Safe Administration of Carbon Nanotubes by Intravenous Pathway in BALB/c Mice
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Nanoparticles
2.2. Functionalization of P-CNTs
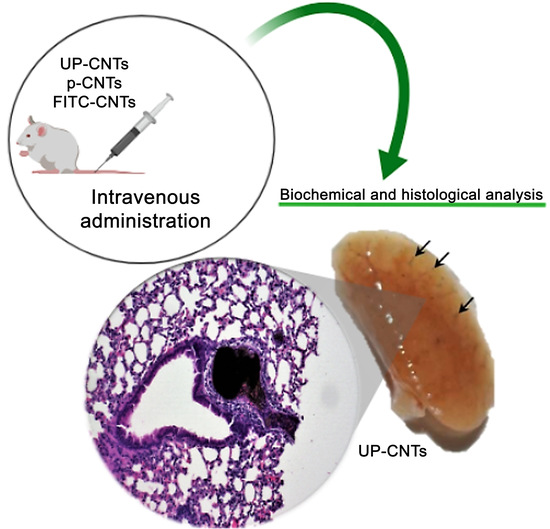
2.3. Animals and CNTs Administration
2.4. Histopathological Analysis
2.5. Biochemical Analysis
2.6. Statistical Analysis
2.7. Creative Images
3. Results
3.1. Nanoparticles Characterization
3.2. Morphological Findings
3.3. Biochemical Findings
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Ethics Approval and Consent to Participate
Consent for Publication
Availability of Data and Material
Competing Interests
Abbreviations
References
- Yang, S.; Wang, S.; Jia, G.; Gu, Y.; Wang, T.; Nie, H.; Ge, C.; Wang, H.; Liu, Y. Long-term accumulation and low toxicity of single-walled carbon nanotubes in intravenously exposed mice. Toxicol. Lett. 2008, 181, 182–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vardharajula, S.; Ali, S.Z.; Tiwari, P.M.; Eroğlu, E.; Vig, K.; Dennis, V.A.; Singh, S.R. Functionalized carbon nanotubes: Biomedical applications. Int. J. Nanomed. 2012, 7, 5361. [Google Scholar]
- Sajid, M.I.; Jamshaid, U.; Jamshaid, T.; Zafar, N.; Fessi, H.; Elaissari, A. Carbon nanotubes from synthesis to in vivo biomedical applications. Int. J. Pharm. 2016, 501, 278–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iijima, S. Helical microtubules of graphitic carbon. Nature 1991, 354, 56–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, R.; Pantarotto, D.; McCarthy, D.; Chaloin, O.; Hoebeke, J.; Partidos, C.D.; Briand, J.P.; Prato, M.; Bianco, A.; Kostarelos, K. Binding and condensation of plasmid DNA onto functionalized carbon nanotubes: Toward the construction of nanotube-based gene delivery vectors. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2005, 127, 4388–4396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, H. Carbon nanotubes: Synthesis, integration, and properties. Acc. Chem. Res. 2002, 35, 1035–1044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, P.M.; Bourgognon, M.; Wang, J.T.; Al-Jamal, K.T. Functionalised carbon nanotubes: From intracellular uptake and cell-related toxicity to systemic brain delivery. J. Control. Release 2016, 241, 200–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, Z.; Chen, K.; Davis, C.; Sherlock, S.; Cao, Q.; Chen, X.; Dai, H.J. Drug delivery with carbon nanotubes for in vivo cancer treatment. Cancer Res. 2008, 68, 6652–6660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kumar, S.; Rani, R.; Dilbaghi, N.; Tankeshwar, K.; Kim, K.-H. Carbon nanotubes: A novel material for multifaceted applications in human healthcare. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2017, 46, 158–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruggiero, A.; Villa, C.H.; Holland, J.P.; Sprinkle, S.R.; May, C.; Lewis, J.S.; Scheinberg, D.A.; McDevitt, M.R. Imaging and treating tumor vasculature with targeted radiolabeled carbon nanotubes. Int. J. Nanomed. 2010, 5, 783. [Google Scholar]
- Jia, G.; Wang, H.; Yan, L.; Wang, X.; Pei, R.; Yan, T.; Zhao, Y.; Guo, X. Cytotoxicity of carbon nanomaterials: Single-wall nanotube, multi-wall nanotube, and fullerene. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2005, 39, 1378–1383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, H.; Ni, Y.; Montana, V.; Haddon, R.C.; Parpura, V. Chemically functionalized carbon nanotubes as substrates for neuronal growth. Nano Lett. 2004, 4, 507–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yandar, N.; Pastorin, G.; Prato, M.; Bianco, A.; Patarroyo, M.E.; Lozano, J.M. Immunological profile of a Plasmodium vivax AMA-1 N-terminus peptide-carbon nanotube conjugate in an infected Plasmodium berghei mouse model. Vaccine 2008, 26, 5864–5873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kolosnjaj-Tabi, J.; Szwarc, H.; Moussa, F. In vivo toxicity studies of pristine carbon nanotubes: A review. In The delivery of Nanoparticles; Chapter (2); In Tech: Paris, France, 2012; pp. 37–58. [Google Scholar]
