Advancements in Plant and Microbe-Based Synthesis of Metallic Nanoparticles and Their Antimicrobial Activity against Plant Pathogens
Abstract
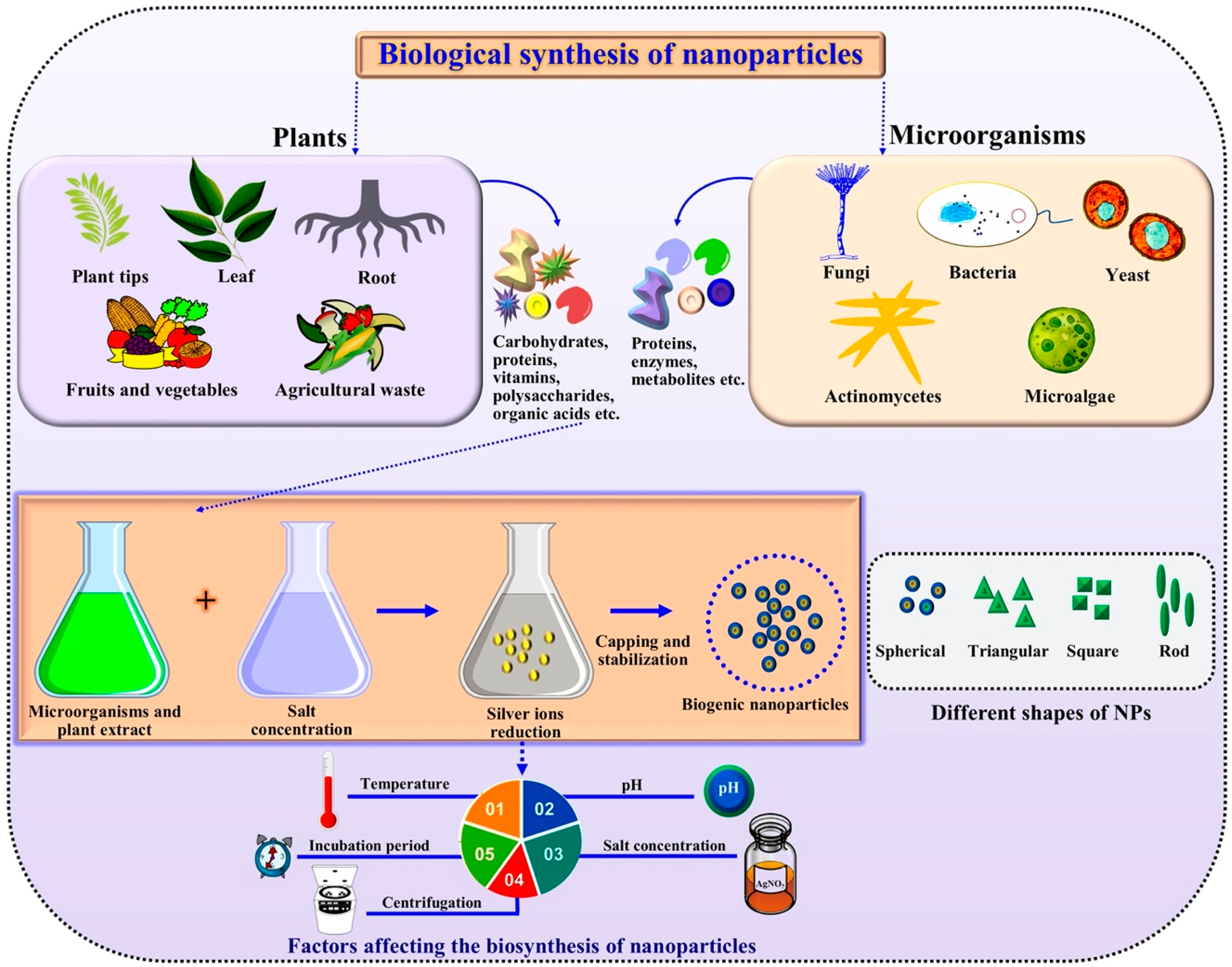
:1. Introduction
2. Green Synthesis of Metallic Nanoparticles
2.1. Microbe-Based Synthesis
2.2. Nanoparticles from Microalgae
2.3. Nanoparticles from Plant Extracts
3. Green Synthesized Metallic Nanoparticles for Control of Phytopathogens
4. Mechanisms of Action of Nanoparticles against Phytopathogens
5. Environmental Consequences of Metallic Nanoparticles
6. Toxicity of Metallic Nanoparticles on Plants
7. Toxicity of Metallic Nanoparticles on Beneficial Microbes Associated with Plants
8. Conclusions and Perspectives
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mujeebur, R.K.; Tanveer, F.R. Nanotechnology: Scope and Application in Plant Disease Management. Plant Pathol. J. 2014, 13, 214–231. [Google Scholar]
- Mohammadlou, M.; Maghsoudi, H.; Jafarizadeh-Malmiri, H. A review on green silver nanoparticles based on plants: Synthesis, potential applications and eco-friendly approach. Int. Food Res. J. 2016, 232, 446–463. [Google Scholar]
- Mie, R.; Samsudin, M.W.; Din, L.B.; Ahmad, A.; Ibrahim, N.; Adnan, S.N. Synthesis of silver nanoparticles with antibacterial activity using the lichen Parmotrema praesorediosum. Int. J. Nanomed. 2014, 9, 121–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kaviya, S.; Santhanalakshmi, J.; Viswanathan, B.; Muthumary, J.; Srinivasan, K. Biosynthesis of silver nanoparticles using Citrussinensis peel extract and its antibacterial activity. Spectrochim. Acta A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2011, 79, 594–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elmer, W.; White, J.C. The Future of Nanotechnology in Plant Pathology. Annu. Rev. Phytopathol. 2018, 56, 111–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Worrall, E.A.; Hamid, A.; Mody, K.T.; Mitter, N.; Pappu, H.R. Nanotechnology for Plant Disease Management. Agronomy 2018, 8, 285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ogunyemi, S.O.; Abdallah, Y.; Zhang, M.; Fouad, H.; Hong, X.; Ibrahim, E.; Masum, M.M.I.; Hossain, A.; Mo, J.; Li, B. Green synthesis of zinc oxide nanoparticles using different plant extracts and their antibacterial activity against Xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzae. Artif. Cells Nanomed. Biotechnol. 2019, 47, 341–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hossain, A.; Hong, X.; Ibrahim, E.; Li, B.; Sun, G.; Meng, Y.; Wang, Y.; An, Q. Green Synthesis of Silver nanoparticles with Culture Supernatant of a Bacterium Pseudomonas rhodesiae and Their Antibacterial Activity against Soft Rot Pathogen Dickeya dadantii. Molecules 2019, 24, 2303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dhuper, S.; Panda, D.; Nayak, P.L. Green synthesis and characterization of zero valent iron nanoparticles from the leaf extract of Mangifera indica. Nano Trends J. Nanotechnol. Appl. 2012, 13, 16–22. [Google Scholar]
- Iravani, S. Green synthesis of metal nanoparticles using plants. Green Chem. 2011, 13, 2638–2650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korbekandi, H.; Mohseni, S.; Mardani Jouneghani, R.; Pourhossein, M.; Iravani, S. Biosynthesis of silver nanoparticles using Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Artif. Cells Nanomed. Biotechnol. 2016, 44, 235–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mittal, A.K.; Chisti, Y.; Banerjee, U.C. Synthesis of metallic nanoparticles using plant extracts. Biotechnol. Adv. 2013, 31, 346–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shah, M.; Fawcett, D.; Sharma, S.; Tripathy, S.K.; Poinern, G.E.J. Green Synthesis of Metallic nanoparticles via Biological Entities. Materials (Basel) 2015, 8, 7278–7308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gahlawat, G.; Choudhury, A.R. A review on the biosynthesis of metal and metal salt nanoparticles by microbes. RSC Adv. 2019, 9, 12944–12967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Thakkar, K.N.; Mhatre, S.S.; Parikh, R.Y. Biological synthesis of metallic nanoparticles. Nanomedicine 2010, 6, 257–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmed, S.; Chaudhry, S.A.; Ikram, S. A review on biogenic synthesis of ZnO nanoparticles usingv plant extracts and microbes: A prospect towards green chemistry. J. Photoch. Photobiol. B 2017, 166, 272–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, J.; Dutta, T.; Kim, K.H.; Rawat, M.; Samddar, P.; Kumar, P. ‘Green’ synthesis of metals and their oxide nanoparticles: Applications for environmental remediation. J. Nanobiotechnol. 2018, 16, 84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, T.; Shahid, M.; Noman, M.; Niazi, M.B.K.; Mahmood, F.; Manzoor, I.; Zhang, Y.; Li, B.; Yang, Y.; Yan, C.; et al. Silver Nanoparticles Synthesized by Using Bacillus cereus SZT1 Ameliorated the Damage of Bacterial Leaf Blight Pathogen in Rice. Pathogens 2020, 9, 160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Singh, P.; Kim, Y.J.; Zhang, D.; Yang, D.C. Biological Synthesis of Nanoparticles from Plants and Microorganisms. Trends Biotechnol. 2016, 34, 588–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibrahim, E.; Zhang, M.; Zhang, Y.; Hossain, A.; Qiu, W.; Chen, Y.; Wang, Y.; Wu, W.; Sun, G.; Li, B. Green-Synthesization of Silver Nanoparticles Using Endophytic Bacteria Isolated from Garlic and Its Antifungal Activity against Wheat Fusarium Head Blight Pathogen Fusariumgraminearum. Nanomaterials (Basel) 2020, 10, 219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Manish, S.; Priya, M.; Anjali, S.; Girish, K.G. Green Nanoparticles: Synthesis and Applications. IOSR J. Biotechnol. Biochem. 2018, 4, 78–83. [Google Scholar]
- Bridges, K.; Kidson, A.; Lowbury, E.J.; Wilkins, M.D. Gentamicin- and silver-resistant Pseudomonas in a burns unit. Br. Med. J. 1979, 1, 446–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Haefeli, C.; Franklin, C.; Hardy, K. Plasmid-determined silver resistance in Pseudomonasstutzeri isolated from a silver mine. J. Bacteriol. 1984, 158, 389–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Brock, T.D.; Gustafson, J. Ferric iron reduction by sulfur- and iron-oxidizing bacteria. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1976, 32, 567–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Iravani, S. Bacteria in Nanoparticle Synthesis: Current Status and Future Prospects. Int. Sch. Res. Not. 2014, 2014, 359316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Prasad, T.N.V.K.V.; Kambala, V.S.R.; Naidu, R. Phyconanotechnology: Synthesis of silver nanoparticles using brown marine algae Cystophoramoniliformis and their characterisation. J. Appl. Phycol. 2013, 25, 177–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saratale, R.G.; Karuppusamy, I.; Saratale, G.D.; Pugazhendhi, A.; Kumar, G.; Park, Y.; Ghodake, G.S.; Bharagava, R.N.; Banu, J.R.; Shin, H.S. A comprehensive review on green nanomaterials using biological systems: Recent perception and their future applications. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2018, 170, 20–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, S.; Singh, B.R.; Naqvi, A.H.; Singh, H.B. Potential of biosynthesized silver nanoparticles using Stenotrophomonas sp. BHU-S7 (MTCC 5978) for management of soil-borne and foliar phytopathogens. