Graphene Quantum Dots with High Yield and High Quality Synthesized from Low Cost Precursor of Aphanitic Graphite
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Synthesis of GO-QDs by Exfoliating of AG
2.2. Preparation of GQDs with Different Functional Groups
2.3. Characterization
2.4. Detection of Metal Ions in Water
3. Results and Discussion
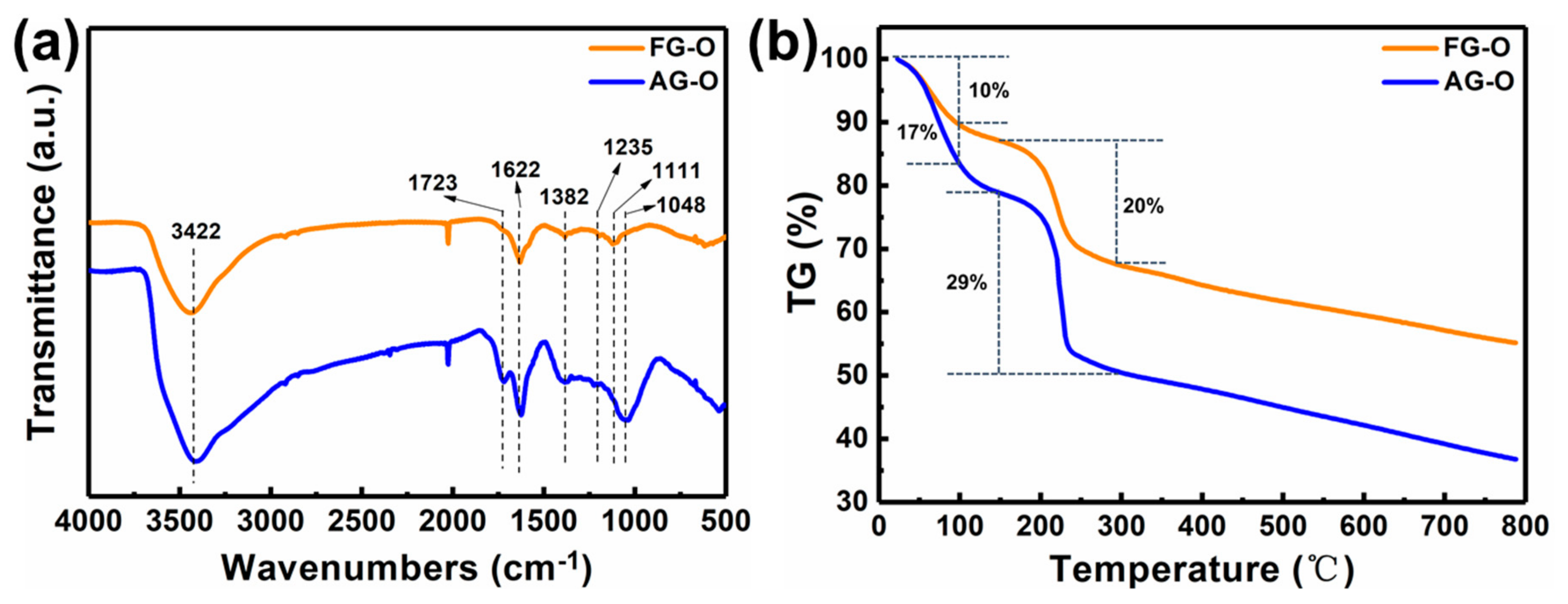
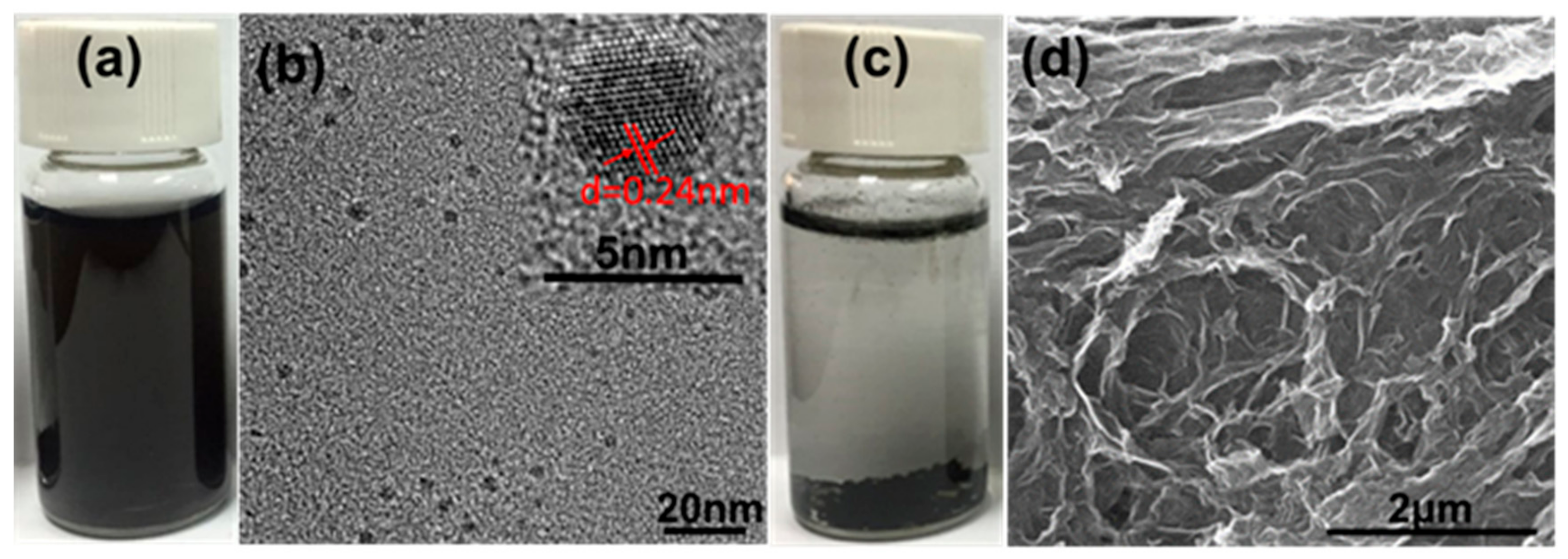
3.1. Synthesis and Characterization of GO-QDs from AG
3.2. Synthesis Mechanism of GO-QDs from AG
3.3. Modification of GO-QDs and Their Applications
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Stankovich, S.; Dikin, D.A.; Piner, R.D.; Kohlhaas, K.A.; Kleinhammes, A.; Jia, Y.; Wu, Y.; Nguyen, S.T.; Ruoff, R.S. Synthesis of graphene-based nanosheets via chemical reduction of exfoliated graphite oxide. Carbon 2007, 45, 1558–1565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geim, A.K.; Novoselov, K.S. The rise of graphene. Nat. Mater. 2007, 6, 183–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, C.; Wei, X.D.; Kysar, J.W.; Hone, J. Measurement of the elastic properties and intrinsic strength of monolayer graphene. Science 2008, 321, 385–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Dong, X.; Chen, P. Biological and chemical sensors based on graphene materials. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2012, 41, 2283–2307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perreault, F.; Fonseca de Faria, A.; Elimelech, M. Environmental applications of graphene-based nanomaterials. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2015, 44, 5861–5896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raccichini, R.; Varzi, A.; Passerini, S.; Scrosati, B. The role of graphene for electrochemical energy storage. Nat. Mater. 2015, 14, 271–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abraham, J.; Vasu, K.S.; Williams, C.D.; Gopinadhan, K.; Su, Y.; Cherian, C.T.; Dix, J.; Prestat, E.; Haigh, S.J.; Grigorieva, I.V.; et al. Tunable sieving of ions using graphene oxide membranes. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2017, 12, 546–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Lee, H.W.; Pasta, M.; Yuan, H.; Zheng, G.; Sun, Y.; Li, Y.; Cui, Y. A phosphorene-graphene hybrid material as a high-capacity anode for sodium-ion batteries. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2015, 10, 980–985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suvarnaphaet, P.; Pechprasarn, S. Graphene-Based Materials for Biosensors: A Review. Sensors 2017, 17, 2161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liao, L.; Peng, H.; Liu, Z. Chemistry makes graphene beyond graphene. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2014, 136, 12194–12200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartolomeo, A.D.; Luongo, G.; Iemmo, L.; Urban, F.; Giubileo, F. Graphene-Silicon Schottky diodes for photodetection. IEEE Trans. Nanotechnol. 2018, 17, 1133–1137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Huang, Y.; Cheng, H.; Shi, G.; Qu, L. Highly Efficient Moisture-Triggered Nanogenerator Based on Graphene Quantum Dots. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2017, 9, 38170–38175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Rui, M.; Song, J.; Shen, Z.; Zeng, H. Carbon and Graphene Quantum Dots for Optoelectronic and Energy Devices: A Review. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2015, 25, 4929–4947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, S.; Zhang, J.; Qiao, C.; Tang, S.; Li, Y.; Yuan, W.; Li, B.; Tian, L.; Liu, F.; Hu, R.; et al. Strongly green-photoluminescent graphene quantum dots for bioimaging applications. Chem. Commun. 2011, 47, 6858–6860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, P.; Wu, N. Fluorescence and Sensing Applications of Graphene Oxide and Graphene Quantum Dots: A Review. Chem. Asian J. 2017, 12, 2343–2353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelarakis, A. Graphene quantum dots: In the crossroad of graphene, quantum dots and carbogenic nanoparticles. Curr. Opin. Colloid Interface Sci. 2015, 20, 354–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Zhang, L.; Ding, Z.; Hu, J.; Liu, J.; Liu, Y. Edge-functionalized graphene quantum dots as a thickness-insensitive cathode interlayer for polymer solar cells. Nano Res. 2018, 11, 4293–4301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Zeng, H.; Sun, L. Graphene quantum dots: versatile photoluminescence for energy, biomedical, and environmental