The Applicability of a Drop Penetration Method to Measure Contact Angles on TiO2 and ZnO Nanoparticles
Abstract
1. Introduction
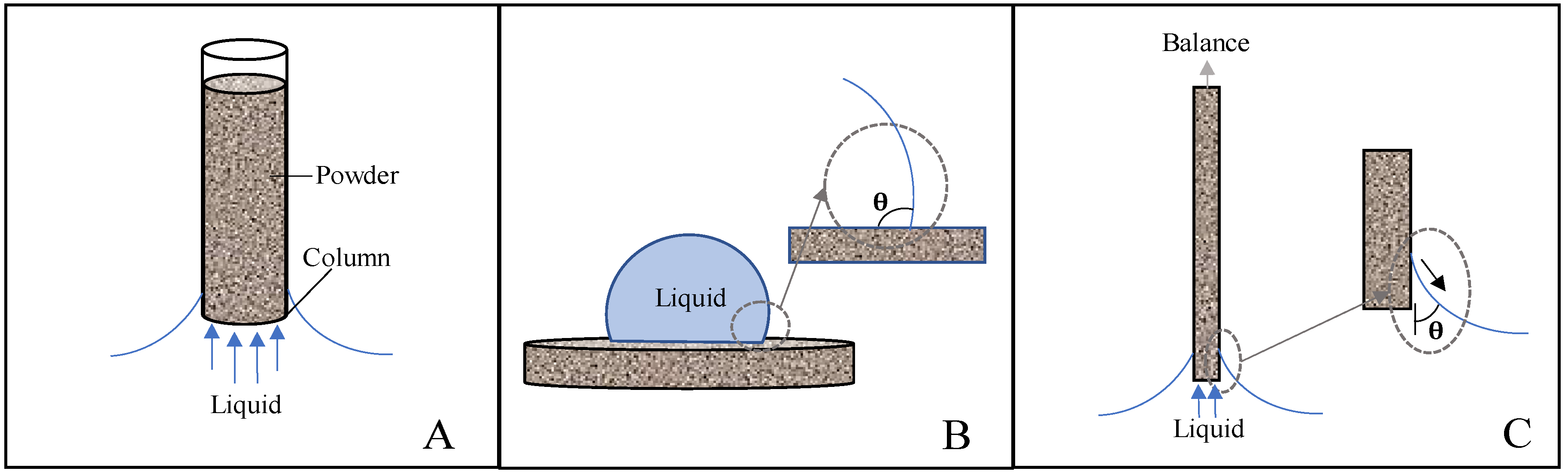
Theory
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Nanoparticle Powders
2.2. Fabrication of Specimens
2.3. Solvents
2.4. Contact Angle Measurements
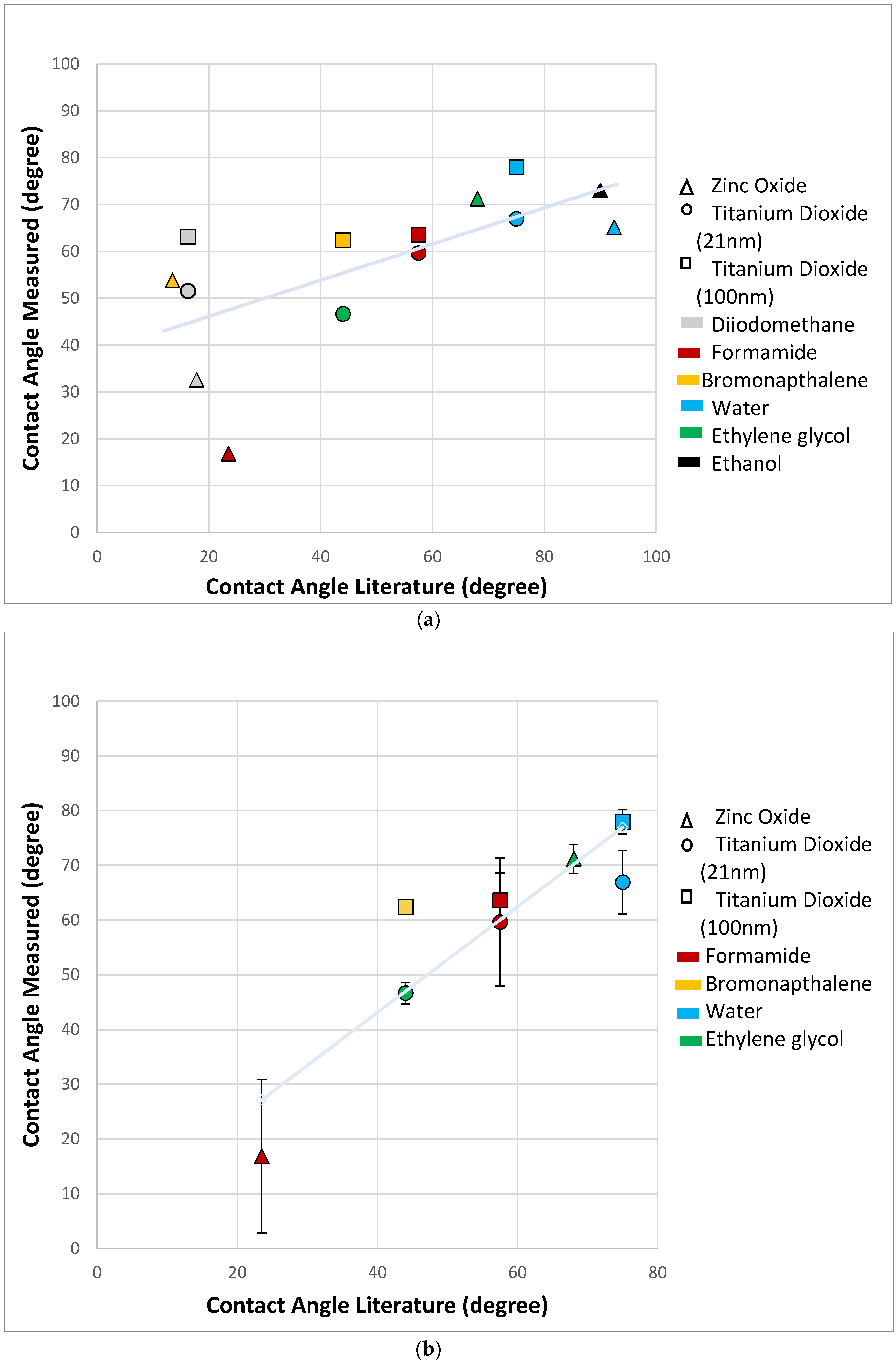
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Jaine, J.E.; Mucalo, M.R. Measurements of the wettability of catalyst support materials using the Washburn capillary rise technique. Powder Technol. 2015, 276, 123–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lefebvre, G.; Galet, L.; Chamayou, A. Dry coating of talc particles with fumed silica: Influence of the silica concentration on the wettability and dispersibility of the composite particles. Powder Technol. 2011, 208, 372–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, L.; Shi, B. A novel method for determining surface free energy of powders using Washburn’s equation without calculating capillary factor and contact angle. Powder Technol. 2015, 271, 88–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Da-Silva, N.S.; Marciano, F.; Lobo, A.O.; Trava-Airoldi, V.; Pacheco-Soares, C.; Wachesk, C.C. Thermodynamic aspects of fibroblastic spreading on diamond-like carbon films containing titanium dioxide nanoparticles. Theor. Chem. Acc. 2011, 130, 1085–1093. [Google Scholar]
- Barnard, A.S.; Zapol, P.; Curtiss, L.A. Modeling the morphology and phase stability of TiO2 nanocrystals in water. J. Chem. Theory Comput. 2005, 1, 107–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dzwigaj, S.; Arrouvel, C.; Breysse, M.; Geantet, C.; Inoue, S.; Toulhoat, H.; Raybaud, P. DFT makes the morphologies of anatase-TiO2 nanoparticles visible to IR spectroscopy. J. Catal. 2005, 236, 245–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buckton, G.; Newton, J.M. Assessment of the wettability of powders by use of compressed powder discs. Powder Technol. 1986, 46, 201–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Honda, R.J.; Keene, V.; Daniels, L.; Walker, S.L. Removal of TiO2 nanoparticles during primary water treatment: Role of coagulant type, dose, and nanoparticle concentration. Environ. Eng. Sci. 2014, 31, 127–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berdan, A.S.; Luke, H. Antibacterial activity of dental composites containing zinc oxide nanoparticles. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. Part B Appl. Biomater. 2010, 94B, 22–31. [Google Scholar]
