A Deep Learning Analysis Reveals Nitrogen-Doped Graphene Quantum Dots Damage Neurons of Nematode Caenorhabditis elegans
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
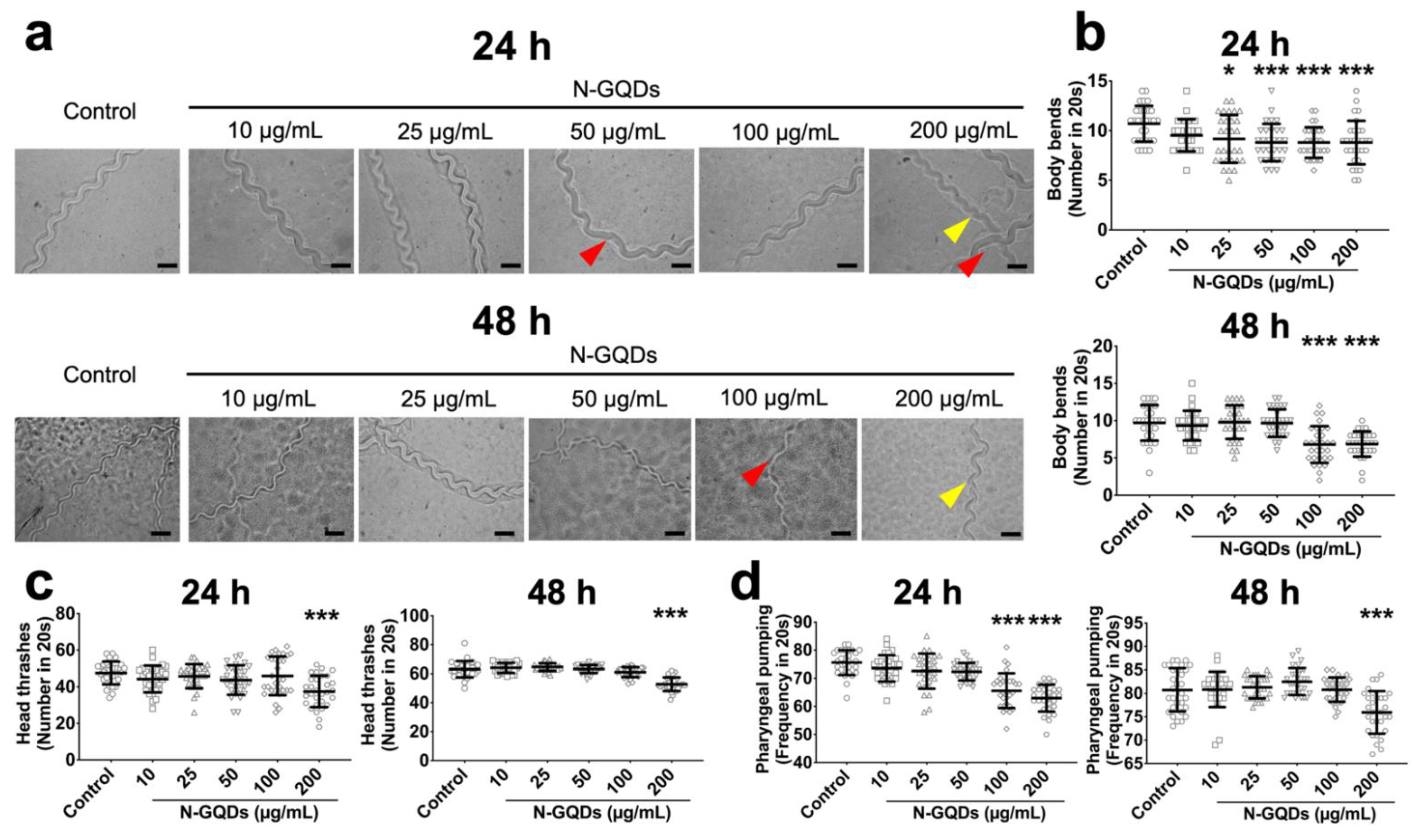
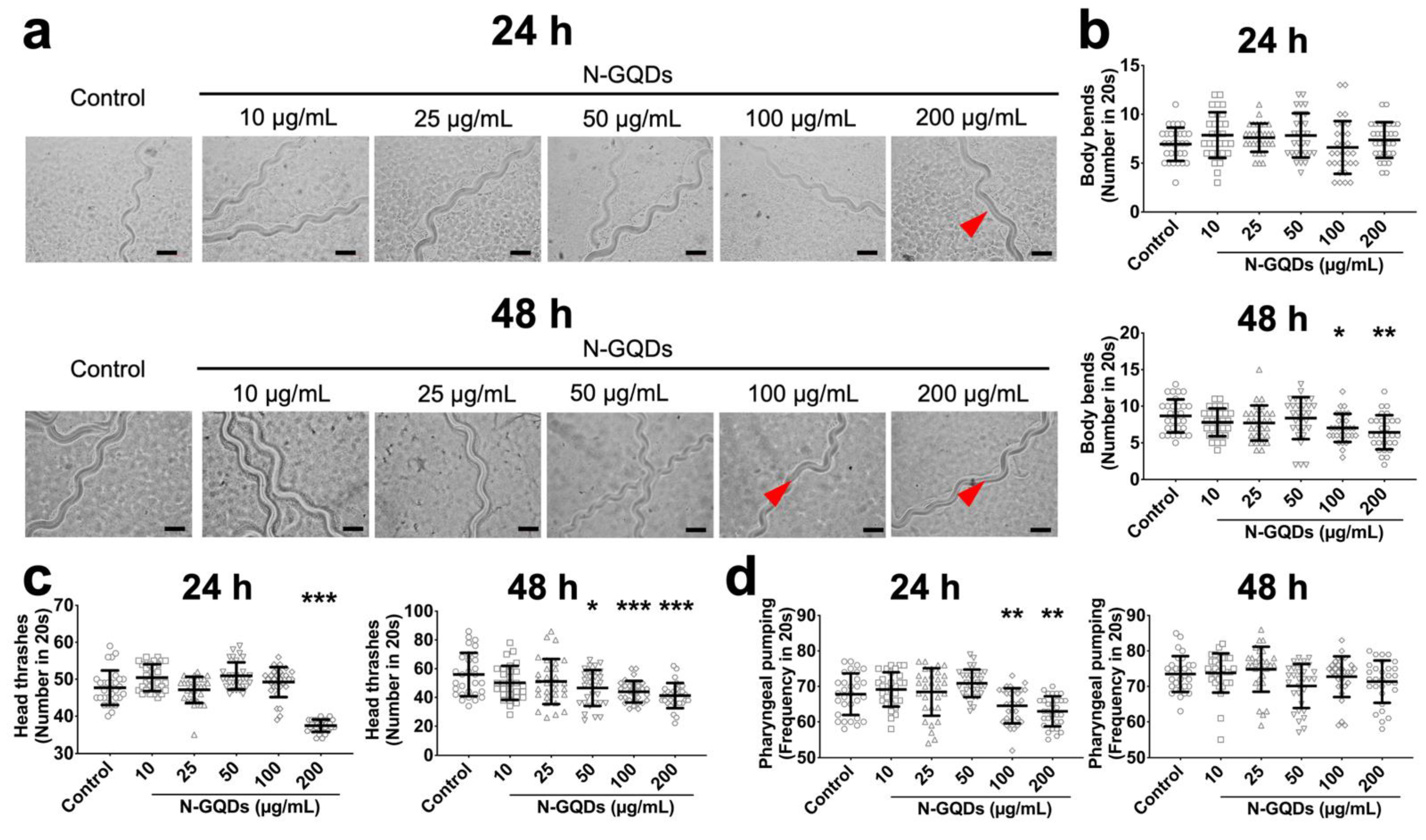
2.1. Nitrogen-Doped Graphene Quantum Dots (N-GQDs) Caused Neurotoxic Effects in Nematode C. elegans
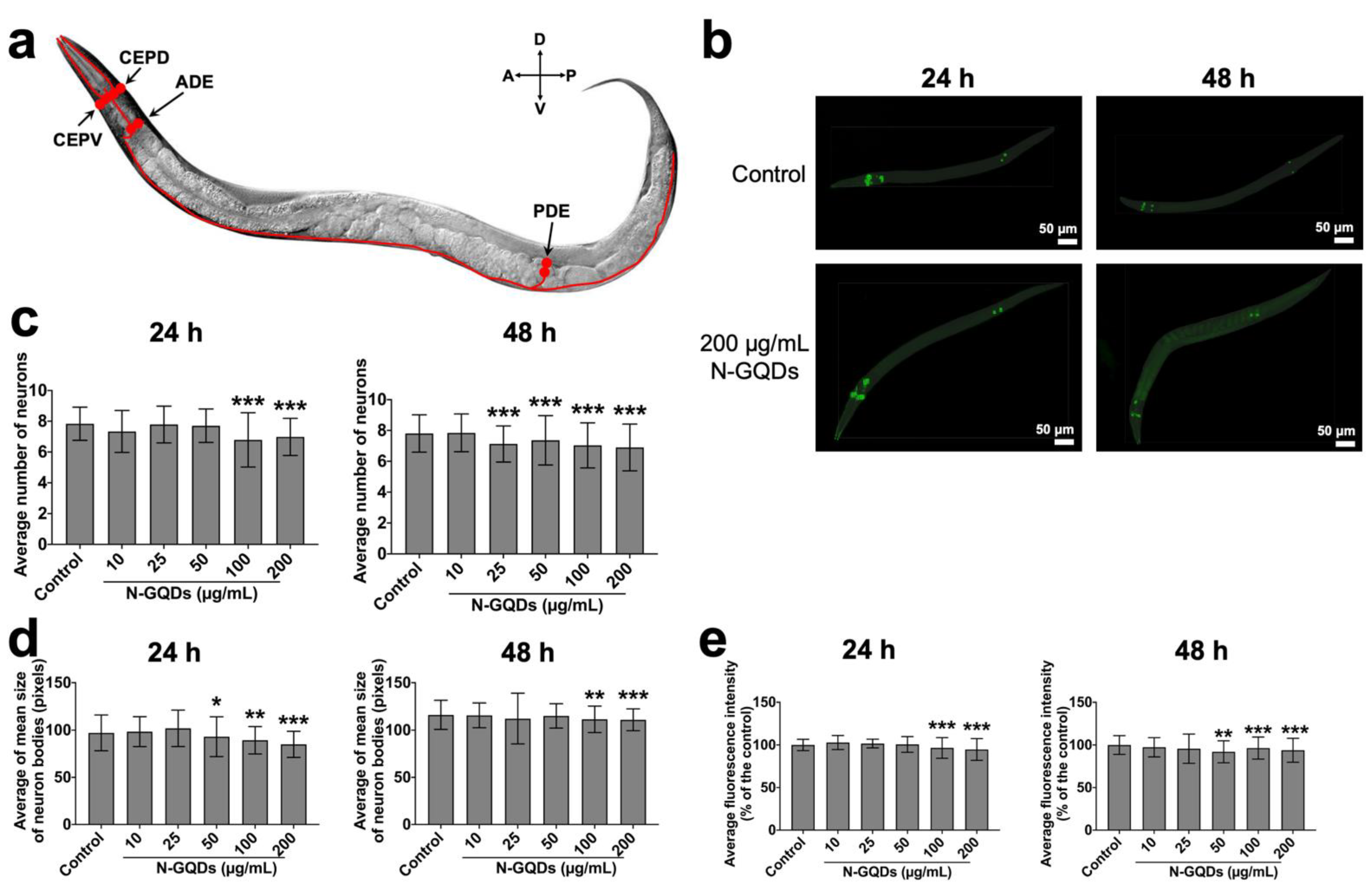
2.2. The Neurotoxicity of N-GQDs Was Associated with Damaging Dopaminergic Neurons and Glutamatergic Neurons in Nematode C. elegans
2.3. The Application of Training YOLACT Algorithm in Image Segmentation and Analysis
2.4. N-GQDs Induced Neurodegeneration of Neurons
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Preparation of N-GQDs
4.2. Strains and Culture Conditions
4.3. Preparation of Plates and Exposure Conditions
4.4. Body Bends Assay
4.5. Head Thrash Assay
4.6. Pharyngeal Pumping Assay
4.7. Quantitative Real-Time Reverse-Transcription Polymerase Chain Reaction (qRT-PCR) Analysis
4.8. Analysis of Morphological Laternations in Dopaminergic Neurons and Glutamatergic Neurons
4.9. YOLACT Algorithm
4.10. Data Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhang, Y.P.; Ma, J.M.; Yang, Y.S.; Ru, J.X.; Liu, X.Y.; Ma, Y.; Guo, H.C. Synthesis of nitrogen-doped graphene quantum dots (N-GQDs) from marigold for detection of Fe(3+) ion and bioimaging. Spectrochim. Acta. Part A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2019, 217, 60–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perini, G.; Palmieri, V.; Ciasca, G.; De Spirito, M.; Papi, M. Unravelling the Potential of Graphene Quantum Dots in Biomedicine and Neuroscience. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 3712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, S.; Chen, X.; Xia, T.; Ma, Q. A novel electrochemiluminescence sensor for the detection of nitroaniline based on the nitrogen-doped graphene quantum dots. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2016, 85, 903–908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaur, M.; Kaur, M.; Sharma, V.K. Nitrogen-doped graphene and graphene quantum dots: A review onsynthesis and applications in energy, sensors and environment. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2018, 259, 44–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bencsik, A.; Lestaevel, P.; Guseva Canu, I. Nano- and neurotoxicology: An emerging discipline. Prog. Neurobiol. 