Cu@Pd/C with Controllable Pd Dispersion as a Highly Efficient Catalyst for Hydrogen Evolution from Ammonia Borane
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Preparation of Catalysts
2.1.1. Cu/C
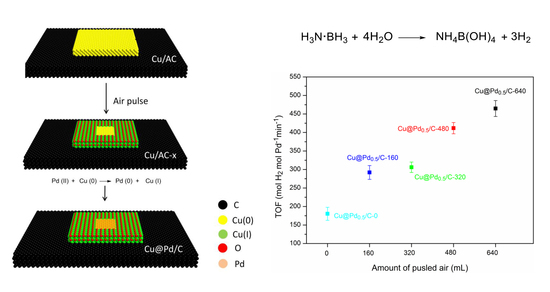
2.1.2. Cu/C-x
2.1.3. Cu@Pdy/C-x
2.1.4. PdyCu/C
2.2. Characterization
2.3. Catalytic Hydrolysis of AB
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Charcaterization
3.2. Hydrogen Evolution from AB
3.3. Effect of Cu(I)
3.4. Catalyst Stability
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhan, W.-W.; Zhu, Q.-L.; Xu, Q. Dehydrogenation of Ammonia Borane by Metal Nanoparticle Catalysts. ACS Catal. 2016, 6, 6892–6905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alpaydın, C.; KarahanGülbay, S.; Colpan, C.O. A Review on the Catalysts Used for Hydrogen Production from Ammonia Borane. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2020, 45, 3414–3434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demirci, U.B. Ammonia Borane, a Material with Exceptional Properties for Chemical Hydrogen Storage. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2017, 42, 9978–10013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akbayrak, S.; Özkar, S. Ammonia Borane as Hydrogen Storage Materials. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2018, 43, 18592–18606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, H.-L.; Xu, Q. Catalytic Hydrolysis of Ammonia Borane for Chemical Hydrogen Storage. Catal. Today 2011, 170, 56–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lang, C.; Jia, Y.; Yao, X. Recent Advances in Liquid-phase Chemical Hydrogen Storage. Energy Storage Mater. 2020, 26, 290–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Pan, Z.; Yu, X. Metal B-N-H Hydrogen-Storage Compound: Development and Perspectives. J. Alloys Compd. 2019, 794, 303–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boom, D.H.A.; Jupp, A.R.; Slootweg, J.C. Dehydrogenation of Amine–Boranes Using p-Block Compounds. Chem.-Eur. J. 2019, 25, 9133–9152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Q.; Wang, N.; Xu, Q.; Yu, J. Nanopore-Supported Metal Nanocatalysts for Efficient Hydrogen Generation from Liquid-Phase Chemical Hydrogen Storage Materials. Adv. Mater. 2020, e2001818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanyal, U.; Demirci, U.B.; Jagirdar, B.R.; Miele, P. Hydrolysis of Ammonia Borane as a Hydrogen Source: Fundamental Issues and Potential Solutions Towards Implementation. ChemSusChem 2011, 4, 1731–1739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Sun, J.-K.; Kitta, M.; Pang, H.; Xu, Q. Encapsulating Highly Catalytically Active Metal Nanoclusters inside Porous Organic Cages. Nat. Catal. 2018, 1, 214–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Q.; Wang, N.; Zhang, T.; Bai, R.; Mayoral, A.; Zhang, P.; Zhang, Q.; Terasaki, O.; Yu, J. Zeolite-Encaged Single-Atom Rh Catalysts: Highly-Efficient Hydrogen Generation and Shape-Selective Tandem Hydrogenation of Nitroarenes. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2019, 58, 18570–18576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Telleria, A.; Vicent, C.; Nacianceno, V.S.; Garralda, M.A.; Freixa, Z. Experimental Evidence Supporting Related Mechanisms for Ru(II)-Catalyzed Dehydrocoupling and Hydrolysis of Amine-Boranes. ACS Catal. 2017, 7, 8394–8405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, H.; Chen, X.; Liu, C.-Y.; Liu, X.-J.; Zheng, X.-C.; Guan, X.-X.; Liu, P. Ultrafine Palladium Nanoparticles Anchoring Graphene Oxide-ionic Liquid Grafted Chitosan Self-assembled Materials: The Novel Organic-inorganic Hybrid Catalysts for Hydrogen Generation in Hydrolysis of Ammonia Borane. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2018, 43, 12081–12090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, H.; Chen, X.; Song, X.; Zheng, X.; Guan, X.; Liu, P. Graphitic Carbon Nitride-chitosan Composites–anchored Palladium Nanoparticles as High-performance Catalyst for Ammonia Borane Hydrolysis. Int. J. Energy Res. 2018, 43, 535–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Ji, J.; Duan, X.; Qian, G.; Li, P.; Zhou, X.; Chen, D.; Yuan, W. Unique Reactivity in Pt/CNT Catalyzed Hydrolytic Dehydrogenation of Ammonia Borane. Chem. Commun. 2014, 50, 2142–2144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akbayrak, S.; Tonbul, Y.; Özkar, S. Ceria Supported Rhodium Nanoparticles: Superb Catalytic Activity in Hydrogen Generation from the Hydrolysis of Ammonia Borane. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2016, 198, 162–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Hu, M.; Ming, M.; Xu, C.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Wu, J.; Gao, D.; Bi, J.; Fan, G. Carbon-supported Small Rh Nanoparticles Prepared with Sodium Citrate: Toward High Catalytic Activity for Hydrogen Evolution from Ammonia Borane Hydrolysis. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2018, 43, 2718–2725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akbayrak, S.; Tonbula, Y.; Özkar, S. Ceria-Supported Ruthenium Nanoparticles as Highly Active and Long-Lived Catalyst in Hydrogen Generation from the Hydrolysis of Ammonia Borane. Dalton Trans. 2016, 27, 10969–10978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Xu, C.; Chen, Q.; Ming, M.; Wang, Y.; Sun, T.; Zhang, Y.; Gao, D.; Bi, J.; Fan, G. Nitrogen-Doped Carbon Stabilized Ru Nanoclusters as Excellent Catalyst for Hydrogen Production. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2018, 7, 1178–1184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Axet, M.R.; Philippot, K. Catalysis with Colloidal Ruthenium Nanoparticles. Chem. Rev. 2020, 120, 1085–1145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, C.; Meng, P.; Waclawik, E.R.; Zhang, C.; Li, X.-H.; Yang, H.; Antonietti, M.; Xu, J. Pd/g-C3N4 Stabilized Emulsion Microreactor as a Temporal Hydrogen Storage for Full Use of Hydrogen from Ammonia Borane toward Efficient Alkene Hydrogenation. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2018, 57, 14857–14861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Kam, L.; Trerise, R.; Williams, T.J. Ruthenium-Catalyzed Ammonia Borane Dehydrogenation: Mechanism and Utility. Acc. Chem. Res. 2017, 50, 86–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, Y.; Li, J.; Togo, T.; Jin, F.; Xiao, Z.; Liu, L.; Drake, H.; Lian, X.; Zhou, H.-C. Ultra-Small Face-Centered-Cubic Ru Nanoparticles Confined within a Porous Coordination Cage for Dehydrogenation. Chem 2018, 4, 555–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rej, S.; Hsia, C.-F.; Chen, T.-Y.; Lin, F.-C.; Huang, J.-S.; Huang, M.H. Facet-Dependent and Light-Assisted Efficient Hydrogen Evolution from Ammonia Borane Using Gold-Palladium Core-Shell Nanocatalysts. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2016, 55, 7222–7226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, M.; Ming, M.; Xu, C.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Gao, D.; Bi, J.; Fan, G. Towards High-Efficiency Hydrogen Production through in situ Formation of Well-Dispersed Rhodium Nanoclusters. ChemSusChem 2018, 11, 3253–3258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Duan, X.; Qian, G.; Chen, D.; Zhou, X. Carbon Nanotubes as Support in the Platinum-Catalyzed Hydrolytic Dehydrogenation of Ammonia Borane. ChemSusChem 2015, 8, 2927–2931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akbayrak, S.; Çakmak, G.; Öztürk, T.; Özkar, S. Rhodium(0), Ruthenium(0) and Palladium(0) Nanoparticles Supported on Carbon-coated Iron: Magnetically Isolable and Reusable Catalysts for Hydrolytic Dehydrogenation of Ammonia Borane. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, M.; Chen, Q.; Wu, J.; Fan, G. Anchoring and Space-confinement Effects to Synthesize Ultrasmall Pd Nanoparticles for Efficient Ammonia Borane Hydrolysis. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Güngörmez, K.; Metin, Ö. Composition-controlled Catalysis of Reduced Graphene Oxide Supported CuPd Alloy Nanoparticles in the Hydrolytic Dehydrogenation of Ammonia Borane. Appl. Catal. A Gen. 2015, 494, 22–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kılıç, B.; Şencanlı, S.; Metin, Ö. Hydrolytic Dehydrogenation of Ammonia Borane Catalyzed by Reduced Graphene Oxide Supported Monodisperse Palladium Nanoparticles: High Activity and Detailed Reaction Kinetics. J. Mol. Catal. A 2012, 361–362, 104–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akbayrak, S.; Ozcifci, Z.; Tabak, A. Noble Metal Nanoparticles Supported on Activated Carbon: Highly Recyclable Catalysts in Hydrogen Generation from the Hydrolysis of Ammonia Borane. J. Colloid. Interface Sci. 2019, 546, 324–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akbayrak, S.; Kaya, M.; Volkan, M.; Özkar, S. Palladium(0) Nanoparticles Supported on Silica-coated Cobalt Ferrite: A Highly Active, Magnetically Isolable and Reusable Catalyst for Hydrolytic Dehydrogenation of Ammonia Borane. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2014, 147, 387–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xi, P.; Chen, F.; Xie, G.; Ma, C.; Liu, H.; Shao, C.; Wang, J.; Xu, Z.; Xu, X.; Zeng, Z. Surfactant Free RGO/Pd Nanocomposites as Highly Active Heterogeneous Catalysts for the Hydrolytic Dehydrogenation of Ammonia Borane for Chemical Hydrogen Storage. Nanoscale 2012, 4, 5597–5601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Qin, Y.-L.; Liu, X.; Zhang, X.-B. In Situ Synthesis of Magnetically Recyclable Graphene-supported Pd@Co Core–shell Nanoparticles as Efficient Catalysts for Hydrolytic Dehydrogenation of Ammonia Borane. J. Mater. Chem. 2012, 22, 12468–12470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, H.; Liu, S.; Zheng, G.-P.; Zheng, X.-C.; Wang, X.-Y.; Liu, P. Collagen-graphene Oxide Magnetic Hybrids Anchoring Pd(0) Catalysts for Efficient H2 Generation from Ammonia Borane. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2019, 44, 27022–27029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, H.; Liu, X.-J.; Chen, X.; Guan, X.-X.; Zheng, X.-C.; Liu, P. Chitosan-Fe3O4 Anchored Palladium Nanoparticles: An Efficiently Magnetic Catalyst for Hydrolytic Dehydrogenation of Ammonia Borane. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2017, 42, 28425–28433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manna, J.; Akbayrak, S.; Özkar, S. Palladium(0) nanoparticles supported on polydopamine coated CoFe2O4 as highly active, magnetically isolable and reusable catalyst for hydrogen generation from the hydrolysis of ammonia borane. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2017, 208, 104–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Lu, Z.-H.; Luo, Y.; Zou, A.; Yao, Q.; Chen, X. Mesoporous Carbon Nitride Supported Pd and Pd-Ni Nanoparticles as Highly Efficient Catalyst for Catalytic Hydrolysis of NH3BH3. ChemCatChem 2018, 10, 1620–1626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakuru, V.R.; Velaga, B.; Peela, N.R.; Kalidindi, S.B. Hybridization of Pd Nanoparticles with UiO-66(Hf) Metal-Organic Framework and the Effect of Nanostructure on the Catalytic Properties. Chem.