Resveratrol-Loaded Levan Nanoparticles Produced by Electrohydrodynamic Atomization Technique
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Enzymatic Production and Purification of Levan
2.3. Hydrolysis of Levan
2.4. Preparation and Characterization of Polymer Solutions
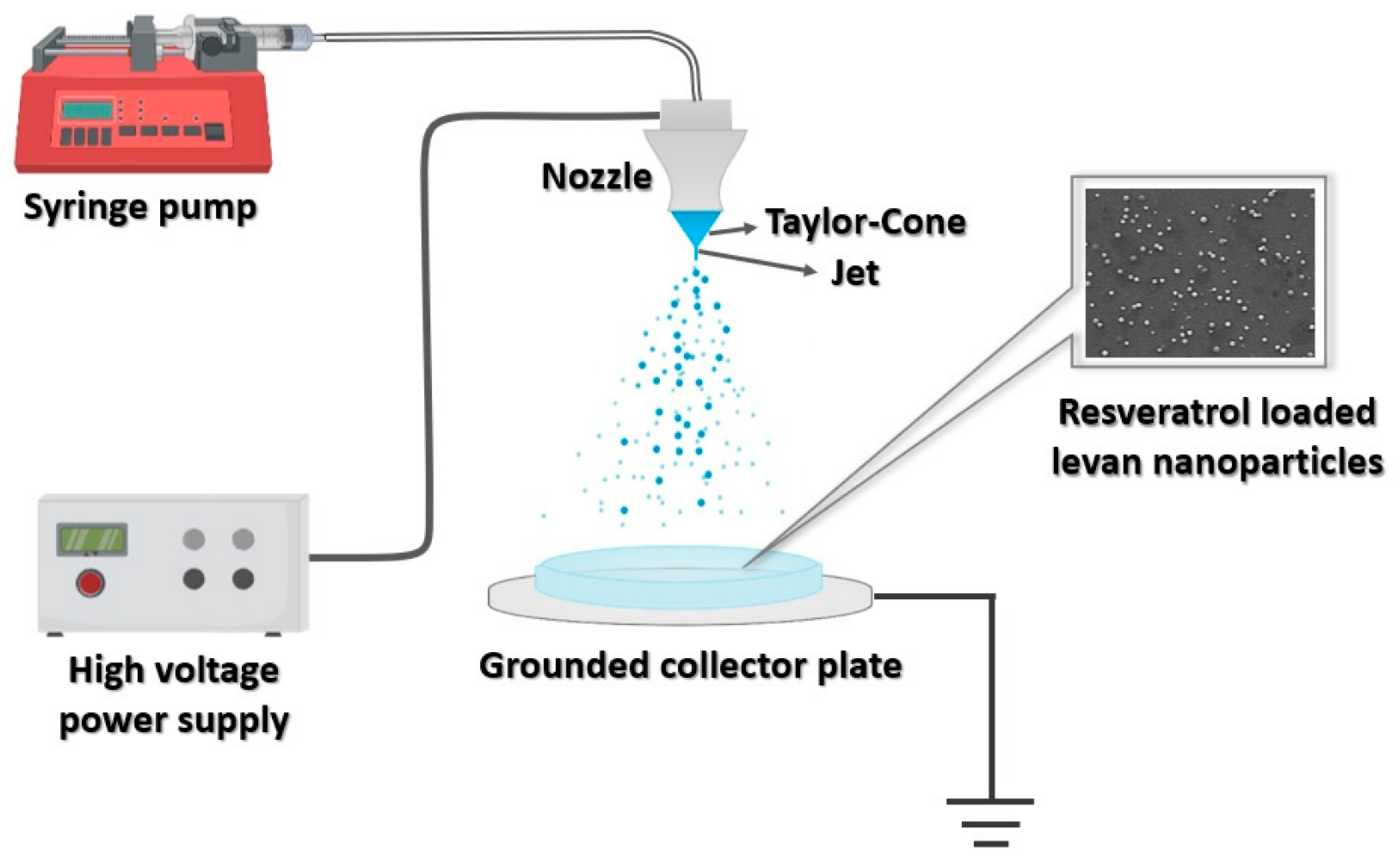
2.5. Experimental Set-Up of EHDA and Fabrication of Levan Nanoparticles
2.6. Morphological and Chemical Characterization of Nanoparticles
2.6.1. Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM) and Optical Microscopy
2.6.2. Fourier-Transformed Infrared (FTIR) Spectroscopy
2.6.3. X-ray Diffraction (XRD)
2.7. Encapsulation Efficiency and In Vitro Release Study
2.8. In Vitro Drug Release Kinetics
2.9. In Vitro Biocompatibility Assay
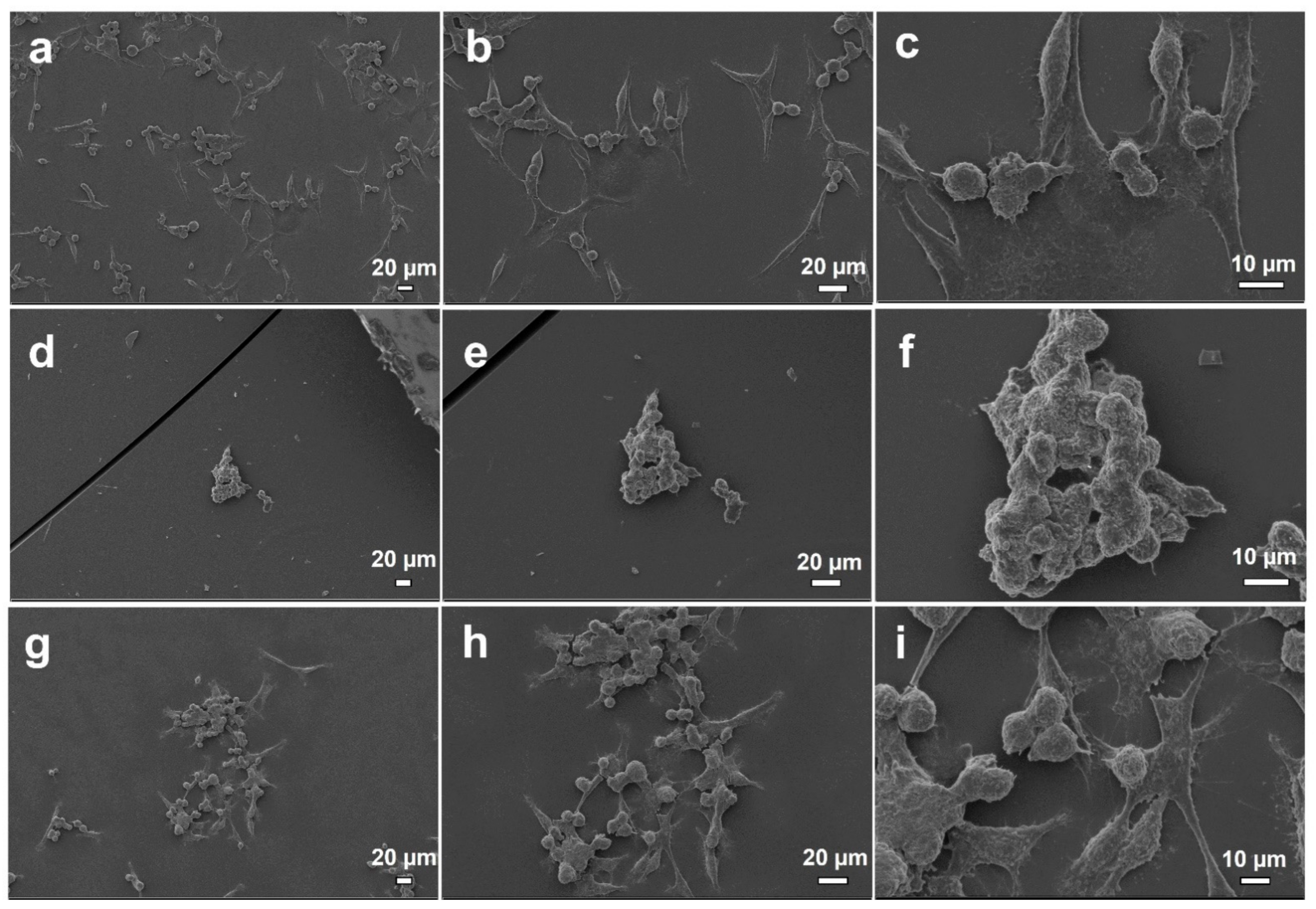
Cell Behavior on Electrosprayed Particle Surfaces
2.10. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Physical Characterization of Polymer Solutions
3.2. Production of Nanoparticles
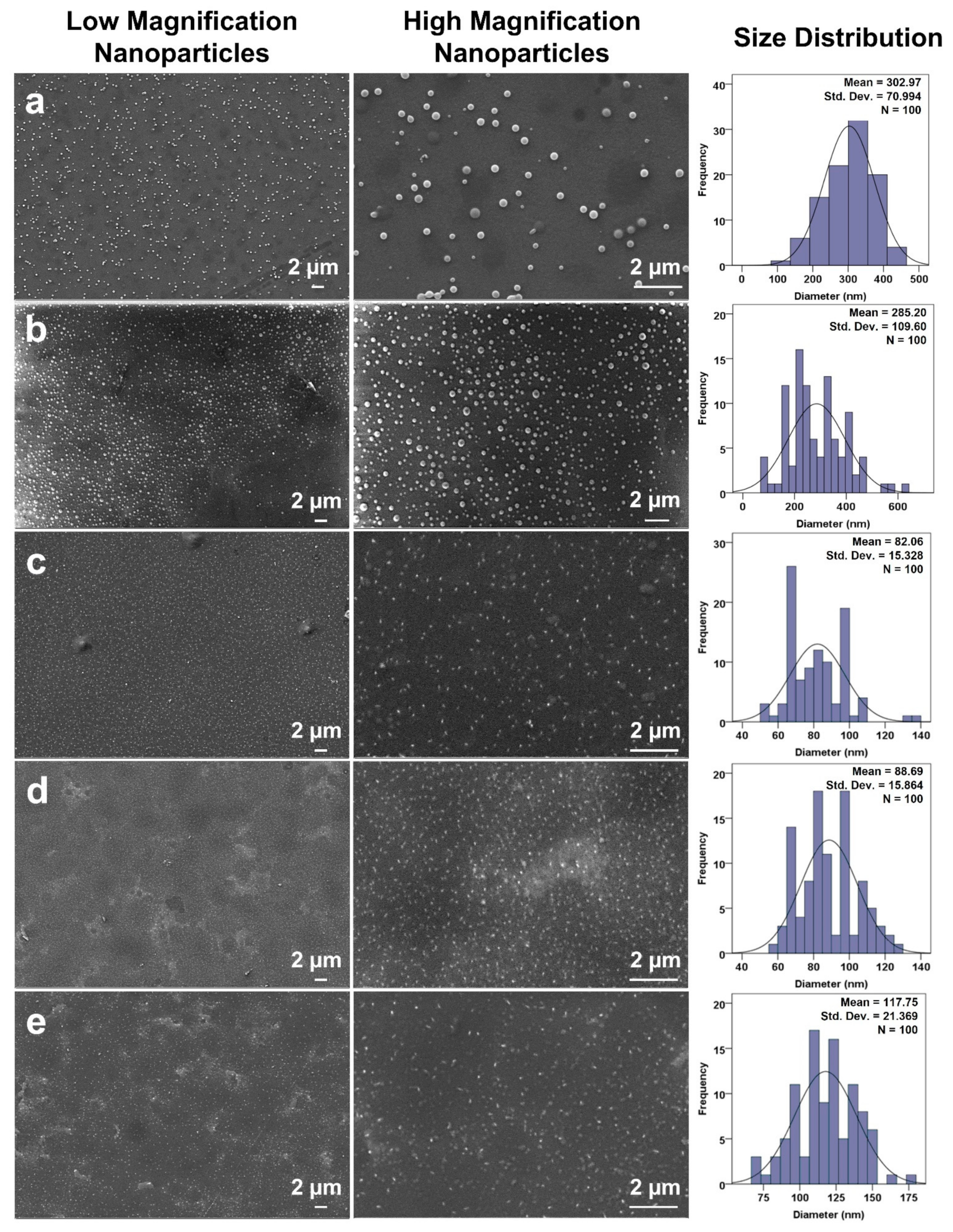
3.3. Morphological Analysis of Produced Nanoparticles
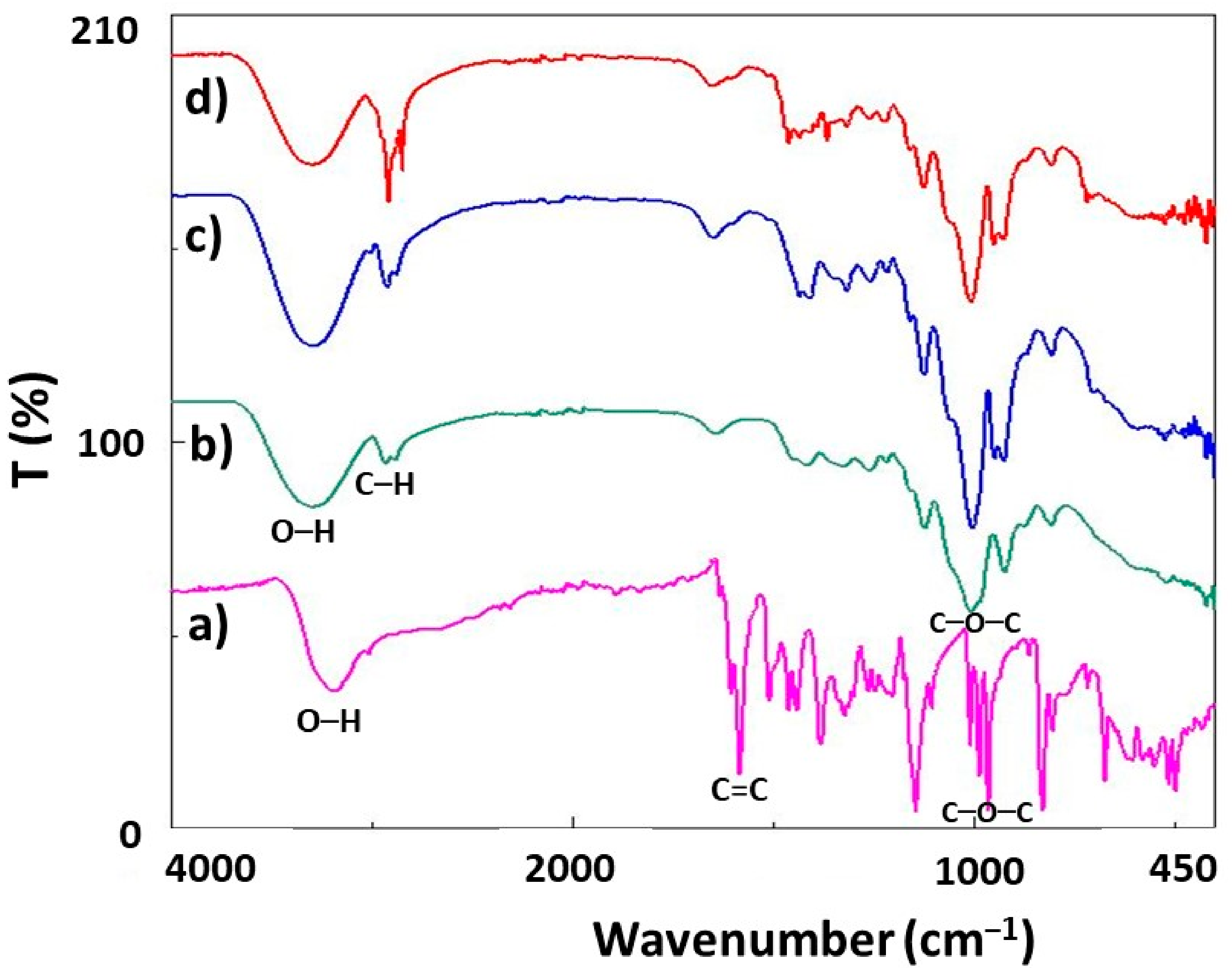
3.4. Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy (FTIR)
3.5. XRD Analysis
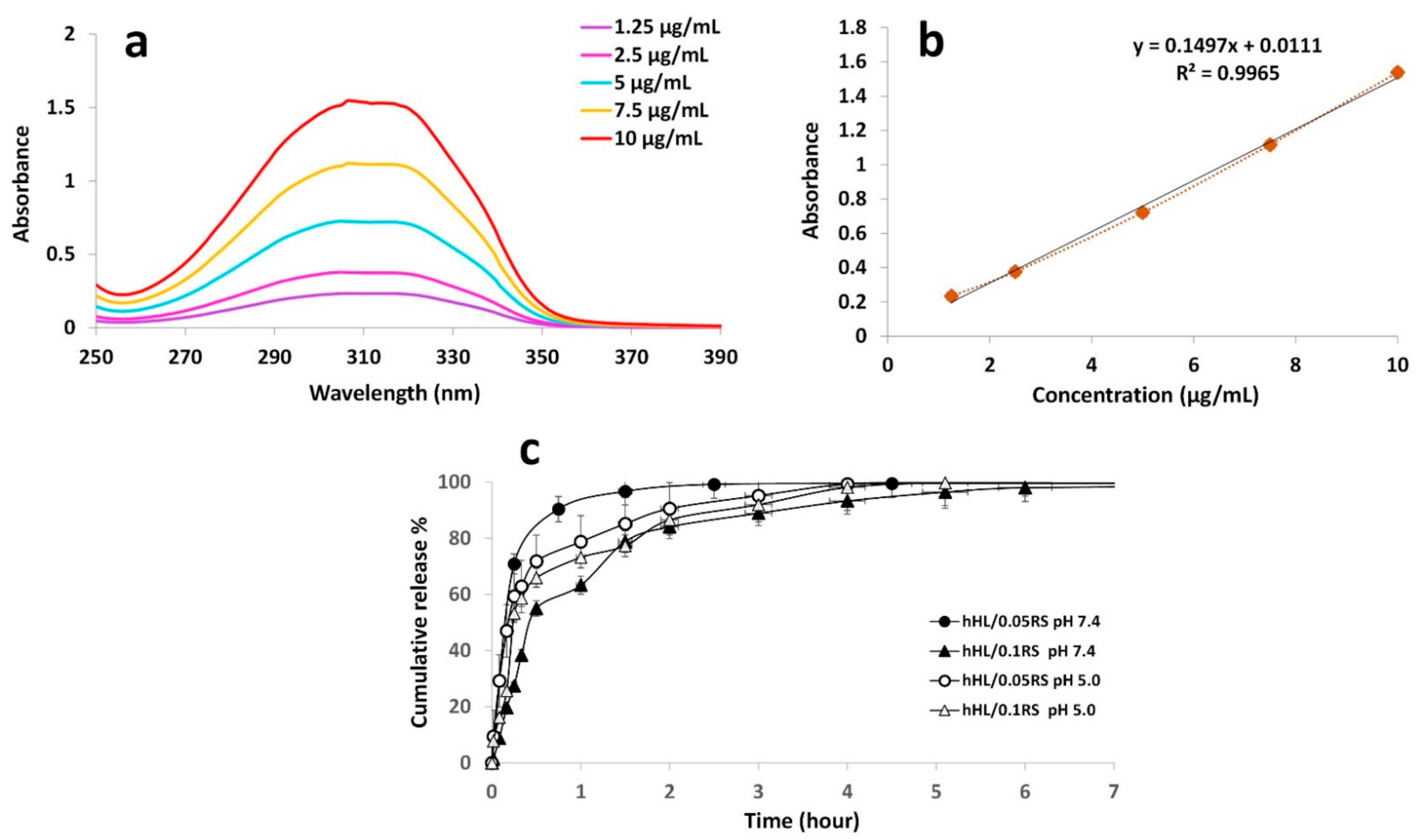
3.6. Encapsulation Efficiency
3.7. In Vitro Release Study
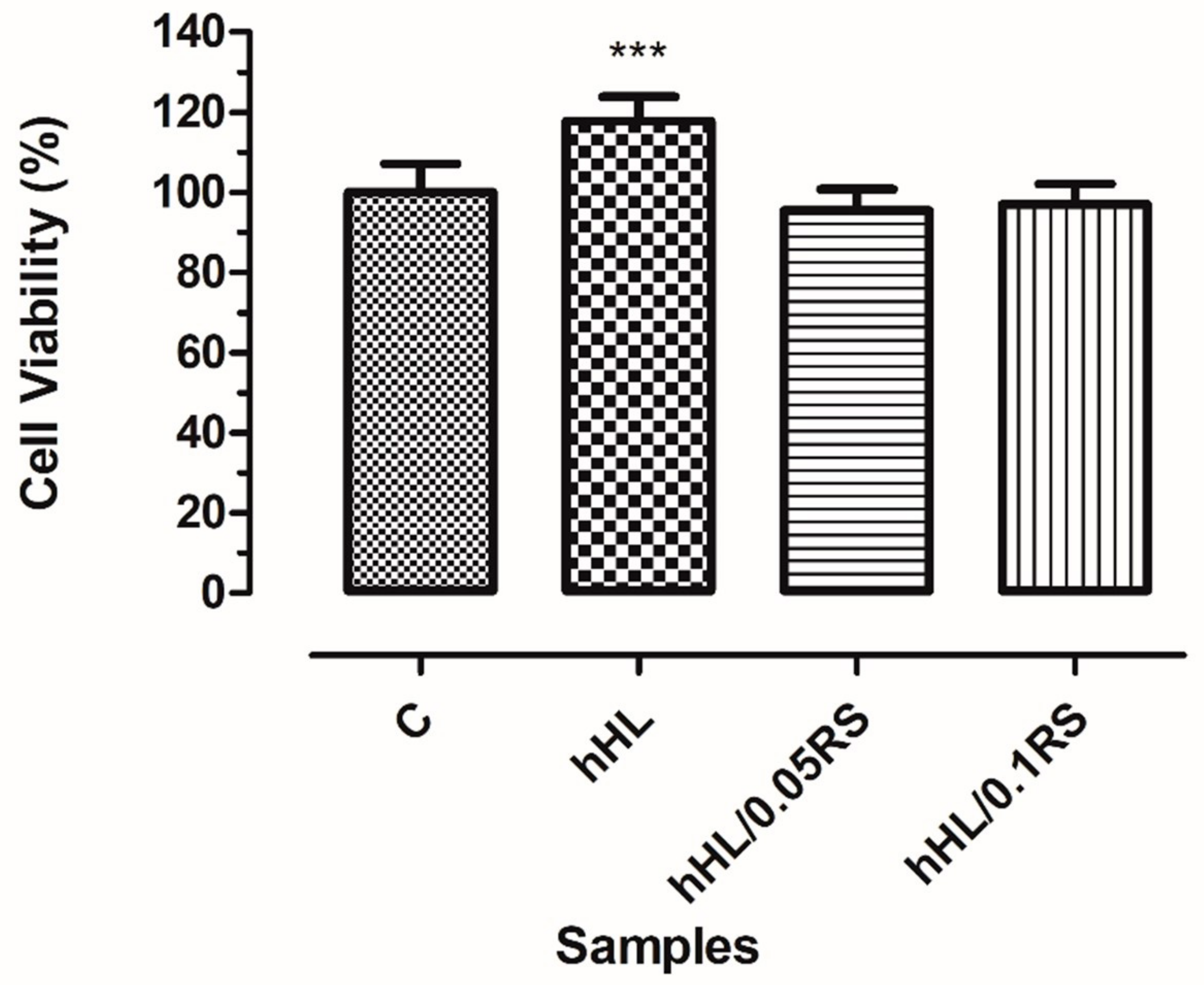
3.8. In Vitro Biocompatibility Assay
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mosaiab, T.; Farr, D.C.; Kiefel, M.J.; Houston, T.A. Carbohydrate-based nanocarriers and their application to target macrophages and deliver antimicrobial agents. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2019, 151, 94–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Zhang, X.; Millican, R.; Sherwood, J.; Martin, S.; Jo, H.; Yoon, Y.-S.; Brott, B.C.; Jun, H.W. Recent advances in nanomaterials for therapy and diagnosis for atherosclerosis. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2021, 170, 142–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumari, A.; Yadav, S.K.; Yadav, S.C. Biodegradable polymeric nanoparticles based drug delivery systems. Colloids Surfaces B Biointerfaces 2010, 75, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nitta, S.K.; Numata, K. Biopolymer-Based Nanoparticles for Drug / Gene Delivery and Tissue Engineering. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2013, 14, 1629–1654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhang, J.; Wang, N.; Li, Q.; Zhou, Y.; Luan, Y. A two-pronged photodynamic nanodrug to prevent metastasis of basal-like breast cancer. Chem. Commun. 2021, 57, 2305–2308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Qin, X.; Xu, W.; Wang, Y.; Song, Y.; Garg, S.; Luan, Y. Engineering of a dual-modal phototherapeutic nanoplatform for single NIR laser-triggered tumor therapy. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2021, 594, 493–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Majumder, J.; Taratula, O.; Minko, T. Nanocarrier-based systems for targeted and site speci fi c therapeutic delivery. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2019, 144, 57–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, T.; Zhou, J.; Piepmeier, J.M.; Saltzman, W.M. Polymeric Nanoparticles for Drug Delivery to the Central Nervous System. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2013, 64, 701–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bihter, E.; Ergul, N.M.; Ozbek, B.; Ekren, N.; Nuzhet, F.O.; Erginer Haskoylu, M.; Toksoy Oner, E.; Eroglu, M.S.; Ozbeyli, D.; Korkut, V.; et al. Materials Science & Engineering C Encapsulated melatonin in polycaprolactone (PCL) microparticles as a promising graft material. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2019, 100, 798–808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hossain, K.M.Z.; Patel, U.; Ahmed, I. Development of microspheres for biomedical applications: A review. Prog. Biomater. 2015, 4, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sezer, A.D.; Kazak Sarılmışer, H.; Rayaman, E.; Çevikbaş, A.; Toksoy Oner, E.; Akbuğa, J. Development and characterization of vancomycin- loaded levan-based microparticular system for drug delivery. Pharm. Dev. Technol. 2017, 22, 627–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miao, T.; Wang, J.; Zeng, Y.; Liu, G.; Chen, X. Polysaccharide-Based Controlled Release Systems for Therapeutics Delivery and Tissue Engineering: From Bench to Bedside. Adv. Sci. 2018, 5, 1700513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tabernero, A.; Cardea, S. Microbial Exopolysaccharides as Drug Carriers. Polymers 2020, 12, 2142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cesur, S.; Çam, M.; Sayin, F.; Su, S.; Gündüz, O. Controlled Release of Metformin Loaded Polyvinyl Alcohol (PVA) Microbubble/Nanoparticles Using Microfluidic Device for the Treatment of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus. In International Work-Conference on Bioinformatics and Biomedical Engineering; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2020; Volume 12108, pp. 185–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cesur, S.; Oktar, F.N.; Ekren, N.; Kilic, O.; Alkaya, D.B.; Seyhan, S.A.; Ege, Z.R.; Lin, C.C.; Kuruca, S.E.; Erdemir, G.; et al. Preparation and characterization of electrospun polylactic acid/sodium alginate/orange oyster shell composite nanofiber for biomedical application. J. Aust. Ceram. Soc. 2020, 56, 533–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toksoy Oner, E.; Hernández, L.; Combie, J. Review of Levan polysaccharide: From a century of past experiences to future prospects. Biotechnol. Adv. 2016, 34, 827–844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Srikanth, R.; Reddy, C.H.S.S.S.; Siddartha, G.; Ramaiah, M.J.; Uppuluri, K.B. Review on production, characterization and applications of microbial levan. Carbohydr. Polym. 