A Novel Route to High-Quality Graphene Quantum Dots by Hydrogen-Assisted Pyrolysis of Silicon Carbide
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. High-Quality GQDs Preparation
2.3. Characterizations
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Morphological Features
3.2. Structural Features
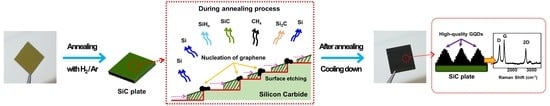
3.3. The Formation Mechanism of High-Quality GQDs
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Qu, D.; Zheng, M.; Du, P.; Zhou, Y.; Zhang, L.; Li, D.; Tan, H.; Zhao, Z.; Xie, Z.; Sun, Z. Highly luminescent S, N co-doped graphene quantum dots with broad visible absorption bands for visible light photocatalysts. Nanoscale 2013, 5, 12272–12277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ju, J.; Chen, W. Synthesis of highly fluorescent nitrogen-doped graphene quantum dots for sensitive, label-free detection of Fe (III) in aqueous media. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2014, 58, 219–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qin, H.; Gong, T.; Jin, Y.; Cho, Y.; Shin, C.; Lee, C.; Kim, T. Near-UV-emitting graphene quantum dots from graphene hydrogels. Carbon 2015, 94, 181–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Fatimy, A.; Myers-Ward, R.L.; Boyd, A.K.; Daniels, K.M.; Gaskill, D.K.; Barbara, P. Epitaxial graphene quantum dots for high-performance terahertz bolometers. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2016, 11, 335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, J.; Zhu, Y.; Yang, X.; Li, C. Graphene quantum dots: Emergent nanolights for bioimaging, sensors, catalysis and photovoltaic devices. Chem. Commun. 2012, 48, 3686–3699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, S.; Zhang, J.; Qiao, C.; Tang, S.; Li, Y.; Yuan, W.; Li, B.; Tian, L.; Liu, F.; Hu, R. Strongly green-photoluminescent graphene quantum dots for bioimaging applications. Chem. Commun. 2011, 47, 6858–6860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ananthanarayanan, A.; Wang, X.; Routh, P.; Sana, B.; Lim, S.; Kim, D.H.; Lim, K.H.; Li, J.; Chen, P. Facile synthesis of graphene quantum dots from 3D graphene and their application for Fe3+ sensing. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2014, 24, 3021–3026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Hu, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Shi, G.; Deng, L.; Hou, Y.; Qu, L. An electrochemical avenue to green-luminescent graphene quantum dots as potential electron-acceptors for photovoltaics. Adv. Mater. 2011, 23, 776–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paulo, S.; Palomares, E.; Martinez-Ferrero, E. Graphene and carbon quantum dot-based materials in photovoltaic devices: From synthesis to applications. Nanomaterials 2016, 6, 157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iannazzo, D.; Pistone, A.; Celesti, C.; Triolo, C.; Patané, S.; Giofré, S.V.; Romeo, R.; Ziccarelli, I.; Mancuso, R.; Gabriele, B. A Smart Nanovector for Cancer Targeted Drug Delivery Based on Graphene Quantum Dots. Nanomaterials 2019, 9, 282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, X.; Niu, X.; Ma, K.; Huang, P.; Grothe, J.; Kaskel, S.; Zhu, Y. Graphene quantum dots-capped magnetic mesoporous silica nanoparticles as a multifunctional platform for controlled drug delivery, magnetic hyperthermia, and photothermal therapy. Small 2017, 13, 1602225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konstantatos, G.; Badioli, M.; Gaudreau, L.; Osmond, J.; Bernechea, M.; De Arquer, F.P.G.; Gatti, F.; Koppens, F.H. Hybrid graphene–quantum dot phototransistors with ultrahigh gain. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2012, 7, 363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, A.; Liu, Z.; Chu, S.; Wu, M.; Ye, Z.; Cai, Z.; Chang, Y.; Wang, S.; Gong, Q.; Liu, Y. A facile one-step method to produce graphene–CdS quantum dot nanocomposites as promising optoelectronic materials. Adv. Mater. 