- Montes-Fonseca, S.L.; Orrantia-Borunda, E.; Duarte-Möller, A.; Luna-Velasco, A.; Román-Aguirre, M.; González-Horta, C.; Sánchez-Ramírez, B. Cytotoxicity of carbon nanotubes on J774 macrophages is a purification-dependent effect. J. Nanomater. 2012, 2012, 16–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montes-Fonseca, S.; Orrantia-Borunda, E.; Aguilar-Elguezabal, A.; Gonzalez-Horta, C.; Talamas-Rohana, P.; Sanchez-Ramirez, B. Cytotoxicity of functionalized carbon nanotubes in J774A macrophages. Nanomedicine 2012, 8, 853–859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montes-Fonseca, S.; Sánchez-Ramírez, B.; Luna-Velasco, A.; Arzate-Quintana, C.; Silva-Cazares, M.B.; González-Horta, C.; Orrantia-Borunda, E. Cytotoxicity of Protein-Carbon Nanotubes on J774 Macrophages Is a Functionalization Grade-Dependent Effect. BioMed Res. Int 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobayashi, N.; Izumi, H.; Morimoto, Y. Review of toxicity studies of carbon nanotubes. J. Occup. Health. 2017, 59, 394–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gref, R.; Domb, A.; Quellec, P.; Blunk, T.; Müller, R.; Verbavatz, J.; Langer, R. The controlled intravenous delivery of drugs using PEG-coated sterically stabilized nanospheres. Adv. Drug Delivery Rev. 1995, 16, 215–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Williams, J.; Lansdown, R.; Sweitzer, R.; Romanowski, M.; LaBell, R.; Ramaswami, R.; Unger, E. Nanoparticle drug delivery system for intravenous delivery of topoisomerase inhibitors. J. Control. Release 2003, 91, 167–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pardridge, W.M.; Wu, D.; Sakane, T. Combined use of carboxyl-directed protein pegylation and vector-mediated blood-brain barrier drug delivery system optimizes brain uptake of brain-derived neurotrophic factor following intravenous administration. Pharm. Res. 1998, 15, 576–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, R.; Lillard, J.W., Jr. Nanoparticle-based targeted drug delivery. Exp. Mol. Pathol. 2009, 86, 215–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bai, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, J.; Mu, Q.; Zhang, W.; Butch, E.R.; Snyder, S.E.; Yan, B. Repeated administrations of carbon nanotubes in male mice cause reversible testis damage without affecting fertility. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2010, 5, 683–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schipper, M.L.; Nakayama-Ratchford, N.; Davis, C.R.; Kam, N.W.S.; Chu, P.; Liu, Z.; Sun, X.; Dai, H.; Gambhir, S.S. A pilot toxicology study of single-walled carbon nanotubes in a small sample of mice. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2008, 3, 216–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ema, M.; Gamo, M.; Honda, K. A review of toxicity studies of single-walled carbon nanotubes in laboratory animals. Regul. Toxicol. Pharm. 2016, 74, 42–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, J.; Zhang, X.; Li, Q.; Li, W. Biodistribution of functionalized multiwall carbon nanotubes in mice. Nucl. Med. Biol. 2007, 34, 579–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Riviere, J.E. Pharmacokinetics of nanomaterials: An overview of carbon nanotubes, fullerenes and quantum dots. Wiley Interdiscipl. Rev. Nanobiotechnol. 2009, 1, 26–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palomäki, J.; Välimäki, E.; Sund, J.; Vippola, M.; Clausen, P.A.; Jensen, K.A.; Savolainen, K.; Matikainen, S. Alenius Long, needle-like carbon nanotubes and asbestos activate the NLRP3 inflammasome through a similar mechanism. ACS Nano. 2011, 5, 6861–6870. [Google Scholar]