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 45154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ahmed, E.; Kalathil, S.; Shi, L.; Alharbi, O.; Wang, P. Synthesis of ultra-small platinum, palladium and gold nanoparticles by Shewanella loihica PV-4 electrochemically active biofilms and their enhanced catalytic activities. J. Saudi Chem. Soc. 2018, 22, 919–929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zonaro, E.; Piacenza, E.; Presentato, A.; Monti, F.; Dell’Anna, R.; Lampis, S.; Vallini, G. Ochrobactrum sp. MPV1 from a dump of roasted pyrites can be exploited as bacterial catalyst for the biogenesis of selenium and tellurium nanoparticles. Microb. Cell Fact. 2017, 16, 215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Malhotra, A.; Dolma, K.; Kaur, N.; Rathore, Y.S.; Ashish Mayilraj, S.; Choudhury, A.R. Biosynthesis of gold and silver nanoparticles using a novel marine strain of Stenotrophomonas. Bioresour. Technol. 2013, 142, 727–731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaur, H.; Dolma, K.; Kaur, N.; Malhotra, A.; Kumar, N.; Dixit, P.; Sharma, D.; Mayilraj, S.; Choudhury, A.R. Marine microbe as nano-factories for copper biomineralization. Biotechnol. Bioprocess. Eng. 2015, 20, 51–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klaus-Joerger, T.; Joerger, R.; Olsson, E.; Granqvist, C. Bacteria as workers in the living factory: Metal-accumulating bacteria and their potential for materials science. Trends Biotechnol. 2001, 19, 15–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srivastava, S.K.; Constanti, M. Room temperature biogenic synthesis of multiple nanoparticles (Ag, Pd, Fe, Rh, Ni, Ru, Pt, Co, and Li) by Pseudomonasaeruginosa SM1. J. Nanopart. Res. 2012, 14, 831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sneha, K.; Sathishkumar, M.; Mao, J.; Kwak, I.S.; Yun, Y.S. Corynebacteriumglutamicum-mediated crystallization of silver ions through sorption and reduction processes. Chem. Eng. J. 2010, 162, 989–996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jayaseelan, C.; Rahuman, A.A.; Kirthi, A.V.; Marimuthu, S.; Santhoshkumar, T.; Bagavan, A.; Gaurav, K.; Karthik, L.; Rao, K.V. Novel microbial route to synthesize ZnO nanoparticles using Aeromonas hydrophila and their activity against pathogenic bacteria and fungi. Spectrochim. Acta A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2012, 90, 78–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hulkoti, N.I.; Taranath, T.C. Biosynthesis of nanoparticles using microbe—A review. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2014, 121, 474–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramanathan, R.; O’Mullane, A.P.; Parikh, R.Y.; Smooker, P.M.; Bhargava, S.K.; Bansal, V. Bacterial kinetics-controlled shape-directed biosynthesis of silver nanoplates using Morganella psychrotolerans. Langmuir 2011, 27, 714–719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nawani, N.; Aigle, B.; Mandal, A.; Bodas, M.; Ghorbel, S.; Prakash, D. Actinomycetes: Role in biotechnology and medicine. BioMed Res. Int. 2013, 2013, 687190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Prakash, D.; Nawani, N.; Prakash, M.; Bodas, M.; Mandal, A.; Khetmalas, M.; Kapadnis, B. Actinomycetes: A repertory of green catalysts with a potential revenue resource. Biomed. Res. Int. 2013, 2013, 264020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subramani, R.; Albersberg, W. Marine actinomycetes: An ongoing source of novel bioactive metabolites. Microbiol. Res. 2012, 167, 571–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hassan, S.E.; Fouda, A.; Radwan, A.A.; Salem, S.S.; Barghoth, M.G.; Awad, M.A.; Abdo, A.M.; El-Gamal, M.S. Endophytic actinomycetes Streptomyces spp mediated biosynthesis of copper oxide nanoparticles as a promising tool for biotechnological applications. J. Biol. Inorg. Chem. 2019, 24, 377–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fouda, A.; Hassan, S.E.; Abdo, A.M.; El-Gamal, M.S. Antimicrobial, Antioxidant and Larvicidal Activities of Spherical Silver Nanoparticles Synthesized by Endophytic Streptomyces spp. Biol. Trace Elem. Res. 2020, 195, 707–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Otari, S.V.; Patil, R.M.; Nadaf, N.H.; Ghosh, S.J.; Pawar, S.H. Green biosynthesis of silver nanoparticles from an actinobacteria Rhodococcus sp. Mater. Lett. 2012, 72, 92–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ranjitha, V.R.; Rai, V.R. Actinomycetes mediated synthesis of gold nanoparticles from the culture supernatant of Streptomyces griseoruber with special reference to catalytic activity. 3 Biotech 2017, 7, 299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bérdy, J. Bioactive microbial metabolites. J. Antibiot. (Tokyo) 2005, 58, 1–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gade, A.K.; Bonde, P.; Ingle, A.P.; Marcato, P.D.; Durán, N.; Rai, M.K. Exploitation of Aspergillus niger for synthesis of silver nanoparticles. J. Biobased Mater. Bioenergy 2008, 2, 243–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahluwalia, V.; Kumar, J.; Sisodia, R.; Shakil, N.A.; Walia, S. Green synthesis of silver nanoparticles by Trichoderma harzianum and their bioefficacy evaluation against Staphylococcus aureus and Klebsiella pneumonia. Ind. Crops Prod. 2014, 55, 202–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azmath, P.; Baker, S.; Rakshith, D.; Satish, S. Mycosynthesis of silver nanoparticles bearing antibacterial activity. Saudi Pharm. J. 2016, 24, 140–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Khan, N.T.; Khan, M.J.; Jameel, J.; Jameel, N.; Rheman, S.U.A. An overview: Biological organisms that serves as nanofactories for metallic nanoparticles synthesis and fungi being the most appropriate. Bioceram Dev. Appl. 2017, 7, 101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vahabi, K.; Mansoori, G.A.; Karimi, S. Biosynthesis of silver nanoparticles by fungus Trichoderma reesei. Insci. J. 2011, 1, 65–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alghuthaymi, M.A.; Almoammar, H.; Rai, M.; Said-Galiev, E.; AbdElsalam, K.A. Myconanoparticles: Synthesis and their role in phytopathogens management. Biotechnol. Biotechnol. Equip. 2015, 29, 221–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guilger-Casagrande, M.; de Lima, R. Synthesis of Silver nanoparticles Mediated by Fungi: A Review. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2019, 7, 287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sabri, M.A.; Umer, A.; Awan, G.H.; Hassan, M.F.; Hasnain, A. Selection of suitable biological method for the synthesis of silver nanoparticles. Nanomater. Nanotechnol. 2016, 6, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Costa Silva, L.P.; Oliveira, J.P.; Keijok, W.J.; Silva, A.R.; Aguiar, A.R.; Guimarães, M.C.C.; Braga, F.R. Extracellular biosynthesis of silver nanoparticles using the cell-free filtrate of nematophagus fungus Duddingtonia flagans. Int. J. Nanomed. 2017, 12, 6373–6381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gudikandula, K.; Vadapally, P.; Charya, M.A.S. Biogenic synthesis of silver nanoparticles from white rot fungi: Their characterization and antibacterial studies. OpenNano 2017, 2, 64–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castro-Longoria, E.; Vilchis-Nestor, A.R.; Avalos-Borja, M. Biosynthesis of silver, gold and bimetallic nanoparticles using the filamentous fungus Neurospora crassa. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2011, 83, 42–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajput, S.; Werezuk, R.; Lange, R.M.; Mcdermott, M.T. Fungal isolate optimized for biogenesis of silver nanoparticles with enhanced colloidal stability. Langmuir 2016, 32, 8688–8697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molnár, Z.; Bódai, V.; Szakacs, G.; Erdélyi, B.; Fogarassy, Z.; Sáfrán, G.; Varga, T.; Kónya, Z.; Tóth-Szeles, E.; Szűcs, R.; et al. Green synthesis of gold nanoparticles by thermophilic filamentous fungi. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 3943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, A.; Senapati, S.; Khan, M.I.; Kumar, R.; Sastry, M. Extra-/intracellular biosynthesis of gold nanoparticles by an alkalotolerant fungus, Trichothecium sp. J. Biomed. Nanotechnol. 2005, 1, 47–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Birla, S.S.; Gaikwad, S.C.; Gade, A.K.; Rai, M.K. Rapid Synthesis of Silver Nanoparticles from Fusarium oxysporum by Optimizing Physicocultural Conditions. Sci. World J. 2013, 2013, 796018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Saxena, J.; Sharma, P.K.; Sharma, M.M.; Singh, A. Process optimization for green synthesis of silver nanoparticles by Sclerotinia sclerotiorum MTCC 8785 and evaluation of its antibacterial properties. Springerplus 2016, 5, 861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Liang, M.; Wei, S.; Jian-Xin, L.; Xiao-Xi, Z.; Zhi, H.; Wen, L.; Liu, Z.C.; Tang, J.X. Optimization for extracellular biosynthesis of silver nanoparticles by Penicilliumaculeatum Su1 and their antimicrobial activity and cytotoxic effect compared with silver ions. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2017, C77, 963–971. [Google Scholar]
- AbdelRahim, K.; Mahmoud, S.Y.; Ali, A.M.; Almaary, K.S.; Mustafa, A.E.-Z.M.A.; Husseiny, S.M. Extracellular biosynthesis of silver nanoparticles using Rhizopusstolonifer. Saudi J. Biol. Sci. 2017, 24, 208–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Husseiny, S.M.; Salah, T.A.; Anter, H.A. Biosynthesis of size controlled silver nanoparticles by Fusariumoxysporum, their antibacterial and antitumor activities. Beni-Suef Univ. J. Basic Appl. Sci. 2015, 4, 225–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Banu, A.; Rathod, V. Synthesis and characterization of silver nanoparticles by Rhizopus stolonier. Int. J. Biomed. Adv. Res. 2011, 2, 148–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kathiravan, V.; Ravi, S.; Ashokkumar, S. Synthesis of silver nanoparticles from Meliadubia leaf extract and their in vitro anticancer activity. Spectrochim. Acta A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2014, 130, 116–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dameron, C.T.; Reese, R.N.; Mehra, R.K.; Kortan, A.R.; Carroll, P.J.; Steigerwald, M.L.; Brus, L.E.; Winge, D.R. Biosynthesis of cadmium sulphide quantum semiconductor crystallites. Nature 1989, 338, 596–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kowshik, M.; Deshmukh, N.; Vogel, W.; Urban, J.; Kulkarni, S.K.; Paknikar, K.M. Microbial synthesis of semiconductor CdS nanoparticles, their characterization, and their use in the fabrication of an ideal diode. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 2002, 78, 583–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siddique, S.; Rovina, K.; Al Azad, S.; Naher, L.; Suryani, S.; Chaikaew, P. Heavy metal contaminants removal from wastewater using the potential filamentous fungi biomass: A review. J. Microb. Biochem. Technol. 2015, 7, 384–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Apte, M.; Sambre, D.; Gaikawad, S.; Joshi, S.; Bankar, A.; Kumar, A.R.; Zinjarde, S. Psychrotrophic yeast Yarrowialipolytica NCYC 789 mediates the synthesis of antimicrobial silver nanoparticles via cell-associated melanin. AMB Express 2013, 3, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gericke, M.; Pinches, A. Microbial production of gold nanoparticles. Gold Bull. 2006, 39, 22–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Waghmare, S.R.; Mulla, M.N.; Marathe, S.R.; Sonawane, K.D. Ecofriendly production of silver nanoparticles using Candida utilis and its mechanistic action against pathogenic microorganisms. 3 Biotech 2015, 5, 33–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- do Nascimento, J.M.; de Oliveira, J.D.; de Lima Rizzo, A.C.; Leite, S.G.F. Biogenic Production of Copper nanoparticles by Saccharomycescerevisiae. J. Bionanosci. 2018, 12, 689–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, A.A.; Fox, E.K.; Górzny, M.Ł.; Nikulina, E.; Brougham, D.F.; Wege, C.; Bittner, A.M. pH Control of the Electrostatic Binding of Gold and Iron Oxide nanoparticles to Tobacco Mosaic Virus. Langmuir 2013, 29, 2094–2098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steinmetz, N.F.; Manchester, M. Viral Nanoparticles: Tools for Materials Science and Biomedicine; Pan Stanford Publishing: Singapore, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Douglas, T.; Young, M. Host–guest encapsulation of materials by assembled virus protein cages. Nature 1998, 393, 152–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.J.; Yi, H.; Kim, W.J.; Kang, K.; Yun, D.S.; Strano, M.S.; Ceder, G.; Belcher, A.M. Fabricating genetically engineered high-power lithium-ion batteries using multiple virus gene. Science 2009, 324, 1051–1055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nam, K.T.; Kim, D.-W.; Yoo, P.J.; Chiang, C.-Y.; Meethong, N.; Hammond, P.T.; Chiang, Y.-M.; Belcher, A.M. Virus-Enabled Synthesis and Assembly of Nanowires for Lithium Ion Battery Electrodes. Science 2006, 312, 885–888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mao, C.; Solis, D.J.; Reiss, B.D.; Kottmann, S.T.; Sweeney, R.Y.; Hayhurst, A.; Georgiou, G.; Iverson, B.; Belcher, A.M. Virus-based toolkit for the directed synthesis of magnetic and semiconducting nanowires. Science 2004, 303, 213–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Merzlyak, A.; Lee, S.-W. Phage as templates for hybrid materials and mediators for nanomaterial synthesis. Curr. Opin. Chem. Biol. 2006, 10, 246–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Douglas, T.; Young, M. Viruses: Making Friends with Old Foes. Science 2006, 312, 873–875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sirotkin, S.; Mermet, A.; Bergoin, M.; Ward, V.; Van Etten, J.L. Viruses as Nanoparticles: Structure versus collective dynamics. Phys. Rev. E 2014, 90, 022718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bothner, B.; Dong, X.F.; Bibbs, L.; Johnson, J.E.; Siuzdak, G. Evidence of viral capsid dynamics using limited proteolysis and mass spectrometry. J. Biol. Chem. 1998, 273, 673–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Blum, A.S.; Soto, C.M.; Wilson, C.D.; Cole, J.D.; Kim, M. Cowpea mosaic virus as a scaffold for 3-D patterning of gold nanoparticles. Nano Lett. 2004, 4, 867–870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thangavelu, R.M.; Ganapathy, R.; Ramasamy, P.; Krishnan, K. Fabrication of virus metal hybrid nanomaterials: An ideal reference for bio semiconductor. Arabian J. Chem. 2020, 13, 2750–2765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kale, A.; Bao, Y.; Zhou, Z.; Prevelige, P.E.; Gupta, A. Directed self-assembly of CdS quantum dots on bacteriophage P22 coat protein templates. Nanotechnology 2013, 24, 045603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Love, A.J.; Makarov, V.; Yaminsky, I.; Kalinina, N.O.; Taliansky, M.E. The use of tobacco mosaic virus and cowpea mosaic virus for the production of novel metal nanomaterials. Virology 2014, 449, 133–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, Y.; Dong, Y.; Zhou, J.; Li, X.; Wang, F. Application of Plant Viruses as a Biotemplate for Nanomaterial Fabrication. Molecules 2018, 23, 2311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Park, J.P.; Do, M.; Jin, H.E.; Lee, S.W.; Lee, H. M13 bacteriophage displaying DOPA on surfaces: Fabrication of various nanostructured inorganic materials without time-consuming screening processes. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2014, 6, 18653–18660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khanna, P.; Kaur, A.; Goyal, D. Algae-based metallic nanoparticles: Synthesis, characterization and applications. J. Microbiol. Methods 2019, 163, 105656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dahoumane, S.A.; Mechouet, M.; Alvarez, F.J.; Agathos, S.N.; Jeffryes, C. Microalgae: An outstanding tool in nanotechnology. Bionatura 2016, 1, 196–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ali, D.M.; Sasikala, M.; Gunasekaran, M.; Thajuddin, N. Biosynthesis and characterization of silver nanoparticles using marine cyanobacterium, Oscillatoria willei NTDM01. Dig. J. Nanomater. 2011, 6, 285–290. [Google Scholar]
- Prasad, R.; Pandey, R.; Barman, I. Engineering tailored nanoparticles with microbes: Quo vadis? Wiley Interdiscip. Rev. Nanomed. Nanobiotechnol. 2016, 8, 316–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prasad, T.N.V.K.V.; Elumalai, E.K. Marine Algae Mediated Synthesis of Silver Nanopaticles using Scaberia agardhiiGreville. J. Biol. Sci. 2013, 13, 566–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Namvar, F.; Azizi, S.; Ahmad, M.B.; Shameli, K.; Mohamad, R.; Mahdavi, M.; Tahir, P.M. Green synthesis and characterization of gold nanoparticles using the marine macroalgae Sargassum muticum. Res. Chem. Intermed. 2015, 41, 5723–5730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, V.; Berthold, D.; Puranik, P.; Gantar, M. Screening of cyanobacteria and microalgae for their ability to synthesize silver nanoparticles with antibacterial activity. Biotechnol. Rep. 2015, 5, 112–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Agarwal, P.; Gupta, R.; Agarwal, N. Advances in Synthesis and Applications of Microalgal nanoparticles for Wastewater Treatment. J. Nanotechnol. 2019, 2019, 7392713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Brayner, R.; Barberousse, H.; Hemadi, M.; Djedjat, C.; Yéprémian, C.; Coradin, T.; Livage, J.; Fiévet, F.; Couté, A. Cyanobacteria as bioreactors for the synthesis of Au, Ag, Pd, and Pt nanoparticles via an enzyme-mediated route. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2007, 7, 2696–2708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Sheekh, M.M.; El-Kassas, H.Y. Algal production of nano-silver and gold: Their antimicrobial and cytotoxic activities: A review. J. Genet. Eng. Biotechnol. 2016, 14, 299–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xie, J.; Lee, J.Y.; Wang, D.I.; Ting, Y.P. Silver nanoplates: From biological to biomimetic synthesis. ACS Nano 2007, 1, 429–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luangpipat, T.; Beattie, I.R.; Chisti, Y.; Haverkamp, R.G. Gold nanoparticles produced in a microalga. J. Nanopart. Res. 2011, 13, 6439–6445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arsiya, F.; Sayadi, M.H.; Sobhani, S. Green synthesis of palladium nanoparticles using Chlorellavulgaris. Mater. Lett. 2017, 186, 113–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merin, D.D.; Prakash, S.; Bhimba, B.V. Antibacterial screening of silver nanoparticles synthesized by marine micro algae. Asian Pac. J. Trop. Med. 2010, 3, 797–799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ibrahim, E.; Fouad, H.; Zhang, M.; Zhang, Y.; Qiu, W.; Yan, C.; Li, B.; Mo, J.; Chen, J. Biosynthesis of silver nanoparticles using endophytic bacteria and their role in inhibition of rice pathogenic bacteria and plant growth promotion. RSC Adv. 2019, 9, 29293–29299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gopinath, V.; Velusamy, P. Extracellular biosynthesis of silver nanoparticles using Bacillus sp. GP-23 and evaluation of their antifungal activity towards Fusariumoxysporum. Spectrochim. Acta Part A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2013, 106, 170–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, S.; Singh, B.R.; Singh, A.; Keswani, C.; Naqvi, A.H.; Singh, H.B. Biofabricated silver nanoparticles act as a strong fungicide against Bipolaris sorokiniana causing spot blotch disease in wheat. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e97881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaur, P.; Thakur, R.; Duhan, J.S.; Chaudhury, A. Management of wilt disease of chickpea in vivo by silver nanoparticles biosynthesized by rhizospheric microflora of chickpea (Cicerarietinum). J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol. 2018, 93, 3233–3243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassan, S.E.L.D.; Salem, S.S.; Fouda, A.; Awad, M.A.; El-Gamal, M.S.; Abdo, A.M. New approach for antimicrobial activity and bio-control of various pathogens by biosynthesized copper nanoparticles using endophytic actinomycetes. J. Radiat. Res. Appl. Sci. 2018, 11, 262–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ponmurugan, P.; Manjukarunambika, K.; Elango, V.; Gnanamangai, B.M. Antifungal activity of biosynthesised copper nanoparticles evaluated against red root-rot disease in tea plants. J. Exp. Nanosci. 2016, 11, 1019–1031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jain, D.; Kothari, S. Green synthesis of silver nanoparticles and their application in plant virus inhibition. J. Mycol. Plant Pathol. 2014, 44, 21–24. [Google Scholar]