applications. J. Mater. Chem. C 2015, 3, 1157–1165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, K.; Liu, W.; Ni, Y.; Li, D.; Lin, D.; Su, Z.; Wei, G. Technical synthesis and biomedical applications of graphene quantum dots. J. Mater. Chem. B 2017, 5, 4811–4826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, S.; Xu, H.; Gan, W.; Yuan, Q. Graphene quantum dots: recent progress in preparation and fluorescence sensing applications. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 110775–110788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, X.T.; Ananthanarayanan, A.; Luo, K.Q.; Chen, P. Glowing graphene quantum dots and carbon dots: properties, syntheses, and biological applications. Small 2015, 11, 1620–1636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, L.B.; Ji, R.B.; Cao, X.K.; Lin, J.Y.; Jiang, H.X.; Li, X.M.; Teng, K.S.; Luk, C.M.; Zeng, S.J.; Hao, J.H.; et al. Deep Ultraviolet Photoluminescence of Water-Soluble Self-Passivated Graphene Quantum Dots. ACS Nano 2012, 6, 5102–5110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, Y.; Shao, J.; Chen, C.; Li, H.; Wang, R.; Chi, Y.; Lin, X.; Chen, G. Blue luminescent graphene quantum dots and graphene oxide prepared by tuning the carbonization degree of citric acid. Carbon 2012, 50, 4738–4743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, R.; Wu, D.; Feng, X.; Mullen, K. Bottom-up fabrication of photoluminescent graphene quantum dots with uniform morphology. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2011, 133, 15221–15223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, X.; Li, B.S.; Li, L.S. Colloidal Graphene Quantum Dots with Well-Defined Structures. Acc. Chem. Res. 2013, 46, 2254–2262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Sun, J.; Li, X.; Zhou, W.; Wang, Z.; He, P.; Ding, G.; Xie, X.; Kang, Z.; Jiang, M. Large-scale fabrication of heavy doped carbon quantum dots with tunable-photoluminescence and sensitive fluorescence detection. J. Mater. Chem. A 2014, 2, 8660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, D.; Zhang, J.; Li, Z.; Wu, M. Hydrothermal route for cutting graphene sheets into blue-luminescent graphene quantum dots. Adv. Mater. 