Micromagnetic Simulations of Chaotic Ferromagnetic Nanofiber Networks
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Simulations
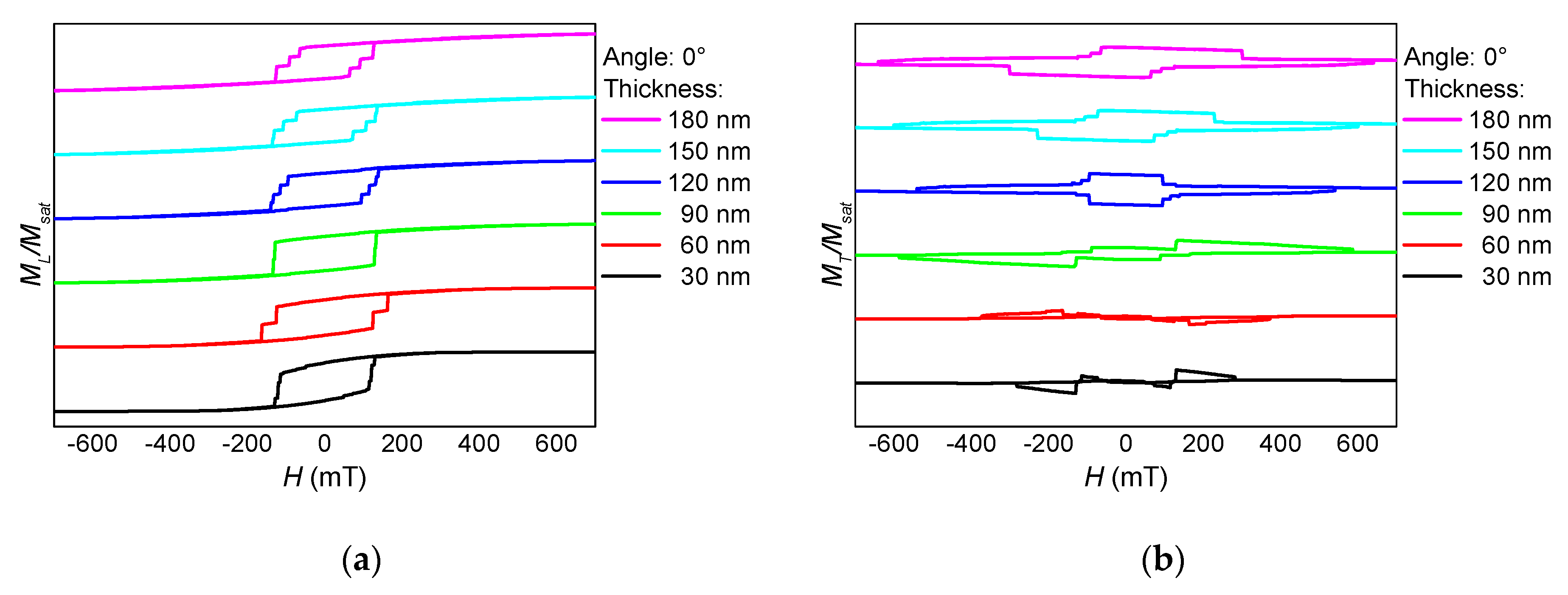
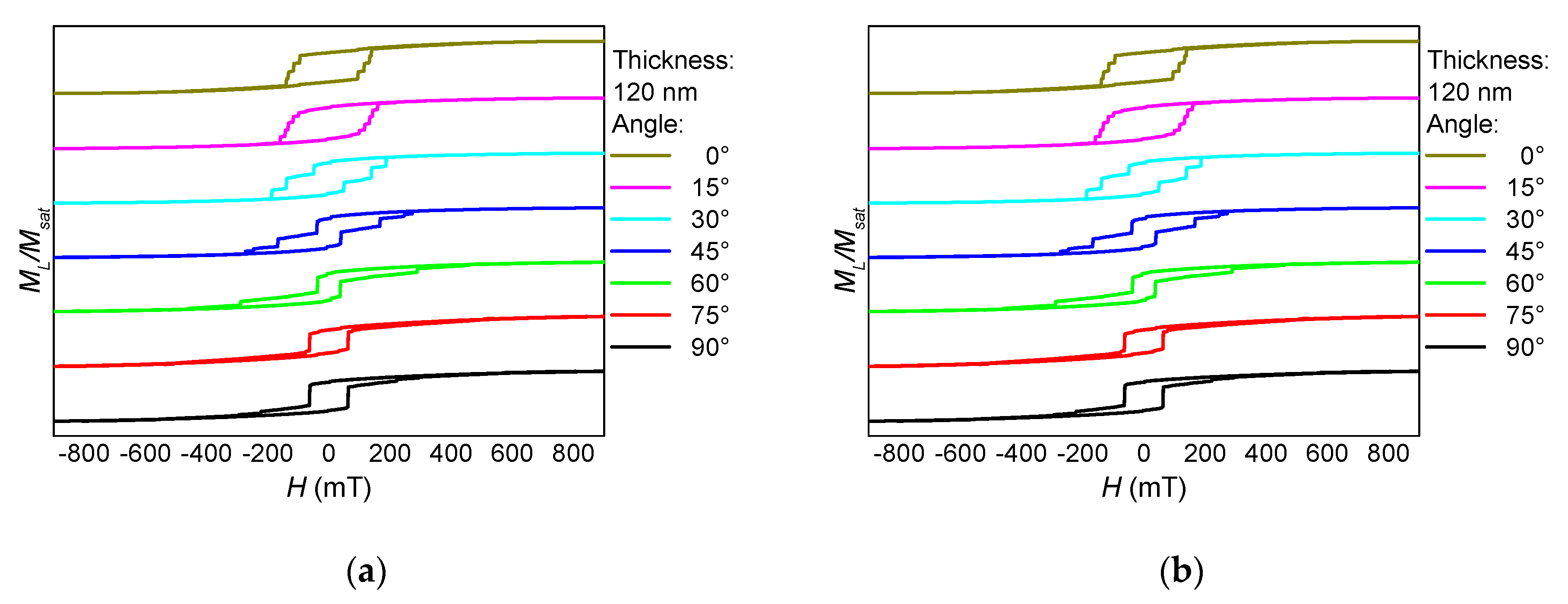
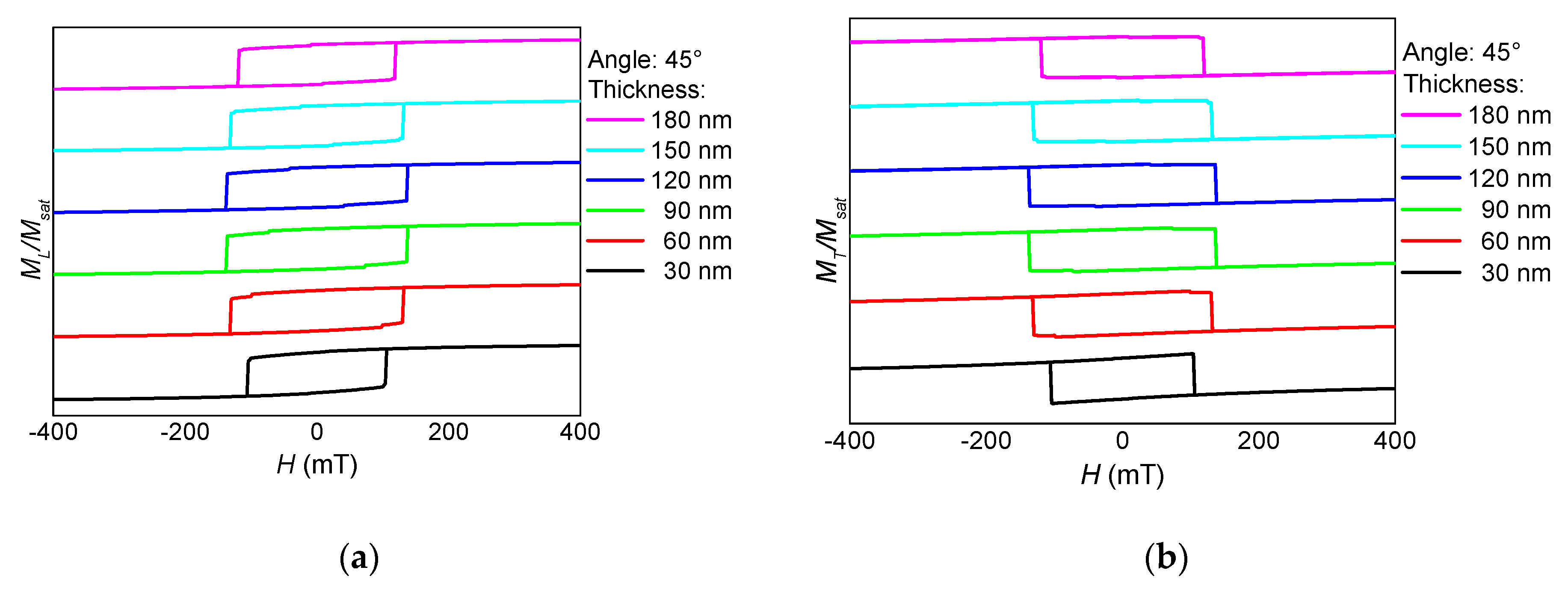
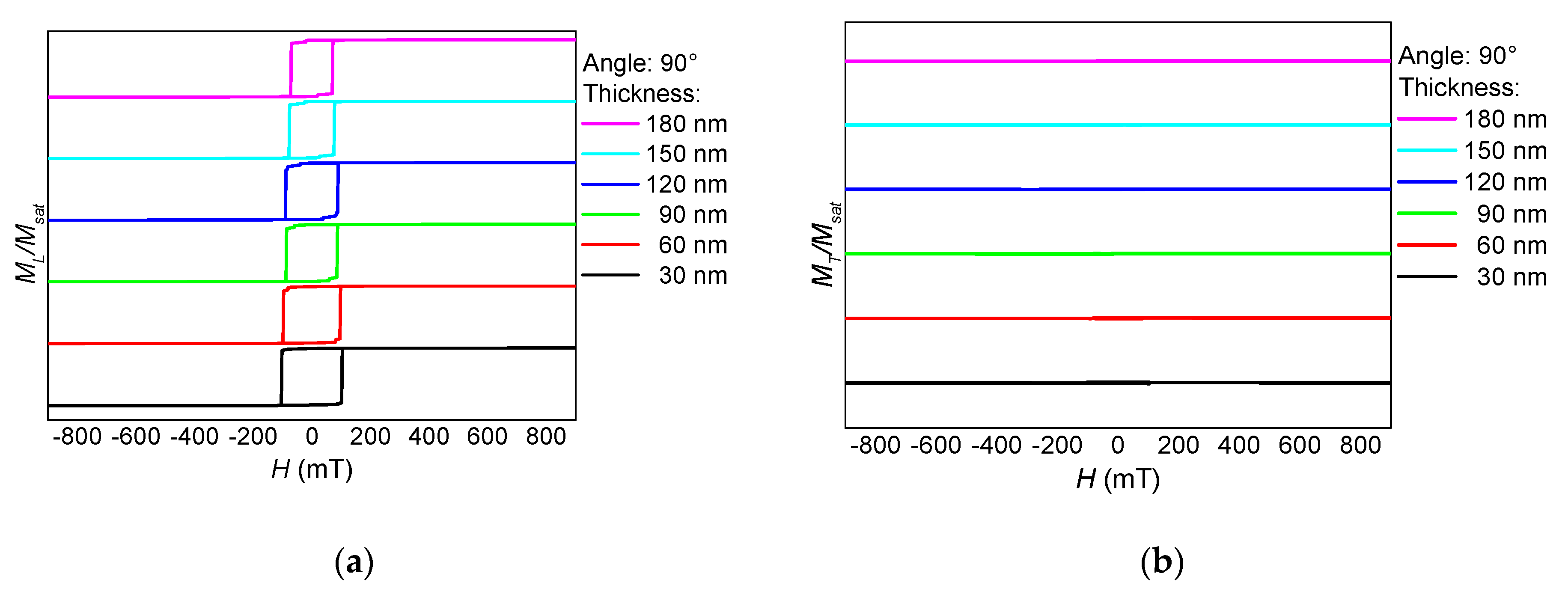
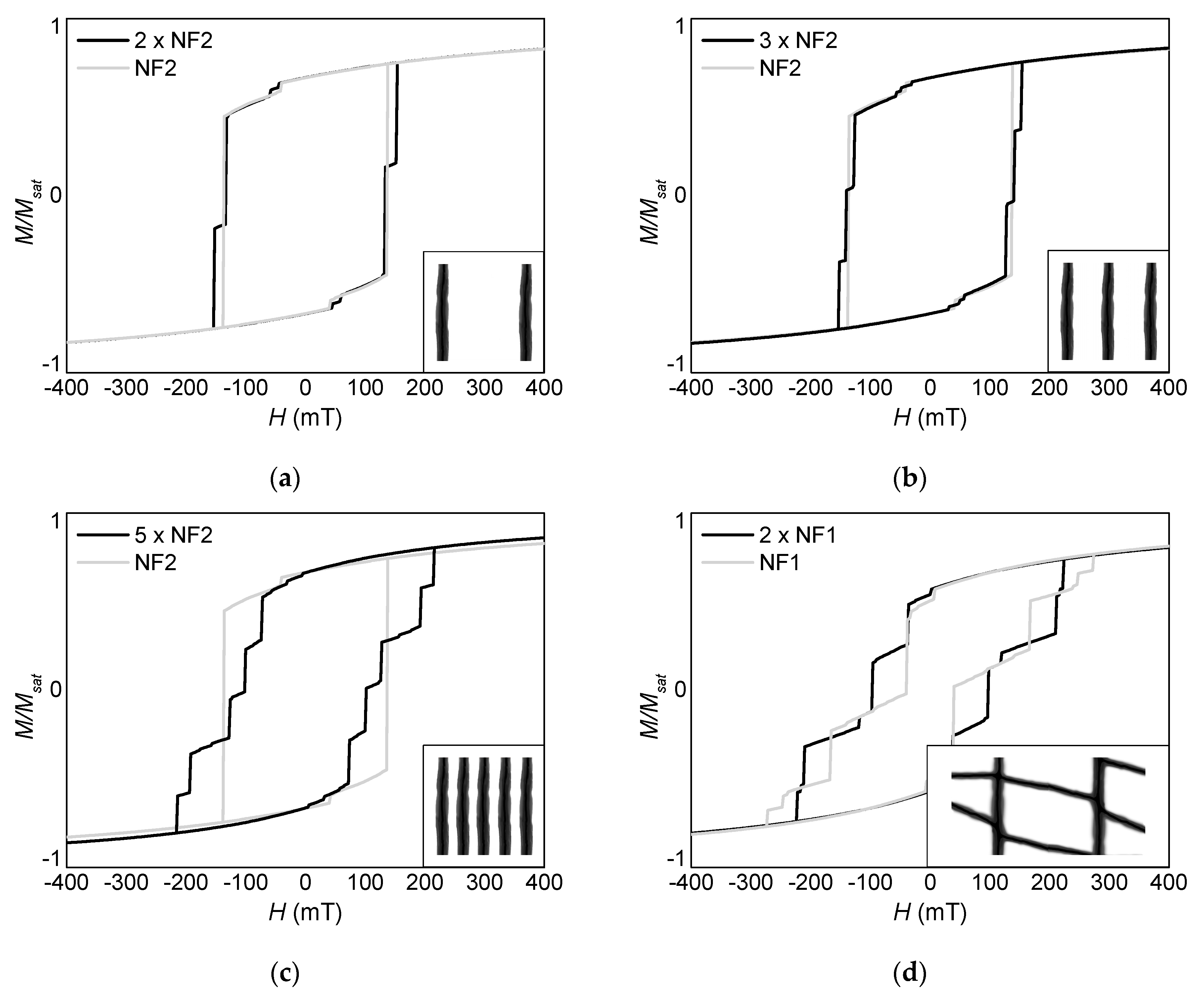
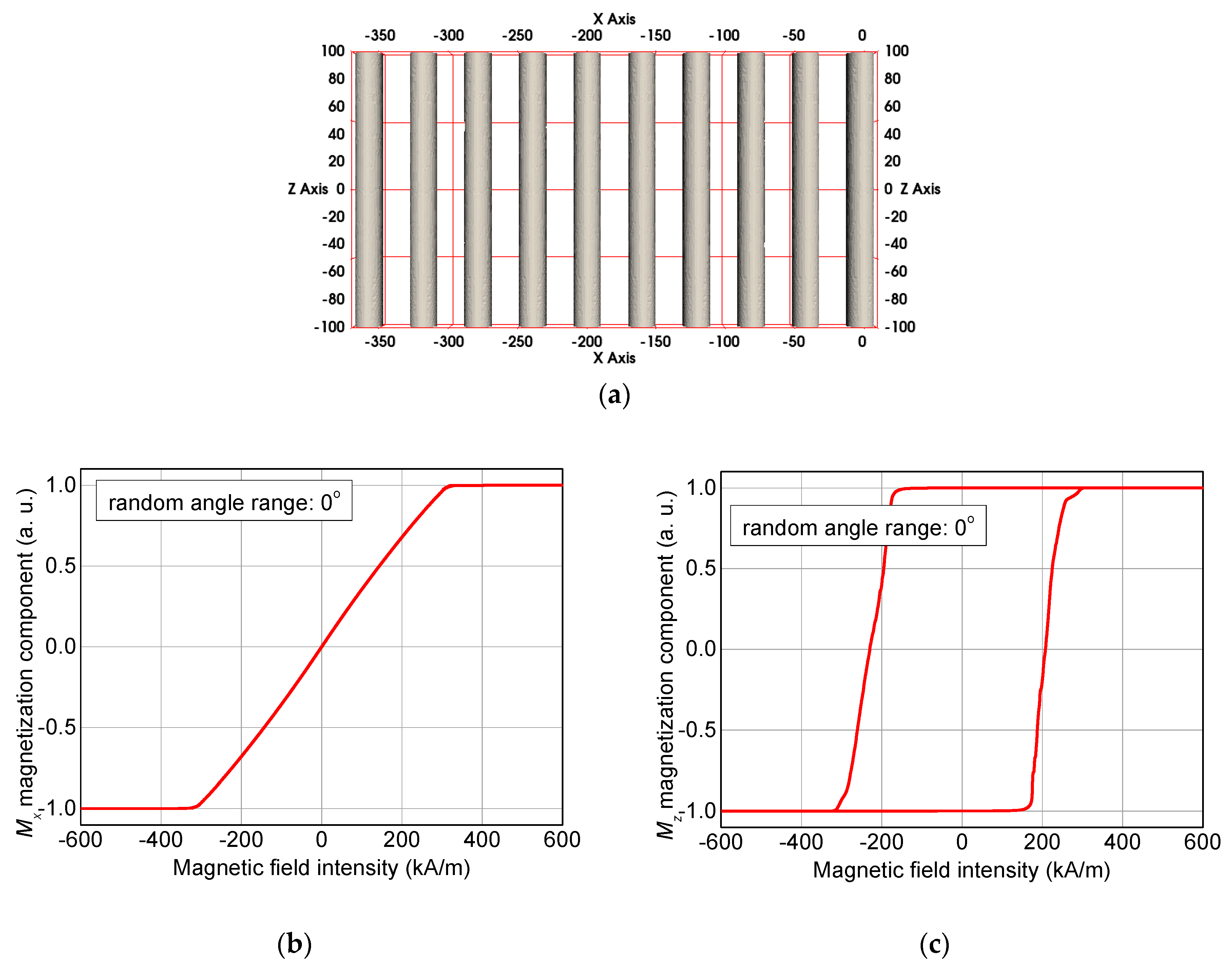
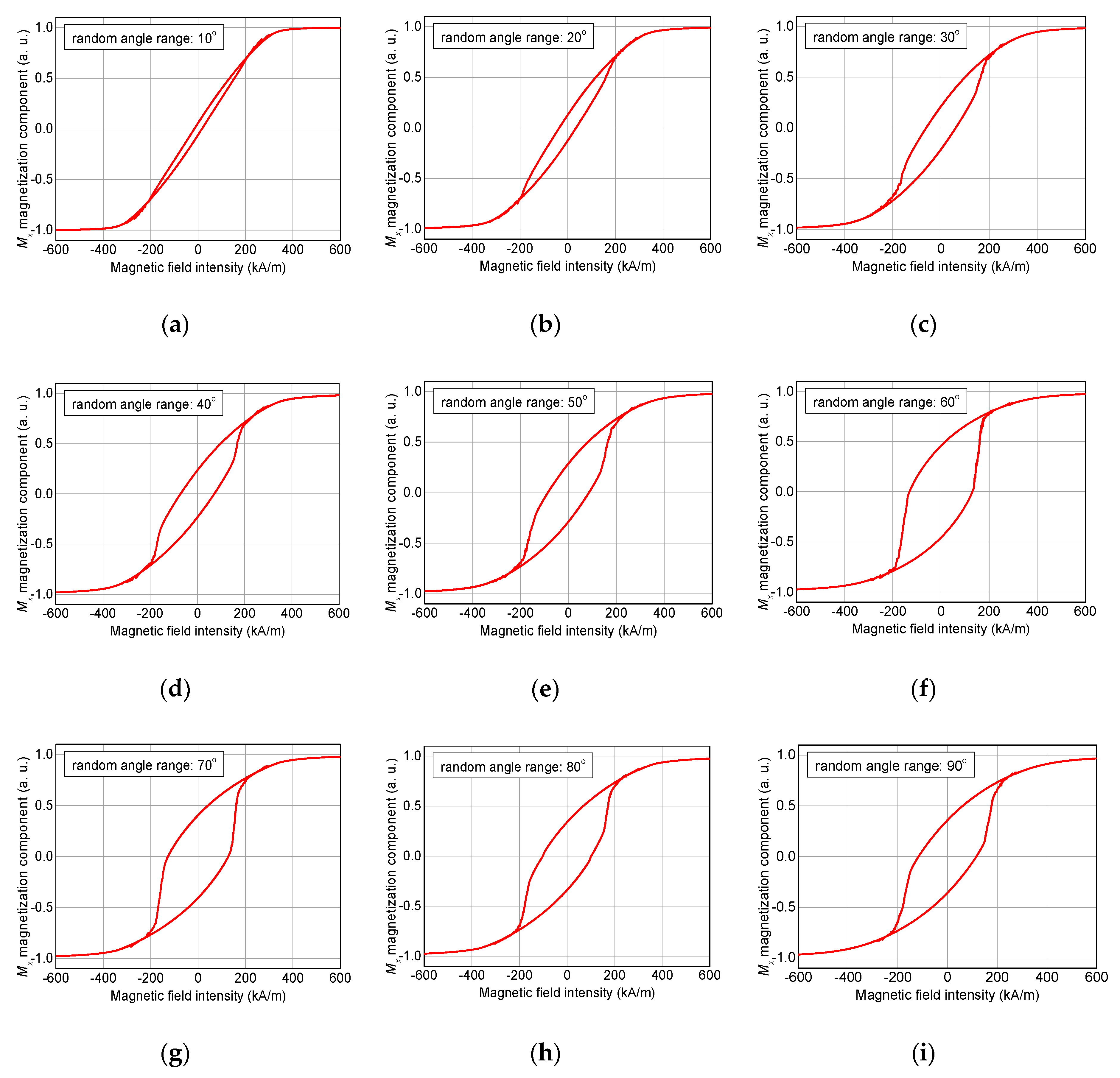
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Pan, J.-F.; Liu, N.-H.; Sun, H.; Xu, F. Preparation and Characterization of Electrospun PLCL/Poloxamer Nanofibers and Dextran/Gelatin Hydrogels for Skin Tissue Engineering. PLOS ONE 2014, 9, e112885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grothe, T.; Wehlage, D.; Böhm, T.; Remche, A.; Ehrmann, A. Needleless Electrospinning of PAN Nanofibre Mats. Tekstilec 2017, 60, 290–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maver, T.; Kurečič, M.; Smrke, D.M.; Kleinschek, K.S.; Maver, U. Electrospun nanofibrous CMC/PEO as a part of an effective pain-relieving wound dressing. J. Sol-Gel Sci. Technol. 