprioglio, A.; MacChi, A.; Piattelli, A.; Mangano, C. Immediate, non-submerged, root-analogue direct laser metal sintering (DLMS) implants: A 1-year prospective study on 15 patients. Lasers Med. Sci. 2014, 29, 1321–1328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mangano, F.G.; Cirotti, B.; Sammons, R.L.; Mangano, C. Custom-made, root-analogue direct laser metal forming implant: A case report. Lasers Med. Sci. 2012, 27, 1241–1245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sannomiya, E.K.; Silva, J.V.L.; Brito, A.A.; Saez, D.M.; Angelieri, F.; da Silva Dalben, G. Surgical planning for resection of an ameloblastoma and reconstruction of the mandible using a selective laser sintering 3D biomodel. Oral Surg. Oral Med. Oral Pathol Oral Radiol. Endodontol. 2008, 106, 36–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leiggener, C.; Messo, E.; Thor, A.; Zeilhofer, H.F.; Hirsch, J.M. A selective laser sintering guide for transferring a virtual plan to real time surgery in composite mandibular reconstruction with free fibula osseous flaps. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2009, 38, 187–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodr, E.; Kypson, A.P.; Moten, S.C.; Nifong, L.W.; Chitwood, W.R., Jr. Robotic mitral surgery at East Carolina University: A 6-year experience. Int. J. Med. Robot. Comput. Assist. Surg. 2006, 2, 211–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, J.V.; Revington, P.J. Novel use of an aerospace selective laser sintering machine for rapid prototyping of an orbital blowout fracture. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2010, 39, 182–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rotaru, H.; Bǎciut, M.; Stan, H.; Bran, S.; Chezan, H.; Iosif, A.; Tomescu, M.; Kim, S.G.; Rotaru, A. Silicone rubber mould cast polyethylmethacrylate-hydroxyapatite plate used for repairing a large skull defect. J. Cranio-Maxillofac. Surg. 2006, 34, 242–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aung, S.C.; Tan, B.K.; Foo, C.L.; Lee, S.T. Selective laser sintering: Application of a rapid prototyping method in craniomaxillofacial reconstructive surgery. Ann. Acad. Med. 1999, 28, 739–743. [Google Scholar]
- Turner, B.N.; Gold, S.A. A review of melt extrusion additive manufacturing processes: II. Materials, dimensional accuracy, and surface roughness. Rapid Prototyp. J. 2015, 21, 250–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turner, B.N.; Strong, R.; Gold, S.A. A review of melt extrusion additive manufacturing processes: I. Process design and modeling. Rapid Prototyp. J. 2014, 20, 192–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valkenaers, H.; Vogeler, F.; Ferraris, E.; Voet, A.; Kruth, J.-P. A novel approach to additive manufacturing: Screw extrusion 3D-printing. In Proceedings of the 10th International Conference on Multi-Material Micro Manufacture, San Sebastian, Spain, 1 October 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Crump, S. Apparatus and Method for Creating Three-Dimensional Objects. US Patent 07/429,012, 30 October 1989. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, R.; Tang, T. Current strategies to improve the bioactivity of PEEK. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2014, 15, 5426–5445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Honigmann, P.; Sharma, N.; Okolo, B.; Popp, U.; Msallem, B.; Thieringer, F.M. Patient-specific surgical implants made of 3D printed PEEK: Material, technology, and scope of surgical application. Biomed. Res. Int. 2018, 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Available online: http://3dprintingindustry.com/3d-printing-basics-free-beginners-guide/materials/ (accessed on 15 December 2020).
- Available online: https://www.stratasysdirect.com/resources/choosing-the-right-material-for-your-application/ (accessed on 15 December 2020).
