Hypericum perforatum L.-Mediated Green Synthesis of Silver Nanoparticles Exhibiting Antioxidant and Anticancer Activities
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Preparation of Hypericum perforatum L. (St John’s Wort) Extract
2.3. Biosynthesis of Silver Nanoparticles
2.4. 1,1-Diphenyl-2-picryl Hydrazyl (DPPH) Assay
2.5. 2,2′-Azino-bis-(3-ethylbenzothiazoline-6-sulfonic Acid Radical Cation) (ABTS) Assay
2.6. Super Oxide Anion Radical (SO) Assay
2.7. Cell Culture and Estimation of In Vitro Cytotoxicity of AgNPs
2.8. Characterization
3. Results and Discussion
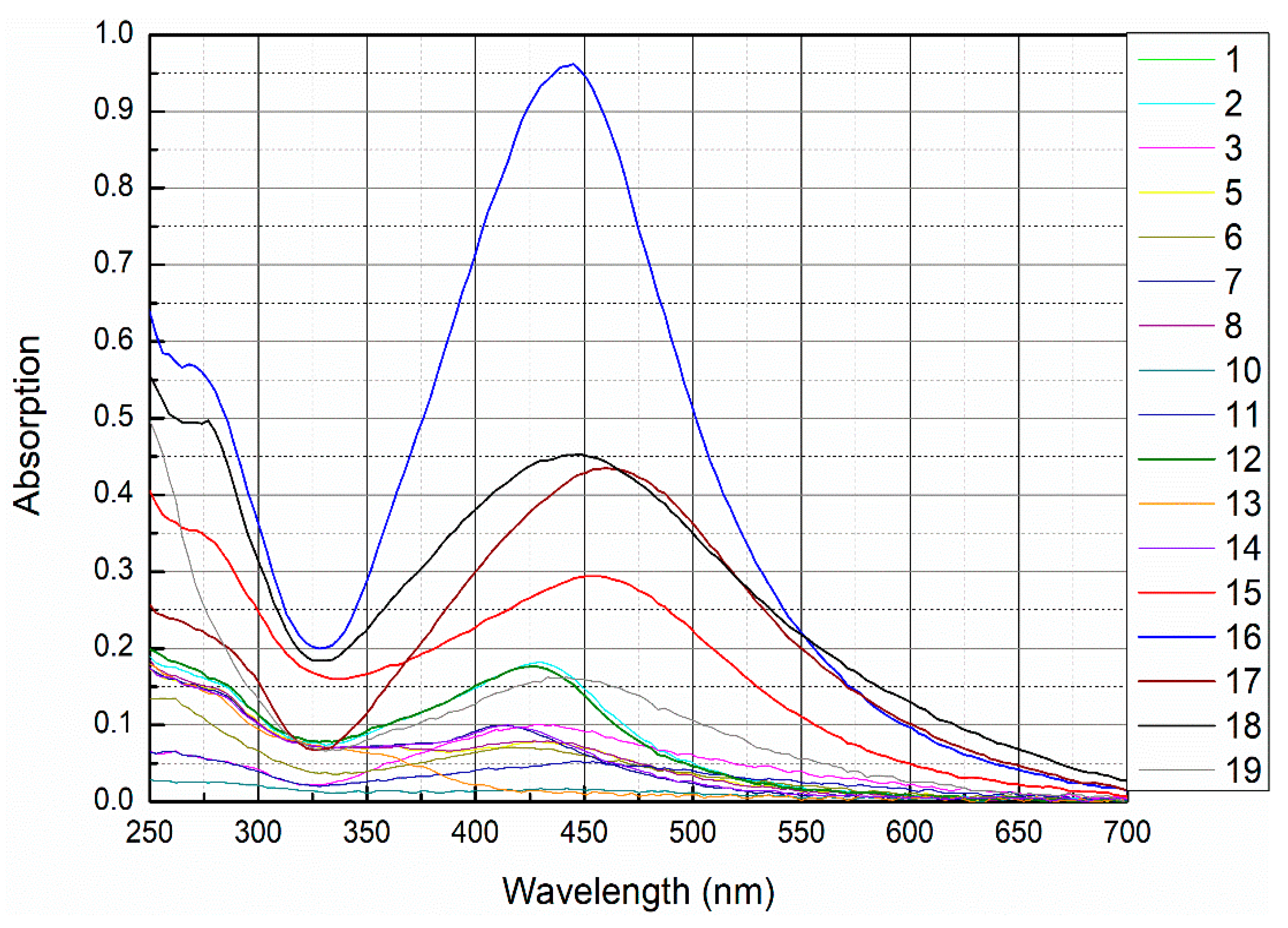
3.1. UV-VIS Absorption Studies
Measurement of Concentration through Absorption Peak in UV-VIS Spectrum
3.2. Dynamic Light Scattering (DLS)
3.3. Fourier transformed infrared (FTIR) Spectroscopy
3.4. Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM)
3.5. Transmission Electron Microscopy (TEM)
3.6. High Resolution Transmission Electron Microscopy and Nano-Diffraction Patterns
3.7. X-ray Diffraction (XRD)
3.8. Possible Mechanism of Biosynthesis of Silver Nanoparticles by Plant
3.9. Determination of Antioxidant Activity
3.9.1. 1-1,1-Diphenyl-2-picryl Hydrazyl Assay
3.9.2. 2-2,2′-Azino-bis-(3-ethylbenzothiazoline-6-sulfonic Acid Radical Cation Scavenging Assay (ABTS)
3.9.3. Super Oxide Anion Radical Scavenging Assay (SO Assay)
3.10. Determination of Time- and Dose-Dependent Cytotoxicity of Biosynthesized AgNPs
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Treguer-Delapierre, M.; Majimel, J.; Mornet, S.; Duguet, E.; Ravaine, S. Synthesis of non-spherical gold nanoparticles. Gold Bull. 2008, 41, 195–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lopez-Sanchez, J.A.; Dimitratos, N.; Hammond, C.; Brett, G.L.; Kesavan, L.; White, S.; Miedziak, P.; Tiruvalam, R.; Jenkins, R.L.; Carley, A.F.; et al. Facile removal of stabilizer-ligands from supported gold nanoparticles. Nat. Chem. 2011, 3, 551–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, T.-H.; Thiagarajan, S.; Chen, S.-M. Green synthesis of silver nanoparticles using ionic liquid and application for the detection of dissolved Oxygen. Electroanalysis 2010, 22, 680–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.-C.; Chou, K.-S. A simple and effective route for the synthesis of nano-silver colloidal dispersions. J. Chin. Inst. Chem. Eng. 2008, 39, 673–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Philip, J.M.; Jeyanthi Rebecca, K.M.L.; Venkatakrishnan, C.J.; Chandran, C.R. Green synthesized silver nanoparticles as an antimicrobial agent in dentistry. Drug Invent. Today 2018, 10, 950–953. [Google Scholar]
- Xie, J.; Lee, J.Y.; Wang, D.I.; Ting, Y.P. Silver nanoplates: From biological to biomimetic synthesis. ACS Nano 2007, 1, 429–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hemath Naveen, K.; Kumar, G.; Karthik, L.; Bhaskara Rao, K. Extracellular biosynthesis of silver nanoparticles using the filamentous fungus Penicillium sp. Arch. Appl. Sci. Res. 2010, 2, 161–167. [Google Scholar]
- Trevors, J. Silver resistance and accumulation in bacteria. Enzym. Microb. Technol. 1987, 9, 331–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pugazhenthiran, N.; Anandan, S.; Kathiravan, G.; Prakash, N.K.U.; Crawford, S.; Ashokkumar, M. Microbial synthesis of silver nanoparticles by Bacillus sp. J. Nanopart. Res. 2009, 11, 1811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beveridge, T.; Hughes, M.; Lee, H.; Leung, K.; Poole, R.; Savvaidis, I.; Silver, S.; Trevors, J. Metal-microbe interactions: Contemporary approaches. In Advances in Microbial Physiology; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1996; Volume 38, pp. 177–243. [Google Scholar]
- Mukherjee, P.; Ahmad, A.; Mandal, D.; Senapati, S.; Sainkar, S.R.; Khan, M.I.; Ramani, R.; Parischa, R.; Ajayakumar, P.; Alam, M. Bioreduction of AuCl4− ions by the fungus, Verticillium sp. and surface trapping of the gold nanoparticles formed. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2001, 40, 3585–3588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukherjee, P.; Ahmad, A.; Mandal, D.; Senapati, S.; Sainkar, S.R.; Khan, M.I.; Parishcha, R.; Ajaykumar, P.; Alam, M.; Kumar, R. Fungus-mediated synthesis of silver nanoparticles and their immobilization in the mycelial matrix: A novel biological approach to nanoparticle synthesis. Nano Lett. 2001, 1, 515–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durán, N.; Marcato, P.D.; Alves, O.L.; De Souza, G.I.; Esposito, E. Mechanistic aspects of biosynthesis of silver nanoparticles by several Fusarium oxysporum strains. J. Nanobiotechnol. 2005, 3, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Shankar, S.S.; Rai, A.; Ahmad, A.; Sastry, M. Rapid synthesis of Au, Ag, and bimetallic Au core—Ag shell nanoparticles using Neem (Azadirachta indica) leaf broth. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2004, 275, 496–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhainsa, K.C.; D’souza, S. Extracellular biosynthesis of silver nanoparticles using the fungus Aspergillus fumigatus. Colloids Surf. B. 2006, 47, 160–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lengke, M.F.; Fleet, M.E.; Southam, G. Biosynthesis of silver nanoparticles by filamentous cyanobacteria from a silver(I) nitrate complex. Langmuir 2007, 23, 2694–2699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vigneshwaran, N.; Kathe, A.A.; Varadarajan, P.V.; Nachane, R.P.; Balasubramanya, R.H. Biomimetics of silver nanoparticles by white rot fungus, Phaenerochaete chrysosporium. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2006, 53, 55–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahverdi, A.R.; Minaeian, S.; Shahverdi, H.R.; Jamalifar, H.; Nohi, A.-A. Rapid synthesis of silver nanoparticles using culture supernatants of Enterobacteria: A novel biological approach. Process Biochem. 2007, 42, 919–923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klaus, T.; Joerger, R.; Olsson, E.; Granqvist, C.G. Silver-based crystalline nanoparticles, microbially fabricated. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1999, 96, 13611–13614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jain, D.; Daima, H.K.; Kachhwaha, S.; Kothari, S. Synthesis of plant-mediated silver nanoparticles using papaya fruit extract and evaluation of their anti microbial activities. Dig. J. Nanomater. Biostruct. 2009, 4, 557–563. [Google Scholar]
- Mallikarjuna, K.; Narasimha, G.; Dillip, G.; Praveen, B.; Shreedhar, B.; Lakshmi, C.S.; Reddy, B.; Raju, B.D.P. Green synthesis of silver nanoparticles using Ocimum leaf extract and their characterization. Dig. J. Nanomater. Biostruct. 2011, 6, 181–186. [Google Scholar]
- Li, S.; Shen, Y.; Xie, A.; Yu, X.; Qiu, L.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, Q. Green synthesis of silver nanoparticles using Capsicum annuum L. extract. Green Chem. 2007, 9, 852–858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mallikarjuna, K.; Sushma, N.J.; Narasimha, G.; Manoj, L.; Raju, B.D.P. Phytochemical fabrication and characterization of silver nanoparticles by using Pepper leaf broth. Arab. J. Chem. 2014, 7, 1099–1103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ahmed, S.; Ahmad, M.; Swami, B.L.; Ikram, S. Green synthesis of silver nanoparticles using Azadirachta indica aqueous leaf extract. J. Radiat. Res. Appl. 2016, 9, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Veerasamy, R.; Xin, T.Z.; Gunasagaran, S.; Xiang, T.F.W.; Yang, E.F.C.; Jeyakumar, N.; Dhanaraj, S.A. Biosynthesis of silver nanoparticles using mangosteen leaf extract and evaluation of their antimicrobial activities. J. Saudi Chem. Soc. 2011, 15, 113–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Borah, D.; Kumar Yadav, A. A novel ‘green’synthesis of antimicrobial silver nanoparticles (AgNPs) by using Garcinia morella (Gaertn) desr. fruit extract. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. Asia 2015, 5, 25–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehmood, A.; Murtaza, G.; Bhatti, T.M.; Kausar, R. Phyto-mediated synthesis of silver nanoparticles from Melia azedarach L. leaf extract: Characterization and antibacterial activity. Arab. J. Chem. 2017, 10, S3048–S3053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Singh, S.; Vidyasagar, G. Green synthesis, characterization and antimicrobial activity of silver nanoparticles by using Sterculia foetida L. young leaves aqueous extract. Int. J. Green Chem. Bioprocess 2014, 4, 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Vijistella Bai, G. Green synthesis of silver nanostructures against human cancer cell lines and certain pathogens. Int. J. Pharm. Chem. Biol. Sci 2014, 4, 101–111. [Google Scholar]
- Kalidasan, M.; Yogamoorthi, A. Biosynthesis of silver nanoparticles using Achyranthus aspera and its characterization. Int. J. Nanomater. Biostruct. 2014, 4, 5–11. [Google Scholar]
- Jayapriya, E.; Lalitha, P. Synthesis of silver nanoparticles using leaf aqueous extract of Ocimum basilicum (L.). Int. J. Chemtech Res. 2013, 5, 2985–2992. [Google Scholar]
