Edge Effect in Electronic and Transport Properties of 1D Fluorinated Graphene Materials
Abstract
:1. Introduction
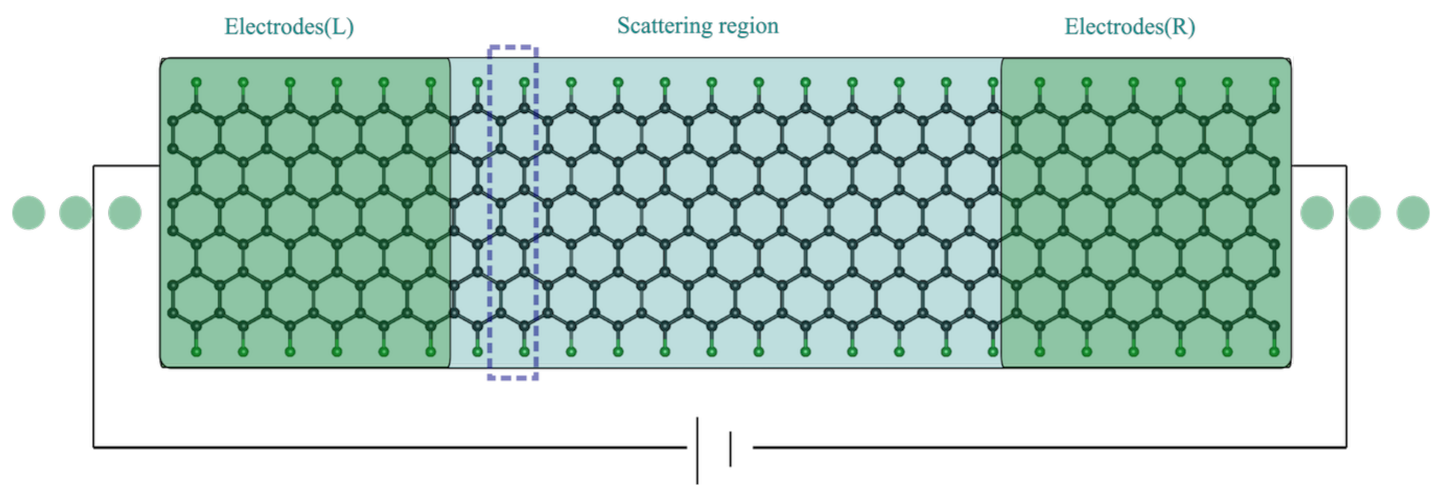
2. Model Construction, Methods, and Computational Details
2.1. Model Construction
2.2. Methods
2.3. Computational Details
3. Results and Discussions
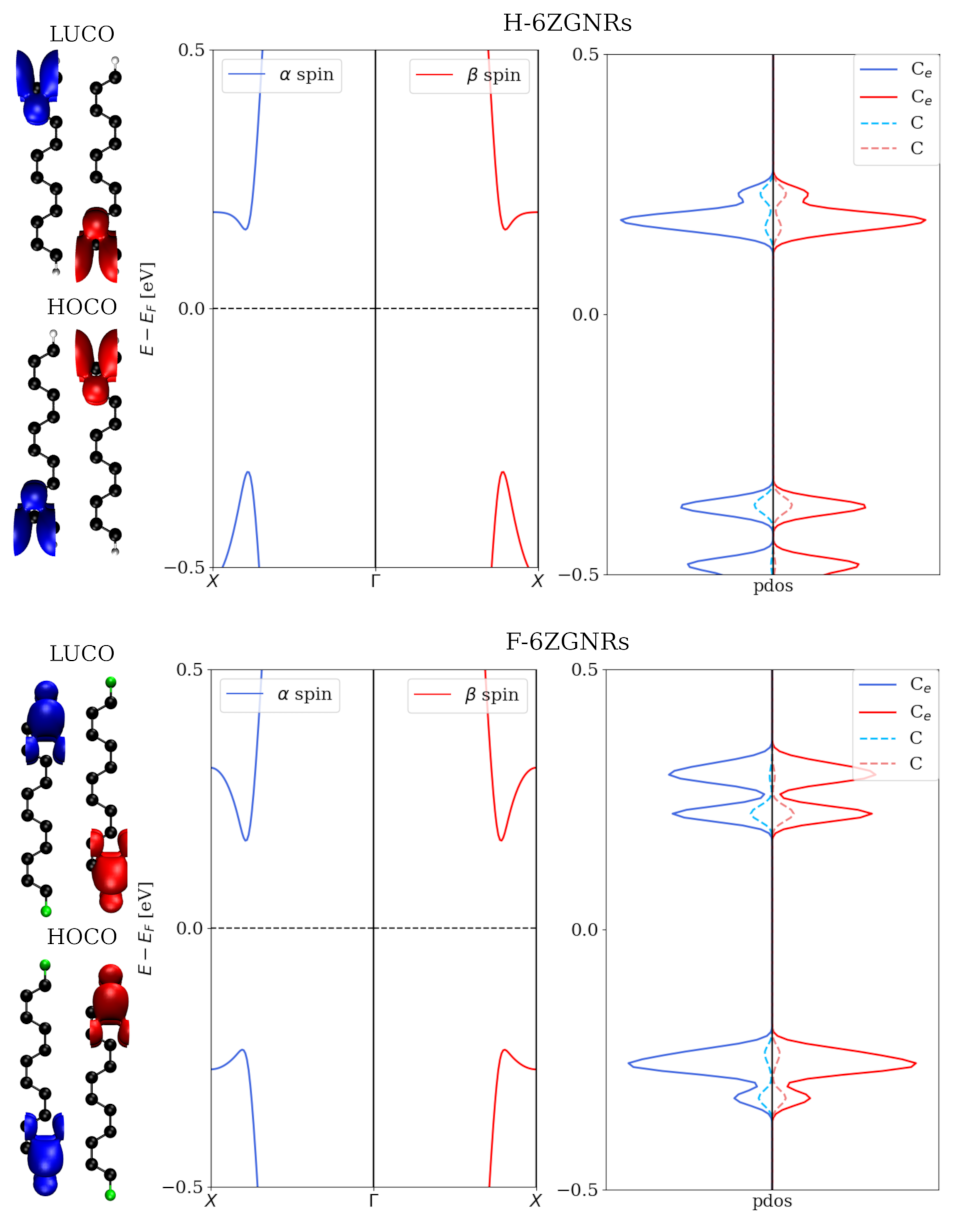
3.1. Hydrogen-Saturated ZGNRs and Fluorine-Saturated ZGNRs
3.2. Fluorination Pattern on Fluorine-Saturated ZGNRs
3.3. Transport Properties on Selected Models
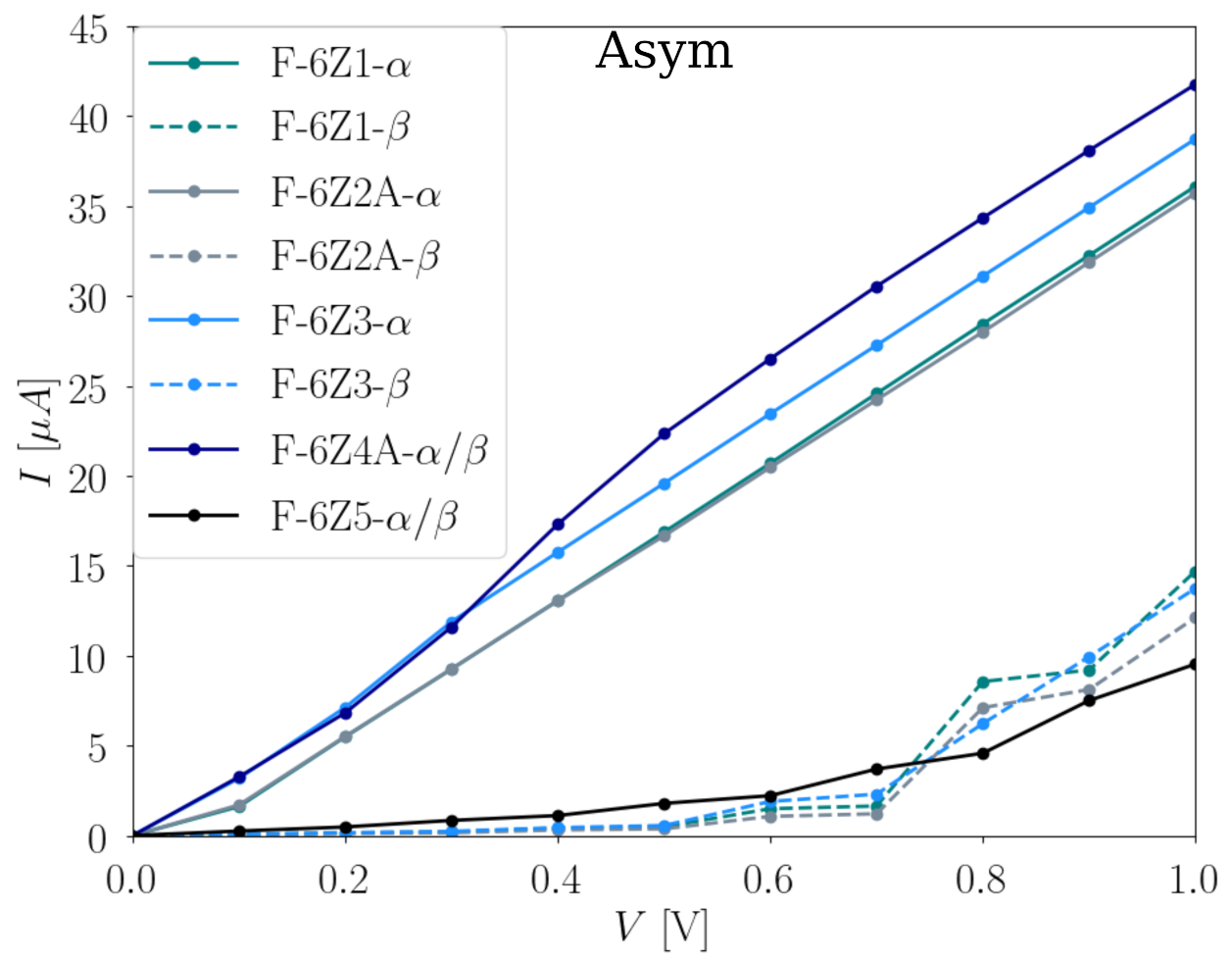
3.3.1. The Width of the F-ZGNRs
3.3.2. Fluorination Degrees of the F-ZGNRs
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Novoselov, K.S. Electric Field Effect in Atomically Thin Carbon Films. Science 2004, 306, 666–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Low, J.; Cheng, B.; Yu, J.; Jaroniec, M. Carbon-based two-dimensional layered materials for photocatalytic CO2 reduction to solar fuels. Energy Storage Mater. 2016, 3, 24–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bianco, A.; Cheng, H.M.; Enoki, T.; Gogotsi, Y.; Hurt, R.H.; Koratkar, N.; Kyotani, T.; Monthioux, M.; Park, C.R.; Tascon, J.M.; et al. All in the Graphene Family—A Recommended Nomenclature for Two-Dimensional Carbon Materials. Carbon 2013, 65, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wick, P.; Louw-Gaume, A.E.; Kucki, M.; Krug, H.F.; Kostarelos, K.; Fadeel, B.; Dawson, K.A.; Salvati, A.; Vázquez, E.; Ballerini, L.; et al. Classification framework for graphene-based materials. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2014, 53, 7714–7718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Robinson, J.T.; Burgess, J.S.; Junkermeier, C.E.; Badescu, S.C.; Reinecke, T.L.; Perkins, F.K.; Zalalutdniov, M.K.; Baldwin, J.W.; Culbertson, J.C.; Sheehan, P.E.; et al. Properties of fluorinated graphene films. Nano Lett. 2010, 10, 3001–3005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Withers, F.; Dubois, M.; Savchenko, A.K. Electron properties of fluorinated single-layer graphene transistors. Phys. Rev. B 2010, 82, 073403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jeon, K.J.; Lee, Z.; Pollak, E.; Moreschini, L.; Bostwick, A.; Park, C.M.; Mendelsberg, R.; Radmilovic, V.; Kostecki, R.; Richardson, T.J.; et al. Fluorographene: A Wide Bandgap Semiconductor with Ultraviolet Luminescence. ACS Nano 2011, 5, 