Rheological and Tribological Properties of Nanocellulose-Based Ecolubricants
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Experimental Design
2.3. Preparation of Nanocellulose-Based Ecolubricants
2.4. Rheological and Tribological Characterization of Nanocellulose-Based Ecolubricants
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Viscous Flow Behavior of Nanocellulose-Based Ecolubricants
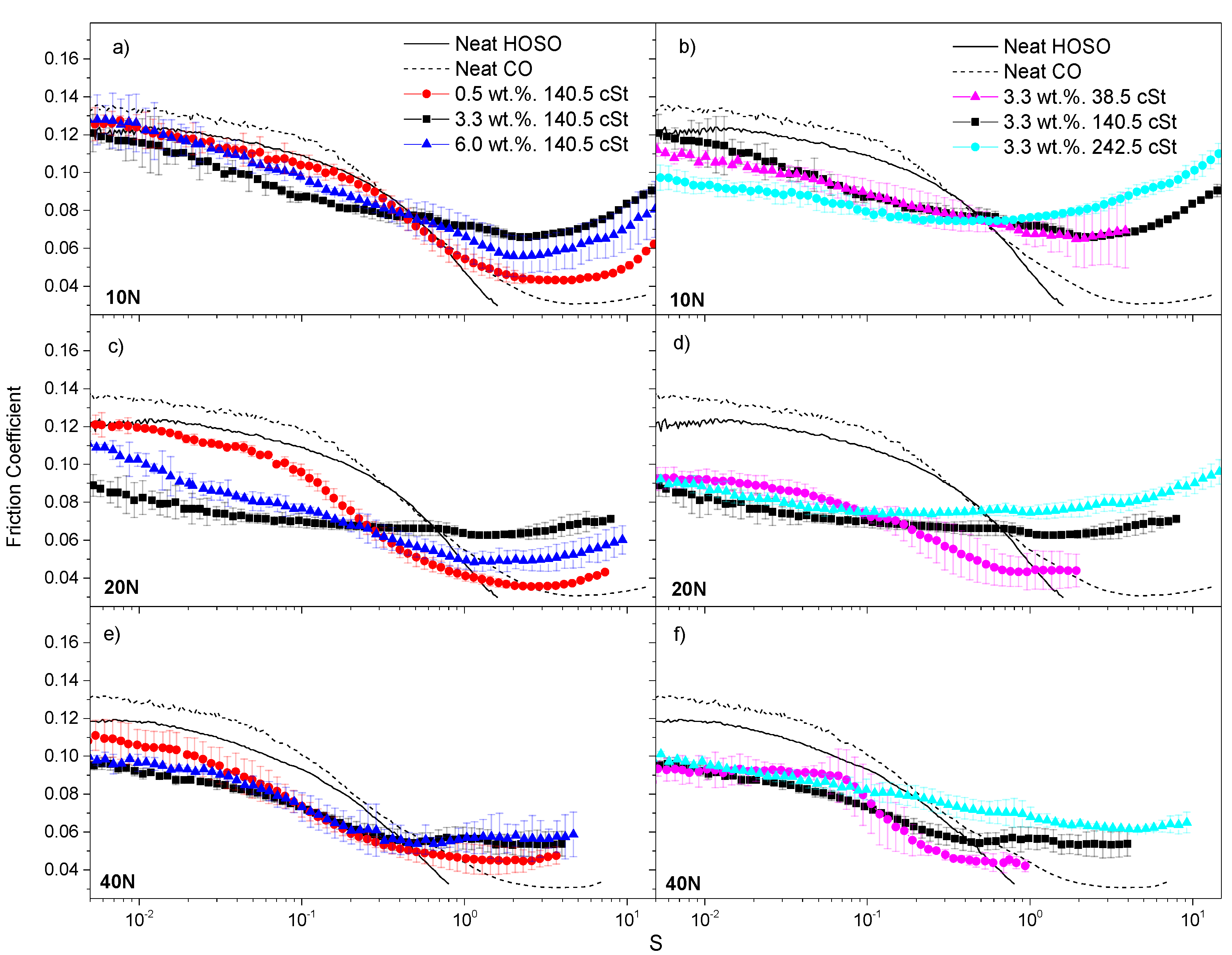
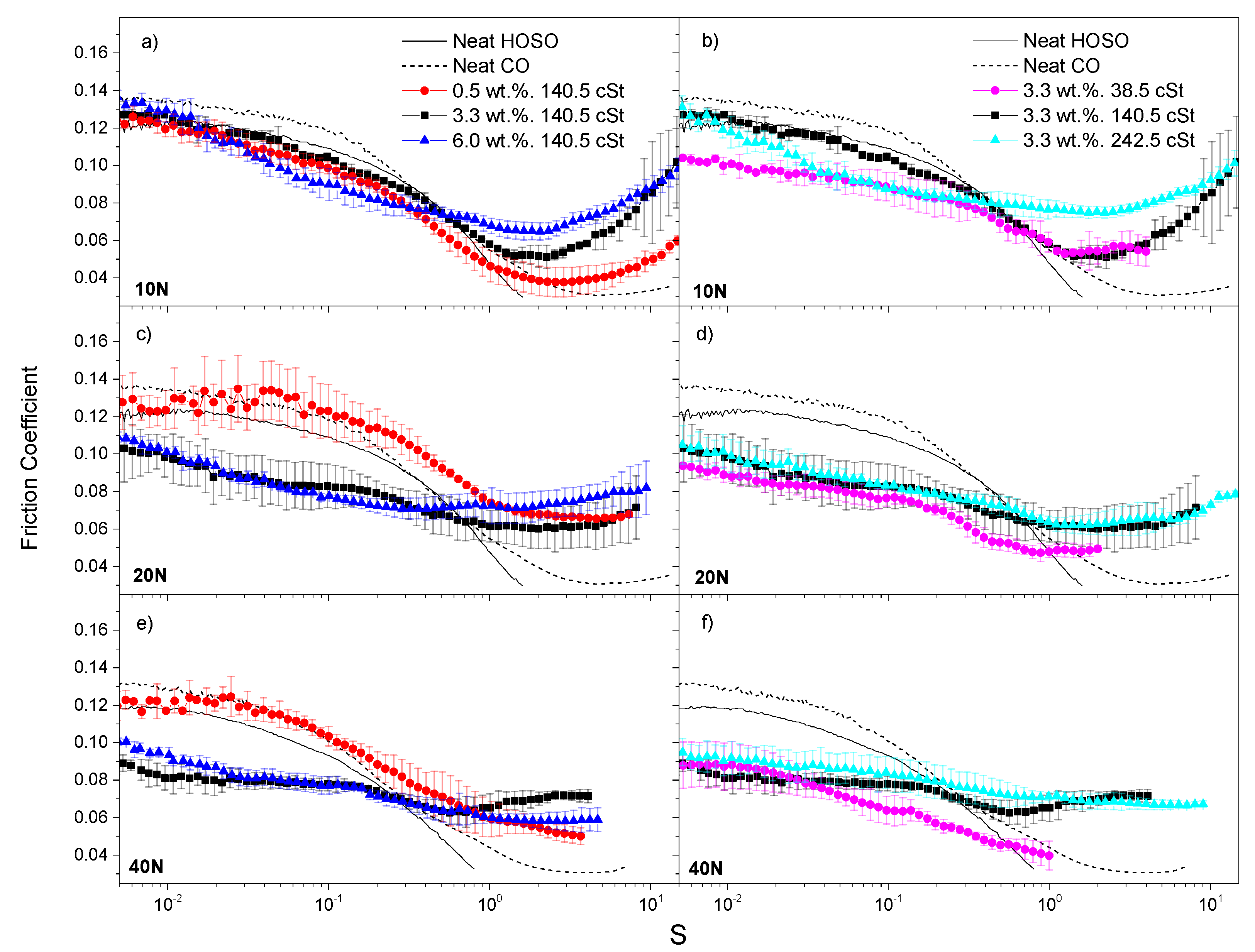
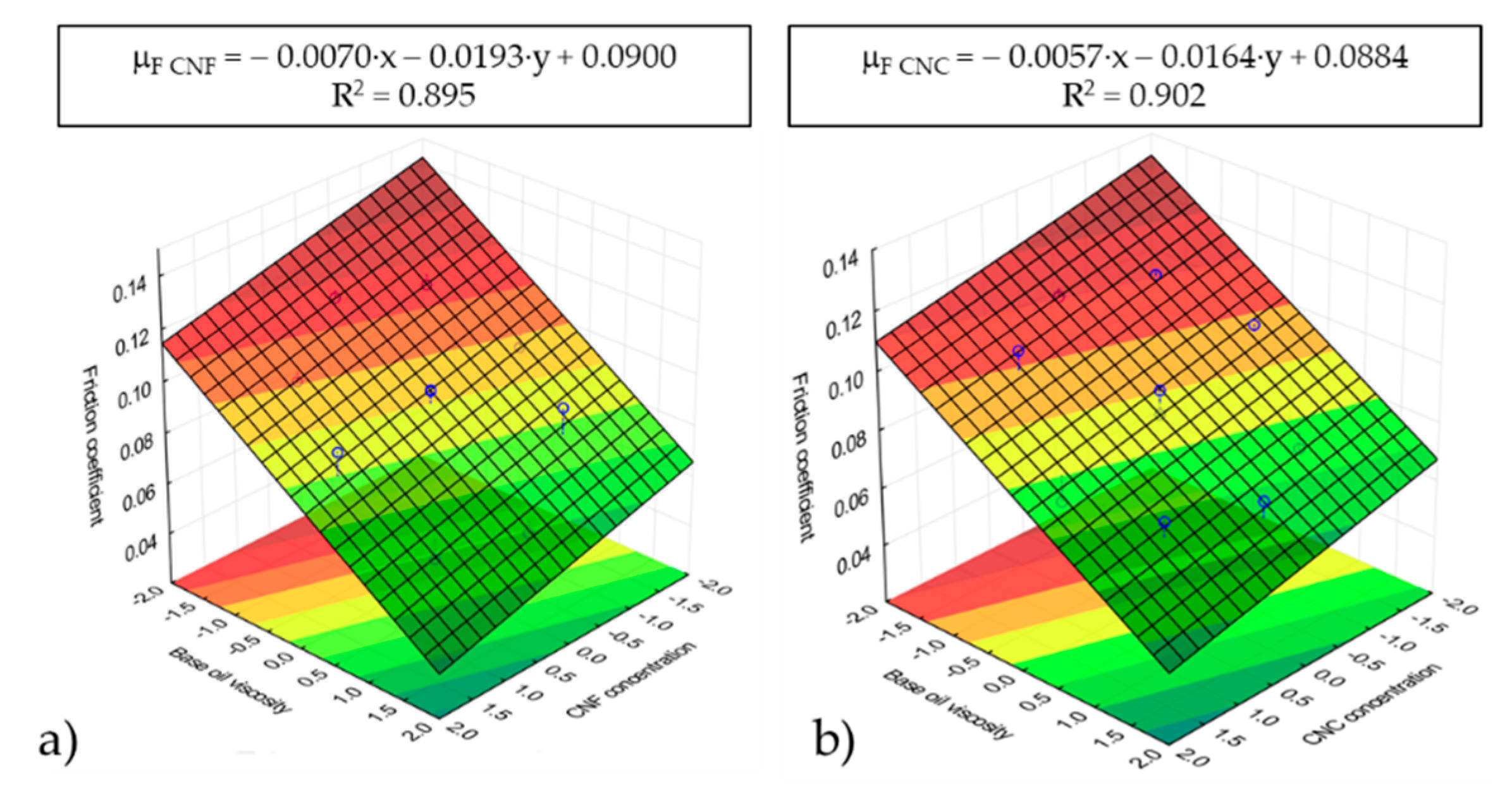
3.2. Friction Behavior of Nanocellulose-Based Ecolubricants
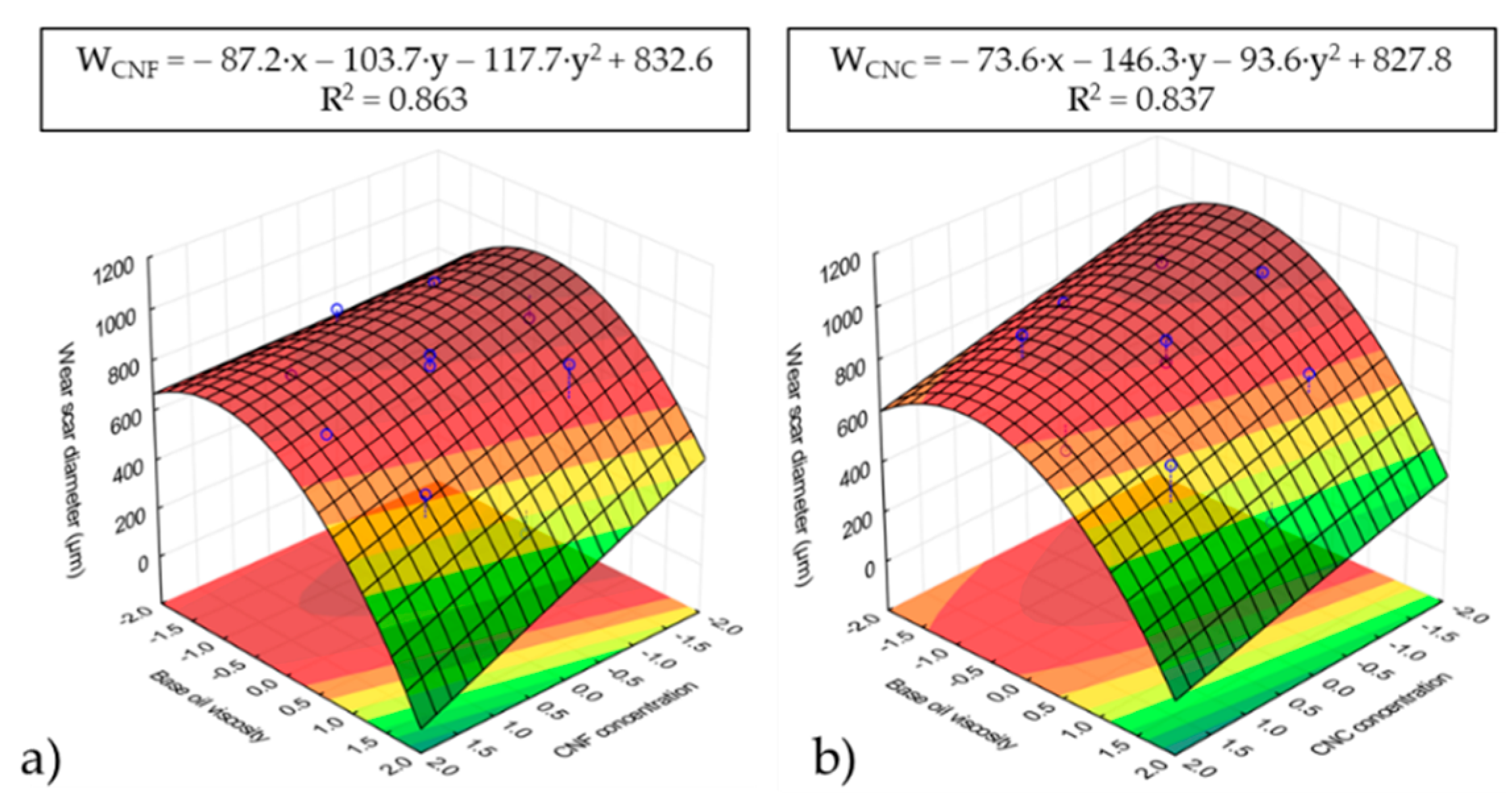
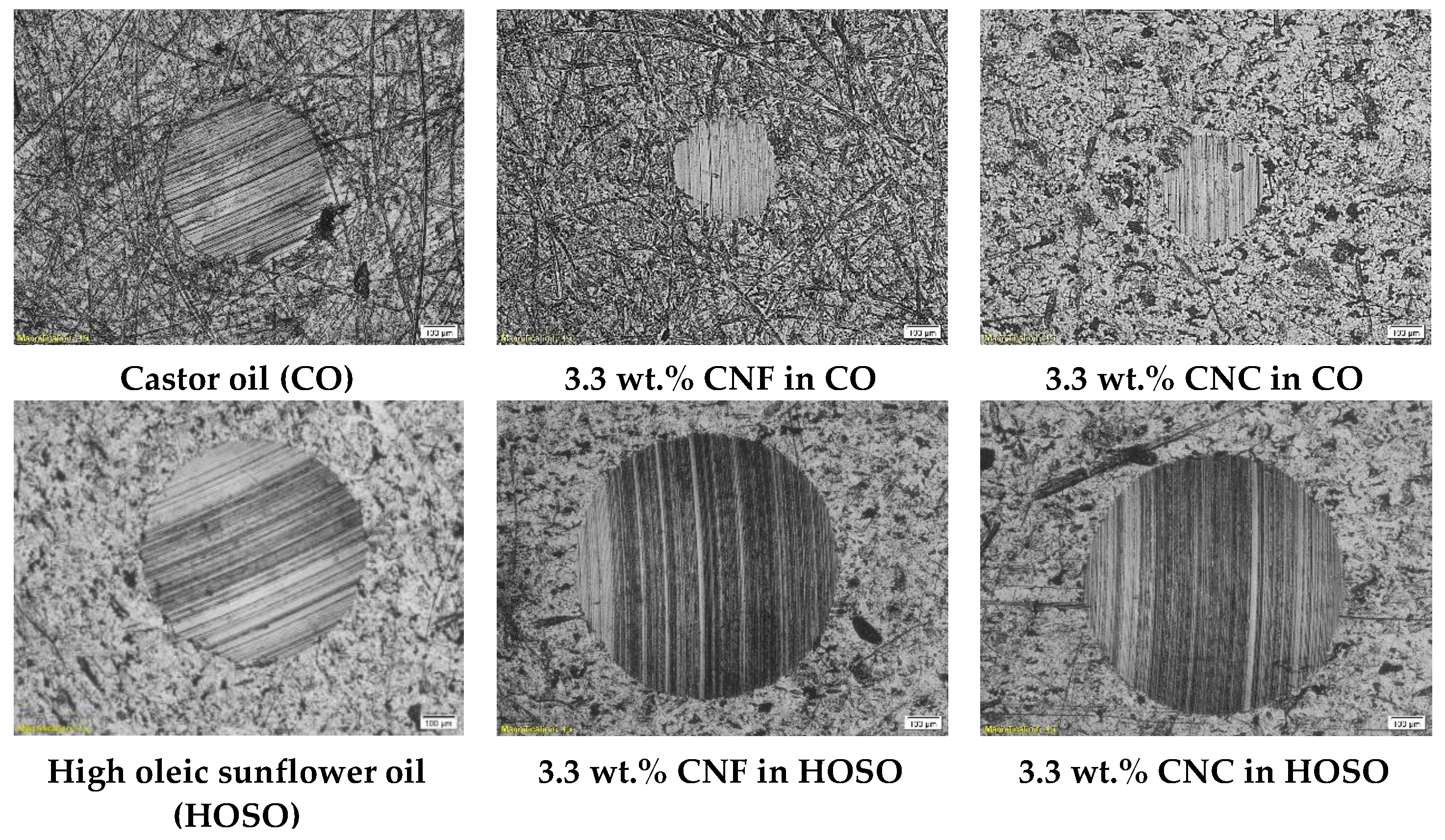
3.3. Wear Analysis of Nanocellulose-Based Ecolubricants
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bart, J.; Gucciardi, E.; Cavallaro, S. Biolubricants: Science and Technology; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Xiao, H.; Liu, S. 2D nanomaterials as lubricant additive: A review. Mater. Des. 2017, 135, 319–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beheshti, A.; Huang, Y.; Ohno, K.; Blakey, I.; Stokes, J.R. Improving tribological properties of oil-based lubricants using hybrid colloidal additives. Tribol. Int. 2020, 144, 106130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, M.A.M.; Azmi, A.I.; Murad, M.N.; Zain, M.Z.M.; Khalil, A.N.M.; Shuaib, N.A. Roles of new bio-based nanolubricants towards eco-friendly and improved machinability of Inconel 718 alloys. Tribol. Int. 2020, 144, 106106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kotia, A.; Ghosh, G.K.; Srivastava, I.; Deval, P.; Ghosh, S.K. Mechanism for improvement of friction/wear by using Al2O3 and SiO2/Gear oil nanolubricants. J. Alloys Compd. 