Change in Magnetic Anisotropy at the Surface and in the Bulk of FINEMET Induced by Swift Heavy Ion Irradiation
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
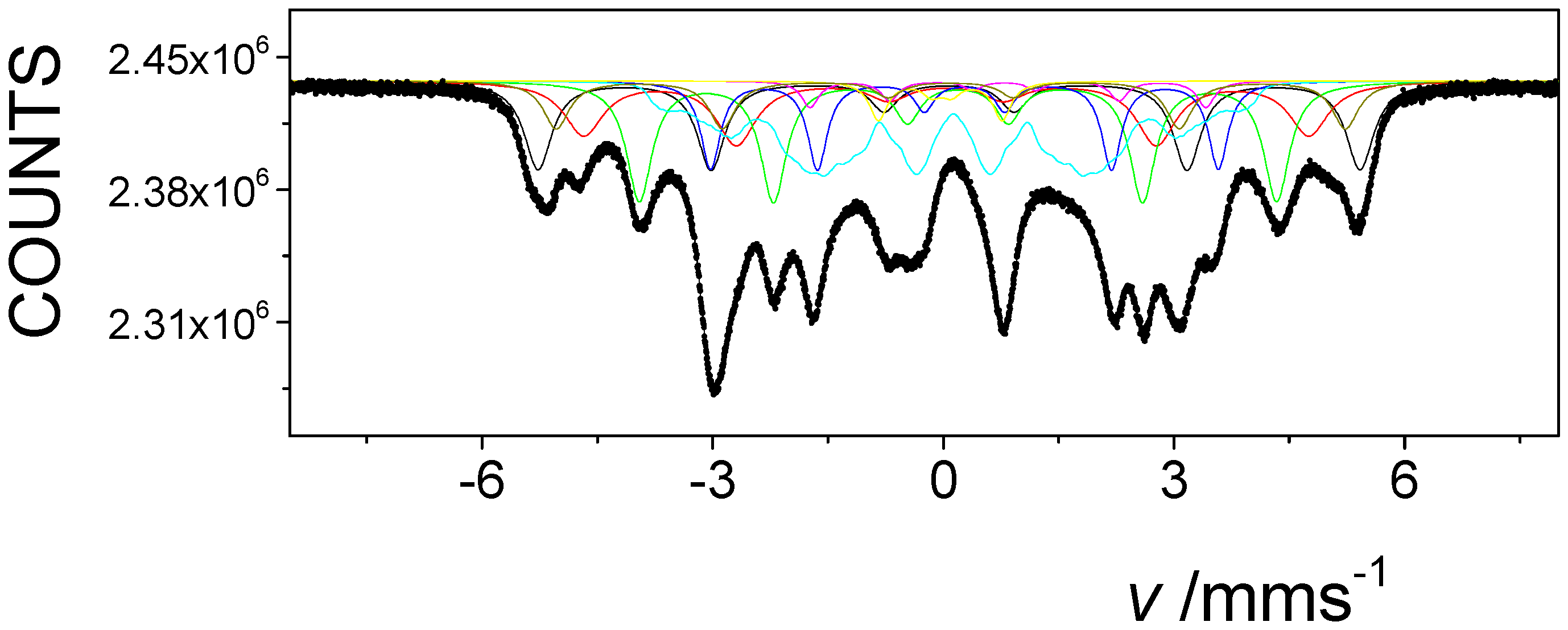
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
- -
- Swift heavy ion irradiation induces considerable changes in the orientation of magnetization (relative to the normal of the ribbon plane), i.e., a decrease in the magnetic anisotropy, both in the bulk and at the surface of the FINEMET ribbons;
- -
- The orientation of magnetization after irradiation is significantly different in the bulk and at the surface. The direction of magnetization is closer to the ribbon plane at the surface than that in the bulk;
- -
- The orientation of magnetization after irradiation depends on the initial magnetic anisotropy produced by stress annealing. The stress-annealing-caused anisotropy is lower at the surface than that in the bulk;
- -
- The decrease in the magnetic anisotropy due to swift heavy ion irradiation can be mostly associated with a change in spin orientation around the radiation-induced defects;
- -
- The present findings for the bulk complement support the previous results [47];
- -
- Swift heavy ion irradiation can be a useful tool for fine tuning the magnetic anisotropy in FINEMET alloys to achieve optimal soft magnetic properties.
