Genotoxicity and Gene Expression in the Rat Lung Tissue following Instillation and Inhalation of Different Variants of Amorphous Silica Nanomaterials (aSiO2 NM)
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals
2.2. Nanomaterials (NM)
2.3. In Vivo Studies
2.3.1. Intratracheal Instillation Study
2.3.2. Short-Term Inhalation Study (STIS)
2.4. Comet Assay
2.4.1. Lung Cells Isolation for Comet Assay
2.4.2. Alkaline and Formamidopyrimidine DNA Glycosylase (FPG)-Modified Comet Assay
2.5. Protein Carbonylation Analysis of the Rat Lung Tissue
2.6. Gene Expression
2.6.1. RNA Extraction and Purification
2.6.2. Gene Expression Analysis of the Rat Lung Tissue—Affymetrix Analysis
2.6.3. Gene Expression Analysis of the Rat Lung Tissue—Custom TaqMan Array Cards (TAC)
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
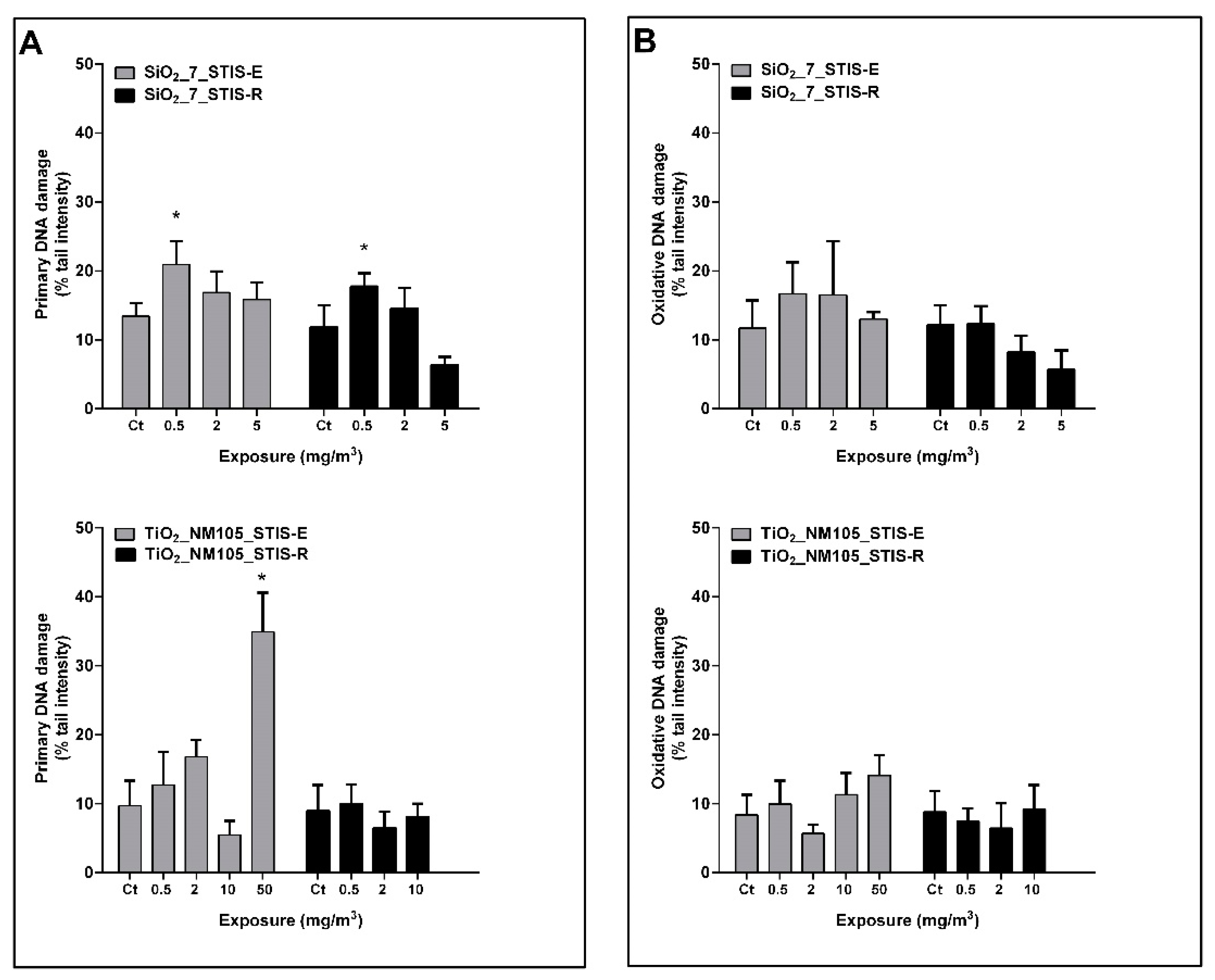
3.1. Primary and Oxidative DNA Damage in the Rat Lung Tissue
3.2. Protein Carbonylation in the Rat Lung Tissue
3.3. Gene Expression
3.3.1. Gene Expression Alterations in the Rat Lung Tissue—Affymetrix Analysis
3.3.2. Gene Expression Alterations in the Rat Lung Tissue—TAC Analysis
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Stark, W.J.; Stoessel, P.R.; Wohlleben, W.; Hafner, A. Industrial applications of nanoparticles. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2015, 44, 5793–5805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hyde, E.D.E.R.; Seyfaee, A.; Neville, F.; Moreno-Atanasio, R. Colloidal Silica Particle Synthesis and Future Industrial Manufacturing Pathways: A Review. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2016, 55, 8891–8913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeelani, P.G.; Mulay, P.; Venkat, R.; Ramalingam, C. Multifaceted Application of Silica Nanoparticles. A Review. Silicon 2019, 12, 1337–1354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guichard, Y.; Maire, M.-A.; Sébillaud, S.; Fontana, C.; Langlais, C.; Micillino, J.-C.; Darne, C.; Roszak, J.; Stępnik, M.; Fessard, V.; et al. Genotoxicity of synthetic amorphous silica nanoparticles in rats following short-term exposure, part 2: Intratracheal instillation and intravenous injection. Environ. Mol. Mutagen. 2015, 56, 228–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murugadoss, S.; Lison, D.; Godderis, L.; Brule, S.V.D.; Mast, J.; Brassinne, F.; Sebaihi, N.; Hoet, P.H. Toxicology of silica nanoparticles: An update. Arch. Toxicol. 2017, 91, 2967–3010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IARC. Arsenic, Metals, Fibres, and Dusts Volume 100 C A Review of Human Carcinogens; International Agency for Research on Cancer: Lyon, France, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- OECD. Silicon Dioxide: Summary of the Dossier; Series on the Safety of Manufactured Nanomaterials 71; Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development: Paris, France, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- ECETOC. Synthetic Amorphous Silica; (CAS No. 7631-86-9) JACC; European Centre for Ecotoxicology and Toxicology of Chemicals: Brussels, Belgium, 2006; ISBN 0773-6339-51. [Google Scholar]
- Gonzalez, L.; Lukamowicz-Rajska, M.; Thomassen, L.C.; Kirschhock, C.E.; Leyns, L.; Lison, D.; Martens, J.A.; Elhajouji, A.; Kirsch-Volders, M. Co-assessment of cell cycle and micronucleus frequencies demonstrates the influence of serum on the in vitro genotoxic response to amorphous monodisperse silica nanoparticles of varying sizes. Nanotoxicology 2014, 8, 876–884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Decan, N.; Wu, D.; Williams, A.; Bernatchez, S.; Johnston, M.; Hill, M.; Halappanavar, S. Characterization of in vitro genotoxic, cytotoxic and transcriptomic responses following exposures to amorphous silica of different sizes. Mutat. Res. Genet. Toxicol. Environ. Mutagen. 2016, 796, 8–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guichard, Y.; Fontana, C.; Chavinier, E.; Terzetti, F.; Gaté, L.; Binet, S.; Darne, C. Cytotoxic and genotoxic evaluation of different synthetic amorphous silica nanomaterials in the V79 cell line. Toxicol. Ind. Health 2016, 32, 1639–1650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haase, A.; Dommershausen, N.; Schulz, M.; Landsiedel, R.; Reichardt, P.; Krause, B.-C.; Tentschert, J.; Luch, A. Genotoxicity testing of different surface-functionalized SiO2, ZrO2 and silver nanomaterials in 3D human bronchial models. Arch. Toxicol. 2017, 91, 3991–4007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maser, E.; Schulz, M.; Sauer, U.G.; Wiemann, M.; Ma-Hock, L.; Wohlleben, W.; Hartwig, A.; Landsiedel, R. In vitro and in vivo genotoxicity investigations of differently sized amorphous SiO2 nanomaterials. Mutat. Res. Genet. Toxicol. Environ. Mutagen. 2015, 794, 57–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pfuhler, S.; Downs, T.R.; Allemang, A.J.; Shan, Y.; Crosby, M.E. Weak silica nanomaterial-induced genotoxicity can be explained by indirect DNA damage as shown by the OGG1-modified comet assay and genomic analysis. Mutagenesis 2017, 32, 5–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.; von Mikecz, A. Formation of nucleoplasmic protein aggregates impairs nuclear function in response to SiO2 nanoparticles. Exp. Cell Res. 2005, 305, 51–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, N.; Ma, L.; Wang, J.; Zheng, L.; Liu, J.; Duan, Y.; Liu, H.; Zhao, X.; Wang, S.; Wang, H.; et al. Interaction Between Nano-Anatase TiO2 and Liver DNA from Mice In Vivo. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2009, 5, 108–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.R.; Kim, M.J.; Lee, S.Y.; Oh, S.M.; Chung, K.H. Genotoxic effects of silver nanoparticles stimulated by oxidative stress in human normal bronchial epithelial (BEAS-2B) cells. Mutat. Res. Toxicol. Environ. Mutagen. 2011, 726, 129–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Li, N.; Zhao, J.; White, J.C.; Qu, P.; Xing, B. CuO Nanoparticle Interaction with Human Epithelial Cells: Cellular Uptake, Location, Export, and Genotoxicity. Chem. Res. Toxicol. 2012, 25, 1512–1521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barnes, C.A.; Elsaesser, A.; Arkusz, J.; Smok, A.; Palus, J.; Leśniak, A.; Salvati, A.; Hanrahan, J.P.; de Jong, W.H.; Dziubałtowska, E.; et al. Reproducible Comet Assay of Amorphous Silica Nanoparticles Detects No Genotoxicity. Nano Lett. 2008, 8, 3069–3074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, N.; Manshian, B.; Jenkins, G.; Griffiths, S.M.; Williams, P.M.; Maffeis, T.G.; Wright, C.; Doak, S.H. NanoGenotoxicology: The DNA damaging potential of engineered nanomaterials. Biomaterials 2009, 30, 3891–3914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doak, S.; Manshian, B.; Jenkins, G.; Singh, N. In vitro genotoxicity testing strategy for nanomaterials and the adaptation of current OECD guidelines. Mutat. Res. Toxicol. Environ. Mutagen. 2012, 745, 104–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jugan, M.-L.; Barillet, S.; Simon-Deckers, A.; Herlin-Boime, N.; Sauvaigo, S.; Douki, T.; Carriere, M. Titanium dioxide nanoparticles exhibit genotoxicity and impair DNA repair activity in A549 cells. Nanotoxicology 2011, 6, 501–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magdolenova, Z.; Collins, A.; Kumar, A.; Dhawan, A.; Stone, V.; Dusinska, M. Mechanisms of genotoxicity. A review of in vitro and in vivo studies with engineered nanoparticles. Nanotoxicology 2014, 8, 233–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Gioacchino, M.; Petrarca, C.; Lazzarin, F.; Di Giampaolo, L.; Sabbioni, E.; Boscolo, P.; Mariani-Costantini, R.; Bernardini, G. Immunotoxicity of nanoparticles. Int. J. Immunopathol. Pharmacol. 2011, 24, 65–71. [Google Scholar]
- Dalle-Donne, I.; Aldini, G.; Carini, M.; Colombo, R.; Rossi, R.; Milzani, A. Protein carbonylation, cellular dysfunction, and disease progression. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2006, 10, 389–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davies, M.J. The oxidative environment and protein damage. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Proteins Proteom. 2005, 1703, 93–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nel, A.; Xia, T.; Mädler, L.; Li, N. Toxic Potential of Materials at the Nanolevel. Science 2006, 311, 622–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arts, J.H.; Muijser, H.; Duistermaat, E.; Junker, K.; Kuper, C.F. Five-day inhalation toxicity study of three types of synthetic amorphous silicas in Wistar rats and post-exposure evaluations for up to 3months. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2007, 45, 1856–1867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brown, D.M.; Kanase, N.; Gaiser, B.; Johnston, H.; Stone, V. Inflammation and gene expression in the rat lung after instillation of silica nanoparticles: Effect of size, dispersion medium and particle surface charge. Toxicol. Lett. 2014, 224, 147–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Landsiedel, R.; Ma-Hock, L.; Hofmann, T.; Wiemann, M.; Strauss, V.; Treumann, S.; Wohlleben, W.; Gröters, S.; Wiench, K.; Van Ravenzwaay, B. Application of short-term inhalation studies to assess the inhalation toxicity of nanomaterials. Part. Fibre Toxicol. 2014, 11, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morris, A.S.; Adamcakova-Dodd, A.; Lehman, S.E.; Wongrakpanich, A.; Thorne, P.S.; Larsen, S.C.; Salem, A.K. Amine modification of nonporous silica nanoparticles reduces inflammatory response following intratracheal instillation in murine lungs. Toxicol. Lett. 2016, 241, 207–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, M.; Jing, L.; Wang, J.; Yu, Y.; Cao, L.; Zhang, L.; Zhou, X.; Sun, Z. Macrophages participate in local and systemic inflammation induced by amorphous silica nanoparticles through intratracheal instillation. Int. J. Nanomed. 2016, 11, 6217–6228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, Y.; Yun, W.Q.; Yue, L.M.; Shan, L.C.; Jian, Z.J. Pulmonary Toxicity in Rats Caused by Exposure to Intratracheal Instillation of SiO2 Nanoparticles. Biomed. Environ. Sci. 2017, 30, 264–279. [Google Scholar]
- Sutunkova, M.P.; Solovyeva, S.N.; Katsnelson, B.A.; Gurvich, V.B.; Privalova, L.I.; Minigalieva, I.A.; Slyshkina, T.V.; Valamina, I.E.; Makeyev, O.H.; Shur, V.Y.; et al. A paradoxical response of the rat organism to long-term inhalation of silica-containing submicron (predominantly nanoscale) particles of a collected industrial aerosol at realistic exposure levels. Toxicology 2017, 384, 59–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Großgarten, M.; Holzlechner, M.; Vennemann, A.; Balbekova, A.; Wieland, K.; Sperling, M.; Lendl, B.; Marchetti-Deschmann, M.; Karst, U.; Wiemann, M. Phosphonate coating of SiO2 nanoparticles abrogates inflammatory effects and local changes of the lipid composition in the rat lung: A complementary bioimaging study. Part. Fibre Toxicol. 