2019, 782, 592–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernández Battez, A.; González, R.; Viesca, J.L.; Fernández, J.E.; Díaz Fernández, J.M.; Machado, A.; Chou, R.; Riba, J. CuO, ZrO2 and ZnO nanoparticles as antiwear additive in oil lubricants. Wear 2008, 265, 422–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, K.; Hwang, Y.; Cheong, S.; Choi, Y.; Kwon, L.; Lee, J.; Kim, S.H. Understanding the role of nanoparticles in nano-oil lubrication. Tribol. Lett. 2009, 35, 127–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghaednia, H.; Jackson, R.L. Fellowship research: The role of nanoparticles in lubricants; Performing lubricated and dry friction tests. Tribol. Lubr. Technol. 2015, 71, 20–24. [Google Scholar]
- Jason, Y.J.J.; How, H.G.; Teoh, Y.H.; Chuah, H.G. A study on the tribological performance of nanolubricants. Processes 2020, 8, 1372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Padgurskas, J.; Rukuiza, R.; Prosyčevas, I.; Kreivaitis, R. Tribological properties of lubricant additives of Fe, Cu and Co nanoparticles. Tribol. Int. 2013, 60, 224–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.L.; Xu, Y.; Shi, P.J.; Xu, B.S.; Wang, X.L.; Liu, Q. Tribological properties and lubricating mechanisms of Cu nanoparticles in lubricant. Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 2008, 18, 636–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernandez Battez, A.; Fernandez Rico, J.E.; Navas Arias, A.; Viesca Rodriguez, J.L.; Chou Rodriguez, R.; Diaz Fernandez, J.M. The