Composite Nanogels Based on Zeolite-Poly(ethylene glycol) Diacrylate for Controlled Drug Delivery
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experimental
2.1. Materials
2.2. Preparation of 5-FU-Loaded Nano-Zeolite (NZ) Particles
2.3. Synthesis and Purification of Composite NGs by Inverse Mini-Emulsion Polymerization
2.4. Swelling Degree Determination
2.5. Release Study of 5-FU from Composite NGs
2.6. Cytotoxicity Study
2.7. Characterization Techniques
3. Results and Discussion
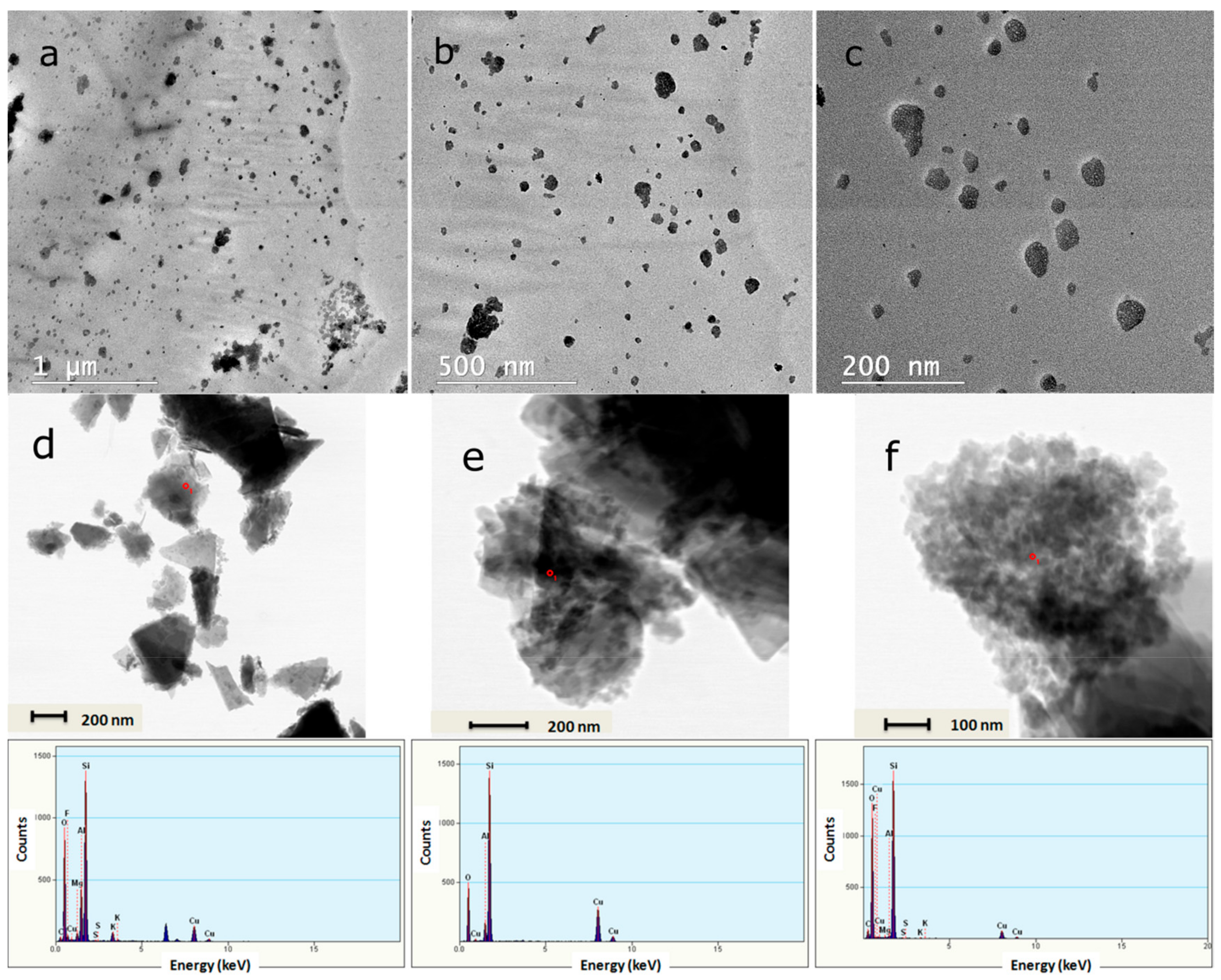
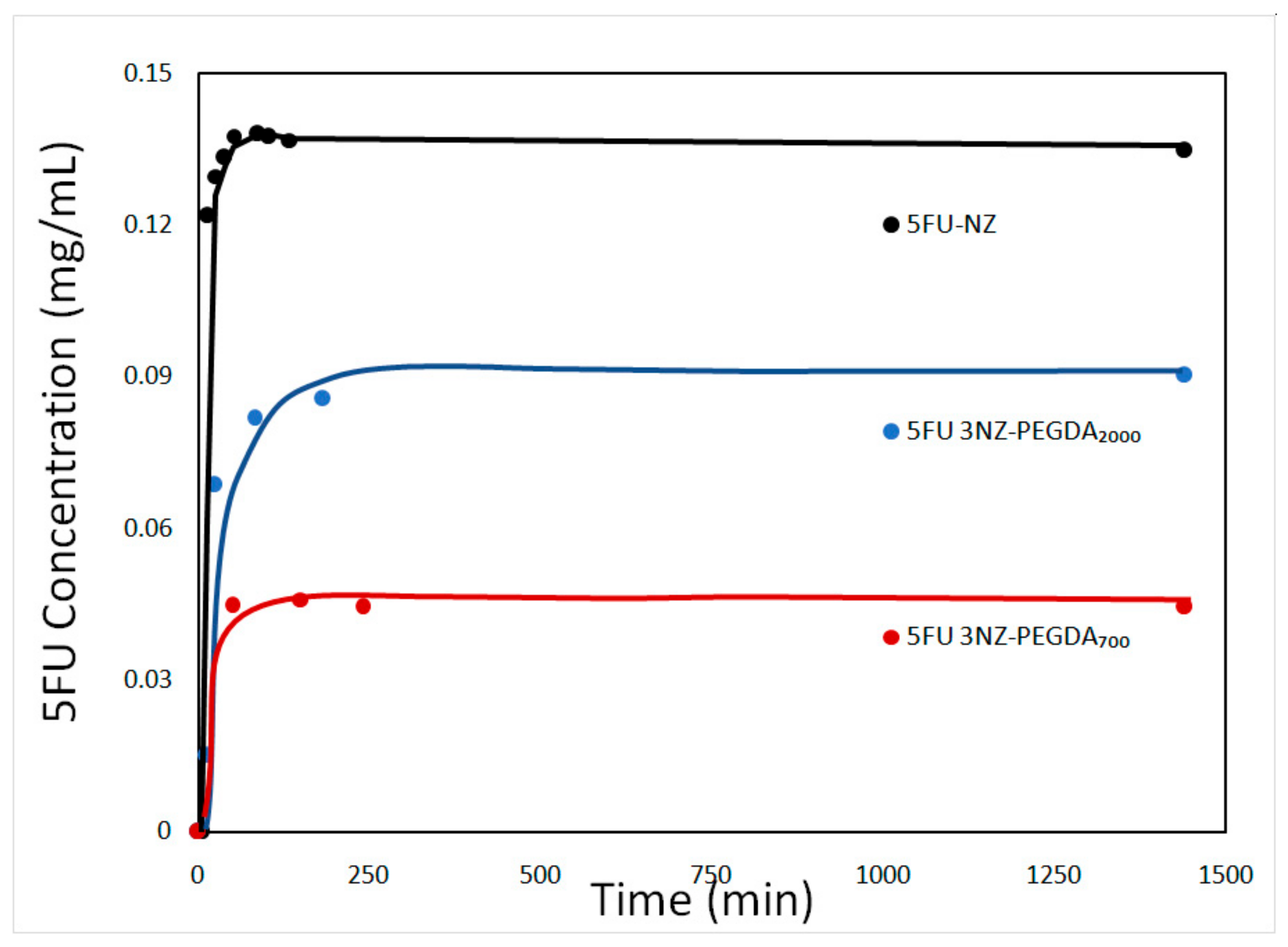
3.1. Characterization of the 5-Fluorouracil-Loaded Zeolite Nanoparticles
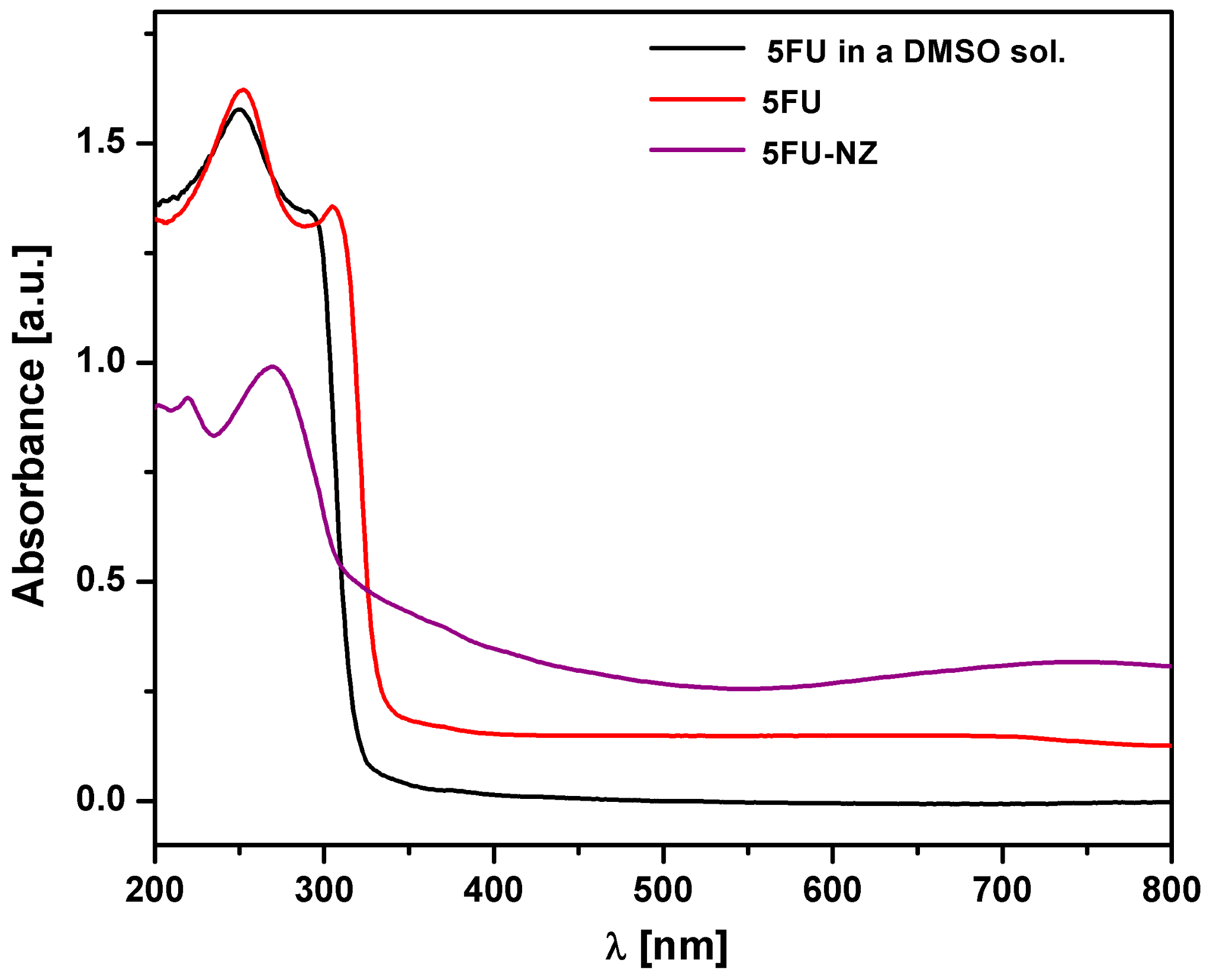
3.1.1. DR-UV-Vis Measurements
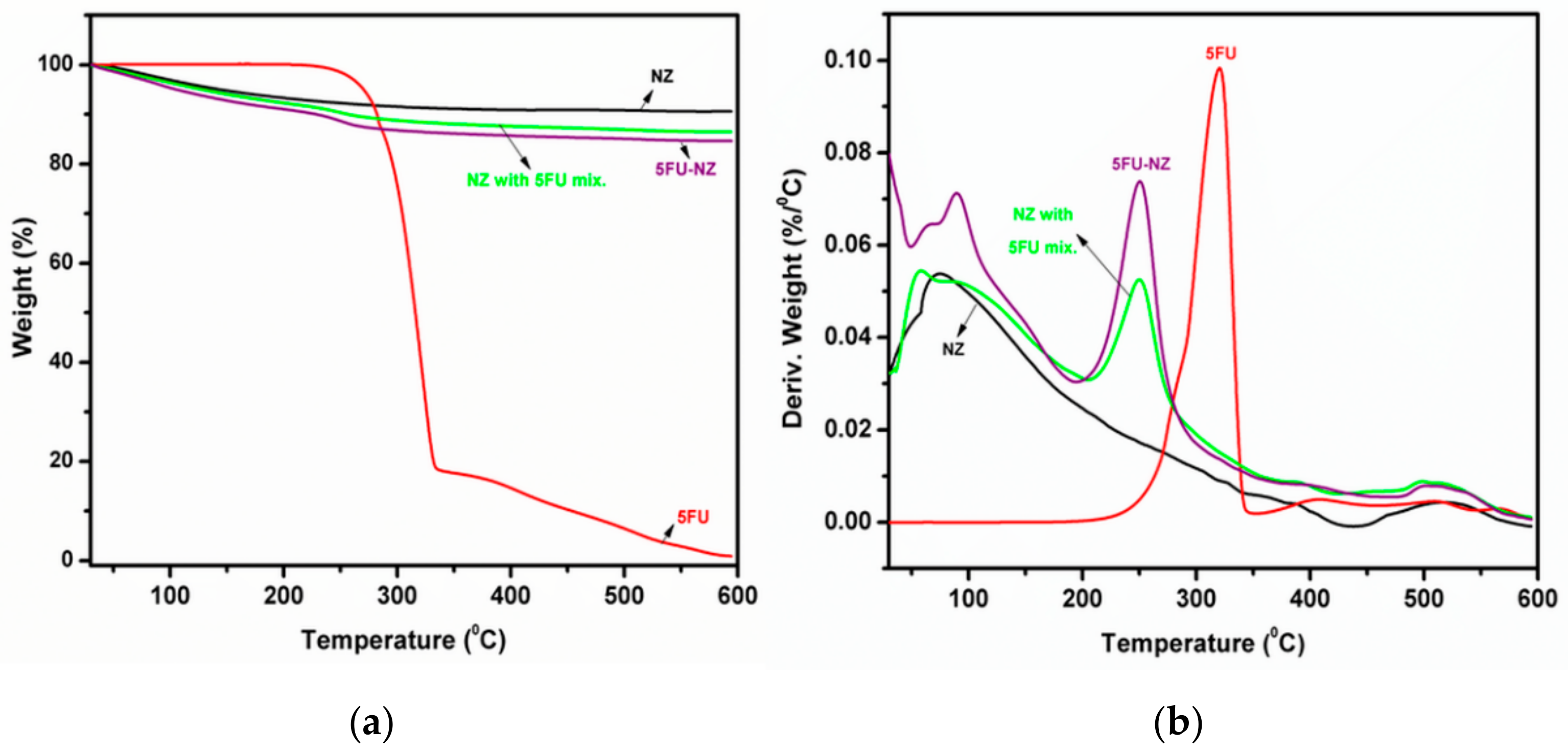
3.1.2. TGA Study
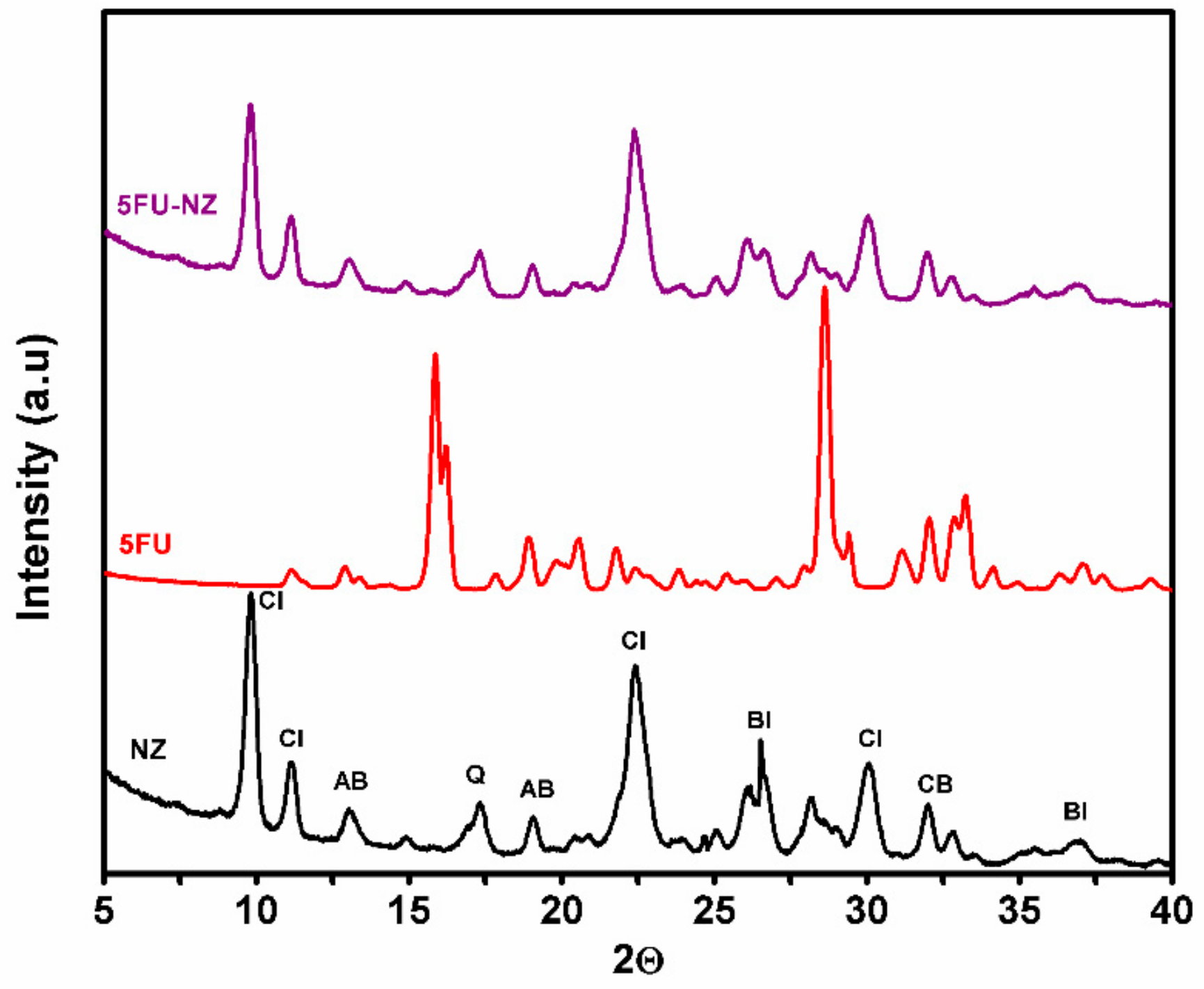
3.1.3. XRD Patterns
3.2. Characterization of Control and Composite NGs
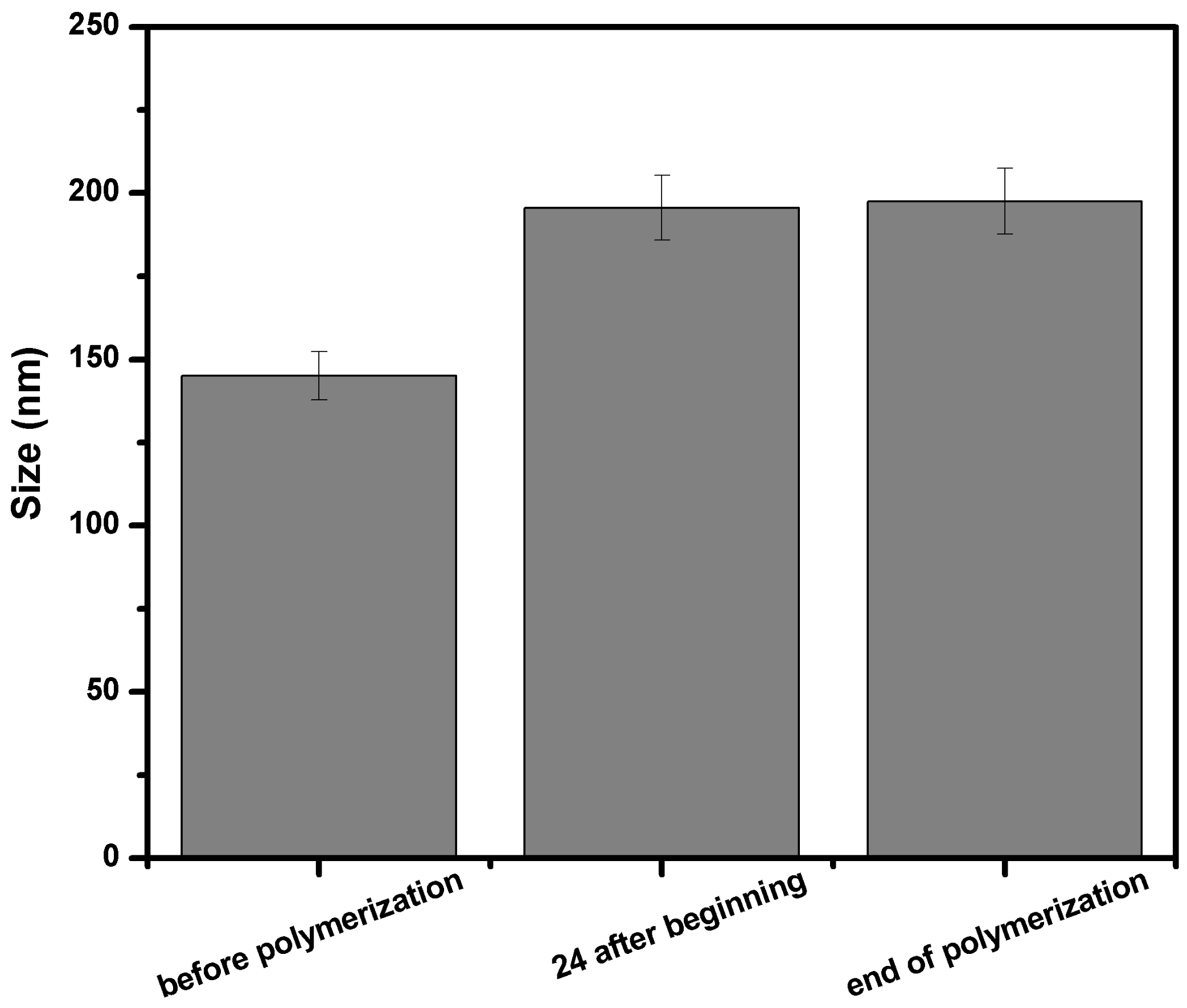
3.2.1. DLS Investigation
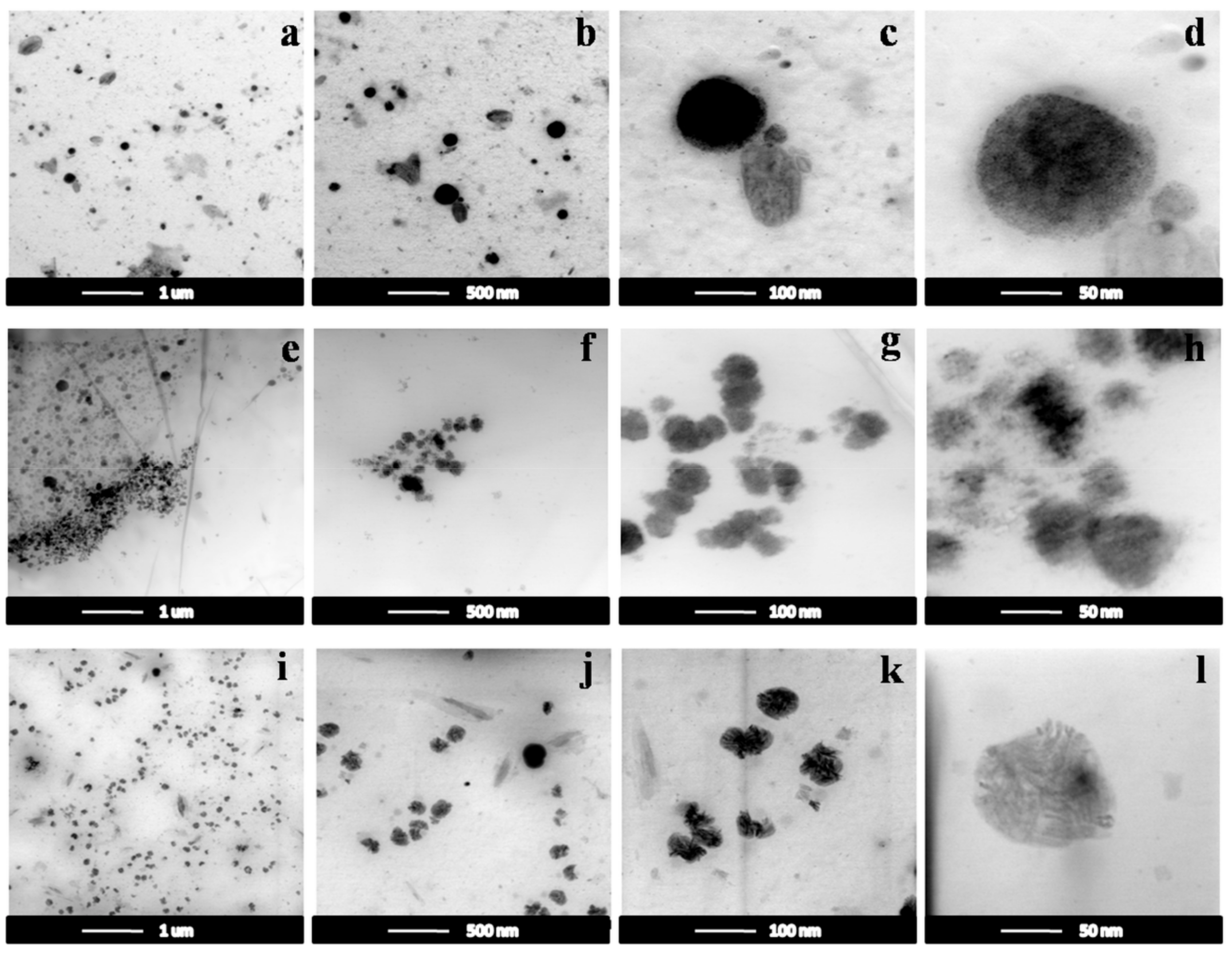
3.2.2. TEM Images
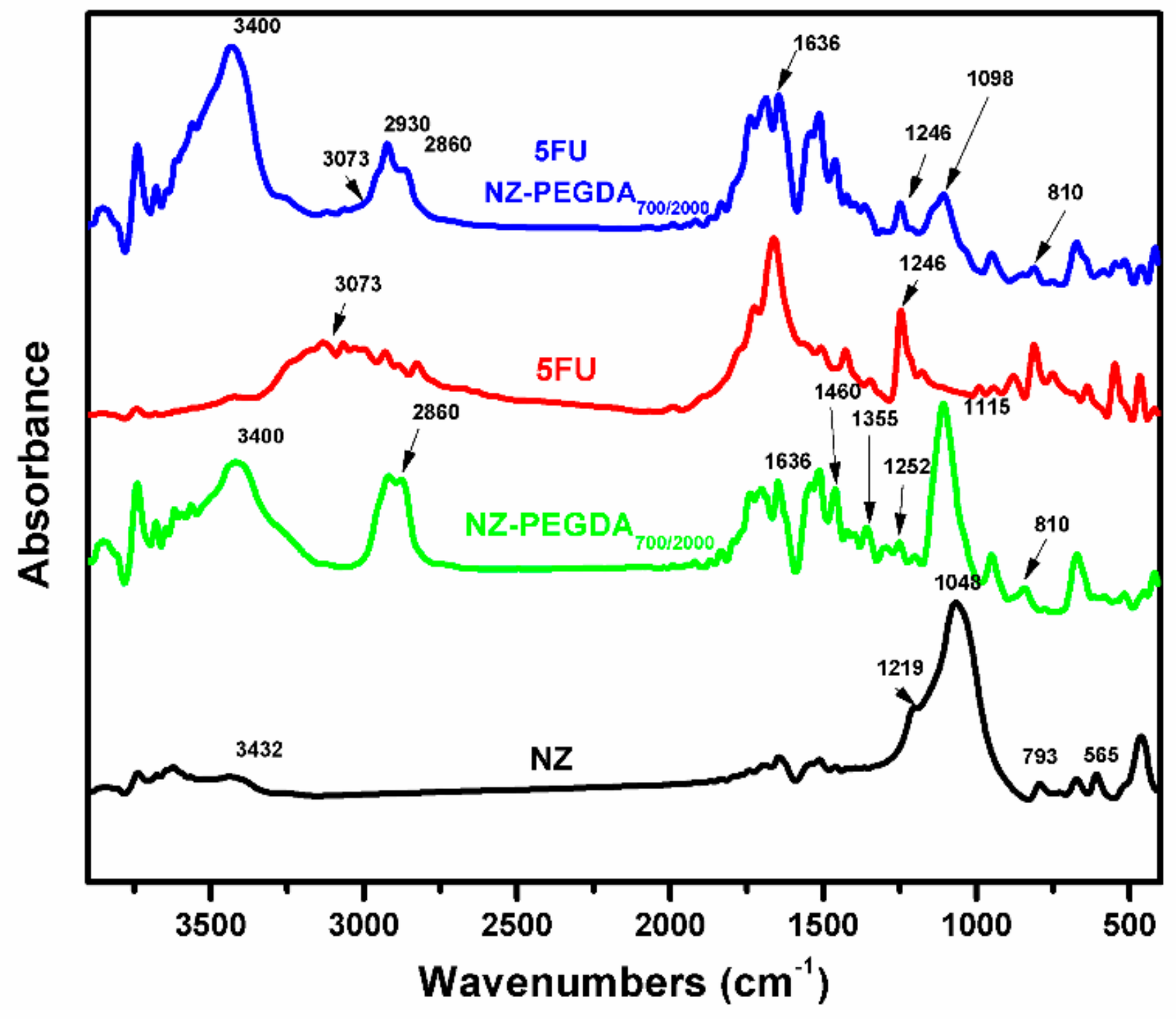
3.2.3. FTIR Measurements
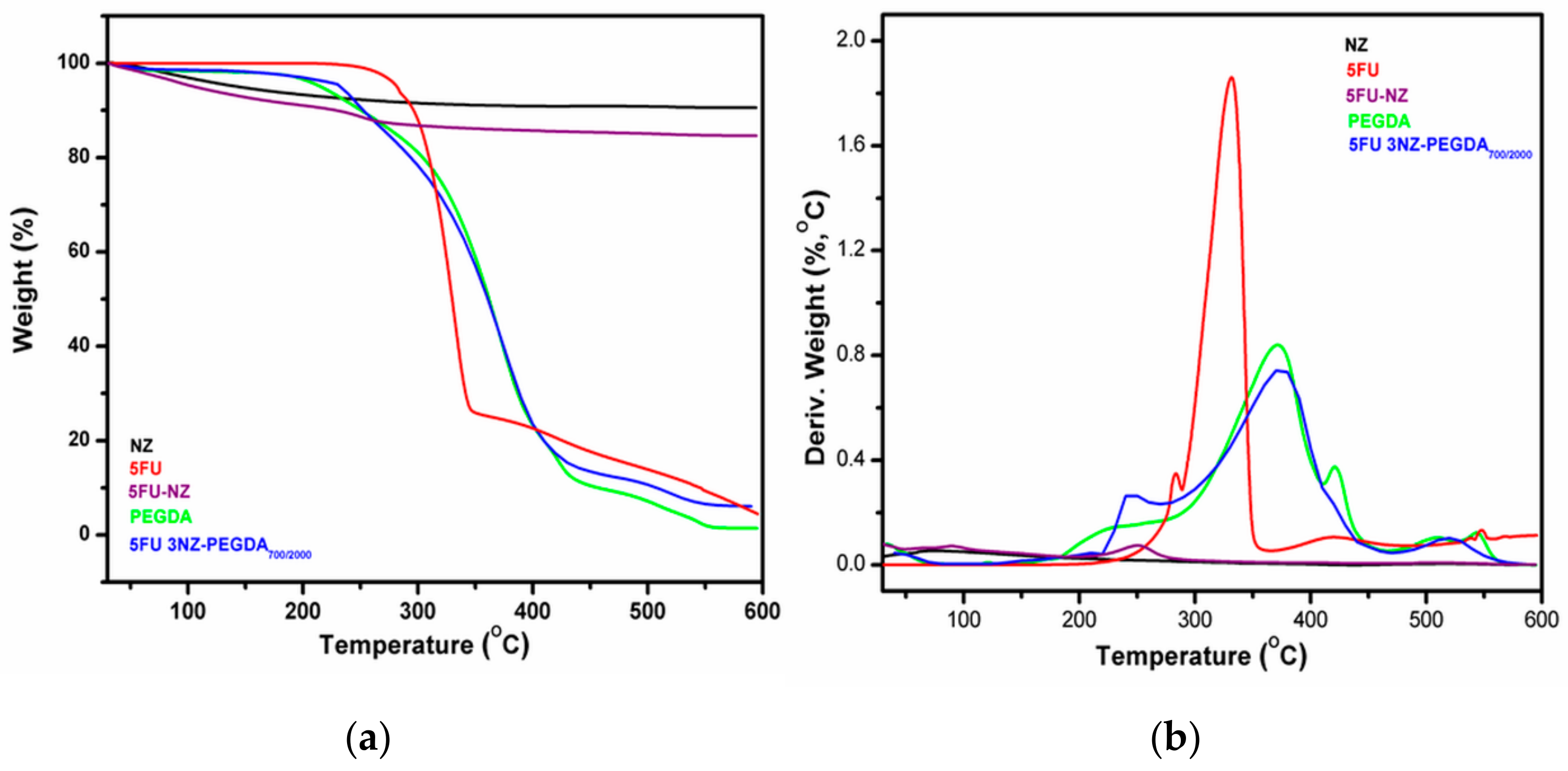
3.2.4. TGA Investigation
3.2.5. Swelling Behaviour
3.2.6. Release Behaviour of the 5-FU-Loaded NG Composites
3.2.7. Cytotoxicity Evaluation of the 5FU-Loaded NG Composites
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Pérez-Herrero, E.; Fernández-Medarde, A. Advanced targeted therapies in cancer: Drug nanocarriers, the future of chemotherapy. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2015, 93, 52–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yallapu, M.M.; Jaggi, M.; Chauhan, S. Design and engineering of nanogels for cancer treatment. Drug Discov. Today 2011, 16, 457–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Blanco, E.; Shen, H.; Ferrari, M. Principles of nanoparticle design for overcoming biological barriers to drug delivery. Nat. Biotechnol. 2015, 33, 941–951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, J.-M.; Park, D.-H.; Choi, S.-J.; Choy, J.-H. LDH Nanocontainers as Bio-Reservoirs and Drug Delivery Carriers. Recent Pat. Nanotechnol. 