2010, 22, 103–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, J.; Gao, W.; Gupta, B.K.; Liu, Z.; Romero-Aburto, R.; Ge, L.; Song, L.; Alemany, L.B.; Zhan, X.; Gao, G.; et al. Graphene quantum dots derived from carbon fibers. Nano Lett. 2012, 12, 844–849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Q.; Zhang, J.; He, H.; Huang, G.; Xing, B.; Jia, J.; Zhang, C. Green preparation of high yield fluorescent graphene quantum dots from coal-tar-pitch by mild oxidation. Nanomaterials 2018, 8, 844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, M.; Bai, L.; Shang, W.; Xie, W.; Ma, H.; Fu, Y.; Fang, D.; Sun, H.; Fan, L.; Han, M. Facile synthesis of water-soluble, highly fluorescent graphene quantum dots as a robust biological label for stem cells. J. Mater. Chem. 2012, 22, 7461–7467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, D.; Zhang, J.; Li, Z.; Wu, M. Hydrothermal route for cutting graphene sheets into blue-luminescent graphene quantum dots. Adv. Mater. 2010, 22, 734–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhuo, S.; Shao, M.; Lee, S.-T. Upconversion and downconversion fluorescent graphene quantum dots: Ultrasonic preparation and photocatalysis. ACS Nano 2012, 6, 1059–1064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, Y.; Lee, J.; Yang, J.; Park, J.; Lee, K.; Kim, S.; Park, Y.; Lee, H. Mass production of graphene quantum dots by one-pot synthesis directly from graphite in high yield. Small 2014, 10, 866–870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, L.; Zhang, S. Creating high yield water soluble luminescent graphene quantum dots via exfoliating and disintegrating carbon nanotubes and graphite flakes. Chem. Commun. 2012, 48, 10177–10179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, S.H.; Jang, M.H.; Chung, J.; Jin, S.H.; Kim, B.H.; Hur, S.H.; Yoo, S.; Cho, Y.H.; Jeon, S. Highly Efficient Light-Emitting Diode of Graphene Quantum Dots Fabricated from Graphite Intercalation Compounds. Adv. Opt. Mater. 2014, 2, 1016–1023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Umrao, S.; Jang, M.-H.; Oh, J.-H.; Kim, G.; Sahoo, S.; Cho, Y.-H.; Srivastva, A.; Oh, I.-K. Microwave bottom-up route for size-tunable and switchable photoluminescent graphene quantum dots using acetylacetone: New platform for enzyme-free detection of hydrogen peroxide. Carbon 2015, 81, 514–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, L.; Ji, R.; Cao, X.; Lin, J.; Jiang, H.; Li, X.; Teng, K.S.; Luk, C.M.; Zeng, S.; Hao, J. Deep ultraviolet photoluminescence of water-soluble self-passivated graphene quantum dots. ACS Nano 2012, 6, 5102–5110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, R.; Wu, D.; Feng, X.; Müllen, K. Bottom-up fabrication of photoluminescent graphene quantum dots with uniform morphology. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2011, 133, 15221–15223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Y.; Shao, J.; Chen, C.; Li, H.; Wang, R.; Chi, Y.; Lin, X.; Chen, G. Blue luminescent graphene quantum dots and graphene oxide prepared by tuning the carbonization degree of citric acid. Carbon 2012, 50, 4738–4743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, J.; Yeo, P.S.E.; Gan, C.K.; Wu, P.; Loh, K.P. Transforming C 60 molecules into graphene quantum dots. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2011, 6, 247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Tian, F.; Wang, W.; Chen, J.; Wu, M.; Zhao, J.X. Fabrication of highly fluorescent graphene quantum dots using L-glutamic acid for in vitro/in vivo imaging and sensing. J. Mater. Chem. C 2013, 1, 4676–4684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, D.; Chen, X.; Hu, Y.; Sun, T.; Song, Z.; Zheng, Y.; Cao, Y.; Cai, Z.; Cao, M.; Peng, L. Raman enhancement on ultra-clean graphene quantum dots produced by quasi-equilibrium plasma-enhanced chemical vapor deposition. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jernigan, G.G.; VanMil, B.L.; Tedesco, J.L.; Tischler, J.G.; Glaser, E.R.; Davidson, A., III; Campbell, P.M.; Gaskill, D.K. Comparison of epitaxial graphene on Si-face and C-face 4H SiC formed by ultrahigh vacuum and RF furnace production. Nano Lett. 2009, 9, 2605–2609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hupalo, M.; Conrad, E.; Tringides, M. Growth mechanism for epitaxial graphene on vicinal 6 H-SiC (0001) surfaces: A scanning tunneling microscopy study. Phys. Rev. B 2009, 80, 041401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emtsev, K.V.; Bostwick, A.; Horn, K.; Jobst, J.; Kellogg, G.L.; Ley, L.; McChesney, J.L.; Ohta, T.; Reshanov, S.A.; Röhrl, J. Towards wafer-size graphene layers by atmospheric pressure graphitization of silicon carbide. Nat. Mater. 