tribological behaviour of ZnO nanoparticles as an additive to PAO6. Wear 2006, 261, 256–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, T.; Wei, X.; Huang, X.; Huang, L.; Yang, F. Tribological properties of Al2O3 nanoparticles as lubricating oil additives. Ceram. Int. 2014, 40, 7143–7149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahnazar, S.; Bagheri, S.; Abd Hamid, S.B. Enhancing lubricant properties by nanoparticle additives. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2016, 41, 3153–3170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zulkifli, N.W.M.; Kalam, M.A.; Masjuki, H.H.; Yunus, R. Experimental analysis of tribological properties of biolubricant with nanoparticle additive. Procedia Eng. 2013, 68, 152–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Darminesh, S.P.; Sidik, N.A.C.; Najafi, G.; Mamat, R.; Ken, T.L.; Asako, Y. Recent development on biodegradable nanolubricant: A review. Int. Commun. Heat Mass Transf. 2017, 86, 159–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogunniyi, D.S. Castor oil: A vital industrial raw material. Bioresour. Technol. 2006, 97, 1086–1091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quinchia, L.A.; Delgado, M.A.; Valencia, C.; Franco, J.M.; Gallegos, C. Viscosity modification of different vegetable oils with EVA copolymer for lubricant applications. Ind. Crops Prod. 2010, 32, 607–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quinchia, L.A.; Delgado, M.A.; Valencia, C.; Franco, J.M.; Gallegos, C. Natural and synthetic antioxidant additives for improving the performance of new biolubricant formulations. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2011, 59, 12917–12924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sánchez, R.; Franco, J.M.; Delgado, M.A.; Valencia, C.; Gallegos, C. Development of new green lubricating grease formulations based on cellulosic derivatives and castor oil. Green Chem. 2009, 11, 686–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Núñez, N.; Martín-Alfonso, J.E.; Valencia, C.; Sánchez, M.C.; Franco, J.M. Rheology of new green lubricating grease formulations containing cellulose pulp and its methylated derivative as thickener agents. Ind. Crops Prod. 2012, 37, 500–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gallego, R.; Arteaga, J.F.; Valencia, C.; Díaz, M.J.; Franco, J.M. Gel-like dispersions of HMDI-cross-linked lignocellulosic materials in castor oil: Toward completely renewable lubricating grease formulations. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2015, 3, 2130–2141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borrero-López, A.M.; Valencia, C.; Franco, J.M. Rheology of lignin-based chemical oleogels prepared using diisocyanate crosslinkers: Effect of the diisocyanate and curing kinetics. Eur. Polym. J. 2017, 89, 311–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cortés-Triviño, E.; Valencia, C.; Delgado, M.A.; Franco, J.M. Modification of alkali lignin with poly(ethylene glycol) diglycidyl ether to be used as a thickener in bio-lubricant formulations. Polymers 2018, 10, 670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Delgado, M.A.; Cortés-Triviño, E.; Valencia, C.; Franco, J.M. Tribological study of epoxide-functionalized