Comparison of Effects of Sodium Chloride and Potassium Chloride on Spray Drying and Redispersion of Cellulose Nanofibrils Suspension
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. CNF Preparation
2.3. Drying and Redispersion
2.4. Field-Emission Scanning Electron Microscopy (FE-SEM)
2.5. Energy-Dispersive X-ray Spectroscopy (EDX)
2.6. Particle Size Distribution
2.7. Sedimentation Test
2.8. Dispersion Stability Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Scanning Electron Microscopy
3.2. Energy-Dispersive X-ray Spectroscopy
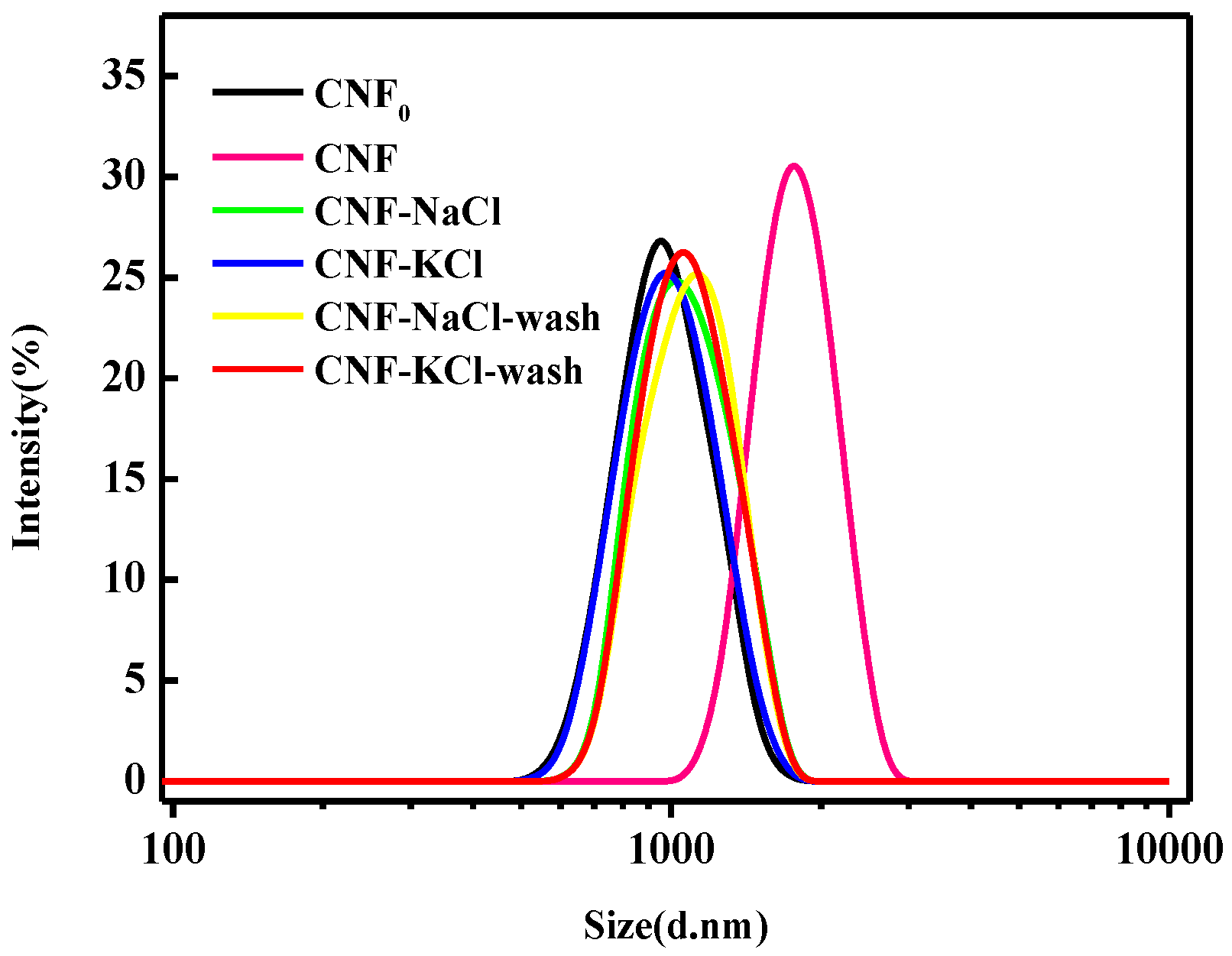
3.3. Particle Size Distribution
3.4. Sedimentation of Redispersed CNFs
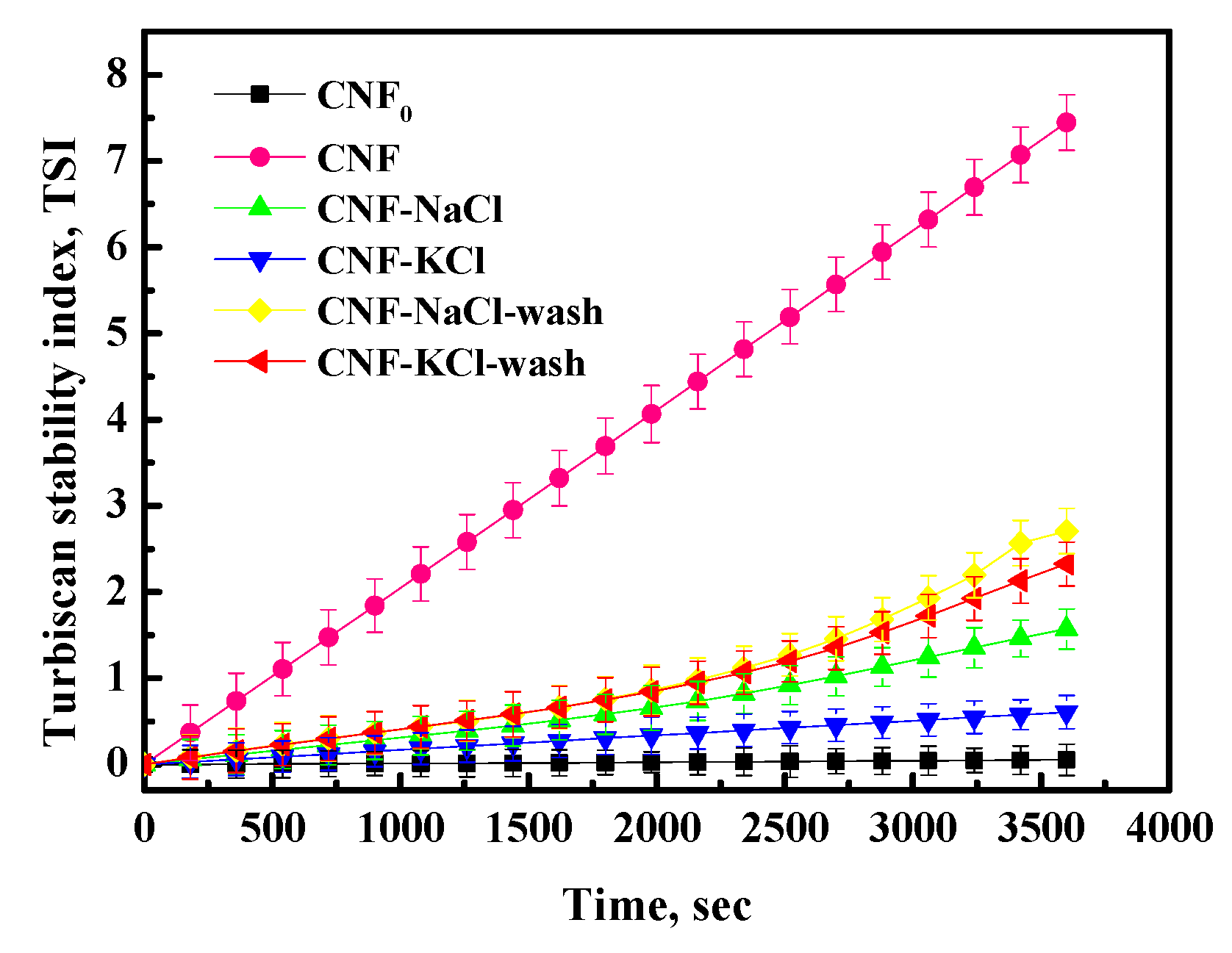
3.5. Dispersion Stability Analysis
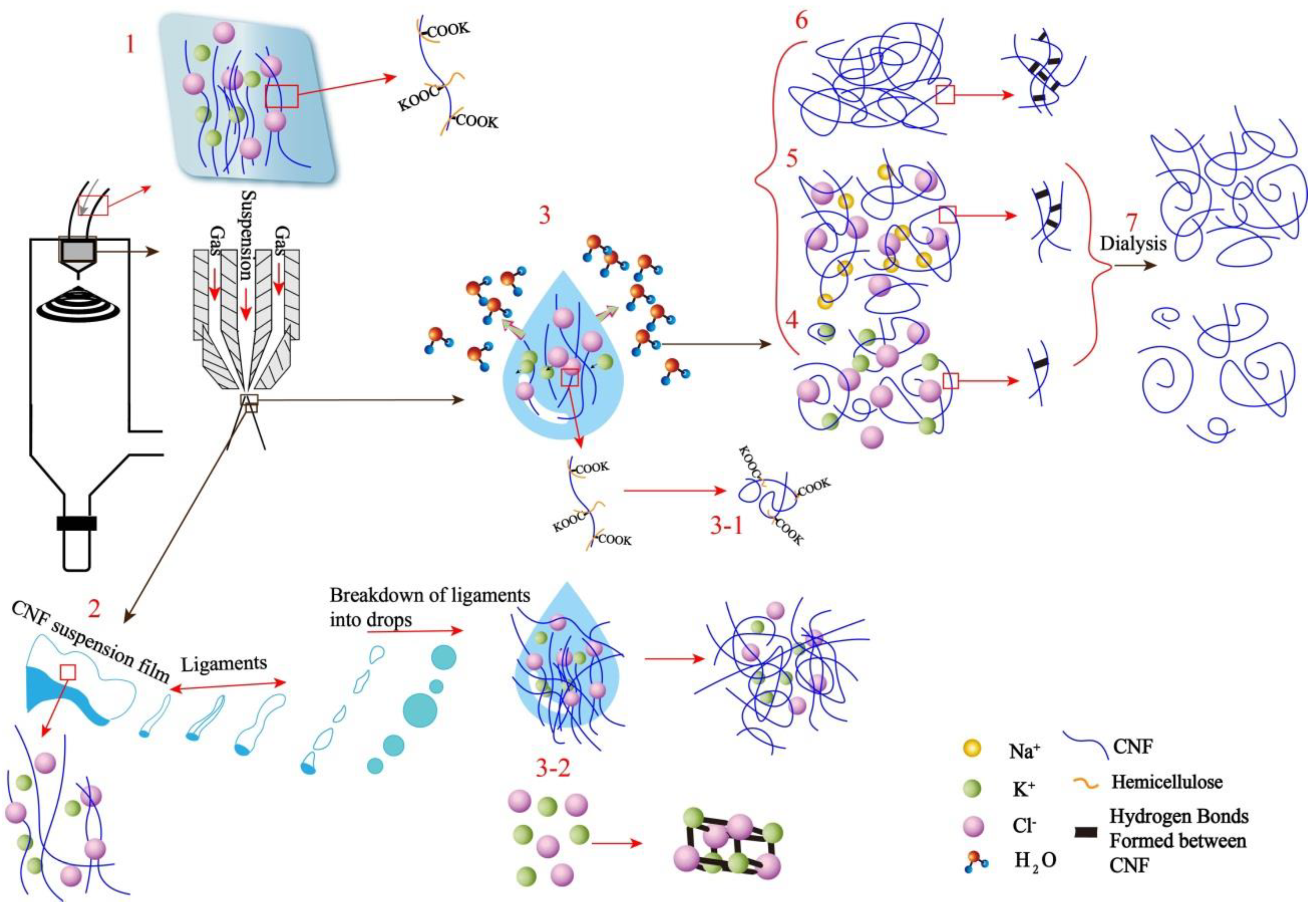
3.6. Proposed Mechanism
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Siqueira, G.; Bras, J.; Dufresne, A. Cellulosic Bionanocomposites: A Review of Preparation, Properties and Applications. Polymers 2010, 2, 728–765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klemm, D.; Kramer, F.; Moritz, S.; Lindström, T.; Ankerfors, M.; Gray, D.; Dorris, A. Nanocelluloses: A new family of nature-based materials. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2011, 50, 5438–5466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moon, R.; Martini, A.; Nairn, J.; Simonsen, J.; Youngblood, J. Cellulose nanomaterials review: Structure, properties and nanocomposites. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2011, 40, 3941–3994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hubbe, M.A.; Rojas, O.J.; Lucia, L.A.; Sain, M. Cellulosic nanocomposites. A review. BioResources 2008, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeronimidis, G. Wood, one of nature’s challenging composites. Symp. Soc. Exp. Biol 1980, 34, 169–182. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Peng, Y.; Gardner, D.J.; Han, Y. Drying cellulose nanofibrils: In search of a suitable method. Cellulose 2012, 19, 91–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bloch, J. UMaine to Build Nation’s Only Cellulose Nanofibrils Pilot Plant; Univesity of UMaine: Orono, ME, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Eyholzer, C.; Bordeanu, N.; Lopez-Suevos, F.; Rentsch, D.; Zimmermann, T.; Oksman, K. Preparation and characterization of water-redispersible nanofibrillated cellulose in powder form. Cellulose 2010, 17, 19–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pakowski, Z. Modern Methods of Drying Nanomaterials. Transp. Porous Media 2007, 66, 19–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quinn, J.J. The economics of spray drying. Ind. Eng. Chem. 1965, 57, 35–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hardy, W.L. COSTS, Process and Construction Spray drying costs. Ind. Eng. Chem. 1955, 47, 73A–74A. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Table of Contents. J. Prosthet. Dent. 2012, 107, A4–A6. [CrossRef]
- Nukiyama, S.; Tanasawa, Y. An Experiment on the Atomization of Liquid by Means of an Air Stream (The 2nd Report). Trans. Jpn. Soc. Mech. Eng. 1938, 4, 138–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hede, P.D.; Bach, P.; Jensen, A.D. Two-fluid spray atomisation and pneumatic nozzles for fluid bed coating/agglomeration purposes: A review. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2008, 63, 3821–3842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, Y.; Han, Y.; Gardner, D.J. Spray-drying cellulose nanofibrils: Effect of drying process parameters on particle morphology and size distribution. Wood Fiber Sci. 2012, 44, 448–461. [Google Scholar]