- Elbeshehy, E.K.F.; Elazzazy, A.M.; Aggelis, G. Silver nanoparticles synthesis mediated by new isolates of Bacillus spp.; nanoparticle characterization and their activity against Bean Yellow Mosaic Virus and human pathogens. Front. Microbiol. 2015, 6, 453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- El-Moslamy, S.H.; Elkady, M.F.; Rezk, A.H.; Abdel-Fattah, Y.R. Applying Taguchi design and large-scale strategy for mycosynthesis of nano-silver from endophytic Trichoderma harzianum SYA.F4 and its application against phytopathogens. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 45297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Al-Zubaidi, S.; Alayafi, A.A.; Abdelkader, H.S. Biosynthesis, Characterization and Antifungal Activity of Silver Nanoparticles by Aspergillus niger Isolate. J. Nanotechnol. Res. 2019, 1, 23–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Almaary, K.S.; Sayed, S.R.M.; Abd-Elkader, O.H.; Dawoud, T.M.; El Orabi, N.F.; Elgorban, A.M. Complete green synthesis of silver- nanoparticles applying seed-borne Penicilliumduclauxii. Saudi J. Biol. Sci. 2020, 27, 133–1339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akther, T.; Hemalatha, S. Mycosilver Nanoparticles: Synthesis, Characterization and its Efficacy against Plant Pathogenic Fungi. BioNanoScience 2019, 9, 296–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elamawi, R.M.; Al-Harbi, R.E.; Hendi, A.A. Biosynthesis and characterization of silver nanoparticles using Trichodermalongibrachiatum and their effect on phytopathogenic fungi. Egypt. J. Biol. Pest Control. 2018, 28, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Guilger, M.; Pasquoto-Stigliani, T.; Bilesky-Jose, N.; Grillo, R.; Abhilash, P.C.; Fraceto, L.F.; Lima, R. Biogenic silver nanoparticles based on Trichodermaharzianum: Synthesis, characterization, toxicity evaluation and biological activity. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 44421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balakumaran, M.D.; Ramachandran, R.; Kalaichelvan, P.T. Exploitation of endophytic fungus, Guignardia mangiferae for extracellular synthesis of silver nanoparticles and their in vitro biological activities. Microbiol. Res. 2015, 178, 9–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, B.; He, D.; Gao, S.; Wang, D.; Yokoyama, K.; Wang, L. Biosynthesis of silver nanoparticles by the fungus Arthroderma fulvum and its antifungal activity against genera of Candida, Aspergillus and Fusarium. Int. J. Nanomed. 2016, 11, 1899–1906. [Google Scholar]
- Elgorban, A.M.; Aref, S.M.; Seham, S.M.; Elhindi, K.M.; Bahkali, A.H.; Sayed, S.R.; Manal, M.A. Extracellular synthesis of silver nanoparticles using Aspergillusversicolor and evaluation of their activity on plant pathogenic fungi. Mycosphere 2016, 7, 844–852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abd El-Aziz, A.R.M.; Al-Othman, M.R.; Mahmoud, M.A.; Metwaly, H.A. Biosynthesis of silver nanoparticles using Fusariumsolani and its impact on grain borne fungi. Dig.J. Nanomater. Biostruct. 2015, 10, 655–662. [Google Scholar]
- Makarov, V.V.; Love, A.J.; Sinitsyna, O.V.; Makarova, S.S.; Yaminsky, I.V.; Taliansky, M.E.; Kalinina, N.O. “Green” nanotechnologies: Synthesis of metal nanoparticles using plants. Acta Nat. 2014, 6, 35–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Harris, A.T.; Bali, R. On the formation and extent of uptake of silver nanoparticles by live plants. J. Nanoparticle Res. 2008, 10, 691–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gardea-Torresdey, J.L.; Parsons, J.G.; Gomez, E.; Peralta-Videa, J.; Troiani, H.E.; Santiago, P.; Yacaman, M.J. Formation and Growth of Au nanoparticles inside Live Alfalfa Plants. Nano Lett. 2002, 2, 397–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manceau, A.; Nagy, K.L.; Marcus, M.A.; Lanson, M.; Geoffroy, N.; Jacquet, T.; Kirpichtchikova, T. Formation of metallic copper nanoparticles at the soil-root interface. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2008, 42, 1766–1772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ghosh, S.; Patil, S.; Ahire, M.; Kitture, R.; Gurav, D.D.; Jabgunde, A.M.; Kale, S.; Pardesi, K.; Shinde, V.; Bellare, J.; et al. Gnidiaglauca flower extract mediated synthesis of gold nanoparticles and evaluation of its chemocatalytic potential. J. Nanobiotechnol. 2012, 10, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Khan, M.; Khan, M.; Adil, S.F.; Tahir, M.N.; Tremel, W.; Alkhathlan, H.Z.; Al-Warthan, A.; Siddiqui, M.R. Green synthesis of silver nanoparticles mediated by Pulicariaglutinosa extract. Int. J. Nanomed. 2013, 8, 1507–1516. [Google Scholar]
- Rai, M.; Yadav, A. Plants as potential synthesiser of precious metal nanoparticles: Progress and prospects. IET Nanobiotechnol. 2013, 7, 117–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masum, M.M.I.; Siddiqa, M.M.; Ali, K.A.; Zhang, Y.; Abdallah, Y.; Ibrahim, E.; Qiu, W.; Yan, C.; Li, B. Biogenic Synthesis of Silver Nanoparticles Using Phyllanthus emblica Fruit Extract and Its Inhibitory Action Against the Pathogen Acidovorax oryzae Strain RS-2 of Rice Bacterial Brown Stripe. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rai, M.; Ingle, A. Role of nanotechnology in agriculture with special reference to management of insect pests. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2012, 94, 287–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdallah, Y.; Ogunyemi, S.O.; Abdelazez, A.; Zhang, M.; Hong, X.; Ibrahim, E.; Hossain, A.; Fouad, H.; Li, B.; Chen, J. The Green Synthesis of MgO Nano-Flowers Using Rosmarinusofficinalis L. (Rosemary) and the Antibacterial Activities against Xanthomonas oryzaepv. oryzae. BioMed Res. Int. 2019, 2019, 5620989. [Google Scholar] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hossain, A.; Abdallah, Y.; Ali, M.A.; Masum, M.M.I.; Li, B.; Sun, G.; Meng, Y.; Wang, Y.; An, Q. Lemon-Fruit-Based Green Synthesis of Zinc Oxide nanoparticles and Titanium Dioxide nanoparticles against Soft Rot Bacterial Pathogen Dickeyadadantii. Biomolecules 2019, 9, 863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ogunyemi, S.O.; Zhang, F.; Abdallah, Y.; Zhang, M.; Wang, Y.; Sun, G.; Qiu, W.; Li, B. Biosynthesis and characterization of magnesium oxide and manganese dioxide nanoparticles using Matricaria chamomilla L. extract and its inhibitory effect on Acidovoraxoryzae strain RS-2. Artif. Cells Nanomed. Biotechnol. 2019, 47, 2230–2239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Prabhu, S.; Poulose, E.K. Silver Nanoparticles: Mechanism of antimicrobial action, synthesis, medical applications, and toxicity effects. Int. Nano Lett. 2012, 2, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Raju, D.; Mehta, U.J.; Ahmad, A. Simple Recovery of Intracellular Gold nanoparticles from Peanut Seedling Roots. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2015, 15, 1575–1581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karthiga, P. Preparation of silver nanoparticles by Garciniamangostana stem extract and investigation of the antimicrobial properties. Biotechnol. Res. Innov. 2018, 2, 30–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajeshkumar, S. Synthesis of silver nanoparticles using fresh bark of Pongamia pinnata and characterization of its antibacterial activity against gram positive and gram negative pathogens. Resour. Eff. Technol. 2016, 2, 30–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yasir, M.; Singh, J.; Tripathi, M.K.; Singh, P.; Shrivastava, R. Green Synthesis of Silver Nanoparticles Using Leaf Extract of Common Arrowhead Houseplant and Its Anticandidal Activity. Pharmacogn. Mag. 2018, 13, S840–S844. [Google Scholar]