2012, 6, 200–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, T.; Zhang, Y.S.; Pang, B.; Hyun, D.C.; Yang, M.; Xia, Y. Engineered Nanoparticles for Drug Delivery in Cancer Therapy. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2014, 53, 12320–12364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Longmire, M.; Choyke, P.L.; Kobayashi, H. Clearance Properties of Nano-sized Particles and Molecules as Imaging Agents: Considerations and Caveats. Nanomedicine 2008, 3, 703–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Osada, K.; Christie, R.J.; Kataoka, K. Polymeric micelles from poly(ethylene glycol)–poly(amino acid) block copolymer for drug and gene delivery. J. R. Soc. Interface 2009, 6, S325–S339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, J.; Mao, W.; Lock, L.L.; Tang, J.; Sui, M.; Sun, W.; Cui, H.; Xu, D.; Shen, Y. The Role of Micelle Size in Tumor Accumulation, Penetration, and Treatment. ACS Nano 2015, 9, 7195–7206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chacko, R.T.; Ventura, J.; Zhuang, J.; Thayumanavan, S. Polymer nanogels: A versatile nanoscopic drug delivery platform. Adv. Drug Deliver. Rev. 2012, 64, 836–851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Oh, J.K.; Drumright, R.; Siegwart, D.J.; Matyjaszewski, K. The development of microgels/nanogels for drug delivery applications. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2008, 33, 448–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamidi, M.; Azadi, A.; Rafiei, P. Hydrogel nanoparticles in drug delivery. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2008, 60, 1638–1649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, N.; Wang, J.; Yang, X.; Li, L. Novel nanogels as drug delivery systems for poorly soluble anticancer drugs. Colloids Surf. B. Biointerfaces 2011, 83, 237–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goenka, S.; Sant, V.; Sant, S. Graphene-based nanomaterials for drug delivery and tissue engineering. J. Control. Release 2014, 173, 75–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, L.W.; Sun, W.Q.; Chan, N.W.; Lai, W.Y.; Leung, W.K.; Tsang, J.C.; Wong, Y.H.; Yeung, K.L. Zeolite microneedles for transdermal drug delivery. Stud. Surf. Sci. Catal. 2007, 170, 525–530. [Google Scholar]