2015, 79, 475–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grimmelsmann, N.; Grothe, T.; Homburg, S.V.; Ehrmann, A. Electrospinning and stabilization of chitosan nanofiber mats. IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2017, 254, 102006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salalha, W.; Dror, Y.; Khalfin, R.L.; Cohen, Y.; Yarin, A.L.; Zussman, E. Single-Walled Carbon Nanotubes Embedded in Oriented Polymeric Nanofibers by Electrospinning. Langmuir 2004, 20, 9852–9855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, J.-M.; Moon, J.H.; Yi, G.-R.; Heo, C.-J.; Yang, S.-M. Fabrication of One-Dimensional Colloidal Assemblies from Electrospun Nanofibers. Langmuir 2006, 22, 3445–3449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Na, K.-H.; Kim, W.-T.; Park, D.-C.; Shin, H.-G.; Lee, S.-H.; Park, J.; Song, T.-H.; Choi, W.-Y. Fabrication and characterization of the magnetic ferrite nanofibers by electrospinning process. Thin Solid Films 2018, 660, 358–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Döpke, C.; Grothe, T.; Steblinski, P.; Klöcker, M.; Sabantina, L.; Kosmalska, D.; Blachowicz, T.; Ehrmann, A. Magnetic Nanofiber Mats for Data Storage and Transfer. Nanomaterials 2019, 9, 92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryu, K.-S.; Thomas, L.; Yang, S.