- Bhirde, A.A.; Patel, S.; Sousa, A.A.; Patel, V.; Molinolo, A.A.; Ji, Y.; Leapman, R.D.; Gutkind, J.S.; Rusling, J.F. Distribution and clearance of PEG-single-walled carbon nanotube cancer drug delivery vehicles in mice. Nanomedicine 2010, 5, 1535–1546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tejral, T.; Nagende, R.; Havel, J. Carbon nanotubes: Toxicological impact on human health and environment. Carbon 2009, 7, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Singh, V.; Kashyap, S.; Yadav, U.; Srivastava, A.; Singh, A.V.; Singh, R.K.; Singh, S.K.; Saxena, P.S. Nitrogen doped carbon quantum dots demonstrate no toxicity under in vitro conditions in a cervical cell line and in vivo in Swiss albino mice. Toxicol. Res. 2019, 8, 395–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, A.V.; Mehta, K.K.; Worley, K.; Dordick, J.S.; Kane, R.S.; Wan, L.Q. Carbon nanotube-induced loss of multicellular chirality on micropatterned substrate is mediated by oxidative stress. ACS Nano. 2014, 8, 2196–2205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Venkatesan, N.; Yoshimitsu, J.; Ito, Y.; Shibata, N.; Takada, K. Liquid filled nanoparticles as a drug delivery tool for protein therapeutics. Biomaterials 2005, 26, 7154–7163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aguilar-Elguezabal, A.; Antúnez, W.; Alonso, G.; Delgado, F.; Espinosa, F.; Miki-Yoshida, M. Study of carbon nanotubes synthesis by spray pyrolysis and model of growth. Diamond Relat. Mater. 2006, 15, 1329–1335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, H.; Bhowmik, P.; Zhao, B.; Hamon, M.A.; Itkis, M.E.; Haddon, R.C. Determination of the acidic sites of purified single-walled carbon nanotubes by acid-base titration. Chem. Phys. Lett. 2001, 345, 25–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Escobar-Chávez, J.J.; López-Cervantes, M.; Naik, A.; Kalia, Y.; Quintanar-Guerrero, D.; Ganem-Quintanar, A. Applications of thermo-reversible pluronic F-127 gels in pharmaceutical formulations. J. Pharm. Pharm. Sci. 2006, 9, 339–358. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Mutlu, G.M.; Budinger, G.S.; Green, A.A.; Urich, D.; Soberanes, S.; Chiarella, S.E.; Alheid, G.F.; McCrimmon, D.R.; Szleifer, I.; Hersam, M.C. Biocompatible nanoscale dispersion of single-walled carbon nanotubes minimizes in vivo pulmonary toxicity. Nano Lett. 2010, 10, 1664–1670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Iudicello, J.J.; Englehardt, J.D. A predictive Bayesian dose-response assessment for evaluating the toxicity of carbon nanotubes relative to crocidolite using a proposed emergent model. Hum. Ecol. Risk Assess. 2009, 15, 1168–1186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alford, R.; Simpson, H.M.; Duberman, J.; Hill, G.C.; Ogawa, M.; Regino, C.; Kobayashi, H.; Choyke, P.L. Toxicity of organic fluorophores used in molecular imaging: Literature review. Mol. Imag. 2009, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lu, N.; Sui, Y.; Tian, R.; Peng, Y.-Y. Adsorption of plasma proteins on single-walled carbon nanotubes reduced cytotoxicity and modulated neutrophil activation. Chem. Res. Toxicol. 2018, 31, 1061–1068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shvedova, A.A.; Kisin, E.R.; Mercer, R.; Murray, A.R.; Johnson, V.J.; Potapovich, A.I.; Tyurina, Y.Y.; Gorelik, O.; Arepalli, S.; Schwegler-Berry, D.; et al. Unusual inflammatory and fibrogenic pulmonary responses to single-walled carbon nanotubes in mice. Am. J. Physiol. Lung Cell. Mol. Physiol. 