- Ahmad, N.; Sharma, S.; Rai, R. Rapid green synthesis of silver and gold nanoparticles using peels of Punica granatum. Adv. Mater. Lett 2012, 3, 376–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ponarulselvam, S.; Panneerselvam, C.; Murugan, K.; Aarthi, N.; Kalimuthu, K.; Thangamani, S. Synthesis of silver nanoparticles using leaves of Catharanthus roseus Linn. G. Don and their antiplasmodial activities. Asian Pac. J. Trop. Biomed. 2012, 2, 574–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jyoti, K.; Baunthiyal, M.; Singh, A. Characterization of silver nanoparticles synthesized using Urtica dioica Linn. leaves and their synergistic effects with antibiotics. J. Radiat. Res. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 217–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mohapatra, B.; Kuriakose, S.; Mohapatra, S. Rapid green synthesis of silver nanoparticles and nanorods using Piper nigrum extract. J. Alloys Compd. 2015, 637, 119–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, I.M.; Park, I.; Seung-Hyun, K.; Thiruvengadam, M.; Rajakumar, G. Plant-mediated synthesis of silver nanoparticles: Their characteristic properties and therapeutic applications. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2016, 11, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mishra, M.; Chauhan, P. Nanosilver and its medical implications. J. Nanomed. Res. 2015, 2, 1–10. [Google Scholar]
- Aswathy Aromal, S.; Philip, D. Green synthesis of gold nanoparticles using Trigonella foenum-graecum and its size-dependent catalytic activity. Spectrochim. Acta A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2012, 97, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chandran, S.P.; Chaudhary, M.; Pasricha, R.; Ahmad, A.; Sastry, M. Synthesis of gold nanotriangles and silver nanoparticles using Aloe vera plant extract. Biotechnol. Prog. 2006, 22, 577–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubey, S.P.; Lahtinen, M.; Sarkka, H.; Sillanpaa, M. Bioprospective of Sorbus aucuparia leaf extract in development of silver and gold nanocolloids. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2010, 80, 26–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shameli, K.; Bin Ahmad, M.; Jaffar Al-Mulla, E.A.; Ibrahim, N.A.; Shabanzadeh, P.; Rustaiyan, A.; Abdollahi, Y.; Bagheri, S.; Abdolmohammadi, S.; Usman, M.S.; et al. Green biosynthesis of silver nanoparticles using Callicarpa maingayi stem bark extraction. Molecules 2012, 17, 8506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gurunathan, S.; Park, J.H.; Han, J.W.; Kim, J.H. Comparative assessment of the apoptotic potential of silver nanoparticles synthesized by Bacillus tequilensis and Calocybe indica in MDA-MB-231 human breast cancer cells: Targeting p53 for anticancer therapy. Int. J. Nanomed. 2015, 10, 4203–4222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, W.R.; Xie, X.B.; Shi, Q.S.; Zeng, H.Y.; Ou-Yang, Y.S.; Chen, Y.B. Antibacterial activity and mechanism of silver nanoparticles on Escherichia coli. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2010, 85, 1115–1122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chernousova, S.; Epple, M. Silver as antibacterial agent: Ion, nanoparticle, and metal. Angew. Chem. Int. 2013, 52, 1636–1653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, D.; Yang, J.; Zhao, Y. Antibacterial materials of silver nanoparticles application in medical appliances and appliances for daily use. Chin. Med. Equip. J. 2004, 4, 26–32. [Google Scholar]
- Hansen, S.F.; Michelson, E.S.; Kamper, A.; Borling, P.; Stuer-Lauridsen, F.; Baun, A. Categorization framework to aid exposure assessment of nanomaterials in consumer products. Ecotoxicology 2008, 17, 438–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, B.; Wang, J.; Xu, S.; Afrin, T.; Xu, W.; Sun, L.; Wang, X. Application of anisotropic silver nanoparticles: Multifunctionalization of wool fabric. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2011, 356, 513–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Atiyeh, B.S.; Costagliola, M.; Hayek, S.N.; Dibo, S.A. Effect of silver on burn wound infection control and healing: Review of the literature. Burns 2007, 33, 139–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, D.; Sun, W.; Qian, W.; Ye, Y.; Ma, X. The synthesis of chitosan-based silver nanoparticles and their antibacterial activity. Carbohydr. Res. 2009, 344, 2375–2382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoon, K.Y.; Hoon Byeon, J.; Park, J.H.; Hwang, J. Susceptibility constants of Escherichia coli and Bacillus subtilis to silver and copper nanoparticles. Sci. Total. Environ. 2007, 373, 572–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lanje, A.S.; Sharma, S.J.; Pode, R.B. Synthesis of silver nanoparticles: A safer alternative to conventional antimicrobial and antibacterial agents. J. Chem. Pharm. Res. 2010, 2, 478–483. [Google Scholar]
- Velmurugan, P.; Cho, M.; Lim, S.-S.; Seo, S.-K.; Myung, H.; Bang, K.-S.; Sivakumar, S.; Cho, K.-M.; Oh, B.-T. Phytosynthesis of silver nanoparticles by Prunus yedoensis leaf extract and their antimicrobial activity. Mater. Lett. 2015, 138, 272–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tripathi, R.; Saxena, A.; Gupta, N.; Kapoor, H.; Singh, R. High antibacterial activity of silver nanoballs against E. coli MTCC 1302, S. typhimurium MTCC 1254, B. subtilis MTCC 1133 and P. aeruginosa MTCC 2295. Dig. J. Nanomater. Bios. 2010, 5, 323–330. [Google Scholar]