- Moteriya, P.; Chanda, S. Synthesis and characterization of silver nanoparticles using Caesalpiniapulcherrima flower extract and assessment of their in vitro antimicrobial, antioxidant, cytotoxic, and genotoxic activities. Artif. Cells Nanomed. Biotechnol. 2017, 45, 1556–1567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pilaquinga, F.; Morejón, B.; Ganchala, D.; Morey, J.; Piña, N.; Debut, A.; Neira, M. Green synthesis of silver nanoparticles using Solanum mammosum L. (Solanaceae) fruit extract and their larvicidal activity against Aedes aegypti L. (Diptera: Culicidae). PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0224109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rautela, A.; Rani, J.; Debnath, M. Green synthesis of silver nanoparticles from Tectona grandis seeds extract: Characterization and mechanism of antimicrobial action on different microorganisms. J. Anal. Sci. Technol. 2019, 10, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vankar, P.S.; Shukla, D. Biosynthesis of silver nanoparticles using lemon leaves extract and its application for antimicrobial finish on fabric. Appl. Nanosci. 2012, 2, 163–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nakhjavani, M.; Mohsen Sarafraz, M.; Nikkhah, V.; Shoja, S.; Sarafraz, M. Green synthesis of silver nanoparticles using green tea leaves: Experimental study on the morphological, rheological and antibacterial behaviour. Heat Mass Transfer. 2017, 53, 3201–3209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhand, V.; Soumya, L.; Bharadwaj, S.; Chakra, S.; Bhatt, D.; Sreedhar, B. Green synthesis of silver nanoparticles using Coffeaarabica seed extract and its antibacterial activity. Mater. Sci. Eng. C. Mater. Biol. Appl. 2016, 58, 36–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmed, S.; Saifullah; Ahmad, M.; Swami, B.L.; Ikram, S. Green synthesis of silver nanoparticles using Azadirachta indica aqueous leaf extract. J. Rad. Res. Appl. Sci. 2016, 9, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Krishnaraj, C.; Ramachandran, R.; Mohan, K.; Kalaichelvan, P.T. Optimization for rapid synthesis of silver nanoparticles and its effect on phytopathogenic fungi. Spectrochim. Acta A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2012, 93, 95–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tippayawat, P.; Phromviyo, N.; Boueroy, P.; Chompoosor, A. Green synthesis of silver nanoparticles in Aloe vera plant extract prepared by a hydrothermal method and their synergistic antibacterial activity. PeerJ 2016, 4, e2589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borase, H.P.; Patil, C.D.; Salunkhe, R.B.; Suryawanshi, R.K.; Salunke, B.K.; Patil, S.V. Transformation of aromatic dyes using green synthesized silver nanoparticles. Bioprocess. Biosyst. Eng. 2014, 37, 1695–1705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suman, T.Y.; Radhika Rajasree, S.R.; Kanchana, A.; Elizabeth, S.B. Biosynthesis, characterization and cytotoxic effect of plant mediated silver nanoparticles using Morindacitrifolia root extract. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2013, 106, 74–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oves, M.; Aslam, M.; Rauf, M.A.; Qayyum, S.; Qari, H.A.; Khan, M.S.; Alam, M.Z.; Tabrez, S.; Pugazhendhi, A.; Ismail, I.M.I. Antimicrobial and anticancer activities of silver nanoparticles synthesized from the root hair extract of Phoenixdactylifera. Mater. Sci. Eng. C Mater. Biol. Appl. 2018, 89, 429–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qayyum, S.; Oves, M.; Khan, A.U. Obliteration of bacterial growth and biofilm through ROS generation by facilely synthesized green silver nanoparticles. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0181363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Dwivedi, A.D.; Gopal, K. Biosynthesis of silver and gold nanoparticles using Chenopodium album leaf extract. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2010, 369, 27–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paulkumar, K.; Gnanajobitha, G.; Vanaja, M.; Rajeshkumar, S.; Malarkodi, C.; Pandian, K.; Annadurai, G. Piper nigrum leaf and stem assisted green synthesis of silver nanoparticles and evaluation of its antibacterial activity against agricultural plant pathogens. Sci. World J. 2014, 2014, 829894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ali, K.A.; Yao, R.; Wu, W.; Masum, M.M.I.; Luo, J.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; An, Q.; Sun, G.; Li, B. Biosynthesis of silver nanoparticle from pomelo (Citrus Maxima) and their antibacterial activity against Acidovorax oryzae RS-2. Mater. Res. Express 2020, 7, 015097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, M.; Kim, B.; Belfield, K.D.; Norman, D.; Brennan, M.; Ali, G.S. Inhibition of Phytophthoraparasitica and P. capsici by silver nanoparticles synthesized using aqueous extract of Artemisia absinthium. Phytopathology 2015, 105, 1183–1190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Jagana, D.; Hegde, Y.R.; Lella, R. Green nanoparticles—A Novel Approach for the Management of Banana Anthracnose Caused by Colletotrichum musae. Int. J. Curr. Microbiol. Appl. Sci. 2017, 6, 1749–1756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jayaseelan, C.; Ramkumar, R.; Rahuman, A.A.; Perumal, P. Green synthesis of gold nanoparticles using seed aqueous extract of Abelmoschusesculentus and its antifungal activity. Ind. Crops Prod. 2013, 45, 423–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajiv, P.; Rajeshwari, S.; Venckatesh, R. Bio-Fabrication of zinc oxide nanoparticles using leaf extract of Parthenium hysterophorus L.; its size-dependent antifungal activity against plant fungal pathogens. Spectrochim. Acta Part A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2013, 112, 384–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajesh, K.M.; Ajitha, B.; Reddy, Y.A.K.; Suneetha, Y.; Reddy, P.S. Assisted green synthesis of copper nanoparticles using Syzygium aromaticum bud extract: Physical, optical and antimicrobial properties. Optik 2018, 154, 593–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassall, K.A. Pesticides: Their Properties, Uses and Disadvantages: Part I: General Introduction; Insecticides and Related Compounds. Br. Vet. J. 1965, 121, 105–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kutz, F.W.; Wood, P.H.; Bottimore, D.P. Organochlorine pesticides and polychlorinated biphenyls in human adipose tissue. Rev. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 1991, 120, 1–82. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Nisar, P.; Ali, N.; Rahman, L.; Ali, M.; Shinwari, Z.K. Antimicrobial activities of biologically synthesized metal nanoparticles: An insight into the mechanism of action. J. Biol. Inorg. Chem. 2019, 24, 929–941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rafique, M.; Sadaf, I.; Rafique, M.S.; Tahir, M.B. A review on green synthesis of silver nanoparticles and their applications. Artif. Cells Nanomed. Biotechnol. 2017, 45, 1272–1291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hajipour, M.J.; Fromm, K.M.; Akbar Ashkarran, A.; Jimenez de Aberasturi, D.; de Larramendi, I.R.; Rojo, T.; Serpooshan, V.; Parak, W.J.; Mahmoudi, M. Antibacterial properties of nanoparticles. Trends Biotechnol. 2012, 30, 499–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lemire, J.A.; Harrison, J.J.; Turner, R.J. Antimicrobial activity of metals: Mechanisms, molecular targets and applications. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2013, 11, 371–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xia, Z.-K.; Ma, Q.-H.; Li, S.-Y.; Zhang, D.-Q.; Cong, L.; Tian, Y.-L.; Yang, R.-Y. The antifungal effect of silver nanoparticles on Trichosporon asahii. J. Microbiol. Immunol. Infect. 2016, 49, 182–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Soenen, S.; Rivera-Gil, P.; Montenegro, J.