alkali lignin-based gel-like biogreases. Tribol. Int. 2020, 146, 106231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, K.; Do Nam, J.; Kwon, S.H.; Choi, H.J.; Islam, M.S.; Kao, N. Microfibrillated cellulose suspension and its electrorheology. Polymers 2019, 11, 2119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hisham, S.M.; Kadirgama, K.; Ramasamy, D.; Rahman, S. Enhancement of Tribological behaviour and thermal properties of hybrid nanocellulose/copper (II) Oxide nanolubricant. J. Adv. Res. Fluid Mech. Therm. Sci. 2020, 72, 47–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amirruddin, A.K. Tribological Performance Analysis of Nanocellulose-AL2O3-Engine Oil. Ph.D. Thesis, Universiti Malaysia Pahang, Pahang, Malaysia, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Awang, N.W.; Ramasamy, D.; Kadirgama, K.; Najafi, G.; Che Sidik, N.A. Study on friction and wear of Cellulose Nanocrystal (CNC) nanoparticle as lubricating additive in engine oil. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 2019, 131, 1196–1204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Renner, P.; Liang, H. Dispersion of nanoparticles in lubricating oil: A critical review. Lubricants 2019, 7, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Montgomery, D. Design and Analysis of Experiments, 9th ed.; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2019; ISBN 9781119638421. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, W.; Xie, H. A review on nanofluids: Preparation, stability mechanisms, and applications. J. Nanomater. 