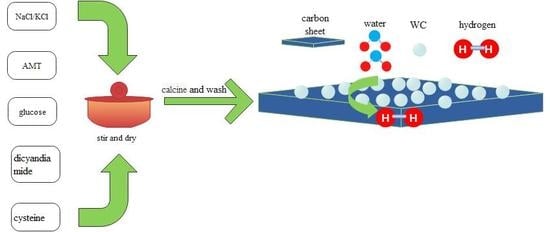
Preparation of Robust Hydrogen Evolution Reaction Electrocatalyst WC/C by Molten Salt
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals and Reagents
2.2. Material Synthesis
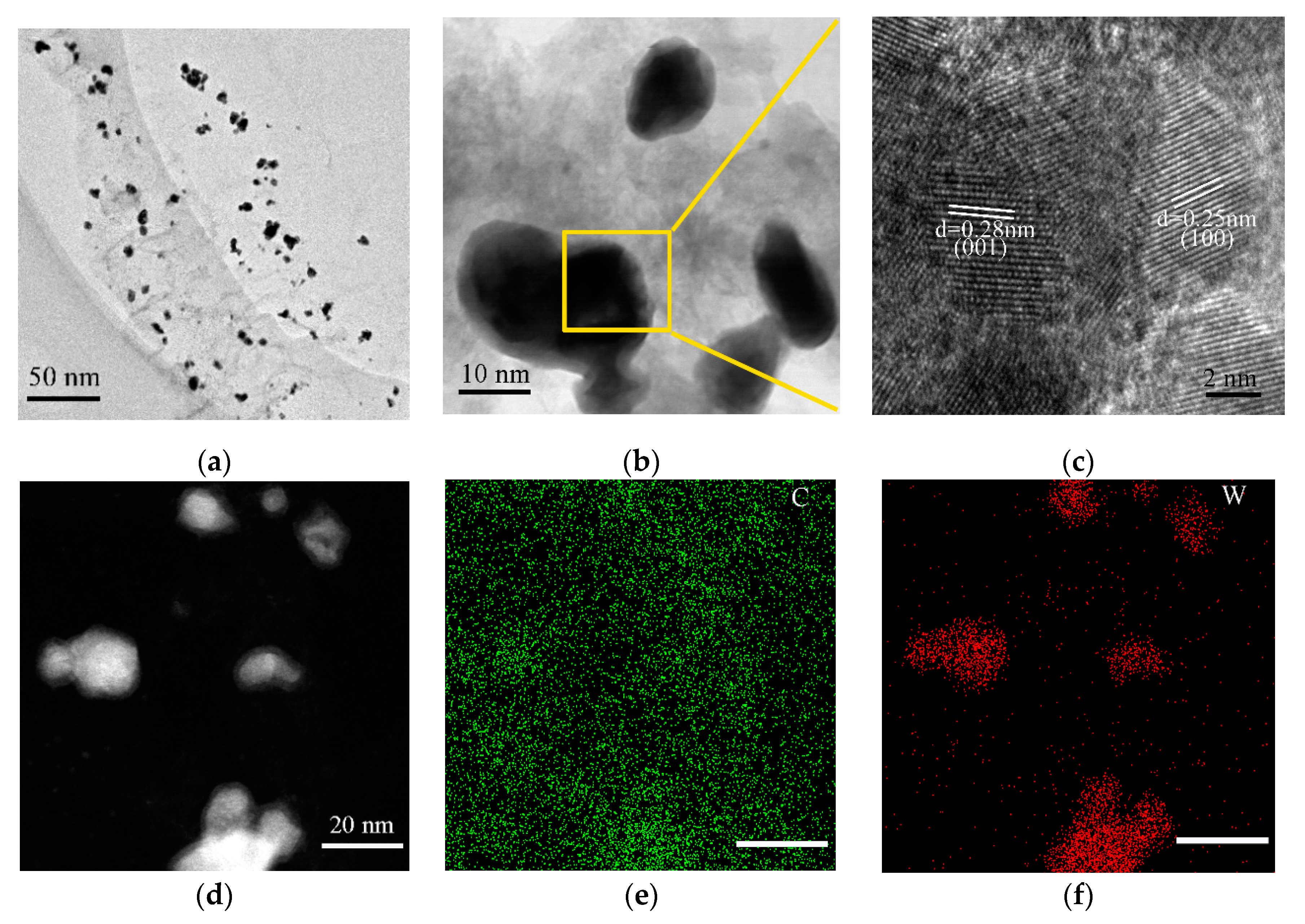
2.3. Characterization
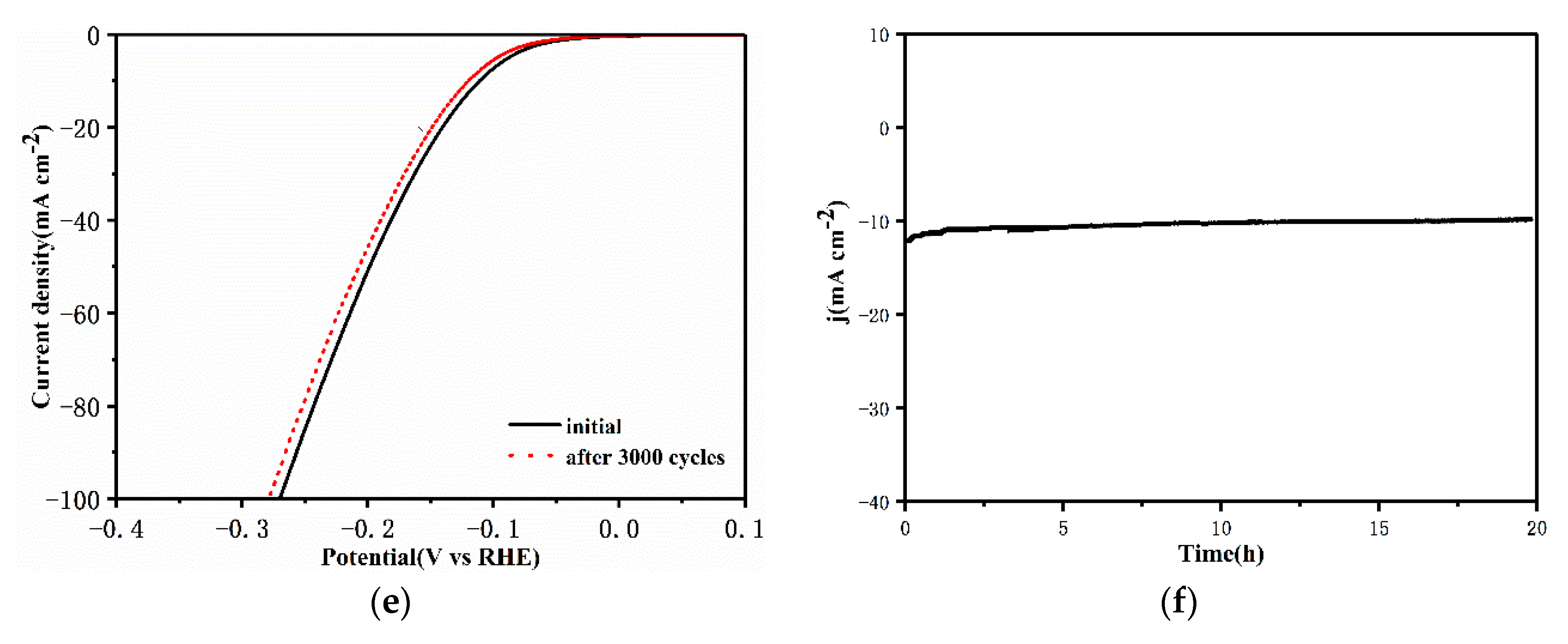
2.4. Electrochemical Measurements
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hisatomi, T.; Kubota, J.; Domen, K. ChemInform Abstract: Recent advances in semiconductors for photocatalytic and photoelectrochemical water splitting. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2014, 43, 7520–7535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gholipour, M.-R.; Dinh, C.-T.; Bél, F.; Do, T.-O. Nanocomposites as sunlight-driven photocatalysts for hydrogen production from water splitting. Nanoscale 2015, 7, 8187–8208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, Q.; Yuan, X.-Z.; Liu, G.; Wei, B.; Zhang, Z.; Li, H.; Wang, H. A review of proton exchange membrane water electrolysis on degradation mechanisms and mitigation strategies. J. Power Sources 2017, 366, 33–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Wang, Z.; Gong, X. The intensification technologies to water electrolysis for hydrogen production—A Review. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2014, 29, 573–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Tranca, D.C.; Zhang, J. Toward activity origin of electrocatalytic hydrogen evolution reaction on carbon-rich crystalline coordination polymers. Small 2017, 13, 1700783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, J.-M.; Peng, Q.-X.; Luo, S.-P. A Nickel Complex, An efficient co-catalyst for both electrochemical and photochemical driven hydrogen production from Water. Mol. Catal. 2018, 448, 10–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K.; Zhao, Y.; Fu, D. Molybdenum carbide nanocrystal embedded n-doped carbon nanotubes as electrocatalysts for hydrogen generation. J. Mater. Chem. A 2015, 3, 5783–5788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, C.; Tranca, D.; Zhang, J.; Hernandez, F.-R.; Su, Y.; Zhuang, X.; Zhang, F.; Seifert, G.; Feng, X. Molybdenum carbide-embedded nitrogen-doped porous carbon nanosheets as electrocatalysts for water splitting in alkaline media. ACS Nano 2017, 11, 3933–3942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia-Esparza, A.