Nanocomposite Membrane Scaffolds for Cell Function Maintaining for Biomedical Purposes
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Methods
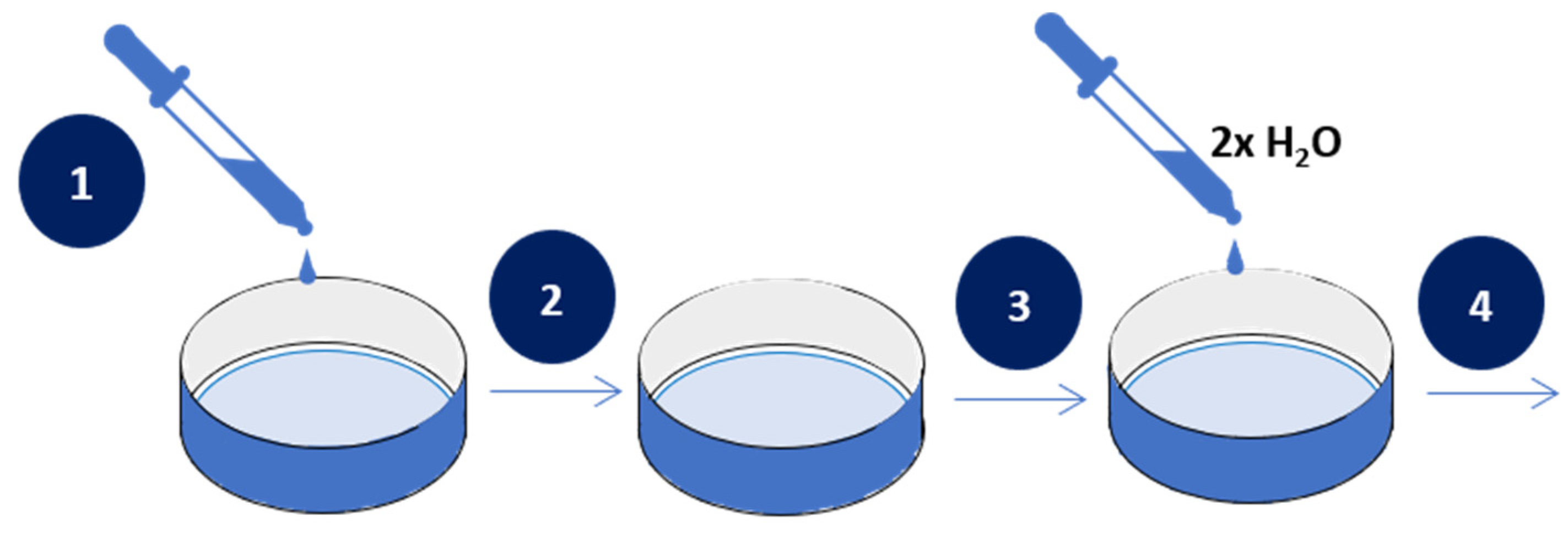
2.2.1. Membrane Preparation
- polyethyleneimine with AuNPs composite (PEI-Au)—20 ppm AuNPs solution in PBS was added to PEI at a 1:1 ratio and subsequently stirred for 4 h, room temperature.
- polyethyleneimine with AgNPs composite (PEI-Ag)—20 ppm AgNPS solution in PBS was added to PEI at a 1:1 ratio and subsequently stirred for 4 h, room temperature.
- the bilayer of polyethyleneimine incorporating AuNPs and hydroxyapatite (PEI-Au|HAP)—the HAP layer of 0.3% hydroxyapatite solution in PBS was deposited on a PEI-Au membrane layer.
- the bilayer of polyethyleneimine incorporating AgNPs and hydroxyapatite (PEI-Ag|HAP)—the HAP layer of 0.3% hydroxyapatite solution in PBS was deposited on a PEI-Ag membrane layer.
- built of the hydroxyapatite mixed with polyethyleneimine incorporating AuNPs (PEI-Au-HAP)—the polyethyleneimine with AuNPs solution (PEI-Au) was added to 0.3% hydroxyapatite solution in PBS at a 1:1 ratio and subsequently stirred for 4 min, room temperature.
- built of the hydroxyapatite mixed with polyethyleneimine incorporating AgNPs (PEI-Ag-HAP)—the polyethyleneimine with AgNPs solution (PEI-Ag) was added to 0.3% hydroxyapatite solution in PBS at a 1:1 ratio and subsequently stirred for 4 min, room temperature.