- Sinquefield, S.; Ciesielski, P.N.; Li, K.; Gardner, D.J.; Ozcan, S. Nanocellulose Dewatering and Drying: Current State and Future Perspectives. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2020, 8, 9601–9615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butchosa, N.; Zhou, Q. Water redispersible cellulose nanofibrils adsorbed with carboxymethyl cellulose. Cellulose 2014, 21, 4349–4358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, Y.; Gallegos, S.A.; Gardner, D.J.; Han, Y.; Cai, Z. Maleic anhydride polypropylene modified cellulose nanofibril polypropylene nanocomposites with enhanced impact strength. Polym. Compos. 2014, 37, 782–793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olszewska, A.; Eronen, P.; Johansson, L.-S.; Malho, J.-M.; Ankerfors, M.; Lindström, T.; Ruokolainen, J.; Laine, J.; Österberg, M. The behaviour of cationic NanoFibrillar Cellulose in aqueous media. Cellulose 2011, 18, 1213–1226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fall, A.B.; Lindström, S.B.; Sundman, O.; Ödberg, L.; Wågberg, L. Colloidal Stability of Aqueous Nanofibrillated Cellulose Dispersions. Langmuir 2011, 27, 11332–11338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, G.; He, M.; Yang, G.; Ji, X.; Lucia, L.A.; Chen, J. A feasible approach efficiently redisperse dried cellulose nanofibrils in water: Vacuum or freeze drying in the presence of sodium chloride. Cellulose 2020, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Missoum, K.; Bras, J.; Belgacem, M.N. Water Redispersible Dried Nanofibrillated Cellulose by Adding Sodium Chloride. Biomacromolecules 2012, 13, 4118–4125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, Y.; Gardner, D.J.; Han, Y.; Kiziltas, A.; Cai, Z.; Tshabalala, M.A. Influence of drying method on the material properties of nanocellulose I: Thermostability and crystallinity. Cellulose 2013, 20, 2379–2392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Ding, J.; Fu, Y.; Dong, Y. Fabrication and characterization of vapor grown carbon nanofiber/epoxy magnetic nanocomposites. Polym. Compos. 