2018, 15, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sayes, C.; Reed, K.L.; Glover, K.P.; Swain, K.A.; Ostraat, M.L.; Donner, E.M.; Warheit, D.B. Changing the dose metric for inhalation toxicity studies: Short-term study in rats with engineered aerosolized amorphous silica nanoparticles. Inhal. Toxicol. 2009, 22, 348–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, J.H.; Jeon, K.; Kim, J.K.; Kim, Y.; Jo, M.S.; Lee, J.S.; Baek, J.E.; Park, H.S.; An, H.J.; Park, J.D.; et al. Subacute inhalation toxicity study of synthetic amorphous silica nanoparticles in Sprague-Dawley rats. Inhal. Toxicol. 2017, 29, 567–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tarantini, A.; Huet, S.; Jarry, G.; Lanceleur, R.; Poul, M.; Tavares, A.M.; Vital, N.; Louro, H.; Silva, M.J.; Fessard, V. Genotoxicity of synthetic amorphous silica nanoparticles in rats following short-term exposure. Part 1: Oral route. Environ. Mol. Mutagen. 2015, 56, 218–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nemmar, A.; Yuvaraju, P.; Beegam, S.; Pathan, J.; Kazzam, E.E.; Ali, B.H. Oxidative stress, inflammation, and DNA damage in multiple organs of mice acutely exposed to amorphous silica nanoparticles. Int. J. Nanomed. 2016, 11, 919–928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mu, Q.; Hondow, N.S.; Krzemiński, Ł.; Brown, A.P.; Jeuken, L.J.C.; Routledge, M.N. Mechanism of cellular uptake of genotoxic silica nanoparticles. Part. Fibre Toxicol. 2012, 9, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- OECD. Test No. 489: In Vivo Mammalian Alkaline Comet Assay. In OECD Guidelines for the Testing of Chemicals, Section 4; OECD Publishing: Paris, France, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Doak, S.H.; Dusinska, M. NanoGenotoxicology: Present and the future. Mutagenesis 2017, 32, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Azqueta, A.; Dusinska, M. The use of the comet assay for the evaluation of the genotoxicity of nanomaterials. Front. Genet. 2015, 6, 239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collins, A.R. Measuring oxidative damage to DNA and its repair with the comet assay. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Gen. Subj. 2014, 1840, 794–800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Yan, J.; Ding, W.; Chen, Y.; Pack, L.M.; Chen, T. Genotoxicity and gene expression analyses of liver and lung tissues of mice treated with titanium dioxide nanoparticles. Mutagenesis 2016, 32, 33–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asare, N.; Duale, N.; Slagsvold, H.H.; Lindeman, B.; Olsen, A.K.; Gromadzka-Ostrowska, J.; Meczynska-Wielgosz, S.; Kruszewski, M.; Brunborg, G.; Instanes, C. Genotoxicity and gene expression modulation of silver and titanium dioxide nanoparticles in mice. Nanotoxicology 2015, 10, 312–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gosens, I.; Costa, P.M.; Olsson, M.; Stone, V.; Costa, A.L.; Brunelli, A.; Badetti, E.; Bonetto, A.; Bokkers, B.G.; de Jong, W.H.; et al. Pulmonary toxicity and gene expression changes after short-term inhalation exposure to surface-modified copper oxide nanoparticles. NanoImpact 2021, 22, 100313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karkossa, I.; Bannuscher, A.; Hellack, B.; Bahl, A.; Buhs, S.; Nollau, P.; Luch, A.; Schubert, K.; Von Bergen, M.; Haase, A. An in-depth multi-omics analysis in RLE-6TN rat alveolar epithelial cells allows for nanomaterial categorization. Part. Fibre Toxicol. 2019, 16, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arts, J.H.; Irfan, M.-A.; Keene, A.M.; Kreiling, R.; Lyon, D.; Maier, M.; Michel, K.; Neubauer, N.; Petry, T.; Sauer, U.G.; et al. Case studies putting the decision-making framework for the grouping and testing of nanomaterials (DF4nanoGrouping) into practice. Regul. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2016, 76, 234–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bahl, A.; Hellack, B.; Balas, M.; Dinischiotu, A.; Wiemann, M.; Brinkmann, J.; Luch, A.; Renard, B.Y.; Haase, A. Recursive feature elimination in random forest classification supports nanomaterial grouping. NanoImpact 2019, 15, 100179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiemann, M.; Vennemann, A.; Sauer, U.G.; Wiench, K.; Ma-Hock, L.; Landsiedel, R. An in vitro alveolar macrophage assay for predicting the short-term inhalation toxicity of nanomaterials. J. Nanobiotechnol. 2016, 14, 1–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karkossa, I.; Bannuscher, A.; Hellack, B.; Wohlleben, W.; Laloy, J.; Stan, M.S.; Dinischiotu, A.; Wiemann, M.; Luch, A.; Haase, A. Nanomaterials Induce Different Levels of Oxidative Stress, Depending on the Used Model System: Comparison of In Vitro and In Vivo Effects; Research Square: Durham, NC, USA, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Driessen, M.D.; Mues, S.; Vennemann, A.; Hellack, B.; Bannuscher, A.; Vimalakanthan, V.; Riebeling, C.; Ossig, R.; Wiemann, M.; Schnekenburger, J.; et al. Proteomic analysis of protein carbonylation: A useful tool to unravel nanoparticle toxicity mechanisms. Part. Fibre Toxicol. 2015, 12, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bannuscher, A.; Hellack, B.; Bahl, A.; Laloy, J.; Herman, H.; Stan, M.S.; Dinischiotu, A.; Giusti, A.; Krause, B.-C.; Tentschert, J.; et al. Metabolomics profiling to investigate nanomaterial toxicity in vitro and in vivo. Nanotoxicology 2020, 14, 807–826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- NanoToxClass. SOP Dispersion. Available online: https://www.nanopartikel.info/data/projekte/NanoToxClass/NanoToxClass-SOP_Dispersion_by_cup_horn_sonication_V2.0.pdf (accessed on 30 April 2021).