2018, 160, 45–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernandes, L.F.; Bruch, G.E.; Massensini, A.R.; Frézard, F. Recent Advances in the Therapeutic and Diagnostic Use of Liposomes and Carbon Nanomaterials in Ischemic Stroke. Front. Neurosci. 2018, 12, 453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Makvandi, P.; Ghomi, M.; Ashrafizadeh, M.; Tafazoli, A.; Agarwal, T.; Delfi, M.; Akhtari, J.; Zare, E.N.; Padil, V.V.T.; Zarrabi, A.; et al. A review on advances in graphene-derivative/polysaccharide bionanocomposites: Therapeutics, pharmacogenomics and toxicity. Carbohydr. Polym. 2020, 250, 116952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, J.; Wang, H.; Chen, M.; Yang, M. Recent advances in graphene-based nanomaterials: Properties, toxicity and applications in chemistry, biology and medicine. Mikrochim. Acta 2019, 186, 395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Marchi, L.; Pretti, C.; Gabriel, B.; Marques, P.; Freitas, R.; Neto, V. An overview of graphene materials: Properties, applications and toxicity on aquatic environments. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 631–632, 1440–1456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xuan, Y.; Zhang, R.Y.; Zhang, X.S.; An, J.; Cheng, K.; Li, C.; Hou, X.L.; Zhao, Y.D. Targeting N-doped graphene quantum dot with high photothermal conversion efficiency for dual-mode imaging and therapy in vitro. Nanotechnology 2018, 29, 355101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, B.Y.; Li, C.; Song, Y.Y.; Tan, F.; Cao, Y.C.; Zhao, Y.D. Nitrogen-doped graphene quantum dot for direct fluorescence detection of Al3+ in aqueous media and living cells. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2018, 100, 41–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Campbell, E.; Hasan, M.T.; Gonzalez-Rodriguez, R.; Truly, T.; Lee, B.H.; Green, K.N.; Akkaraju, G.; Naumov, A.V. Graphene quantum dot formulation for cancer imaging and redox-based drug delivery. Nanomed. Nanotechnol. Biol. Med. 2021, 37, 102408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuo, W.S.; Shao, Y.T.; Huang, K.S.; Chou, T.M.; Yang, C.H. Antimicrobial Amino-Functionalized Nitrogen-Doped Graphene Quantum Dots for Eliminating Multidrug-Resistant Species in Dual-Modality Photodynamic Therapy and Bioimaging under Two-Photon Excitation. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2018, 10, 14438–14446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, T.; Xu, H.; Liang, X.; Tang, M. Caenorhabditis elegans as a complete model organism for biosafety assessments of nanoparticles. Chemosphere 2019, 221, 708–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzalez-Moragas, L.; Roig, A.; Laromaine, A.C. Elegans as a tool for in vivo nanoparticle assessment. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2015, 219, 10–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Zhong, L.; Zhang, L.; Shen, X.; Kong, L.; Wu, T. Research Advances on the Adverse Effects of Nanomaterials in a Model Organism, Caenorhabditis elegans. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2021, 40, 2406–2424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, T.; He, K.; Zhan, Q.; Ang, S.; Ying, J.; Zhang, S.; Zhang, T.; Xue, Y.; Tang, M. MPA-capped CdTe quantum dots exposure causes neurotoxic effects in nematode Caenorhabditis elegans by affecting the transporters and receptors of glutamate, serotonin and dopamine at the genetic level, or by increasing ROS, or both. Nanoscale 2015, 7, 20460–20473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nicoletti, M.; Loppini, A.; Chiodo, L.; Folli, V.; Ruocco, G.; Filippi, S. Biophysical modeling of C. elegans neurons: Single ion currents and whole-cell dynamics of AWCon and RMD. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0218738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, X.; Wang, Y.; Cheng, J.; Ji, Q.; Wang, Y.; Wu, T.; Tang, M. Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles at Predicted Environmentally Relevant Concentrations Cause Impairments in GABAergic Motor Neurons of Nematode Caenorhabditis elegans. Chem. Res. Toxicol. 2020, 33, 1665–1676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piechulek, A.; von Mikecz, A. Life span-resolved nanotoxicology enables identification of age-associated neuromuscular vulnerabilities in the nematode Caenorhabditis elegans. Environ. Pollut. (Barking Essex 1987) 2018, 233, 1095–1103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- San-Miguel, A.; Kurshan, P.T.; Crane, M.M.; Zhao, Y.; McGrath, P.T.; Shen, K.; Lu, H. Deep phenotyping unveils hidden traits and genetic relations in subtle mutants. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 12990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saberi-Bosari, S.; Huayta, J.; San-Miguel, A. A microfluidic platform for lifelong high-resolution and high throughput imaging of subtle aging phenotypes in C. elegans. Lab Chip 2018, 18, 3090–3100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Camacho, D.M.; Collins, K.M.; Powers, R.K.; Costello, J.C.; Collins, J.J. Next-Generation Machine Learning for Biological Networks. Cell 2018, 173, 1581–1592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soares, M.V.; Charão, M.F.; Jacques, M.T.; Dos Santos, A.L.A.; Luchese, C.; Pinton, S.; Ávila, D.S. Airborne toluene exposure causes germline apoptosis and neuronal damage that promotes neurobehavioural changes in Caenorhabditis elegans. Environ. Pollut. (Barking Essex 1987) 2020, 256, 113406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hart, A. Behavior. In Wormbook; Massachusetts General Hospital Cancer Center: Boston, MA, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Brenner, S. The genetics of Caenorhabditis elegans. Genetics 1974, 77, 71–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hobert, O. Neurogenesis in the Nematode Caenorhabditis elegans. Wormbook 2010, 1–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hobert, O. Specification of the nervous system. Wormbook 2005, 12, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Lieke, T.; Steinberg, C.E.; Ju, J.; Saul, N. Natural Marine and Synthetic Xenobiotics Get on Nematode’s Nerves: Neuro-Stimulating and Neurotoxic Findings in Caenorhabditis elegans. Mar. Drugs 2015, 13, 2785–2812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, K.; Zhang, X.; Ren, S.; Sun, J. Deep Residual Learning for Image Recognition. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Las Vegas, NV, USA, 27–30 June 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Goodfellow, I.; Bengio, Y.; Courville, A. Deep Learning. In Deep Learning; MIT Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, T.Y.; Maire, M.; Belongie, S.; Hays, J.; Zitnick, C.L. Microsoft COCO: Common Objects in Context; Springer International Publishing: New York, NY, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Chase, D.L.; Pepper, J.S.; Koelle, M.R. Mechanism of extrasynaptic dopamine signaling in Caenorhabditis elegans. Nat. Neurosci. 2004, 7, 1096–1103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D. Endpoints for Toxicity Assessment of Nanomaterials. In Nanotoxicology in Caenorhabditis elegans; Springer: Singapore, 2018; pp. 11–31. [Google Scholar]
