Atomic-Scale Characterization of Droplet Epitaxy Quantum Dots
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Self-Assembled III-V Semiconductor Quantum Dots
3. Characterization Techniques
3.1. Atomic Force Microscopy
3.2. Transmission Electron Microscopy
3.3. Atom Probe Tomography
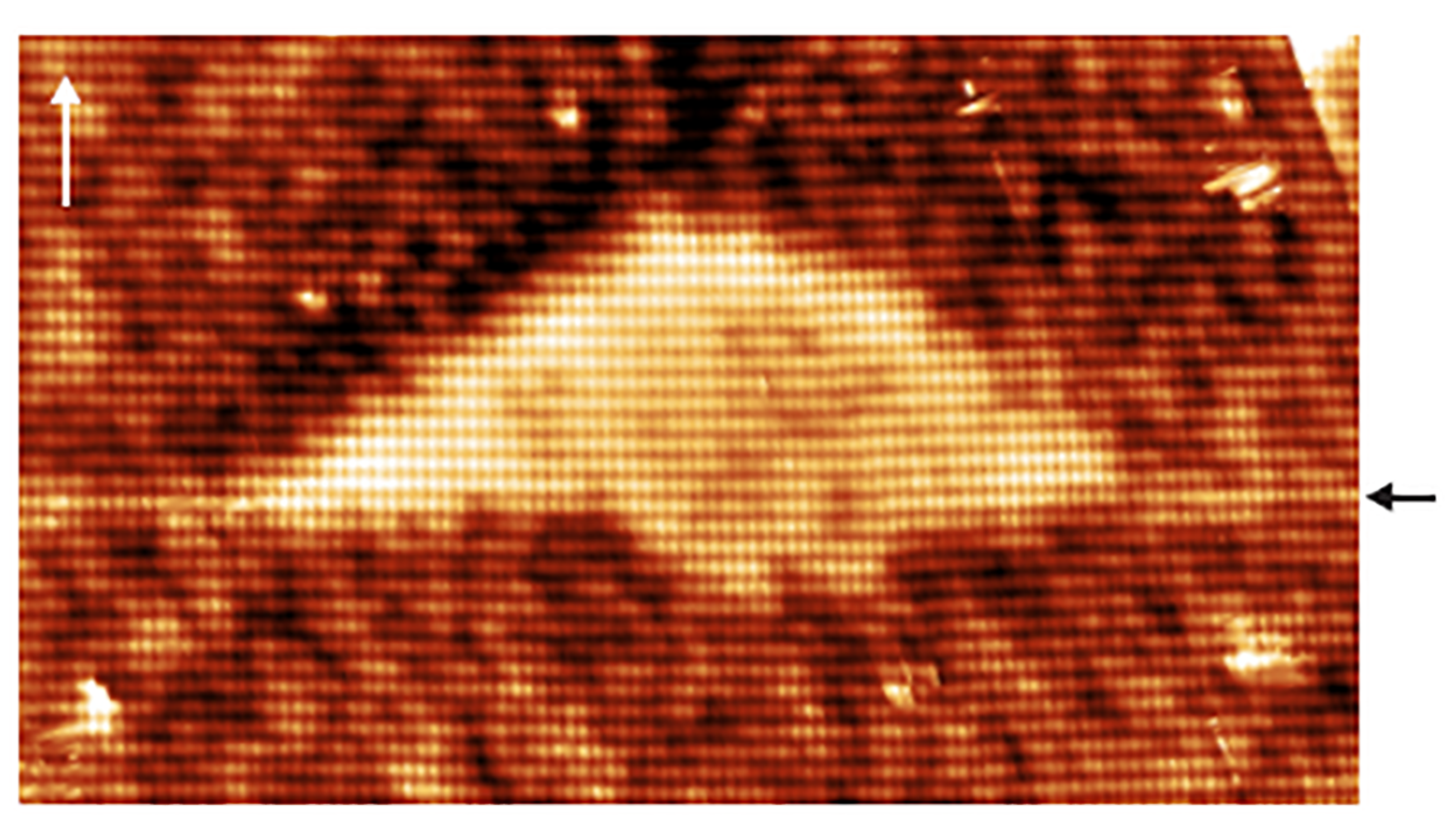
3.4. Cross-Sectional Scanning Tunneling Microscopy
4. Strain-Free GaAs/AlGaAs DEQDs
4.1. Size and Shape of the QDs
4.2. GaAs-Rich Intrusions and Al Intermixing
4.3. Size Control and Composition of GaAs/AlGaAs DEQDs
4.4. GaAs/AlGaAs Quantum Dots and Quantum Wires on GaAs(311)A Substrate
5. Strained InAs/InP DEQDs
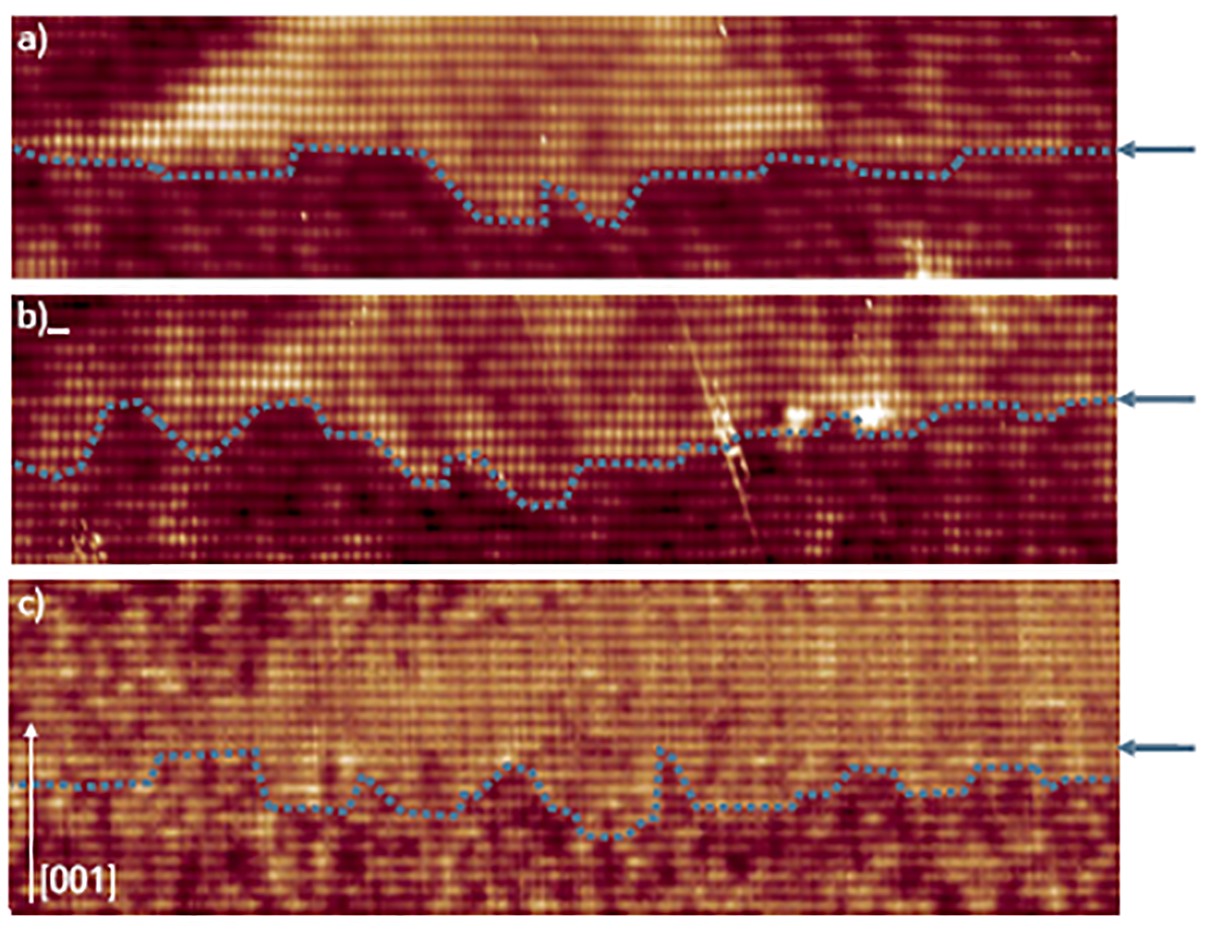
X-STM of Strained InAs/InP DEQDs
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Jiang, H.; Singh, J. Self-assembled semiconductor structures: Electronic and optoelectronic properties. IEEE J. Quantum Electron. 1998, 34, 1188–1196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bimberg, D.; Kirstaedter, N.; Ledentsov, N.; Alferov, Z.; Kop’ev, P.; Ustinov, V. InGaAs-GaAs quantum-dot lasers. IEEE J. Select. Top. Quantum Electron. 1997, 3, 196–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bimberg, D. Quantum dots for lasers, amplifiers and computing. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 2005, 38, 2055–2058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mikhrin, S.S.; Zhukov, A.E.; Kovsh, A.R.; Maleev, N.A.; Ustinov, V.M.; Shernyakov, Y.M.; Soshnikov, I.P.; Livshits, D.A.; Tarasov, I.S.; Bedarev, D.A.; et al. 0.94 µm diode lasers based on Stranski-Krastanow and sub-monolayer quantum dots. Semiconduct. Sci. Technol. 2000, 15, 1061–1064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hopfer, F.; Mutig, A.; Fiol, G.; Kuntz, M.; Shchukin, V.A.; Haisler, V.A.; Warming, T.; Stock, E.; Mikhrin, S.S.; Krestnikov, I.L.; et al. 20 Gb/s 85 °C Error-Free Operation of VCSELs Based on Submonolayer Deposition of Quantum Dots. IEEE J. Select. Top. Quantum Electron. 2007, 13, 1302–1308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sugawara, M.; Arakawa, Y.; Tanabe, K. Advanced self-assembled indium arsenide (InAs) quantum-dot lasers. In Semiconductor Lasers; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2013; pp. 272–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herzog, B.; Lingnau, B.; Kolarczik, M.; Helmrich, S.; Achtstein, A.W.; Thommes, K.; Alhussein, F.; Quandt, D.; Strittmatter, A.; Pohl, U.W.; et al. Broadband Semiconductor Light Sources Operating at 1060 nm Based on InAs:Sb/GaAs Submonolayer Quantum Dots. IEEE J. Select. Top. Quantum Electron. 2019, 25, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Müller, T.; Skiba-Szymanska, J.; Krysa, A.B.; Huwer, J.; Felle, M.; Anderson, M.; Stevenson, R.M.; Heffernan, J.; Ritchie, D.A.; Shields, A.J. A quantum light-emitting diode for the standard telecom window around 1550 nm. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martín-Sánchez, J.; Muñoz-Matutano, G.; Herranz, J.; Canet-Ferrer, J.; Alén, B.; González, Y.; Alonso-González, P.; Fuster, D.; González, L.; Martínez-Pastor, J.; et al. Single Photon Emission from Site-Controlled InAs Quantum Dots Grown on GaAs(001) Patterned Substrates. ACS Nano 2009, 3, 1513–1517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yuan, Z. Electrically Driven Single-Photon Source. Science 2002, 295, 102–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Salter, C.L.; Stevenson, R.M.; Farrer, I.; Nicoll, C.A.; Ritchie, D.A.; Shields, A.J. An entangled-light-emitting diode. Nature 2010, 465, 594–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aberl, J.; Klenovský, P.; Wildmann, J.S.; Martín-Sánchez, J.; Fromherz, T.; Zallo, E.; Humlíček, J.; Rastelli, A.; Trotta, R. Inversion of the exciton built-in dipole moment in In(Ga)As quantum dots via nonlinear piezoelectric