2016, 37, 1728–1734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, M.; Yang, G.; Chen, J.; Ji, X.; Wang, Q. Production and Characterization of Cellulose Nanofibrils from Different Chemical and Mechanical Pulps. J. Wood Chem. Technol. 2018, 38, 149–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Im, W.; Lee, S.; Rajabi-Abhari, A.; Youn, H.J.; Lee, H.L. Optimization of carboxymethylation reaction as a pretreatment for production of cellulose nanofibrils. Cellulose 2018, 25, 3873–3883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wågberg, L.; Decher, G.; Norgren, M.; Lindström, T.; Ankerfors, M.; Axnäs, K. The Build-Up of Polyelectrolyte Multilayers of Microfibrillated Cellulose and Cationic Polyelectrolytes. Langmuir 2008, 24, 784–795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brodin, F.W.; Theliander, H. A comparison of softwood and birch kraft pulp fibers as raw materials for production of TEMPO-oxidized pulp, MFC and superabsorbent foam. Cellulose 2013, 20, 2825–2838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Noulty, R.A.; Leaist, D.G. Activity coefficients and diffusion coefficients of dilute aqueous solutions of lithium, sodium, and potassium hydroxides. J. Solut. Chem. 1984, 13, 767–778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dunham, E.T.; Glynn, I.M. Adenosinetriphosphatase activity and the active movements of alkali metal ions. J. Physiol. 1961, 156, 274–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ermak, D.L.; McCammon, J.A. Brownian dynamics with hydrodynamic interactions. J. Chem. Phys. 1978, 69, 1352–1360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, X.; Zhang, F. Preparation of an ionic/nonionic polyurethane-silicone dispersion (PUSD) with a high solid content and low viscosity using complex soft segments. J. Coat. Technol. Res. 2018, 15, 1229–1237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Posch, H.A.; Narnhofer, H.; Thirring, W. Condensation phenomena in thermodynamically unstable systems. Phys. A Stat. Mech. Appl. 1993, 194, 482–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Velásquez-Cock, J.; Gañán, P.; Gómez, C.H.; Posada, P.; Castro, C.; Dufresne, A.; Zuluaga, R. Improved redispersibility of cellulose nanofibrils in water using maltodextrin as a green, easily removable and non-toxic additive. Food Hydrocoll. 