- Harvey, A.L.; Balkus, K.J., Jr. Novel Delivery System for the Bioregulatory Agent Nitric Oxide. Chem. Mater. 2009, 21, 5032–5041. [Google Scholar]
- Mirzakhanian, Z.; Faghihi, K.; Barati, A.; Momeni, H.R. Synthesis of superabsorbent hydrogel nanocomposites for use as hemostaticagent. Int. J. Polym. Mater. 2016, 65, 779–788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sotoudeh, S.; Barati, A.; Davarnejad, R.; Farahani, M.A. Antibiotic Release Process from Hydrogel Nano Zeolite Composites. MiddleEast J. Sci. Res. 2012, 12, 392–396. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.; Xu, C.; He, Y.; Wang, X.; Xing, F.; Qiu, H.; Liu, Y.; Ma, D.; Lin, T.; Gao, J. Zeolite/Polymer Composite Hollow Microspheres Containing Antibiotics and the In Vitro Drug Release. J. Biomater. Sci. Polym. E 2011, 22, 809–822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pavelic, K.; Hadzija, M.; Bedrica, L.; Pavelic, J.; Dikic, I.; Katic, M.; Kralj, M.; Herak, M.; Kapitanovic, B.S.; Poljak-Blazi, M.; et al. Natural zeolite clinoptilolite: New adjuvant in anticancer therapy. J. Mol. Med. 2001, 78, 708–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, F.; Wang, X.; Li, Q.; Liao, L.; Zhang, C. Nanocomposite Hydrogels and Their Applications in Drug Delivery and Tissue Engineering. J. Biomed. Nanotechnol. 2015, 11, 40–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaharwar, A.K.; Peppas, N.A.; Khademhosseini, A. Nanocomposite hydrogels for biomedical applications. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 2014, 111, 441–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cursaru, B.; Radu, A.-L.; Perrin, F.-X.; Sarbu, A.; Teodorescu, M.; Gavrilă, A.-M.; Damian, C.M.; Sandu, T.; Iordache, T.V.; Zaharia, A. Poly (ethylene glycol) Composite Hydrogels with Natural Zeolite as Filler for Controlled Delivery Applications. Macromol. Res. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, Y.; Wang, L.; Yang, W.; Fu, S.; Elaissari, A. Preparation of magnetic polymeric particles via inverse microemulsion polymerization process. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2003, 257, 69–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Egodawatte, S.; Dominguez, S.; Larsen, S. Solvent effects in the development of a drug delivery system for 5-fluorouracil using magnetic mesoporous silica nanoparticles. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2016, 237, 108–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braun, O.; Selb, J.; Candau, F. Synthesis in microemulsion and characterization of stimuli-responsive polyelectrolytes and polyampholytes based on N-isopropylacrylamide. Polymer 2001, 42, 8499–8510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandez, V.V.A.; Tepale, N.; Sanchez-Diaz, J.C.; Mendizabal, E.; Puig, J.E.; Soltero, J.F.A. Thermoresponsive nanostructured poly(N-isopropylacrylamide) hydrogels made via inverse microemulsion polymerization. Colloid Polym. Sci. 2006, 284, 387–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, D.; Rameshbabu, A.P.; Ghosh, P.; Patra, P.; Dhara, S.; Pal, S. Biocompatible nanogel derived from functionalized dextrin for targeted delivery of doxorubicin hydrochloride to MG 63 cancer cells. Carbohydr. Polym. 2017, 171, 27–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korsmeyer, R.W.; Gurnya, R.; Doelker, E.; Buri, P.; Peppas, N.A. Mechanisms of solute release from porous hydrophilic polymers. Int. J. Pharm. 1983, 15, 25–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gustavsson, T.; Sarkar, N.; Banyasz, A.; Markovitsi, D.; Improta, R. Solvent Effects on the Steady-state Absorption and Fluorescence Spectra of Uracil, Thymine and 5-Fluorouracil. Photochem. Photobiol. 2007, 83, 595–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Datt, A. Applications of mesoporous silica and zeolites for drug delivery. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Iowa, Iowa City, IA, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, R.; Pang, W.; Yu, J.; Huo, Q.; Chen, J. Chemistry of Zeolites and Related Porous Materials: Synthesis and Structure; John Wiley & Sons: Singapore, 2007; pp. 547–548. [Google Scholar]