- Lozano, O.; Colaux, J.L.; Laloy, J.; Alpan, L.; Dogné, J.-M.; Lucas, S. Fast, asymmetric and nonhomogeneous clearance of SiC nanoaerosol assessed by micro-particle-induced x-ray emission. Nanomedicine 2018, 13, 145–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bessa, M.J.; Costa, C.; Reinosa, J.; Pereira, C.; Fraga, S.; Fernández, J.; Bañares, M.A.; Teixeira, J.P. Moving into advanced nanomaterials. Toxicity of rutile TiO2 nanoparticles immobilized in nanokaolin nanocomposites on HepG2 cell line. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2017, 316, 114–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Møller, P.; Azqueta, A.; Boutet-Robinet, E.; Koppen, G.; Bonassi, S.; Milić, M.; Gajski, G.; Costa, S.; Teixeira, J.P.; Pereira, C.C.; et al. Minimum Information for Reporting on the Comet Assay (MIRCA): Recommendations for describing comet assay procedures and results. Nat. Protoc. 2020, 15, 3817–3826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bahl, A.; Hellack, B.; Wiemann, M.; Giusti, A.; Werle, K.; Haase, A.; Wohlleben, W. Nanomaterial categorization by surface reactivity: A case study comparing 35 materials with four different test methods. NanoImpact 2020, 19, 100234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ihaka, R.; Gentleman, R. R: A Language for Data Analysis and Graphics. J. Comput. Graph. Stat. 1996, 5, 299–314. [Google Scholar]
- Carvalho, B.S.; Irizarry, R.A. A framework for oligonucleotide microarray preprocessing. Bioinformatics 2010, 26, 2363–2367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gentleman, R.C.; Carey, V.J.; Bates, D.M.; Bolstad, B.; Dettling, M.; Dudoit, S.; Ellis, B.; Gautier, L.; Ge, Y.; Gentry, J.; et al. Bioconductor: Open software development for computational biology and bioinformatics. Genome Biol. 2004, 5, R80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmittgen, T.D.; Livak, K.J. Analyzing real-time PCR data by the comparative C T method. Nat. Protoc. 2008, 3, 1101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashburner, M.; Ball, C.A.; Blake, J.; Botstein, D.; Butler, H.; Cherry, J.M.; Davis, A.P.; Dolinski, K.; Dwight, S.S.; Eppig, J.T.; et al. Gene Ontology: Tool for the unification of biology. Nat. Genet. 2000, 25, 25–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yazdimamaghani, M.; Moos, P.J.; Dobrovolskaia, M.A.; Ghandehari, H. Genotoxicity of amorphous silica nanoparticles: Status and prospects. Nanomed. Nanotechnol. Biol. Med. 2019, 16, 106–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neyrinck, A.; Van Hée, V.; Piront, N.; De Backer, F.; Toussaint, O.; Cani, P.D.; Delzenne, N.M. Wheat-derived arabinoxylan oligosaccharides with prebiotic effect increase satietogenic gut peptides and reduce metabolic endotoxemia in diet-induced obese mice. Nutr. Diabetes 2012, 2, e28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osier, M.; Oberörster, G. Intratracheal Inhalation vs Intratracheal Instillation: Differences in Particle Effects. Toxicol. Sci. 1997, 40, 220–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ECETOC. Poorly Soluble Particles/Lung Overload; Technical Report No. 122; European Center for Ecotoxicology and Toxicology of Chemicals: Brussels, Belgium, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Alessandrini, F.; Pimentel, J.A.A.; Landsiedel, R.; Wohlleben, W.; Mempel, M.; Marzaioli, V.; Weichenmeier, I.; Luxenhofer, G.; Wiemann, M.; Eiden, S.; et al. Surface modifications of silica nanoparticles are crucial for their inert versus proinflammatory and immunomodulatory properties. Int. J. Nanomed. 2014, 9, 2815–2832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gosens, I.; Post, J.A.; De La Fonteyne, L.J.J.; Jansen, E.H.J.M.; Geus, J.W.; Cassee, F.R.; De Jong, W.H. Impact of agglomeration state of nano- and submicron sized gold particles on pulmonary inflammation. Part. Fibre Toxicol. 2010, 7, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Von Essen, S.G.; Robbins, R.A.; Thompson, A.B.; Ertl, R.F.; Linder, J.; Rennard, S. Mechanisms of Neutrophil Recruitment to the Lung by Grain Dust Exposure. Am. Rev. Respir. Dis. 1988, 138, 921–927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fujiwara, N.; Kobayashi, K. Macrophages in inflammation. Curr. Drug Targets Inflamm. Allergy 2005, 4, 281–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyata, R.; van Eeden, S.F. The innate and adaptive immune response induced by alveolar macrophages exposed to ambient particulate matter. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2011, 257, 209–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liberman, A.C.; Budziñski, M.L.; Sokn, C.; Gobbini, R.P.; Steininger, A.; Arzt, E. Regulatory and Mechanistic Actions of Glucocorticoids on T and Inflammatory Cells. Front. Endocrinol. 2018, 9, 235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liberman, A.C.; Druker, J.; Perone, M.J.; Arzt, E. Glucocorticoids in the regulation of transcription factors that control cytokine synthesis. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2007, 18, 45–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abidin, Z.; Syafiq, A.; Rahim, R.A.; Arshad, M.; Khairuddin, M.; Nabilah, F.; Faudzi, M.; Voon, C.H.; Tang, T.-H.; Citartan, M. Current and potential developments of cortisol aptasensing towards point-of-care diagnostics (POTC). Sensors 2017, 17, 1180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lillehoj, E.P.; Kato, K.; Lu, W.; Kim, K.C. Cellular and Molecular Biology of Airway Mucins. Int. Rev. Cell Mol. Biol. 2013, 303, 139–202. [Google Scholar]
