Dual-Tunable Memristor Based on Carbon Nanotubes and Graphene Quantum Dots
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Composite Material Preparation
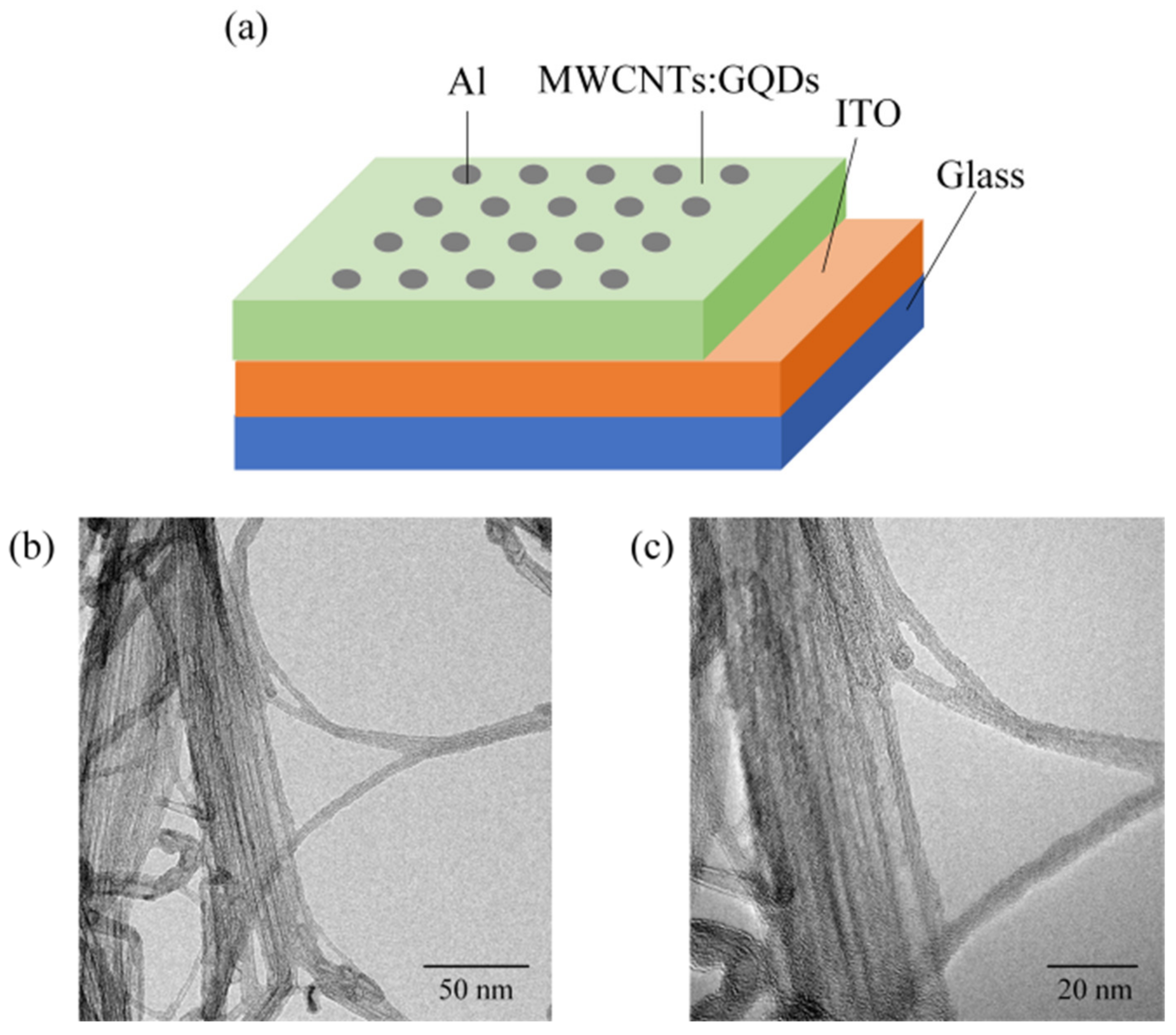
2.3. Fabrication of the Memory Devices
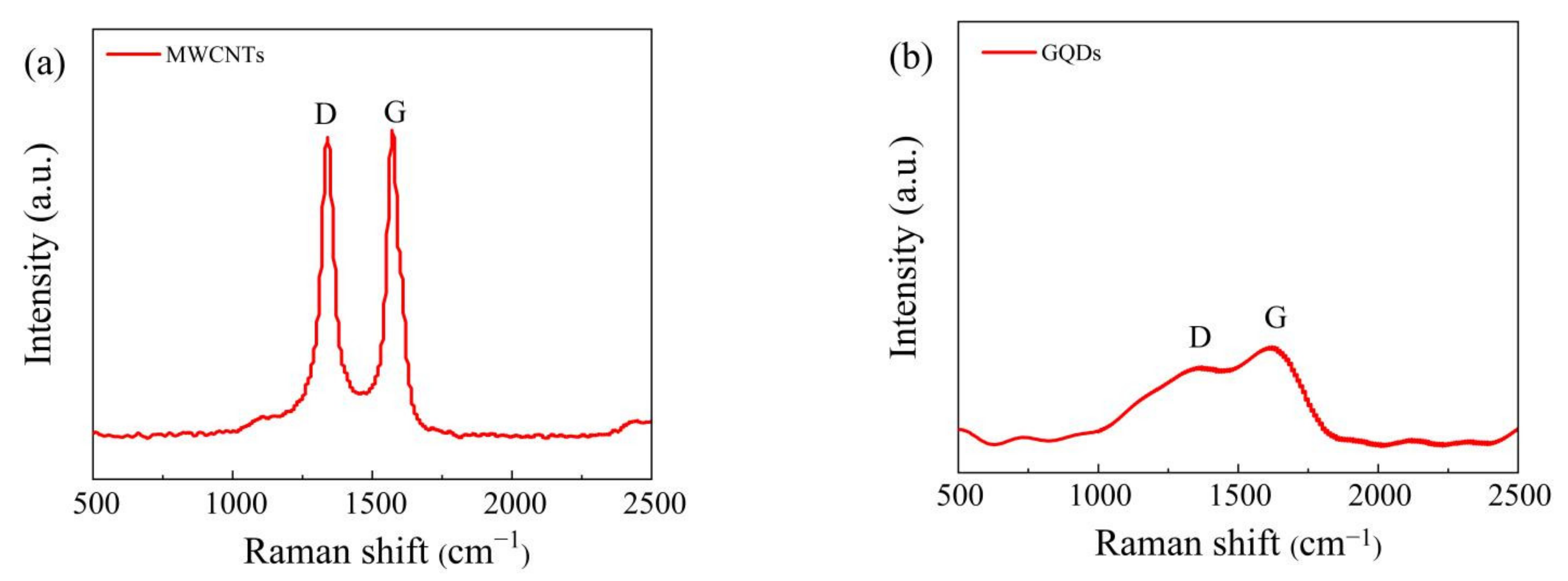
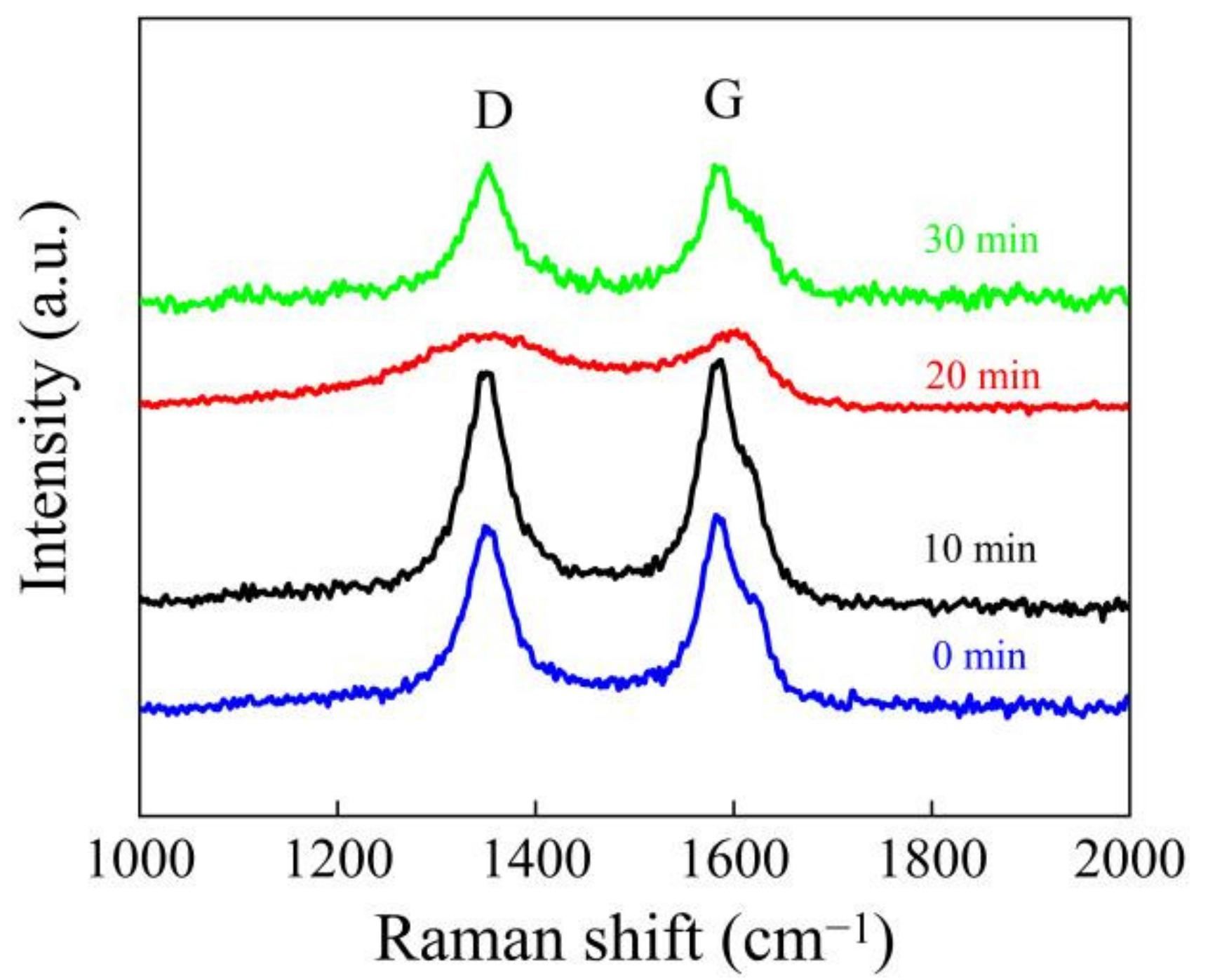
2.4. Characterization
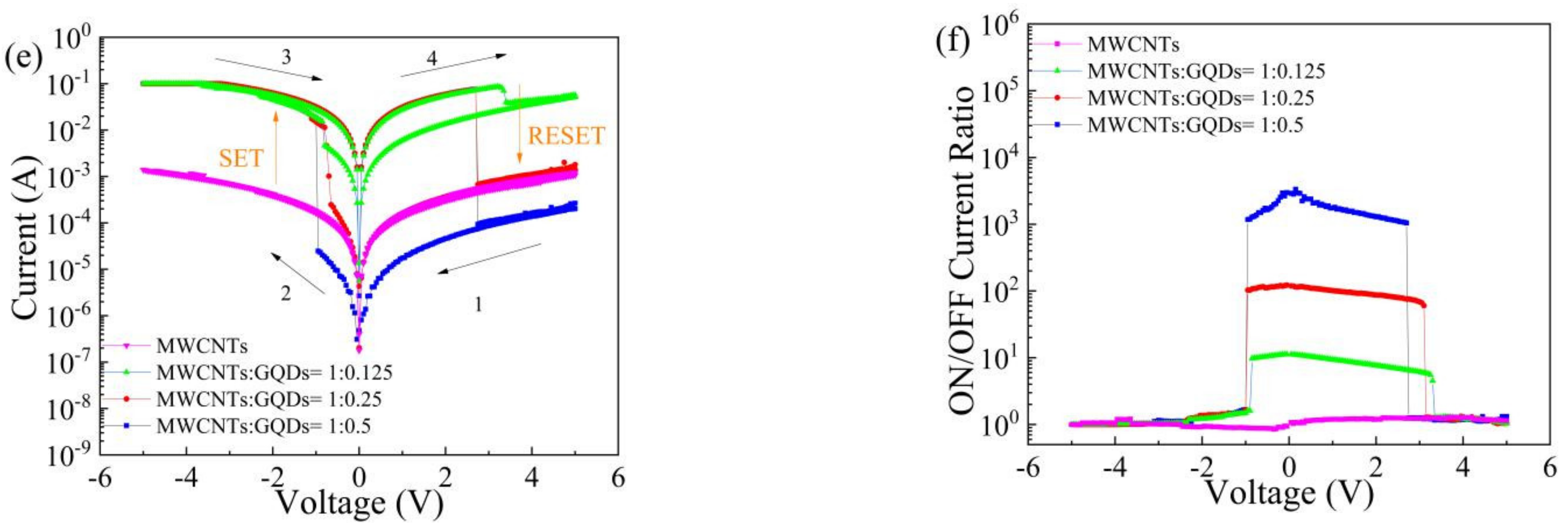
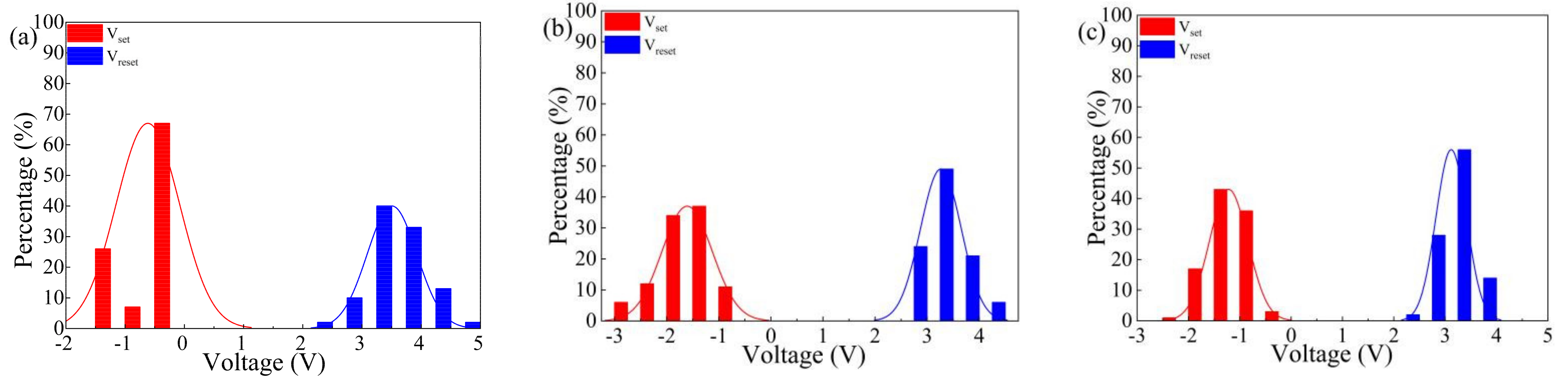
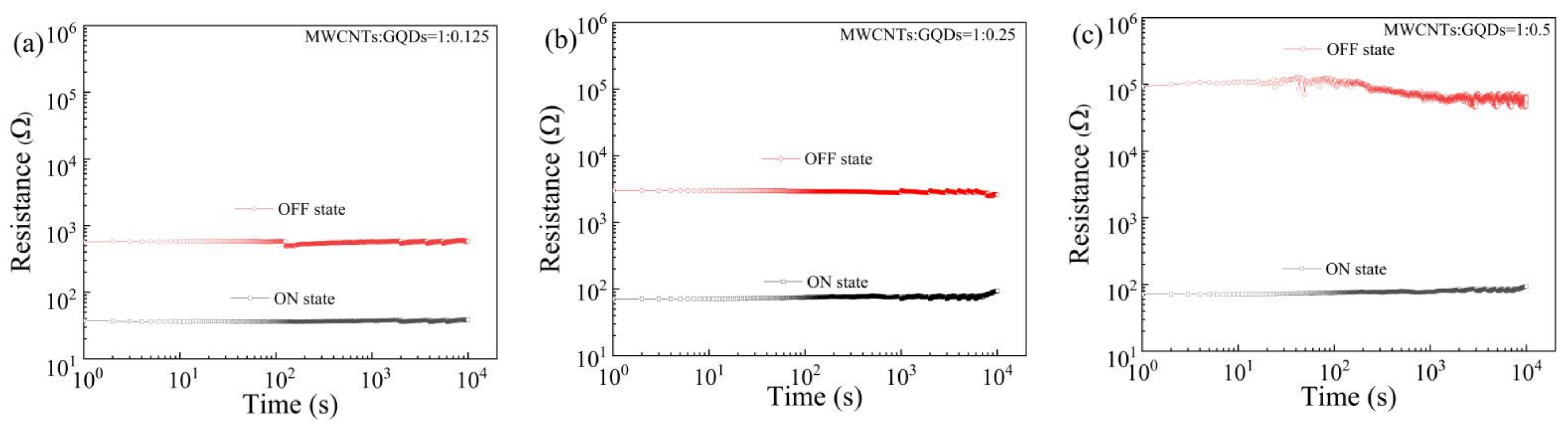
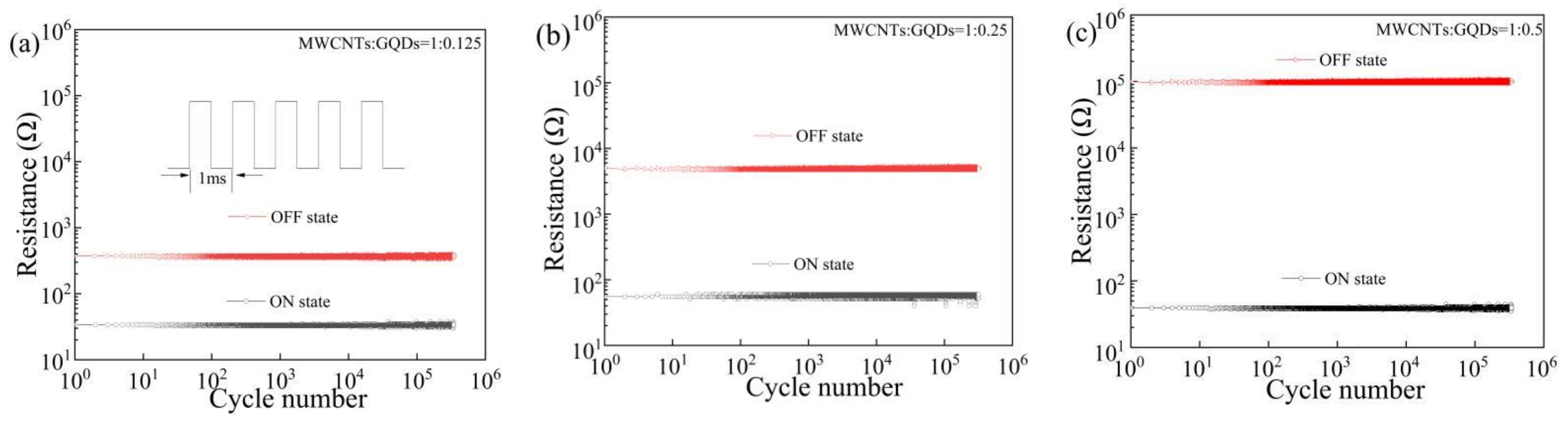
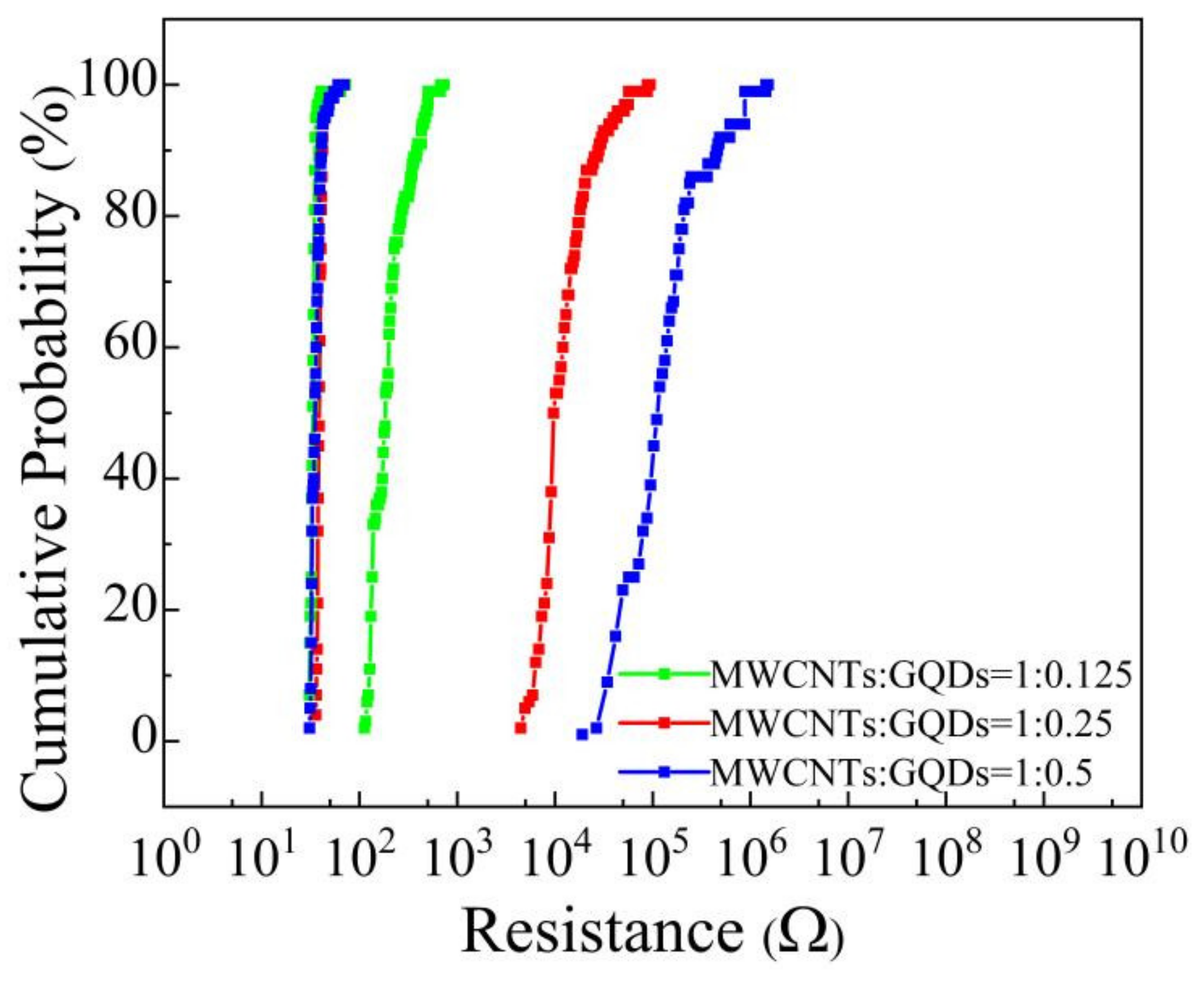
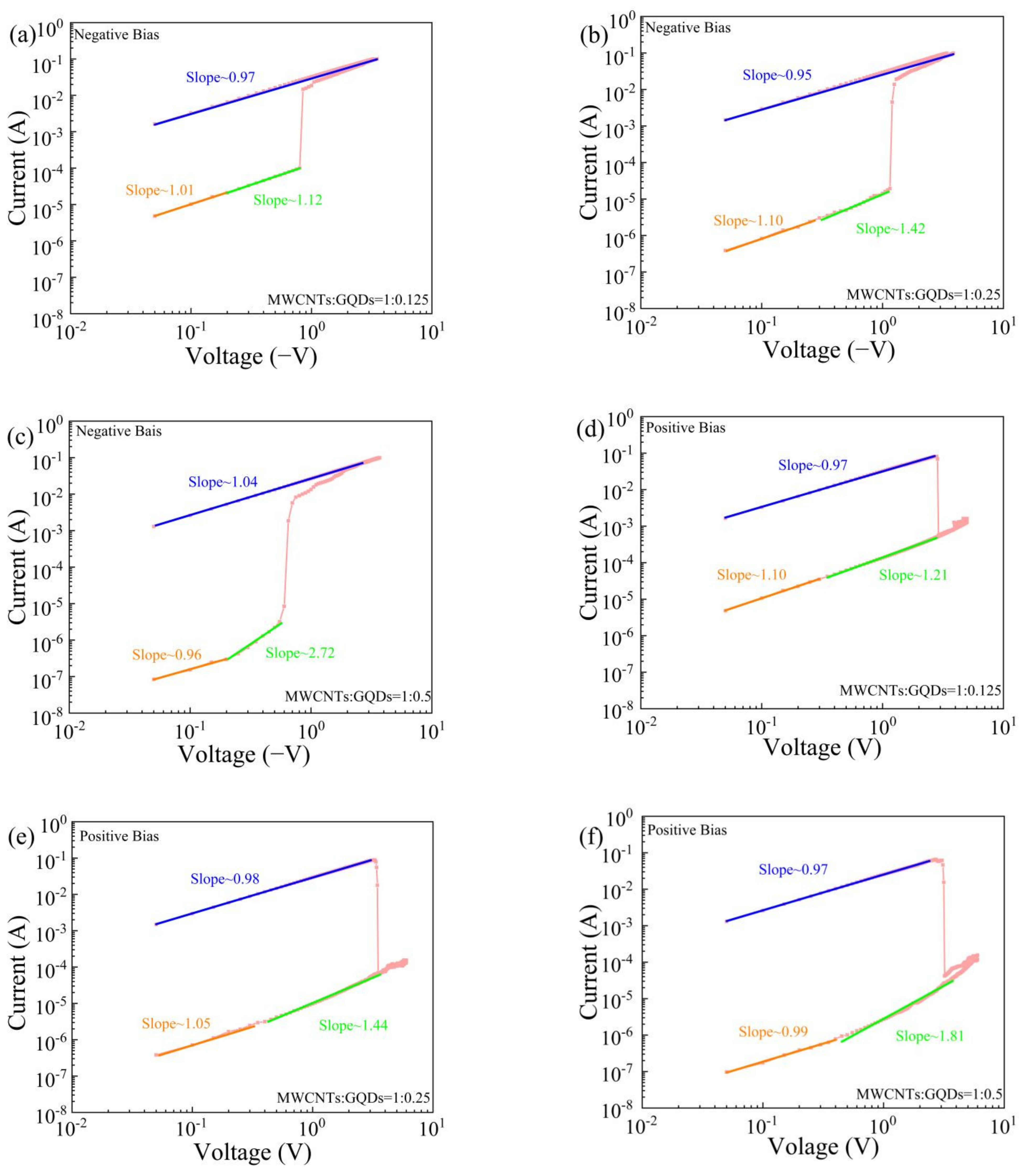
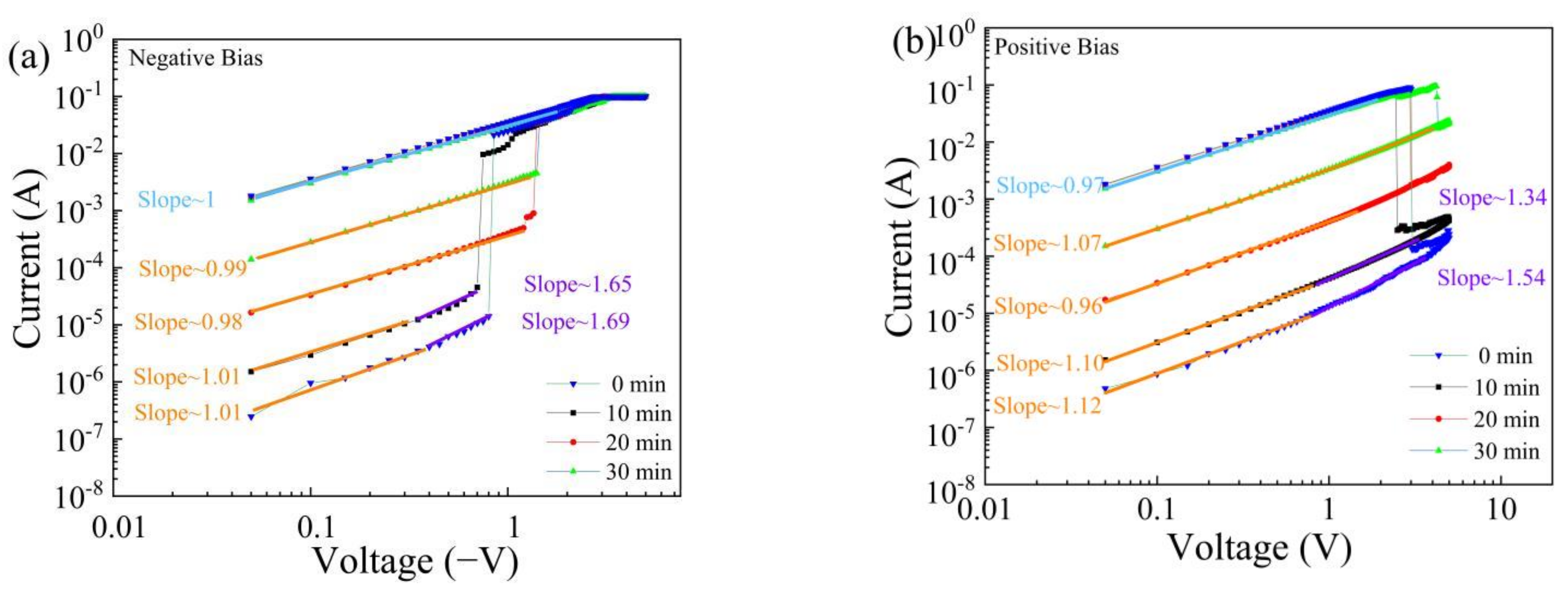
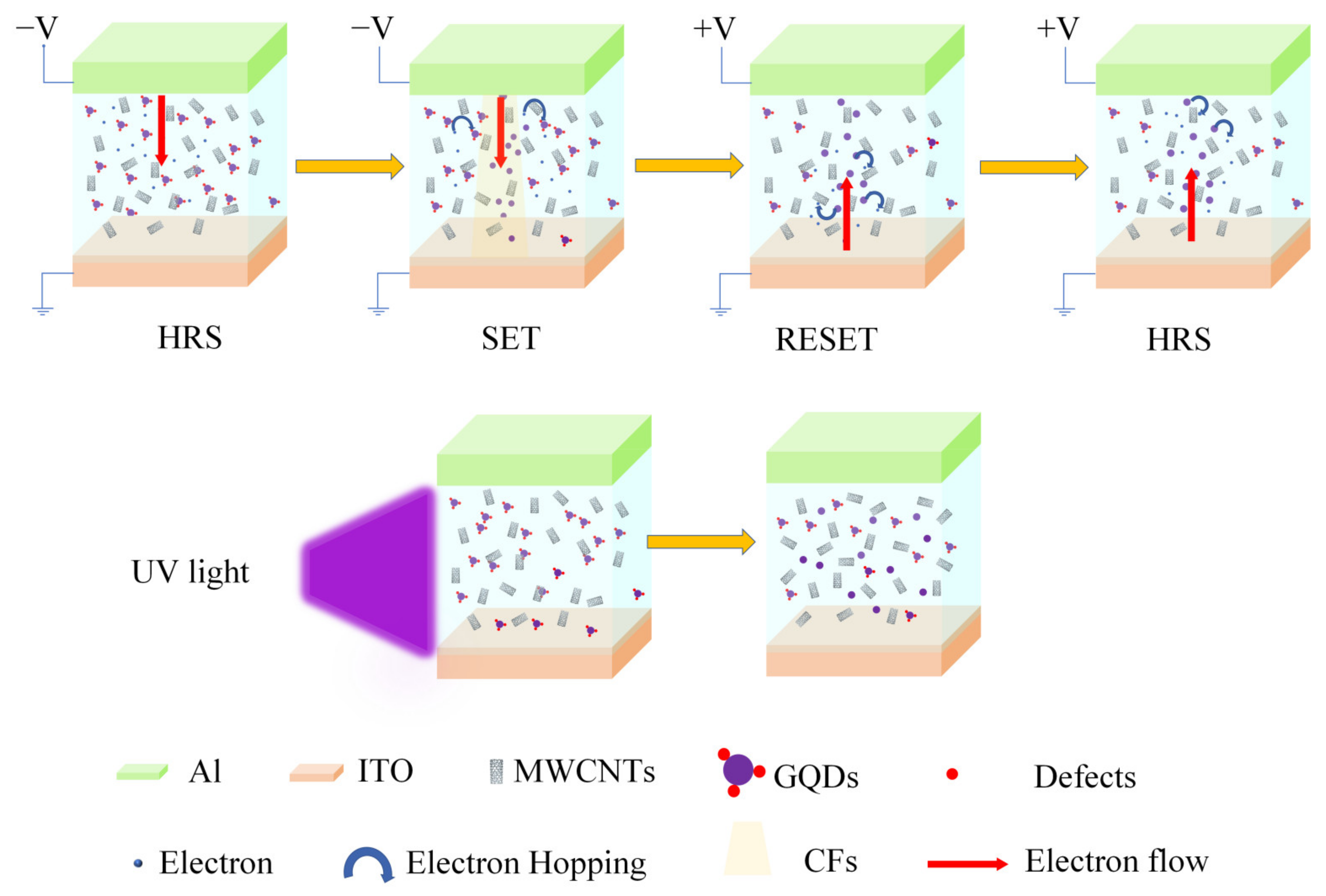
3. Results
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Aziz, T.N.T.A.; Rosli, A.B.; Yusoff, M.M.; Herman, S.H.; Zulkifli, Z. Transparent hybrid ZnO-graphene film for high stability switching behavior of memristor device. Mater. Sci. Semicond. Process. 2019, 89, 68–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Min, S.-Y.; Cho, W.-J. High-performance resistive switching in solution-derived IGZO:N memristors by microwave-assisted nitridation. Nanomaterials 2021, 11, 1081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bera, S.; Mondal, S.P.; Naskar, D.; Kundu, S.C.; Ray, S.K. Flexible and transparent nanocrystal floating gate memory devices using silk protein. Org. Electron. 