Nonenzymatic DNA-Based Fluorescence Biosensor Combining Carbon Dots and Graphene Oxide with Target-Induced DNA Strand Displacement for microRNA Detection
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Reagents
2.2. Apparatus
2.3. Preparation of GO Solution
2.4. Preparation of CDs
2.5. Preparation of Fuel DNA-CDs Conjugates
2.6. Preparation of dsDNA-AuNPs
2.7. Let-7a Fluorescence Detection
3. Results and Discussion
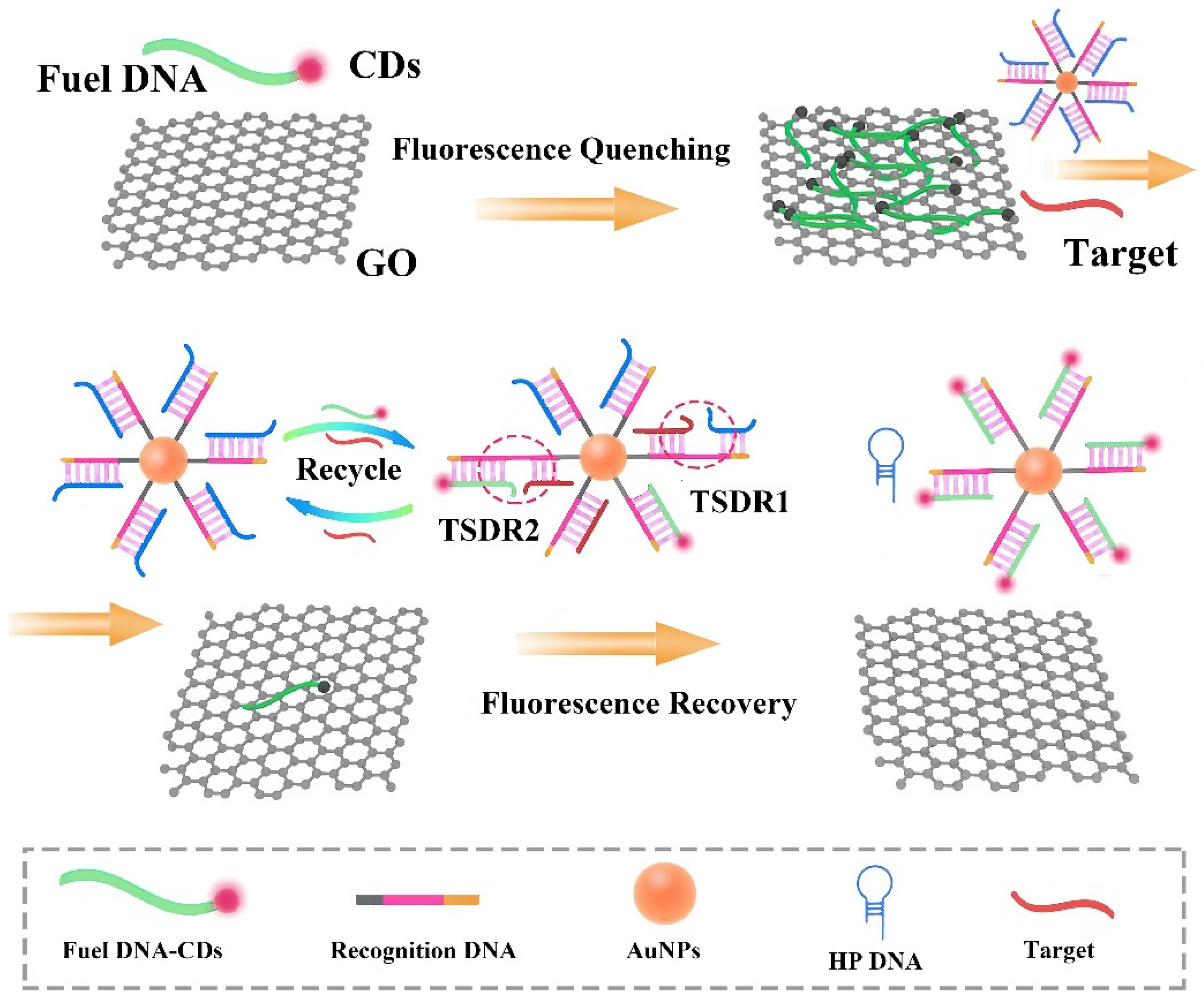
3.1. Design of the Biosensor
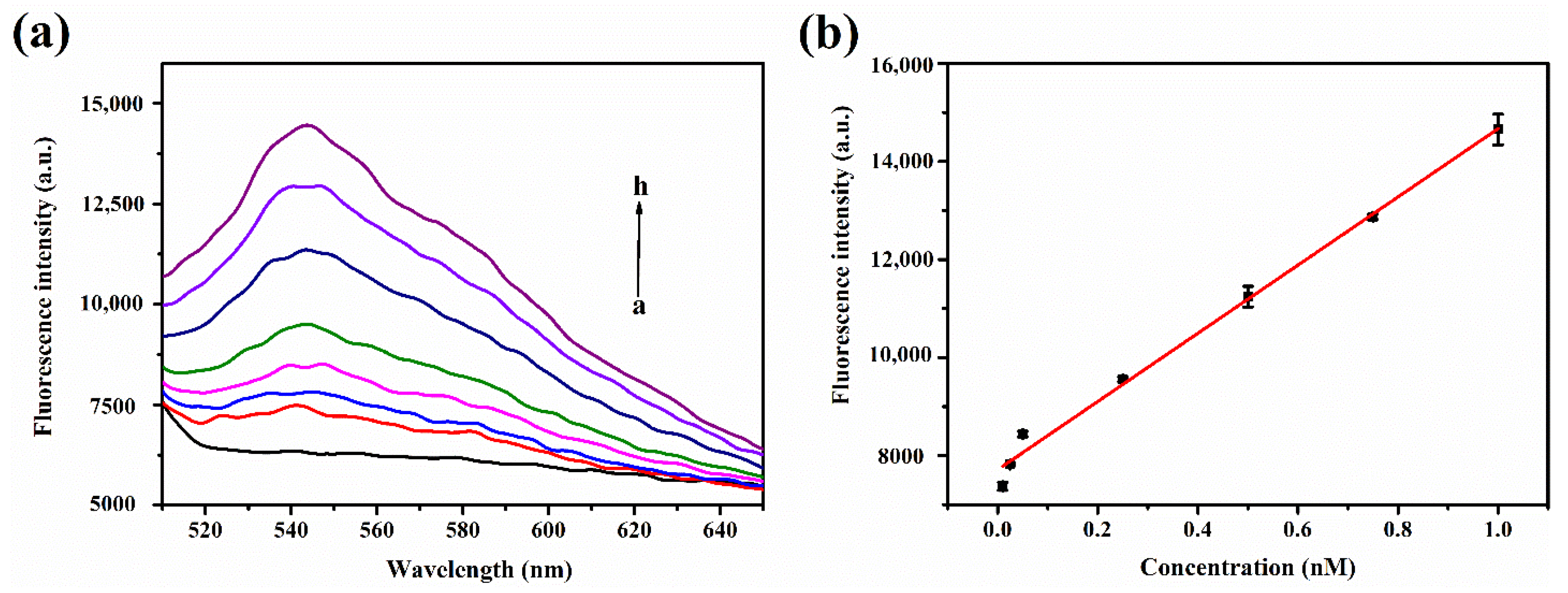
3.2. Detection of Target miRNA by the Biosensor
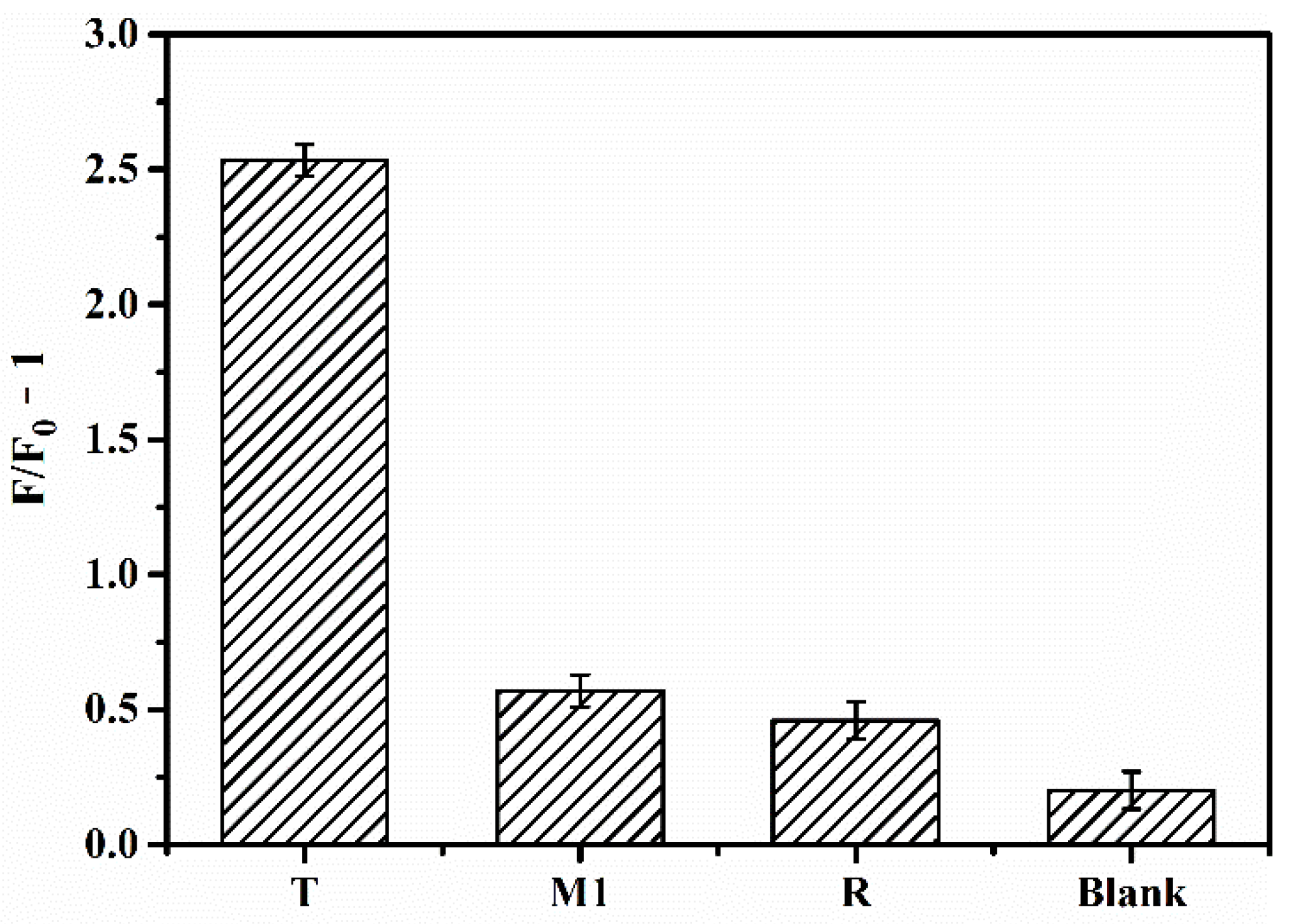
3.3. Performance and Selectivity of the Biosensor
3.4. Detection of miRNA in Serum by the Biosensor
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| Rank | Acronym | Common Meaning |
| 1 | miRNA | microRNA |
| 2 | CDs | Carbon dots |
| 3 | GO | Graphene oxide |
| 4 | AuNPs | Gold nanoparticles |
| 5 | TSDRs | Toehold-mediated strand displacement reactions |
| 6 | FRET | Fluorescence resonance energy transfer |
| 7 | NHS | N-Hydroxysuccinimide |
| 8 | EDC | 1-ethyl-3-(3-dimethylaminopropyl)carbodiimide |
| 9 | TCEP | Tris (2-carboxyethyl) phosphine hydrochloride |
| 10 | UV–vis | Ultraviolet–visible |
| 11 | FT-IR | Fourier transform infrared |
| 12 | HP | Hairpin |
| 13 | LOD | The limit of detection |
| 14 | LOQ | The limit of quantitation |
References
- De Planell-Saguer, M.; Rodicio, M.C. Analytical aspects of microRNA in diagnostics: A review. Anal. Chim. Acta 2011, 699, 134–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, D.; Sung, Y.M.; Park, J.; Kim, S.; Kim, J.; Park, J.; Ha, H.; Bae, J.Y.; Kim, S.; Baek, D. General rules for functional microRNA targeting. Nat. Genet. 2016, 48, 1517–1526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, X.; Li, Z.; Shen, J.; Chan, M.; Wu, W.K. Role of microRNAs in primary central nervous system lymphomas. Cell Prolif. 2016, 49, 147–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, B.; Chen, P.; Chang, Y.; Qi, J.; Fu, H.; Guo, H. Let-7a inhibits tumor cell growth and metastasis by directly targeting RTKN in human colon cancer. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2016, 478, 739–745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, D.; Chen, J.; Liu, J.; Luo, Z.; Jiang, W.; Huang, J.; Qiu, Z.; Yue, W.; Wu, L. Expression of microRNA let-7a positively cor-relates with hepatitis B virus replication in hepatocellular carcinoma tissues. Exp. Biol. Med. 2017, 242, 939–944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rybak-Wolf, A.; Fuchs, H.; Smirnova, L.; Brandt, C.; Pohl, E.E.; Nitsch, R.; Wulczyn, F.G. A feedback loop comprising lin-28 and let-7 controls pre-let-7 maturation during neural stem-cell commitment. Nature 2008, 10, 987–993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilles, M.