- Davies, D.E. The Role of the Epithelium in Airway Remodeling in Asthma. Proc. Am. Thorac. Soc. 2009, 6, 678–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- David, R.; Luu, O.; Damm, E.; Wen, J.; Nagel, M.; Winklbauer, R. Tissue cohesion and the mechanics of cell rearrangement. Development 2014, 141, 3672–3682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tremi, I.; Havaki, S.; Georgitsopoulou, S.; Lagopati, N.; Georgakilas, V.; Gorgoulis, V.; Georgakilas, A. A Guide for Using Transmission Electron Microscopy for Studying the Radiosensitizing Effects of Gold Nanoparticles In Vitro. Nanomaterials 2021, 11, 859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Engin, A.B.; Nikitovic, D.; Neagu, M.; Henrich-Noack, P.; Docea, A.O.; Shtilman, M.I.; Golokhvast, K.; Tsatsakis, A.M. Mechanistic understanding of nanoparticles’ interactions with extracellular matrix: The cell and immune system. Part. Fibre Toxicol. 2017, 14, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huwyler, J.; Kettiger, H.; Schipanski, A.; Wick, P. Engineered nanomaterial uptake and tissue distribution: From cell to organism. Int. J. Nanomed. 2013, 8, 3255–3269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, P.; Van Kirk, E.A.; Zhan, Y.; Murdoch, W.J.; Radosz, M.; Shen, Y. Targeted Charge-Reversal Nanoparticles for Nuclear Drug Delivery. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2007, 46, 4999–5002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asati, A.; Santra, S.; Kaittanis, C.; Perez, J.M. Surface-Charge-Dependent Cell Localization and Cytotoxicity of Cerium Oxide Nanoparticles. ACS Nano 2010, 4, 5321–5331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Tang, Y.; Xu, L.; Kong, X.; Zhang, L.; Chang, Y.; Zhao, H.; Zhang, H.; Liu, X. Dependence between cytotoxicity and dynamic subcellular localization of up-conversion nanoparticles with different surface charges. RSC Adv. 2017, 7, 33502–33509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soenen, S.J.; Rivera-Gil, P.; Montenegro, J.-M.; Parak, W.J.; De Smedt, S.C.; Braeckmans, K. Cellular toxicity of inorganic nanoparticles: Common aspects and guidelines for improved nanotoxicity evaluation. Nano Today 2011, 6, 446–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albi, E. Role of intranuclear lipids in health and disease. Clin. Lipidol. 2011, 6, 59–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lehman, S.E.; Morris, A.S.; Mueller, P.S.; Salem, A.K.; Grassian, V.H.; Larsen, S.C. Silica nanoparticle-generated ROS as a predictor of cellular toxicity: Mechanistic insights and safety by design. Environ. Sci. Nano 2016, 3, 56–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wajner, M.; Amaral, A.U. Mitochondrial dysfunction in fatty acid oxidation disorders: Insights from human and animal studies. Biosci. Rep. 2015, 36, e00281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rinaldo, P.; Cowan, T.M.; Matern, D. Acylcarnitine profile analysis. Genet. Med. 2008, 10, 151–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pannkuk, E.L.; Laiakis, E.C.; Authier, S.; Wong, K.; Fornace, A.J., Jr. Targeted metabolomics of nonhuman primate serum after exposure to ionizing radiation: Potential tools for high-throughput biodosimetry. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 51192–51202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma-Hock, L.; Burkhardt, S.; Strauss, V.; Gamer, A.O.; Wiench, K.; Van Ravenzwaay, B.; Landsiedel, R. Development of a Short-Term Inhalation Test in the Rat Using Nano-Titanium Dioxide as a Model Substance. Inhal. Toxicol. 2009, 21, 102–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klein, C.L.; Wiench, K.; Wiemann, M.; Ma-Hock, L.; Van Ravenzwaay, B.; Landsiedel, R. Hazard identification of inhaled nanomaterials: Making use of short-term inhalation studies. Arch. Toxicol. 2012, 86, 1137–1151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Wang, Y.; Ba, T.; Li, Y.; Pu, J.; Chen, T.; Song, Y.; Gu, Y.; Qian, Q.; Yang, J. Genotoxic evaluation of titanium dioxide nanoparticles in vivo and in vitro. Toxicol. Lett. 2014, 226, 314–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noël, A.; Truchon, G. Inhaled Titanium Dioxide Nanoparticles: A Review of Their Pulmonary Responses with Particular Focus on the Agglomeration State. Nano Life 2015, 5, 1450008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naya, M.; Kobayashi, N.; Ema, M.; Kasamoto, S.; Fukumuro, M.; Takami, S.; Nakajima, M.; Hayashi, M.; Nakanishi, J. In vivo genotoxicity study of titanium dioxide nanoparticles using comet assay following intratracheal instillation in rats. Regul. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2012, 62, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindberg, H.K.; Falck, G.C.-M.; Catalán, J.; Koivisto, A.J.; Suhonen, S.; Järventaus, H.; Rossi, E.M.; Nykäsenoja, H.; Peltonen, Y.; Moreno, C.; et al. Genotoxicity of inhaled nanosized TiO2 in mice. Mutat. Res. Toxicol. Environ. Mutagen. 2012, 745, 58–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Relier, C.; Dubreuil, M.; Cordelli, E.; Mejia, J.; Eleuteri, P.; Robidel, F.; Loret, T.; Pacchierotti, F.; Lucas, S.; Lacroix, G.; et al. Study of TiO 2 P25 nanoparticles genotoxicity on lung, blood and liver cells in lung overload and non-overload conditions after repeated respiratory exposure in rats. Toxicol. Sci. 2017, 156, 527–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Jacobsen, N.R.; Møller, P.; Jensen, K.A.; Vogel, U.; Ladefoged, O.; Loft, S.; Wallin, H. Lung inflammation and genotoxicity following pulmonary exposure to nanoparticles in ApoE-/-mice. Part. Fibre Toxicol. 2009, 6, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kane, A.B.; Hurt, R.H.; Gao, H. The asbestos-carbon nanotube analogy: An update. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2018, 361, 68–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, X.; Zhang, X.; Sun, L.; Wei, Y.; Wei, X. Cellular Toxicity and Immunological Effects of Carbon-based Nanomaterials. Part. Fibre Toxicol. 2019, 16, 1–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| NM | Exposure Conditions | Applied Dose [mg/m3] | Effective Dose [mg/m3] |