2005, 289, L698–L708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Salvador-Morales, C.; Townsend, P.; Flahaut, E.; Vénien-Bryan, C.; Vlandas, A.; Green, M.L.; Sim, R.B. Binding of pulmonary surfactant proteins to carbon nanotubes; potential for damage to lung immune defense mechanisms. Carbon 2007, 45, 607–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Christensen, P.J.; Goodman, R.E.; Pastoriza, L.; Moore, B.; Toews, G.B. Induction of lung fibrosis in the mouse by intratracheal instillation of fluorescein isothiocyanate is not T-cell-dependent. Am. J. Pathol. 1999, 155, 1773–1779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, Z.; Zhang, D.; Li, L.; Shen, X.; Deng, X.; Dong, L.; Wu, M.; Liu, Y. The hepatotoxicity of multi-walled carbon nanotubes in mice. Nanotechnology 2009, 20, 445101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bishop, M.L.; Fody, E.P.; Schoeff, L.E. Química Clínica: Principios, Procedimientos y Correlaciones, 5th ed.; Editorial McGraw-Hill: New York, NY, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Meng, L.; Zhang, X.; Lu, Q.; Fei, Z.; Dyson, P.J. Single walled carbon nanotubes as drug delivery vehicles: Targeting doxorubicin to tumors. Biomaterials 2012, 33, 1689–1698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warheit, D.B.; Laurence, B.R.; Reed, K.L.; Roach, D.H.; Reynolds, G.A.; Webb, T.R. Comparative pulmonary toxicity assessment of single-wall carbon nanotubes in rats. Toxicol. Sci. 2004, 77, 117–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]








| Groups | 24 h | 14 days | 29 days | 60 days |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Final body weight (g) | ||||
| CTL | 35.7 ± 1.9 | 27.3 ± 6.8 | 42.2 ± 4.4 | 38.6 ± 3.9 |
| UP-CNT | 38.1 ± 5.7 | 38.5 ± 2.6 * | 41.2 ± 2.8 | 40 ± 2.1 |
| P-CNT | 36.5 ± 5.6 | 37.8 ± 5.6 * | 44.2 ± 4.3 | 38.7 ± 2.9 |
| FITC-CNT | 37.15 ± 4.7 | 33.3 ± 1.6 | 37.7 ± 1.8 | 37.2 ± 3.2 |
| Body weight gain (g) | ||||
| CTL | –1.3 ± 0.9 | –1.53 ± 4.2 | 7.9 ± 2.07 | 5.8 ± 1.5 |
| UP-CNT | –1.1 ± 1.5 | 2.5 ± 1.08 | 2.12 ± 1.3 * | 10.15 ± 3.4 * |
| P-CNT | –0.8 ± 1.7 | 1.6 ± 1.2 | 10 ± 2.04 | 9.2 ± 2.1 |
| FITC-CNT | –1.8 ± 0.8 | 0.75 ± 2.6 | 7.2 ± 3.6 | 7.8 ± 3.6 |
| Biomarker | Time Post Exposure (Days) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 14 | 29 | 60 | |
| Urea (mg/dL) | 16.08 | 75.95 | 77.72 | 87.52 |
| Creatinine (mg/dL) | 2.91 | 1.79 | 0.30 | 0.34 |
| Urea/Creatinine Ratio * | 2.58 | 19.83 | 121.03 | 120.26 |
| Damage | Hepatic damage | Pre-renal kidney injury | Pre-renal/Hemorrhagic Status | |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Guzmán-Mendoza, J.J.; Montes-Fonseca, S.L.; Ramos-Martínez, E.; González-Horta, C.; Hernández-Rodríguez, P.d.C.; Orrantia-Borunda, E.; Chávez-Flores, D.; Sánchez-Ramírez, B. Safe Administration of Carbon Nanotubes by Intravenous Pathway in BALB/c Mice. Nanomaterials 2020, 10, 400. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano10020400
Guzmán-Mendoza JJ, Montes-Fonseca SL, Ramos-Martínez E, González-Horta C, Hernández-Rodríguez PdC, Orrantia-Borunda E, Chávez-Flores D, Sánchez-Ramírez B. Safe Administration of Carbon Nanotubes by Intravenous Pathway in BALB/c Mice. Nanomaterials. 2020; 10(2):400. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano10020400
Chicago/Turabian StyleGuzmán-Mendoza, José Jesús, Silvia Lorena Montes-Fonseca, Ernesto Ramos-Martínez, Carmen González-Horta, Pilar del Carmen Hernández-Rodríguez, Erasmo Orrantia-Borunda, David Chávez-Flores, and Blanca Sánchez-Ramírez. 2020. "Safe Administration of Carbon Nanotubes by Intravenous Pathway in BALB/c Mice" Nanomaterials 10, no. 2: 400. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano10020400
APA StyleGuzmán-Mendoza, J. J., Montes-Fonseca, S. L., Ramos-Martínez, E., González-Horta, C., Hernández-Rodríguez, P. d. C., Orrantia-Borunda, E., Chávez-Flores, D., & Sánchez-Ramírez, B. (2020). Safe Administration of Carbon Nanotubes by Intravenous Pathway in BALB/c Mice. Nanomaterials, 10(2), 400. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano10020400