2014, 15, 1767–1772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, T.; Chen, W.; Liu, L.; Wang, Y.; Zhao, X. Large magnetization modulation in ZnO-based memory devices with embedded graphene quantum dots. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2019, 21, 16047–16054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hao, C.; Wen, F.; Xiang, J.; Yuan, S.; Yang, B.; Li, L.; Wang, W.; Zeng, Z.; Wang, L.; Liu, Z.; et al. Liquid-exfoliated black phosphorous nanosheet thin films for flexible resistive random access memory applications. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2016, 26, 2016–2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vu, Q.A.; Kim, H.; Nguyen, V.L.; Won, U.Y.; Adhikari, S.; Kim, K.; Lee, Y.H.; Yu, W.J. A high-on/off-ratio floating-gate memristor array on a flexible substrate via CVD-grown large-area 2D layer stacking. Adv. Mater. 2017, 29, 1703363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hota, M.K.; Bera, M.K.; Kundu, B.; Kundu, S.C.; Maiti, C.K. A natural silk fibroin protein-based transparent bio-memristor. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2012, 22, 4493–4499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Wen, D. Resistive switching memory devices based on body fluid of Bombyx mori L. Micromachines 2019, 10, 540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kim, S.K.; Kim, J.Y.; Jang, B.C.; Cho, M.S.; Choi, S.-Y.; Lee, J.Y.; Jeong, H.Y. Conductive graphitic channel in graphene oxide-based memristive devices. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2016, 26, 7406–7414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukherjee, C.; Hota, M.K.; Naskar, D.; Kundu, S.C.; Maiti, C.K. Resistive switching in natural silk fibroin protein-based bio-memristors. Phys. Status Solidi 2013, 210, 1797–1805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, Z.; Wang, Y.; Chen, Z.; Sun, L.; Wang, J.; Chen, M.; Xu, Z.; Liao, Q.; Zhou, L.; Chen, X.; et al. Phototunable biomemory based on light-mediated charge trap. Adv. Sci. 2018, 5, 1800714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dragoman, M.; Aldrigo, M.; Dragoman, D. Perspectives on atomic-scale switches for high-frequency applications based on nanomaterials. Nanomaterials 2021, 11, 625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, X.; Wang, Z.; Li, W.; Sun, S.; Xu, H.; Zhou, P.; Xu, J.; Lin, Y.; Liu, Y. Photoassisted electroforming method for reliable low-power organic–inorganic perovskite memristors. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2020, 30, 1910151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryu, H.; Kim, S. Self-rectifying resistive switching and short-term memory characteristics in Pt/HfO2/TaOx/TiN artificial synaptic device. Nanomaterials 2020, 10, 2159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Wang, J.; Wen, D. Devices with tuneable resistance switching characteristics