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- McHenry, M.E.; Willard, M.A.; Laughlin, D.E. Amorphous and nanocrystalline materials for applications as soft magnets. Prog. Mat. Sci. 1999, 44, 291–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tumanski, S. Magnetic materials. In Handbook of Magnetic Measurements; CRC Press: London, UK, 2011; pp. 117–158. [Google Scholar]
- Lashgari, H.R.; Chu, D.; Xi, S.; Sun, H.; Ferry, M.; Li, S. Composition dependence of the microstructure and soft magnetic properties of Fe-based amorphous/nanocrystalline alloys: A review study. J. Non-Cryst. Solids 2014, 391, 61–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fiorillo, F.; Pasquale, M.; Appino, C. Soft magnetic materials. In Wiley Encyclopedia of Electrical and Electronics Engineering; Webster, J., Ed.; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2016; pp. 1–34. [Google Scholar]
- Koba, K.; Arakawa, D.; Fujieda, M.; Ikegami, K.; Ishi, Y.; Kanai, Y.; Kubota, C.; Machida, S.; Mori, Y.; Ohmori, C.; et al. Longitudinal impedance tuner using new material FINEMET. Rev. Sci. Instr. 1999, 70, 2988–2992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chizhik, A.; Stupakiewicz, A.; Gonzalez, J. Tunable magnetic anisotropy and magnetization reversal in microwires. In High Performance Soft Magnetic Materials; Zhukov, A., Ed.; Springer Series in Materials Science: New York, NY, USA, 2017; Volume 252, pp. 111–129. [Google Scholar]
- Ohmori, C.; Paoluzzi, M.; Tamura, F.; Hasegawa, K.; Sugiyama, Y.; Shirakata, M.; Yoshii, M. J-PARC Contributions to LHC Injector; Liu Project; CERN: Meyrin, Switzerland, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- FINEMET Catalog, Hitachi Metals, Ltd. 2020. Available online: http://www.hitachi-metals.co.jp/e/prod/prod02 (accessed on 10 May 2022).
- Guo, Z.; Wang, J.; Chen, W.; Chen, D.; Sun, H.; Xue, Z.; Wang, C. Crystal-like microstructural FINEMET/FeSi compound powder core with excellent soft magnetic properties and its loss separation analysis. Mater. Des. 2020, 192, 108769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshizawa, Y.; Oguma, S.; Yamauchi, K. New Fe-based soft magnetic alloys composed of ultrafine grain structure. J. Appl. Phys. 1988, 64, 6044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomez-Polo, C.; Perez-Landazabal, J.I.; Recarte, V.; Mendoza, P.; Zelis, P.; Lib, Y.F.; Vazquez, Y.F. Magnetic properties of Mn-doped FINEMET nanocrystalline alloy. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2005, 290–291, 1517–1519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silveyra, J.M.; Moya, J.A.; Cremaschi, V.J.; Janickovic, D.; Švec, P. Structure and soft magnetic properties of FINEMET type alloys: Fe73.5Si13.5Nb3−xMoxB9Cu1 (x = 1.5, 2). Hyperfine Interact. 2010, 195, 173–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ershov, N.V.; Chernenkov, Y.P. Structure of Nanocrystals in FINEMETS with Different Silicon Content and Stress-Induced Magnetic Anisotropy in Nanocrystal. Masuda, Y., Ed.; InTech: London, UK, 2011; pp. 416–437. [Google Scholar]
- Mikhalitsyna, E.A.; Kataev, V.A.; Lepalovskij, V.N.; Larranga, A.; Volegov, A.S. Heat treatment effect on magnetic properties of FINEMET-type films. In Proceedings of the IV Sino-Russian ASRTU Symposium on Advanced Materials and Processing Technology (ASRTU), Ekaterinburg, Russia, 23–26 June 2016; pp. 109–114. [Google Scholar]
- Yoshizawa, Y. Magnetic properties and microstructure of nanocrystalline Fe-based alloys. J. Metast. Nanocryst. Mater. 1999, 1, 51–62. [Google Scholar]