2012, 2012, 435873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Maheswaran, R.; Sunil, J. Effect of nano sized garnet particles dispersion on the viscous behavior of extreme pressure lubricant oil. J. Mol. Liq. 2016, 223, 643–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heyer, P.; Läuger, J. Correlation between friction and flow of lubricating greases in a new tribometer device. Lubr. Sci. 2009, 21, 253–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez, R.; Franco, J.M.; Delgado, M.A.; Valencia, C.; Gallegos, C. Thermal and mechanical characterization of cellulosic derivatives-based oleogels potentially applicable as bio-lubricating greases: Influence of ethyl cellulose molecular weight. Carbohydr. Polym. 2011, 83, 151–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delgado, M.A.; Quinchia, L.A.; Spikes, H.A.; Gallegos, C. Suitability of ethyl cellulose as multifunctional additive for blends of vegetable oil-based lubricants. J. Clean. Prod. 2017, 151, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonçalves, D.; Graça, B.; Campos, A.V.; Seabra, J. On the friction behaviour of polymer greases. Tribol. Int. 2016, 93, 399–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gunsel, S.; Smeeth, M.; Spikes, H. Friction and wear reduction by boundary film-forming viscosity index improvers. J. Fuels Lubr. 1996, 105, 1831–1855. [Google Scholar]
- Biresaw, G.; Bantchev, G. Effect of chemical structure on film-forming properties of seed oils. J. Synth. Lubr. 2008, 25, 159–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamrock, B.J.; Dowson, D. Ball Bearing Lubrication. The Elastohydrodynamics of Elliptical Contacts; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 1981; ISBN 047103553X. [Google Scholar]