-T.; Cha, D.; Ou, Y.; Kubota, J.; Domen, K.; Takanabe, K. Tungsten carbide nanoparticles as efficient cocatalysts for photocatalytic overall water splitting. ChemSusChem 2013, 6, 168–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Shi, J.; Hu, J.; Asiri, A.-M.; Luo, Y.; Sun, X. CoSe2 nanowires array as a 3D electrode for highly efficient electrochemical hydrogen evolution. ACS Appl. Mater. Interface 2015, 7, 3877–3881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.-N.; Ma, Y.-Y.; Lang, Z.-L.; Wang, Y.-H.; Khan, S.-U.; Yan, G.; Tan, H.-Q.; Zang, H.-Y.; Li, Y.-G. Ultrafine cablel-like WC/W2C heterojunction nanowires covered by graphitic carbon towards highly efficient electrocatalytic hydrogen evolution. J. Mater. Chem. A 2018, 6, 15395–15403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peppernick, S.-J.; Gunaratne, K.-D.; Castleman, A.-W. Superatom spectroscopy and the electronic statec correlation between elements and isoelectronic molecular counterparts. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 975–980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chen, W.-F.; Muckerman, J.-T.; Fujita, E. Recent developments in transition metal carbides and nitrides as hydrogen evolution electrocatalysts. Chem. Commun. 2013, 49, 8896–8909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greeley, J.; Jaramillo, T.-F.; Bonde, J.; Chorkendorff, I.; Nørskov, J.-K. Computational high-throughput screening of electrocatalytic materials for hydrogen evolution. Nat. Mater. 2006, 5, 909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, Y.; Jiao, Y.; Li, L.-H.; Xing, T.; Chen, Y.; Jaroniec, M.; Qiao, S.-Z. Toward design of synergistically active carbon-based catalysts for electrocatalytic hydrogen evolution. ACS Nano 2014, 8, 5290–5296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhao, Y.; Kamiya, K.; Hashimoto, K.; Nakanishi, S. Hydrogen evolution by tungsten carbonitride nanoelectrocatalysts synthesized by the formation of a tungsten acid/polymer hybrid in situ. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2013, 52, 13638–13641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, L.; Wang, J.; Teng, X.; Dong, H.; He, X.; Chen, Z. N,P-doped molybdenum carbide nanofibers for efficient hydrogen production. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2018, 10, 14632–14640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.-Y.; Lang, Z.-L.; Yan, L.-K.; Wang, Y.-H.; Tan, H.-Q.; Feng, K.; Xia, Y.-J.; Zhong, J.; Liu, Y.; Kang, Z.