- Hofmann, B.; Kronmüller, H. Creep induced magnetic anisotropy in nanocrystalline Fe73.5Cu1Nb3Si13.5B9. Nanostruct. Mater. 1995, 6, 961–964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazaleyrat, F.; Gercsi, Z.; Lécrivain, M.; Varga, L.K. A novel method determining longitudinally induced magnetic anisotropy in amorphous and nanocrystalline soft materials. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2004, 280, 391–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Varga, L.K. Soft magnetic nanocomposites for high-frequency and high-temperature applications. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2007, 316, 442–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Životský, O.; Postava, K.; Hrabovská, K.; Hendrych, A.; Pištora, J.; Kraus, L. Depth-sensitive characterization of surface magnetic properties of as-quenched FeNbB ribbons. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2008, 255, 3322–3327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Životský, O.; Klimša, L.; Hendrych, A.; Jirásková, Y.; Buršík, J. A new phenomenon on the surface of FINEMET alloy. J. Supercond. Nov. Magn. 2013, 26, 1349–1352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varga, L.K.; Kovács, G. Effect of transversal applied bias field on the longitudinal soft magnetic properties of nanocrystalline Finemet cores. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2012, 48, 1360–1362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gheiratmand, T.; Hosseini, H.R.M.; Davami, P.; Ostadhossein, F.; Song, M.; Gjokac, M. On the effect of cooling rate during melt spinning of FINEMET ribbons. Nanoscale 2013, 5, 7520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Talaat, A.; Zhukova, V.; Ipatov, M.; Blanco, J.M.; Gonzalez-Legarreta, L.; Hernando, B.; del Val, J.; Gonzalez, J.; Zhukov, A. Optimization of the giant magnetoimpedance effect of FINEMET-type microwires through the nanocrystallization. J. Appl. Phys. 2014, 115, 17A313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mikhalitsyna, E.; Zakharchuk, I.; Soboleva, E.; Geydt, P.; Kataev, V.; Lepalovskij, V.; Lahderanta, E. Heat treatment effect on magnetic microstructure of Fe73.9Cu1Nb3Si13.2B8.9. Thin Films EPJ Web Conf. 2018, 185, 04001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Salinas, D.R.; Garcıa, S.G.; Bessone, J.B.; Pierna, A.R. Nanocrystallization process of the Fe69.5Cu1Nb3B9Si13.5Cr4 FINEMET-type alloy: An AFM study. Surf. Interface Anal. 2000, 30, 305–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okumura, H.; Laughlin, D.E.; McHenry, M.E. Magnetic and structural properties and crystallization behavior of Si-rich FINEMET materials. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2003, 267, 347–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herzer, G. Grain structure and magnetism of nanocrystalline ferromagnets. IEEE Trans. Magn. 1989, 25, 3327–3329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.; Clavaguera, N.; Clavaguera-Mora, M.T.; Howells, W.S. Neutron diffraction analysis on FINEMET alloys. J. Appl. Phys. 1998, 84, 6565–6569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Um, C.-Y.; Johnson, F.; Simone, M.; Barrow, J.; McHenry, M.E. Effect of crystal fraction on hardness in FINEMET and NANOPERM nanocomposite alloys. J. Appl. Phys. 2005, 97, 10F504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blagojevic, V.A.; Vasic, M.; David, B.; Minic, D.M.; Pizúrová, N.; Zák, T.; Minic, D.M. Thermally induced crystallization of Fe73.5Cu1Nb3Si15.5B7 amorphous alloy. Intermetallics 2014, 45, 53–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alves, M.J.P.; Gonzalez-Chavez, D.E.; Bohn, F.; Sommer, R.L. Annealing effects on the microwave linewidth broadening of FeCuNbSiB ferromagnetic films. J. Appl. Phys. 2015, 117, 123913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kováč, J.; Kunca, B.; Novák, L. Investigation of Rayleigh region in strip like amorphous FINEMET samples after different heat treatments. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2020, 502, 166555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zighem, F.; Belmeguenai, M.; Faurie, D.; Haddadi, H.; Moulin, J. Combining ferromagnetic resonator and digital image correlation to study the strain induced resonance tunability in magnetoelectric heterostructures. Rev. Sci. Instr. 2014, 85, 103905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sadovnikov, A.V.; Bublikov, K.V.; Beginin, E.N.; Sheshukova, S.E.; Sharaevskii, Y.P.; Nikitov, S.A. Nonreciprocal propagation of hybrid electromagnetic waves in a layered ferrite-ferroelectric structure with a finite width. JETP Lett. 2015, 102, 142–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zemčik, T.; Jirásková, Y.; Závéta, K.; Eckert, D.; Schneider, J.; Mattern, N.; Hesske, D. Structure, magnetic properties and Mössbauer spectroscopy of amorphous and nanocrystalline Fe73.5Cu1Nb3Si16.5B6. Mater. Lett. 1991, 10, 313–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cserei, A.; Jiang, J.; Aubertin, F.; Gonser, U. Study of the crystallization kinetics in amorphous Fe73.5Cu1Nb3Si13.5B9 alloy. J. Mater. Sci. 1994, 29, 1213–1216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miglierini, M. Mössbauer-effect study of the hyperfine field distributions in the residual amorphous phase of Fe-Cu-Nb-Si-B nanocrystalline alloys. J. Phys. Condens. Matter. 1994, 6, 1431–1438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borrego, J.M.; Peña Rodrígez, V.A.; Conde, A. Crystallization of Co-containing FINEMET alloys. Hyperfine Interact. 1997, 110, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vértes, A.; Korecz, L.; Burger, K. Mössbauer Spectroscopy; Akadémiai Kiadó: Budapest, Hungary, 1979; pp. 1–432. [Google Scholar]
- Kuzmann, E.; Nagy, S.; Vértes, A. Critical review of analytical applications of Mössbauer spectroscopy illustrated by Mineralogical and geological examples. Pure Appl. Chem. 2003, 75, 801–858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kuzmann, E.; Homonnay, Z.; Nagy, S.; Nomura, K. Mössbauer spectroscopy. In Handbook of Nuclear Chemistry; Vértes, A., Nagy, S., Klencsár, Z., Lovas, R.G., Rösch, F., Eds.; Springer: Boston, MA, USA, 2011; pp. 1381–1446. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, J.; Zemčik, T.; Aubertin, F.; Gonser, U. Investigation of the phases and magnetization orientation in crystalline Fe73.5Cu1Nb3Si16.5B6 alloy. J. Mater. Sci. Lett. 1991, 10, 763–764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hampel, G.; Pundt, A.; Hesse, J. Crystallization of Fe73.5Cu1Nb3Si13.5B9: Structure and kinetics examined by X-ray diffraction and Mössbauer effect spectroscopy. J. Phys. Condens. Matter. 1992, 4, 3195–3214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, A.; Bhagat, N.; Principi, G. Mössbauer study of magnetic interactions in nanocrystalline Fe73.5Cu1Nb3Si16.5B6. J. Phys. Condens. Matter. 1995, 7, 2237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borrego, J.M.; Conde, A.; Pena-Rodríguez, V.A.; Grenèche, J.M. Mössbauer spectrometry of FINEMET-type nanocrystallibe alloy. Hyperfine Interact. 2000, 131, 67–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kane, S.N.; Bhagat, N.; Gupta, A.; Varga, L.K. Effect of quenching rate on spin texture in amorphous Fe73.5Cu1Nb3Si13.5B9 alloys. J. Mag. Mag. Mater. 1997, 167, 241–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuzmann, E.; Stichleutner, S.; Sápi, A.; Varga, L.K.; Havancsák, K.; Skuratov, V.; Homonnay, Z.; Vértes, A. Mössbauer study of FINEMET type nanocrystalline ribbons irradiated with swift heavy ions. Hyperfine Interact. 