- Gendrel, M.; Atlas, E.G.; Hobert, O. A cellular and regulatory map of the GABAergic nervous system of C. elegans. Elife 2016, 5, e17686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, R.Y.; Sawin, E.R.; Chalfie, M.; Horvitz, H.R.; Avery, L. EAT-4, a homolog of a mammalian sodium-dependent inorganic phosphate cotransporter, is necessary for glutamatergic neurotransmission in Caenorhabditis elegans. J. Neurosci. Off. J. Soc. Neurosci. 1999, 19, 159–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D. Confirmation of Nanomaterials with Low-Toxicity or Non-Toxicity Property. In Nanotoxicology in Caenorhabditis elegans; Springer: Singapore, 2018; pp. 205–226. [Google Scholar]
- Ruszkiewicz, J.A.; Pinkas, A.; Miah, M.R.; Weitz, R.L.; Lawes, M.J.A.; Akinyemi, A.J.; Ijomone, O.M.; Aschner, M.C. Elegans as a model in developmental neurotoxicology. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2018, 354, 126–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Avila, D.; Helmcke, K.; Aschner, M. The Caenorhabiditis elegans model as a reliable tool in neurotoxicology. Hum. Exp. Toxicol. 2012, 31, 236–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bargmann, C.I. Neurobiology of the Caenorhabditis elegans genome. Science 1998, 282, 2028–2033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leung, M.C.; Williams, P.L.; Benedetto, A.; Au, C.; Helmcke, K.J.; Aschner, M.; Meyer, J.N. Caenorhabditis elegans: An emerging model in biomedical and environmental toxicology. Toxicol. Sci. Off. J. Soc. Toxicol. 2008, 106, 5–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schultz, W. Multiple dopamine functions at different time courses. Annu. Rev. Neurosci. 2007, 30, 259–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Björklund, A.; Dunnett, S.B. Dopamine neuron systems in the brain: An update. Trends Neurosci. 2007, 30, 194–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tanimoto, Y.; Zheng, Y.G.; Fei, X.; Fujie, Y.; Hashimoto, K.; Kimura, K.D. In actio optophysiological analyses reveal functional diversification of dopaminergic neurons in the nematode C. elegans. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 26297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suo, S.; Ishiura, S.; Van Tol, H.H. Dopamine receptors in C. elegans. Eur. J. Pharm. 2004, 500, 159–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serrano-Saiz, E.; Poole, R.J.; Felton, T.; Zhang, F.; De La Cruz, E.D.; Hobert, O. Modular control of glutamatergic neuronal identity in C. elegans by distinct homeodomain proteins. Cell 2013, 155, 659–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewis, J.A.; Fleming, J.T. Basic culture methods. Methods Cell Biol. 1995, 48, 3–29. [Google Scholar]