1042–1046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matochová, D.; Medved, M.; Bakandritsos, A.; Steklý, T.; Zbořil, R.; Otyepka, M. 2D Chemistry: Chemical Control of Graphene Derivatization. J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 2018, 9, 3580–3585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, W.; Long, P.; Feng, Y.; Li, Y. Two-dimensional fluorinated graphene: Synthesis, structures, properties and applications. Adv. Sci. 2016, 3, 1500413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Wang, J.; Li, Z.; Gong, P.; Liu, X.; Zhang, L.; Ren, J.; Wang, H.; Yang, S. Synthesis of fluorinated graphene with tunable degree of fluorination. Carbon 2012, 50, 5403–5410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mathkar, A.; Narayanan, T.; Alemany, L.B.; Cox, P.; Nguyen, P.; Gao, G.; Chang, P.; Romero-Aburto, R.; Mani, S.A.; Ajayan, P. Synthesis of fluorinated graphene oxide and its amphiphobic properties. Part. Part. Syst. Charact. 2013, 30, 266–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Q.; Cao, Q.; Li, M.; Liu, F.; Tang, N.; Du, Y. Synthesis and photoluminescence of fluorinated graphene quantum dots. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2013, 102, 013111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Withers, F.; Bointon, T.H.; Dubois, M.; Russo, S.; Craciun, M.F. Nanopatterning of fluorinated graphene by electron beam irradiation. Nano Lett. 2011, 11, 3912–3916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kashtiban, R.J.; Dyson, M.A.; Nair, R.R.; Zan, R.; Wong, S.L.; Ramasse, Q.; Geim, A.K.; Bangert, U.; Sloan, J. Atomically resolved imaging of highly ordered alternating fluorinated graphene. Nat. Commun. 2014, 5, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Li, H.; Daukiya, L.; Haldar, S.; Lindblad, A.; Sanyal, B.; Eriksson, O.; Aubel, D.; Hajjar-Garreau, S.; Simon, L.; Leifer, K. Site-selective local fluorination of graphene induced by focused ion beam irradiation. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Şahin, H.; Topsakal, M.; Ciraci, S. Structures of fluorinated graphene and their signatures. Phys. Rev. B 2011, 83, 115432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, X.; Dai, Y.; Gao, J.; Huang, J.; Li, B.; Fan, C.; Yang, J.; Liu, X. High-yield production of highly fluorinated graphene by direct heating fluorination of graphene-oxide. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2013, 5, 8294–8299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, H.; Hou, Z.; Hu, C.; Yang, Y.; Zhu, Z. Electronic and magnetic properties of fluorinated graphene with different coverage of fluorine. J. Phys. Chem. C 2012, 116, 18193–18201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, L.; Jandhyala, S.; Mordi, G.; Lucero, A.T.; Huang, J.; Azcatl, A.; Addou, R.; Wallace, R.M.; Colombo, L.; Kim, J. Partially fluorinated graphene: Structural and electrical characterization. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2016, 8, 5002–5008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panighel, M.; Quiroga, S.; Brandimarte, P.; Moreno, C.; Garcia-Lekue, A.; Vilas-Varela, M.; Rey, D.; Sauthier, G.; Ceballos, G.; Peña, D.; et al. Stabilizing Edge Fluorination in Graphene Nanoribbons. ACS Nano 2020, 14, 11120–11129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, C.; Kong, L.; Li, Y.; Fu, H.; Sun, L.; Feng, Y.; Feng, W. Fluorinated graphene nanoribbons from unzipped single-walled carbon nanotubes for ultrahigh energy density lithium-fluorinated carbon batteries. Sci. China Mater. 2021, 64, 1367–1377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Son, Y.W.; Cohen, M.L.; Louie, S.G. Half-metallic graphene nanoribbons. Nature 2006, 444, 347–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Son, Y.W.; Cohen, M.L.; Louie, S.G. Energy gaps in graphene nanoribbons. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2006, 97, 216803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Han, M.Y.; Özyilmaz, B.; Zhang, Y.; Kim, P. Energy band-gap engineering of graphene nanoribbons. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2007, 98, 206805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Slota, M.; Keerthi, A.; Myers, W.K.; Tretyakov, E.; Baumgarten, M.; Ardavan, A.; Sadeghi, H.; Lambert, C.J.; Narita, A.; Müllen, K.; et al. Magnetic edge states and coherent manipulation of graphene nanoribbons. Nature 2018, 557, 691–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Guo, J.; Gunlycke, D.; White, C. Field effect on spin-polarized transport in graphene nanoribbons. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2008, 92, 163109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papior, N.; Calogero, G.; Leitherer, S.; Brandbyge, M. Removing all periodic boundary conditions: Efficient nonequilibrium Green’s function calculations. Phys. Rev. B 2019, 100, 195417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nag Chowdhury, B.; Chattopadhyay, S. Investigating the impact of source/drain doping dependent effective masses on the transport characteristics of ballistic Si-nanowire field-effect-transistors. J. Appl. Phys. 2014, 115, 124502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biswas, S.; Seo, K.H.; Lee, Y.; Kim, Y.H.; Bae, J.H.; Kim, H. Effect of Source–Drain Electric Field on Charge Transport Mechanism in Polymer-Based Thin-Film Transistors. Phys. Status Solidi A 2021, 218, 2000753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Datta, S. Electronic Transport in Mesoscopic Systems; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Xue, Y.; Datta, S.; Ratner, M.A. First-principles based matrix Green’s function approach to molecular electronic devices: General formalism. Chem. Phys. 2002, 281, 151–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Di Ventra, M. Electrical Transport in Nanoscale Systems; Cambridge University Press: New York, NY, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Varga, K. Time-dependent density functional study of transport in molecular junctions. Phys. Rev. B 2011, 83, 195130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wolf, S.A.; Chtchelkanova, A.Y.; Treger, D.M. Spintronics—A retrospective and perspective. IBM J. Res. Dev. 2006, 50, 101–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stefanucci, G.; Kurth, S. Steady-state density functional theory for finite bias conductances. Nano Lett. 2015, 15, 8020–8025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kurth, S.; Stefanucci, G. Dynamical correction to linear Kohn-Sham conductances from static density functional theory. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2013, 111, 030601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mirjani, F.; Thijssen, J. Density functional theory based many-body analysis of electron transport through molecules. Phys. Rev. B 2011, 83, 035415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schmitteckert, P.; Evers, F. Exact ground state density-functional theory for impurity models coupled to external reservoirs and transport calculations. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2008, 100, 086401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mera, H.; Niquet, Y. Are Kohn-Sham Conductances Accurate? Phys. Rev. Lett. 2010, 105, 216408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papior, N.; Lorente, N.; Frederiksen, T.; García, A.; Brandbyge, M. Improvements on non-equilibrium and transport Green function techniques: The next-generation transiesta. Comput. Phys. Commun. 2017, 212, 8–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shao, J.; Pohl, V.; Marsoner Steinkasserer, L.E.; Paulus, B.; Tremblay, J.C. Electronic Current Mapping of Transport through Defective Zigzag Graphene Nanoribbons. J. Phys. Chem. C 2020, 124, 23479–23489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sancho, M.L.; Sancho, J.L.; Rubio, J. Quick iterative scheme for the calculation of transfer matrices: Application to Mo (100). J. Phys. Met. Phys. 1984, 14, 1205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christensen, R.B.; Frederiksen, T.; Brandbyge, M. Identification of pristine and defective graphene nanoribbons by phonon signatures in the electron transport characteristics. Phys. Rev. B 2015, 91, 075434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Koch, M.; Ample, F.; Joachim, C.; Grill, L. Voltage-dependent conductance of a single graphene nanoribbon. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2012, 7, 713–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verzijl, C.; Seldenthuis, J.; Thijssen, J. Applicability of the wide-band limit in DFT-based molecular transport calculations. J. Chem. Phys. 2013, 138, 094102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Covito, F.; Eich, F.; Tuovinen, R.; Sentef, M.; Rubio, A. Transient charge and energy flow in the wide-band limit. J. Chem. Theory Comput. 2018, 14, 2495–2504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walz, M.; Wilhelm, J.; Evers, F. Current Patterns and Orbital Magnetism in Mesoscopic dc Transport. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2014, 113, 136602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilhelm, J.; Walz, M.; Evers, F. Ab initio spin-flip Conductance of Hydrogenated Graphene Nanoribbons: Spin-orbit Interaction and Scattering with Local Impurity Spins. Phys. Rev. B 2015, 92, 014405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Walz, M.; Bagrets, A.; Evers, F. Local Current Density Calculations for Molecular Films from ab initio. J. Chem. Theory Comput. 