- Chow, J. A novel device for template-guided surgery of the zygomatic implants. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2016, 45, 1253–1255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, C.I.; Cho, S.H.; Cho, D.; Ducote, C.; Reddy, L.V.; Sinada, N. A 3D-Printed Guide to Assist in Sinus Slot Preparation for the Optimization of Zygomatic Implant Axis Trajectory. J. Prosthodont. 2020, 29, 179–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Becker, C.M.; Kaiser, D.A. Surgical guide for dental implant placement. J. Prosthet Dent. 2000, 83, 248–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goiato, M.C.; Pellizzer, E.P.; Moreno, A.; Gennari-Filho, H.; Dos Santos, D.M.; Santiago, J.F.; Santos, E.G. Implants in the zygomatic bone for maxillary prosthetic rehabilitation: A systematic review. Int J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2014, 43, 748–757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rocchietta, I.; Fontana, F.; Simion, M. Clinical outcomes of vertical bone augmentation to enable dental implant placement: A systematic review. J. Clin. Periodontol. 2008, 35, 203–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esposito, M.; Grusovin, M.G.; Coulthard, P.; Worthington, H.V. The efficacy of various bone augmentation procedures for dental implants: A Cochrane systematic review of randomized controlled clinical trials. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Implant. 2006, 21, 696–710. [Google Scholar]
- Jensen, O.T.; Greer, R.O., Jr.; Johnson, L.K.D. Vertical guided bone-graft augmentation in a new canine mandibular model. Int J. Oral Maxillofac. Implant. 1995, 10, 335–344. [Google Scholar]
- Jung, R.E.; Fenner, N.; Hämmerle, C.H.F.; Zitzmann, N.U. Long-term outcome of implants placed with guided bone regeneration (GBR) using resorbable and non-resorbable membranes after 12–14 years. Clin. Oral Implant. Res. 2013, 24, 1065–1073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- McCarthy, J.G.; Schreiber, J.; Karp, N.; Thorne, C.H.; Grayson, B. Lengthening the human mandible by gradual distraction. Plast Reconstr. Surg. 1992, 89, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rachmiel, A.; Srouji, S.; Peled, M. Alveolar ridge augmentation by distraction osteogenesis. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2001, 30, 510–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cerea, M.; Dolcini, G.A. Custom-made direct metal laser sintering titanium subperiosteal implants: A retrospective clinical study on 70 patients. Biomed. Res. Int. 2018, 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Shin, J.W.; Lim, J.S.; Yoo, G.; Byeon, J.H. An analysis of pure blowout fractures and associated ocular symptoms. J. Craniofac. Surg. 2013, 24, 703–707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schwartz, M.L.; Baredes, S.; Mignogna, F.V. Metastatic Disease To the Mandible. Laryngoscope 1988, 98, 270–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghantous, Y.; Nashef, A.; Abu-Elnaaj, I. Epigenetic Alterations Associated with the Overall Survival and Recurrence Free Survival among Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma Patients. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 1035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Joo, Y.H.; Cho, J.K.; Koo, B.S.; Kwon, M.; Kwon, S.K.; Kwon, S.Y.; Kim, M.-S.; Kim, J.K.; Kim, H.; Nam, I.; et al. Guidelines for the surgical management of oral cancer: Korean society of thyroid-head and neck surgery. Clin. Exp. Otorhinolaryngol. 2019, 12, 107–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pfister, D.G.; Spencer, S.; Brizel, D.M.; Burtness, B.; Busse, P.M.; Caudell, J.J.; Cmelak, A.J.; Colevas, A.D.; Dunphy, F.; Eisele, D.W.; et al. Head and neck cancers, version 2.2014. JNCCN J. Natl. Compr. Cancer Netw. 2014, 12, 1454–1487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Di Taranto, G.; Chen, S.H.; Elia, R.; Sitpahul, N.; Chan, J.C.Y.; Losco, L.; Cigna, E.; Ribuffo, D.; Chen, H. Outcomes following head neck free flap reconstruction