-Eur. J. 2018, 24, 15978–15982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Filiz, B.C.; Figen, A.K.; Pişkin, S. The Remarkable Role of Metal Promoters on the Catalytic Activity of Co-Cu Based Nanoparticles for Boosting Hydrogen Evolution: Ammonia Borane Hydrolysis. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2018, 238, 365–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Zhang, J.; Guan, H.; Zhao, Y.; Yang, J.-H.; Zhang, B. Preparation of Bimetallic Cu-Co Nanocatalysts on Poly (diallyldimethylammonium chloride) Functionalized Halloysite Nanotubes for Hydrolytic Dehydrogenation of Ammonia Borane. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2018, 427, 106–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Li, H.; Zhang, H.; Zhu, Y.; Mi, G. Porously Hierarchical Cu@Ni Cubic-cage Microstructure: Very Active and Durable Catalyst for Hydrolytically Liberating H2 Gas from Ammonia Borane. Renew. Energy 2016, 99, 1038–1045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Zhu, Q.-L.; Xu, Q. Non-noble Bimetallic CuCo Nanoparticles Encapsulated in the Pores of Metal–organic Frameworks: Synergetic Catalysis in the Hydrolysis of Ammonia Borane for Hydrogen Generation. Catal. Sci. Technol. 2015, 5, 525–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Wang, H.; Wang, Z.; Li, X.; Chi, Y.; Wang, M.; Gao, D.; Zhao, Z. Mo Remarkably Enhances Catalytic Activity of Cu@MoCo Core-shell Nanoparticles for Hydrolytic Dehydrogenation of Ammonia Borane. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2018, 43, 7347–7355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, X.; Jiang, R.; Li, Q.; Zeng, F.; Zheng, X.; Xu, Z.; Chen, C.; Peng, J. The Hydrolysis of Ammonia Borane Catalyzed by NiCoP/OPC-300 Nanocatalysts: High Selectivity and Efficiency, and Mechanism. Green Chem. 2019, 21, 850–860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.Z.; Aijaz, A.; Xu, Q. Highly Dispersed Surfactant-free Nickel Nanoparticles and Their Remarkable Catalytic Activity in the Hydrolysis of Ammonia Borane for Hydrogen Generation. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2012, 51, 6753–6756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, Q.; Lu, Z.-H.; Yang, Y.; Chen, Y.; Chen, X.; Jiang, H.-L. Facile Synthesis of Graphene-supported Ni-CeOx Nanocomposites as Highly Efficient Catalysts for Hydrolytic Dehydrogenation of Ammonia Borane. Nano Res. 2018, 11, 4412–4422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, K.; Zhong, J.; Zhao, B.; Zhang, H.; Xu, L.; Sun, X.; Lee, S.-T. CuxCo1−xO Nanoparticles on Graphene Oxide as A Synergistic Catalyst for High-Efficiency Hydrolysis of Ammonia–Borane. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2016, 55, 11950–11954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, P.; Gu, X.; Kang, K.; Zhang, H.; Cheng, J.; Su, H. Highly Efficient Catalytic Hydrogen Evolution from Ammonia Borane Using the Synergistic Effect of Crystallinity and Size of Noble-MetalFree Nanoparticles Supported by Porous Metal-Organic Frameworks. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2017, 9, 10759–10767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, J.; Hou, J.; Li, B.; Qin, R.; Xu, C.; Liu, H. Support-free 3D Hierarchical Nanoporous Cu@Cu2O for Fast Tandemm Ammonia Borane Dehydrogenation and Nitroarenes Hydrogenation under Mild Conditions. J. Alloys Compd. 2020, 815, 152372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Tuninetti, J.