2015, 120, 102–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kirtel, O.; Menéndez, C.; Versluys, M.; Van Den Ende, W.; Hernández, L.; Toksoy Oner, E. Levansucrase from Halomonas smyrnensis AAD6 T: First halophilic GH-J clan enzyme recombinantly expressed, purified, and characterized. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2018, 102, 9207–9220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berg, A.; Toksoy Oner, E.; Combie, J.; Schneider, B.; Ellinger, R.; Weisser, J.; Wyrwa, R.; Schnabelrauch, M. Formation of new, cytocompatible hydrogels based on photochemically crosslinkable levan methacrylates. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 107, 2312–2319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poli, A.; Kazak, H.; Gürleyendaǧ, B.; Tommonaro, G.; Pieretti, G.; Toksoy Oner, E.; Nicolaus, B. High level synthesis of levan by a novel Halomonas species growing on defined media. Carbohydr. Polym. 2009, 78, 651–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poli, A.; Nicolaus, B.; Denizci, A.A.; Yavuzturk, B. Halomonas smyrnensis sp. nov., a moderately halophilic, exopolysaccharide-producing bacterium. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2013, 63, 10–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erkorkmaz, B.A.; Kırtel, O.; Ateş Duru, Ö.; Toksoy Oner, E. Development of a cost-effective production process for Halomonas levan. Bioprocess Biosyst. Eng. 2018, 41, 1247–1259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Özcan, E.; Toksoy Oner, E. Microbial Production of Extracellular Polysaccharides from Biomass Sources. In Polysaccharides; Ramawat, K.G., Mérillon, J.-M., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2015; pp. 161–184. ISBN 9783319162980. [Google Scholar]
- Kazak Sarilmiser, H.; Toksoy Oner, E. Investigation of anti-cancer activity of linear and aldehyde-activated levan from Halomonas smyrnensis AAD6T. Biochem. Eng. J. 2014, 92, 28–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erginer, M.; Akcay, A.; Coskunkan, B.; Morova, T.; Rende, D.; Toksoy, E.; Bucak, S.; Baysal, N.; Ozisik, R.; Eroglu, M.S.; et al. Sulfated levan from Halomonas smyrnensis as a bioactive, heparin-mimetic glycan for cardiac tissue engineering applications. Carbohydr. Polym. 2016, 149, 289–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sennaroglu Bostan, M.; Cansever Mutlu, E.; Kazak, H.; Keskin, S.S.; Toksoy Oner, E.; Eroglu, M.S. Comprehensive characterization of chitosan/PEO/levan ternary blend films. Carbohydr. Polym. 2014, 102, 993–1000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, R.R.; Neto, A.I.; Calgeris, I.; Correia, C.R.; Pinho, A.C.M.; Fonseca, J.; Toksoy Oner, E.; Mano, J.F. Adhesive nanostructured multilayer films using a bacterial exopolysaccharide for biomedical applications. J. Mater. Chem. B 2013, 1, 2367–2374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sezer, A.D.; Kazak, H.; Toksoy Oner, E.; Akbuğa, J. Levan-based nanocarrier system for peptide and protein drug delivery: Optimization and influence of experimental parameters on the nanoparticle characteristics. Carbohydr. Polym. 