- Izquierdo, P.; Esquena, J.; Tadros, T.F.; Dederen, C.; Garcia, M.J.; Azemar, N.; Solans, C. Formation and Stability of Nano-Emulsions Prepared Using the Phase Inversion Temperature Method. Langmuir 2002, 18, 26–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vogel, N. Surface Patterning with Colloid Monolayers; Springer: Berling/Heidelberg, Germany, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Radu, A.L.; Gavrila, A.M.; Cursaru, B.; Spatarelu, C.P.; Sandu, T.; Sarbu, A.; Teodorescu, M.; Perrin, F.-X.; Iordache, T.V.; Zaharia, A. Poly(ethylene Glycol) Diacrylate-Nanogels Synthesized by Mini-emulsion Polymerization. Mater. Plast. 2019, 56, 514–519. [Google Scholar]
- Gref, R.; Lück, M.; Quellec, P.; Marchand, M.; Dellacherie, E.; Harnisch, S.; Blunk, T.; Müller, R.H. Stealth’ corona-core nanoparticles surface modified by polyethylene glycol (PEG): Influences of the corona (PEG chain length and surface density) and of the core composition on phagocytic uptake and plasma protein adsorption. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2000, 18, 301–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stanescu, P.O.; Cursaru, B.; Teodorescu, M. Thermal properties of networks prepared from α, ω-diepoxy terminated poly (ethylene glycol) s and aliphatic polyamines. Mater. Plast. 2009, 46, 419–425. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, A.; Ma, H.; Zhang, H.; Ying, W.; Fang, D. Effect of boron on ZSM-5 catalyst for methanol to propylene conversion. Pol. J. Chem. Technol. 2013, 15, 95–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kariminezhad, H.; Habibi, M.; Mirzababayi, N. Nanosized ZSM-5 will improve photodynamic therapy using Methylene blue. J. Photochim. Photobiol. B 2015, 148, 107–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pelras, P.; Glass, S.; Scherzer, T.; Elsner, C.; Schulze, A.; Abel, B. Transparent Low Molecular Weight Poly(Ethylene Glycol) Diacrylate-Based Hydrogels as Film Media for Photoswitchable Drugs. Polymers 2017, 9, 639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Moisescu-Goia, C.; Muresan-Pop, M.; Simon, V. New solid-state forms of antineoplastic 5-Fluorouracil with anthelmintic piperazine. J. Mol. Struct. 