Chemically-Gated and Sustained Molecular Transport through Nanoporous Gold Thin Films in Biofouling Conditions
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Fabrication and Characterization of np-Au Thin Films
2.2. Transport Characterization
2.3. Biofouling Resilience
2.4. Chemical Gating
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
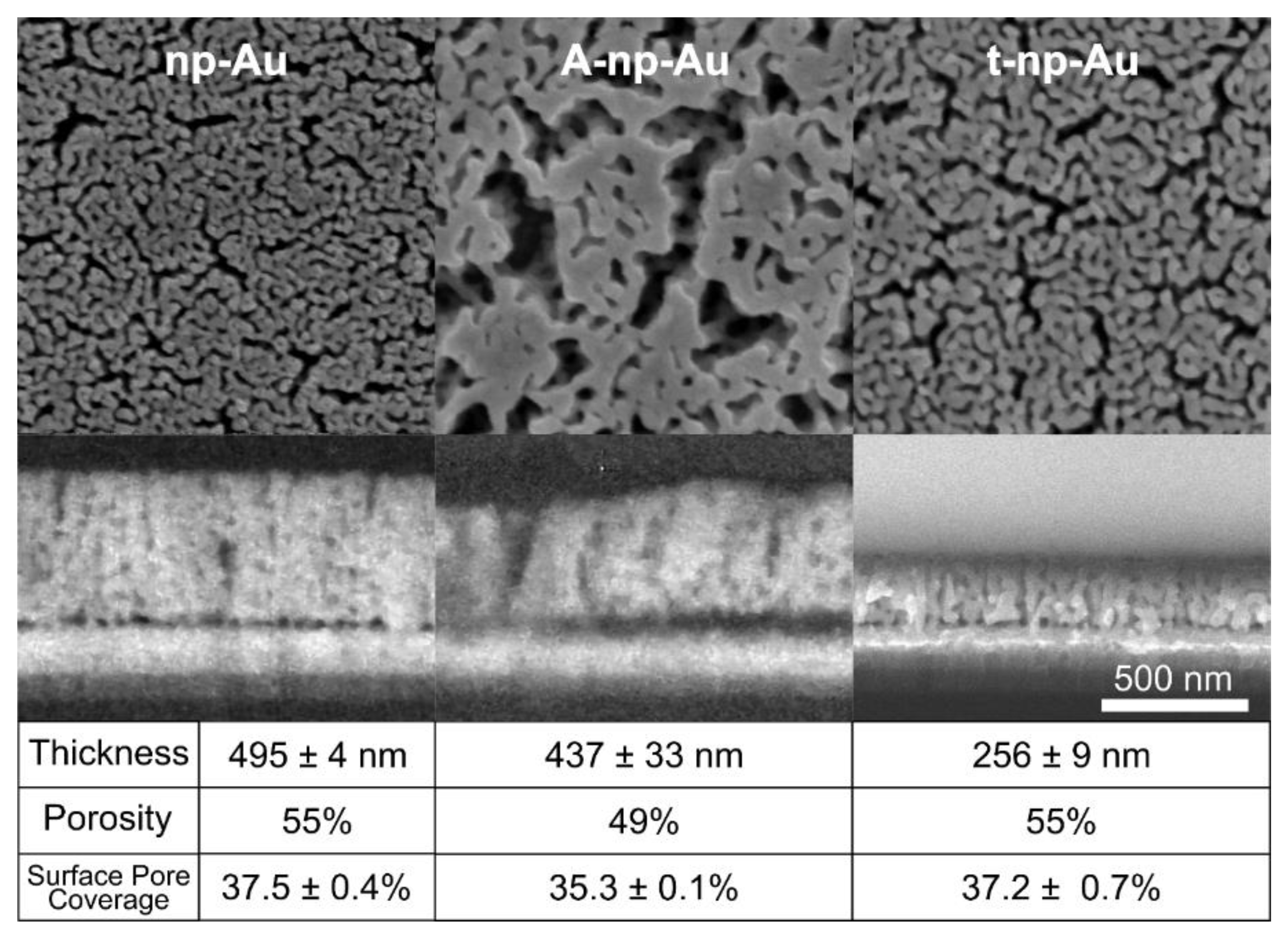
3.1. Nanoporous Gold Thin Film Properties
3.2. In-Plane Fluorescein Transport
3.3. Biofouling Resilience
3.4. Chemical Gating
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Vaccari, L.; Canton, D.; Zaffaroni, N.; Villa, R.; Tormen, M.; di Fabrizio, E. Porous silicon as drug carrier for controlled delivery of doxorubicin anticancer agent. Microelectron. Eng. 2006, 83, 1598–1601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gensler, H.; Sheybani, R.; Li, P.; Lo, R.; Zhu, S.; Yong, K.; Prasad, P.N.; Masood, R.; Sinha, U.K.; Meng, E. Implantable MEMS drug delivery device for cancer radiation reduction. In Proceedings of the 2010 IEEE 23rd International Conference on Micro Electro Mechanical Systems (MEMS), Hong Kong, China, 24–28 January 2010; pp. 27–30. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, L.; Wang, L.; Zhang, Y.; Xiao, S.; Bi, F.; Zhao, J.; Gai, G.; Ding, J. Glucose Oxidase-based Glucose-sensitive Drug Delivery for Diabetes treatment. Polymers 2017, 9, 255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Proctor, C.M.; Slézia, A.; Kaszas, A.; Ghestem, A.; del Agua, I.; Pappa, A.M.; Bernard, C.; Williamson, A.; Malliaras, G.G. Electrophoretic drug delivery for seizure control. Sci. Adv. 2018, 4, eaau1291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sershen, S.; West, J. Implantable, polymeric systems for modulated drug delivery. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2002, 54, 1225–1235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kleiner, L.W.; Wright, J.C.; Wang, Y. Evolution of implantable and insertable drug delivery systems. J. Control. Release 2014, 181, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Razzacki, S.Z.; Thwar, P.K.; Yang, M.; Ugaz, V.M.; Burns, M.A. Integrated microsystems for controlled drug delivery. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2004, 56, 185–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sonabend, A.M.; Stupp, R. Overcoming the blood-brain barrier with an implantable ultrasound device. Clin. Cancer Res. 2019, 25, 3750–3752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pons-Faudoa, F.P.; Ballerini, A.; Sakamoto, J.; Grattoni, A. Advanced implantable drug delivery technologies: Transforming the clinical landscape of therapeutics for chronic diseases. Biomed. Microdevices 2019, 21, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dauphin-Ducharme, P.; Yang, K.; Arroyo-Currás, N.; Ploense, K.L.; Zhang, Y.; Gerson, J.; Kurnik, M.; Kippin, T.E.; Stojanovic, M.N.; Plaxco, K.W. Electrochemical Aptamer-Based Sensors for Improved Therapeutic Drug Monitoring and High-Precision, Feedback-Controlled Drug Delivery. ACS Sens. 2019, 4, 2832–2837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lo, R.; Li, P.Y.; Saati, S.; Agrawal, R.; Humayun, M.S.; Meng, E. A refillable microfabricated drug delivery device for treatment of ocular diseases. Lab Chip 2008, 8, 