based on a multilayer structure of graphene oxide and egg albumen. Nanomaterials 2020, 10, 1491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, X.; Li, X.; Zhou, Z.; Zhao, J.; Wang, H.; Wang, J.; Zhang, L.; Ren, D.; Zhang, X.; Chen, J.; et al. Flexible transparent organic artificial synapse based on the tungsten/egg albumen/indium tin oxide/polyethylene terephthalate memristor. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2019, 11, 18654–18661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Lu, J.; Ai, C.; Wen, D. Nonvolatile memory devices based on poly(vinyl alcohol) + graphene oxide hybrid composites. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2016, 18, 11341–11347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Il’ina, M.V.; Il’in, O.I.; Blinov, Y.F.; Smirnov, V.A.; Kolomiytsev, A.S.; Fedotov, A.A.; Konoplev, B.G.; Ageev, O.A. Memristive switching mechanism of vertically aligned carbon nanotubes. Carbon 2017, 123, 514–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, S.K.; Lee, J.M.; Kim, S.; Park, J.S.; Park, H.I.; Ahn, C.W.; Lee, K.J.; Lee, T.; Kim, S.O. Flexible multilevel resistive memory with controlled charge trap B- and N-doped carbon nanotubes. Nano Lett. 2012, 12, 2217–2221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kodgire, P.V.; Bhattacharyya, A.R.; Bose, S.; Gupta, N.; Kulkarni, A.R.; Misra, A. Control of multiwall carbon nanotubes dispersion in