- Tosic, J.; Stanojevic, Z.; Vidicevic, S.; Isakovic, A.; Ciric, D.; Martinovic, T.; Kravic-Stevovic, T.; Bumbasirevic, V.; Paunovic, V.; Jovanovic, S.; et al. Graphene quantum dots inhibit T cell-mediated neuroinflammation in rats. Neuropharmacology 2019, 146, 95–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.; Yoo, J.M.; Hwang, H.; Lee, J.; Lee, S.H.; Yun, S.P.; Park, M.J.; Lee, M.; Choi, S.; Kwon, S.H.; et al. Graphene quantum dots prevent α-synucleinopathy in Parkinson’s disease. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2018, 13, 812–818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, S.; Zhou, D.; Luan, P.; Gu, B.; Feng, L.; Fan, S.; Liao, W.; Fang, W.; Yang, L.; Tao, E.; et al. Graphene quantum dots conjugated neuroprotective peptide improve learning and memory capability. Biomaterials 2016, 106, 98–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Wang, X.; Wu, Q.; Li, Y.; Wang, D. Translocation and neurotoxicity of CdTe quantum dots in RMEs motor neurons in nematode Caenorhabditis elegans. J. Hazard. Mater. 2015, 283, 480–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ju, J.; Ruan, Q.; Li, X.; Liu, R.; Li, Y.; Pu, Y.; Yin, L.; Wang, D. Neurotoxicological evaluation of microcystin-LR exposure at environmental relevant concentrations on nematode Caenorhabditis elegans. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2013, 20, 1823–1830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Yu, S.; Wu, Q.; Tang, M.; Wang, D. Transmissions of serotonin, dopamine, and glutamate are required for the formation of neurotoxicity from Al2O3-NPs in nematode Caenorhabditis elegans. Nanotoxicology 2013, 7, 1004–1013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Y.L.; Wu, Q.L.; Li, Y.P.; Wang, D.Y. Translocation, transfer, and in vivo safety evaluation of engineered nanomaterials in the non-mammalian alternative toxicity assay model of nematode Caenorhabditis elegans. RSC Adv. 2013, 3, 5741–5757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ju, J.; Lieke, T.; Saul, N.; Pu, Y.; Yin, L.; Kochan, C.; Putschew, A.; Baberschke, N.; Steinberg, C.E. Neurotoxic evaluation of two organobromine model compounds and natural AOBr-containing surface water samples by a Caenorhabditis elegans test. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2014, 104, 194–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ju, J.; Saul, N.; Kochan, C.; Putschew, A.; Pu, Y.; Yin, L.; Steinberg, C.E. Cyanobacterial xenobiotics as evaluated by a Caenorhabditis elegans neurotoxicity screening test. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2014, 11, 4589–4606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boulin, T.; Etchberger, J.F.; Hobert, O. Reporter gene fusions. WormBook 2006, 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bolya, D.; Zhou, C.; Xiao, F.; Lee, Y.J. YOLACT++: Better Real-time Instance Segmentation. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2020, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bolya, D.; Zhou, C.; Xiao, F.; Lee, Y.J. YOLACT: Real-time Instance Segmentation. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), Seoul, Korea, 27 October–2 November 2019; pp. 9157–9166. [Google Scholar]
- He, K.; Gkioxari, G.; Dollár, P.; Girshick, R. Mask R-CNN. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2017, 2980–2988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, T.Y.; Dollar, P.; Girshick, R.; He, K.; Hariharan, B.; Belongie, S. Feature Pyramid Networks for Object Detection. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017. [Google Scholar]




Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xu, H.; Wang, X.; Zhang, X.; Cheng, J.; Zhang, J.; Chen, M.; Wu, T. A Deep Learning Analysis Reveals Nitrogen-Doped Graphene Quantum Dots Damage Neurons of Nematode Caenorhabditis elegans. Nanomaterials 2021, 11, 3314. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano11123314
Xu H, Wang X, Zhang X, Cheng J, Zhang J, Chen M, Wu T. A Deep Learning Analysis Reveals Nitrogen-Doped Graphene Quantum Dots Damage Neurons of Nematode Caenorhabditis elegans. Nanomaterials. 2021; 11(12):3314. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano11123314
Chicago/Turabian StyleXu, Hongsheng, Xinyu Wang, Xiaomeng Zhang, Jin Cheng, Jixiang Zhang, Min Chen, and Tianshu Wu. 2021. "A Deep Learning Analysis Reveals Nitrogen-Doped Graphene Quantum Dots Damage Neurons of Nematode Caenorhabditis elegans" Nanomaterials 11, no. 12: 3314. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano11123314
APA StyleXu, H., Wang, X., Zhang, X., Cheng, J., Zhang, J., Chen, M., & Wu, T. (2021). A Deep Learning Analysis Reveals Nitrogen-Doped Graphene Quantum Dots Damage Neurons of Nematode Caenorhabditis elegans. Nanomaterials, 11(12), 3314. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano11123314