2015, 11, 5161–5176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buluç, A.; Fineman, J.T.; Frigo, M.; Gilbert, J.R.; Leiserson, C.E. Parallel Sparse Matrix-Vector and Matrix-Transpose-Vector Multiplication Using Compressed Sparse Blocks. In Proceedings of the Twenty-First Annual Symposium on Parallelism in Algorithms and Architectures, Calgary, AB, Canada, 11–13 August 2009; pp. 233–244. [Google Scholar]
- Shao, J.; Paulus, B.; Tremblay, J.C. Local current analysis on defective zigzag graphene nanoribbons devices for biosensor material applications. J. Comput. Chem. 2021, 42, 1475–1485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mortensen, J.J.; Hansen, L.B.; Jacobsen, K.W. Real-space grid implementation of the projector augmented wave method. Phys. Rev. B 2005, 71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Enkovaara, J.; Rostgaard, C.; Mortensen, J.J.; Chen, J.; Dułak, M.; Ferrighi, L.; Gavnholt, J.; Glinsvad, C.; Haikola, V.; Hansen, H.A.; et al. Electronic structure calculations with GPAW: A real-space implementation of the projector augmented-wave method. J. Phys. Condens. Matter 2010, 22, 253202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marques, M.A.; Oliveira, M.J.; Burnus, T. Libxc: A Library of Exchange and Correlation Functionals for Density Functional Theory. Comput. Phys. Commun. 2012, 183, 2272–2281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lehtola, S.; Steigemann, C.; Oliveira, M.J.; Marques, M.A. Recent Developments in libxc: A Comprehensive Library of Functionals for Density Functional Theory. SoftwareX 2018, 7, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perdew, J.P.; Burke, K.; Ernzerhof, M. Generalized gradient approximation made simple. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1996, 77, 3865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Larsen, A.H.; Vanin, M.; Mortensen, J.J.; Thygesen, K.S.; Jacobsen, K.W. Localized atomic Basis Set in the Projector augmented Wave Method. Phys. Rev. B 2009, 80, 195112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Larsen, A.H.; Mortensen, J.J.; Blomqvist, J.; Castelli, I.E.; Christensen, R.; Dułak, M.; Friis, J.; Groves, M.N.; Hammer, B.; Hargus, C.; et al. The Atomic Simulation Environment—A Python Library for working with Atoms. J. Phys. Condens. Matter 2017, 29, 273002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Thygesen, K.S.; Bollinger, M.; Jacobsen, K.W. Conductance