2010, 22, 734–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, Y.; Park, J.; Hyun, D.; Yang, J.; Lee, J.H.; Kim, J.H.; Lee, H. Acid-free and oxone oxidant-assisted solvothermal synthesis of graphene quantum dots using various natural carbon materials as resources. Nanoscale 2015, 7, 5633–5637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahirwar, S.; Mallick, S.; Bahadur, D. Electrochemical method to prepare graphene quantum dots and graphene oxide quantum dots. ACS Omega 2017, 2, 8343–8353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, Y.; Hu, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Shi, G.; Deng, L.; Hou, Y.; Qu, L. An electrochemical avenue to green-luminescent graphene quantum dots as potential electron-acceptors for photovoltaics. Adv. Mater. 2011, 23, 776–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ananthanarayanan, A.; Wang, X.; Routh, P.; Sana, B.; Lim, S.; Kim, D.-H.; Lim, K.-H.; Li, J.; Chen, P. Facile Synthesis of Graphene Quantum Dots from 3D Graphene and their Application for Fe3+ Sensing. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2014, 24, 3021–3026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.J.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, C.; Wu, X.C.; Yang, Y.Q.; Zheng, B.; Wu, H.X.; Guo, S.W.; Zhang, J.Y. Photo-Fenton Reaction of Graphene Oxide: A new strategy to prepare graphene quantum dots for DNA cleavage. ACS Nano 2012, 6, 6592–6599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Z.; Li, Z.; Wu, Y.; Nan, J.; Wang, H.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, J.; Yang, B. Tuning the bandgap of graphene quantum dots by gold nanoparticle-assisted O2 plasma etching. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 97853–97860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Hnayn, R.; Canabady-Rochelle, L.; Desmarets, C.; Balan, L.; Rinnert, H.; Joubert, O.; Medjahdi, G.; Ouada, H.B.; Schneider, R. One-step synthesis of diamine-functionalized graphene quantum dots from graphene oxide and their chelating and antioxidant activities. Nanomaterials 2020, 10, 104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, G.; Zhuo, Z.; Ni, K.; Kim, N.Y.; Zhao, Y.; Chen, Z.; Xiang, B.; Yang, L.; Zhang, Q.; Lee, Z.; et al. Rupturing C60 molecules into graphene-oxide-like quantum dots: structure, photoluminescence, and