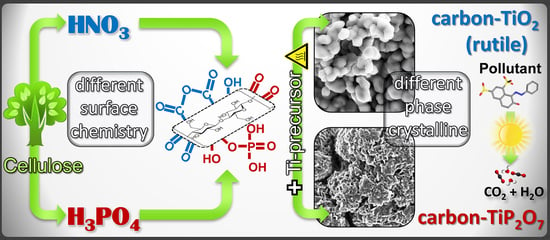
Functionalized Cellulose for the Controlled Synthesis of Novel Carbon–Ti Nanocomposites: Physicochemical and Photocatalytic Properties
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals
2.2. Synthesis of Carbon–Ti Composites
2.3. Characterization Techniques
2.4. Photocatalytic Tests
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Materials Characterization
3.2. Removal of Orange G (OG) Azo Dye
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Cai, M.-Q.; Zhu, Y.-Z.; Wei, Z.-S.; Hu, J.-Q.; Pan, S.-D.; Xiao, R.-Y.; Dong, C.-Y.; Jin, M.-C. Rapid decolorization of dye Orange G by microwave enhanced Fenton-like reaction with delafossite-type CuFeO2. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 580, 966–973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, F.; Chen, J.; Chen, L.; Huai, J.; Gong, W.; Yuan, Z.; Wang, J.; Ma, J. Magnetic carbon nanotubes synthesis by Fenton’s reagent method and their potential application for removal of azo dye from aqueous solution. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2012, 378, 175–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nath, R.K.; Zain, M.F.M.; Jamil, M. An environment-friendly solution for indoor air purification by using renewable photocatalysts in concrete: A review. Renew. Sust. Energ. Rev. 2016, 62, 1184–1194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bailón-García, E.; Elmouwahidi, A.; Álvarez, M.A.; Carrasco-Marín, F.; Pérez-Cadenas, A.F.; Maldonado-Hódar, F.J. New carbon xerogel-TiO2 composites with high performance as visible-light photocatalysts for dye mineralization. Appl. Catal. B-Environ. 2017, 201, 29–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujishima, A.; Honda, K. Electrochemical photolysis of water at a semiconductor electrode. Nature 1972, 238, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pelaez, M.; Nolan, N.T.; Pillai, S.C.; Seery, M.K.; Falaras, P.; Kontos, A.G.; Dunlop, P.S.M.; Hamilton, J.W.J.; Byrne, J.A.; O’Shea, K.; et al. A review on the visible light active titanium dioxide photocatalysts for environmental applications. Appl. Catal. B-Environ. 2012, 125, 331–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pastrana-Martínez, L.M.; Morales-Torres, S.; Likodimos, V.; Figueiredo, J.L.; Faria, J.L.; Falaras, P.; Silva, A.M.T. Advanced nanostructured photocatalysts based on reduced graphene oxide-TiO2 composites for degradation of diphenhydramine pharmaceutical and methyl orange dye. Appl. Catal. B-Environ. 2012, 123–124, 241–256. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, W.; Liu, Y.; Pei, X.; Chen, X. Effects of indium doping on properties of xIn-0.1%Gd-TiO2 photocatalyst synthesized by sol-gel method. J. Phys. Chem. Solids 2017, 104, 45–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iliev, V.; Tomova, D.; Bilyarska, L. Promoting the oxidative removal rate of 2,4-dichlorophenoxyacetic acid on gold-doped WO3/TiO2/reduced graphene oxide photocatalysts under UV light irradiation. J. Photochem. Photobiol. A 2018, 351, 69–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, W.C.; Ting, J.-M. Novel nitrogen-doped anatase TiO2 mesoporous bead photocatalysts for enhanced visible light response. Ceram. Int. 2017, 43, 9992–9997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brindha, A.; Sivakumar, T. Visible active N, S co-doped TiO2/graphene photocatalysts for the degradation of hazardous dyes. J. Photochem. Photobiol. A 2017, 340, 46–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seri-Levy, A.; Samuel, J.; Farin, D.; Avnir, D. Photoprocesses on Fractal Surfaces. In Studies in Surface Science and Catalysis; Anpo, M., Matsuura, T., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1989; Volume 47, pp. 353–374. [Google Scholar]