Calculations with a Wavelet Basis Set. Phys. Rev. B 2003, 67, 115404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Thygesen, K.S.; Jacobsen, K.W. Molecular Transport Calculations with Wannier functions. Chem. Phys. 2005, 319, 111–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Thygesen, K.S.; Jacobsen, K.W. Interference and k-point Sampling in the Supercell Approach to Phase-coherent Transport. Phys. Rev. B 2005, 72, 033401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Strange, M.; Kristensen, I.; Thygesen, K.S.; Jacobsen, K.W. Benchmark Density Functional Theory Calculations for Nanoscale Conductance. J. Chem. Phys. 2008, 128, 114714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hermann, G.; Pohl, V.; Tremblay, J.C.; Paulus, B.; Hege, H.C.; Schild, A. ORBKIT: A Modular Python Toolbox for Cross-Platform Postprocessing of Quantum Chemical Wavefunction Data. J. Comput. Chem. 2016, 37, 1511–1520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hermann, G.; Pohl, V.; Tremblay, J.C. An Open-Source Framework for Analyzing N-electron Dynamics. II. Hybrid Density Functional Theory/Configuration Interaction Methodology. J. Comput. Chem. 2017, 38, 2378–2387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pohl, V.; Hermann, G.; Tremblay, J.C. An Open-Source Framework for Analyzing N-electron Dynamics. I. Multideterminantal Wave Functions. J. Comput. Chem. 2017, 38, 1515–1527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Clot, E.; Eisenstein, O.; Jasim, N.; Macgregor, S.A.; McGrady, J.E.; Perutz, R.N. C-F and C-H bond activation of fluorobenzenes and fluoropyridines at transition metal centers: How fluorine tips the scales. Acc. Chem. Res. 2011, 44, 333–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, K.; Shao, J.; Paulus, B. Electronic and optical properties of fluorinated graphene within many-body Green’s function framework. J. Chem. Phys. 2021, 154, 104705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crowley, J.M.; Tahir-Kheli, J.; Goddard, W.A., III. Resolution of the band gap prediction problem for materials design. J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 2016, 7, 1198–1203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perdew, J.P.; Yang, W.; Burke, K.; Yang, Z.; Gross, E.K.; Scheffler, M.; Scuseria, G.E.; Henderson, T.M.; Zhang, I.Y.; Ruzsinszky, A.; et al. Understanding band gaps of solids in generalized Kohn–Sham theory. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2017, 114, 2801–2806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]