effect. Phys. Rev. B 2017, 96, 045414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Huber, D.; Lehner, B.U.; Csontosová, D.; Reindl, M.; Schuler, S.; Covre da Silva, S.F.; Klenovský, P.; Rastelli, A. Single-particle-picture breakdown in laterally weakly confining GaAs quantum dots. Phys. Rev. B 2019, 100, 235425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Csontosová, D.; Klenovský, P. Theory of magneto-optical properties of neutral and charged excitons in GaAs/AlGaAs quantum dots. Phys. Rev. B 2020, 102, 125412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nozik, A. Quantum dot solar cells. Physica E 2002, 14, 115–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lam, P.; Wu, J.; Tang, M.; Jiang, Q.; Hatch, S.; Beanland, R.; Wilson, J.; Allison, R.; Liu, H. Submonolayer InGaAs/GaAs quantum dot solar cells. Sol. Energy Mater. Sol. Cells 2014, 126, 83–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kim, Y.; Ban, K.Y.; Honsberg, C.B. Multi-stacked InAs/GaAs quantum dots grown with different growth modes for quantum dot solar cells. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2015, 106, 222104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stanojević, L.; Gonzalo, A.; Utrilla, A.D.; Reyes, D.F.; Braza, V.; González, D.; Marrón, D.F.; Hierro, A.; Ulloa, J.M. Effect of capping rate on InAs/GaAs quantum dot solar cells. In Physics, Simulation, and Photonic Engineering of Photovoltaic Devices VIII; Freundlich, A., Lombez, L., Sugiyama, M., Eds.; International Society for Optics and Photonics, SPIE: San Diego, CA, USA, 2019; Volume 10913, pp. 111–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vichi, S.; Bietti, S.; Khalili, A.; Costanzo, M.; Cappelluti, F.; Esposito, L.; Somaschini, C.; Fedorov, A.; Tsukamoto, S.; Rauter, P.; et al. Droplet epitaxy quantum dot based infrared photodetectors. Nanotechnology 2020, 31, 245203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.T.; Chen, Y.C.; Lee, S.C. Improved photoresponse of InAs/GaAs quantum dot infrared photodetectors by using GaAs1-xSbx strain reducing layer. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2012, 100, 043512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, I.S.; Kim, J.S.; Shin, J.C.; Kim, J.O.; Noh, S.K.; Lee, S.J.; Krishna, S. Photoluminescence study of InAs/InGaAs sub-monolayer quantum dot infrared photodetectors with various numbers of multiple stack layers. J. Lumin. 2019, 207, 512–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Claro, M.; Stroppa, D.; da Silva, E.; Quivy, A. Strong photovoltaic effect in high-density InAlAs and InAs/InAlAs quantum-dot infrared photodetectors. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 2020, 315, 112262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michler, P. (Ed.) Quantum Dots for Quantum Information Technologies. In Nano-Optics and Nanophotonics; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Swizerland, 2017; pp. 1–3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hadfield, R.H. Single-photon detectors for optical quantum information applications. Nat. Photonics 2009, 3, 696–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X. An All-Optical Quantum Gate in a Semiconductor Quantum Dot. Science 2003, 301, 809–811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Nilsson, J.; Stevenson, R.M.; Chan, K.H.; Skiba-Szymanska, J.; Lucamarini, M.; Ward, M.B.; Bennett, A.J.; Salter, C.L.; Farrer, I.; Ritchie, D.A.; et al. Quantum teleportation using a light-emitting diode. Nat. Photonics 2013, 7, 311–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varnava, C.; Stevenson, R.M.; Nilsson, J.; Skiba-Szymanska, J.; Dzurňák, B.; Lucamarini, M.; Penty, R.V.; Farrer, I.; Ritchie, D.A.; Shields, A.J. An entangled-LED-driven quantum relay over 1 km. NPJ Quantum Inform. 