Graphene Oxide Derivatives and Their Nanohybrid Structures for Laser Desorption/Ionization Time-of-Flight Mass Spectrometry Analysis of Small Molecules
Abstract
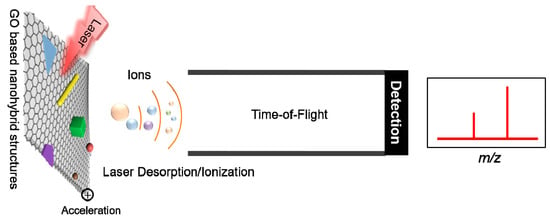
:1. Introduction
2. GO Derivatives for LDI-TOF-MS Analysis
3. GO/CNT Hybrid Structures for LDI-TOF-MS Analysis
4. GO/Metal Hybrid Structures for LDI-TOF-MS Analysis
5. GO/Metal Oxide Hybrid Structures for LDI-TOF-MS Analysis
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Liu, T.; Belov, M.E.; Jaitly, N.; Qian, W.J.; Smith, R.D. Accurate mass measurements in proteomics. Chem. Rev. 2007, 107, 3621–3653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gao, X.; Tan, B.H.; Sugrue, R.J.; Tang, K. MALDI mass spectrometry for nucleic acid analysis. Top. Curr. Chem. 2013, 331, 55–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hyzak, L.; Moos, R.; Von Rath, F.; Wulf, V.; Wirtz, M.; Melchior, D.; Kling, H.W.; Köhler, M.; Gäb, S.; Schmitz, O.J. Quantitative matrix-assisted laser desorption ionization-time-of-flight mass spectrometry analysis of synthetic polymers and peptides. Anal. Chem. 2011, 83, 9467–9471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karas, M.; Bahr, U.; Giessmann, U. Matrix-assisted laser desorption ionization mass spectrometry. Mass Spectrom. Rev. 1991, 10, 335–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aebersold, R.; Goodlett, D.R. Mass spectrometry in proteomics. Chem. Rev. 2001, 101, 269–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Z.; Zhang, Q.; Zou, H.; Guo, B.; Ni, J. A method for the analysis of low-mass molecules by MALDI-TOF mass spectrometry. Anal. Chem. 2002, 74, 1637–1641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silina, Y.E.; Volmer, D.A. Nanostructured solid substrates for efficient laser desorption/ionization mass spectrometry (LDI-MS) of low molecular weight compounds. Analyst 2013, 138, 7053–7065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiang, C.K.; Chen, W.T.; Chang, H.T. Nanoparticle-based mass spectrometry for the analysis of biomolecules. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2011, 40, 1269–1281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawasaki, H.; Sugitani, T.; Watanabe, T.; Yonezawa, T.; Moriwaki, H.; Arakawa, R. Layer-by-layer self-assembled mutilayer films of gold nanoparticles for surface-assisted laser desorption/ionization mass spectrometry. Anal. Chem. 2008, 80, 7524–7533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McLean, J.A.; Stumpo, K.A.; Russel, D.H. Size-selected (2–10 nm) gold nanoparticles for matrix assisted laser desorption ionization of peptides. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2005, 127, 5304–5305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brodoceanu, D.; Elnathan, R.; Prieto-Simón, B.; Delalat, B.; Guinan, T.; Kroner, E.; Voelcker, N.H.; Kraus, T. Dense arrays of uniform submicron pores in silicon and their applications. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2015, 7, 1160–1169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, Q.; Wang, Z.; Wang, Y.; Teng, F.; Du, J.; Dou, S.; Lu, N. Investigation of surface morphology on ion desorption in SALDI-MS on tailored silicon nanopillar arrays. J. Phys. Chem. C 2020, 124, 2450–2457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Q.; Teng, F.; Wang, Z.; Wang, Y.; Lu, N. Confining analyte droplets on visible Si pillars for improbing reproducibility and sensitivity of SALDI-TOF MS. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2019, 411, 1135–1142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Teng, F.; Wang, Y.; Lu, N. Rapid liquid-phase microextraction of analytes from complex samples on superwetting porous silicon for onsite SALDI-MS analysis. Talanta 2019, 198, 63–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rainer, M.; Qureshi, M.N.; Bonn, G.K. Matrix-free and material-enhanced laser desorption/ionization mass spectrometry for the analysis of low molecular weight compounds. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2011, 400, 2281–2288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, S.; Zheng, H.; Wang, J.; Hou, J.; He, Q.; Liu, H.; Xiong, C.; Kong, X.; Nie, Z. Carbon nanodots as a matrix for the analysis of low-molecular-weight molecules in both positive- and negative-ion matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization time-of-flight mass spectrometry and quantification of glucose and uric acid in real samples. Anal. Chem. 2013, 85, 6646–6652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, S.; Li, Y.; Zou, H.; Qiu, J.; Guo, Z.; Guo, B. Carbon nanotubes as assisted matrix for laser desorption/ionization time-of-flight mass spectrometry. Anal. Chem. 2003, 75, 6191–6195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, H.W.; Ng, K.M.; Lu, W.; Che, C.M. Ion desorption efficiency and internal energy transfer in carbon-based surface-assisted laser desorption/ionization mass spectrometry: Desorption mechanism(s) and the design of SALDI substrates. Anal. Chem. 2009, 81, 4720–4729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, M.; Yang, X.; Yang, Y.; Qin, P.; Wu, X.; Cai, Z. Nanomaterials as assisted matrix of laser desorption/ionization time-of-flight mass spectrometry for the analysis of small molecules. Nanomaterials 2017, 7, 87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Cheng, M.; Jiang, G. Mildly oxidized graphene: Facile synthesis, characterization, and application as a matrix in MALDI mass spectrometry. Chem. Eur. J. 2013, 19, 5561–5565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.K.; Min, D.H. Mechanistic study of laser desorption/ionization of small molecules on graphene oxide multilayer films. Langmuir 2014, 30, 12675–12683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, J.; Buriak, J.M.; Siuzdak, G. Desorption-ionization mass spectrometry on porous silicon. Nature 1999, 399, 243–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakamura, Y.; Soejima, T. TiO2 Nanocoral structures as versatile substrates for surface-assisted laser desorption/ionization mass spectrometry. ChemNanoMat 2019, 5, 447–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewis, W.G.; Shen, Z.; Finn, M.G.; Siuzdak, G. Desorption/ionization on silicon (DIOS) mass spectrometry: Background and applications. Int. J. Mass Spectrom. 2003, 226, 107–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, J.J.; Shen, Z.; Crowell, J.E.; Finn, M.G.; Siuzdak, G. Desorption/ionization on silicon (DIOS): A diverse mass spectrometry platform for protein characterization. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2001, 98, 4932–4937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sweetman, M.J.; Mclnnes, S.J.P.; Vasani, R.B.; Guinan, T.; Blencowe, A.; Voelcker, N.H. Rapid, metal-free hydrosilanisation chemistry for porous silicon surface modification. Chem. Commun. 2015, 51, 10640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, G.; Chen, Y.; Siuzdak, G.; Vertes, A. Surface modification and laser pulse length effects on internal energy transfer in DIOS. J. Phys. Chem. B 2005, 109, 24450–24456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.N.; Tang, W.; Gordon, A.; Wang, H.Y.; Xu, L.; Li, P.; Li, B. Porous TiO2 film immobilized with gold nanoparticles for dual-polarity SALDI MS detection and imaging . ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2020, 12, 42567–42575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Q.; Teng, F.; Wang, Z.; Wang, Y.; Lu, N. Superhydrophobic glass substrates coated with fluorosilane-coated silica nanoparticles and silver nanoparticles for surface-assisted laser desorption/ionization mass spectrometry. ACS Appl. Nano Mater. 2019, 2, 3813–3818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Min, Q.; Zhang, X.; Chen, X.; Li, S.; Zhu, J.J. N-Doped graphene: An alternative carbon-based matrix for highly efficient detection of small molecules by negative ion MALDI-TOF-MS. Anal. Chem. 2014, 86, 9122–9130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Liu, Q.; Huang, X.; Nie, Z.; Ruan, T.; Du, Y.; Jiang, G. Fluorographene as a mass spectrometry probe for high-throughput identification and screening of emerging chemical contaminants in complex samples. Anal. Chem. 2017, 89, 1307–1314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, H.; Li, Y.; Wang, J.; Cheng, M.; Zhao, Z.; Zhang, H.; Wang, C.; Wang, J.; Qiao, Y.; Wang, J. Dual-Ion-Mode MALDI MS Detection of small molecules with the O-P,N-Doped carbon/graphene matrix. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2018, 10, 37732–37742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, D.; Jiamg, X.; Li, J.; He, B.; Liu, Q.; Hu, L.; Jiang, G. 3D printing of graphene-doped target for “matrix-free” laser desorption/ionization mass spectrometry. Chem. Commun. 2018, 54, 2723–2726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, X.; Liu, Q.; Fu, J.; Nie, Z.; Gao, K.; Jiang, G. Screening of toxic chemicals in a single drop of human whole blood using ordered mesoporous carbon as a mass spectrometry probe. Anal. Chem. 2016, 88, 4107–4113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, D.; Guo, S.; Zhang, M.; Liu, Y.; Chen, T.; Li, Z. Mass spectrometry imaging of small molecules in biological tissues using graphene oxide as a matrix. Anal. Chim. Acta 2017, 962, 52–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, C.; Deng, C.; Zhang, X.; Yang, P. Synthesis of highly water-dispersible polydopamine-modified multiwalled carbon nanotubes for matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization mass spectrometry analysis. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2013, 5, 7770–7776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, W.; Li, Y.; Li, R.; Shuang, S.; Dong, C.; Cai, Z. Facile synthesis of N-Doped Carbon dots as a new matrix for detection of hydroxy-polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons by negative-ion matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization time-of-flight mass spectrometry. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2016, 8, 12976–12984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, X.; Li, S.; Peng, Z.; Al-Yuobi, A.O.; Bashammakh, A.S.O.; El-Shahawi, M.S.; Leblanc, R.M. Interactions between carbon nanomaterials and biomolecules. J. Oleo Sci. 2016, 65, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Perreault, F.; Fonseca De Faria, A.; Elimelech, M. Environmental applications of graphene-based nanomaterials. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2015, 44, 5861–5896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, S.; Wang, X.; Yao, W.; Wang, J.; Ji, Y.; Ai, Y.; Alsaedi, A.; Hayat, T.; Wang, X. Macroscopic, spectroscopic, and theoretical investigation for the interaction of phenol and naphthol on reduced graphene oxide. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2017, 51, 3278–3286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.; Murthy, B.N.; Shapter, J.G.; Constantopoulos, K.T.; Voelcker, N.H.; Ellis, A.V. Benzene carboxylic acid derivatized graphene oxide nanosheets on natural zeolites as effective adsorbents for cationic dye removal. J. Hazard. Mater. 2013, 260, 330–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Claramunt, S.; Varea, A.; López-Díaz, D.; Velázquez, M.M.; Cornet, A.; Cirera, A. The importance of interbands on the interpretation of the Raman spectrum of graphene oxide. J. Phys. Chem. C 2015, 119, 10123–10129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cançado, L.G.; Jorio, A.; Martins Ferreira, E.H.; Stavale, F.; Achete, C.A.; Capaz, R.B.; Moutinho, M.V.O.; Lombardo, A.; Kulmala, T.S.; Ferrari, A.C. Quantifying Defects in Graphene via Raman Spectroscopy at Different Excitation Energies. Nano Lett. 2011, 11, 3190–3196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gómez, J.; Villaro, E.; Navas, A.; Recio, I. Testing the influence of the temperature, RH and filler type and content on the universal power law for new reduced graphene oxide TPU composites. Mater. Res. Express 2017, 4, 105020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dave, S.H.; Gong, C.; Robertson, A.W.; Warner, J.H.; Grossman, J.C. Chemistry and structure of graphene oxide via direct imaging. ACS Nano 2016, 10, 7515–7522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dreyer, D.R.; Park, S.; Bielawski, C.W.; Ruoff, R.S. The chemistry of graphene oxide. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2010, 39, 228–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shojaeenezhad, S.S.; Farbod, M.; Kazeminezhad, I. Effects of initial graphite particle size and shape on oxidation time in graphene oxide prepared by Hummers’ method. J. Sci. Adv. Mater. Devices 2017, 2, 470–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mouhat, F.; Coudert, F.; Bocquet, M. Structure and chemistry of graphene oxide in liquid water from first principles. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 1566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brisebois, P.P.; Siaj, M. Harvesting Graphene Oxide-Years: 1859 to 2019 A Review of its Structure, Synthesis, Properties and Exfoliation. J. Mater. Chem. C 2020, 8, 1517–1547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, D.; Feng, H.; Li, J. Graphene Oxide: Preparation, functionalization, and electrochemical applications. Chem. Rev. 2012, 112, 6027–6053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loh, K.P.; Bao, Q.; Eda, G.; Chhowalla, M. Graphene oxide as a chemically tunable platform for optical applications. Nat. Chem. 2010, 2, 1015–1024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guex, L.G.; Sacchi, B.; Peuvot, K.F.; Andersson, R.L.; Pourrahimi, A.M.; Ström, V.; Farris, S.; Olsson, R.T. Experimental review: Chemical reduction of graphene oxide (GO) to reduced graphene oxide (rGO) by aqueous chemistry. Nanoscale 2017, 9, 9562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhang, J.; Zheng, X.; Ni, Y. Selective enrichment and MALDI-TOF MS analysis of small molecule compounds with vicinal diols by boric acid-functionalized graphene oxide. J. Am. Soc. Mass Spectrom. 2015, 26, 1291–1298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, B.; Qu, Y.; Zhang, L.; Liang, Z.; Zhang, Y. 4-Mercaptophenylboronic acid functionalized graphene oxide composites: Preparation, characterization and selective enrichment of glycopeptides. Anal. Chim. Acta 2016, 912, 41–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, L.A.L.; Wang, J.; Loh, K.P. Graphene-based SELDI probe with ultrahigh extraction and sensitivity for DNA oligomer. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2010, 132, 10976–10977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.Y.; Long, X.Y.; Sheng, D.; Lian, H.Z. Organic molecule-assisted synthesis of Fe3O4/graphene oxide nanocomposites for selective capture of low-abundance peptides and phosphopeptides. Talanta 2020, 208, 120437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, X.; Cheng, J.; Li, J.; Wang, Y. Graphene as a novel matrix for the analysis of small molecules by MALDI-TOF MS. Anal. Chem. 2010, 82, 6208–6214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bøggild, P. The war on fake graphene. Nature 2018, 562, 502–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Georgakilas, V.; Perman, J.A.; Tucek, J.; Zboril, R. Broad family of carbon nanoallotropes: Classification, chemistry, and applications of fullerenes, carbon dots, nanotubes, graphene, nanodiamonds, and combined superstructures. Chem. Rev. 2015, 115, 4744–4822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, H.; Tang, L.; Wang, Y.; Jiang, J.; Li, J. Graphene fluorescence resonance energy transfer aptasensor for the thrombin detection. Anal. Chem. 2010, 82, 2341–2346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Wei, Y.; He, Q.; Boey, F.; Zhang, Q.; Zhang, H. Reduced graphene oxide films used as matrix of MALDI-TOF-MS for detection of octachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin. Chem. Commun. 2010, 46, 6974–6976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, M.; Lai, Y.; Chen, G.; Cai, Z. Matrix interference-free method for the analysis of small molecules by using negative ion laser desorption/ionization on graphene flakes. Anal. Chem. 2011, 83, 3161–3169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, C.W.; Chien, M.W.; Su, C.Y.; Chen, H.Y.; Li, L.J.; Lai, C.C. Analysis of flavonoids by graphene-based surface-assisted laser desorption/ionization time-of-flight mass spectrometry. Analyst 2012, 137, 5809–5816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, Y.K.; Min, D.H. The structural influence of graphene oxide on its fragmentation during laser desorption/ionization mass spectrometry for efficient small-molecule analysis. Chem. Eur. J. 2015, 21, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Z.; Zhang, W.; Luo, Y.; Yang, J.; Hou, J.G. How graphene is cut upon oxidation? J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2009, 131, 6320–6321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hong, Y.L.; Lee, J.; Ku, B.C.; Kang, K.; Lee, S.; Ryu, S.; Kim, Y.K. The influence of