|---|---|---|---|
| SiO2_7 | Exposure group | 0.5 | 0.74 |
| 2 | 2.58 | ||
| 5 | 5.02 | ||
| Recovery group | 0.5 | 0.97 | |
| 2 | 1.41 | ||
| 5 | 5.30 | ||
| TiO2_NM105 | Exposure group | 0.5 | 2.5 |
| 2 | 4.92 | ||
| 10 | 14.98 | ||
| 50 | 41.97 | ||
| Recovery group | 0.5 | 2.47 | |
| 2 | 3.41 | ||
| 10 | 11.57 |
| Protein Carbonylation (Relative to Controls, %) | Category | Oxidative Stress Potential |
|---|---|---|
| 100 ± 15 | 1 | None (No) |
| 115–150 | 2 | Low (L) |
| 150–200 | 3 | Medium (M) |
| >200 | 4 | High (H) |
| NM | 0.09 mg | 0.18 mg | 0.36 mg | Overall Category |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| SiO2_15_Unmod_E | 0.80 (No) | 1.30 (L) | 0.71 (No) | L |
| SiO2_15_Amino_E | 1.09 (No) | 0.76 (No) | 1.67 (M) | M |
| SiO2_7_E | 1.03 (No) | 0.51 (No) | 1.30 (L) | L |
| SiO2_40_E | 1.16 (L) | 0.78 (No) | 0.74 (No) | L |
| NM | 0.5 mg/m3 | 2 mg/m3 | 5 mg/m3 | 10 mg/m3 | 50 mg/m3 | Overall Category |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SiO2_7 STIS-E | 0.79 (L) | 1.01 (L) | 1.57 (M) | NA | NA | M |
| TiO2_NM105_STIS-E | 0.68 (L) | 1.04 (L) | NA | 1.41 (M) | 5.53 (H) | H |
| NM | Exposure Condition | Rank | Id | Size | p Value | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SiO2_15_Unmod | Exposure Group | 1 | GO:0007127 | 83 (112) | 6.00 × 10−7 | meiosis I |
| 2 | GO:0048247 | 42 (46) | 3.50 × 10−6 | lymphocyte chemotaxis | ||
| 3 | GO:0071459 | 15 (21) | 5.20 × 10−6 | protein localization to chromosome, centromeric | ||
| 4 | GO:0060340 | 10 (11) | 8.20 × 10−6 | positive regulation of type I interferon-mediated | ||
| 5 | GO:0070098 | 63 (66) | 1.30 × 10−5 | chemokine-mediated signaling pathway | ||
| 6 | GO:0072676 | 73 (78) | 2.00 × 10−5 | lymphocyte migration | ||
| 7 | GO:0045132 | 67 (93) | 3.20 × 10−5 | meiotic chromosome segregation | ||
| 8 | GO:0034501 | 13 (18) | 4.20 × 10−5 | protein localization to kinetochore | ||
| 9 | GO:0034502 | 64 (76) | 1.80 × 10−4 | protein localization to chromosome | ||
| 10 | GO:0070192 | 53 (72) | 1.90 × 10−4 | chromosome organization involved in meiotic cell cycle | ||
| Recovery Group | 1 | GO:0048680 | 9 (11) | 2.20 × 10−5 | positive regulation of axon regeneration | |
| 2 | GO:0070572 | 10 (12) | 8.80 × 10−5 | positive regulation of neuron projection | ||
| 3 | GO:2001223 | 10 (11) | 1.60 × 10−4 | negative regulation of neuron migration | ||
| 4 | GO:2000849 | 11 (11) | 1.60 × 10−4 | regulation of glucocorticoid secretion | ||
| 5 | GO:0071300 | 65 (76) | 3.30 × 10−4 | cellular response to retinoic acid | ||
| 6 | GO:0003348 | 6 (6) | 3.60 × 10−4 | cardiac endothelial cell differentiation | ||
| 7 | GO:0060956 | 6 (6) | 3.60 × 10−4 | endocardial cell differentiation | ||
| 8 | GO:0006297 | 5 (5) | 3.70 × 10−4 | nucleotide-excision repair, DNA gap filling | ||
| 9 | GO:0035933 | 12 (12) | 5.10 × 10−4 | glucocorticoid secretion | ||
| 10 | GO:2000852 | 5 (5) | 5.50 × 10−4 | regulation of corticosterone secretion | ||
| SiO2_15_Amino | Exposure Group | 1 | GO:0000910 | 96 (110) | 1.50 × 10−7 | cytokinesis |
| 2 | GO:0000281 | 42 (47) | 4.00 × 10−7 | mitotic cytokinesis | ||
| 3 | GO:0033260 | 23 (30) | 5.40 × 10−6 | nuclear DNA replication | ||
| 4 | GO:0071459 | 15 (21) | 7.60 × 10−6 | protein localization to chromosome, centromeric | ||
| 5 | GO:0051383 | 12 (14) | 1.80 × 10−5 | kinetochore organization | ||
| 6 | GO:0051414 | 7 (7) | 2.00 × 10−5 | response to cortisol | ||
| 7 | GO:0040020 | 31 (35) | 2.30 × 10−5 | regulation of meiotic nuclear division | ||
| 8 | GO:0061640 | 49 (56) | 2.50 × 10−5 | cytoskeleton-dependent cytokinesis | ||
| 9 | GO:0051445 | 45 (51) | 2.50 × 10−5 | regulation of meiotic cell cycle | ||
| 10 | GO:1902969 | 9 (10) | 3.90 × 10−5 | mitotic DNA replication | ||
| Recovery Group | 1 | GO:0035082 | 44 (60) | 1.90 × 10−14 | axoneme assembly | |
| 2 | GO:0003341 | 44 (64) | 7.10 × 10−13 | cilium movement | ||
| 3 | GO:0001578 | 66 (89) | 4.80 × 10−8 | microtubule bundle formation | ||
| 4 | GO:0002385 | 25 (39) | 2.60 × 10−5 | mucosal immune response | ||
| 5 | GO:0060294 | 15 (17) | 3.50 × 10−5 | cilium movement involved in cell motility | ||
| 6 | GO:0030199 | 38 (44) | 5.10 × 10−5 | collagen fibril organization | ||
| 7 | GO:0001539 | 19 (22) | 5.20 × 10−5 | cilium or flagellum-dependent cell motility | ||
| 8 | GO:0060285 | 19 (22) | 5.20 × 10−5 | cilium-dependent cell motility | ||
| 9 | GO:0002251 | 26 (40) | 5.20 × 10−5 | organ or tissue specific immune response | ||
| 10 | GO:0048755 | 13 (13) | 6.50 × 10−5 | branching morphogenesis of a nerve |
| Gene Symbol | Gene Name | 3 Days_E | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SiO2_15_Unmod | SiO2_15_Amino | ||||
| p Value | FC | p Value | FC | ||
| Retnla | resistin like alpha | 1.61 × 10−5 | 4.37 | 1.40 × 10−6 | 6.00 |
| Spp1 | secreted phosphoprotein 1 | 2.00 × 10−5 | 4.05 | 7.86 × 10−4 | 2.67 |
| Slc26a4 | solute carrier family 26-member 4 | 2.72 × 10−5 | 5.77 | 3.57 × 10−4 | 3.95 |
| Clvs2 | clavesin 2 | 4.04 × 10−5 | 0.60 | 2.74 × 10−4 | 0.66 |
| Zbp1 | Z-DNA binding protein 1 | 5.22 × 10−5 | 0.49 | 1.55 × 10−3 | 0.60 |
| Nupr1 | nuclear protein 1, transcriptional regulator | 1.47 × 10−4 | 1.64 | 1.18 × 10−3 | 1.48 |
| Gas2l3 | growth arrest-specific 2 like 3 | 1.51 × 10−4 | 2.01 | 2.23 × 10−4 | 1.96 |
| Cfi | complement factor I | 1.78 × 10−4 | 2.22 | 8.85 × 10−4 | 1.96 |
| Ect2 | epithelial cell transforming 2 | 2.52 × 10−4 | 2.53 | 4.20 × 10−5 | 3.00 |