2011, 84, 358–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avsar, G.; Agirbasli, D.; Ali, M.; Gunduz, O. Levan based fibrous scaffolds electrospun via co-axial and single-needle techniques for tissue engineering applications. Carbohydr. Polym. 2018, 193, 316–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davidov-pardo, G.; Mcclements, D.J. Resveratrol encapsulation: Designing delivery systems to overcome solubility, stability and bioavailability issues. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2014, 38, 88–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Wang, L.; Han, L.; Wang, Y.; Dai, B.; Song, X. Anchoring resveratrol on surface of electrospun star-shaped PCL-COOH/PLLA fibers. Int. J. Polym. Mater. Polym. Biomater. 2019, 69, 739–747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salehi, B.; Mishra, A.P.; Nigam, M.; Sener, B.; Kilic, M. Resveratrol: A Double-Edged Sword in Health Benefits. Biomedicines 2018, 6, 91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jayan, H.; Leena, M.M.; Sundari, S.K.S.; Moses, J.A.; Anandharamakrishnan, C. Improvement of bioavailability for resveratrol through encapsulation in zein using electrospraying technique. J. Funct. Foods 2019, 57, 417–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peñalva, R.; Morales, J.; Gonz, C.J.; Larrañeta, E.; Quincoces, G.; Peñuelas, I.; Irache, J.M. Increased Oral Bioavailability of Resveratrol by Its Encapsulation in Casein Nanoparticles. Int. J. Mol. Sci. Artic. 2018, 19, 2816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Amri, A.; Chaumeil, J.C.; Sfar, S.; Charrueau, C. Administration of resveratrol: What formulation solutions to bioavailability limitations ? J. Control. Release 2012, 158, 182–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zupančič, Š.; Lavric, Z.; Kristl, J. Stability and solubility of trans -resveratrol are strongly influenced by pH and temperature. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2015, 93, 196–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arya, N.; Chakraborty, S.; Dube, N.; Katti, D.S. Electrospraying: A Facile Technique for Synthesis of Chitosan-Based Micro / Nanospheres for Drug Delivery Applications. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. Part B Appl. Biomater. 2008, 88, 17–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cesur, S.; Cam, M.E.; Sayın, F.S.; Su, S.; Harker, A.; Edirisinghe, M.; Gunduz, O. Metformin-Loaded Polymer-Based Microbubbles/Nanoparticles Generated for the Treatment of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus. Langmuir 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oliveira, M.B.; Mano, J.F. Polymer-Based Microparticles in Tissue Engineering and Regenerative Medicine. Biotechnol. Prog. 2011, 27, 