2018, 79, 30–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xhanari, K.; Syverud, K.; Chinga-Carrasco, G.; Paso, K.; Stenius, P. Reduction of water wettability of nanofibrillated cellulose by adsorption of cationic surfactants. Cellulose 2011, 18, 257–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiśniewska, M. Influences of polyacrylic acid adsorption and temperature on the alumina suspension stability. Powder Technol. 2010, 198, 258–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Li, L.; Xiao, N.; Li, M.; Xie, X. Physical properties of oil-in-water nanoemulsions stabilized by OSA-modified starch for the encapsulation of lycopene. Coll. Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2018, 552, 59–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dombrowski, N.; Johns, W.R. The aerodynamic instability and disintegration of viscous liquid sheets. Chem. Eng. Sci. 1963, 18, 203–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thybo, P.; Pedersen, B.L.; Hovgaard, L.; Holm, R.; Müllertz, A. Characterization and Physical Stability of Spray Dried Solid Dispersions of Probucol and PVP-K30. Pharm. Dev. Technol. 2008, 13, 375–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peralta-Inga, Z.; Johnson, G.P.; Dowd, M.K.; Rendleman, J.A.; Stevens, E.D.; French, A.D. The crystal structure of the α-cellobiose·2·NaI2·H2O complex in the context of related structures and conformational analysis. Carbohydr. Res. 2002, 337, 851–861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| Samples | IO | IC | ICl | IK | INa | INa/IC | IK/IC |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CNF | 51.54 ± 0.21 | 48.47 ± 0.18 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| CNF-NaCl | 30.21 ± 0.28 | 48.61 ± 0.13 | 11.76 ± 0.01 | 0 | 9.46 ± 0.02 | 0.20 ± 0.01 | 0 |