- Leary, R.; Westwood, A. Carbonaceous nanomaterials for the enhancement of TiO2 photocatalysis. Carbon 2011, 49, 741–772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morales-Torres, S.; Pastrana-Martínez, L.M.; Figueiredo, J.L.; Faria, J.L.; Silva, A.M.T. Design of graphene-based TiO2 photocatalysts-a review. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2012, 19, 3676–3687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li Puma, G.; Bono, A.; Krishnaiah, D.; Collin, J.G. Preparation of titanium dioxide photocatalyst loaded onto activated carbon support using chemical vapor deposition: A review paper. J. Hazard. Mater. 2008, 157, 209–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, C.G.; Faria, J.L. Photocatalytic oxidation of benzene derivatives in aqueous suspensions: Synergic effect induced by the introduction of carbon nanotubes in a TiO2 matrix. Appl. Catal. B 2010, 101, 81–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morales-Torres, S.; Pastrana-Martínez, L.M.; Figueiredo, J.L.; Faria, J.L.; Silva, A.M.T. Graphene oxide-P25 photocatalysts for degradation of diphenhydramine pharmaceutical and methyl orange dye. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2013, 275, 361–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rus, A.Z.M. Biopolymers for superhydrophobic photocatalytic coatings. In Biopolymers and Biotech Admixtures for Eco-Efficient Construction Materials; Pacheco-Torgal, F., Ivanov, V., Karak, N., Jonkers, H., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2016; pp. 421–447. [Google Scholar]
- Ananpattarachai, J.; Kajitvichyanukul, P. Enhancement of chromium removal efficiency on adsorption and photocatalytic reduction using a bio-catalyst, titania-impregnated chitosan/xylan hybrid film. J. Cleaner Prod. 2016, 130, 126–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohamed, M.A.; Mutalib, M.A.; Hir, Z.A.M.; Zain, M.F.M.; Mohamad, A.B.; Minggu, L.J.; Awang, N.A.; Salleh, W.N.W. An overview on cellulose-based material in tailoring bio-hybrid nanostructured photocatalysts for water treatment and renewable energy applications. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2017, 103, 1232–1256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ortelli, S.; Blosi, M.; Albonetti, S.; Vaccari, A.; Dondi, M.; Costa, A.L. TiO2 based nano-photocatalysis immobilized on cellulose substrates. J. Photochem. Photobiol. A 2014, 276, 58–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jallouli, N.; Elghniji, K.; Trabelsi, H.; Ksibi, M. Photocatalytic degradation of paracetamol on TiO2 nanoparticles and TiO2/cellulosic fiber under UV and sunlight irradiation. Arabian J. Chem. 2017, 10, S3640–S3645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Morawski, A.W.; Kusiak-Nejman, E.; Przepiórski, J.; Kordala, R.; Pernak, J. Cellulose-TiO2 nanocomposite with enhanced UV–Vis light absorption. Cellulose 2013, 20, 1293–1300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Thomas, M.; Naikoo, G.A.; Sheikh, M.U.D.; Bano, M.; Khan, F. Effective photocatalytic degradation of Congo red dye using alginate/carboxymethyl cellulose/TiO2 nanocomposite hydrogel under direct sunlight irradiation. J. Photochem. Photobiol. A 2016, 327, 33–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garusinghe, U.M.; Raghuwanshi, V.S.; Batchelor, W.; Garnier, G. Water Resistant Cellulose—Titanium Dioxide Composites for Photocatalysis. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 2306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hamad, H.; Bailón-García, E.; Morales-Torres, S.; Carrasco-Marín, F.; Pérez-Cadenas, A.F.; Maldonado-Hódar, F.J. Physicochemical properties of new cellulose-TiO2 composites for the removal of water pollutants: Developing specific interactions and performances by cellulose functionalization. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2018, 6, 5032–5041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Habibi, S.; Jamshidi, M. Sol–gel synthesis of carbon-doped TiO2 nanoparticles based on microcrystalline cellulose for efficient photocatalytic degradation of methylene blue under visible light. Environ. Technol. 2019, 1, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stoeckli, F. Porosity in Carbons. Characterization and Applications; Arnold: London, UK, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Bansal, R.C.; Donnet, J.B.; Stoeckli, F. Active Carbon; Marcel Dekker: New York, NY, USA, 1988. [Google Scholar]