2.2.2. Wettability and Work of Adhesion Evaluation
2.2.3. Assessment of the Transport Properties of the Membranes
2.2.4. Cell Culture
2.2.5. Fluorescent Staining
2.2.6. Flow Cytometry
2.2.7. Scanning Electron Microscopy Evaluation
2.2.8. Transmission Electron Microscopy Evaluation
2.2.9. Atomic Forces Microscopy Evaluation
2.2.10. Fourier-Transform Infrared Spectroscopy Analysis
2.2.11. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Characterization of Nanocomposite Membrane Scaffolds
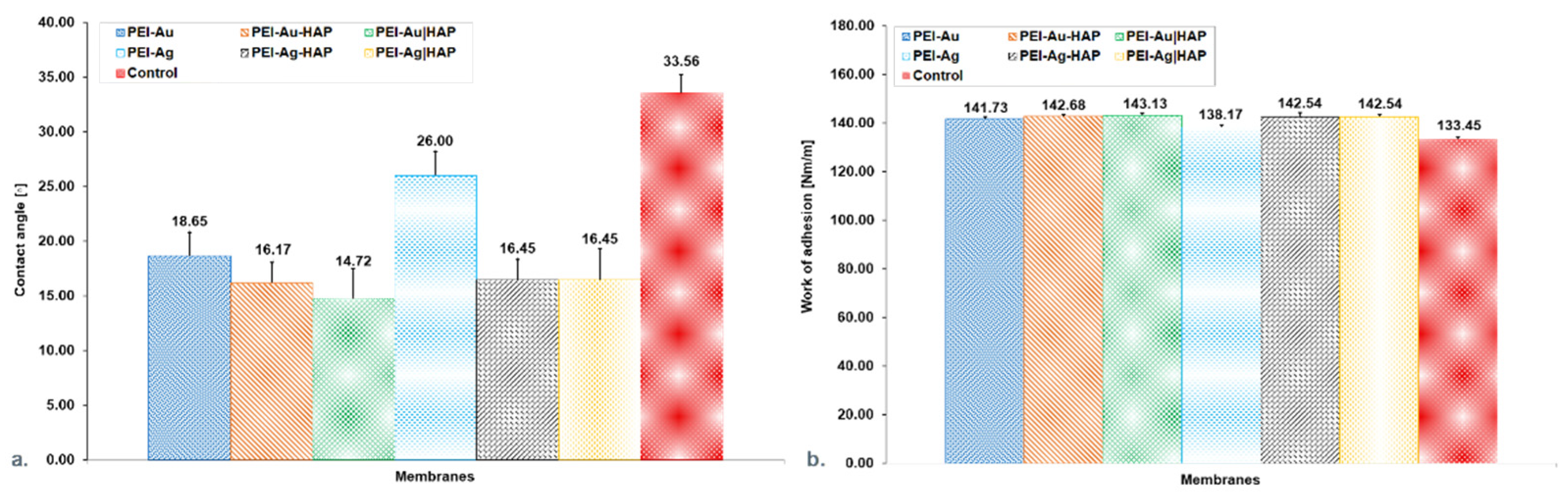
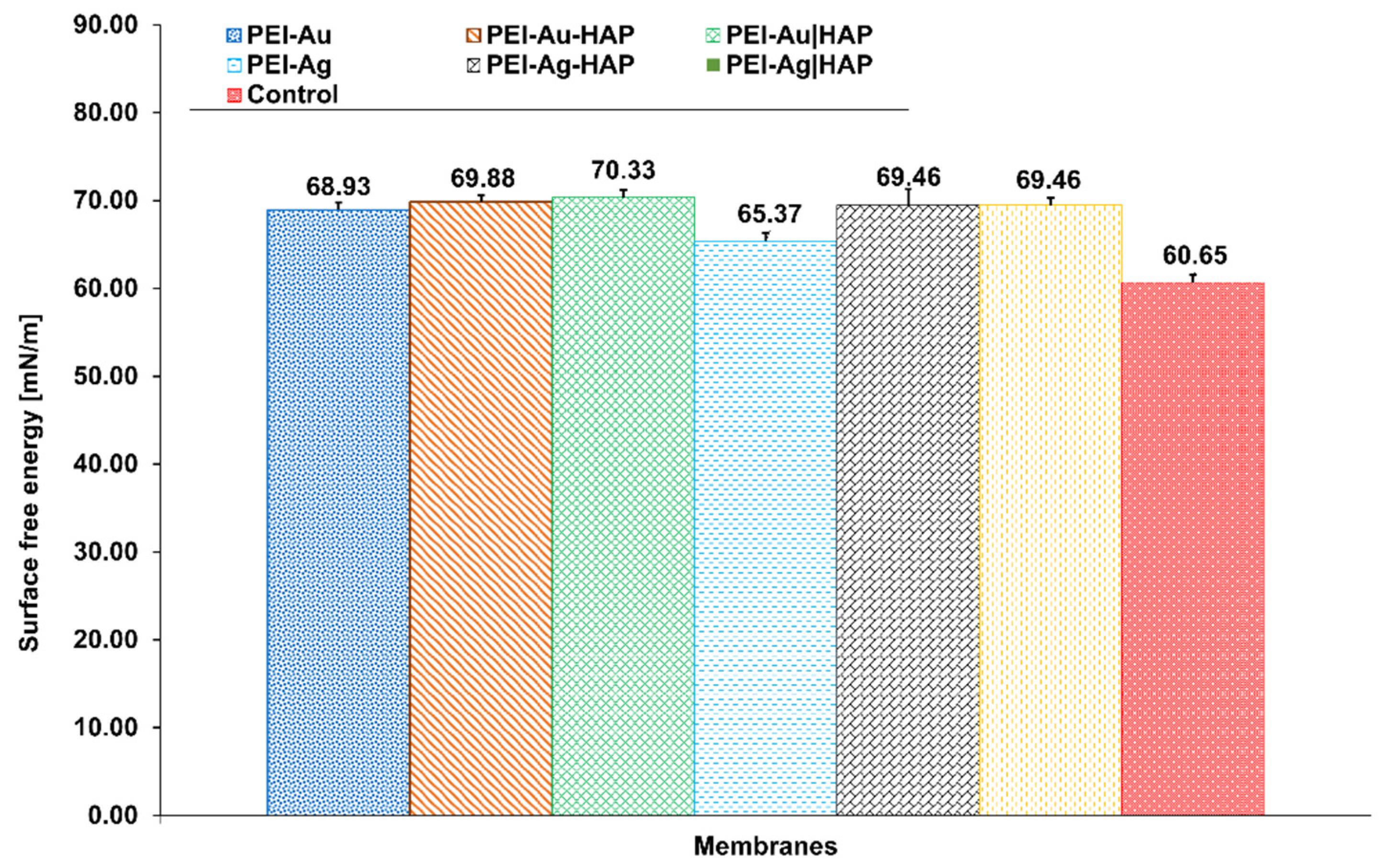
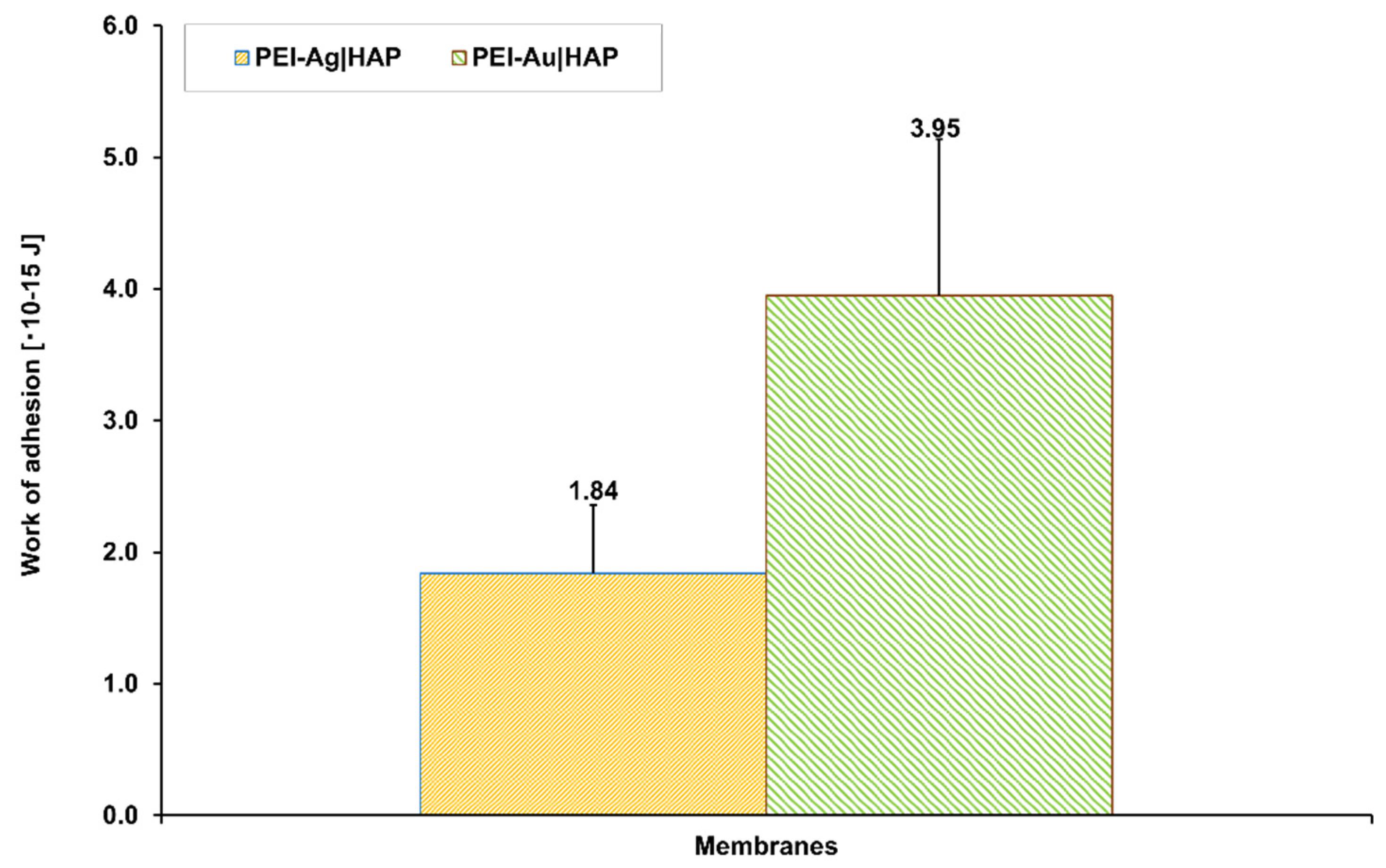
3.1.1. Water Contact Angle Measurements
3.1.2. Assessment of the Transport Properties of the Membranes
3.1.3. Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy
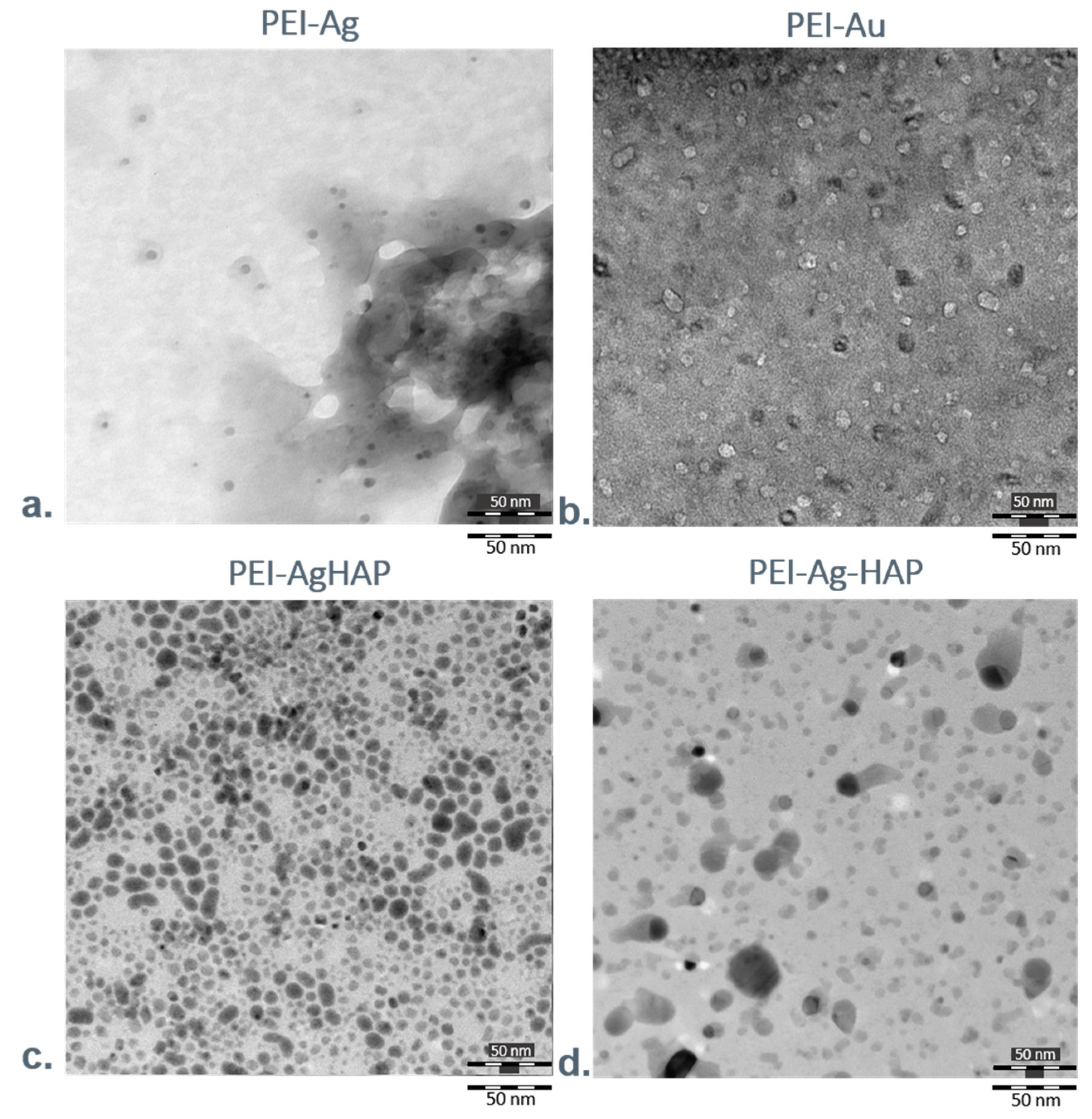
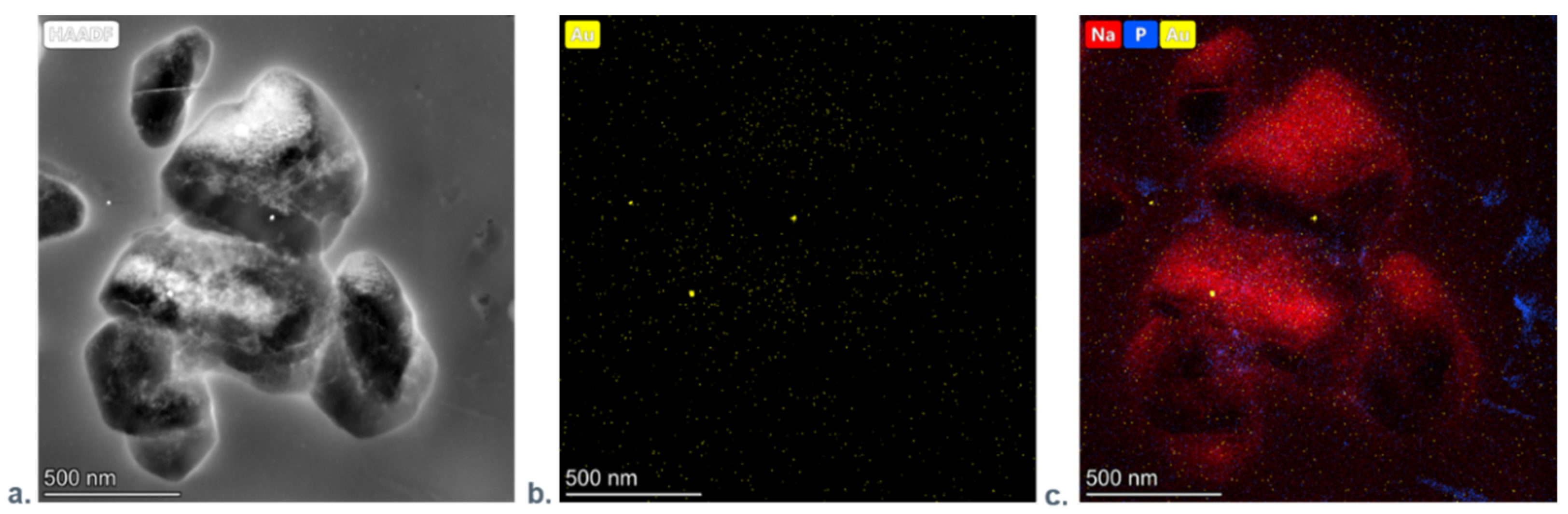
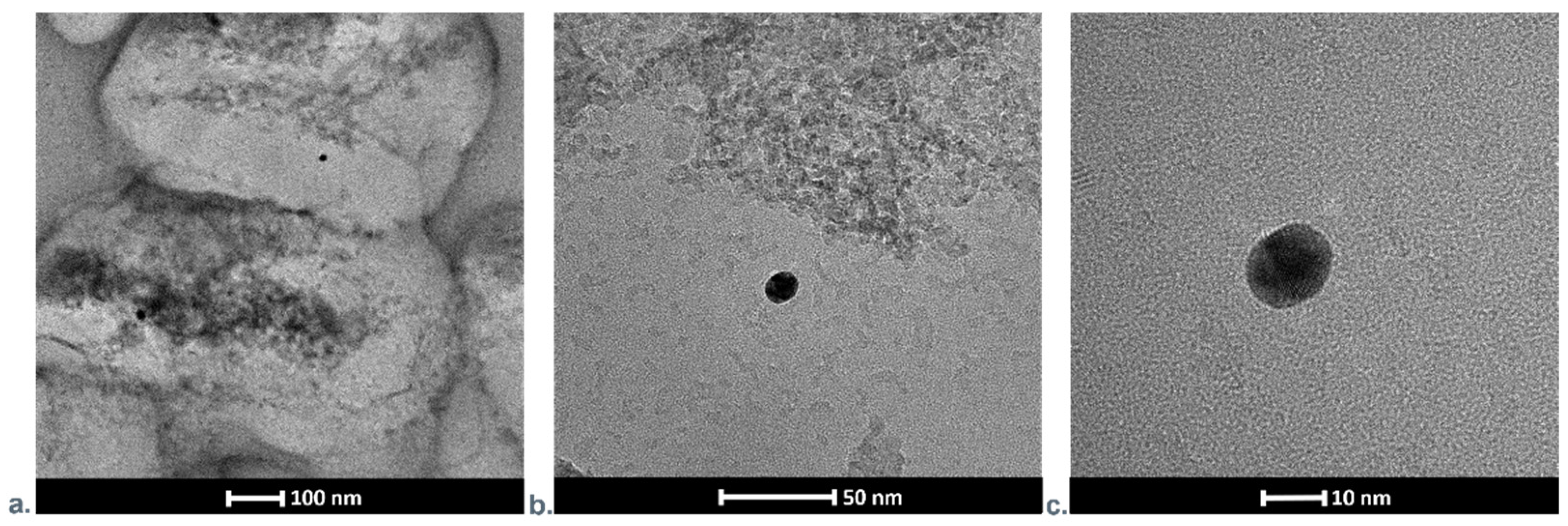
3.1.4. Transmission Electron Microscopy Investigations
3.1.5. Atomic Forces Microscopy Evaluation