-M.; Parak, W.J.; De Smedt, S.; Braeckmans, K. Cellular toxicity of inorganic nanoparticles: Common aspects and guidelines for improved nanotoxicity evaluation. Nano Today 2011, 6, 446–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Wu, L.; Si, Y.; Shu, K. Size-dependent cytotoxicity of silver nanoparticles to Azotobacter vinelandii: Growth inhibition, cell injury, oxidative stress and internalization. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0209020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Morales-Díaz, A.B.; Ortega-Ortíz, H.; Juárez-Maldonado, A.; Cadenas-Pliego, G.; González-Morales, S.; Benavides-Mendoza, A. Application of nanoelements in plant nutrition and its impact in ecosystems. Adv. Nat. Sci. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2017, 8, 013001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gardea-Torresdey, J.L.; Rico, C.M.; White, J.C. Trophic Transfer, Transformation, and Impact of Engineered Nanomaterials in Terrestrial Environments. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2014, 48, 2526–2540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.I.; Park, H.-G.; Chang, K.-H.; Nam, D.H.; Yeo, M.-K. Trophic transfer of nano-TiO2 in a paddy microcosm: A comparison of single-dose versus sequential multi-dose exposures. Environ. Pollut. 2016, 212, 316–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De la Torre Roche, R.; Servin, A.; Hawthorne, J.; Xing, B.; Newman, L.A.; Ma, X.; Chen, G.; White, J.C. Terrestrial Trophic Transfer of Bulk and Nanoparticle La2O3 Does Not Depend on Particle Size. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2015, 49, 11866–11874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shimizu, M.; Tainaka, H.; Oba, T.; Mizuo, K.; Umezawa, M.; Takeda, K. Maternal exposure to nanoparticulate titanium dioxide during the prenatal period alters gene expression related to brain development in the mouse. Part. Fibre Toxicol. 2009, 6, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bielmyer-Fraser, G.K.; Jarvis, T.A.; Lenihan, H.S.; Miller, R.J. Cellular Partitioning of Nanoparticulate versus Dissolved Metals in Marine Phytoplankton. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2014, 48, 13443–13450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.; Wang, J.; Zhang, X.; Chang, Y.; Chen, Y. Trophic transfer of TiO2 nanoparticles from daphnia to zebrafish in a simplified freshwater food chain. Chemosphere 2010, 79, 928–933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Werlin, R.; Priester, J.H.; Mielke, R.E.; Krämer, S.; Jackson, S.; Stoimenov, P.K.; Stucky, G.D.; Cherr, G.N.; Orias, E.; Holden, P.A. Biomagnification of cadmium selenide quantum dots in a simple experimental microbial food chain. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2011, 6, 65–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurepa, J.; Paunesku, T.; Vogt, S.; Arora, H.; Rabatic, B.M.; Lu, J.; Wanzer, M.B.; Woloschak, G.E.; Smalle, J.A. Uptake and distribution of ultrasmall anatase TiO2 Alizarin red S nanoconjugates in Arabidopsis thaliana. Nano Lett. 2010, 10, 2296–2302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, S.; Kurepa, J.; Smalle, J.A. Ultra-small TiO nanoparticles disrupt microtubular networks in Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant Cell Environ. 2011, 34, 811–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, S.H.; Ali, S.A. Nanotechnology Is the Potential Cause of Phytotoxicity. J. Biomater. 2019, 3, 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Servin, A.D.; White, J.C. Nanotechnology in agriculture: Next steps for understanding engineered nanoparticle exposure and risk. NanoImpact 2016, 1, 9–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dimkpa, C.O.; McLean, J.E.; Martineau, N.; Britt, D.W.; Haverkamp, R.; Anderson, A.J. Silver nanoparticles disrupt wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) growth in a sand matrix. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2013, 47, 1082–1090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Faisal, M.; Saquib, Q.; Alatar, A.A.; Al-Khedhairy, A.A.; Hegazy, A.K.; Musarrat, J. Phytotoxic hazards of NiO- nanoparticles in tomato: A study on mechanism of cell death. J. Hazard. Mater. 2013, 250, 318–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pakrashi, S.; Jain, N.; Dalai, S.; Jayakumar, J.; Chandrasekaran, P.T.; Raichur, A.M.; Chandrasekaran, N.; Mukherjee, A. In vivo genotoxicity assessment of titanium dioxide nanoparticles by Allium cepa root tip assay at high exposure concentrations. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e87789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pagano, L.; Servin, A.D.; De La Torre-Roche, R.; Mukherjee, A.; Majumdar, S.; Hawthorne, J.; Marmiroli, M.; Maestri, E.; Marra, R.E.; Isch, S.M.; et al. Molecular Response of Crop Plants to Engineered Nanomaterials. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2016, 50, 7198–7207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanzari, I.; Leone, A.; Ambrosone, A. Nanotechnology in Plant Science: To Make a Long Story Short. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2019, 7, 120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Abdallah, Y.; Yang, M.; Zhang, M.; Masum, M.M.I.; Ogunyemi, S.O.; Hossain, A.; An, Q.; Yan, C.; Li, B. Plant growth promotion and suppression of bacterial leaf blight in rice by Paenibacilluspolymyxa Sx3. Lett. Appl. Microbiol. 2019, 68, 423–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simonin, M.; Richaume, A. Impact of engineered nanoparticles on the activity, abundance, and diversity of soil microbial communities: A review. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2015, 22, 13710–13723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xu, C.; Peng, C.; Sun, L.; Zhang, S.; Huang, H.; Chen, Y.; Shi, J. Distinctive effects of TiO2 and CuO nanoparticles on soil microbes and their community structures in flooded paddy soil. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2015, 86, 24–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- You, T.; Liu, D.; Chen, J.; Yang, Z.; Dou, R.; Gao, X.; Wang, L. Effects of metal oxide nanoparticles on soil enzyme activities and bacterial communities in two different soil types. J. Soils Sedim. 2018, 18, 211–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chai, H.; Yao, J.; Sun, J.; Zhang, C.; Liu, W.; Zhu, M.; Ceccanti, B. The effect of metal oxide nanoparticles on functional bacteria and metabolic profiles in agricultural soil. Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2015, 94, 490–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chavan, S.; Nadanathangam, V. Effects of nanoparticles on plant growth-promoting bacteria in Indian agricultural soil. Agronomy 2019, 9, 140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bandyopadhyay, S.; Peralta-Videa, J.R.; Plascencia-Villa, G.; José-Yacamán, M.; Gardea-Torresdey, J.L. Comparative toxicity assessment of CeO2 and ZnO nanoparticles towards Sinorhizobium meliloti, a symbiotic alfalfa associated bacterium: Use of advanced microscopic and spectroscopic techniques. J. Hazard. Mater. 2012, 241, 379–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Collins, D.; Luxton, T.; Kumar, N.; Shah, S.; Walker, V.K.; Shah, V. Assessing the Impact of Copper and Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles on Soil: A Field Study. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e42663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Microbes | Sources of Isolation | MetalNPs | Features | Major Application | Plant Disease Management | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Size (nm) | Shape | Pathogen | Host | References | ||||