- Barrett, E.P.; Joyner, L.G.; Halenda, P.P. The determination of pore volume and area distributions in porous substances. I. computations from nitrogen isotherms. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1951, 73, 373–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamad, H.; Bailón-García, E.; Maldonado-Hódar, F.J.; Pérez-Cadenas, A.F.; Carrasco-Marín, F.; Morales-Torres, S. Synthesis of TixOy nanocrystals in mild synthesis conditions for the degradation of pollutants under solar light. Appl. Catal. B. 2019, 241, 385–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miranda, M.I.G.; Bica, C.I.D.; Nachtigall, S.M.B.; Rehman, N.; Rosa, S.M.L. Kinetical thermal degradation study of maize straw and soybean hull celluloses by simultaneous DSC–TGA and MDSC techniques. Thermochim. Acta 2013, 565, 65–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dumanlı, A.G.; Windle, A.H. Carbon fibres from cellulosic precursors: A review. J. Mater. Sci. 2012, 47, 4236–4250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Figueiredo, J.L.; Pereira, M.F.R.; Freitas, M.M.A.; Órfão, J.J.M. Modification of the surface chemistry of activated carbons. Carbon 1999, 37, 1379–1389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prauchner, M.J.; Rodríguez-Reinoso, F. Chemical versus physical activation of coconut shell: A comparative study. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2012, 152, 163–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elmouwahidi, A.; Bailón-García, E.; Pérez-Cadenas, A.F.; Maldonado-Hódar, F.J.; Carrasco-Marín, F. Activated carbons from KOH and H3PO4-activation of olive residues and its application as supercapacitor electrodes. Electrochim. Acta 2017, 229, 219–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Rockstraw, D.A. Physical and chemical properties of carbons synthesized from xylan, cellulose, and Kraft lignin by H3PO4 activation. Carbon 2006, 44, 1464–1475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vivo-Vilches, J.F.; Bailón-García, E.; Pérez-Cadenas, A.F.; Carrasco-Marín, F.; Maldonado-Hódar, F.J. Tailoring the surface chemistry and porosity of activated carbons: Evidence of reorganization and mobility of oxygenated surface groups. Carbon 2014, 68, 520–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pastrana-Martínez, L.M.; Morales-Torres, S.; Likodimos, V.; Falaras, P.; Figueiredo, J.L.; Faria, J.L.; Silva, A.M.T. Role of oxygen functionalities on the synthesis of photocatalytically active graphene–TiO2 composites. Appl. Catal. B-Environ. 2014, 158–159, 329–340. [Google Scholar]
- Mohamed, M.A.; Wan Salleh, W.N.; Jaafar, J.; Rosmi, M.S.; Hir, Z.A.M.; Abd Mutalib, M.; Ismail, A.F.; Tanemura, M. Carbon as amorphous shell and interstitial dopant in mesoporous rutile TiO2: Bio-template assisted sol-gel synthesis and photocatalytic activity. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2017, 393, 46–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosas, J.M.; Bedia, J.; Rodríguez-Mirasol, J.; Cordero, T. HEMP-derived activated carbon fibers by chemical activation with phosphoric acid. Fuel 2009, 88, 19–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, L.; Yang, Y.; Xiao, M.; Bian, L.; Yuan, B.; Liu, Y.; Jiang, F.; Pan, X. A novel biotemplated synthesis of TiO2/wood charcoal composites for synergistic removal of bisphenol A by adsorption and photocatalytic degradation. Chem. Eng. J. 2015, 262, 1275–1283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreno-Castilla, C.; Maldonado-Hodar, F.J. Synthesis and surface characteristics of silica- and alumina-carbon composite xerogels. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2000, 2, 4818–4822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreno-Castilla, C.; Maldonado-Hódar, F.J.; Carrasco-Marín, F.; Rodríguez-Castellón, E. Surface Characteristics of Titania/Carbon Composite Aerogels. Langmuir 2002, 18, 2295–2299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khatun, N.; Anita; Rajput, P.; Bhattacharya, D.; Jha, S.N.; Biring, S.; Sen, S. Anatase to rutile phase transition promoted by vanadium substitution in TiO2: A structural, vibrational and optoelectronic study. Ceram. Int. 2017, 43, 14128–14134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Liang, R.; Hu, A.; Huang, Z.; Zhou, Y.N. Generation of oxygen vacancies in visible light activated one-dimensional iodine TiO2 photocatalysts. RSC Adv. 2014, 4, 36959–36966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muto, A.; Ida, K.; Bhaskar, T.; Uddin, M.A.; Takashima, S.; Hirai, T.; Sakata, Y. Preparation of novel TiP2O7 carbon composite using ion-exchanged resin (C467) and evaluation for photocatalytic decomposition of 2-propanol. Appl. Catal. A-Gen. 2004, 260, 163–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Gai, L.; Zhou, Y.; Zuo, X.; Zhou, J.; Jiang, H. Polyhierarchically structured TiP2O7/C microparticles with enhanced electrochemical performance for lithium-ion batteries. CrystEngComm 2014, 16, 10681–10691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patoux, S.; Masquelier, C. Lithium insertion into titanium phosphates, silicates, and sulfates. Chem. Mater. 2002, 14, 5057–5068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Da Silva Souza, D.R.; de Mesquita, J.P.; Lago, R.M.; Caminhas, L.D.; Pereira, F.V. Cellulose nanocrystals: A versatile precursor for the preparation of different carbon structures and luminescent carbon dots. Ind. Crop. Prod. 2016, 93, 121–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López, R.; Gómez, R. Band-gap energy estimation from diffuse reflectance measurements on sol–gel and commercial TiO2: A comparative study. J. Sol-Gel Sci. Technol. 2012, 61, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, X.; Hao, M.; Shi, J.; Cao, Z.; He, W.; Gao, Y.; Liu, J.; Li, Z. Novel visible light response Ag3PO4/TiP2O7 composite photocatalyst with low Ag consumption. Adv. Powder Technol. 2017, 28, 1047–1053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bailón-García, E.; Elmouwahidi, A.; Carrasco-Marín, F.; Pérez-Cadenas, A.F.; Maldonado-Hódar, F.J. Development of Carbon-ZrO2 composites with high performance as visible-light photocatalysts. Appl. Catal. B-Environ. 2017, 217, 540–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jose, M.; Harsha, N.; Suhailath, K.; Mohamed, A.P.; Shukla, S. Hydrogen phosphate anions modified hydrogen titanate nanotubes for methylene blue adsorption from aqueous solution: Validating novel method of predicting adsorption capacity. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2016, 4, 1295–1307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stylidi, M.; Kondarides, D.I.; Verykios, X.E. Pathways of solar light-induced photocatalytic degradation of azo dyes in aqueous TiO2 suspensions. Appl. Catal., B 2003, 40, 271–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lachheb, H.; Puzenat, E.; Houas, A.; Ksibi, M.; Elaloui, E.; Guillard, C.; Herrmann, J.-M. Photocatalytic degradation of various types of dyes (Alizarin S, Crocein Orange G, Methyl Red, Congo Red, Methylene Blue) in water by UV-irradiated titania. Appl. Catal., B 2002, 39, 75–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Wang, X.; Sun, J.; Sun, R.; Sun, S.; Qiao, L. Photocatalytic degradation and kinetics of Orange G using nano-sized Sn(IV)/TiO2/AC photocatalyst. J. Mol. Catal. A-Chem. 2006, 260, 241–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khataee, A.R.; Pons, M.N.; Zahraa, O. Photocatalytic degradation of three azo dyes using immobilized TiO2 nanoparticles on glass plates activated by UV light irradiation: Influence of dye molecular structure. J. Hazard. Mater. 2009, 168, 451–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jagadale, T.; Kulkarni, M.; Pravarthana, D.; Ramadan, W.; Thakur, P. Photocatalytic degradation of azo dyes using Au:TiO2, γ-Fe2O3:TiO2 functional nanosystems. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2012, 12, 928–936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hemalatha, K.; Ette, P.M.; Madras, G.; Ramesha, K. Visible light assisted photocatalytic degradation of organic dyes on TiO2–CNT nanocomposites. J. Sol-Gel Sci. Technol. 