1027–1030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.Y.; Shih, J.; Lo, R.; Saati, S.; Agrawal, R.; Humayun, M.S.; Tai, Y.C.; Meng, E. An electrochemical intraocular drug delivery device. Sens. Actuators, A Phys. 2008, 143, 41–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forouzandeh, F.; Ahamed, N.N.; Hsu, M.C.; Walton, J.P.; Frisina, R.D.; Borkholder, D.A. A 3D-Printed Modular Microreservoir for Drug Delivery. Micromachines 2020, 11, 648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gultepe, E.; Nagesha, D.; Sridhar, S.; Amiji, M. Nanoporous inorganic membranes or coatings for sustained drug delivery in implantable devices. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2010, 62, 305–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran, P.A.; Zhang, L.; Webster, T.J. Carbon nanofibers and carbon nanotubes in regenerative medicine. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2009, 61, 1097–1114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bianco, A.; Kostarelos, K.; Prato, M. Applications of carbon nanotubes in drug delivery. Curr. Opin. Chem. Biol. 2005, 9, 674–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anglin, E.J.; Cheng, L.; Freeman, W.R.; Sailor, M.J. Porous silicon in drug delivery devices and materials. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2008, 60, 1266–1277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pillai, O.; Panchagnula, R. Polymers in Drug Delivery. Curr. Opin. Chem. Biol. 2001, 5, 447–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Binauld, S.; Stenzel, M.H. Acid-degradable polymers for drug delivery: A decade of innovation. Chem. Commun. 2013, 49, 2082–2102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blaszykowski, C.; Sheikh, S.; Thompson, M. Surface chemistry to minimize fouling from blood-based fluids. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2012, 41, 5599–5612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Q.; Yan, F.; Yao, L.; Su, B. Anti-Biofouling Isoporous Silica-Micelle Membrane Enabling Drug Detection in Human Whole Blood. Anal. Chem. 2016, 88, 8364–8368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.C.; Xie, R.; Chu, L.Y. Stimuli-responsive gating membranes responding to temperature, pH, salt concentration and anion species. J. Memb. Sci. 2013, 442, 206–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aznar, E.; Coll, C.; Dolores Marcos, M.; Artínez-M Áñez, R.M.; Sancenón, F.; Soto, J.; Amorós, P.; Cano, J.; Ruiz, E. Borate-driven gatelike scaffolding using mesoporous materials functionalised with saccharides. Chem.—A Eur. J. 2009, 15, 6877–6888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acar, E.T.; Buchsbaum, S.F.; Combs, C.; Fornasiero, F.; Siwy, Z.S. Biomimetic potassium-selective nanopores. Sci. Adv. 2019, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCurry, D.A.; Bailey, R.C. Electrolyte Gradient-Based Modulation of Molecular Transport through Nanoporous Gold Membranes. Langmuir 2017, 33, 1552–1562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brudno, Y.; Silva, E.A.; Kearney, C.J.; Lewin, S.A.; Miller, A.; Martinick, K.D.; Aizenberg, M.; Mooney, D.J. Refilling drug delivery depots through the blood. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, 12722–12727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Erlebacher, J.; Aziz, M.J.; Karma, A.; Dimitrov, N.; Sieradzki, K. Evolution of nanoporosity in dealloying. Nature 2001, 410, 450–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hakamada, M.; Mabuchi, M. Thermal coarsening of nanoporous gold: Melting or recrystallization. J. Mater. Res. 2009, 24, 301–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seker, E.; Reed, M.L.; Begley, M.R. Nanoporous Gold: Fabrication, Characterization, and Applications. Materials 2009, 2, 2188–2215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen-Wiegart, Y.C.K.; Wang, S.; Chu, Y.S.; Liu, W.; McNulty, I.; Voorhees, P.W.; Dunand, D.C. Structural evolution of nanoporous gold during thermal coarsening. Acta Mater. 2012, 60, 4972–4981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dorofeeva, T.S.; Seker, E. Electrically tunable pore morphology in nanoporous gold thin films. Nano Res. 2015, 8, 2188–2198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, A.; Bhattarai, J.K.; Alla, A.J.; Demchenko, A.V.; Stine, K.J. Electrochemical annealing of nanoporous gold by application of cyclic potential sweeps. Nanotechnology 2015, 26, 085602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arnob, M.M.P.; Zhao, F.; Zeng, J.; Santos, G.M.; Li, M.; Shih, W.C. Laser rapid thermal annealing enables tunable plasmonics in nanoporous gold nanoparticles. Nanoscale 2014, 6, 12470–12475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chapman, C.A.R.; Wang, L.; Biener, J.; Seker, E.; Biener, M.M.; Matthews, M.J. Engineering on-chip nanoporous gold material libraries via precision photothermal treatment. Nanoscale 2016, 8, 785–795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qian, L.H.; Chen, M.W. Ultrafine nanoporous gold by low-temperature dealloying and kinetics of nanopore formation. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2007, 91, 083105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rouya, E.; Cattarin, S.; Reed, M.L.; Kelly, R.G.; Zangari, G. Electrochemical Characterization of the Surface Area of Nanoporous Gold Films. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2012, 159, K97–K102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, R.; Wang, J.L.; Wang, R.; Li, X.; Zhang, X.; Feng, X.Q.; Ding, Y. Correlation of the thermal and electrical conductivities of nanoporous gold. Nanotechnology 2010, 21, 085703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seker, E.; Shih, W.C.; Stine, K.J. Nanoporous metals by alloy corrosion: Bioanalytical and biomedical applications. MRS Bull. 2018, 43, 49–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Daggumati, P.; Matharu, Z.; Wang, L.; Seker, E. Biofouling-Resilient Nanoporous Gold Electrodes for DNA Sensing. Anal. Chem. 2015, 87, 8618–8622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, J.; Motwani, P.; Gheewala, M.; Brennan, C.; Wolfe, J.C.; Shih, W.C. Surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy with monolithic nanoporous gold disk substrates. Nanoscale 2013, 5, 4105–4109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seker, E.; Berdichevsky, Y.; Begley, M.R.; Reed, M.L.; Staley, K.J.; Yarmush, M.L. The fabrication of low-impedance nanoporous gold multiple-electrode arrays for neural electrophysiology studies. Nanotechnology 