| CNF-KCl | 26.52 ± 0.31 | 58.29 ± 0.11 | 6.72 ± 0.02 | 8.47 ± 0.03 | 0 | 0 | 0.15 ± 0.02 |
| CNF-NaCl-wash | 52.44 ± 0.21 | 47.57 ± 0.10 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| CNF-KCl-wash | 52.54 ± 0.30 | 47.46 ± 0.14 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| CNF-NaCl | CNF-KCl | CNF-NaCl-Wash | CNF-KCl-Wash | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| D (%) | 21.10 ± 3.27 | 8.06 ± 2.71 | 36.29 ± 3.67 | 31.18 ± 3.58 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yang, G.; Ma, G.; He, M.; Ji, X.; Li, W.; Youn, H.J.; Lee, H.L.; Chen, J. Comparison of Effects of Sodium Chloride and Potassium Chloride on Spray Drying and Redispersion of Cellulose Nanofibrils Suspension. Nanomaterials 2021, 11, 439. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano11020439
Yang G, Ma G, He M, Ji X, Li W, Youn HJ, Lee HL, Chen J. Comparison of Effects of Sodium Chloride and Potassium Chloride on Spray Drying and Redispersion of Cellulose Nanofibrils Suspension. Nanomaterials. 2021; 11(2):439. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano11020439
Chicago/Turabian StyleYang, Guihua, Guangrui Ma, Ming He, Xingxiang Ji, Weidong Li, Hye Jung Youn, Hak Lae Lee, and Jiachuan Chen. 2021. "Comparison of Effects of Sodium Chloride and Potassium Chloride on Spray Drying and Redispersion of Cellulose Nanofibrils Suspension" Nanomaterials 11, no. 2: 439. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano11020439
APA StyleYang, G., Ma, G., He, M., Ji, X., Li, W., Youn, H. J., Lee, H. L., & Chen, J. (2021). Comparison of Effects of Sodium Chloride and Potassium Chloride on Spray Drying and Redispersion of Cellulose Nanofibrils Suspension. Nanomaterials, 11(2), 439. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano11020439