-E.; Slack, F.J. Let-7 microRNA as a potential therapeutic target with implications for immunotherapy. Expert Opin. Ther. Targets 2018, 22, 929–939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Q.; Li, Y.S.F. Enzyme- and label-free fluorescence microRNA biosensor based on the distance-dependent photoinduced electron transfer of DNA/Cu nanoparticles. Microchem. J. 2021, 160, 105646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krawczyk, P.; Powrózek, T.; Olesinski, T.; Dmitruk, A.; Dziwota, J.; Kowalski, D.; Milanowski, J. Evaluation of miR-506 and miR-4316 expression in early and non-invasive diagnosis of colorectal cancer. Int. J. Color. Dis. 2017, 32, 1057–1060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, H.-H.; Wang, X.-J.; Li, G.-X.; Yang, E.; Yang, N.-M. Detection of let-7a microRNA by real-time PCR in gastric carcinoma. World J. Gastroenterol. 2007, 13, 2883–2888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fang, W.-J.; Lin, C.-Z.; Zhang, H.-H.; Qian, J.; Zhong, L.; Xu, N. Detection of let-7a MicroRNA by Real-time PCR in Colorectal Cancer: A Single-centre Experience from China. J. Int. Med. Res. 2007, 35, 716–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Resnick, K.E.; Alder, H.; Hagan, J.P.; Richardson, D.L.; Croce, C.M.; Cohn, D.E. The detection of differentially expressed mi-croRNAs from the serum of ovarian cancer patients using a novel real-time PCR platform. Gynecol. Oncol. 2009, 112, 55–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Curry, E.; Ellis, S.; Pratt, S. Detection of porcine sperm microRNAs using a heterologous microRNA microarray and reverse transcriptase polymerase chain reaction. Mol. Reprod. Dev. 2008, 76, 218–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McClure, L.V.; Lin, Y.-T.; Sullivan, C.S. Detection of Viral microRNAs by Northern Blot Analysis. In Antiviral RNAi; Humana Press: Totowa, NJ, USA, 2011; pp. 153–171. [Google Scholar]
- Konishi, H.; Ichikawa, D.; Komatsu, S.; Shiozaki, A.; Tsujiura, M.; Takeshita, H.; Morimura, R.; Nagata, H.; Arita, T.; Ka-waguchi, T.; et al. Detection of gastric cancer-associated microRNAs on mi-croRNA microarray comparing pre- and post-operative plasma. Br. J. Cancer 2012, 106, 740–747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Boriachek, K.; Umer, M.; Islam, M.N.; Gopalan, V.; Lam, A.K.; Nguyen, N.T.; Shiddiky, M.J.A. An