2017, 1150, 37–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaharia, A.; Sarbu, A.; Radu, A.-L.; Jankova, K.; Daugaard, A.; Hvilsted, S.; Perrin, F.-X.; Teodorescu, M.; Munteanu, C.; Fruth-Oprisan, V. Preparation and characterization of polyacrylamide-modified kaolinite containing poly [acrylic acid-co-methylene bisacrylamide] nanocomposite hydrogels. Appl. Clay Sci. 2015, 103, 46–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Tang, Y.; Zhang, W.; Liu, S.; Zhao, Y.; Wang, W.; Wang, J.; Xu, L.; Liu, K. Sustained drug release and cancer treatment by an injectable and biodegradable cyanoacrylate-based local drug delivery system. J. Mater. Chem. B 2018, 6, 1216–1225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soni, K.S.; Desale, S.S.; Bronich, T.K. Nanogels: An overview of properties, biomedical applications and obstacles to clinical translation. J. Control. Release 2016, 240, 109–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Udofot, O.; Affram, K.; Smith, T.; Tshabe, B.; Krishnan, S.; Sachdeva, M.; Agyare, E. Pharmacokinetic, biodistribution and therapeutic efficacy of 5-fluorouracil-loaded pH-sensitive PEGylated liposomal nanoparticles in HCT-116 tumor bearing mouse. J. Nat. Sci. 2016, 2, e171. [Google Scholar]
- Cursaru, B.; Teodorescu, M.; Boscornea, C.; Stanescu, P.O.; Stoleriu, S. Drug absorption and release properties of crosslinked hydrogels based on diepoxy-terminated poly(ethylene glycol)s and aliphatic polyamines-a study on the effect of the gel molecular structure. Mater. Sci. Eng. C Mater. Biol. Appl. 2013, 33, 1307–1314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serra, L.; Domenech, J.; Peppas, N.A. Drug Transport Mechanisms and Release Kinetics from Molecularly Designed Poly(Acrylic Acid-G-Ethylene Glycol) Hydrogels. Biomaterials 2006, 27, 5440–5451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ritger, P.L.; Peppas, N.A. A