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, C.; Ciganda, R.; Salmon, L.; Moya, S.; Ruiz, J.; Astruc, D. Hydrolysis of Ammonia-Borane over Ni/ZIF-8 Nanocatalyst: High Efficiency, Mechanism, and Controlled Hydrogen Release. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2017, 139, 11610–11615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Shen, G.; Zhang, Y.; Pan, L.; Zhang, X.; Zou, J.-J. Visible-light-induced Unbalanced Charge on NiCoP/TiO2 Sensitized System for Rapid H2 Generation from Hydrolysis of Ammonia Borane. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2020, 260, 118183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, R.; Chen, Q.; Luo, Q.; Zhou, L.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Fan, G. Salt Template-assisted in situ Construction of Ru Nanoclusters and Porous Carbon: Excellent Catalysts toward Hydrogen Evolution, Ammonia-borane Hydrolysis, and 4-nitrophenol Reduction. Green Chem. 2020, 22, 835–842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.-J.; Zhang, D.-X.; Li, D.; Ke, S.-C.; Ma, X.-C.; Chang, G.-G.; Chena, J.; Yang, X.-Y. All-around Coating of CoNi Nanoalloy by Hierarchically Porous Carbon Derived from Bimetallic MOFs for Highly Efficient Hydrolytic Dehydrogenation of Ammonia-borane. New J. Chem. 2020, 44, 3021–3027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Zhou, L.; Yang, K.; Gao, D.; Huang, C.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, F.; Xiong, X.; Li, L.; Xia, Q. Pd Ni Nanoparticles Supported on MIL-101 as High-performance Catalysts for Hydrogen Generation from Ammonia Borane. J. Alloys Compd. 2016, 677, 87–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, X.; Li, H.; Yu, G.; Yuan, M.; Yang, J.; Xu, D.; Hou, Y.; Dong, Z. Pt Coated Co Nanoparticles Supported on N-doped Mesoporous Carbon as Highly Efficient, Magnetically Recyclable and Reusable Catalyst for Hydrogen Generation from Ammonia Borane. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2017, 42, 27055–27065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Cui, Z.; Ma, J.; Dong, Z. Ru Coated Co Nanoparticles Decorated on Cotton Derived Carbon Fibers as a Highly Efficient and Magnetically Recyclable Catalyst for Hydrogen Generation from Ammonia Borane. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2018, 43, 1355–1364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shang, N.; Zhou, X.; Feng, C.; Gao, S.; Wu, Q.; Wang, C. Synergetic Catalysis of Ni Pd Nanoparticles Supported on Biomass-derived Carbon Spheres for Hydrogen Production from Ammonia Borane at Room Temperature. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2017, 42, 5733–5740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Chen, W.; Ge, H.; Chen, C.; Yan, W.; Gao, Z.; Gan, J.; Zhang, B.; Duan, X.; Qin, Y. Synergistic Effects in Atomic-layer-deposited PtCox/CNTs Catalysts Enhancing Hydrolytic Dehydrogenation of Ammonia Borane. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2018, 235, 256–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, X.; Zhou, L.; Yu, G.; Yang, K.; Ye, M.; Xia, Q. Synthesis and Catalytic Performance of a Novel RuCuNi/CNTs Nanocomposite in Hydrolytic Dehydrogenation of Ammonia Borane. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2015, 40, 15521–15528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; He, T.; Matsumura, D.; Miao, S.; Wu, A.; Liu, L.; Wu, G.; Chen, P. Atomically Dispersed Pt on the Surface of Ni Particles: Synthesis and Catalytic Function in Hydrogen Generation from Aqueous Ammonia–borane. ACS Catal. 