catalytic application. Small 2015, 11, 5296–5304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Li, J.; Zeng, X.; Yuan, Z.; Zhao, N. Graphene quantum dots derived from hollow carbon nano-onions. Nano Res. 2018, 11, 174–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, J.; Gao, W.; Gupta, B.K.; Liu, Z.; Romero-Aburto, R.; Ge, L.; Song, L.; Alemany, L.B.; Zhan, X.; Gao, G.; et al. Graphene quantum dots derived from carbon fibers. Nano Lett. 2012, 12, 844–849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, R.; Xiang, C.; Lin, J.; Peng, Z.; Huang, K.; Yan, Z.; Cook, N.P.; Samuel, E.L.; Hwang, C.C.; Ruan, G.; et al. Coal as an abundant source of graphene quantum dots. Nat. Commun. 2013, 4, 2943–2948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Y.; Lin, J.; Chen, Y.; Fu, F.; Chi, Y.; Chen, G. Graphene quantum dots, graphene oxide, carbon quantum dots and graphite nanocrystals in coals. Nanoscale 2014, 6, 7410–7415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.; Jang, M.H.; Ha, H.D.; Kim, J.H.; Cho, Y.H.; Seo, T.S. Facile synthetic method for pristine graphene quantum dots and graphene oxide quantum dots: origin of blue and green luminescence. Adv. Mater. 2013, 25, 3657–3662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Yu, J.; Zhang, X.; Li, N.; Liu, B.; Li, Y.; Wang, Y.; Wang, W.; Li, Y.; Zhang, L.; et al. Large-scale and controllable synthesis of graphene quantum dots from rice husk biomass: a comprehensive utilization strategy. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2016, 8, 1434–1439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, S.F.; Liu, F.X.; Chen, G.H. Effective production of nano-sized graphene via straight-forward exfoliation of microcrystalline graphite. RSC Adv. 2014, 4, 45885–45889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Huang, J.; Yan, R.; Wang, F.; Cheng, W.; Guo, Q.; Wang, J. Graphene microsheets from natural microcrystalline graphite minerals: scalable synthesis and unusual energy storage. J. Mater. Chem. A 2015, 3, 3144–3150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Z.; Tang, Z.; Li, P.; Yang, G.; Zheng, Q.; Yang, J. Ammonia solution strengthened three-dimensional macro-porous graphene aerogel. Nanoscale 2013, 5, 