- Singh, H.; Bhowmick, H. Influence of nanoclay on the thermophysical properties and lubricity characteristics of mineral oil. Mater. Today Proc. 2019, 18, 1058–1066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Z.; Xia, Y.; Xi, X. Nano-montmorillonite-doped lubricating grease exhibiting excellent insulating and tribological properties. Friction 2017, 5, 219–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Guangteng, G.; Spikes, H. Fractionation of liquid lubricants at solid surfaces. Wear 1996, 200, 336–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Sample Code | Nanocellulose Concentration (wt.%) | Base Oil Viscosity (cSt) [ ] * | CNF | CNC |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| µ (Pa·s) | µ (Pa·s) | |||
| 0, 0A | 3.3 | 140.5 [70] | 0.338 ± 0.006 | 0.347 ± 0.007 |
| 0, 0B | 3.3 | 140.5 [70] | 0.353 ± 0.005 | 0.346 ± 0.005 |
| +1.414, 0 | 6.0 | 140.5 [70] | 0.398 ± 0.007 | 0.400 ± 0.014 |
| −1.414, 0 | 0.5 | 140.5 [70] | 0.312 ± 0.002 | 0.313 ± 0.004 |
| 0, +1.414 | 3.3 | 242.5 [100] | 0.783 ± 0.020 | 0.767 ± 0.010 |
| 0, −1.414 | 3.3 | 38.5 [0] | 0.082 ± 0.006 | 0.085 ± 0.009 |
| +1, +1 | 5.2 | 212.6 [93] | 0.696 ± 0.012 | 0.696 ± 0.012 |
| +1, −1 | 5.2 | 68.4 [31] | 0.148 ± 0.002 | 0.145 ± 0.001 |
| −1, +1 | 1.3 | 212.6 [93] | 0.597 ± 0.014 | 0.589 ± 0.006 |
| −1, −1 | 1.3 | 68.4 [31] | 0.129 ± 0.005 | 0.132 ± 0.007 |
| Sample | Nanoparticle Concentration (wt.%) | Base Oil Viscosity (cSt) | CNF Diameter (μm) | CNC Diameter (μm) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Castor oil | 0 | 242.5 | 520 ± 13 * | 520 ± 13 * |