| Qrfpr | pyroglutamylated RFamide peptide receptor | 3.43 × 10−4 | 2.39 | 8.19 × 10−4 | 2.21 |
| Cdk1 | cyclin-dependent kinase 1 | 4.72 × 10−4 | 2.32 | 5.76 × 10−5 | 2.81 |
| Clybl | citrate lyase beta like | 5.64 × 10−4 | 1.90 | 3.12 × 10−5 | 2.33 |
| LOC100909700 | CD177 antigen-like | 5.97 × 10−4 | 2.55 | 1.88 × 10−5 | 3.68 |
| Lcn2 | lipocalin 2 | 6.94 × 10−4 | 2.32 | 1.71 × 10−4 | 2.64 |
| Hmmr | hyaluronan-mediated motility receptor | 8.12 × 10−4 | 2.25 | 1.30 × 10−4 | 2.67 |
| Fbxo5 | F-box protein 5 | 8.13 × 10−4 | 1.81 | 2.49 × 10−4 | 1.96 |
| Cdkn3 | cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor 3 | 1.07 × 10−3 | 2.36 | 1.85 × 10−4 | 2.82 |
| Olr196 | olfactory receptor 196 | 2.04 × 10−3 | 0.69 | 6.58 × 10−4 | 0.66 |
| Mmp12 | matrix metallopeptidase 12 | 2.09 × 10−3 | 3.65 | 7.07 × 10−4 | 4.36 |
| Wdr35 | WD repeat domain 35 | 2.09 × 10−3 | 1.59 | 1.46 × 10−3 | 1.62 |
| Ndc80 | NDC80 kinetochore complex component | 2.15 × 10−3 | 2.19 | 7.57 × 10−4 | 2.42 |
| Cxcl9 | C-X-C motif chemokine ligand 9 | 2.17 × 10−3 | 1.84 | 6.51 × 10−4 | 2.02 |
| Nusap1 | nucleolar and spindle associated protein 1 | 2.26 × 10−3 | 2.89 | 1.49 × 10−3 | 3.06 |
| Ncapg | non-SMC condensin I complex, subunit G | 2.39 × 10−3 | 1.99 | 5.72 × 10−4 | 2.26 |
| L2hgdh | L-2-hydroxyglutarate dehydrogenase | 3.08 × 10−3 | 1.42 | 6.31 × 10−4 | 1.53 |
| Cenpw | centromere protein W | 3.33 × 10−3 | 2.20 | 3.75 × 10−4 | 2.77 |
| Fabp5 | fatty acid binding protein 5 | 3.45 × 10−3 | 1.43 | 1.56 × 10−4 | 1.66 |
| Gene symbol | Gene name | 21 days_R | |||
| SiO2_15_Unmod | SiO2_15_Amino | ||||
| p value | FC | p value | FC | ||
| Nrg1 | neuregulin 1 | 2.55 × 10−5 | 2.05 | 1.71 × 10−4 | 2.35 |
| Olfml3 | olfactomedin-like 3 | 3.8 × 10−4 | 0.66 | 8.39 × 10−6 | 0.43 |
| Gas8 | growth arrest specific 8 | 4.69 × 10−4 | 1.47 | 5.29 × 10−5 | 1.96 |
| Emp1 | epithelial membrane protein 1 | 6.32 × 10−4 | 0.53 | 1.41 × 10−4 | 0.35 |
| Col6a1 | collagen, type VI, alpha 1 | 1.13 × 10−3 | 0.69 | 6.35 × 10−5 | 0.49 |
| Tsnaxip1 | translin-associated factor X interacting protein 1 | 1.76 × 10−3 | 1.62 | 2.92 × 10−5 | 2.82 |
| Cfap45 | cilia and flagella associated protein 45 | 2.45 × 10−3 | 1.87 | 4.48 × 10−4 | 2.95 |
| Creg1 | cellular repressor of E1A-stimulated genes 1 | 2.92 × 10−3 | 1.50 | 1.05 × 10−4 | 2.30 |
| Syt5 | synaptotagmin 5 | 3.41 × 10−3 | 1.58 | 1.62 × 10−4 | 2.51 |
| Pigr | polymeric immunoglobulin receptor | 3.94 × 10−3 | 1.48 | 3.09 × 10−4 | 2.12 |
| Tekt4 | tektin 4 | 3.96 × 10−3 | 1.44 | 6.31 × 10−5 | 2.25 |
| SiO2_7 | SiO2_40 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gene Symbol | NM | 3 Days_E | 21 Days_R | 3 Days_E | 21 Days_R |
| Adrb2 | NM_012492 | 0.96 ± 0.10 | 1.06 ± 0.22 | 0.78 ± 0.02 | 0.94 ± 0.19 |
| Anxa3 | NM_012823 | 1.26 ± 0.35 | 0.93 ± 0.08 | 0.60 ± 0.04 * | 0.98 ± 0.08 |
| Casp1 | NM_012762 | 1.09 ± 0.11 | 1.04 ± 0.07 | 1.14 ± 0.64 | 1.08 ± 0.17 |
| Casp3 | NM_012922 | 1.18 ± 0.16 | 1.45 ± 0.23 * | 1.25 ± 0.27 | 1.17 ± 0.02 |
| CD40 | NM_134360 | 1.00 ± 0.13 | 1.13 ± 0.33 | 0.83 ± 0.07 | 0.75 ± 0.08 |
| CD 40 lg | NM_053353 | 1.56 ± 1.21 | 1.14 ± 0.43 | 1.71 ± 0.52 | 1.32 ± 0.21 |
| CXCL1 | NM_030845 | 2.99 ± 2.45 | 0.96 ± 0.47 | 3.93 ± 3.10 | 1.38 ± 0.77 |
| GSTA1 | NM_031509 | 0.86 ± 0.13 | 0.73 ± 0.03 * | 0.67 ± 0.07 | 0.97 ± 0.05 |
| HMOX-1 | NM_012580 | 1.65 ± 0.33 * | 1.31 ± 0.45 | 1.63 ± 0.81 | 1.27 ± 0.35 |
| Icam1 | NM_012967 | 1.09 ± 0.23 | 1.09 ± 0.08 | 0.79 ± 0.07 * | 1.05 ± 0.09 |
| IL-1b | NM_031512 | 1.12 ± 0.59 | 1.50 ± 0.27 | 1.36 ± 0.08 | 1.47 ± 0.14 * |
| Il1r1 | NM_013123 | 1.01 ± 0.06 | 1.15 ± 0.09 | 0.90 ± 0.12 | 1.08 ± 0.06 |
| Il1rl1 | NM_013037 | 1.05 ± 0.48 | 1.12 ± 0.37 | 1.31 ± 0.55 | 1.21 ± 0.05 * |
| Itga1 | NM_030994 | 1.44 ± 0.34 | 1.11 ± 0.02 | 1.05 ± 0.14 | 1.10 ± 0.08 |
| Itgam | NM_012711 | 1.01 ± 0.22 | 1.10 ± 0.28 | 0.99 ± 0.26 | 1.34 ± 0.39 |
| Itgb1 | NM_017022 | 1.22 ± 0.48 | 1.09 ± 0.10 | 1.25 ± 0.90 | 1.08 ± 0.05 |
| Itgb2 | NM_001037780 | 1.59 ± 0.80 | 1.15 ± 0.06 | 1.17 ± 0.40 | 1.36 ± 0.04 |
| Mapk3 | NM_017347 | 1.13 ± 0.41 | 1.24 ± 0.19 | 0.80 ± 0.08 | 0.97 ± 0.11 |
| Mapk8 | NM_053829 | 1.60 ± 0.53 | 1.18 ± 0.13 | 0.82 ± 0.10 | 1.00 ± 0.16 |
| Mapk14 | NM_031020 | 1.20 ± 0.29 | 1.10 ± 0.03 | 0.91 ± 0.09 | 1.01 ± 0.08 |
| Nos2 | NM_012611 | 0.73 ± 0.47 | 1.03 ± 0.23 | 1.13 ± 0.75 | 0.28 ± 0.53 |
| NQO1 | NM_017000 | 1.16 ± 0.25 | 1.03 ± 0.13 | 1.11 ± 0.38 | 1.01 ± 0.12 |
| OGG1 | NM_030870 | 1.12 ± 0.19 | 1.16 ± 0.12 | 1.19 ± 0.10 | 1.10 ± 0.26 |
| Pde4d | NM_001113328 | 1.14 ± 0.18 | 1.18 ± 0.07 | 1.09 ± 0.14 | 1.07 ± 0.04 |
| Pla2g7 | NM_001009353 | 1.13 ± 0.32 | 1.13 ± 0.55 | 1.72 ± 0.51 | 1.39 ± 0.11 |
| Plcb2 | NM_053478 | 1.30 ± 0.22 | 1.37 ± 0.25 | 0.83 ± 0.12 | 1.24 ± 0.13 |
| Plcb3 | NM_033350 | 1.11 ± 0.02 | 1.08 ± 0.03 | 1.02 ± 0.18 | 1.11 ± 0.14 |
| Plcd1 | NM_017035 | 1.39 ± 0.20 * | 1.33 ± 0.13 | 0.97 ± 0.18 | 1.26 ± 0.20 |
| Ptgir | NM_001077644 | 1.18 ± 0.50 | 1.23 ± 0.16 | 1.00 ± 0.18 | 1.03 ± 0.12 |
| Ptgis | NM_031557 | 1.00 ± 0.14 | 1.06 ± 0.11 | 1.20 ± 0.46 | 0.85 ± 0.21 |
| Ptgs2 | NM_017232 | 1.39 ± 0.58 | 0.90 ± 0.37 | 1.76 ± 0.26 | 1.76 ± 1.50 |
| RPLPO | NM_022402 | 0.85 ± 0.47 | 1.14 ± 0.08 | 0.50 ± 0.12 | 1.14 ± 0.04 |
| SOD2 | NM_017051 | 1.44 ± 0.33 | 0.96 ± 0.19 | 1.36 ± 0.20 * | 1.14 ± 0.24 |
| TNF | NM_012675 | 0.91 ± 0.57 | 1.14 ± 0.06 | 1.11 ± 0.47 | 1.31 ± 0.58 |
| Tnfrsf1a | NM_013091 | 1.06 ± 0.24 | 1.07 ± 0.10 | 1.05 ± 0.21 | 0.99 ± 0.03 |
| Vcam1 | NM_012889 | 0.87 ± 0.23 | 1.33 ± 0.05 * | 1.05 ± 0.13 | 1.20 ± 0.21 |
| SiO2_7 | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| STIS-E | STIS-R | ||||||
| Gene Symbol | NM | 0.5 mg/m3 | 2 mg/m3 | 5 mg/m3 | 0.5 mg/m3 | 2 mg/m3 | 5 mg/m3 |