897–912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhang, L.; Huang, J.; Si, T.; Xu, R.X. Coaxial electrospray of microparticles and nanoparticles for biomedical applications. Expert Rev. Med. Devices 2012, 9, 595–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tasci, M.E.; Dede, B.; Tabak, E.; Gur, A.; Sulutas, R.B.; Cesur, S.; Ilhan, E.; Lin, C.C.; Paik, P.; Ficai, D.; et al. Production, optimization and characterization of polylactic acid microparticles using electrospray with porous structure. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 5090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, D.N.; Clasen, C.; Mooter, G. Van Den Pharmaceutical Applications of Electrospraying. J. Pharm. Sci. 2016, 2601–2620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Correira, C.R.; Ghasemzadeh-hasankolaei, M.; Mano, J.F. Cell encapsulation in liquified compartments: Protocol optimization and challenges. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0218045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, J.; Jiang, J.; Davoodi, P.; Srinivasan, M.P.; Wang, C. Electrohydrodynamic atomization: A two-decade effort to produce and process micro- / nanoparticulate materials. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2015, 125, 32–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chakraborty, S.; Liao, I.; Adler, A.; Leong, K.W. Electrohydrodynamics: A facile technique to fabricate drug delivery systems ☆. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2009, 61, 1043–1054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wu, Y.; Mackay, J.A.; Mcdaniel, J.R.; Chilkoti, A.; Clark, R.L. Fabrication of Elastin-Like Polypeptide Nanoparticles for Drug Delivery by Electrospraying. Biomacromolecules 2009, 10, 19–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nikolaou, M.; Krasia-christoforou, T. Electrohydrodynamic methods for the development of pulmonary drug delivery systems. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2018, 113, 29–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Siqueira, E.C.; Rebouças, J.D.S.; Pinheiro, I.O. Levan-based nanostructured systems: An overview. Int. J. Pharm. 2020, 580, 119242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.; Bae, P.K.; Chung, B.H. Self-assembled levan nanoparticles for targeted breast cancer imaging. Chem. Commun. 2015, 51, 107–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González-Garcinuño, Á.; Masa, R.; Hernández, M.; Domínguez, Á.; Tabernero, A.; Martín del Valle, E. Levan-Capped Silver Nanoparticles for Bactericidal Formulations: Release and Activity Modelling. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 1502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kim, K.H.; Chung, C.B.; Kim, Y.H.; Kim, K.S.; Han, C.S.; Kim, C.H. Cosmeceutical properties of levan produced by Zymomonas mobilis. J. Cosmet. Sci. 2005, 56, 395–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.C.; Kim, D.H.; Song, Y.H.; Cha, H.J.; Seo, J.H. Electrohydrodynamic Sprayable Amphiphilic Polysaccharide- Clasped Nanoscale Self-Assembly for In Vivo Imaging. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2020, 12, 38899–38905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, I.H.; Khalil, I.; El-sherbiny, I. Single-Dose Electrospun Nanoparticles-in-Nanofibers Wound Dressings with Single-Dose Electrospun Nanoparticles-in-Nano fi bers Wound Dressings with Enhanced Epithelialization, Collagen Deposition, and Granulation Properties. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2016, 8, 14453–14469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gouda, R.; Baishya, H.; Qing, Z. Application of Mathematical Models in Drug Release Kinetics of Carbidopa and Levodopa ER Tablets. J. Dev. Drugs 2017, 6, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciach, T. Application of electro-hydro-dynamic atomization in drug delivery. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2007, 17, 367–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, A.d.S.B.F.; Brito, G.A.d.C.; Lima, M.L.d.S.; Silva Júnior, A.A.d.; Silva, E.d.S.; De Rezende, A.A.; Bortolin, R.H.; Galvan, M.; Pirih, F.Q.; Araújo Júnior, R.F.d.; et al. Metformin Hydrochloride-Loaded PLGA Nanoparticle in Periodontal Disease Experimental Model Using Diabetic Rats. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 3488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bhushani, J.A.; Kurrey, N.K.; Anandharamakrishnan, C. Nanoencapsulation of green tea catechins by electrospraying technique and its effect on controlled release and in-vitro permeability. J. Food Eng. 2017, 199, 82–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pujara, N.; Jambhrunkar, S.; Wong, K.Y.; McGuckin, M.; Popat, A. Enhanced colloidal stability, solubility and rapid dissolution of resveratrol by nanocomplexation with soy protein isolate. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2017, 488, 303–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mendes, J.B.E.; Riekes, M.K.; De Oliveira, V.M.; Michel, M.D.; Stulzer, H.K.; Khalil, N.M.; Zawadzki, S.F.; Mainardes, R.M.; Farago, P.V. PHBV/PCL microparticles for controlled release of resveratrol: Physicochemical characterization, antioxidant potential, and effect on hemolysis of human erythrocytes. Sci. World J. 2012, 2012, 542937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Huang, X.; Dai, Y.; Cai, J.; Zhong, N.; Xiao, H.; McClements, D.J.; Hu, K. Resveratrol encapsulation in core-shell biopolymer nanoparticles: Impact on antioxidant and anticancer activities. Food Hydrocoll. 2017, 64, 157–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sun, R.; Zhao, G.; Ni, S.; Xia, Q. Lipid based nanocarriers with different lipid compositions for topical delivery of resveratrol: Comparative analysis of characteristics and performance. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2014, 24, 591–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manandhar, S.; Vidhate, S.; Souza, N.D. Water soluble levan polysaccharide biopolymer electrospun fibers. Carbohydr. Polym. 