simple equation for description of solute release I. Fickian and non-fickian release from non-swellable devices in the form of slabs, spheres, cylinders or discs. J. Control. Release 1987, 5, 23–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Sample | PEGDA700/PEGDA2000 | Zeolite (wt%) |
|---|---|---|
| PEGDA700 | 100/0 | 0 |
| PEGDA2000 | 0/100 | 0 |
| PEGDA700/2000 | 75/25 | 0 |
| 1NZ-PEGDA700 | 100/0 | 1 |
| 1NZ-PEGDA2000 | 0/100 | 1 |
| 1NZ-PEGDA700/2000 | 75/25 | 1 |
| 2NZ-PEGDA700 | 100/0 | 2 |
| 2NZ-PEGDA2000 | 0/100 | 2 |
| 2NZ-PEGDA700/2000 | 75/25 | 2 |
| 2NZ-PEGDA700 | 100/0 | 3 |
| 2NZ-PEGDA2000 | 0/100 | 3 |
| 3NZ-PEGDA700/2000 | 75/25 | 3 |
| Sample | Lipophobic Agent | SPAN 80 Concentration (wt%) | Mean Particle Size (nm) | Conversion(%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PEGDA700 | - | - | 195 ± 8.1 | 15% |
| PEGDA700 | NaCl | - | 197 ± 19.9 | 89% |
| PEGDA700 * | NaCl | [SPAN 80] = 5% | 179± 5.9 | 78% |
| PEGDA700 ** | NaCl | [SPAN 80] = 5% | 189 ± 19.3 | 99% |
| PEGDA700/2000 | NaCl | [SPAN 80] = 5% | 154± 8.6 | 69% |
| PEGDA2000 | NaCl | [SPAN 80] = 5% | 178 ± 13.8 | 46% |
| 3NZ-PEGDA700 | - | - | 171 ± 69 | 10% |
| 3NZ-PEGDA700 | NaCl | [SPAN 80] = 5% | 19± 24.6 | 85% |
| 3NZ-PEGDA2000 | NaCl | [SPAN 80] = 5% | 17± 10.2 | 37% |
| 3NZ-PEGDA700/2000 | NaCl | [SPAN 80] = 5% | 197 ± 14.2 | 91% |
| Sample | NZ (wt.%) | Mean Particle Size (nm) | PDI |
|---|---|---|---|
| NZ | 100 | 148 ± 7.7 | 0.577 |
| 1NZ-PEGDA700 | 1 | 203 ± 0.5 | 0.187 |
| 1NZ-PEGDA2000 | 1 | 166 ± 1.1 | 0.189 |
| 1NZ-PEGDA700/2000 | 1 | 153 ± 0.5 | 0.183 |
| 2NZ-PEGDA700 | 2 | 195 ± 0.7 | 0.200 |
| 2NZ-PEGDA2000 | 2 | 225 ± 9.2 | 0.267 |
| 2NZ-PEGDA700/2000 | 2 | 189 ± 1 | 0.173 |
| 3NZ-PEGDA700/2000 | 3 | 192 ± 0.6 | 0.180 |
| Sample | SD (%) | |
|---|---|---|
| Nanogels | PEGDA700 | 210± 0.5 |
| PEGDA700/2000 | 296± 0.2 | |
| PEGDA2000 | 439± 1 | |
| Composite Nanogels | 3NZ-PEGDA700 | 160± 0.5 |
| 3NZ-PEGDA700/2000 | 257± 1.5 | |
| 3NZ-PEGDA2000 | 388± 0.8 |