| HOSO | 0 | 38.5 | 689 ± 29 * | 689 ± 29 * |
| 0, 0A | 3.3 | 140.5 | 843 ± 23 | 858 ± 54 |
| 0, 0B | 3.3 | 140.5 | 812 ± 34 | 773 ± 51 |
| +1.414, 0 | 6.0 | 140.5 | 711 ± 24 | 619 ± 81 |
| −1.414, 0 | 0.5 | 140.5 | 925 ± 14 | 948 ± 65 |
| 0, +1.414 | 3.3 | 242.5 | 312 ± 32 | 329 ± 9 |
| 0, −1.414 | 3.3 | 38.5 | 843 ± 13 | 821 ± 31 |
| +1, +1 | 5.2 | 212.6 | 543 ± 47 | 634 ± 45 |
| −1, +1 | 1.3 | 212.6 | 806 ± 10 | 722 ± 44 |
| +1, −1 | 5.2 | 68.4 | 727 ± 30 | 886 ± 38 |
| −1, −1 | 1.3 | 68.4 | 860 ± 29 | 922 ± 35 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Fernández-Silva, S.D.; Delgado, M.A.; Roman, C.; García-Morales, M. Rheological and Tribological Properties of Nanocellulose-Based Ecolubricants. Nanomaterials 2021, 11, 2987. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano11112987
Fernández-Silva SD, Delgado MA, Roman C, García-Morales M. Rheological and Tribological Properties of Nanocellulose-Based Ecolubricants. Nanomaterials. 2021; 11(11):2987. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano11112987
Chicago/Turabian StyleFernández-Silva, Samuel D., Miguel A. Delgado, Claudia Roman, and Moisés García-Morales. 2021. "Rheological and Tribological Properties of Nanocellulose-Based Ecolubricants" Nanomaterials 11, no. 11: 2987. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano11112987
APA StyleFernández-Silva, S. D., Delgado, M. A., Roman, C., & García-Morales, M. (2021). Rheological and Tribological Properties of Nanocellulose-Based Ecolubricants. Nanomaterials, 11(11), 2987. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano11112987