2009, 78, 794–798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caldas, A.R.; Catita, J.; Machado, R.; Ribeiro, A.; Cerqueira, F.; Horta, B.; Medeiros, R.; Marlene, L.; Lopes, C.M. Omega-3- and Resveratrol-Loaded Lipid Nanosystems for Potential Use as Topical Formulations in Autoimmune, Inflammatory, and Cancerous Skin Diseases. Pharmaceutics 2021, 13, 1202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Proksch, E. pH in nature, humans and skin. J. Dermatol. 2018, 45, 1044–1052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruschi, M.L. Strategies to Modify the Drug Release from Pharmaceutical Systems, 1st ed.; Woodhead Publishing: Cambridge, UK, 2015; ISBN 9780081000922. [Google Scholar]
- Mihailescu, N.; Erginer Haskoylu, M.; Ristoscu, C.; Sennaroglu, M.; Sopronyi, M.; Eroglu, M.S.; Chifiriuc, M.C.; Mustaciosu, C.C.; Axente, E.; Toksoy Oner, E.; et al. Gradient multifunctional biopolymer thin film assemblies synthesized by combinatorial MAPLE. Appl. Surf. Sci. J. 2019, 466, 628–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osman, A.; Toksoy Oner, E.; Eroglu, M.S. Novel levan and pNIPA temperature sensitive hydrogels for 5-ASA controlled release. Carbohydr. Polym. 2017, 165, 61–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Axente, E.; Sima, F.; Sima, L.E.; Erginer, M.; Eroglu, M.S.; Serban, N.; Ristoscu, C.; Petrescu, S.M.; Toksoy Oner, E.; Mihailescu, I.N. Combinatorial MAPLE gradient thin fi lm assemblies signalling to human osteoblasts. Biofabrication 2014, 6, 035010:1–035010:9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sima, F.; Cansever Mutlu, E.; Eroglu, M.S.; Sima, L.E.; Serban, N.; Ristoscu, C.; Petrescu, S.M.; Toksoy Oner, E.; Mihailescu, I.N. Levan Nanostructured Thin Films by MAPLE Assembling. Biomacromolecules 2011, 12, 2251–2256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Demirci, T.; Erginer Hasköylü, M.; Eroğlu, M.S.; Hemberger, J.; Toksoy Oner, E. Levan-based hydrogels for controlled release of Amphotericin B for dermal local antifungal therapy of Candidiasis. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2020, 145, 105255:1–105255:10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, W.I.; Hwang, Y.; Sahu, A.; Min, K.; Sung, D.; Tae, G.; Chang, J.H. An injectable and physical levan-based hydrogel as a dermal filler for soft tissue augment. Biomater. Sci. 2018, 6, 2627–2638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cansever Mutlu, E.; Bahadori, F.; Sennaroglu Bostan, M.; Kazak Sarilmiser, H.; Toksoy Oner, E.; Eroglu, M.S. Halomonas levan-coated phospholipid based nano-carrier for active targeting of A549 lung cancer cells. Eur. Polym. J. 2021, 144, 110239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suktham, K.; Koobkokkruad, T.; Wutikhun, T.; Surassmo, S. Efficiency of resveratrol-loaded sericin nanoparticles: Promising bionanocarriers for drug delivery. Int. J. Pharm. 