2016, 2, 16006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huwer, J.; Stevenson, R.M.; Skiba-Szymanska, J.; Ward, M.B.; Shields, A.J.; Felle, M.; Farrer, I.; Ritchie, D.A.; Penty, R.V. Quantum-dot-based telecommunication-wavelength quantum relay. Phys. Rev. Appl. 2017, 8, 024007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Stevenson, R.M.; Young, R.J.; Atkinson, P.; Cooper, K.; Ritchie, D.A.; Shields, A.J. A semiconductor source of triggered entangled photon pairs. Nature 2006, 439, 179–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ledentsov, N.N.; Ustinov, V.M.; Shchukin, V.A.; Kop’ev, P.S.; Alferov, Z.I.; Bimberg, D. Quantum dot heterostructures: Fabrication, properties, lasers (Review). Semiconductors 1998, 32, 343–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smakman, E.P.; DeJarld, M.; Luengo-Kovac, M.; Martin, A.J.; Sih, V.; Koenraad, P.M.; Millunchick, J. Height stabilization of GaSb/GaAs quantum dots by Al-rich capping. APL Mater. 2014, 2, 096111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shiramine, K.-i.; Horisaki, Y.; Suzuki, D.; Itoh, S.; Ebiko, Y.; Muto, S.; Nakata, Y.; Yokoyama, N. Threading Dislocations in Multilayer Structure of InAs Self-Assembled Quantum Dots. Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 1998, 37, 5493–5496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, K.M.; Park, Y.J.; Roh, C.H.; Park, Y.M.; Kim, E.K.; Hyon, C.K.; Park, J.H.; Kim, T.W. Shape and Interband Transition Behavior of InAs Quantum Dots Dependent on Number of Stacking Cycles. Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 2003, 42, 54–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koguchi, N.; Takahashi, S.; Chikyow, T. New MBE growth method for InSb quantum well boxes. J. Cryst. Growth 1991, 111, 688–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Somaschini, C.; Bietti, S.; Koguchi, N.; Sanguinetti, S. Fabrication of Multiple Concentric Nanoring Structures. Nano Lett. 2009, 9, 3419–3424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koguchi, N.; Ishige, K. Growth of GaAs Epitaxial Microcrystals on an S-Terminated GaAs Substrate by Successive Irradiation of Ga and As Molecular Beams. Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 1993, 32, 2052–2058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanguinetti, S.; Watanabe, K.; Tateno, T.; Gurioli, M.; Werner, P.; Wakaki, M.; Koguchi, N. Modified droplet epitaxy GaAs/AlGaAs quantum dots grown on a variable thickness wetting layer. J. Cryst. Growth 2003, 253, 71–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bietti, S.; Somaschini, C.; Sanguinetti, S.; Koguchi, N.; Isella, G.; Chrastina, D. Fabrication of high efficiency III-V quantum nanostructures at low thermal budget on Si. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2009, 95, 241102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.H.; Wang, Z.M.; Kim, N.Y.; Salamo, G.J. Size and density control of In droplets at near room temperatures. Nanotechnology 2009, 20, 285602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mano, T.; Watanabe, K.; Tsukamoto, S.; Fujioka, H.; Oshima, M.; Koguchi, N. New Self-Organized Growth Method for InGaAs Quantum Dots on GaAs(001) Using Droplet Epitaxy. Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 1999, 38, L1009–L1011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, N.; Lyeo, H.K.; Shih, C.K.; Oshima, M.; Mano, T.; Koguchi, N. Cross-sectional scanning tunneling microscopy study of InGaAs quantum dots on GaAs(001) grown by heterogeneous droplet epitaxy. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2002, 80, 4345–4347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanguinetti, S.; Bietti, S.; Koguchi, N. Droplet Epitaxy of Nanostructures. In Molecular Beam Epitaxy; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2018; pp. 293–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiravittaya, S.; Rastelli, A.; Schmidt, O.G. Advanced quantum dot configurations. Rep. Prog. Phys. 2009, 72, 046502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gurioli, M.; Wang, Z.; Rastelli, A.; Kuroda, T.; Sanguinetti, S. Droplet epitaxy of semiconductor nanostructures for quantum photonic devices. Nat. Mater. 2019, 18, 799–810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Wang, Z.M. Droplet epitaxy for advanced optoelectronic materials and devices. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 2014, 47, 173001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Binnig, G.; Quate, C.; Gerber, C. Atomic Force Microscope. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1986, 56, 930–933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- García, R. Dynamic atomic force microscopy methods. Surf. Sci. Rep. 2002, 47, 197–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giessibl, F.J. Advances in atomic force microscopy. Rev. Mod. Phys. 2003, 75, 949–983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Offermans, P. Study of III-V Semiconductor Nanostructures by Cross-Sectional Scanning Tunneling Microscopy. Ph.D. Thesis, Technische Universiteit Eindhoven, Eindhoven, The Netherland, 2005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Offermans, P.; Koenraad, P.M.; Wolter, J.H.; Pierz, K.; Roy, M.; Maksym, P.A. Atomic-scale structure and photoluminescence of InAs quantum dots in GaAs and AlAs. Phys. Rev. B 2005, 72, 165332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Walther, T. Transmission Electron Microscopy of Nanostructures. In Microscopy Methods in Nanomaterials Characterization; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2017; pp. 105–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inoue, T.; Kita, T.; Wada, O.; Konno, M.; Yaguchi, T.; Kamino, T. Electron tomography of embedded semiconductor quantum dot. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2008, 92, 031902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cerezo, A.; Godfrey, T.J.; Smith, G.D.W. Application of a position-sensitive detector to atom probe microanalysis. Rev. Sci. Instrum. 1988, 59, 862–866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thompson, K.; Flaitz, P.L.; Ronsheim, P.; Larson, D.J.; Kelly, T.F. Imaging of Arsenic Cottrell Atmospheres Around Silicon Defects by Three-Dimensional Atom Probe Tomography. Science 2007, 317, 1370–1374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Müller, M.; Cerezo, A.; Smith, G.D.W.; Chang, L.; Gerstl, S.S.A. Atomic scale characterization of buried InxGa1-xAs quantum dots using pulsed laser atom probe tomography. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2008, 92, 233115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giddings, A.D.; Keizer, J.G.; Hara, M.; Hamhuis, G.J.; Yuasa, H.; Fukuzawa, H.; Koenraad, P.M. Composition profiling of InAs quantum dots and wetting layers by atom probe tomography and cross-sectional scanning tunneling microscopy. Phys. Rev. B 2011, 83, 205308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gault, B.; Moody, M.P.; de Geuser, F.; Tsafnat, G.; La Fontaine, A.; Stephenson, L.T.; Haley, D.; Ringer, S.P. Advances in the calibration of atom probe tomographic reconstruction. J. Appl. Phys. 2009, 105, 034913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelly, T.F. Atom-Probe Tomography. In Springer Handbooks; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2019; pp. 715–763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kelly, T.F.; Miller, M.K. Atom probe tomography. Rev. Sci. Instrum. 2007, 78, 031101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Binnig, G.; Rohrer, H. Scanning tunneling microscopy. Surf. Sci. 1983, 126, 236–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Binnig, G.; Rohrer, H.; Gerber, C.; Weibel, E. Tunneling through a controllable vacuum gap. Appl. Phys. Lett. 1982, 40, 178–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Binning, G.; Rohrer, H. Scanning tunneling microscopy. Helv. Phys. Acta 1982, 55, 726–735. [Google Scholar]