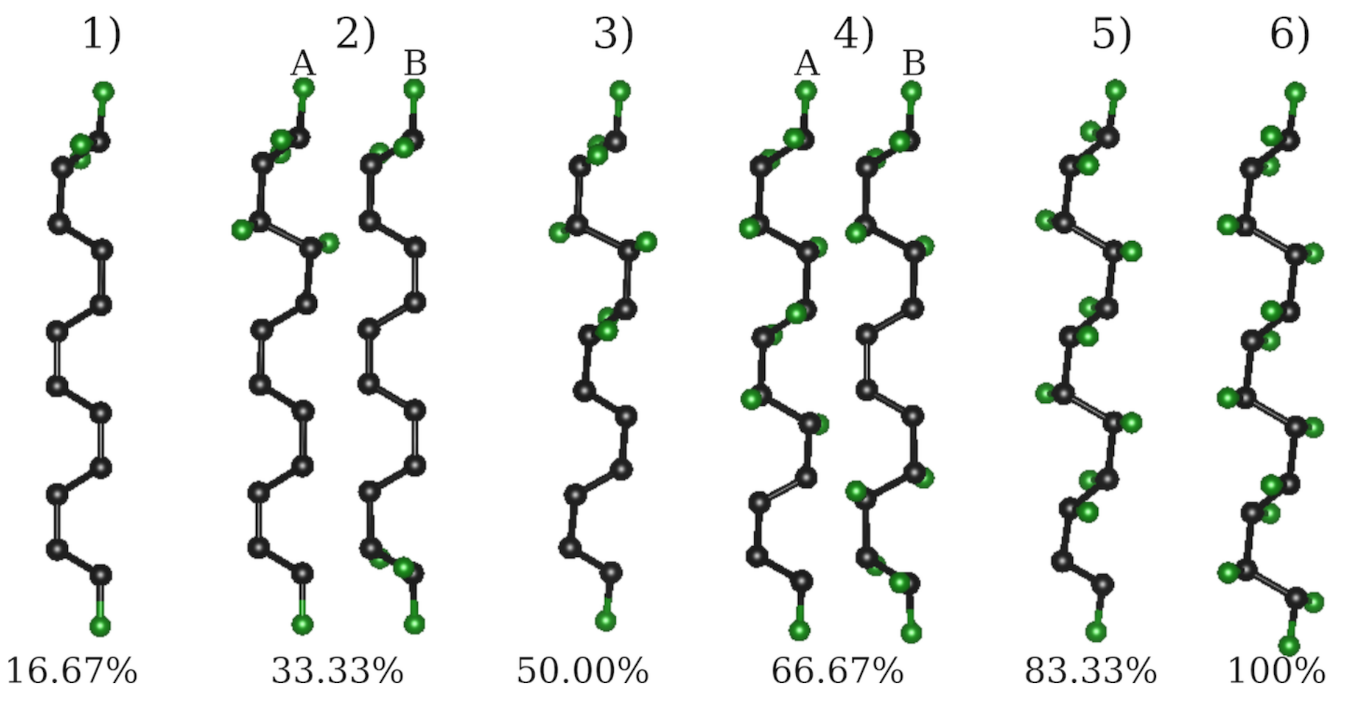

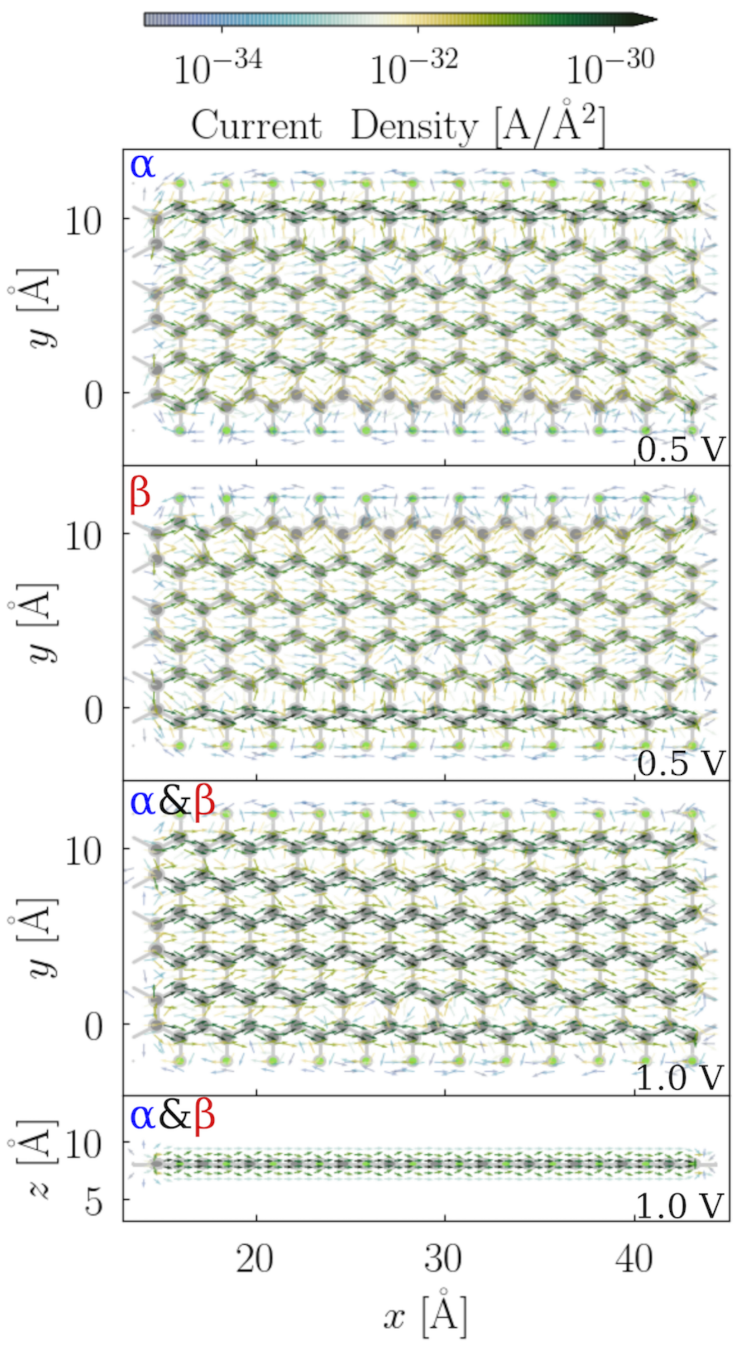


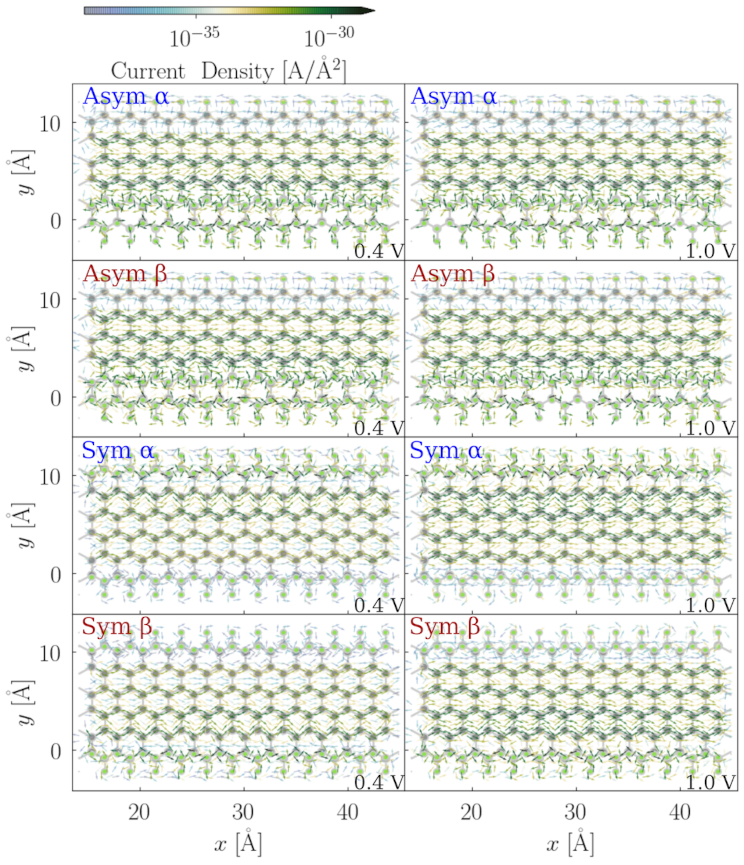
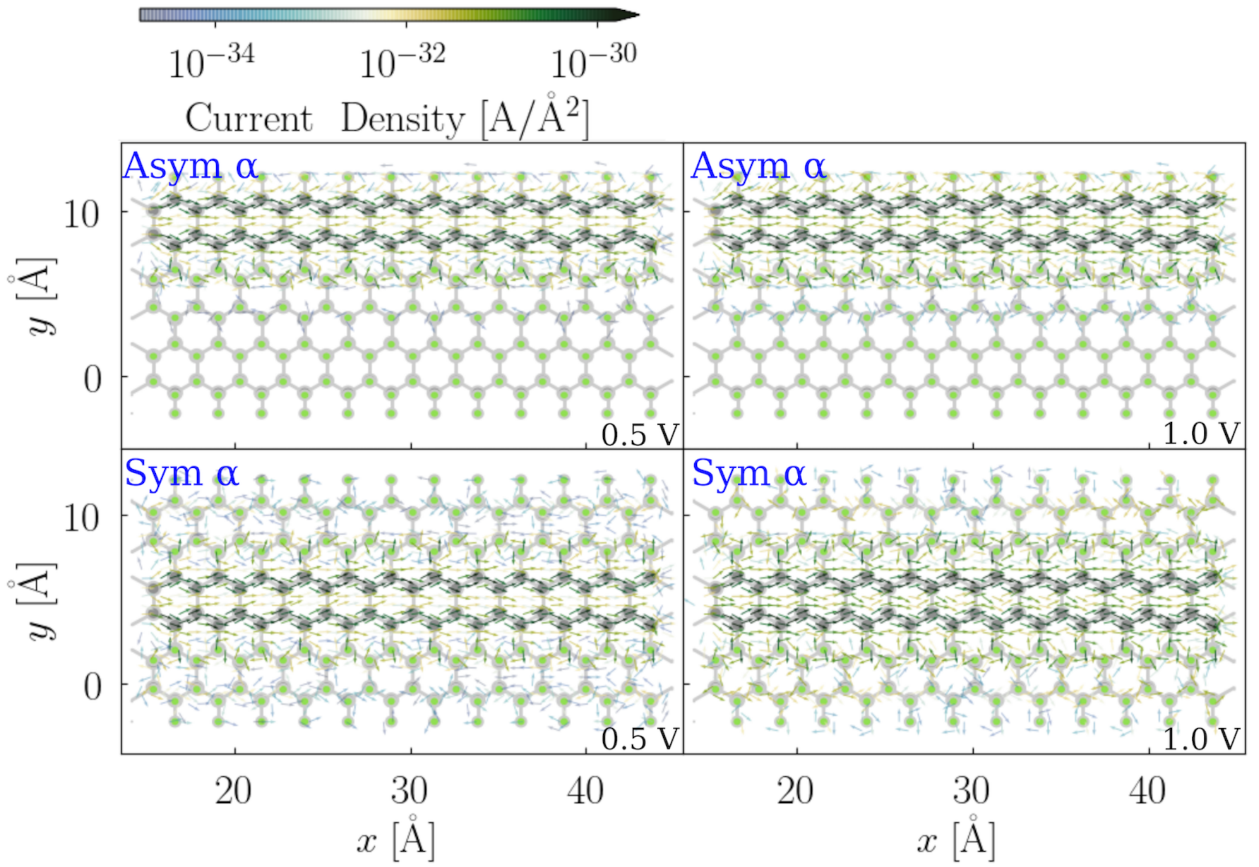
| No. | Fluorination Degree | Bandgap | E/F | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| (1) | 16.67% | 0.006 | 0.785 | −3.905 |
| (2A) | 33.33% | 0.087 | 0.712 | −3.756 |
| (2B) | 33.33% | 0.416 | 0.416 | −3.997 |
| (3) | 50.00% | 0.092 | 0.686 | −3.692 |
| (4A) | 66.67% | 0.184 | 0.184 | −3.677 |
| (4B) | 66.67% | 0.419 | 0.419 | −3.798 |
| (5) | 83.33% | 0.645 | 0.645 | −3.694 |
| (6) | 100.00% | 3.174 | 3.174 | −3.761 |
| No. | Fluorination Degree | X-ZGNRs | Bandgap | E/F |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| (a) | 33.33% | 6ZGNRs | 0.416 | −3.997 |
| (b) | 66.67% | 6ZGNRs | 0.419 | −3.798 |
| (c) | 100.00% | 6ZGNRs | 3.174 | −3.761 |
| (d) | 25.00% | 8ZGNRs | 0.339 | −3.985 |
| (e) | 50.00% | 8ZGNRs | 0.409 | −3.804 |
| (f) | 75.00% | 8ZGNRs | 0.423 | −3.716 |
| (g) | 100.00% | 8ZGNRs | 3.113 | −3.697 |
| (h) | 16.67% | 12ZGNRs | 0.188 | −3.933 |
| (i) | 33.33% | 12ZGNRs | 0.209 | −3.776 |
| (j) | 50.00% | 12ZGNRs | 0.319 | −3.694 |
| (k) | 66.67% | 12ZGNRs | 0.395 | −3.657 |
| (l) | 83.33% | 12ZGNRs | 0.423 | −3.637 |
| (m) | 100.00% | 12ZGNRs | 3.044 | −3.630 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Shao, J.; Paulus, B. Edge Effect in Electronic and Transport Properties of 1D Fluorinated Graphene Materials. Nanomaterials 2022, 12, 125. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano12010125
Shao J, Paulus B. Edge Effect in Electronic and Transport Properties of 1D Fluorinated Graphene Materials. Nanomaterials. 2022; 12(1):125. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano12010125
Chicago/Turabian StyleShao, Jingjing, and Beate Paulus. 2022. "Edge Effect in Electronic and Transport Properties of 1D Fluorinated Graphene Materials" Nanomaterials 12, no. 1: 125. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano12010125
APA StyleShao, J., & Paulus, B. (2022). Edge Effect in Electronic and Transport Properties of 1D Fluorinated Graphene Materials. Nanomaterials, 12(1), 125. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano12010125