- Shen, M.; Liang, G.; Gu, A.; Yuan, L. Development of high performance dental resin composites with outstanding antibacterial activity, high mechanical properties and low polymerization shrinkage based on a SiO2 hybridized tetrapod-like zinc oxide whisker with C-C bonds. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 56353–56364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez-Díaz, M.A.; Boegli, L.; James, G.; Velasquillo, C.; Sánchez-Sánchez, R.; Martínez-Martínez, R.E.; Martínez-Castañón, G.A.; Martinez-Gutierrez, F. Silver nanoparticles with antimicrobial activities against Streptococcus mutans and their cytotoxic effect. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2015, 55, 360–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hojati, S.T.; Alaghemand, H.; Hamze, F.; Babaki, F.A.; Rajab-Nia, R.; Rezvani, M.B.; Kaviani, M.; Atai, M. Antibacterial, physical and mechanical properties of flowable resin composites containing zinc oxide nanoparticles. Dent. Mater. 2013, 29, 495–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Florez, F.L.; Hiers, R.D.; Larson, P.; Johnson, M.; O’Rear, E.; Rondinone, A.J.; Khajotia, S.S. Antibacterial dental adhesive resins containing nitrogen-doped titanium dioxide nanoparticles. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2018, 93, 931–943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Good, R.J.; van Oss, C.J. Modern Approaches to Wettability: Theory and Applications; Springer Science & Business Media: Boston, MA, USA, 1992. [Google Scholar]
- Redzuan, M.; Tripathy, M.; Majeed, A. Solubility enhancement of simvastatin and atorvastatin by arginine: Contact angle determination, wettability and surface energy characteristics. J. Mol. Liq. 2017, 240, 340–344. [Google Scholar]
- van Oss, C.J.; Chaudhury, M.K.; Good, R.J. Monopolar surfaces. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 1987, 28, 35–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alghunaim, A.; Kirdponpattara, S.; Newby, B.Z. Techniques for determining contact angle and wettability of powders. Powder Technol. 2016, 287, 201–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, J.S.; Lee, J.; Chang, Y.H. Surface properties of silane-treated titania nanoparticles and their rheological behavior in silicone oil. Macromol. Res. 2005, 13, 409–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durán, J.D.G.; Delgado, A.V.; González-Caballero, F.; Chibowski, E. Surface free energy components of monodisperse zinc sulfide. Mater. Chem. Phys. 1994, 38, 42–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Oss, C.J.; Giese, R.F.; Li, Z.; Murphy, K.; Norris, J.; Chaudhury, M.K.; Good, R.J. Determination of contact angles and pore sizes of porous media by column and thin layer wicking. J. Adhes. Sci. Technol. 1992, 6, 413–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramírez-Flores, J.C.; Bachmann, J. Analyzing capillary-rise method settings for contact-angle determination of granular media. J. Plant Nutr. Soil Sci. 2013, 176, 16–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chawla, A.; Buckton, G.; Taylor, K.M.G.; Newton, J.M.; Johnson, M.C.R. Wilhelmy plate contact angle data on powder compacts: Considerations of plate perimeter. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 1994, 2, 253–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Wang, Y.; Muzzio, F.J.; Callegari, G.; Drazer, G. Capillary drop penetration method to characterize the liquid wetting of powders. Langmuir 2017, 33, 56–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mišljenović, N.; Mosbye, J.; Schüller, R.B.; Lekang, O.-I.; Salas-Bringas, C. Physical quality and surface hydration properties of wood based pellets blended with waste vegetable oil. Fuel Process. Technol. 2015, 134, 214–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Liu, Z.; Muzzio, F.; Drazer, G.; Callegari, G. A drop penetration method to measure powder blend wettability. Int. J. Pharm. 2018, 538, 112–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van Oss, C.J. (Ed.) Interfacial Forces in Aqueous Media, 2nd ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2006; Volume 64. [Google Scholar]
- Wildemuth, C.R.; Williams, M.C. A new interpretation of viscosity and yield stress in dense slurries: Coal and other irregular particles. Rheol. Acta 1985, 24, 75–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Villiers, M.M.; Lötter, A.P.; van der Watt, J.G. Influence of surfactants and interactive mixing on the cohesiveproperties of a poorly wettable solid. Powder Technol. 1993, 75, 159–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirchberg, S.; Abdin, Y.; Ziegmann, G. Influence of particle shape and size on the wetting behavior of soft magnetic micropowders. Powder Technol. 2011, 207, 311–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garbacz, H.; Wieciński, P.; Kuczyńska, D.; Kubacka, D.; Kurzydłowski, K.J. The effect of grain size on the surface properties of titanium grade 2 after different treatments. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2018, 335, 13–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirdponpattara, S.; Phisalaphong, M.; Newby, B.Z. Applicability of washburn capillary rise for determining contact angles of powders and porous materials. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2013, 397, 169–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Banfield, J.F. Nanoparticles in the environment. Rev. Mineral. Geochem. 2001, 44, 1–58. [Google Scholar]
- Bourikas, K.; Kordulis, C.; Lycourghiotis, A. Titanium dioxide (anatase and rutile): Surface chemistry, liquid–solid interface chemistry, and scientific synthesis of supported catalysts. Chem. Rev. 2014, 114, 9754–9823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pantaroto, H.N.; Ricomini-Filho, A.P.; Bertolini, M.M.; da Silva, J.H.; Neto, N.F.; Sukotjo, C.; Rangel, E.C.; Barão, V.A. Antibacterial photocatalytic activity of different crystalline TiO2 phases in oral multispecies biofilm. Dent. Mater. 2018, 34, 3182–3195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ranade, M.R.; Navrotsky, A.; Zhang, H.Z.; Banfield, J.F.; Elder, S.H.; Zaban, A.; Borse, P.H.; Kulkarni, S.K.; Doran, G.S.; Whitfield, H.J. Energetics of nanocrystalline TiO2. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2002, 99 (Suppl. 2), 6476–6481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grzmil, B.; Gleń, M.; Kic, B.; Lubkowski, K. Study of the anatase to rutile transformation kinetics of the modified TiO2. Pol. J. Chem. Technol. 2013, 15, 73–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, K.H.; Rawal, S.K. Contact angle hysteresis, wettability and optical studies of sputtered zinc oxide nanostructured thin films. Indian J. Eng. Mater. Sci. 2017, 24, 469–476. [Google Scholar]