- Lara, H.H.; Ayala-Nunez, N.V.; Ixtepan-Turrent, L.; Rodriguez-Padilla, C. Mode of antiviral action of silver nanoparticles against HIV-1. J. Nanobiotechnol. 2010, 8, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, L.; Singh, A.K.; Vig, K.; Pillai, S.R.; Singh, S.R. Silver nanoparticles inhibit replication of respiratory syncytial virus. J. Biomed. Nanotechnol. 2008, 4, 149–158. [Google Scholar]
- Speshock, J.L.; Murdock, R.C.; Braydich-Stolle, L.K.; Schrand, A.M.; Hussain, S.M. Interaction of silver nanoparticles with Tacaribe virus. J. Nanobiotechnol. 2010, 8, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rajan, K.; Roppolo, I.; Chiappone, A.; Bocchini, S.; Perrone, D.; Chiolerio, A. Silver nanoparticle ink technology: State of the art. Nanotechnol. Sci. Appl. 2016, 9, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ko, S.-J.; Choi, H.; Lee, W.; Kim, T.; Lee, B.R.; Jung, J.-W.; Jeong, J.-R.; Song, M.H.; Lee, J.C.; Woo, H.Y. Highly efficient plasmonic organic optoelectronic devices based on a conducting polymer electrode incorporated with silver nanoparticles. Energy Environ. Sci. 2013, 6, 1949–1955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gensler, R.; Gröppel, P.; Muhrer, V.; Müller, N. Application of nanoparticles in polymers for electronics and electrical engineering. Part. Part. Syst. Charact. 2002, 19, 293–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sankar, R.; Karthik, A.; Prabu, A.; Karthik, S.; Shivashangari, K.S.; Ravikumar, V. Origanum vulgare mediated biosynthesis of silver nanoparticles for its antibacterial and anticancer activity. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2013, 108, 80–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balakumaran, M.; Ramachandran, R.; Kalaichelvan, P. Exploitation of endophytic fungus, Guignardia mangiferae for extracellular synthesis of silver nanoparticles and their in vitro biological activities. Microbiol. Res. 2015, 178, 9–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, V.K.; Yngard, R.A.; Lin, Y. Silver nanoparticles: Green synthesis and their antimicrobial activities. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2009, 145, 83–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Harrison, N.; Richards-Kortum, R.; Sokolov, K. Plasmonic nanosensors for imaging intracellular biomarkers in live cells. Nano Lett. 2007, 7, 1338–1343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schrand, A.M.; Braydich-Stolle, L.K.; Schlager, J.J.; Dai, L.; Hussain, S.M. Can silver nanoparticles be useful as potential biological labels? Nanotechnology 2008, 19, 235104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davidović, S.; Lazić, V.; Vukoje, I.; Papan, J.; Anhrenkiel, S.P.; Dimitrijević, S.; Nedeljković, J.M. Dextran coated silver nanoparticles—Chemical sensor for selective cysteine detection. Colloids Surf. B 2017, 160, 184–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Z.J.; Liu, C.Y.; Sun, L.W. Catalytic properties of silver nanoparticles supported on silica spheres. J. Phys. Chem. B 2005, 109, 1730–1735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, K.; Sarkar, C.; Ghosh, C. Photocatalytic activity of biogenic silver nanoparticles synthesized using yeast (Saccharomyces cerevisiae) extract. Appl. Nanosci. 2015, 5, 953–959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benyettou, F.; Rezgui, R.; Ravaux, F.; Jaber, T.; Blumer, K.; Jouiad, M.; Motte, L.; Olsen, J.C.; Platas-Iglesias, C.; Magzoub, M.; et al. Synthesis of silver nanoparticles for the dual delivery of doxorubicin and alendronate to cancer cells. J. Mater. Chem. B 2015, 3, 7237–7245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brown, P.K.; Qureshi, A.T.; Moll, A.N.; Hayes, D.J.; Monroe, W.T. Silver nanoscale antisense drug delivery system for photoactivated gene silencing. ACS Nano 2013, 7, 2948–2959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lara-González, J.H.; Gomez-Flores, R.; Tamez-Guerra, P.; Monreal-Cuevas, E.; Tamez-Guerra, R.; Rodríguez-Padilla, C. In vivo antitumor activity of metal silver and silver nanoparticles in the L5178Y-R murine lymphoma model. Br. J. Med. Med. Res. 2013, 3, 1308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jeyaraj, M.; Sathishkumar, G.; Sivanandhan, G.; MubarakAli, D.; Rajesh, M.; Arun, R.; Kapildev, G.; Manickavasagam, M.; Thajuddin, N.; Premkumar, K.; et al. Biogenic silver nanoparticles for cancer treatment: An experimental report. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2013, 106, 86–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thombre, R.; Mehta, S.; Mohite, J.; Jaisinghani, P. Synthesis of silver nanoparticles and its cytotoxic effect against THP-1 cancer cell line. Int. J. Pharm. Bio. Sci. 2013, 4, 184–192. [Google Scholar]