| Mathematical Models | 5FU-NZ | 5FU NZ-PEGDA700 | 5FU NZ-PEGDA700/2000 | 5FU NZ-PEGDA2000 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| First-order | ||||
| K min−1 | 0.00018 | 0.00011 | 0.00015 | 0.00016 |
| R2 | 0.6810 | 0.5672 | 0.7309 | 0.5738 |
| Zero-order | ||||
| K0, µg/mL | 0.0196 | 0.0196 | 0.02 | 0.0238 |
| R2 | 0.927 | 0.788 | 0.731 | 0.773 |
| Higuchi | ||||
| KH, µg/mL∙min−1/2 | 2.055 | 2.136 | 1.212 | 2.650 |
| R2 | 0.982 | 0.899 | 0.976 | 0.914 |
| Korsmeyer–Peppas | ||||
| K | 3.306 | 2.321 | 6.087 | 1.736 |
| n | 0.319 | 0.406 | 0.256 | 0.450 |
| R2 | 0.988 | 0.963 | 0.984 | 0.968 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Spatarelu, C.P.; Chiriac, A.-L.; Cursaru, B.; Iordache, T.-V.; Gavrila, A.-M.; Cojocaru, C.-T.; Botez, R.-E.; Trica, B.; Sarbu, A.; Teodorescu, M.; et al. Composite Nanogels Based on Zeolite-Poly(ethylene glycol) Diacrylate for Controlled Drug Delivery. Nanomaterials 2020, 10, 195. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano10020195
Spatarelu CP, Chiriac A-L, Cursaru B, Iordache T-V, Gavrila A-M, Cojocaru C-T, Botez R-E, Trica B, Sarbu A, Teodorescu M, et al. Composite Nanogels Based on Zeolite-Poly(ethylene glycol) Diacrylate for Controlled Drug Delivery. Nanomaterials. 2020; 10(2):195. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano10020195
Chicago/Turabian StyleSpatarelu, Catalina Paula, Anita-Laura (Radu) Chiriac, Bogdan Cursaru, Tanta-Verona Iordache, Ana-Mihaela Gavrila, Crina-Thea Cojocaru, Razvan-Edward Botez, Bogdan Trica, Andrei Sarbu, Mircea Teodorescu, and et al. 2020. "Composite Nanogels Based on Zeolite-Poly(ethylene glycol) Diacrylate for Controlled Drug Delivery" Nanomaterials 10, no. 2: 195. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano10020195
APA StyleSpatarelu, C. P., Chiriac, A.-L., Cursaru, B., Iordache, T.-V., Gavrila, A.-M., Cojocaru, C.-T., Botez, R.-E., Trica, B., Sarbu, A., Teodorescu, M., Tofan, V., Perrin, F.-X., & Zaharia, A. (2020). Composite Nanogels Based on Zeolite-Poly(ethylene glycol) Diacrylate for Controlled Drug Delivery. Nanomaterials, 10(2), 195. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano10020195