amplification-free elec-trochemical detection of exosomal miRNA-21 in serum samples. Analyst 2018, 143, 1662–1669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.; Liao, L.; Chai, Y.; Wang, H.; Yuan, R. Ultrasensitive Electrochemiluminescence Biosensor for MicroRNA Detection by 3D DNA Walking Machine Based Target Conversion and Distance-Controllable Signal Quenching and Enhancing. Anal. Chem. 2017, 89, 8282–8287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daneshpour, M.; Karimi, B.; Omidfar, K. Simultaneous detection of gastric cancer-involved miR-106a and let-7a through a dual-signal-marked electrochemical nanobiosensor. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2018, 109, 197–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azzouzi, S.; Mak, W.C.; Kor, K.; Turner, A.P.; Ben Ali, M.; Beni, V. An integrated dual functional recognition/amplification bio-label for the one-step impedimetric detection of Micro-RNA-21. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2017, 92, 154–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- He, D.; Wong, K.-W.; Dong, Z.-Z.; Li, H.-W. Recent progress in live cell mRNA/microRNA imaging probes based on smart and versatile nanomaterials. J. Mater. Chem. B 2018, 6, 7773–7793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhong, D.; Yang, K.; Wang, Y.; Yang, X. Dual-channel sensing strategy based on gold nanoparticles cooperating with carbon dots and hairpin structure for assaying RNA and DNA. Talanta 2017, 175, 217–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, J.; Lv, W.; Yang, Q.; Li, H.; Li, F. Label-free homogeneous electrochemical detection of MicroRNA based on target-induced anti-shielding against the catalytic activity of two-dimension nanozyme. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2020, 171, 112707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, Z.; Liu, Y.; Xia, L.; Hu, Z.; Yin, J.; Mu, Y. A multiplex and fast detection platform for microRNAs based on a self-priming microfluidic chip and duplex-specific nuclease. Analyst 2020, 146, 628–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, S.Y.; Shen, W.; Gao, Z. Carbon quantum dots and their applications. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2014, 44, 362–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, Z.; Han, X.; Li, S.; Al-Youbi, A.O.; Bashammakh, A.S.; El-Shahawi, M.S.; Leblanc, R.M. Carbon dots: Biomacromolecule interaction, bioimaging and nanomedicine. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2017, 343, 256–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, S.; Meng, Q.; Wang, L.; Zhang, J.; Song, Y.; Jin, H.; Zhang, K.; Sun, H.; Wang, H.; Yang, B. Highly photoluminescent carbon dots for multicolor patterning, sensors, and bioimaging. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 2013, 52, 3953–3957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, K.M.; Xu, W.; Kwon, H.; Kietrys, A.M.; Kool, E.T. Luminescent Carbon Dot Mimics Assembled on DNA. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2017, 139, 13147–13155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kudr, J.; Richtera, L.; Xhaxhiu, K.; Hynek, D.; Heger, Z.; Zitka, O.; Adam, V. Carbon dots based FRET for the detection of DNA damage. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2017, 92, 133–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, X.; Gu, D.; Zhao, S.; Zhou, N.; Zhang, H. A dual-readout method for biothiols detection based on the NSET of nitro-gen-doped carbon quantum dots–Au nanoparticles system. J. Fluoresc. 2017, 27, 1597–1605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cui, X.; Zhu, L.; Wu, J.; Hou, Y.; Wang, P.; Wang, Z.; Yang, M. A fluorescent biosensor based on carbon dots-labeled oli-godeoxyribonucleotide and graphene oxide for mercury (II) detection. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2015, 63, 506–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, C.; Wang, R.; Wang, K.; Xu, H.; Sui, M.; Li, J.; Xu, K. Highly fluorescent carbon dots as selective and sensitive “on-off-on” probes for iron(III) ion and apoferritin detection and imaging in living cells. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2016, 83, 229–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heng, Z.; Zhang, H.; Fan, H.; Jiang, X.; Zhao, W.; Xiang, G.Q. Carbon-dot-based dual-emission silica nanoparticles as a ratiometric fluorescent probe for vanadium(V) detection in mineral water samples. Spectrochim. Acta Part A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2018, 189, 51–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atchudan, R.; Edison, T.N.J.I.; Aseer, K.R.; Perumal, S.; Karthik, N.; Lee, Y.R. Highly fluorescent nitrogen-doped carbon dots derived from Phyllanthus acidus utilized as a fluorescent probe for label-free selective detection of Fe3+ ions, live cell imaging and fluorescent ink. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2018, 99, 303–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, N.; Liu, S.G.; Zhu, Y.D.; Liu, T.; Lin, S.M.; Shi, Y.; Luo, H.Q.; Li, N.B. Tuning gold nanoparticles growth via DNA and carbon dots for nucleic acid and protein detection. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2017, 251, 455–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, J.; Ni, G.; Tu, J.; Jin, X.; Peng, J. Green synthesis of fluorescent carbon dots for sensitive detection of Fe2+ and hydrogen peroxide. J. Nanoparticle Res. 2017, 19, 209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Song, L.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, P.; Xiao, Z.; Guo, Y.-G.; Cao, F. Nitrogen and Sulfur Codoped Reduced Graphene Oxide as a General Platform for Rapid and Sensitive Fluorescent Detection of Biological Species. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2016, 8, 11255–11261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, S.-S.; Qi, L.; Zhang, R.-L.; Jin, M.; Zhang, Z.-Q. Ratiometric fluorescence biosensor based on CdTe quantum and carbon dots for double strand DNA detection. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2017, 244, 585–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, C.; Yang, H.; Zhu, C.; Chen, X.; Chen, G. A Graphene Platform for Sensing Biomolecules. Angew. Chem. 2009, 121, 4879–4881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Zhang, H.; Aldalbahi, A.; Zuo, X.; Fan, C.; Mi, X. Fluorescent biosensors enabled by graphene and graphene oxide. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2017, 89, 96–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, B.; Sun, Z.; Zhang, X.; Liu, J. Mechanisms of DNA Sensing on Graphene Oxide. Anal. Chem. 2013, 85, 7987–7993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wu, M.; Kempaiah, R.; Huang, P.-J.J.; Maheshwari, V.; Liu, J. Adsorption and Desorption of DNA on Graphene Oxide Studied by Fluorescently Labeled Oligonucleotides. Langmuir 2011, 27, 2731–2738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, Z.; Liu, B.; Ding, J.; Liu, J. Fluorescent sensors using DNA-functionalized graphene oxide. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2014, 406, 6885–6902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, M.; Zhao, H.; Chen, S.; Yu, H.; Zhang, Y.; Quan, X. A “turn-on” fluorescent copper biosensor based on DNA cleav-age-dependent graphene-quenched DNAzyme. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2011, 26, 4111–4116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, S.; Song, B.; Li, D.; Zhu, C.; Qi, W.; Wen, Y.; Wang, L.; Song, S.; Fang, H.; Fan, C. A Graphene Nanoprobe for Rapid, Sensitive, and Multicolor Fluorescent DNA Analysis. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2010, 20, 453–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumke, M.; Shu, L.; McGown, L.B.; Walker, G.T.; Pitner, J.B.; Linn, C.P. Temperature and Quenching Studies of Fluorescence Polarization Detection of DNA Hybridization. Anal. Chem. 1997, 69, 500–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.-K.; Hu, L.-Y.; Niu, C.-G.; Huang, D.-W.; Zeng, G.-M. A fluorescent DNA based probe for Hg (II) based on thy-mine-Hg(II)-thymine interaction and enrichment via magnetized graphene oxide. Mikrochim. Acta. 2018, 185, 207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giust, D.; Lucío, M.I.; El-Sagheer, A.H.; Brown, T.; Williams, L.E.; Muskens, O.L.; Kanaras, A.G. Graphene Oxide–Upconversion Nanoparticle Based Portable Sensors for Assessing Nutritional Deficiencies in Crops. ACS Nano 2018, 12, 6273–6279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kermani, H.A.; Hosseini, M.; Dadmehr, M.; Hosseinkhani, S.; Ganjali, M.R. DNA methyltransferase activity detection based on graphene quantum dots using fluorescence and fluorescence anisotropy. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2016, 241, 217–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Xu, G.; Wei, F.; Ma, Y.; Ma, Y.; Song, Y.; Cen, Y.; Hu, Q. Highly sensitive and selective aptasensor for detection of adenosine based on fluorescence resonance energy transfer from carbon dots to nano-graphite. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2017, 508, 455–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeh, Y.-C.; Creran, B.; Rotello, V.M. Gold nanoparticles: Preparation, properties, and applications in bionanotechnology. Nanoscale 2011, 4, 1871–1880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mieszawska, A.J.; Mulder, W.; Fayad, Z.A.; Cormode, D.P. Multifunctional Gold Nanoparticles for Diagnosis and Therapy of Disease. Mol. Pharm. 2013, 10, 831–847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cao, X.; Ye, Y.; Liu, S. Gold nanoparticle-based signal amplification for biosensing. Anal. Biochem. 2011, 417, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boisselier, E.; Astruc, D. Gold nanoparticles in nanomedicine: Preparations, imaging, diagnostics, therapies and toxicity. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2009, 38, 1759–1782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.X.; Ma, L.N. Gold nanoparticle probes. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2009, 253, 1607–1618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Zhou, W.; Yuan, R.; Xiang, Y. A DNA-fueled and catalytic molecule machine lights up trace under-expressed mi-croRNAs in living cells. Anal. Chem. 2017, 89, 9934–9940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, S.; Su, W.; Li, Z.; Ding, X. Electrochemical detection of lung cancer specific microRNAs using 3D DNA origami nanostructures. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2015, 71, 57–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, D.; Wang, Z.; Jiang, X. Gold nanoparticles for the colorimetric and fluorescent detection of ions and small organic molecules. Nanoscale 2011, 3, 1421–1433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Hua, E.; Liang, M.; Ma, C.; Liu, Z.; Sheng, S.; Liu, M.; Xie, G.; Feng, W. Graphene sheets, polyaniline and AuNPs based DNA sensor for electrochemical determination of BCR/ABL fusion gene with functional hairpin probe. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2013, 51, 201–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.; Zhang, L.; Li, T.; Dong, S.; Wang, E. Enzyme-Free Unlabeled DNA Logic Circuits Based on Toehold-Mediated Strand Displacement and Split G-Quadruplex Enhanced Fluorescence. Adv. Mater. 2013, 25, 2440–2444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srinivas, N.; Ouldridge, T.E.; Šulc, P.; Schaeffer, J.M.; Yurke, B.; Louis, A.; Doye, J.; Winfree, E. On the biophysics and kinetics of toehold-mediated DNA strand displacement. Nucleic Acids Res. 2013, 41, 10641–10658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Tang, W.; Wu, X.; Wang, X.; Chen, G.; Chen, Q.; Li, N.; Liu, F. Highly Selective Detection of Single-Nucleotide Polymorphisms Using a Quartz Crystal Microbalance Biosensor Based on the Toehold-Mediated Strand Displacement Reaction. Anal. Chem. 2012, 84, 7008–7014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Zou, M.; Huang, H.; Ren, Y.; Li, L.; Yang, X.; Li, N. Gold nanoparticle enhanced fluorescence anisotropy for the assay of single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) based on toehold-mediated strand-displacement reaction. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2013, 41, 569–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, N.; Shi, X.-M.; Guo, H.-Q.; Zhao, X.-Z.; Zhao, W.-W.; Xu, J.-J.; Chen, H.-Y. Gold Nanoparticle Couples with Entro-py-Driven Toehold-Mediated DNA Strand Displacement Reaction on Magnetic Beads: Toward Ultrasensitive Energy-Transfer-Based Photoelectrochemical Detection of miRNA-141 in Real Blood Sample. Anal. Chem. 2018, 90, 11892–11898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kong, W.; Wu, H.; Ye, Z.; Li, R.; Xu, T.; Zhang, B. Optical properties of pH-sensitive carbon-dots with different modifications. J. Lumin. 2014, 148, 238–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Name | Sequences (5′ to 3′) |