-H.; et al. Highly efficient hydrogen evolution triggered by a multi-interfacial Ni/WC hybrid electrocatalyst. Energy Environ. Sci. 2018, 11, 2114–2123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Q.; Xiong, Y.-H.; Xie, L.-J.; Zhang, Z.; Lu, X.; Wang, Y.; Yuan, X.-Z.; Fan, J.-T.; Li, H.; Wang, H.-J. Tungsten carbide encapsulated in grape-like N-doped carbon nanospheres: One-step facile synthesis for low-Cost and highly active electrocatalysts in proton exchange membrane water electrolyzers. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2019, 11, 25123–25132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, J.; Yin, S.; Shen, P.-K. Carbon-encapsulated electrocatalysts for the hydrogen evolution reaction. electrochem. Energy Rev. 2019, 2, 105–127. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, Z.; Yang, Y.; Gu, D.; Li, Q.; Feng, D.; Chen, Z.; Tu, B.; Webley, P.-A.; Zhao, D. Silica-templated synthesis of ordered mesoporous tungsten carbide/graphitic carbon composites with nanocrystalline alls and high surface areas via a temperature programmed carburization route. Small 2009, 5, 2738–2749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, Y.; Zhang, L.; Qi, X.; Song, H.; Wang, J.-Y.; Zhang, H.; Wang, X. Template-Free pseudomorphic synthesis of tungsten carbide nanorods. Small 2012, 8, 3350–3356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, W.-F.; Schneider, J.-M.; Sasaki, K.; Wang, C.-H.; Schneider, J.; Iyer, S.; Iyer, S.; Zhu, Y.; Muckerman, J.-T.; Fujita, E. Tungsten carbide-nitride on graphene nanoplatelets as a durable hydrogen evolution electrocatalyst. ChemSusChem 2014, 7, 2414–2418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Z.; Qin, M.-L.; Chen, P.-Q.; Jia, B.-R.; He, Q.; Qu, X.-H. Tungsten carbide/carbon composite synthesized by combustion-carbothermal reduction method as Melectrocatalyst for hydrogen evolution reaction. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2016, 41, 13005–13013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.-T.; Xiao, X.-F.; Ye, Z.-M.; Zhao, S.-L.; Shen, R.-G.; He, C.-T.; Zhang, J.-P.; Li, Y.-D.; Chen, X.-M. Cage-confinement pyrolysis route to ultrasmall tungsten carbide nanoparticles for efficient electrocatalytic hydrogen evolution. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2017, 139, 5285–5288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hunt, S.-T.; Nimmanwudipong, T.; Roman, L.-Y. Engineering non-sintered, metal-terminated tungsten carbide nanoparticles for catalysis. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2014, 53, 5131–5136. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, R.-S.; Xing, T.-Y.; Xu, R.-B.; Li, M.-T. Molten salt synthesis of tungsten carbide powder using a mechanically activated powder. Int. J. Refract. Met. Hard Mater. 2011, 29, 138–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.-F.; Cristina, G.; Markus, A. A Facile Molten-Salt Route to graphene synthesis. Small 2014, 10, 193–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.-H.; Kurasch, S.; Kaiser, U.; Antonietti, M. Synthesis of monolayer-patched graphene from Glucose. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2012, 51, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, N.-N.; Yang, K.-R.; Lu, Z.-Y.; Li, Y.-J.; Xu, W.-W.; Gao, T.-F.; Cai, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Baista, V.-S.; Liu, W.; et al. Nitrogen-doped tungsten carbide nanoarray as an efficient bifunctional electrocatalyst for water splitting in acid. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, L.-P.; Yang, H.-B.; Wanigarathna, D.; Li, B. Ultrasmall transition metal carbide nanoparticles encapsulated in N,S-doped graphene for all-pH hydrogen evolution. Small Methods 2018, 2, 1700353–1700359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyn, T.-P.; Kim, S.-Y.; Lee, T.-H.; Jang, H.-W.; Lee, Q.-V.; Kim, I.-T. Facile Synthesis of W2C@WS2 Alloy Nanoflowers and their Hydrogen Generation Performance. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2020, 504, 144389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Wu, X.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, J. Interface designing over WS2/WC for enhanced hydrogen evolution catalysis. ACS Appl. Energy Mater. 2018, 1, 3377–3384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Lang, Z.; Yu, F.; Tan, H.; Yan, G.; Wang, Y.; Ma, Y.; Li, Y. A Co2P/WC Nano-heterojunction covered with N-doped carbon as highly efficient electrocatalyst for hydrogen evolution reaction. ChemSusChem 2018, 11, 1082–1091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zou, X.; Huang, X.; Goswami, A.; Silva, R.; Sathe, B.-R.; Mikmekova, E.; Asefa, T. Cobalt-embedded nitrogen-rich carbon nanotubes efficiently catalyze hydrogen evolution reaction at all pH values. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2014, 53, 4372–4376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Yu, G.; Li, G.