requiring interposition vein graft or vascular bridge flap. Head Neck 2019, 41, 2914–2920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jain, P.V.; Sharan, R.; Manikantan, K.; Clark, G.M.; Chatterjee, S.; Mallick, I.; Roy, P.; Arun, P. Redefining adequate margins in oral squamous cell carcinoma: Outcomes from close and positive margins. Eur. Arch Oto-Rhino-Laryngol. 2020, 277, 1155–1165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chi, A.C.; Day, T.A.; Neville, B.W. Oral cavity and oropharyngeal squamous cell carcinoma-an update. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2015, 65, 401–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diment, L.E.; Thompson, M.S.; Bergmann, J.H.M. Clinical efficacy and effectiveness of 3D printing: A systematic review. BMJ Open 2017, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tack, P.; Victor, J.; Gemmel, P.; Annemans, L. 3D-printing techniques in a medical setting: A systematic literature review. Biomed. Eng. Online 2016, 15, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kruth, J.P. Material Incress Manufacturing by Rapid Prototyping Techniques. CIRP Ann. Manuf. Technol. 1991, 40, 603–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heller, T.B.; Hill, R.M.; Saggal, A.F. Apparatus for Forming a Solid Three-Dimensional Article from a Liquid Medium. U.S. Patent 5,071,337, 10 December 1991. [Google Scholar]
- Maroulakos, M.; Kamperos, G.; Tayebi, L.; Halazonetis, D.; Ren, Y. Applications of 3D printing on craniofacial bone repair: A systematic review. J. Dent. 2019, 80, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roth, E.A.; Xu, T.; Das, M.; Gregory, C.; Hickman, J.J.; Boland, T. Inkjet printing for high-throughput cell patterning. Biomaterials 2004, 25, 3707–3715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ringeisen, B.R.; Othon, C.M.; Barron, J.A.; Young, D.; Spargo, B.J. Jet-based methods to print living cells. Biotechnol. J. 2006, 1, 930–948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, P.K.; Ringeisen, B.R. Development