|---|---|
| Recognition DNA | (SH)- AAAAAAAAAAACTATACAACCTACTACCTCATAGGTAC |
| Hairpin DNA | ACAACCTATGAGGTAGTAGGTTGT |
| Fuel DNA | NH2-G*T*A*CCTATGAGGTAGTAGGT*T*G* |
| MicroRNA let-7a | UGAGGUAGUAGGUUGUAUAGUU |
| Non-recognition sequences | (SH)- AAAAAAAAACCGATCACAACGTACTACCTCAAAGGTTG |
| One base mismatch microRNA | UGAGGUAGUAGGUUGUCUAGUU |
| Methodology | Analyte | Linear Range | LOD | Refs |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Distance-dependent photoinduced electron transfer of DNA/Cu nanoparticles | miRNA let-7a | 0.5 nM–100 nM | 0.2 nM | [8] |
| Target-induced anti-shielding against the catalytic activity of two-dimensional nanozyme | miRNA let-7a | 0.4 nM–140 nM | 0.25 nM | [22] |
| Self-priming microfluidic chip | miRNA 100 | 100 pM–10 nM | 45.35 pM | [23] |
| 3D DNA origami nanostructures | miRNA | 100 pM–1 μM | 10.0 pM | [56] |
| Toehold-mediated nonenzymatic amplification on CDs and GO | miRNA let-7a | 10 pM–1 nM | 7.8 pM | This study |
| Sample Number | Added (nM) | Founded (nM) | Recovery (%) | RSD (%) (n = 3) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 0.01 | 0.00931 | 93.10 | 6.3 |
| 0.50 | 0.47110 | 94.22 | 5.1 | |
| 1.00 | 0.97030 | 97.03 | 3.9 | |
| 2 | 0.01 | 0.00908 | 90.80 | 4.7 |
| 0.50 | 0.481010 | 96.20 | 4.6 | |
| 1.00 | 0.94120 | 94.12 | 3.2 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gao, Y.; Yu, H.; Tian, J.; Xiao, B. Nonenzymatic DNA-Based Fluorescence Biosensor Combining Carbon Dots and Graphene Oxide with Target-Induced DNA Strand Displacement for microRNA Detection. Nanomaterials 2021, 11, 2608. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano11102608
Gao Y, Yu H, Tian J, Xiao B. Nonenzymatic DNA-Based Fluorescence Biosensor Combining Carbon Dots and Graphene Oxide with Target-Induced DNA Strand Displacement for microRNA Detection. Nanomaterials. 2021; 11(10):2608. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano11102608
Chicago/Turabian StyleGao, Yuanyuan, Hong Yu, Jingjing Tian, and Botao Xiao. 2021. "Nonenzymatic DNA-Based Fluorescence Biosensor Combining Carbon Dots and Graphene Oxide with Target-Induced DNA Strand Displacement for microRNA Detection" Nanomaterials 11, no. 10: 2608. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano11102608
APA StyleGao, Y., Yu, H., Tian, J., & Xiao, B. (2021). Nonenzymatic DNA-Based Fluorescence Biosensor Combining Carbon Dots and Graphene Oxide with Target-Induced DNA Strand Displacement for microRNA Detection. Nanomaterials, 11(10), 2608. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano11102608