2018, 537, 48–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.Y.; Lee, J.-J.; Park, J.-H.; Lee, J.-Y.; Ko, S.-H.; Shim, J.-S.; Lee, J.; Heo, M.Y.; Kim, D.-D.; Cho, H.-J. Electrosprayed nanocomposites based on hyaluronic acid derivative and Soluplus for tumor-targeted drug delivery. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2016, 145, 267–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fischer, D.; Li, Y.; Ahlemeyer, B.; Krieglstein, J.; Kissel, T. In vitro cytotoxicity testing of polycations: Influence of polymer structure on cell viability and hemolysis. Biomaterials 2003, 24, 1121–1131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.H.; Jung, H.W.; Kang, I.; Lee, H.B. Cell behaviour on polymer surfaces with different functional groups. Biomaterials 1994, 15, 705–711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Solutions | Density (g/mL) | Electrical Conductivity (µS/cm) | Surface Tension (mN/m) | Viscosity (mPA s) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| hHL | 1.131 ± 0.001 | 40.6 ± 0.2 | 42.70 ± 0.07 | 634.7 ± 0.5 |
| hHL/0.05RS | 1.085 ± 0.005 | 39.5 ± 0.1 | 43.40 ± 0.08 | 658.7 ± 1.2 |
| hHL/0.1RS | 1.095 ± 0.001 | 47.6 ± 0.2 | 43.60 ± 0.10 | 609.0 ± 2.6 |
| Zero Order | First Order | Higuchi | Korsmeyer–Peppas | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Samples | R2 | k0 | R2 | k1 | R2 | kH | R2 | n |
| hHL/0.05RS (pH 7.4) | 0.193 | 2.501 | 0.794 | −0.186 | 0.403 | 15.589 | 0.082 | 0.325 |
| hHL/0.1RS (pH 7.4) | 0.551 | 8.854 | 0.895 | −0.196 | 0.820 | 34.707 | 0.494 | 0.5949 |
| hHL/0.05RS (pH 5.0) | 0.603 | 19.628 | 0.958 | −0.454 | 0.832 | 47.043 | 0.119 | 0.289 |
| hHL/0.1RS (pH 5.0) | 0.651 | 16.775 | 0.962 | −0.431 | 0.855 | 44.198 | 0.224 | 0.381 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cinan, E.; Cesur, S.; Erginer Haskoylu, M.; Gunduz, O.; Toksoy Oner, E. Resveratrol-Loaded Levan Nanoparticles Produced by Electrohydrodynamic Atomization Technique. Nanomaterials 2021, 11, 2582. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano11102582
Cinan E, Cesur S, Erginer Haskoylu M, Gunduz O, Toksoy Oner E. Resveratrol-Loaded Levan Nanoparticles Produced by Electrohydrodynamic Atomization Technique. Nanomaterials. 2021; 11(10):2582. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano11102582
Chicago/Turabian StyleCinan, Ezgi, Sumeyye Cesur, Merve Erginer Haskoylu, Oguzhan Gunduz, and Ebru Toksoy Oner. 2021. "Resveratrol-Loaded Levan Nanoparticles Produced by Electrohydrodynamic Atomization Technique" Nanomaterials 11, no. 10: 2582. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano11102582
APA StyleCinan, E., Cesur, S., Erginer Haskoylu, M., Gunduz, O., & Toksoy Oner, E. (2021). Resveratrol-Loaded Levan Nanoparticles Produced by Electrohydrodynamic Atomization Technique. Nanomaterials, 11(10), 2582. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano11102582