-D.; Sun, Y.; Asefa, T.; Chen, W.; Zou, X. Coupling Mo2C with nitrogen-rich nanocarbon leads to efficient hydrogen-evolution electrocatalytic sites. Angew. Chem. 2015, 127, 10902–10907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, J.; Ren, P.; Deng, D.; Bao, X. Enhanced electron penetration through an ultrathin graphene layer for highly efficient catalysis of the hydrogen evolution reaction. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2015, 54, 2100–2104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Wang, J.; Zhu, M.; Bao, X.; Xiao, B.; Su, D.; Li, H.; Wang, Y. Molybdenum-carbide-modified nitrogen-doped carbon vesicle encapsulating nickel nanoparticles: A highly efficient, low cost catalyst for hydrogen evolution reaction. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2015, 137, 15753–15759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussain, S.; Akbar, K.; Vikraman, D.; Afzal, R.A.; Song, W.; An, K.S.; Farooq, A.; Park, J.Y.; Chun, S.H.; Jung, J. WS(1-X)SeX nanoparticles decorated three-dimensional graphene on nickel foam: A robust and highly efficient electrocatalyst for the hydrogen evolution reaction. Nanomaterials 2018, 8, 929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sajjad, H.; Jinwoong, C.; Kamran, A.; Dhanasekaran, V.; Linh, T.; Bilal, A.-N.; Yawar, A.; Hyun, S.-K.; Seung, H.-C.; Gunn, K.; et al. Fabrication of robust hydrogen evolution reaction electrocatalyst using Ag2Se by vacuum evaporation. Nanomaterials 2019, 9, 1460. [Google Scholar]




© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yan, P.; Wu, Y.; Wei, X.; Zhu, X.; Su, W. Preparation of Robust Hydrogen Evolution Reaction Electrocatalyst WC/C by Molten Salt. Nanomaterials 2020, 10, 1621. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano10091621
Yan P, Wu Y, Wei X, Zhu X, Su W. Preparation of Robust Hydrogen Evolution Reaction Electrocatalyst WC/C by Molten Salt. Nanomaterials. 2020; 10(9):1621. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano10091621
Chicago/Turabian StyleYan, Pengpeng, Yuchen Wu, Xiaofeng Wei, Xuewei Zhu, and Wei Su. 2020. "Preparation of Robust Hydrogen Evolution Reaction Electrocatalyst WC/C by Molten Salt" Nanomaterials 10, no. 9: 1621. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano10091621
APA StyleYan, P., Wu, Y., Wei, X., Zhu, X., & Su, W. (2020). Preparation of Robust Hydrogen Evolution Reaction Electrocatalyst WC/C by Molten Salt. Nanomaterials, 10(9), 1621. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano10091621