3.2. Evaluation of the Functioning of Cells within Different Membranes
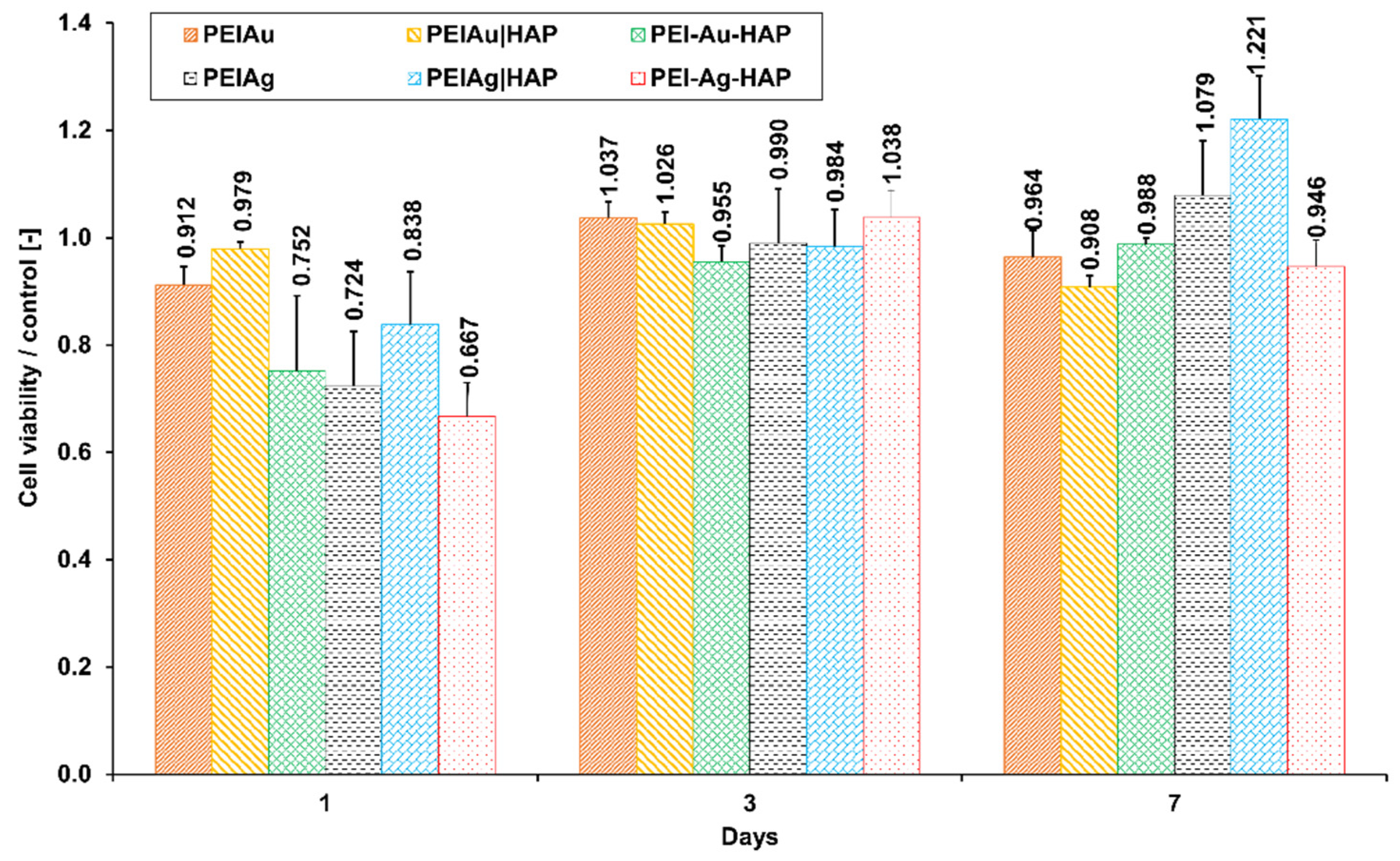
3.2.1. Flow Cytometry Analysis
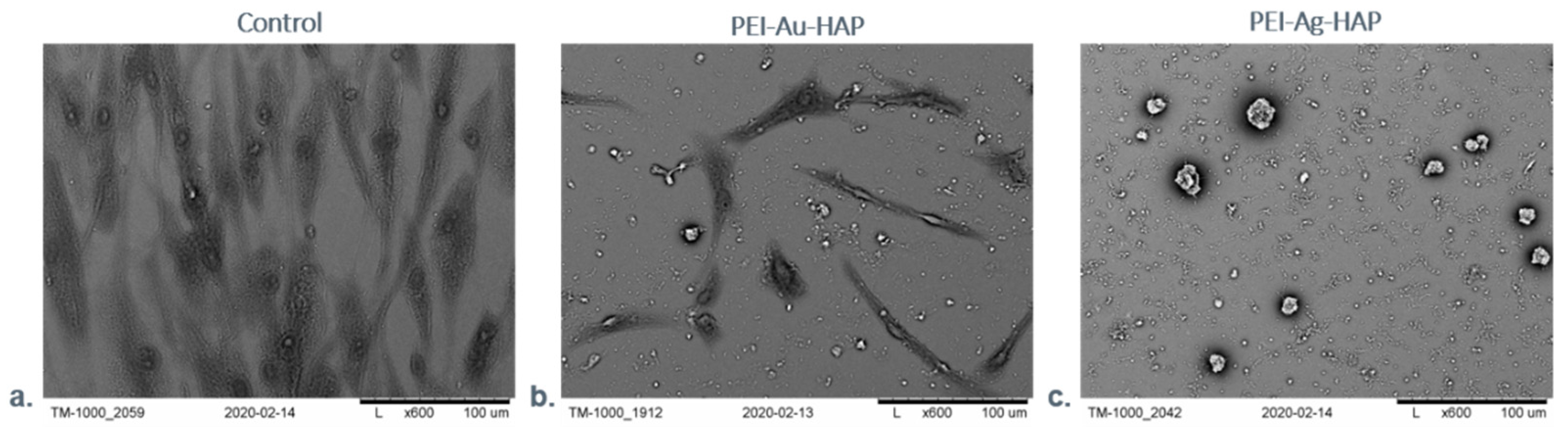
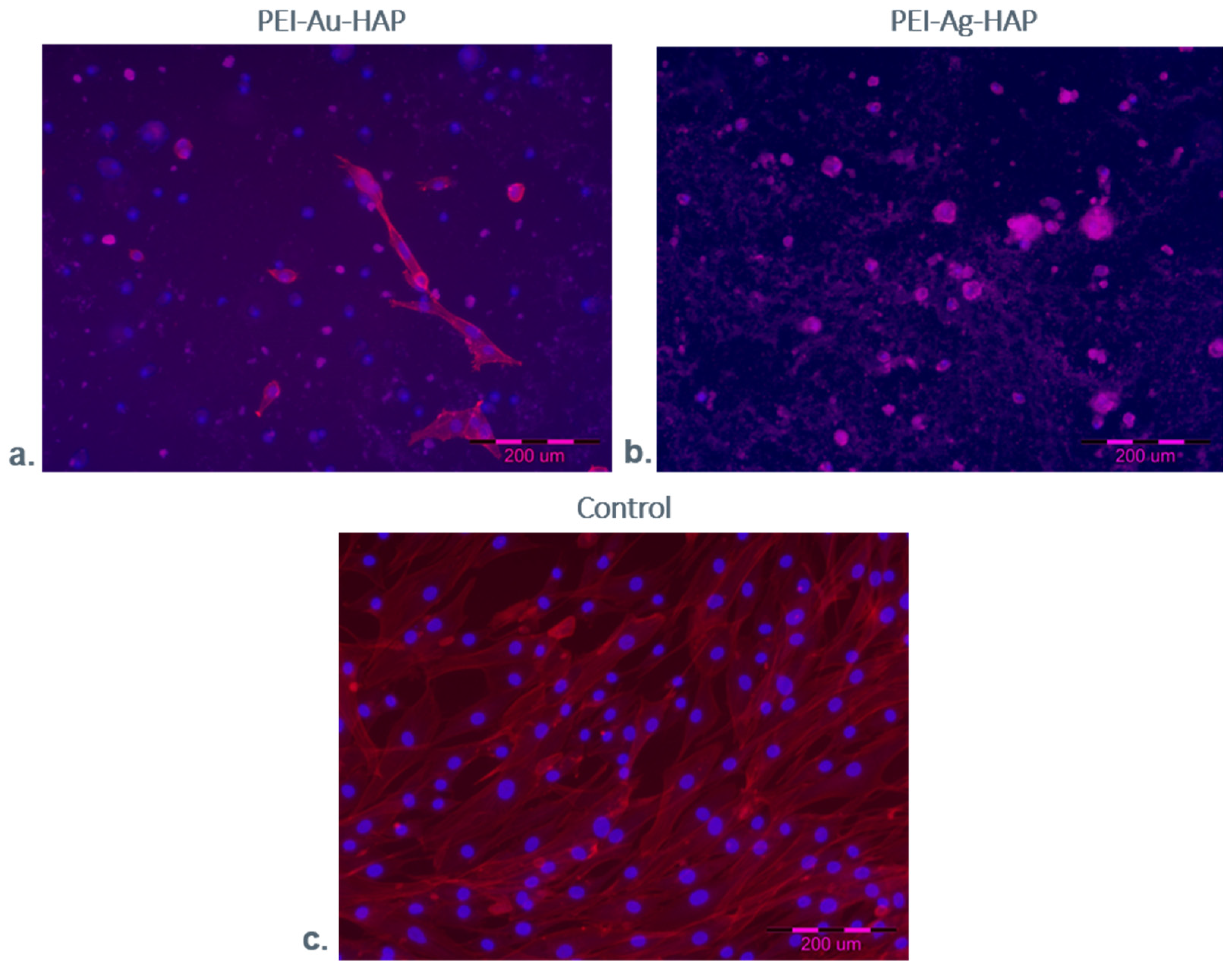
3.2.2. Microscopic Evaluation of Immobilized Cells
3.2.3. Fluorescent Staining
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Dhivya, S.; Padma, V.V.; Santhini, E. Wound Dressings—A Review. BioMedicine 2015, 5, 24–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qin, Y. Functional Wound Dressings. In Medical Textile Materials; Elsevier Woodhead Publishing: Sawston, UK, 2016; pp. 89–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finn, G.; Kirsner, R.; Meaume, S.; Munter, C.; Sibbald, G. Clinical Wound Assessment—A Pocket Guide; Coloplast Corp.: Minneapolis, MN, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Tan, H.L.; Teow, S.Y.; Pushpamalar, J. Application of metal nanoparticle–hydrogel composites in tissue regeneration. Bioengineering 