of human umbilical vein endothelial cell (HUVEC) and human umbilical vein smooth muscle cell (HUVSMC) branch/stem structures on hydrogel layers via biological laser printing (BioLP). Biofabrication 2010, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, X.; Breitenkamp, K.; Finn, M.G.; Lotz, M.; D’Lima, D.D. Direct human cartilage repair using three-dimensional bioprinting technology. Tissue Eng. Part. A 2012, 18, 1304–1312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Choi, J.Y.; Choi, J.H.; Kim, N.K.; Kim, Y.; Lee, J.K.; Kim, M.K. Analysis of errors in medical rapid prototyping models. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2002, 31, 23–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Y.; Loh, H.T.; Fuh, J.Y.H.; Wong, Y.S.; Lu, L.; Ning, Y.; Wang, X. Accuracy analysis and improvement for direct laser sintering. Innov. Manuf. Syst. Technol. 2004, 119260. [Google Scholar]
- Nizama, A.; Gopal, R.; Naing, N.L.; Hakim, A.B.; Samsudin, A.R. Dimensional accuracy of the skull models produced by rapid prototyping technology using stereolithography apparatus. Arch. Orofac. Sci. 2006, 1, 60–66. [Google Scholar]
- Eschbach, L. Nonresorbable polymers in bone surgery. Injury 2000, 31, 22–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jardini, A.L.; Larosa, M.A.; Maciel Filho, R.; de Carvalho Zavaglia, C.A.; Bernardes, L.F.; Lambert, C.S.; Calderoni, D.R.; Kharmandayan, P. Cranial reconstruction: 3D biomodel and custom-built implant created using additive manufacturing. J. Cranio-Maxillofac. Surg. 2014, 42, 1877–1884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, M.M.; Boahene, K.D.O.; Byrne, P.J. Use of customized polyetheretherketone (PEEK) implants in the reconstruction of complex maxillofacial defects. Arch Facial Plast Surg. 2009, 11, 53–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thieringer, F.M.; Sharma, N.; Mootien, A.; Schumacher, R.; Honigmann, P. Patient Specific Implants from a 3D Printer—An Innovative Manufacturing