oxidative debris on the fragmentation and laser desorption/ionization process of graphene oxide derivatives. New J. Chem. 2018, 42, 12692–12697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, Y.L.; Seo, T.H.; Jang, H.J.; Kim, Y.K. The effect of oxidative debris on the laser desorption/ionization efficiency of graphene oxide derivates for mass spectrometric analysis of small molecules and synthetic polymers. Anal. Sci. 2019, 35, 1097–1102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rourke, J.P.; Pandey, P.A.; Moore, J.J.; Bates, M.; Kinloch, I.A.; Young, R.J.; Wilson, N.R. The real graphene oxide revealed: Stripping the oxidative debris from the graphene-like sheets. Angew. Chem. 2011, 50, 3173–3177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lee, J.; Kim, Y.K.; Min, D.H. Laser desorption/ionization mass spectrometric assay for phospholipase activity based on graphene oxide/carbon nanotube double-layer films. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2010, 132, 14714–14717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.K.; Min, D.H. Durable large-area thin films of graphene/carbon nanotube double layers as a transparent electrode. Langmuir 2009, 25, 11302–11306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.K.; Na, H.K.; Kwack, S.J.; Ryoo, S.R.; Lee, Y.; Hong, S.; Hong, S.; Jeong, Y.; Min, D.H. Synergistic effect of graphene oxide/MWCNT films in laser desorption/ionization mass spectrometry of small molecules and tissue imaging. ACS Nano 2011, 5, 4550–4561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, Y.K.; Min, D.H. Fabrication of alternating multilayer films of graphene oxide and carbon nanotube and its application in mechanistic study of laser desorption/ionization of small molecules. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2012, 4, 2088–2095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Decher, G.; Hong, J.D. Buildup of ultrathin multilayer films by a self-assembly process: 11. Consecutive adsorption of anionic and cationic bipolar amphiphiles and polyelectrolytes on charged surfaces. Ber. Bunsenges. Phys. Chem. 1991, 95, 1430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ariga, K.; Hill, J.P.; Ji, Q. Layer-by-layer assembly as a versatile bottom-up nanofabrication technique for exploratory research and realistic application. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2007, 9, 2319–2340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, S.W.; Kim, B.S.; Chen, S.; Yang, S.H.; Hammond, P.T. Layer-by-layer assembly of all carbon nanotube ultrathin films for electrochemical applicaions. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2009, 131, 671–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.P.; Yu, C.J.; Lin, C.Y.; Lin, Y.H.; Tseng, W.L. Gold nanoparticles as assisted matrices for the detection of biomolecules in a high-salt solution through laser desorption/ionization mass spectrometry. J. Am. Soc. Mass Spectrom. 2009, 20, 875–882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Duan, J.; Linman, M.J.; Chen, C.Y.; Cheng, Q.J. CHCA-Modified Au nanoparticles for laser desorption ionization mass spectrometric analysis of peptides. J. Am. Soc. Mass Spectrom. 2009, 20, 1530–1539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chiang, C.K.; Lin, Y.W.; Chen, W.T.; Chang, H.T. Accurate quantitation of glutathione in cell lysates through surface-assisted laser desorption/ionization mass spectrometry using gold nanoparticles. Nanomed. Nanotechnol. Biol. Med. 2010, 6, 530–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.T.; Chiang, C.K.; Lin, Y.W.; Chang, H.T. Quantification of captopril in urine through surface-assisted laser desorption/ionization mass spctrometry using 4-mercaptobenzoic acid-capped gold nanoparticles as an internal standard. J. Am. Soc. Mass Spectrom. 