2019, 6, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bacteria and Wound Healing: Current Opinion in Infectious Diseases. Available online: https://journals.lww.com/co-infectiousdiseases/Abstract/2004/04000/Bacteria_and_wound_healing.4.aspx (accessed on 14 June 2020).
- Bierkandt, F.S.; Leibrock, L.; Wagener, S.; Laux, P.; Luch, A. The impact of nanomaterial characteristics on inhalation toxicity. Toxicol. Res. 2018, 7, 321–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Azharuddin, M.; Zhu, G.H.; Das, D.; Ozgur, E.; Uzun, L.; Turner, A.P.; Patra, H.K. A repertoire of biomedical applications of noble metal nanoparticles. Chem. Commun. 2019, 55, 6964–6996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossi, A.; Donati, S.; Fontana, L.; Porcaro, F.; Battocchio, C.; Proietti, E.; Venditti, I.; Bracci, L.; Fratoddi, I. Negatively charged gold nanoparticles as a dexamethasone carrier: Stability in biological media and bioactivity assessment in vitro. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 99016–99022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drabik, M.; Kazimierczak, B.; Grzeczkowicz, A.; Antosiak-Iwanska, M.; Kwiatkowska, A.; Granicka, L. The Membrane Composite with Silver Nanoparticles for Fibroblastic Cell Growth Sustaining. Desalin. Water Treat. 2018, 101, 70–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- You, C.; Li, Q.; Wang, X.; Wu, P.; Ho, J.K.; Jin, R.; Zhang, L.; Shao, H.; Han, C. Silver Nanoparticle Loaded Collagen/Chitosan Scaffolds Promote Wound Healing via Regulating Fibroblast Migration and Macrophage Activation. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 10489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sandri, G.; Miele, D.; Faccendini, A.; Bonferoni, M.C.; Rossi, S.; Grisoli, P.; Taglietti, A.; Ruggeri, M.; Bruni, G.; Vigani, B.; et al. Chitosan/Glycosaminoglycan Scaffolds: The Role of Silver Nanoparticles to Control Microbial Infections in Wound Healing. Polymers 2019, 11, 1207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kwiatkowska, A.; Granicka, L.H.; Grzeczkowicz, A.; Stachowiak, R.; Bacal, P.; Sobczak, K.; Darowski, M.; Kozarski, M.; Bielecki, J. Gold Nanoparticle-Modified Poly(Vinyl Chloride) Surface with Improved Antimicrobial Properties for Medical Devices. J. Biomed. Nanotechnol. 2018, 14, 922–932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antosiak-Iwańska, M.; Kazimierczak, B.; Kinasiewicz, J. The Membrane Composite Scaffolds with Antithrombotic Features for Adherent Cells Function Sustention. Desalin. Water Treat. 2018, 128, 45–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aminov, R.I. A Brief History of the Antibiotic Era: Lessons Learned and Challenges for the Future. Front. Microbiol. 2010, 1, 134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ten Threats to Global Health in 2019. Available online: https://www.who.int/news-room/feature-stories/ten-threats-to-global-health-in-2019 (accessed on 16 February 2020).