| Adrb2 | NM_012492 | 0.68 ± 0.07 * | 0.74 ± 0.01 * | 0.60 ± 0.06 * | 0.63 ± 0.02 * | 0.56 ± 0.17 * | 0.65 ± 0.08 |
| Anxa3 | NM_012823 | 0.70 ± 0.13 | 0.74 ± 0.10 | 0.49± 0.14 * | 0.74 ± 0.08 * | 0.62 ± 0.02 * | 0.64 ± 0.04 * |
| Casp1 | NM_012762 | 0.88 ± 0.06 | 0.72 ± 0.10 | 0.61 ± 0.07 * | 1.05 ± 0.47 | 1.09 ± 0.22 | 1.02 ± 0.09 |
| Casp3 | NM_012922 | 0.96 ± 0.05 | 1.26 ± 0.22 | 0.83 ± 0.01 | 1.27 ± 0.40 | 0.82 ± 0.11 * | 0.96 ± 0.07 |
| CD40 | NM_134360 | 3.33 ± 4.03 | 0.82 ± 0.37 | 1.04 ± 0.31 | 1.33 ± 0.46 | 1.03 ± 0.17 | 1.00 ± 0.17 |
| CD 40 lg | NM_053353 | 1.21 ± 0.37 | 2.35 ± 0.75 * | 1.05 ± 0.11 | 0.50 ± 0.05 | 0.48 ± 0.06 | 0.57 ± 0.06 |
| CXCL1 | NM_030845 | 2.34 ± 0.97 | 10.55 ± 8.86 | 7.25 ± 2.00 * | 1.32 ± 0.25 | 1.53 ± 0.56 | 1.99 ± 1.12 |
| GSTA1 | NM_031509 | 0.47 ± 0.97 | 0.63 ± 0.31 | 0.48 ± 0.03 | 0.77 ± 0.08 | 0.93 ± 0.26 | 0.68 ± 0.14 |
| HMOX-1 | NM_012580 | 0.97 ± 0.20 | 1.78 ± 0.36 | 1.17 ± 0.05 | 0.86 ± 0.09 | 0.81 ± 0.17 | 0.89 ± 0.24 |
| Icam1 | NM_012967 | 1.04 ± 0.15 | 0.93 ± 0.13 | 0.86 ± 0.09 | 1.08 ± 0.08 | 0.93 ± 0.17 | 1.10 ± 0.04 |
| IL-1b | NM_031512 | 2.05 ± 0.45 * | 3.70 ± 0.39 * | 2.91 ± 0.79 * | 0.85 ± 0.02 | 0.49 ± 0.05 * | 0.72 ± 0.13 |
| Il1r1 | NM_013123 | 0.96 ± 0.12 | 0.96 ± 0.13 | 0.89 ± 0.04 * | 0.97 ± 0.08 | 0.72 ± 0.16 * | 0.92 ± 0.07 |
| Il1rl1 | NM_013037 | 0.97 ± 0.28 | 1.19 ± 0.22 | 0.70 ± 0.05 * | 0.94 ± 0.46 | 0.92 ± 0.21 | 0.93 ± 0.16 |
| Itga1 | NM_030994 | 1.16 ± 0.09 | 1.44 ± 0.42 | 0.96 ± 0.11 | 1.25 ± 0.16 | 0.84 ± 0.18 | 0.95 ± 0.10 |
| Itgam | NM_012711 | 1.45 ± 0.42 | 3.10 ± 0.84 * | 3.70 ± 1.18 * | 1.01 ± 0.45 | 0.69 ± 0.27 | 1.00 ± 0.02 |
| Itgb1 | NM_017022 | 0.86 ± 0.15 | 0.74 ± 0.03 * | 0.65 ± 0.05 * | 0.71 ± 0.09 * | 0.75 ± 0.16 | 0.81 ± 0.34 |
| Itgb2 | NM_001037780 | 0.90 ± 0.09 | 1.01 ± 0.19 | 0.83 ± 0.10 | 0.87 ± 0.07 | 0.76 ± 0.13 * | 1.00 ± 0.11 |
| Mapk3 | NM_017347 | 0.90 ± 0.18 | 0.90 ± 0.12 | 0.85 ± 0.14 | 0.96 ± 0.29 | 0.85 ± 0.36 | 0.93 ±0.25 |
| Mapk8 | NM_053829 | 0.74 ± 0.23 | 0.98 ± 0.23 | 0.73 ± 0.07 | 0.87 ± 0.10 | 0.91 ± 0.33 | 1.33 ± 0.41 |
| Mapk14 | NM_031020 | 0.98 ± 0.09 | 1.01 ± 0.10 | 0.79 ± 0.07 * | 1.08 ± 0.18 | 0.88 ± 0.08 | 0.96 ± 0.02 |
| Nos2 | NM_012611 | 5.13 ± 2.31 * | 13.29 ± 3.29 * | 11.71 ± 5.97 * | 1.92 ± 2.45 | 0.46 ± 0.34 | 1.41 ± 1.39 |
| NQO1 | NM_017000 | 0.71 ± 0.05 * | 0.96 ± 0.31 | 0.69 ± 0.05 * | 1.31 ± 0.38 | 0.94 ± 0.22 | 1.10 ± 0.07 |
| OGG1 | NM_030870 | 0.79 ± 0.10 | 0.92 ± 0.18 | 0.59 ± 0.07 | 0.82 ± 0.10 | 0.93 ± 0.26 | 0.81 ± 0.07 |
| Pde4d | NM_001113328 | 0.91 ± 0.27 | 1.04 ± 0.06 | 0.65 ± 0.10 * | 1.02 ± 0.20 | 0.91 ± 0.21 | 1.03 ± 0.14 |
| Pla2g7 | NM_001009353 | 1.09 ± 0.23 | 2.10 ± 0.42 * | 0.92 ± 0.24 | 0.77 ± 0.10 | 0.39 ± 0.06 * | 0.83 ± 0.28 |
| Plcb2 | NM_053478 | 0.74 ± 0.08 * | 1.31 ± 0.32 | 0.71 ± 0.11 * | 1.04 ± 0.18 | 0.79 ± 0.14 | 0.99 ± 0.32 |
| Plcb3 | NM_033350 | 1.05 ± 0.16 | 1.18 ± 0.06 * | 0.83 ± 0.04 * | 0.99 ± 0.12 | 0.71 ± 0.10 * | 0.81 ± 0.04 * |
| Plcd1 | NM_017035 | 0.97 ± 0.20 | 1.09 ± 0.28 | 0.71 ± 0.06 * | 0.68 ± 0.06 | 0.57 ± 0.12 * | 0.60 ± 0.06 * |
| Ptgir | NM_001077644 | 0.84 ± 0.15 | 0.99 ± 0.26 | 0.70 ± 0.17 | 1.12 ± 0.12 | 0.89 ± 0.07 | 1.07 ± 0.35 |
| Ptgis | NM_031557 | 0.83 ± 0.16 | 1.08 ± 0.29 | 0.68 ± 0.09 * | 1.11 ± 0.23 | 1.00 ± 0.10 | 0.76 ± 0.05 |
| Ptgs2 | NM_017232 | 0.96 ± 0.30 | 2.31 ± 0.57 * | 0.89 ± 0.39 | 1.55 ± 0.54 | 0.94 ± 0.59 | 0.77 ± 0.23 |
| RPLPO | NM_022402 | 0.98 ± 0.02 | 1.57 ± 1.00 | 0.92 ± 0.06 | 1.39 ± 0.29 | 0.91 ± 0.18 | 0.96 ± 0.07 |
| SOD2 | NM_017051 | 1.19 ± 0.15 | 2.21 ± 0.40 * | 2.68 ± 0.30 * | 1.31 ± 0.68 | 1.11 ± 0.22 | 1.09 ± 0.11 |
| TNF | NM_012675 | 2.05 ± 0.26 * | 5.49 ± 1.90 * | 6.39 ± 3.37 * | 1.41 ± 0.34 | 1.28 ± 0.22 | 1.38 ± 0.53 |
| Tnfrsf1a | NM_013091 | 0.90 ± 0.04 | 0.97 ± 0.21 | 0.80 ± 0.11 | 1.04 ± 0.13 | 0.85 ± 0.17 | 0.97 ± 0.06 |
| Vcam1 | NM_012889 | 0.95 ± 0.17 | 1.15 ± 0.10 | 1.07 ± 0.24 | 1.22 ± 0.11 | 1.32 ± 0.46 | 1.10 ± 0.24 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Brandão, F.; Costa, C.; Bessa, M.J.; Dumortier, E.; Debacq-Chainiaux, F.; Hubaux, R.; Salmon, M.; Laloy, J.; Stan, M.S.; Hermenean, A.; et al. Genotoxicity and Gene Expression in the Rat Lung Tissue following Instillation and Inhalation of Different Variants of Amorphous Silica Nanomaterials (aSiO2 NM). Nanomaterials 2021, 11, 1502. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano11061502
Brandão F, Costa C, Bessa MJ, Dumortier E, Debacq-Chainiaux F, Hubaux R, Salmon M, Laloy J, Stan MS, Hermenean A, et al. Genotoxicity and Gene Expression in the Rat Lung Tissue following Instillation and Inhalation of Different Variants of Amorphous Silica Nanomaterials (aSiO2 NM). Nanomaterials. 2021; 11(6):1502. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano11061502
Chicago/Turabian StyleBrandão, Fátima, Carla Costa, Maria João Bessa, Elise Dumortier, Florence Debacq-Chainiaux, Roland Hubaux, Michel Salmon, Julie Laloy, Miruna S. Stan, Anca Hermenean, and et al. 2021. "Genotoxicity and Gene Expression in the Rat Lung Tissue following Instillation and Inhalation of Different Variants of Amorphous Silica Nanomaterials (aSiO2 NM)" Nanomaterials 11, no. 6: 1502. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano11061502
APA StyleBrandão, F., Costa, C., Bessa, M. J., Dumortier, E., Debacq-Chainiaux, F., Hubaux, R., Salmon, M., Laloy, J., Stan, M. S., Hermenean, A., Gharbia, S., Dinischiotu, A., Bannuscher, A., Hellack, B., Haase, A., Fraga, S., & Teixeira, J. P. (2021). Genotoxicity and Gene Expression in the Rat Lung Tissue following Instillation and Inhalation of Different Variants of Amorphous Silica Nanomaterials (aSiO2 NM). Nanomaterials, 11(6), 1502. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano11061502