5462–5467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.Q.; Lu, C.J.; Xia, Z.P.; Zhou, Y.; Luo, Z. X-ray diffraction patterns of graphite and turbostratic carbon. Carbon 2007, 45, 1686–1695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dimiev, A.M.; Tour, J.M. Mechanism of graphene oxide formation. ACS Nano 2014, 8, 3060–3068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wasalathilake, K.C.; Galpaya, D.G.D.; Ayoko, G.A.; Yan, C. Understanding the structure-property relationships in hydrothermally reduced graphene oxide hydrogels. Carbon 2018, 137, 282–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
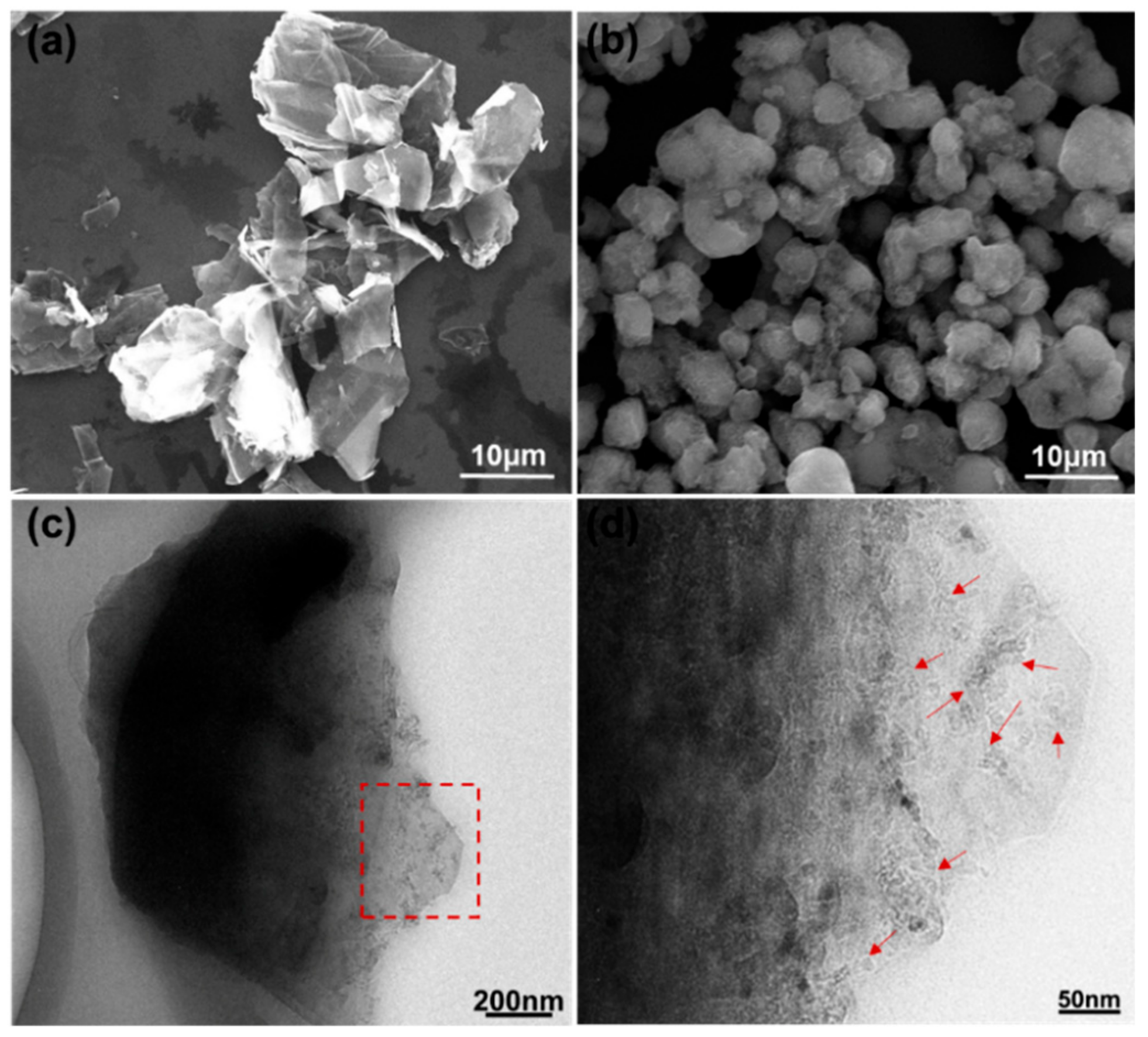






| Measurements | Pristine | After Intercalation | After Oxidation | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2θ(°) | AG | 26.5 | 26.4 | 10.7 |
| FG | 26.5 | 25.7 | 11.3 | |
| ID/IG | AG | 0.48 | 0.60 | 2.65 |
| FG | 0 | 0.71 | 1.31 | |
| Samples | τ1(ns) | A1(%) | τ2(ns) | A2(%) | Lifetime(ns) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| GO-QDs | 0.6056 | 75.95 | 2.5346 | 24.05 | 1.07 ns |
| GQDs-NH3·H2O | 2.1349 | 36.59 | 8.1989 | 63.41 | 5.98 ns |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Shen, S.; Wang, J.; Wu, Z.; Du, Z.; Tang, Z.; Yang, J. Graphene Quantum Dots with High Yield and High Quality Synthesized from Low Cost Precursor of Aphanitic Graphite. Nanomaterials 2020, 10, 375. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano10020375
Shen S, Wang J, Wu Z, Du Z, Tang Z, Yang J. Graphene Quantum Dots with High Yield and High Quality Synthesized from Low Cost Precursor of Aphanitic Graphite. Nanomaterials. 2020; 10(2):375. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano10020375
Chicago/Turabian StyleShen, Shuling, Junjie Wang, Zhujun Wu, Zheng Du, Zhihong Tang, and Junhe Yang. 2020. "Graphene Quantum Dots with High Yield and High Quality Synthesized from Low Cost Precursor of Aphanitic Graphite" Nanomaterials 10, no. 2: 375. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano10020375
APA StyleShen, S., Wang, J., Wu, Z., Du, Z., Tang, Z., & Yang, J. (2020). Graphene Quantum Dots with High Yield and High Quality Synthesized from Low Cost Precursor of Aphanitic Graphite. Nanomaterials, 10(2), 375. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano10020375