2009, 8, 203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boeckl, J.; Mitchel, W.; Clarke, E.; Barbosa, R.L.; Lu, W.J. Structural Evaluation of Graphene/SiC (0001) Grown in Atmospheric Pressure. In Materials Science Forum; Trans Tech Publications Ltd.: Stafa, Zurich, Switzerland, 2010; Volume 645, pp. 573–576. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, Q.; Kim, J.J.; Ali, G.; Cho, S.O. Width-tunable graphene nanoribbons on a SiC substrate with a controlled step height. Adv. Mater. 2013, 25, 1144–1148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, Z.; Li, F.; Wen, J.; Wang, X.; Sun, R. Gram-scale synthesis of single-crystalline graphene quantum dots derived from lignin biomass. Green Chem. 2018, 20, 1383–1390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Guo, S.; Zhong, P.; Xie, Y.; Li, Z.; Ma, X. Large scale production of graphene quantum dots through the reaction of graphene oxide with sodium hypochlorite. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 54644–54648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Z.; Shen, Y.; Li, Y.; Zheng, W.; Xue, Y.; Qin, C.; Zhang, B.; Hao, J.; Feng, W. Facile synthesis of analogous graphene quantum dots with sp 2 hybridized carbon atom dominant structures and their photovoltaic application. Nanoscale 2014, 6, 13043–13052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakajima, A.; Yokoya, H.; Furukawa, Y.; Yonezu, H. Step control of vicinal 6H–SiC (0001) surface by H 2 etching. J. Appl. Phys. 2005, 97, 104919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumagawa, M.; Kuwabara, H.; Yamada, S. Hydrogen etching of silicon carbide. Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 1969, 8, 421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Heer, W.A.; Berger, C.; Ruan, M.; Sprinkle, M.; Li, X.; Hu, Y.; Zhang, B.; Hankinson, J.; Conrad, E. Large area and structured epitaxial graphene produced by confinement controlled sublimation of silicon carbide. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 16900–16905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.; Dong, Y.; Kong, W.; Han, W.; Tan, P.; Liao, Z.; Wu, X.; Yu, D. Growth of large domain epitaxial graphene on the C-face of SiC. J. Appl. Phys. 2012, 112, 104307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, T.; Jia, Z.; Yan, B.; Yu, D.; Wu, X. Hydrogen assisted growth of high quality epitaxial graphene on the C-face of 4H-SiC. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2015, 106, 013106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X. Epitaxial graphene films on SiC: Growth, Characterization, and Devices. Ph.D. Thesis, Georgia Institute of Technology, Atlanta, GA, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Nyakiti, L.; Wheeler, V.; Garces, N.; Myers-Ward, R.; Eddy, C.; Gaskill, D. Enabling graphene-based technologies: Toward wafer-scale production of epitaxial graphene. MRS Bull. 2012, 37, 1149–1157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lee, N.E.; Lee, S.Y.; Lim, H.S.; Yoo, S.H.; Cho, S.O. A Novel Route to High-Quality Graphene Quantum Dots by Hydrogen-Assisted Pyrolysis of Silicon Carbide. Nanomaterials 2020, 10, 277. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano10020277
Lee NE, Lee SY, Lim HS, Yoo SH, Cho SO. A Novel Route to High-Quality Graphene Quantum Dots by Hydrogen-Assisted Pyrolysis of Silicon Carbide. Nanomaterials. 2020; 10(2):277. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano10020277
Chicago/Turabian StyleLee, Na Eun, Sang Yoon Lee, Hyung San Lim, Sung Ho Yoo, and Sung Oh Cho. 2020. "A Novel Route to High-Quality Graphene Quantum Dots by Hydrogen-Assisted Pyrolysis of Silicon Carbide" Nanomaterials 10, no. 2: 277. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano10020277
APA StyleLee, N. E., Lee, S. Y., Lim, H. S., Yoo, S. H., & Cho, S. O. (2020). A Novel Route to High-Quality Graphene Quantum Dots by Hydrogen-Assisted Pyrolysis of Silicon Carbide. Nanomaterials, 10(2), 277. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano10020277