2015, 73, 72–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.-N.; Chen, Z.-Y.; Wang, M.-Q.; Zhang, L.-Z.; Bao, S.-J. Interface engineered construction of porous g-C3N4/TiO2 heterostructure for enhanced photocatalysis of organic pollutants. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2018, 440, 229–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anshuman, A.; Saremi-Yarahmadi, S.; Vaidhyanathan, B. Enhanced catalytic performance of reduced graphene oxide–TiO2 hybrids for efficient water treatment using microwave irradiation. RSC Adv. 2018, 8, 7709–7715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]








| Sample | pHPZC (±0.2) | Atomic Content (±0.1 wt. %) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| C | O | N | P | Ti | ||
| CPTi | n.d. | 8.5 | 47.3 | - | 26.8 | 17.4 |
| CPTi1 | 2.7 | 22.0 | 42.7 | - | 21.9 | 13.4 |
| CPTi2 | 2.8 | 27.3 | 36.4 | - | 22.8 | 13.5 |
| CNTi | n.d. | 18.7 | 36.2 | 1.2 | - | 43.9 |
| CNTi2 | 6.5 | 16.4 | 35.4 | - | - | 48.2 |
| Sample | SBET (±5 m2·g−1) | Smicro (±5 m2·g−1) | L0 (±0.1 nm) | W0 (±0.01 cm3·g−1) | Vmeso (±0.01 cm3·g−1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CP1 | 17 | 20 | 2.2 | 0.01 | 0.02 |
| CP2 | 552 | 624 | 1.5 | 0.22 | 0.07 |
| CN1 | 226 | 253 | 1.5 | 0.09 | 0.06 |
| CN2 | 115 | 122 | 1.7 | 0.04 | 0.06 |
| CPTi1 | 28 | 35 | 1.4 | 0.01 | 0.27 |
| CPTi2 | 30 | 48 | 1.8 | 0.02 | 0.35 |
| CNTi1 | 124 | 141 | 1.6 | 0.05 | 0.13 |
| CNTi2 | 319 | 360 | 1.5 | 0.13 | 0.34 |
| Material | OG Concentration | Irradiation Source | Removal (%) | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| TiO2 (Degussa P25) | 84.2 μM, 2.5 g/L catalyst | UV high-pressure mercury lamp | 100%, 120 min | [56] |
| Sn(IV)/TiO2/AC | 110.5 μM, 12.5 g/L catalyst | UV high-pressure mercury light | 99.1%, 60 min | [57] |
| TiO2 (99% anatase) on glass plates | 66.3 μM | UV lamp (λ = 365 nm) | 100%, 130 min | [58] |
| Au–TiO2 | 25 μM | UV low-pressure mercury lamp | 100%, 60 min | [59] |
| 10%CNT–TiO2 | 110.5 μM, 1 g/L catalyst | Metal halide lamp + cut-off filter (λ > 400 nm) | 100%, 120 min | [60] |
| CX–TiO2 | 55.3 μM, 1 g/L catalyst | Vis TeptoLux 2.0 lamp | 90%, 400 min | [4] |
| g-C3N4–TiO2 | 200 μM, 0.5 g/L | Simulated solar light (Xe Lamp) | 82%, 10 min | [61] |
| rGO–TiO2 | 10 μM | Microwave irradiation | 88%, 20 min | [62] |
| CNTi1 | 22 μM, 1.0 g/L | UV low-pressure mercury lamp | 99%, 40 min | This work |
| CPTi1 | 22 μM, 1.0 g/L | UV low-pressure mercury lamp | 100%, 40 min | This work |
| TiO2 (Degussa P25) | 22 μM, 1.0 g/L | UV low-pressure mercury lamp | 79%, 40 min | This work |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hamad, H.; Bailón-García, E.; Morales-Torres, S.; Carrasco-Marín, F.; Pérez-Cadenas, A.F.; Maldonado-Hódar, F.J. Functionalized Cellulose for the Controlled Synthesis of Novel Carbon–Ti Nanocomposites: Physicochemical and Photocatalytic Properties. Nanomaterials 2020, 10, 729. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano10040729
Hamad H, Bailón-García E, Morales-Torres S, Carrasco-Marín F, Pérez-Cadenas AF, Maldonado-Hódar FJ. Functionalized Cellulose for the Controlled Synthesis of Novel Carbon–Ti Nanocomposites: Physicochemical and Photocatalytic Properties. Nanomaterials. 2020; 10(4):729. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano10040729
Chicago/Turabian StyleHamad, Hesham, Esther Bailón-García, Sergio Morales-Torres, Francisco Carrasco-Marín, Agustín F. Pérez-Cadenas, and Francisco J. Maldonado-Hódar. 2020. "Functionalized Cellulose for the Controlled Synthesis of Novel Carbon–Ti Nanocomposites: Physicochemical and Photocatalytic Properties" Nanomaterials 10, no. 4: 729. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano10040729
APA StyleHamad, H., Bailón-García, E., Morales-Torres, S., Carrasco-Marín, F., Pérez-Cadenas, A. F., & Maldonado-Hódar, F. J. (2020). Functionalized Cellulose for the Controlled Synthesis of Novel Carbon–Ti Nanocomposites: Physicochemical and Photocatalytic Properties. Nanomaterials, 10(4), 729. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano10040729