-H.; Parkin, S.S.P. Current Induced Tilting of Domain Walls in High Velocity Motion along Perpendicularly Magnetized Micron-Sized Co/Ni/Co Racetracks. Appl. Phys. Express 2012, 5, 093006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.-H.; Ryu, K.-S.; Parkin, S. Domain-wall velocities of up to 750 m s−1 driven by exchange-coupling torque in synthetic antiferromagnets. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2015, 10, 221–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alejos, O.; Raposo, V.; Sánchez-Tejerina, L.; Martínez, E. Efficient and controlled domain wall nucleation for magnetic shift registers. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 11909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garg, C.; Yang, S.-H.; Phung, T.; Pushp, A.; Parkin, S.S.P. Dramatic influence of curvature of nanowire on chiral domain wall velocity. Sci. Adv. 2017, 3, e1602804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blachowicz, T.; Ehrmann, A. Magnetization reversal in bent nanofibers of different cross sections. J. Appl. Phys. 2018, 124, 152112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kern, P.; Döpke, C.; Blachowicz, T.; Steblinski, P.; Ehrmann, A. Magnetization reversal in ferromagnetic Fibonacci nano-spirals. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2019, 484, 37–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Crandall, C.; Sahadevan, R.; Menkhaus, T.; Fong, H. Microfiltration performance of electrospun nanofiber membranes with varied fiber diameters and different membrane porosities and thicknesses. Polymer 2017, 114, 64–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yalcinkaya, F.; Hruza, J. Effect of Laminating Pressure on Polymeric Multilayer Nanofibrous Membranes for Liquid Filtration. Nanomaterials 2018, 8, 272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tripathy, M.; Hota, G. Maghemite and Graphene Oxide Embedded Polyacrylonitrile Electrospun Nanofiber Matrix for Remediation of Arsenate Ions. ACS Appl. Polym. Mater. 2019, 2, 604–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fokin, N.; Grothe, T.; Mamun, A.; Trabelsi, M.; Klöcker, M.; Sabantina, L.; Döpke, C.; Blachowicz, T.; Hütten, A.; Ehrmann, A. Magnetic Properties of Electrospun Magnetic Nanofiber Mats after Stabilization and Carbonization. Materials 2020, 13, 1552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bica, I.; Anitas, E.M.; Choi, H.; Sfirloaga, P. Microwave-assisted