polyamide6 matrix: An assessment through electrical conductivity. Chem. Phys. Lett. 2006, 432, 480–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Russo, P.; Xiao, M.; Zhou, N.Y. Carbon nanowalls: A new material for resistive switching memory devices. Carbon 2017, 120, 54–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raeber, T.J.; Zhao, Z.C.; Murdoch, B.J.; McKenzie, D.R.; McCulloch, D.G.; Partridge, J.G. Resistive switching and transport characteristics of an all-carbon memristor. Carbon 2018, 136, 280–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Yang, C.; Li, N.; Yin, J.; Zhao, X.; Li, J.; Zhao, H.; Zhu, C.; Chen, M.; Su, B.; et al. The effects of MCNTs on electro-spinning carbonization microstructure of polyimide composite film and resistive switching behavior. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2019, 359, 438–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rehman, M.M.; Siddiqui, G.U.; Kim, S.; Choi, K.H. Resistive switching effect in the planar structure of all-printed, flexible and rewritable memory device based on advanced 2D nanocomposite of graphene quantum dots and white graphene flakes. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 2017, 50, 335104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, T.; Wang, H.; Zhang, B.; Yan, X. Enhanced memory characteristics of charge trapping memory by employing graphene oxide quantum dots. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2020, 116, 103501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Che, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Cao, X.; Song, X.; Cao, M.; Dai, H.; Yang, J.; Zhang, G.; Yao, J. Low operating voltage ambipolar graphene oxide-floating-gate memory devices based on quantum dots. J. Mater. Chem. C 2016, 4, 1420–1424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarkar, K.J.; Sarkar, K.; Pal, B.; Banerji, P. Graphene quantum dots as charge trap elements for nonvolatile flash memory. J. Phys. Chem. Solids 2018, 122, 137–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, M.; Bai, L.; Xu, H.; Wang, Z.; Kang, Z.; Zhao, X.; Liu, W.; Ma, J.; Liu, Y. Oxidized carbon quantum dot–graphene oxide nanocomposites for improving data retention of resistive switching memory. J. Mater. Chem. C 2018, 6, 2026–2033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, X.; Zeng, T.; Bai, L.; Kang, Z.; Wang, C.; Zhao, X.; Xu, H.; Liu, Y. Photoreduced nanocomposites of graphene oxide/N-doped carbon dots toward all-carbon memristive synapses. NPG Asia Mater. 2020, 12, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, T.; Gao, Y.; Chen, W.; Zhao, X. Improved resistive memory based on ZnO–graphene hybrids through redox process of graphene quantum dots. Phys. Status Solidi Rapid Res. Lett. 2019, 13, 1900153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, R.C.; Gogoi, K.K.; Das, N.S.; Chowdhury, A. Optimization of quantum yield of highly luminescent graphene oxide quantum dots and their application in resistive memory devices. Semicond. Sci. Technol. 