- He, Y.; Du, Z.; Ma, S.; Cheng, S.; Jiang, S.; Liu, Y.; Li, D.; Huang, H.; Zhang, K.; Zheng, X. Biosynthesis, antibacterial activity and anticancer effects against prostate cancer (PC-3) cells of silver nanoparticles using Dimocarpus longan lour. peel extract. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2016, 11, 300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hosni, K.; Msaâda, K.; Taârit, M.B.; Ouchikh, O.; Kallel, M.; Marzouk, B. Essential oil composition of Hypericum perfoliatum L. and Hypericum tomentosum L. growing wild in Tunisia. Ind. Crops Prod. 2008, 27, 308–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ravisankar, N.; Joseph, J.; Radhakrishana, M.; Rajasekar, T. In vitro cytotoxicity of methanol extracts of Hypericum wightianum and Hypericum hookerianuim against 3T3L1 cell lines. Bangladesh J. Pharmacol. 2016, 11, 328–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Azizi, M. Change in content and chemical composition of Hypericum perforatum L. oil at three harvest time. J. Herbs Spices Med. Plants. 2008, 13, 79–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saddiqe, Z.; Naeem, I.; Maimoona, A. A review of the antibacterial activity of Hypericum perforatum L. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2010, 131, 511–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davidson, J.R.; St. Connor, K.M. John’s wort in generalized anxiety disorder: Three case reports. J. Clin. Psychopharmacol. 2001, 21, 635–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gurib-Fakim, A. Medicinal plants: Traditions of yesterday and drugs of tomorrow. Mol. Asp. Med. 2006, 27, 1–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shafaghat, A. Antioxidant, antimicrobial activities and fatty acid components of flower, leaf, stem and seed of Hypericum scabrum. Nat. Prod. Commun. 2011, 6, 1739–1742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Upton, R.; Upton, R.; Pharmacopoeia, A.H.; Cott, J.; Williamson, E.; St. Graff, A. John’s Wort: Hypericum Perforatum: Quality Control, Analytical and Therapeutic Monograph; American Herbal Pharmacopoeia: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Chopra, R.N.; Nayar, S.L. Glossary of Indian Medicinal Plants; Council of Scientific And Industrial Research: New Delhi, India, 1956. [Google Scholar]
- Bukhari, I.A.; Dar, A.; Khan, R.A. Antinociceptive activity of methanolic extracts of St. John’s Wort (Hypericum perforatum) preparation. Pak. J. Pharm. Sci. 2004, 17, 13–19. [Google Scholar]
- Vattikuti, U.; Ciddi, V. An Overview on Hypericum Perforatum Linn. 2005. Available online: http://nopr.niscair.res.in/handle/123456789/8123 (accessed on 13 February 2021).
- Lavie, G.; Mazur, Y.; Lavie, D.; Prince, A.; Pascual, D.; Liebes, L.; Levin, B.; Meruelo, D. Hypericin as an inactivator of infectious viruses in blood components. Transfusion 1995, 35, 392–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopez-Bazzocchi, I.; Hudson, J.B.; Towers, G.H. Antiviral activity of the photoactive plant pigment hypericin. Photochem. Photobiol. 1991, 54, 95–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hudson, J.B.; Lopez-Bazzocchi, I.; Towers, G.H. Antiviral activities of hypericin. Antivir. Res. 1991, 15, 101–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lenard, J.; Rabson, A.; Vanderoef, R. Photodynamic inactivation of infectivity of human immunodeficiency virus and other enveloped viruses using hypericin and rose bengal: Inhibition of fusion and syncytia formation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1993, 90, 158–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Logeswari, P.; Silambarasan, S.; Abraham, J. Ecofriendly synthesis of silver nanoparticles from commercially available plant powders and their antibacterial properties. Sci. Iran. 2013, 20, 1049–1054. [Google Scholar]
- Bose, D.; Chatterjee, S. Biogenic synthesis of silver nanoparticles using guava (Psidium guajava) leaf extract and its antibacterial activity against Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Appl. Nanosci. 2016, 6, 895–901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sastry, M.; Patil, V.; Sainkar, S. Electrostatically controlled diffusion of carboxylic acid derivatized silver colloidal particles in thermally evaporated fatty amine films. J. Phys. Chem. B 1998, 102, 1404–1410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mulvaney, P. Surface plasmon spectroscopy of nanosized metal particles. Langmuir 1996, 12, 788–800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basavaraja, S.; Balaji, S.; Lagashetty, A.; Rajasab, A.; Venkataraman, A. Extracellular biosynthesis of silver nanoparticles using the fungus Fusarium semitectum. Mater. Res. Bull. 2008, 43, 1164–1170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paramelle, D.; Sadovoy, A.; Gorelik, S.; Free, P.; Hobley, J.; Fernig, D.G. A rapid method to estimate the concentration of citrate capped silver nanoparticles from UV-visible light spectra. Analyst 2014, 139, 4855–4861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, D.B.; Carter, C.B.; Veyssiere, P. Transmission Electron Microscopy: A Textbook for Materials Science. MRS Bulletin-Materials Research Society: Warrendale, PA, USA, 1974. [Google Scholar]