2012, 207, 73–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuzmann, E.; Stichleutner, S.; Sápi, A.; Klencsár, Z.; Oshtrakh, M.I.; Semionkin, V.A.; Kubuki, S.; Homonnay, Z.; Varga, L.K. Mössbauer study of FINEMET with different permeability. Hyperfine Interact. 2013, 219, 63–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Oshtrakh, M.I.; Klencsar, Z.; Semionkin, V.A.; Kuzmann, E.; Homonnay, Z.; Varga, L.K. Annealed FINEMET ribbons: Structure and magnetic anisotropy as revealed by the high velocity resolution Mössbauer spectroscopy. Mat. Chem. Phys. 2016, 180, 66–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshizawa, Y.; Yamauchi, K. Magnetic properties of nanocrystalline Fe-based soft magnetic alloys. Mat. Res. Soc. Proc. 1991, 232, 457–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herzer, G. Nanocrystalline soft magnetic materials. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 1992, 192, 258–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glazer, A.A.; Kleinerman, N.M.; Lukshina, V.A.; Potapov, A.P.; Serikov, V.V. Thermomechanical treatment of the nanocrystalline alloy Fe73.5Cu1Nb3Si13.5B9. Phys. Metals Metallog. 1991, 12, 53–58. [Google Scholar]
- Herzer, G. Creep induced magnetic anisotropy in nanocrystalline Fe–Cu–Nb–Si–B alloys. IEEE Trans. Magn. 1994, 30, 4800–4802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hofmann, B.; Kronmuller, H. Stress-induced magnetic anisotropy in nanocrystalline FeCuNbSiB alloy. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 1996, 152, 91–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varga, L.K.; Gercsi, Z.; Kovacs, G.; Kakay, A.; Mazaleyrat, F. Stress-induced magnetic anisotropy in nanocrystalline alloys. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2003, 254–255, 477–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Csizmadia, E.; Varga, L.K.; Palánki, Z.; Zámborszky, F. Creep or tensile stress induced anisotropy in FINEMET-type ribbons? J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2015, 374, 587–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, Z.; Li, X.; Sohrabi, S.; Ren, Y.; Wang, W. Magnetic properties in finemet-type soft magnetic toroidal cores annealed under radial stresses. Metals 2020, 10, 122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kuzmann, E.; Spirov, I.N. Mössbauer study of amorphous alloys irradiated with energetic heavy ions. J. Nucl. Mater. 1986, 137, 22–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spiller, P.; Blasche, K.; Franczak, B.; Kirk, M.; Husmann, P.; Omet, C.; Ratschow, S.; Stadlmann, J. Accelerator plans at GSI for plasma physics applications. Nucl. Instr. Meth. Phys. Res. A 2005, 544, 117–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kollár, P.; Ramin, D.; Zeleňáková, A.; Riehemann, W.; Kuzminski, M. Magnetic properties of laser-treated FINEMET. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 1999, 302, 301–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubey, R.; Gupta, A.; Sharma, P.; Darowski, N.; Schumacher, G. Tailoring of magnetic anisotropy in amorphous and nanocrystalline soft magnetic alloys using swift heavy ions. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2007, 310, 2491–2493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miglierini, M.; Lancok, A.; Pavlovic, M. Ion bombardment of Fe-based amorphous metallic alloys. Hyperfine Interact. 2009, 189, 45–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miglierini, M.; Hasiak, M. Impact of ion irradiation upon structure and magnetic properties of NANOPERM-type amorphous and nanocrystalline alloys. J. Nanomat. 