2019, 34, 125016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xin, Y.; Zhao, X.; Zhang, H.; Wang, S.; Wang, C.; Ma, D.; Yan, P. Bistable electrical switching and nonvolatile memory effect in poly (9,9-dioctylfluorene-2,7-diyl) and multiple-walled carbon nanotubes. Org. Electron. 2019, 74, 110–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, Y.; Sun, B.; Fu, G.; Li, T.; Zhu, S.; Zheng, L.; Mao, S.; Kan, X.; Lei, M.; Chen, Y. A nonvolatile organic resistive switching memory based on lotus leaves. Chem. Phys. 2019, 516, 168–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Tian, S.; Sun, B.; Li, X.; Guo, B.; Zeng, Y.; Li, B.; Luo, W. From natural biomaterials to environment-friendly and sustainable nonvolatile memory device. Chem. Phys. 2018, 513, 7–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaafar, M.M.; Ooi, P.C.; Wee, M.M.R.; Mohammad Haniff, M.A.S.; Mohamed, M.A.; Chang, E.Y.; Yeop Majlis, B.; Dee, C.F. Electrical bistabilities behaviour of all-solution-processed non-volatile memories based on graphene quantum dots embedded in graphene oxide layers. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 2019, 30, 16415–16420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P.; Xu, B.; Gao, C.; Chen, G.; Gao, M. Facile synthesis of Co9Se8 quantum dots as charge traps for flexible organic resistive switching memory device. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2016, 8, 30336–30343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, H.Y.; Kim, J.Y.; Kim, J.W.; Hwang, J.O.; Kim, J.-E.; Lee, J.Y.; Yoon, T.H.; Cho, B.J.; Kim, S.O.; Ruoff, R.S.; et al. Graphene oxide thin films for flexible nonvolatile memory applications. Nano Lett. 2010, 10, 4381–4386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, L.; Yang, J.; Zhang, Y.; Wen, D. Dual-Tunable Memristor Based on Carbon Nanotubes and Graphene Quantum Dots. Nanomaterials 2021, 11, 2043. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano11082043
Wang L, Yang J, Zhang Y, Wen D. Dual-Tunable Memristor Based on Carbon Nanotubes and Graphene Quantum Dots. Nanomaterials. 2021; 11(8):2043. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano11082043
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Lu, Jing Yang, Yukai Zhang, and Dianzhong Wen. 2021. "Dual-Tunable Memristor Based on Carbon Nanotubes and Graphene Quantum Dots" Nanomaterials 11, no. 8: 2043. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano11082043
APA StyleWang, L., Yang, J., Zhang, Y., & Wen, D. (2021). Dual-Tunable Memristor Based on Carbon Nanotubes and Graphene Quantum Dots. Nanomaterials, 11(8), 2043. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano11082043