2010, 21, 125504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polat, O.; Seker, E. Effect of Surface-Molecule Interactions on Molecular Loading Capacity of Nanoporous Gold Thin Films. J. Phys. Chem. C 2016, 120, 19189–19194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurtulus, O.; Daggumati, P.; Seker, E. Molecular release from patterned nanoporous gold thin films. Nanoscale 2014, 6, 7062–7071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Veselinovic, J.; Almashtoub, S.; Seker, E. Anomalous Trends in Nucleic Acid-Based Electrochemical Biosensors with Nanoporous Gold Electrodes. Anal. Chem. 2019, 91, 11923–11931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wittstock, A.; Biener, J.; Bäumer, M. Nanoporous gold: A new material for catalytic and sensor applications. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2010, 12, 12919–12930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fujita, T.; Guan, P.; McKenna, K.; Lang, X.; Hirata, A.; Zhang, L.; Tokunaga, T.; Arai, S.; Yamamoto, Y.; Tanaka, N.; et al. Atomic origins of the high catalytic activity of nanoporous gold. Nat. Mater. 2012, 11, 775–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daggumati, P.; Kurtulus, O.; Chapman, C.A.R.; Dimlioglu, D.; Seker, E. Microfabrication of nanoporous gold patterns for cell-material interaction studies. J. Vis. Exp. 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seker, E.; Gaskins, J.T.; Bart-Smith, H.; Zhu, J.; Reed, M.L.; Zangari, G.; Kelly, R.; Begley, M.R. The effects of post-fabrication annealing on the mechanical properties of freestanding nanoporous gold structures. Acta Mater. 2007, 55, 4593–4602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, A.; Pillai, J. Chapter 13—Implantable drug delivery systems: An overview. In Nanostructures for the Engineering of Cells, Tissues and Organs; Grumezescu, A., Ed.; William Andrew Publishing: Norwich, NY, USA, 2018; ISBN 9780128136669. [Google Scholar]
- Gultepe, E.; Nagesha, D.; Casse, B.D.F.; Banyal, R.; Fitchorov, T.; Karma, A.; Amiji, M.; Sridhar, S. Sustained Drug Release from Non-eroding Nanoporous Templates. Small 2010, 6, 213–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, Q.H.; Ali, M.; Nasir, S.; Ensinger, W. Transport properties of track-etched membranes having variable effective pore-lengths. Nanotechnology 2015, 26, 485502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Trani, N.; Silvestri, A.; Sizovs, A.; Wang, Y.; Erm, D.R.; Demarchi, D.; Liu, X.; Grattoni, A. Electrostatically gated nanofluidic membrane for ultra-low power controlled drug delivery. Lab Chip 2020, 20, 1562–1576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, Y.; Markmann, J.; Duan, H.; Weissmüller, J.; Huber, P. Switchable imbibition in nanoporous gold. Nat. Commun. 2014, 5, 4237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seker, E.; Berdichevsky, Y.; Staley, K.J.; Yarmush, M.L. Microfabrication-compatible nanoporous gold foams as biomaterials for drug delivery. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2012, 1, 172–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Polat, O.; Seker, E. Halide-Gated Molecular Release from Nanoporous Gold Thin Films. J. Phys. Chem. C 2015, 119, 24812–24818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butler, J.A.V.; Ockrent, C. Studies in electrocapillarity. Part III: The surface tensions of solutions containing two surface-active solutes. J. Phys. Chem. 1930, 34, 2841–2859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choy, K.K.H.; Porter, J.F.; McKay, G. Langmuir isotherm models applied to the multicomponent sorption of acid dyes from effluent onto activated carbon. J. Chem. Eng. Data 2000, 45, 575–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terdputtakun, A.; Arqueropanyo, O.A.; Sooksamiti, P.; Janhom, S.; Naksata, W. Adsorption isotherm models and error analysis for single and binary adsorption of Cd(II) and Zn(II) using leonardite as adsorbent. Environ. Earth Sci. 2017, 76, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, Y.S.; McKay, G. Correlative biosorption equilibria model for a binary batch system. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2000, 55, 817–825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boving, T.B.; Grathwohl, P. Tracer diffusion coefficients in sedimentary rocks: Correlation to porosity and hydraulic conductivity. J. Contam. Hydrol 2001, 53, 85–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chenyakin, Y.; Ullmann, A.D.; Evoy, E.; Renbaum-Wolff, L.; Kamal, S.; Bertram, K.A. Diffusion coefficients of organic molecules in sucrose-water solutions and comparison with Stokes-Einstein predictions. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2017, 17, 2423–2435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grathwohl, P. Diffusion in Natural Porous Media: Contaminant Transport, Sorption/Desorption and Dissolution Kinetics; Grumezescu, A., Ed.; Kluwer Academic Publishers: New York, NY, USA, 1998; ISBN 978-1-4615-5683-1. [Google Scholar]
- Rashapov, R.; Imami, F.; Gostick, J.T. A method for measuring in-plane effective diffusivity in thin porous media. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 2015, 85, 367–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casalini, T.; Salvalaglio, M.; Perale, G.; Masi, M.; Cavallotti, C. Diffusion and aggregation of sodium fluorescein in aqueous solutions. J. Phys. Chem. B 2011, 115, 12896–12904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seker, E.; Reed, M.L.; Begley, M.R. A thermal treatment approach to reduce microscale void formation in blanket nanoporous gold films. Scr. Mater. 2009, 60, 435–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adiga, S.P.; Jin, C.; Curtiss, L.A.; Monteiro-Riviere, N.A.; Narayan, R.J. Nanoporous membranes for medical and biological applications. Wiley Interdiscip. Rev. Nanomed. Nanobiotechnol. 2009, 1, 568–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saraf, S.; Neal, C.J.; Park, S.; Das, S.; Barkam, S.; Cho, H.J.; Seal, S. Electrochemical study of nanoporous gold revealing anti-biofouling properties. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 46501–46508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, J.; Radhakrishnan, L.; Zhao, B.; Uppalapati, B.; Daniels, R.C.; Ward, K.R.; Collinson, M.M. Electrochemical Properties of Nanostructured Porous Gold Electrodes in Biofouling Solutions. Anal. Chem. 2013, 85, 11610–11618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chapman, C.A.R.; Wang, L.; Chen, H.; Garrison, J.; Lein, P.J.; Seker, E. Nanoporous Gold Biointerfaces: Modifying Nanostructure to Control Neural Cell Coverage and Enhance Electrophysiological Recording Performance. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2017, 27, 1604631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Polat, O.; Seker, E. Voltage-Gated Closed-Loop Control of Small-Molecule Release from Alumina-Coated Nanoporous Gold Thin Film Electrodes. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2018, 28, 1801292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Song, P.; Liu, J.; Tng, D.J.H.; Hu, R.; Chen, H.; Hu, Y.; Tan, C.H.; Wang, J.; Liu, J.; et al. An in-vivo evaluation of a MEMS drug delivery device using Kunming mice model. Biomed. Microdevices 2015, 17, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hakamada, M.; Taniguchi, S.; Mabuchi, M. Antibacterial activity of nanoporous gold against Escherichia coli and Staphylococcus epidermidis. J. Mater. Res. 2017, 32, 1787–1795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmutz, M.; Borges, O.; Jesus, S.; Borchard, G.; Perale, G.; Zinn, M.; Sips, Ä.A.J.A.M.; Soeteman-Hernandez, L.G.; Wick, P.; Som, C. A Methodological Safe-by-Design Approach for the Development of Nanomedicines. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2020, 8, 258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhattarai, J.K.; Neupane, D.; Nepal, B.; Demchenko, A.V.; Stine, K.J. Nanoporous Gold Monolith for High Loading of Unmodified Doxorubicin and Sustained Co-Release of Doxorubicin-Rapamycin. Nanomaterials 2021, 11, 208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gittard, S.D.; Pierson, B.E.; Ha, C.M.; Wu, C.A.M.; Narayan, R.J.; Robinson, D.B. Supercapacitive transport of pharmacologic agents using nanoporous gold electrodes. Biotechnol. J. 2010, 5, 192–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]





| Film Type | Porosity, ε | Tortuosity, τ | Exp. Effective Diffusivity (cm2 s−1) | Theo. Effective Diffusivity (cm2 s−1) | Relative Error w.r.t Theoretical Diffusivity |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| np-Au | 0.55 | 1.35 | 2.46 × 10−6 | 1.71 × 10−6 | 44% |
| A-np-Au | 0.49 | 1.42 | 2.22 × 10−6 | 1.44 × 10−6 | 54% |
| t-np-Au | 0.55 | 1.35 | 1.65 × 10−6 | 1.71 × 10−6 | −4% |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Palanisamy, B.; Goshi, N.; Seker, E. Chemically-Gated and Sustained Molecular Transport through Nanoporous Gold Thin Films in Biofouling Conditions. Nanomaterials 2021, 11, 498. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano11020498
Palanisamy B, Goshi N, Seker E. Chemically-Gated and Sustained Molecular Transport through Nanoporous Gold Thin Films in Biofouling Conditions. Nanomaterials. 2021; 11(2):498. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano11020498
Chicago/Turabian StylePalanisamy, Barath, Noah Goshi, and Erkin Seker. 2021. "Chemically-Gated and Sustained Molecular Transport through Nanoporous Gold Thin Films in Biofouling Conditions" Nanomaterials 11, no. 2: 498. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano11020498
APA StylePalanisamy, B., Goshi, N., & Seker, E. (2021). Chemically-Gated and Sustained Molecular Transport through Nanoporous Gold Thin Films in Biofouling Conditions. Nanomaterials, 11(2), 498. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano11020498