Process for Custom PEEK Implants in Cranio-Maxillofacial Surgery; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Cohen, D.J.; Cheng, A.; Kahn, A.; Aviram, M.; Whitehead, A.J.; Hyzy, S.L.; Clohessy, R.M.; Boyan, B.; Schwartz, Z. Novel osteogenic Ti-6Al-4V device for restoration of dental function in patients with large bone deficiencies: Design, development and implementation. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Thompson, M.K.; Moroni, G.; Vaneker, T.; Fadel, G.; Campbell, R.I.; Gibson, I.; Bernard, A.; Schulz, J.; Graf, P.; Ahuja, B.; et al. Design for Additive Manufacturing: Trends, opportunities, considerations, and constraints. CIRP Ann. 2016, 65, 737–760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
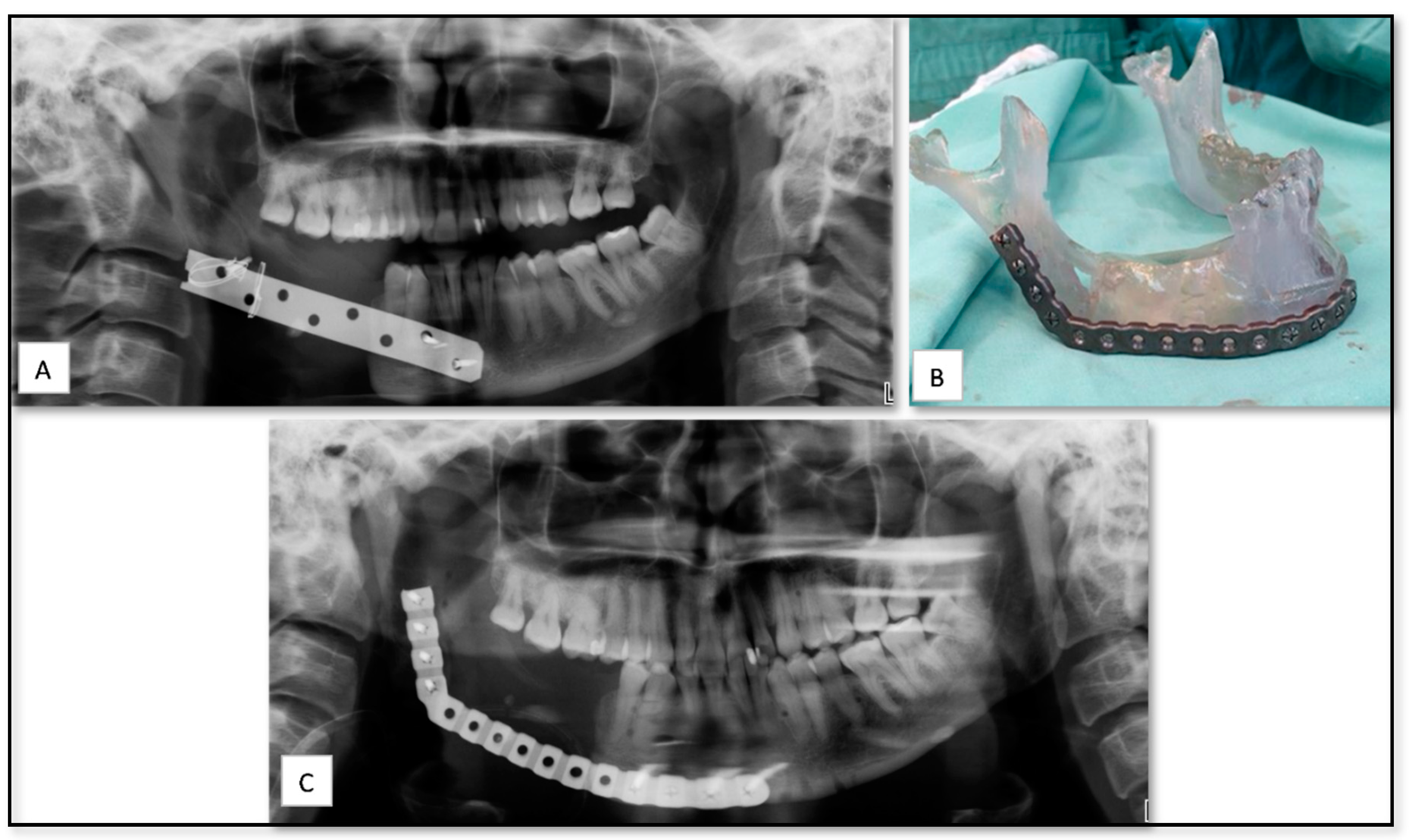
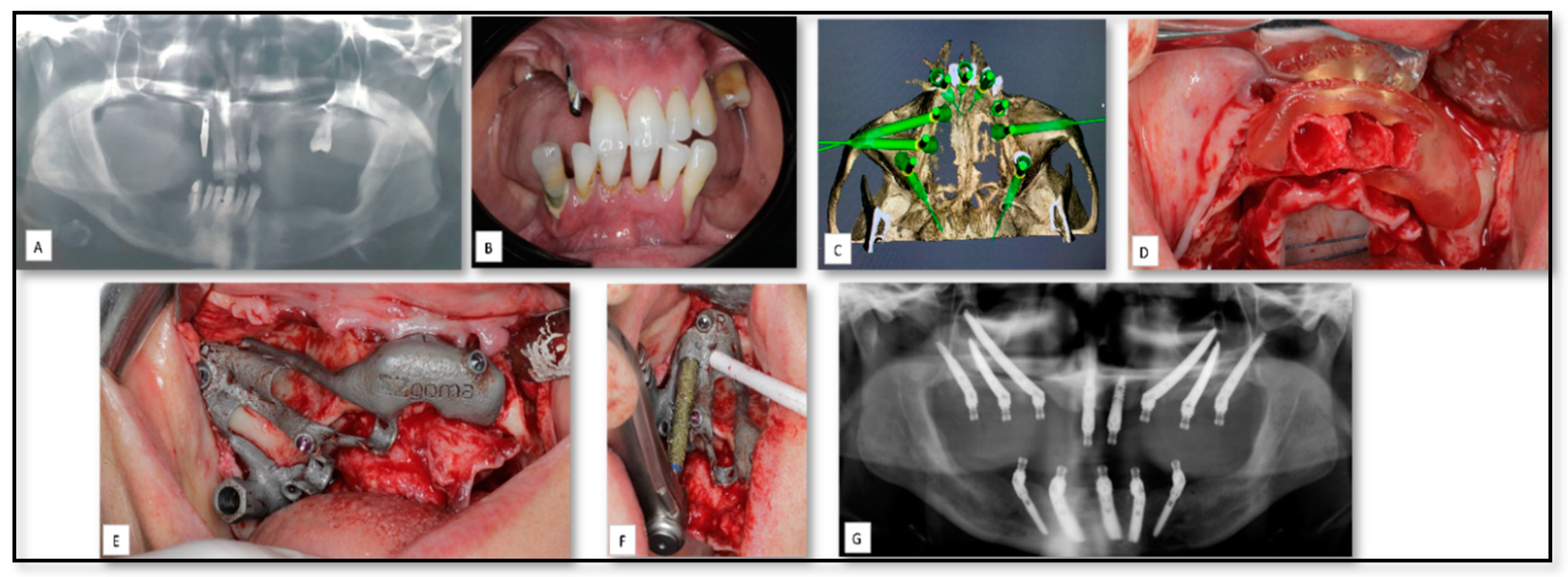
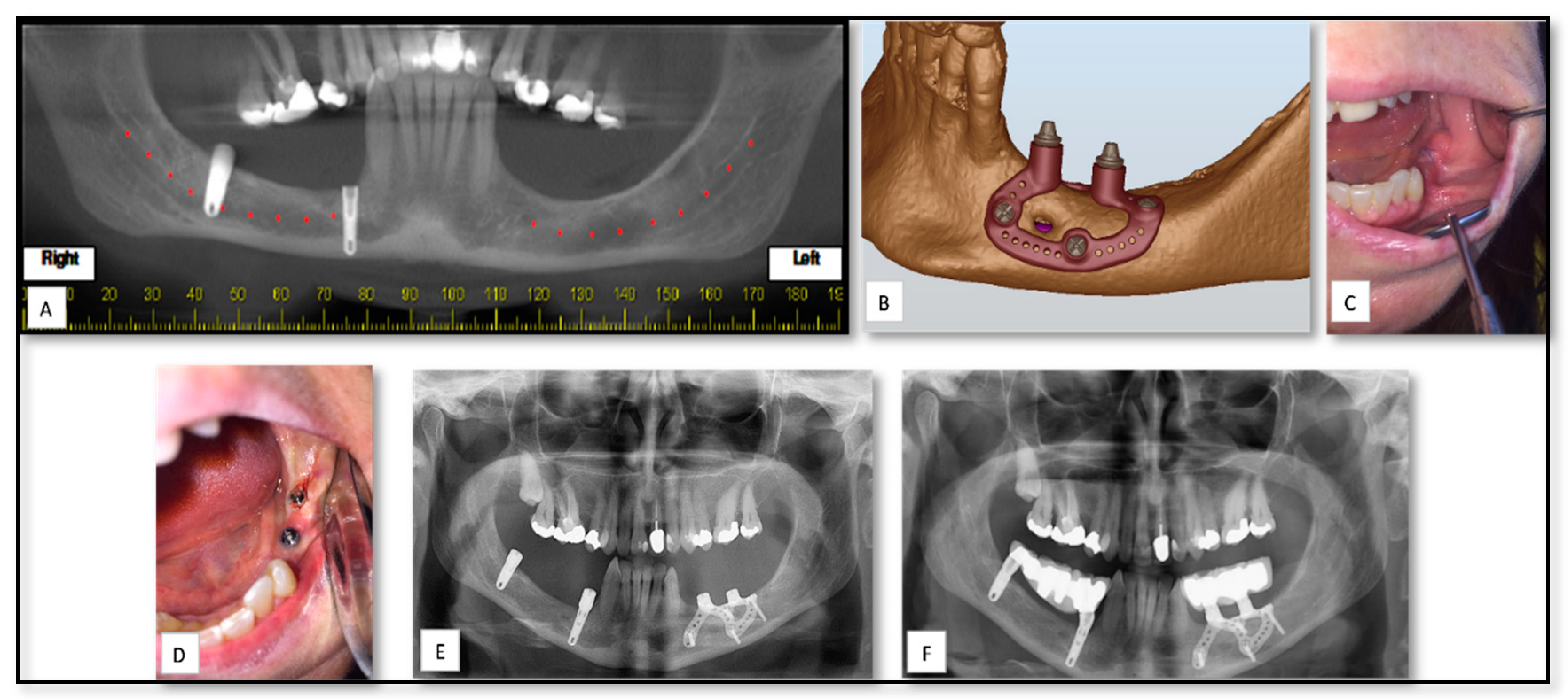
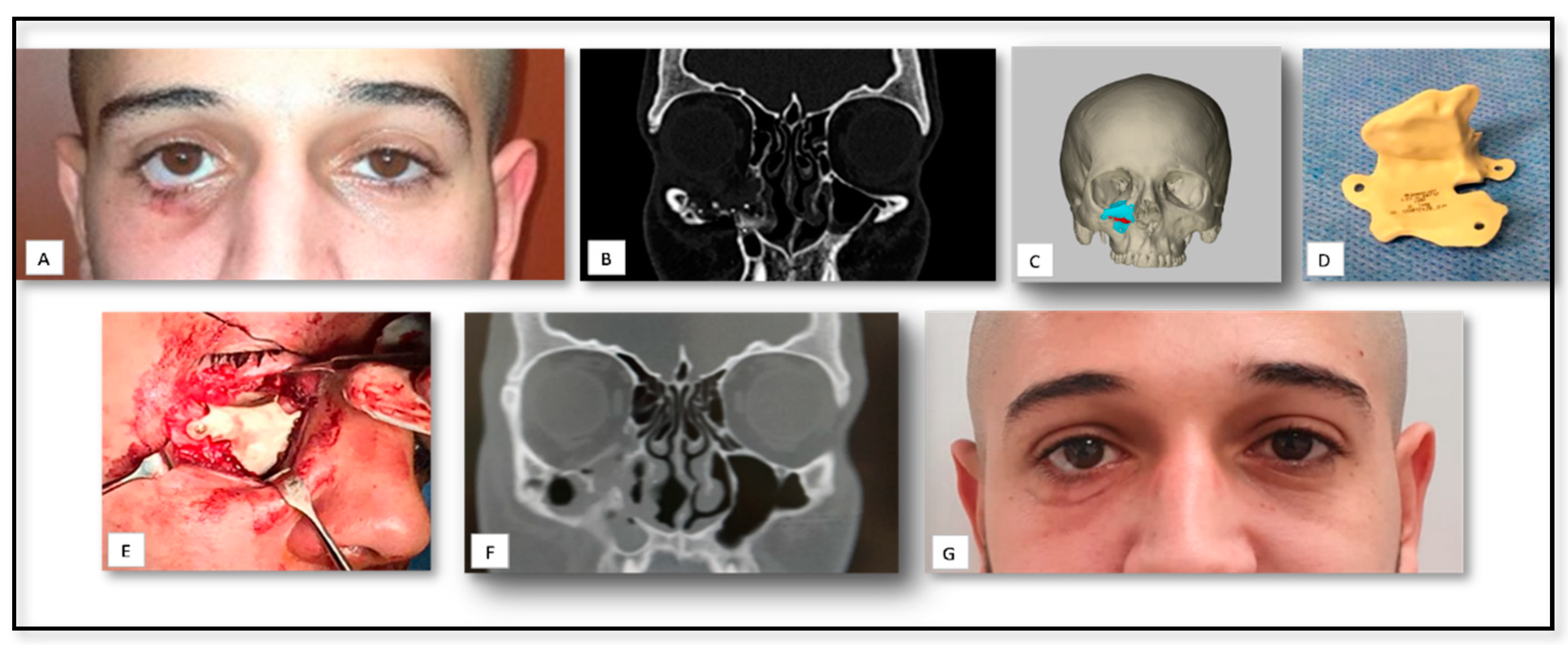
| Case Nu. | Age | Sex | Surgical Disciplines | Site | Printed Object | Material | IO. Complication | PO. Complication |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 33 | F | Trauma | Mandible | SLA model for pre-bending of reconstruction plate | Resin | − | Mild edema |
| 2 | 80 | M | Oncology | Mandible | PSI for of mandibular body reconstruction including dental implants | Titanium | − | Severe edema, exposure of implant and infection |
| 3 | 40 | M | Trauma | Orbit | PSI for floor of orbit reconstruction | Titanium | − | Mild edema |
| 4 | 64 | M | Oncology | Mandible | PSI of mandibular body with ramus and condyle | Titanium | − | Moderate edema |
| 5 | 21 | M | Trauma | Nose | PSI for nasal bone reconstruction | PEEK | − | Edema and improper contour |
| 6 | 50 | M | TMJ Ankylosis | TMJ | PSI for ramus and condyle reconstruction | Titanium | − | Mild edema |
| 7 | 49 | M | Trauma | Orbit | PSI for floor of orbit reconstruction | Titanium | − | Mild peri-orbital edema |
| 8 | 20 | F | Trauma | Orbital cavity, frontal bone and temporal bone | PSI for temporal and frontal bone reconstruction | PEEK | Loss of accurate fitting | Moderate peri-orbital edema |