- Nathan, C.; Cars, O. Antibiotic Resistance—Problems, Progress, and Prospects. N. Engl. J. Med. 2014, 371, 1761–1763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Y.; Luo, X.; Li, W.; Song, R.; Li, J.; Li, Y.; Li, B.; Liu, S. Green and Biodegradable Composite Films with Novel Antimicrobial Performance Based on Cellulose. Food Chem. 2016, 197, 250–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Z.; Wu, Y.; Wang, J.; Cao, B.; Tang, C.Y. In Situ Reduction of Silver by Polydopamine: A Novel Antimicrobial Modification of a Thin-Film Composite Polyamide Membrane. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2016, 50, 9543–9550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, S.; Chen, L.; Huang, L.; Cao, S.; Luo, X.; Liu, K. Novel Antimicrobial Chitosan-Cellulose Composite Films Bioconjugated with Silver Nanoparticles. Ind. Crops Prod. 2015, 70, 395–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torres-Giner, S.; Ocio, M.J.; Lagaron, J.M. Novel Antimicrobial Ultrathin Structures of Zein/Chitosan Blends Obtained by Electrospinning. Carbohydr. Polym. 2009, 77, 261–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venditti, I. Engineered gold-based nanomaterials: Morphologies and functionalities in biomedical applications. A mini review. Bioengineering 2019, 6, 53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Burdușel, A.C.; Gherasim, O.; Grumezescu, A.M.; Mogoantă, L.; Ficai, A.; Andronescu, E. Biomedical applications of silver nanoparticles: An up-to-date overview. Nanomaterials 2018, 8, 681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Aljabali, A.A.; Akkam, Y.; Al Zoubi, M.S.; Al-Batayneh, K.M.; Al-Trad, B.; Abo Alrob, O.; Evans, D.J. Synthesis of gold nanoparticles using leaf extract of Ziziphus zizyphus and their antimicrobial activity. Nanomaterials 2018, 8, 174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rai, M.; Ingle, A.P.; Gaikwad, S.; Padovani, F.H.; Alves, M. The role of nanotechnology in control of human diseases: Perspectives in ocular surface diseases. Crit. Rev. Biotechnol. 2016, 36, 777–787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yaqoob, S.B.; Adnan, R.; Khan, R.M.R.; Rashid, M. Gold, silver, and palladium nanoparticles: A chemical tool for biomedical applications. Front. Chem. 2020, 8, 376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prabhu, S.; Poulose, E.K. Silver Nanoparticles: Mechanism of Antimicrobial Action, Synthesis, Medical Applications, and Toxicity Effects. Int. Nano Lett. 2012, 2, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gwinn, M.R.; Vallyathan, V. Nanoparticles: Health Effects—Pros and Cons. Environ. Health Perspect. 2006, 114, 1818–1825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hamdan, S.; Pastar, I.; Drakulich, S.; Dikici, E.; Tomic-Canic, M.; Deo, S.; Daunert, S. Nanotechnology-Driven Therapeutic Interventions in Wound Healing: Potential Uses and Applications. ACS Cent. Sci. 2017, 3, 163–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pal, S.; Nisi, R.; Stoppa, M.; Licciulli, A. Silver-Functionalized Bacterial Cellulose as Antibacterial Membrane for Wound-Healing Applications. ACS Omega 2017, 2, 3632–3639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Radulescu, M.; Andronescu, E.; Dolete, G.; Popescu, R.C.; Fufă, O.; Chifiriuc, M.C.; Mogoantă, L.; Bălşeanu, T.A.; Mogoşanu, G.D.; Grumezescu, A.M.; et al. Silver Nanocoatings for Reducing the Exogenous Microbial Colonization of Wound Dressings. Materials 2016, 9, 345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vijayakumar, V.; Samal, S.K.; Mohanty, S.; Nayak, S.K. Recent advancements in biopolymer and metal nanoparticle-based materials in diabetic wound healing management. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 122, 137–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arafa, M.G.; El-Kased, R.F. Thermoresponsive gels containing gold nanoparticles as smart antibacterial and wound healing agents. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 13674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mârza, S.M.; Magyari, K.; Bogdan, S.; Moldovan, M.; Peştean, C.; Nagy, A.; Tăbăran, F.; Licarete, E.; Suarasan, S.; Dreanca, A.; et al. Skin wound regeneration with bioactive glass-gold nanoparticles ointment. Biomed. Mater. 2019, 14, 025011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, W.; Chen, C.; Zhang, X.; Wen, X.; Xiao, Y.; Li, L.; Xu, Q.; Fu, F.; Dia, H.; Liu, X. Layer-by-layer coating of carboxymethyl chitosan-gelatin-alginate on cotton gauze for hemostasis and wound healing. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2021, 406, 126644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mandapalli, P.K.; Labala, S.; Bojja, J.; Venuganti, V.V.K. Effect of pirfenidone delivered using layer-by-layer thin film on excisional wound healing. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2016, 83, 166–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asadi, N.; Pazoki-Toroudi, H.; Del Bakhshayesh, A.R.; Akbarzadeh, A.; Davaran, S.; Annabi, N. Multifunctional hydrogels for wound healing: Special focus on biomacromolecular based hydrogels. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 170, 728–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, K.; Wang, S.; Zhou, C.; Cheng, L.; Gao, X.; Xie, X.; Sun, J.; Wang, H.; Weir, M.D.; Reynolds, M.A.; et al. Advanced smart biomaterials and constructs for hard tissue engineering and regeneration. Bone Res. 2018, 6, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borkowska, M.; Godlewska, E.; Antosiak-Iwańska, M.; Kinasiewicz, J.; Borkowska, M.; Godlewska, E.; Antosiak-Iwa´nskaiwa´nska, M.; Kinasiewicz, J.; Strawski, M.; Szklarczyk, M.; et al. Suitability of Polyelectrolyte Shells Modified with Fullerene Derivate for Immunoisolation of Cells. Experimental Study. Artic. J. Biomed. Nanotechnol. 