2017, 7, 6762–6769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, F.; Wang, C.; Wang, Q.; Martinez-Villacorta, A.M.; Escobar, A.; Chong, H.; Wang, X.; Moya, S.; Salmon, L.; Fouquet, E.; et al. Highly Selective and Sharp Volcano-type Synergistic Ni2Pt@ZIF-8-Catalyzed Hydrogen Evolution from Ammonia Borane Hydrolysis. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2018, 140, 10034–10042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Q.; Fu, F.; Yang, S.; Moro, M.M.; Ramirez, M.d.l.A.; Moya, S.; Salmon, L.; Ruiz, J.; Astruc, D. Dramatic Synergy in CoPt Nanocatalysts Stabilized by “Click”Dendrimers for Evolution of Hydrogen from Hydrolysis of Ammonia Borane. ACS Catal. 2019, 9, 1110–1119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, M.-M.; Du, X.-L.; Zhao, Y.; Mei, B.-B.; Zhang, Q.; Sun, F.-F.; Jiang, Z.; Liu, Y.-M.; He, H.-Y.; Cao, Y. Ring-Opening Transformation of 5-Hydroxymethylfurfural Using a Golden Single-Atomic-Site Palladium Catalyst. ACS Catal. 2019, 9, 6212–6222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- You, L.; Mao, Y.; Ge, J. Synthesis of Stable SiO2@Au-Nanoring Colloids as Recyclable Catalysts: Galvanic Replacement Taking Place on the Surface. J. Phys. Chem. C 2012, 116, 10753–10759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahara, Y.; Ohyama, J.; Sawabe, K.; Satsuma, A. Synthesis of Supported Bimetal Catalysts using Galvanic Deposition Method. Chem. Rec. 2018, 18, 1306–1313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mintsouli, I.; Georgieva, J.; Armyanov, S.; Valova, E.; Avdeev, G.; Hubin, A.; Steenhaut, O.; Dille, J.; Tsiplakides, D.; Balomenou, S.; et al. Pt-Cu Electrocatalysts for Methanol Oxidation Prepared by Partial Galvanic Replacement of Cu/carbon Powder Precursors. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2013, 136–137, 160–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, G.; Wang, H.; Tian, J.; Pei, Y.; Fan, K.; Qiao, M.; Sun, B.; Zong, B. Ru-Zn/ZrO2 Nanocomposite Catalysts Fabricated by Galvanic Replacement for Benzene Partial Hydrogenation. ChemCatChem 2018, 10, 1184–1191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Diao, W.; Monnier, J.R.; Williams, C.T. Pd-AgSiO2 Bimetallic Catalysts Prepared by Galvanic Displacement for Selective Hydrogenation of Acetylene in Excesse Thylene. Catal. Sci. Technol. 2015, 5, 4123–4132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobayashi, Y.; Cai, Z.; Chang, G.; He, Y.; Oyama, M. Palladium Deposition on Nickel Microparticles by a Galvanic Replacement Reaction for Electrocatalytic Oxidation of Ethanol. ACS Appl. Energy Mater. 2019, 2, 6023–6030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodrigues, T.S.; da Silva, A.G.M.; Camargo, P.H.C. Nanocatalysis by Noble Metal Nanoparticles: Controlled Synthesis for the Optimization and Understanding of Activities. J. Mater. Chem. A 2019, 7, 5857–5874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, Y.; Zheng, M.; Li, D.; Deng, D.; Wu, C.; Yang, Y. Synthesis of Pd/SBA-15 Catalyst Employing Surface-bonded Vinyl as a Reductant and its Application in the Hydrogenation of Nitroarenes. RSC Adv. 2017, 7, 3443–3449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, Y.; Zheng, M.; Li, D.; Deng, D.; Ma, L.-F.; Yang, Y. Conversion of HMF to Methyl Cyclopentenolone by the Pd/Nb2O5 and Ca-Al Catalysts via Two-steps Procedure. Green Chem. 2017, 19, 5103–5113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Xie, Y.; Zhang, J.; Li, D.; Deng, D.; Duan, Y. Fabrication of Pd/SiO2 with Controllable Wettability for Enhanced Catalytic Hydrogenation Activity at Ambient H2 Pressure. ChemCatChem 2019, 11, 5430–5434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Deng, D.; Sui, D.; Xie, Y.; Li, D.; Duan, Y. Facile Preparation of Pd/UiO-66-v for the Conversion of Furfuryl Alcohol to Tetrahydrofurfuryl Alcohol under Mild Conditions in Water. Nanomaterials 2019, 9, 1698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, K.; Ning, G.; Yang, J.