| Bacteria | ||||||||
| Pseudomonas rhodesiae | Rhizospheric soil of cotton | Ag | 20–100 | Spherical | Antibacterial agent | Dickeyadadantii | Sweet potato | [8] |
| Bacillus siamensis | Coriandrumsativum | Ag | 25–50 | Spherical | Antibacterial agent | Xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzae | Rice | [105] |
| Bacilluscereus | Wastewater contaminated soil | Ag | 18–39 | Spherical | Antibacterial agent | Xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzae | Rice | [18] |
| Pseudomonas poae | Garlic | Ag | 20–45 | Spherical | Antifungal agent | Fusarium graminearum | Wheat | [20] |
| Bacillus sp. | Soil | Ag | 7–21 | Spherical | Antifungal agent | Fusarium oxysporum | Tomato | [106] |
| Serratia sp. | Soil | Ag | 10–20 | Spherical | Antifungal agent | Bipolaris sorokiniana | Wheat | [107] |
| Stenotrophomonas sp. | Soil | Ag | 12 | Spherical | Antifungal agent | Sclerotium rolfsii | Chickpea | [28] |
| Pseudomonas sp., and Achromobacter sp. | Rhizospheric soil of chickpea | Ag | 20–50 | Spherical | Antifungal agent | Fusarium oxysporum f. sp. ciceri | Chickpea | [108] |
| Aeromonas hydrophila | Missing | ZnO | 57–72 | Crystalline | Aspergillus flavus | Maize | [36] | |
| Streptomyces spp. | Oxalis corniculata leaves | CuO | 78–80 | Spherical | Antifungal agent | Alternaria alternata, Fusarium oxysporum, Pythium ultimum, and Aspergillus niger | Multiple crops | [42] |
| Streptomyces capillispiralis | Convolvulus arvensis leaves | Cu | 4–59 | Spherical | Antifungal agent | Alternaria spp., Aspergillus niger, Pythium spp., and Fusarium spp. | Multiple crops | [109] |
| Streptomyces griseus | Rhizospheric soil of tea | Cu | 5–50 | Spherical | Antifungal agent | Poria hypolateritia | Tea | [110] |
| Bacillus thuringensis | Soil | Ag | 10–20 | Polymorphic | Antiviral agent | Sun hemp rosette virus | Cluster bean | [111] |
| Bacillus licheniformis | Soil | Ag | 77–92 | Polymorphic | Antiviral agent | Bean yellow mosaic virus | Faba bean | [112] |
| Fungi | ||||||||
| Trichiderma hazarium | Tomato | Ag | 11–13 | Spherical | Antifungal agent | Helminthosporium sp., Alternaria alternata, Phytophthora arenaria, and Botrytis sp. | Multiple crops | [113] |
| Aspergillus niger | Grape | Ag | 10–100 | Spherical | Antifungal agent | Penicillin digitatum, Aspergillus flavus, and Fusarium oxysporum | Multiple crops | [114] |
| Penicillium duclauxii | Corn seeds | Ag | 3–32 | Spherical | Antifungal agent | Bipolaris sorghicola | Sorghum | [115] |
| Setosphaeria rostrata | Solanum nigrum leaves | Ag | 2–50 | Spherical | Antifungal agent | Aspergillus niger, Rhizoctonia solani, Fusarium graminearum, and Fusarium udum | Multiple crops | [116] |
| Trichoderma longibrachiatum | Cucumber | Ag | 1–25 | Spherical | Antifungal agent | Alternaria alternata, Pyricularia grisea, Fusarium verticillioides,Helminthosporium oryzae, and Penicillium glabrum | Multiple crops | [117] |
| Trichoderma harzianum | Soil | Ag | 20–30 | Spherical | Antifungal agent | Sclerotinia sclerotiorum | Cabbage | [118] |
| Guignardia mangiferae | Leaves of medicinal plants | Ag | 5–30 | Spherical | Antifungal agent | Rhizoctonia solani | Rice | [119] |
| Arthroderma fulvum | Soil | Ag | 13–18 | Spherical | Antifungal agent | Aspergillus flavus | Maize | [120] |
| Aspergillus versicolor | Soil | Ag | 5–39 | Spherical | Antifungal agent | Sclerotinia sclerotiorum and Botrytis cinerea | Strawberry | [121] |
| Fusarium solani | Wheat grain | Ag | 5–30 | Spherical | Antifungal agent | Fusarium spp., Aspergillus spp., Alternaria spp. and Rhizopus stolonifer | wheat, barley and corn | [122] |
| Cephalosporium sp. and Trichoderma sp. | Rhizospheric soil of chickpea | Ag | 20–50 | Antifungal agent | Fusarium oxysporum f. sp. ciceri | Chickpea | [108] | |
| Plants | Plant Parts Used | Metal NPs | Features | Plant Disease Management | References | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Size (nm) | Shape | Pathogen | Host | ||||
| Citrus limon | Fruits | ZnO and TiO2 | 20–200 | Polymorphic | Dickeya dadantii | Sweet potato | [133] |
| Phyllanthu semblica | Fruits | Ag | 20–93 | Spherical | Acidovorax oryzae | Rice | [130] |
| Rosmarinus officinalis | Flowers | MgO | <20 | Flower | Xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzae | Rice | [132] |
| Matricaria chamomilla | Flowers | MgO and MnO2 | 9–112 | Disk-shapedSpherical | Acidovorax oryzae | Rice | [134] |
| Matricaria chamomilla | Flowers | ZnO | 50–192 | Crystalline | Xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzae | Rice | [7] |
| Olea europaea | Leaves | ZnO | 41–124 | Crystalline | Xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzae | Rice | [7] |
| Lycopersicon esculentum | Fruits | ZnO | 66–133 | Crystalline | Xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzae | Rice | [7] |
| Piper nigrum | Stem | Ag | 9–30 | crystalline | Erwinia cacticida | Watermelon | [154] |
| Citrus maxima | Fruits | Ag | 11–13 | Spherical | Acidovorax oryzae | Rice | [155] |
| Artemisia absinthium | Leaves | Ag | 5–100 | Spherical | Phytophthora parasitica | Citrus | [156] |
| Trachyspermum ammi | Leaves | Ni | 68 | Missing | Colletotrichum musae | Banana | [157] |
| Abelmoschus esculentus | Seed | Au | 45–75 | Spherical | Puccinia graminis pv. tritci | Wheat | [158] |
| Parthenium hysterophorus | Leaves | ZnO | 28–84 | Spherical andHexagonal | Fusarium culmorum | Barley | [159] |
| Syzygium aromaticum | Bud | Cu | 15 | Spherical | Aspergillus niger, Aspergillus flavus, and Penicillium spp. | Multiple crops | [160] |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ali, M.A.; Ahmed, T.; Wu, W.; Hossain, A.; Hafeez, R.; Islam Masum, M.M.; Wang, Y.; An, Q.; Sun, G.; Li, B. Advancements in Plant and Microbe-Based Synthesis of Metallic Nanoparticles and Their Antimicrobial Activity against Plant Pathogens. Nanomaterials 2020, 10, 1146. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano10061146
Ali MA, Ahmed T, Wu W, Hossain A, Hafeez R, Islam Masum MM, Wang Y, An Q, Sun G, Li B. Advancements in Plant and Microbe-Based Synthesis of Metallic Nanoparticles and Their Antimicrobial Activity against Plant Pathogens. Nanomaterials. 2020; 10(6):1146. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano10061146
Chicago/Turabian StyleAli, Md. Arshad, Temoor Ahmed, Wenge Wu, Afsana Hossain, Rahila Hafeez, Md. Mahidul Islam Masum, Yanli Wang, Qianli An, Guochang Sun, and Bin Li. 2020. "Advancements in Plant and Microbe-Based Synthesis of Metallic Nanoparticles and Their Antimicrobial Activity against Plant Pathogens" Nanomaterials 10, no. 6: 1146. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano10061146
APA StyleAli, M. A., Ahmed, T., Wu, W., Hossain, A., Hafeez, R., Islam Masum, M. M., Wang, Y., An, Q., Sun, G., & Li, B. (2020). Advancements in Plant and Microbe-Based Synthesis of Metallic Nanoparticles and Their Antimicrobial Activity against Plant Pathogens. Nanomaterials, 10(6), 1146. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano10061146