2012, 8, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tripathi, G.; Basu, B. A Porous Hydroxyapatite Scaffold for Bone Tissue Engineering: Physico-Mechanical and Biological Evaluations. Ceram. Int. 2012, 38, 341–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Almeida, A.; Figueredo, F.; Gonzaga da Cunha, A.; Casabona, G.; Ribeiro Costa de Faria, J.; Vicente Alves, E.; Sato, M.; Branco, A.; Guarnieri, C.; Palermo, E. Consensus Recommendations for the Use of Hyperdiluted Calcium Hydroxyapatite (Radiesse) as a Face and Body Biostimulatory Agent. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. Glob. Open 2019, 7, e2160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, L.; Mu, Z.; Yu, Y.; Zhang, L.; Hu, J. Polyethyleneimine-stabilized hydroxyapatite nanoparticles modified with hyaluronic acid for targeted drug delivery. RSC. Adv. 2016, 6, 101790–101799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Z.; Li, J.; Qu, J.; Sheng, W.; Yang, J.; Li, M. Cationized bombyx mori silk fibroin as a delivery carrier of the VEGF165–Ang-1 coexpression plasmid for dermal tissue regeneration. J. Mater. Chem. B 2019, 7, 80–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- David, G.; Clima, L.; Calin, M.; Constantinescu, C.A.; Balan-Porcarasu, M.; Uritu, C.M.; Simionescu, B.C. Squalene/polyethylenimine based non-viral vectors: Synthesis and use in systems for sustained gene release. Polym. Chem. 2018, 9, 1072–1081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, B.; Yang, J.; Peng, C.; Zhu, J.; Tang, Y.; Zhu, X.; Shi, X. PEGylated polyethylenimine-entrapped gold nanoparticles modified with folic acid for targeted tumor CT imaging. Colloids Surf. B 2016, 140, 489–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, B.; Zhao, L.; Shen, M.; Zhao, J.; Shi, X. A multifunctional polyethylenimine-based nanoplatform for targeted anticancer drug delivery to tumors in vivo. J. Mater. Chem. B 2017, 5, 1542–1550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grzeczkowicz, A.; Gruszczynska-Biegala, J.; Czeredys, M.; Kwiatkowska, A.; Strawski, M.; Szklarczyk, M.; Koźbiał, M.; Kuźnicki, J.; Granicka, L.H. Polyelectrolyte Membrane Scaffold Sustains Growth of Neuronal Cells. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. Part A 2019, 107, 839–850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Granicka, L.H.; Kawiak, J.W.; Glowacka, E.; Werynski, A. Encapsulation of OKT3 Cells in Hollow Fibers. ASAIO J. 1996, 42, M863–M865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Menzies, K.L.; Jones, L. The Impact of Contact Angle on the Biocompatibility of Biomaterials. Optom. Vis. Sci. 2010, 87, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diem, P.H.N.; Thao, D.T.T.; Van Phu, D.; Duy, N.N.; Quy, H.T.D.; Hoa, T.T.; Hien, N.Q. Synthesis of Gold Nanoparticles Stabilized in Dextran Solution by Gamma Co-60 Ray Irradiation and Preparation of Gold Nanoparticles/Dextran Powder. J. Chem. 2017, 2017, 6836375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mohandas, A.; Deepthi, S.; Biswas, R.; Jayakumar, R. Chitosan based metallic nanocomposite scaffolds as antimicrobial wound dressings. Bioact. Mater. 2018, 3, 267–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klębowski, B.; Depciuch, J.; Parlińska-Wojtan, M.; Baran, J. Applications of noble metal-based nanoparticles in medicine. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 4031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Panzarini, E.; Mariano, S.; Carata, E.; Mura, F.; Rossi, M.; Dini, L. Intracellular transport of silver and gold nanoparticles and biological responses: An update. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 1305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]




Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Drabik, M.; Grzeczkowicz, A.; Bącal, P.; Kwiatkowska, A.; Strawski, M.; Antosiak-Iwańska, M.; Kazimierczak, B.; Godlewska, E.; Granicka, L.H. Nanocomposite Membrane Scaffolds for Cell Function Maintaining for Biomedical Purposes. Nanomaterials 2021, 11, 1094. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano11051094
Drabik M, Grzeczkowicz A, Bącal P, Kwiatkowska A, Strawski M, Antosiak-Iwańska M, Kazimierczak B, Godlewska E, Granicka LH. Nanocomposite Membrane Scaffolds for Cell Function Maintaining for Biomedical Purposes. Nanomaterials. 2021; 11(5):1094. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano11051094
Chicago/Turabian StyleDrabik, Monika, Anna Grzeczkowicz, Paweł Bącal, Angelika Kwiatkowska, Marcin Strawski, Magdalena Antosiak-Iwańska, Beata Kazimierczak, Ewa Godlewska, and Ludomira H. Granicka. 2021. "Nanocomposite Membrane Scaffolds for Cell Function Maintaining for Biomedical Purposes" Nanomaterials 11, no. 5: 1094. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano11051094
APA StyleDrabik, M., Grzeczkowicz, A., Bącal, P., Kwiatkowska, A., Strawski, M., Antosiak-Iwańska, M., Kazimierczak, B., Godlewska, E., & Granicka, L. H. (2021). Nanocomposite Membrane Scaffolds for Cell Function Maintaining for Biomedical Purposes. Nanomaterials, 11(5), 1094. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano11051094