- Prokofiev, E.A.; Burow, J.A.; Payton, E.J.; Zarnetta, R.; Frenzel, J.; Gunderov, D.V.; Valiev, R.Z.; Eggeler, G. Suppression of Ni4Ti3 Precipitation by grain size refinement in Ni-Rich NiTi shape memory alloys. Adv. Eng. Mater. 2010, 12, 747–753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bendersky, L.A.; Gayle, F.W. Gayle, Electron diffraction using Transmission electron microscopy. J. Res. Natl. Inst. Stand. Technol. 2001, 106, 997–1012. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, Z.; Ngan, A. TEM study of electron beam-induced crystallization of amorphous GeSi films. Philos. Mag. Lett. 2004, 84, 719–728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mogilevsky, P.; Hay, R.S.; Boakye, E.E.; Keller, K.A. Evolution of Texture in Rhabdophane-derived Monazite coatings. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 2003, 86, 1767–1772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Egerton, R.F. Physical Principles of Electron Microscopy; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2005; Volume 56. [Google Scholar]
- Filippo, E.; Serra, A.; Buccolieri, A.; Manno, D. Green synthesis of silver nanoparticles with sucrose and maltose: Morphological and structural characterization. J. Non-Cryst. Solids 2010, 356, 344–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varshney, R.; Bhadauria, S.; Gaur, M. Biogenic synthesis of silver nanocubes and nanorods using sundried Stevia rebaudiana leaves. Adv. Mat. Lett 2010, 1, 232–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wani, I.A.; Ganguly, A.; Ahmed, J.; Ahmad, T. Silver nanoparticles: Ultrasonic wave assisted synthesis, optical characterization and surface area studies. Mater. Lett. 2011, 65, 520–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kenneth, O. Elementary Analysis; Courier Dover Publications: New York, NY, USA, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Patocka, J. The chemistry, pharmacology, and toxicology of the biologically active constituents of the herb Hypericum perforatum L. J. Appl. Biomed. 2003, 1, 61–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nahrstedt, A.; Butterweck, V. Biologically active and other chemical constituents of the herb of Hypericum perforatum L. Pharmacopsychiatry 1997, 30 (Suppl. S2), 129–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borodina, V.; Mirgorod, Y.A. Kinetics and mechanism of the interaction between HAuCl 4 and rutin. Kinet. Catal. 2014, 55, 683–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makarov, V.; Love, A.; Sinitsyna, O.; Makarova, S.; Yaminsky, I.; Taliansky, M.; Kalinina, N. “Green” nanotechnologies: Synthesis of metal nanoparticles using plants. Acta Nat. (англоязычная версия) 2014, 6, 35–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jain, S.; Mehata, M.S. Medicinal plant leaf extract and pure flavonoid mediated green synthesis of silver nanoparticles and their enhanced antibacterial property. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 15867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cherrak, S.A.; Mokhtari-Soulimane, N.; Berroukeche, F.; Bensenane, B.; Cherbonnel, A.; Merzouk, H.; Elhabiri, M. In vitro antioxidant versus metal ion chelating properties of flavonoids: A structure-activity investigation. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0165575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, T.V.R.; Murthy, J.; Rao, M.N.; Bhargava, Y. Evaluation of silver nanoparticles synthetic potential of Couroupita guianensis Aubl., flower buds extract and their synergistic antibacterial activity. 3 Biotech 2016, 6, 92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mirgorod, Y.A.; Borodina, V.; Borsch, N. Investigation of interaction between silver ions and rutin in water by physical methods. Biophysics 2013, 58, 743–747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Zhan, G.; Zheng, B.; Sun, D.; Lu, F.; Lin, Y.; Chen, H.; Zheng, Z.; Zheng, Y.; Li, Q. Biogenic silver nanoparticles by Cacumen platycladi extract: Synthesis, formation mechanism, and antibacterial activity. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2011, 50, 9095–9106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalaiselvi, M.; Subbaiya, R.; Selvam, M. Synthesis and characterization of silver nanoparticles from leaf extract of Parthenium hysterophorus and its anti-bacterial and antioxidant activity. Int. J. Curr. Microbiol. Appl. Sci. 2013, 2, 220–227. [Google Scholar]