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, X.; Qin, Y.; Luan, C.; Yu, L.; Jiang, Y.; Luan, X.; et al. Restructured PtNi on Ultrathin Nickel Hydroxide for Enhanced Performance in Hydrogen Evolution and Methanol Oxidation. J. Catal. 2019, 375, 267–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Xie, Y.; Deng, D.; Li, D.; Zheng, M.; Duan, Y. Highly Selective Conversion of HMF to 1-hydroxy-2,5-hexanedione on Pd/MIL-101(Cr). ChemistrySelect 2019, 4, 11165–11171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brun, M.; Berthet, A.; Bertolini, J.C. XPS, AES and Auger Parameter of Pd and PdO. J. Electron. Spectrosc. Relat. Phenom. 1999, 104, 55–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Yang, D.; Zhang, C.; Zheng, M.; Duan, Y. Preparation of 1-hydroxy-2,5-hexanedione from HMF by the Combination of Commercial Pd/C and Acetic Acid. Molecules 2020, 25, 2475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Platzman, I.; Brener, R.; Haick, H.; Tannenbaum, R. Oxidation of Polycrystalline Copper Thin Films at Ambient Conditions. J. Phys. Chem. C 2008, 112, 1101–1108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.-N.; Shi, L.; Li, W.; Li, W.-C.; Si, R.; Schüthc, F.; Lu, A.-H. Cu Supported on Thin Carbon Layer Coated Porous SiO2 for Efficient Ethanol Dehydrogenation. Catal. Sci. Technol. 2018, 8, 472–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]









| Entry | Catalysts | Temperature (K) | TOF (molH2 min−1 molPd−1) | Ea (kJ mol−1) | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Cu@Pd0.5/C-640 | 298 | 465 | - | This work |
| 2 | Cu@Pd0.5/C-320 | 298 | 306 | 57 | This work |
| 3 | Pd0/CoFe2O4 | 298 | 290 | 42 | [38] |
| 4 | Pd(0)/SiO2–CoFe2O4 | 298 | 254 | 52 | [33] |
| 5 | Pd74Ni26/MCN | rt | 247 | 54 | [39] |
| 6 | Pd@UiO-66 | 353 | 231 | 37 | [40] |
| 7 | Pd/RCC3 | 303 | 176 | - | [11] |
| 8 | Pd0/PDA–CoFe2O4 | 298 | 175 | 65 | [38] |
| 9 | Pd/IPCNs | 298 | 113 | 29 | [29] |
| 10 | Pd/AC | 303 | 40 | 68 | [32] |
| 11 | Pd0/CeFe | 298 | 29 | - | [28] |
| 12 | Pd(0)/g-C3N4-CS | 303 | 28 | 35 | [15] |
| 13 | Pd/CGP-GO-Fe3O4 | 303 | 27 | 37 | [36] |
| 14 | Pd(0)/GO-ILCS | 303 | 26 | 38 | [14] |
| 15 | Pd(0)/CS-Fe3O4 | 303 | 15 | 36 | [37] |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yang, Y.; Duan, Y.; Deng, D.; Li, D.; Sui, D.; Gao, X. Cu@Pd/C with Controllable Pd Dispersion as a Highly Efficient Catalyst for Hydrogen Evolution from Ammonia Borane. Nanomaterials 2020, 10, 1850. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano10091850
Yang Y, Duan Y, Deng D, Li D, Sui D, Gao X. Cu@Pd/C with Controllable Pd Dispersion as a Highly Efficient Catalyst for Hydrogen Evolution from Ammonia Borane. Nanomaterials. 2020; 10(9):1850. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano10091850
Chicago/Turabian StyleYang, Yanliang, Ying Duan, Dongsheng Deng, Dongmi Li, Dong Sui, and Xiaohan Gao. 2020. "Cu@Pd/C with Controllable Pd Dispersion as a Highly Efficient Catalyst for Hydrogen Evolution from Ammonia Borane" Nanomaterials 10, no. 9: 1850. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano10091850
APA StyleYang, Y., Duan, Y., Deng, D., Li, D., Sui, D., & Gao, X. (2020). Cu@Pd/C with Controllable Pd Dispersion as a Highly Efficient Catalyst for Hydrogen Evolution from Ammonia Borane. Nanomaterials, 10(9), 1850. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano10091850