synthesis and characterization of iron oxide microfibers. J. Mater. Chem. C 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petropoulou, A.; Kralj, S.; Karagiorgis, X.; Savva, I.; Loizides, E.; Panagi, M.; Krasia-Christoforou, T.; Riziotis, C. Multifunctional Gas and pH Fluorescent Sensors Based on Cellulose Acetate Electrospun Fibers Decorated with Rhodamine B-Functionalised Core-Shell Ferrous Nanoparticles. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.J.; Sun, Y.; Zong, Y.; Zhu, T.G.; Zhang, L.X.; Li, X.H.; Xing, H.N.; Zheng, X.L. Carbon nanofibers supported by FeCo nanocrystals as difunctional magnetic/dielectric composites with broadband microwave absorption performance. J. Allows Compd. 2020, 824, 153980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, J.; Guo, H.; Wang, M.; Yang, H.; Hu, H.; Liu, P.; Zhu, H. Shape anisotropic Fe3O4 nanotubes for efficient microwave absorption. Nano Res. 2020, 13, 621–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhugra, V.S.; Williams, G.V.M.; Chong, S.V.; Nann, T. Electrospun, oriented, ferromagnetic Ni1-xFex nanofibers. Front. Chem. 2020, 8, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zambano, A.J.; Pratt, W.P. Detecting domain-wall trapping and motion at a constriction in narrow ferromagnetic wires using perpendicular-current giant magnetoresistance. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2004, 85, 1562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nasirpouri, F.; Peighambari-Sattari, S.-M.; Bran, C.; Palmero, E.M.; Eguiarte, E.B.; Vazquez, M.; Patsopoulos, A.; Kechrakos, D. Geometrically designed domain wall trap in tri-segmented nickel magnetic nanowires for spintronics devices. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 9010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbas, N.; Wang, F.; Ren, H.; Liu, J.P.; Xia, W.; Du, J.; Zhao, G.; Zhang, J. Determination of interface layer effects on magnetic properties of nanocomposite magnets and exchange coupling between magnetic entities. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2019, 480, 454–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donahue, M.J.; Porter, D.G. OOMMF User’s Guide, version 1.0; National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST): Gaithersburg, MD, USA, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Ehrmann, A.; Blachowicz, T. Vortex and double-vortex nucleation during magnetization reversal in Fe nanodots of different dimensions. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2019, 475, 727–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blachowicz, T.; Döpke, C.; Ehrmann, A. Micromagnetic Simulations of Electrospun Nanofiber Networks; Works of the Institute of Engineering Materials and Biomedical Materials, Silesian University of Technology: Gliwice, Poland, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Scholz, W.; Fidler, J.; Schrefl, T.; Suess, D.; Dittrich, R.; Forster, H.; Tsiantos, V. Scalable parallel micromagnetic solvers for magnetic nanostructures. Comput. Mater. Sci. 2003, 28, 366–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blachowicz, T.; Ehrmann, A. Fourfold nanosystems for quaternary storage devices. J. Appl. Phys. 2011, 110, 73911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stoner, E.C.; Wohlfarth, E.P. A mechanism of magnetic hysteresis in heterogeneous alloys. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. London. Ser. A Math. Phys. Sci. 1948, 240, 599–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabantina, L.; Rodríguez-Cano, M.Á.; Klöcker, M.; Mateos, F.J.G.; Hidalgo, J.J.T.; Mamun, A.; Beermann, F.; Schwakenberg, M.; Voigt, A.-L.; Rodríguez-Mirasol, J.; et al. Fixing PAN Nanofiber Mats during Stabilization for Carbonization and Creating Novel Metal/Carbon Composites. Polymers 2018, 10, 735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]








© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Blachowicz, T.; Döpke, C.; Ehrmann, A. Micromagnetic Simulations of Chaotic Ferromagnetic Nanofiber Networks. Nanomaterials 2020, 10, 738. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano10040738
Blachowicz T, Döpke C, Ehrmann A. Micromagnetic Simulations of Chaotic Ferromagnetic Nanofiber Networks. Nanomaterials. 2020; 10(4):738. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano10040738
Chicago/Turabian StyleBlachowicz, Tomasz, Christoph Döpke, and Andrea Ehrmann. 2020. "Micromagnetic Simulations of Chaotic Ferromagnetic Nanofiber Networks" Nanomaterials 10, no. 4: 738. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano10040738
APA StyleBlachowicz, T., Döpke, C., & Ehrmann, A. (2020). Micromagnetic Simulations of Chaotic Ferromagnetic Nanofiber Networks. Nanomaterials, 10(4), 738. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano10040738