- Muster, T.H.; Cole, I.S. The protective nature of passivation films on zinc: Surface charge. Corros. Sci. 2004, 46, 2319–2335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trino, L.D.; Dias, L.F.; Albano, L.G.; Bronze-Uhle, E.S.; Rangel, E.C.; Graeff, C.F.; Lisboa-Filho, P.N. Zinc oxide surface functionalization and related effects on corrosion resistance of titanium implants. Ceram. Int. 2018, 44, 4000–4008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, J.L.; Chang, Y.H. Surface Modification and Characterization of Zinc Oxide for Use in Organic Photovaltaic Devices. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Washtington, Washtington, DC, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Stepien, M.; Saarinen, J.J.; Teisala, H.; Tuominen, M.; Aromaa, M.; Kuusipalo, J.; Mäkelä, J.M.; Toivakka, M. Surface chemical characterization of nanoparticle coated paperboard. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2012, 258, 3119–3125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Solvent | Viscosity × 103 (Pa·s) | Surface Tension × 103 (N/m) | Density × 103 (kg/m3) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Diiodomethane | 2.6 | 50.8 | 3.33 |
| Formamide | 3.34 | 58 | 1.13 |
| Ethylene glycol | 16.2 | 48 | 1.11 |
| Bromonaphthalene | 4.8 a | 44.4 | 1.48 |
| Water | 0.89 | 72.8 | 1 |
| Ethanol | 1.095 | 22.4 | 0.79 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Garner, S.M.; O’Rear, E.A.; Khajotia, S.S.; Florez, F.L.E. The Applicability of a Drop Penetration Method to Measure Contact Angles on TiO2 and ZnO Nanoparticles. Nanomaterials 2020, 10, 1099. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano10061099
Garner SM, O’Rear EA, Khajotia SS, Florez FLE. The Applicability of a Drop Penetration Method to Measure Contact Angles on TiO2 and ZnO Nanoparticles. Nanomaterials. 2020; 10(6):1099. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano10061099
Chicago/Turabian StyleGarner, Sabrina M., Edgar A. O’Rear, Sharukh Soli Khajotia, and Fernando Luis Esteban Florez. 2020. "The Applicability of a Drop Penetration Method to Measure Contact Angles on TiO2 and ZnO Nanoparticles" Nanomaterials 10, no. 6: 1099. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano10061099
APA StyleGarner, S. M., O’Rear, E. A., Khajotia, S. S., & Florez, F. L. E. (2020). The Applicability of a Drop Penetration Method to Measure Contact Angles on TiO2 and ZnO Nanoparticles. Nanomaterials, 10(6), 1099. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano10061099