| 9 | 19 | M | Trauma | Orbit | PSI for floor of orbit reconstruction | PEEK | − | Mild edema |
| 10 | 44 | F | Trauma | Orbit | PSI for floor of orbit reconstruction | Titanium | Loss of accurate fitting | Mild edema |
| 11 | 22 | F | Facial deformity | Mandible | Surgical cutting guide of mandibular lower border | Resin | Loss of accurate fitting | |
| 12 | 44 | F | Pre-prosthetics | Mandible | PSI of sub-periostal dental implant | Titanium | − | Mild edema |
| 13 | 50 | F | Pre-prosthetics | Maxilla | Surgical guide stent | Titanium | − | |
| 14 | 71 | M | Pre-prosthetics | Maxilla | Surgical guide stent | Titanium | − | |
| 15 | 66 | F | Pre-prosthetics | Maxilla | Surgical guide stent | Titanium | − | |
| 16 | 56 | F | Pre-prosthetics | Maxilla | Surgical guide stent | Titanium | − |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ghantous, Y.; Nashef, A.; Mohanna, A.; Abu-El-naaj, I. Three-Dimensional Technology Applications in Maxillofacial Reconstructive Surgery: Current Surgical Implications. Nanomaterials 2020, 10, 2523. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano10122523
Ghantous Y, Nashef A, Mohanna A, Abu-El-naaj I. Three-Dimensional Technology Applications in Maxillofacial Reconstructive Surgery: Current Surgical Implications. Nanomaterials. 2020; 10(12):2523. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano10122523
Chicago/Turabian StyleGhantous, Yasmin, Aysar Nashef, Aladdin Mohanna, and Imad Abu-El-naaj. 2020. "Three-Dimensional Technology Applications in Maxillofacial Reconstructive Surgery: Current Surgical Implications" Nanomaterials 10, no. 12: 2523. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano10122523
APA StyleGhantous, Y., Nashef, A., Mohanna, A., & Abu-El-naaj, I. (2020). Three-Dimensional Technology Applications in Maxillofacial Reconstructive Surgery: Current Surgical Implications. Nanomaterials, 10(12), 2523. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano10122523