- Moteriya, P.; Chanda, S. Biosynthesis of silver nanoparticles formation from Caesalpinia pulcherrima stem metabolites and their broad spectrum biological activities. J. Genet. Eng. Biotechnol. 2018, 16, 105–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seralathan, J.; Stevenson, P.; Subramaniam, S.; Raghavan, R.; Pemaiah, B.; Sivasubramanian, A.; Veerappan, A. Spectroscopy investigation on chemo-catalytic, free radical scavenging and bactericidal properties of biogenic silver nanoparticles synthesized using Salicornia brachiata aqueous extract. Spectrochim. Acta A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2014, 118, 349–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moteriya, P.; Chanda, S. Synthesis and characterization of silver nanoparticles using Caesalpinia pulcherrima flower extract and assessment of their in vitro antimicrobial, antioxidant, cytotoxic, and genotoxic activities. Artif. Cells Nanomed. Biotechnol. 2017, 45, 1556–1567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ramachandran, L.; Nair, C.K.K. Therapeutic potentials of silver nanoparticle complex of α-lipoic acid. Nanomater. Nanotechnol. 2011, 1, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chanda, S.; Rakholiya, K.; Dholakia, K.; Baravalia, Y. Antimicrobial, antioxidant, and synergistic properties of two nutraceutical plants: Terminalia catappa L. and Colocasia esculenta L. Turk. J. Biol. 2013, 37, 81–91. [Google Scholar]
- Mittal, A.K.; Bhaumik, J.; Kumar, S.; Banerjee, U.C. Biosynthesis of silver nanoparticles: Elucidation of prospective mechanism and therapeutic potential. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2014, 415, 39–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ajayi, E.; Afolayan, A. Green synthesis, characterization and biological activities of silver nanoparticles from alkalinized Cymbopogon citratus Stapf. ANSN 2017, 8, 015017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sudha, A.; Jeyakanthan, J.; Srinivasan, P. Green synthesis of silver nanoparticles using Lippia nodiflora aerial extract and evaluation of their antioxidant, antibacterial and cytotoxic effects. Resour. Effic. Technol. 2017, 3, 506–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keshari, A.K.; Srivastava, R.; Singh, P.; Yadav, V.B.; Nath, G. Antioxidant and antibacterial activity of silver nanoparticles synthesized by Cestrum nocturnum. J. Ayurveda Integr. Med. 2020, 11, 37–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inbathamizh, L.; Ponnu, T.M.; Mary, E.J. In vitro evaluation of antioxidant and anticancer potential of Morinda pubescens synthesized silver nanoparticles. J. Pharm. Res. 2013, 6, 32–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guntur, S.R.; Kumar, N.S.; Hegde, M.M.; Dirisala, V.R. In vitro studies of the antimicrobial and free-radical scavenging potentials of silver nanoparticles biosynthesized from the extract of Desmostachya bipinnata. Anal. Chem. Insights 2018, 13, 1177390118782877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mata, R.; Nakkala, J.R.; Sadras, S.R. Biogenic silver nanoparticles from Abutilon indicum: Their antioxidant, antibacterial and cytotoxic effects in vitro. Colloids Surf. B 2015, 128, 276–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mata, R.; Reddy Nakkala, J.; Rani Sadras, S. Catalytic and biological activities of green silver nanoparticles synthesized from Plumeria alba (frangipani) flower extract. Mater. Sci. Eng. C Mater. Biol. Appl. 2015, 51, 216–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasanth, K.; Ilango, K.; MohanKumar, R.; Agrawal, A.; Dubey, G.P. Anticancer activity of Moringa oleifera mediated silver nanoparticles on human cervical carcinoma cells by apoptosis induction. Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces 2014, 117, 354–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salazar, L.; Vallejo López, M.J.; Grijalva, M.; Castillo, L.; Maldonado, A. Biological effect of organically coated Grias neuberthii and Persea americana silver nanoparticles on HeLa and MCF-7 cancer cell lines. J. Nanotechnol. 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Datta, K.P.; Sandeep, A.; Sonu, A. Anti-proliferative effect of silver nanoparticles in HeLa cells due to enhanced oxidative stress. Res. J. Biotechnol. 2018, 13, 68–74. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X.; Li, T.; Su, X.; Li, J.; Li, W.; Gan, J.; Wu, T.; Kong, L.; Zhang, T.; Tang, M.; et al. Genotoxic effects of silver nanoparticles with/without coating in human liver HepG2 cells and in mice. J. Appl. Toxicol. 2019, 39, 908–918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prasannaraj, G.; Sahi, S.V.; Ravikumar, S.; Venkatachalam, P. Enhanced cytotoxicity of biomolecules loaded metallic silver nanoparticles against human Liver (HepG2) and Prostate (PC3) cancer cell lines. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2016, 16, 4948–4959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xue, Y.; Zhang, T.; Zhang, B.; Gong, F.; Huang, Y.; Tang, M. Cytotoxicity and apoptosis induced by silver nanoparticles in human liver HepG2 cells in different dispersion media. J. Appl. Toxicol. 2016, 36, 352–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suliman, Y.A.; Ali, D.; Alarifi, S.; Harrath, A.H.; Mansour, L.; Alwasel, S.H. Evaluation of cytotoxic, oxidative stress, proinflammatory and genotoxic effect of silver nanoparticles in human lung epithelial cells. Environ. Toxicol. 2015, 30, 149–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Venugopal, K.; Ahmad, H.; Manikandan, E.; Arul, K.T.; Kavitha, K.; Moodley, M.; Rajagopal, K.; Balabhaskar, R.; Bhaskar, M. The impact of anticancer activity upon Beta vulgaris extract mediated biosynthesized silver nanoparticles (ag-NPs) against human breast (MCF-7), lung (A549) and pharynx (Hep-2) cancer cell lines. J. Photochem. Photobiol. B 2017, 173, 99–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
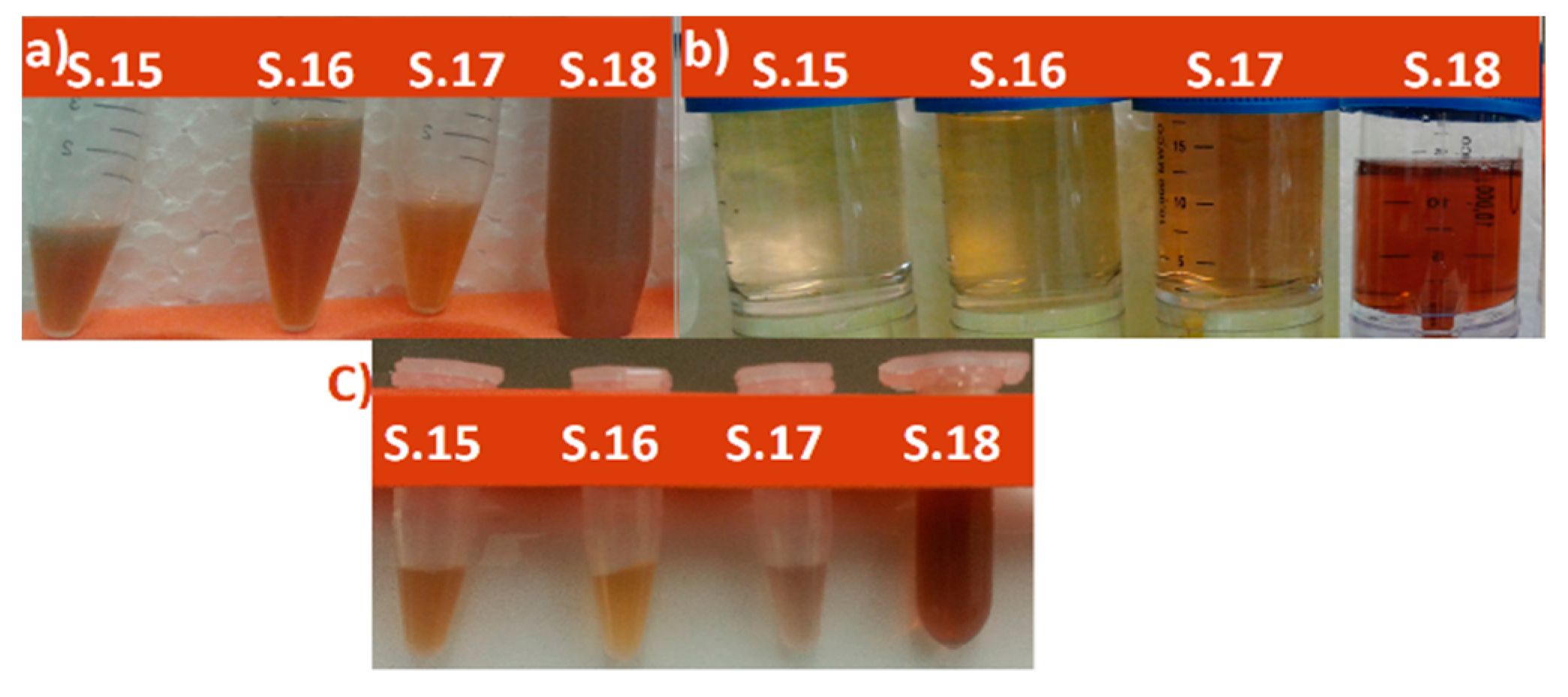













| Sample Number | Volume of Silver in the Sample [mL] (Concentration: 0.001 M) | Volume of Plant Extract in the Sample [mL] | Other Conditions |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 10 | 0.6 | The sample was diluted up to 10% [23] |
| 2 | 5 | 10 | Mixture was heated to 37 °C while stirring at 200 rpm for 72 h [89] |
| 3 | 95 | 5 | - |
| 5 | 10 | 10 | [27] |
| 6 | 9 | 1 | Sample was stirred at 200 rpm [26,30] for 48 h without heating |
| 7 | 5 | 1 | Sample was put it in a microwave oven for 5 to 15 min [90] |
| 8 | 5 | 1 | Sample was placed in the incubator (37 °C) for one hour [90] |
| 10 | 50 | 2 | [32] |
| 11 | 20 | 200 | Sample was heated in a water bath at a temperature of 75 °C for one hour |
| 12 | 5 | 30 | Room temperature for 2 days |
| 13 | 5 | 95 | Sample was heated to 65 °C while stirring at 200 rpm for 6 h |
| 14 | 15 | 1 | Sample was heated to 37 °C while stirring at 200 rpm for 2 h |
| 15 | 5 | 5 | Sample was heated to 37 °C while stirring at 400 rpm for 2 weeks [31] |
| 16 | 5 | 15 | Sample was heated to 60 °C while stirring at 700 rpm for 4–6 h |
| 17 | 5 | 25 | Sample was heated to 37 °C while stirring at 400 rpm for 2 weeks |
| 18 | 5 | 30 | Sample was heated to 37 °C while stirring at 400 rpm for 2 weeks |
| 19 | 5 mL (Concentration: 0.01 M) | 15 | Sample was heated to 60 °C while stirring at 700 rpm for 4 h |
| 20 | 5 mL (Concentration: 0.1 M) | 15 | Sample was heated to 60 °C while stirring at 700 rpm for 2 h |
| 2θ (o) | Sin 2θ | Sin 2θ/Sin 2θ for the First Peak | (Sin 2θ/Sin 2θ for the First Peak) × 3 | (h2 + k2 + l2) | (hkl) | Sin 2θ/ h2 + k2 + l2 | d (Å) | a (Å) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 38.2461 | 0.1073 | 1 | 3 | 3 | 111 | 0.036 | 2.3531 | 4.07 |
| 44.4345 | 0.14297 | 1.332 | 3.996 | 4 | 200 | 0.036 | 2.0387 | 4.07 |
| 64.596 | 0.28551 | 2.661 | 7.983 | 8 | 220 | 0.036 | 1.4427 | 4.07 |
| 77.5785 | 0.39245 | 3.658 | 10.974 | 11 | 311 | 0.036 | 1.2306 | 4.07 |
| 81.7060 | 0.42787 | 3.988 | 11.963 | 12 | 222 | 0.036 | 1.1785 | 4.07 |
| Diffraction Peaks | Sample Value | Theoretical Value |
|---|---|---|
| (200) and (111) | from 0.24 to 0.38 | 0.45 |
| (220) and (111) | from 0.19 to 0.35 | 0.24 |
| (311) and (111) | From 0.15 to 0.25 | 0.25 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Alahmad, A.; Feldhoff, A.; Bigall, N.C.; Rusch, P.; Scheper, T.; Walter, J.-G. Hypericum perforatum L.-Mediated Green Synthesis of Silver Nanoparticles Exhibiting Antioxidant and Anticancer Activities. Nanomaterials 2021, 11, 487. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano11020487
Alahmad A, Feldhoff A, Bigall NC, Rusch P, Scheper T, Walter J-G. Hypericum perforatum L.-Mediated Green Synthesis of Silver Nanoparticles Exhibiting Antioxidant and Anticancer Activities. Nanomaterials. 2021; 11(2):487. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano11020487
Chicago/Turabian StyleAlahmad, Abdalrahim, Armin Feldhoff, Nadja C. Bigall, Pascal Rusch, Thomas Scheper, and Johanna-Gabriela Walter. 2021. "Hypericum perforatum L.-Mediated Green Synthesis of Silver Nanoparticles Exhibiting Antioxidant and Anticancer Activities" Nanomaterials 11, no. 2: 487. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano11020487
APA StyleAlahmad, A., Feldhoff, A., Bigall, N. C., Rusch, P., Scheper, T., & Walter, J. -G. (2021). Hypericum perforatum L.-Mediated Green Synthesis of Silver Nanoparticles Exhibiting Antioxidant and Anticancer Activities. Nanomaterials, 11(2), 487. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano11020487