- Feenstra, R.M.; Fein, A.P. Surface morphology of GaAs(110) by scanning tunneling microscopy. Phys. Rev. B 1985, 32, 1394–1396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feenstra, R.M.; Yu, E.T.; Woodall, J.M.; Kirchner, P.D.; Lin, C.L.; Pettit, G.D. Cross-sectional imaging and spectroscopy of GaAs doping superlattices by scanning tunneling microscopy. Appl. Phys. Lett. 1992, 61, 795–797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feenstra, R.M.; Stroscio, J.A.; Tersoff, J.; Fein, A.P. Atom-selective imaging of the GaAs(110) surface. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1987, 58, 1192–1195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Offermans, P.; Koenraad, P.M.; Wolter, J.H.; Song, J.D.; Kim, J.M.; Bae, S.J.; Lee, Y.T. Annealing of InGaAlAs digital alloy studied with scanning-tunneling microscopy and filled-states topography. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2003, 82, 1191–1193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Offermans, P.; Koenraad, P.; Wolter, J.; Pierz, K.; Roy, M.; Maksym, P. Formation of InAs quantum dots and wetting layers in GaAs and AlAs analyzed by cross-sectional scanning tunneling microscopy. Physica E 2005, 26, 236–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, Q.; Offermans, P.; Nötzel, R.; Koenraad, P.M.; Wolter, J.H. Capping process of InAs/GaAs quantum dots studied by cross-sectional scanning tunneling microscopy. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2004, 85, 5697–5699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- He, J.; Nötzel, R.; Offermans, P.; Koenraad, P.M.; Gong, Q.; Hamhuis, G.J.; Eijkemans, T.J.; Wolter, J.H. Formation of columnar (In,Ga)As quantum dots on GaAs(100). Appl. Phys. Lett. 2004, 85, 2771–2773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ulloa, J.; Offermans, P.; Koenraad, P. InAs Quantum Dot Formation Studied at the Atomic Scale by Cross-sectional Scanning Tunnelling Microscopy. In Handbook of Self Assembled Semiconductor Nanostructures for Novel Devices in Photonics and Electronics; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2008; pp. 165–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Blokland, J.H.; Bozkurt, M.; Ulloa, J.M.; Reuter, D.; Wieck, A.D.; Koenraad, P.M.; Christianen, P.C.M.; Maan, J.C. Ellipsoidal InAs quantum dots observed by cross-sectional scanning tunneling microscopy. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2009, 94, 023107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bruls, D.M.; Koenraad, P.M.; Salemink, H.W.M.; Wolter, J.H.; Hopkinson, M.; Skolnick, M.S. Stacked low-growth-rate InAs quantum dots studied at the atomic level by cross-sectional scanning tunneling microscopy. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2003, 82, 3758–3760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Keizer, J.G.; Bocquel, J.; Koenraad, P.M.; Mano, T.; Noda, T.; Sakoda, K. Atomic scale analysis of self assembled GaAs/AlGaAs quantum dots grown by droplet epitaxy. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2010, 96, 062101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keizer, J.G.; Bozkurt, M.; Bocquel, J.; Mano, T.; Noda, T.; Sakoda, K.; Clark, E.C.; Bichler, M.; Abstreiter, G.; Finley, J.J.; et al. Shape control of quantum dots studied by cross-sectional scanning tunneling microscopy. J. Appl. Phys. 2011, 109, 102413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Keizer, J.G.; Jo, M.; Mano, T.; Noda, T.; Sakoda, K.; Koenraad, P.M. Structural atomic-scale analysis of GaAs/AlGaAs quantum wires and quantum dots grown by droplet epitaxy on a (311)A substrate. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2011, 98, 193112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keizer, J.G.; Henriques, A.B.; Maia, A.D.B.; Quivy, A.A.; Koenraad, P.M. Atomically resolved study of the morphology change of InAs/GaAs quantum dot layers induced by rapid thermal annealing. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2012, 101, 243113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bocquel, J.; Giddings, A.D.; Mano, T.; Prosa, T.J.; Larson, D.J.; Koenraad, P.M. Composition profiling of GaAs/AlGaAs quantum dots grown by droplet epitaxy. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2014, 105, 153102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gajjela, R.S.R.; Hendriks, A.L.; Alzeidan, A.; Cantalice, T.F.; Quivy, A.A.; Koenraad, P.M. Cross-sectional scanning tunneling microscopy of InAs/GaAs(001) submonolayer quantum dots. Phys. Rev. Mater. 2020, 4, 114601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fain, B.; Girard, J.C.; Elvira, D.; David, C.; Beaudoin, G.; Beveratos, A.; Robert-Philip, I.; Sagnes, I.; Wang, Z.Z. Electronic structure of cleaved InAsP/InP(001) quantum dots measured by scanning tunneling spectroscopy. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2010, 97, 171903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaan, S.; He, G.; Feenstra, R.M.; Walker, J.; Towe, E. Electronic states of InAs/GaAs quantum dots by scanning tunneling spectroscopy. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2010, 97, 123110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gaan, S.; He, G.; Feenstra, R.M.; Walker, J.; Towe, E. Size, shape, composition, and electronic properties of InAs/GaAs quantum dots by scanning tunneling microscopy and spectroscopy. J. Appl. Phys. 2010, 108, 114315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Maltezopoulos, T.; Bolz, A.; Meyer, C.; Heyn, C.; Hansen, W.; Morgenstern, M.; Wiesendanger, R. Wave-Function Mapping of InAs Quantum Dots by Scanning Tunneling Spectroscopy. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2003, 91, 196804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.D.; Park, C.; Lee, H.J.; Noh, S.K.; Lee, K.S.; Park, S.J. Formation of self-assembled GaAs/AlGaAs quantum dots by low-temperature epitaxy. Appl. Phys. Lett. 1998, 73, 2615–2617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yeo, I.; Yi, K.S.; Lee, E.H.; Song, J.D.; Kim, J.S.; Han, I.K. Post-thermal-Induced Recrystallization in GaAs/Al0.3Ga0.7As Quantum Dots Grown by Droplet Epitaxy with Near-Unity Stoichiometry. ACS Omega 2018, 3, 8677–8682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mano, T.; Kuroda, T.; Mitsuishi, K.; Noda, T.; Sakoda, K. High-density GaAs/AlGaAs quantum dots formed on GaAs (311)A substrates by droplet epitaxy. J. Cryst. Growth 2009, 311, 1828–1831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeo, I.; Kim, D.; Lee, K.T.; Kim, J.S.; Song, J.D.; Park, C.H.; Han, I.K. Comparative Chemico-Physical Analyses of Strain-Free GaAs/Al0.3Ga0.7As Quantum Dots Grown by Droplet Epitaxy. Nanomaterials 2020, 10, 1301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watanabe, K.; Koguchi, N.; Gotoh, Y. Fabrication of GaAs Quantum Dots by Modified Droplet Epitaxy. Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 2000, 39, L79–L81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Q.; Chen, P.; Madhukar, A. InAs island-induced-strain driven adatom migration during GaAs overlayer growth. Appl. Phys. Lett. 1994, 65, 2051–2053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heyn, C.; Stemmann, A.; Schramm, A.; Welsch, H.; Hansen, W.; Nemcsics, A. Regimes of GaAs quantum dot self-assembly by droplet epitaxy. Phys. Rev. B 2007, 76, 075317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruls, D.; Koenraad, P.; Hopkinson, M.; Wolter, J.; Salemink, H. Determination of the outward relaxation of cleaved strained InAs structures by scanning tunneling microscopy. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2002, 190, 258–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mano, T.; Mitsuishi, K.; Nakayama, Y.; Noda, T.; Sakoda, K. Structural properties of GaAs nanostructures formed by a supply of intense As4 flux in droplet epitaxy. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2008, 254, 7770–7773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.M.; Liang, B.L.; Sablon, K.A.; Salamo, G.J. Nanoholes fabricated by self-assembled gallium nanodrill on GaAs(100). Appl. Phys. Lett. 2007, 90, 113120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keizer, J.G. Atomic-Scale Probing of Metallic and Semiconductor Nanostructures. Ph.D. Thesis, Technische Universiteit Eindhoven, Eindhoven, The Netherland, 2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stemmann, A.; Heyn, C.; Köppen, T.; Kipp, T.; Hansen, W. Local droplet etching of nanoholes and rings on GaAs and AlGaAs surfaces. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2008, 93, 123108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bocquel, J. Atomic Scale Exploration of Natural and Self-Assembled Quantum Structures. Ph.D. Thesis, Technische Universiteit Eindhoven, Eindhoven, The Netherland, 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bietti, S.; Bocquel, J.; Adorno, S.; Mano, T.; Keizer, J.G.; Koenraad, P.M.; Sanguinetti, S. Precise shape engineering of epitaxial quantum dots by growth kinetics. Phys. Rev. B 2015, 92, 075425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nemcsics, A.; Toth, L.; Dobos, L.; Stemmann, A. Facetting of the self-assembled droplet epitaxial GaAs quantum dot. Microelectron. Reliabil. 2011, 51, 927–930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, Y.A.; Hsu, W.T.; Huang, S.H.; Chiu, P.C.; Chyi, J.I.; Chang, W.H. Band alignment tuning of InAs quantum dots with a thin AlGaAsSb capping layer. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2013, 102, 173104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lu, W.; Bozkurt, M.; Keizer, J.G.; Rohel, T.; Folliot, H.; Bertru, N.; Koenraad, P.M. Shape and size control of InAs/InP (113)B quantum dots by Sb deposition during the capping procedure. Nanotechnology 2011, 22, 055703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bozkurt, M.; Ulloa, J.M.; Koenraad, P.M. An atomic scale study on the effect of Sb during capping of MBE grown III–V semiconductor QDs. Semiconduct. Sci. Technol. 2011, 26, 064007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Utrilla, A.D.; Grossi, D.F.; Reyes, D.F.; Gonzalo, A.; Braza, V.; Ben, T.; González, D.; Guzman, A.; Hierro, A.; Koenraad, P.M.; et al. Size and shape tunability of self-assembled InAs/GaAs nanostructures through the capping rate. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2018, 444, 260–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ulloa, J.M.; Koenraad, P.M.; Gapihan, E.; Létoublon, A.; Bertru, N. Double capping of molecular beam epitaxy grown InAs/InP quantum dots studied by cross-sectional scanning tunneling microscopy. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2007, 91, 073106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keizer, J.G.; Clark, E.C.; Bichler, M.; Abstreiter, G.; Finley, J.J.; Koenraad, P.M. An atomically resolved study of InGaAs quantum dot layers grown with an indium flush step. Nanotechnology 2010, 21, 215705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abbarchi, M.; Mano, T.; Kuroda, T.; Sakoda, K. Exciton Dynamics in Droplet Epitaxial Quantum Dots Grown on (311)A-Oriented Substrates. Nanomaterials 2020, 10, 