2010, 21, 864–867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Huang, Y.F.; Chang, H.T. Analysis of adenosine triphosphate and glutathione through gold nanoparticles assisted laser desorption/ionization mass spectrometry. Anal. Chem. 2007, 79, 4852–4859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, C.L.; Tseng, W.L. Gold nanoparticles as assisted matrix for determining neutral small carbohydrates through laser desorption/ionization time-of-flight mass spectrometry. Anal. Chem. 2007, 79, 1626–1633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, Y.K.; Min, D.H. Preparation of the hybrid film of poly(allylamine hydrochloride)- functionalized graphene oxide and gold nanoparticle and its application for laser-induced desorption/ionization of small molecules. Langmuir 2012, 28, 4453–4458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, Y.K.; Na, H.K.; Min, D.H. Influence of surface functionalization on the growth of gold nanostructures on graphene thin films. Langmuir 2010, 26, 13065–13070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, Y.K.; Na, H.K.; Lee, Y.W.; Jang, H.; Han, S.W.; Min, D.H. The direct growth of gold rods on graphene thin films. Chem. Commun. 2010, 46, 3185–3187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuo, T.R.; Wang, D.Y.; Chiu, Y.C.; Yeh, Y.C.; Chen, W.T.; Chen, C.H.; Chen, C.W.; Chang, H.C.; Hu, C.C.; Chen, C.C. Layer-by-layer thin film of reduced graphene oxide and gold nanoparticles as an effective sample plate in laser-induced desorption/ionization mass spectrometry. Anal. Chim. Acta 2014, 809, 97–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hong, M.; Xu, L.; Wang, F.; Geng, Z.; Li, H.; Wang, H.; Li, C.Z. A direct assay of carboxyl-containing small molecules by SALDI-MS on a AgNP/rGO-based nanoporous hybrid film. Analyst 2016, 141, 2712–2726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tiwari, P.M.; Vig, K.; Dennis, V.A.; Singh, S.R. Functionalized gold nanoparticles and their biomedical applications. Nanomaterials 2011, 1, 31–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Huan, W.; Xu, K.; Wang, B.; Zhang, J.; Zhu, B.; Wu, M.; Wang, J. Gold nanoparticle-glutathione-functionalized porous graphene oxide-based hydrophilic beads for the selective enrichment of N-linked glycopeptides. Microchim. Acta 2020, 187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanamoto, S.; Nakada, N.; Jürgens, M.D.; Johnson, A.C.; Yamashita, N.; Tanaka, H. The different fate of antibiotics in the Thams River, UK, and the Katsura River, Japan. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2018, 25, 1903–1913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mojica, E.R.; Aga, D.S. Antibiotics pollution in soil and water: Potential ecological and human health issues. Encycl. Environ. Health. 2011, 97–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Danner, M.C.; Robertson, A.; Behrends, V.; Reiss, J. Antibiotic pollution in surface fresh waters: Occurrence and effects. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 664, 793–804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, H.Z.; Wang, Y.H.; Li, S.; Wu, J.; Li, J.W.; Zhou, H.Y.; Gao, Z.X. Graphene oxide composites for magnetic solid-phase extraction of twelve quinolones in water samples followed by MALDI-TOF MS. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2019, 411, 7039–7049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rusu, A.; Hancu, G.; Uivarosi, V. Fluoroquinolone pollution of food, water and soil, and bacterial resistance. Environ. Chem. Lett. 2015, 13, 21–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turiel, E.; Bordin, G.; Rodriguez, A.R. Trace enrichment of (fluoro)quinolone antibiotics in surface waters by solid-phase extraction and their determination by liquid chromatography-ultraviolet detection. J. Chromatogr. A 2003, 1008, 145–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parsamehr, P.S.; Zahed, M.; Tofighy, M.A.; Mohammadi, T.; Rezakazemi, M. Preparation of novel cross-linked graphene oxide membrane for desalination applications using (EDC and NHS)-activated graphene oxide and PEI. Desalination 2019, 468, 114079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iwaki, Y.; Kawasaki, H.; Arakawa, R. Human Serum Albumin-modified Fe3O4 magnetic nanoparticles for affinity-SALDI-MS of small-molecule drugs in biological liquids. Anal. Sci. 2012, 28, 893–900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chien, H.J.; Lai, S.M.; Wang, W.C.; Lin, H.Y.; Juang, Y.M.; Lai, P.S.; Lai, C.C. Preparation and comparison of Fe3O4@graphene oxide nanoclusters for analysis of glimepiride in urine by surface-assisted laser desorption/ionization time-of-flight mass spectrometry. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2020, 412, 4057–4065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, K.; Um, K.; Yoon, C.; Ryoo, W.S.; Lee, K. Wafer-level detection of organic contamination by ZnO-rGO hybrid-assisted laser desorption/ionization time-of-flight mass spectrometry. Talanta 2018, 182, 273–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tseng, B.H.J.; You, M.D.; Hsin, S.C. Characterization and control of microcontamination for advanced technology nodes and 300-mm wafer processing: Overview and challenges. IEEE Trans. Device Mater. Reliab. 2005, 5, 623–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, B.; Kim, S.T.; Kim, C.S.; Saha, K.; Moyano, D.F.; Xing, Y.; Jiang, Y.; Roberts, A.L.; Alfonso, F.S.; Rotello, V.M.; et al. Multiplexed imaging of nanoparticles in tissues using laser desroption/ionization mass spectrometry. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2013, 135, 12564–12567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Watanabe, T.; Kawasaki, H.; Yonezawa, T.; Arakawa, R. Surface-assisted laser desorption/ionization mass spectrometry (SALDI-MS) of low molecular weight organic compounds and synthetic polymers using zinc oxide (ZnO) nanoparticles. J. Mass Spectrom. 2008, 43, 1063–1071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Chen, Z.; Chen, B. Adsorption of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons by graphene and graphene oxide nanosheets. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2014, 48, 4817–4825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vállez-Gomis, V.; Grau, J.; Benedé, J.L.; Chisvert, A.; Salvador, A. Reduced graphene oxide-based magnetic composite for trace determination of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in cosmetics by stir bar sorptive dispersive microextraction. J. Chromatogr. A 2020, 1624, 461229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Y.; Apul, O.G.; Karanfil, T. Adsorption of halogenated aliphatic contaminants by graphene nanomaterials. Water Res. 2015, 79, 57–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]








| Platform | Analytes | LOD | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|
| RGO films | OCDD | 1 pmol | [61] |
| GO | Flavonoids | 1 pmol | [63] |
| NGO | BDPD | 50 pmol | [64] |
| B[a]P | 600 pmol | ||
| PBA | 70 nmol | ||
| bwGO | Amino acids and saccharides | 10 pmol | [67] |
| GO/MWCNT-NH2 hybrid films | Leu-enkephalin | 1 pmol | [71] |
| Saccharides | 10 pmol | ||
| Amino acids | 100 pmol | ||
| Multi-layered GO/MWCNT-NH2 hybrid films | Cellobiose | 10 pmol | [72] |
| Leu-enkephalin | |||
| Phenylalanine | |||
| Glucose | 100 pmol | ||
| Lysine | |||
| Leucine | |||
| Au/PAA-GO film | Saccharides and amino acids | 100 pmol | [82] |
| LBL assembled Au NPs/RGO hybrid films | Amino acids | 150 pmol | [85] |
| AuNPs/GO porous hybrid bead | N-linked glycopeptide | 2 fmol | [88] |
| Fe3O4@graphene oxide nanocluster | Glimepiride | 26 pmol | [97] |
| ZnO-RGO hybrid | B[a]P | 13 pmol | [98] |
| Strengths | Weaknesses |
|
|
| Opportunities | Threats |
|
|
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kim, S.-W.; Kwon, S.; Kim, Y.-K. Graphene Oxide Derivatives and Their Nanohybrid Structures for Laser Desorption/Ionization Time-of-Flight Mass Spectrometry Analysis of Small Molecules. Nanomaterials 2021, 11, 288. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano11020288
Kim S-W, Kwon S, Kim Y-K. Graphene Oxide Derivatives and Their Nanohybrid Structures for Laser Desorption/Ionization Time-of-Flight Mass Spectrometry Analysis of Small Molecules. Nanomaterials. 2021; 11(2):288. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano11020288
Chicago/Turabian StyleKim, Seung-Woo, Sunbum Kwon, and Young-Kwan Kim. 2021. "Graphene Oxide Derivatives and Their Nanohybrid Structures for Laser Desorption/Ionization Time-of-Flight Mass Spectrometry Analysis of Small Molecules" Nanomaterials 11, no. 2: 288. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano11020288
APA StyleKim, S.-W., Kwon, S., & Kim, Y.-K. (2021). Graphene Oxide Derivatives and Their Nanohybrid Structures for Laser Desorption/Ionization Time-of-Flight Mass Spectrometry Analysis of Small Molecules. Nanomaterials, 11(2), 288. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano11020288