1833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nötzel, R.; Ledentsov, N.N.; Däweritz, L.; Ploog, K.; Hohenstein, M. Semiconductor quantum-wire structures directly grown on high-index surfaces. Phys. Rev. B 1992, 45, 3507–3515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jo, M.; Keizer, J.G.; Mano, T.; Koenraad, P.M.; Sakoda, K. Self-Assembly of GaAs Quantum Wires Grown on (311)A Substrates by Droplet Epitaxy. Appl. Phys. Express 2011, 4, 055501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bietti, S.; Basset, F.B.; Tuktamyshev, A.; Bonera, E.; Fedorov, A.; Sanguinetti, S. High–temperature droplet epitaxy of symmetric GaAs/AlGaAs quantum dots. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 6532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kuroda, T.; Mano, T.; Ha, N.; Nakajima, H.; Kumano, H.; Urbaszek, B.; Jo, M.; Abbarchi, M.; Sakuma, Y.; Sakoda, K.; et al. Symmetric quantum dots as efficient sources of highly entangled photons: Violation of Bell’s inequality without spectral and temporal filtering. Phys. Rev. B 2013, 88, 041306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, X.; Ha, N.; Nakajima, H.; Mano, T.; Kuroda, T.; Urbaszek, B.; Kumano, H.; Suemune, I.; Sakuma, Y.; Sakoda, K. Vanishing fine-structure splittings in telecommunication-wavelength quantum dots grown on (111)A surfaces by droplet epitaxy. Phys. Rev. B 2014, 90, 081301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tuktamyshev, A.; Fedorov, A.; Bietti, S.; Tsukamoto, S.; Sanguinetti, S. Temperature Activated Dimensionality Crossover in the Nucleation of Quantum Dots by Droplet Epitaxy on GaAs(111)A Vicinal Substrates. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 14520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bietti, S.; Esposito, L.; Fedorov, A.; Ballabio, A.; Martinelli, A.; Sanguinetti, S. Characterization and Effect of Thermal Annealing on InAs Quantum Dots Grown by Droplet Epitaxy on GaAs(111)A Substrates. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2015, 10, 247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Huo, Y.H.; Rastelli, A.; Schmidt, O.G. Ultra-small excitonic fine structure splitting in highly symmetric quantum dots on GaAs (001) substrate. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2013, 102, 152105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Skiba-Szymanska, J.; Stevenson, R.M.; Varnava, C.; Felle, M.; Huwer, J.; Müller, T.; Bennett, A.J.; Lee, J.P.; Farrer, I.; Krysa, A.B.; et al. Universal Growth Scheme for Quantum Dots with Low Fine-Structure Splitting at Various Emission Wavelengths. Phys. Rev. Appl. 2017, 8, 014013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Urbańczyk, A.; Keizer, J.G.; Koenraad, P.M.; Nötzel, R. Long wavelength (>1.55 μm) room temperature emission and anomalous structural properties of InAs/GaAs quantum dots obtained by conversion of In nanocrystals. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2013, 102, 073103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]















Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gajjela, R.S.R.; Koenraad, P.M. Atomic-Scale Characterization of Droplet Epitaxy Quantum Dots. Nanomaterials 2021, 11, 85. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano11010085
Gajjela RSR, Koenraad PM. Atomic-Scale Characterization of Droplet Epitaxy Quantum Dots. Nanomaterials. 2021; 11(1):85. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano11010085
Chicago/Turabian StyleGajjela, Raja S. R., and Paul M. Koenraad. 2021. "Atomic-Scale Characterization of Droplet Epitaxy Quantum Dots" Nanomaterials 11, no. 1: 85. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano11010085
APA StyleGajjela, R. S. R., & Koenraad, P. M. (2021). Atomic-Scale Characterization of Droplet Epitaxy Quantum Dots. Nanomaterials, 11(1), 85. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano11010085