2015, 2015, 175407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, P.; Gupta, A. Ion beam sputtered thin films of finemet alloy for soft magnetic applications. Nucl. Instr. Meth. Phys. Res. B 2006, 244, 105–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dunlop, A.; Jaskierowicz, G.; Rizza, G. Partial crystallization of an amorphous alloy by electronic energy deposition. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2003, 90, 015503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rizza, G.; Dunlop, A.; Jaskierowicz, G.; Kopcewicz, M. High electronic excitation-induced crystallization in Fe73.5Cu1Nb3Si13.5B9 amorphous alloy: I. Irradiation with swift heavy monoatomic projectiles. Nucl. Instr. Meth. Phys. Res. B 2004, 226, 609–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klencsár, Z.; Kuzmann, E.; Vértes, A. User-friendly software for Mössbauer spectrum analysis. J. Radioanal. Nucl. Chem. 1996, 210, 105–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oshtrakh, M.I.; Semionkin, V.A.; Milder, O.B.; Novikov, E.G. Mössbauer spectroscopy with high velocity resolution: An increase of analytical possibilities in biomedical research. J. Radioanal. Nucl. Chem. 2009, 281, 63–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oshtrakh, M.I.; Semionkin, V.A. Mössbauer spectroscopy with a high velocity resolution: Advances in biomedical, pharmaceutical, cosmochemical and nanotechnological research. Spectrochim. Acta Part A Molec. Biomolec. Spectrosc. 2013, 100, 78–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Oshtrakh, M.I.; Semionkin, V.A. Mössbauer spectroscopy with a high velocity resolution: Principles and applications. AIP Conf. Proc. 2016, 1781, 020019. [Google Scholar]
- Friedrich, H. Theoretical Atomic Physics; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Ziegler, J.F.; Biersack, J.P.; Ziegler, M.D. SRIM, the Stopping and Range of Ions in Matter; SRIM Company: Langley, BC, Canada, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Stiller, M.; Barzola-Quiquia, J.; Esquinazi, P.; Spemann, D.; Meijer, J.; Lorenz, M.; Grundmann, M. Strong out-of-plane magnetic anisotropy in ion irradiated anatase TiO2 thin films. AIP Adv. 2016, 6, 125009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Teixeira, B.M.S.; Timopheev, A.A.; Cacoilo, N.F.F.; Auffret, S.; Sousa, R.C.; Dieny, B.; Alves, E.; Sobolev, N.A. Ion irradiation-induced easy-cone anisotropy in double-MgO free layers for perpendicular magnetic tunnel junctions. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2018, 112, 202403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazalski, P.; Kurant, Z.; Sveklo, I.; Dobrogowski, W.; Fassbender, J.; Wawro, A.; Maziewski, A. On irradiation driven changes of magnetic anisotropy in ultrathin Co films sandwiched between Au or Pt covers. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2019, 479, 332–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| Sample | A2,5/A1,6 | θ (°) |
|---|---|---|
| CK021 | ||
| non-irradiated | 2.59 | 62.5 |
| µ = 2000 | ||
| CK021 | ||
| first irradiated from the air side | ||
| 160 MeV 132Xe, 1 × 1013 ion cm−2 | 1.36 | 45.4 |
| CK021 | ||
| second irradiated from the wheel side | ||
| (both side irradiated) | ||
| 160 MeV 132Xe, 1 × 1013 ion cm−2 | 1.15 | 41.93 |
| CK022 | ||
| non-irradiated | 3.18 | 70.3 |
| µ = 8000 | ||
| CK022 | ||
| first irradiated from the air side | ||
| 160 MeV 132Xe, 1 × 1013 ion cm−2 | 1.89 | 53.3 |
| CK022 | ||
| second irradiated from the wheel side | ||
| (both side irradiated) | ||
| 160 MeV 132Xe, 1 × 1013 ion cm−2 | 1.2 | 42.79 |
| Sample | A2,5/A1,6 | θ (°) |
|---|---|---|
| CK023 | ||
| non-irradiated | 3.9 | 83.54 |
| µ = 190,000 | ||
| CK023 | ||
| first irradiated from the air side | ||
| 160 MeV 132Xe, 1 × 1013 ion cm−2 | 1.8 | 51.98 |
| CK023 | ||
| first irradiated from the wheel side | ||
| 160 MeV 132Xe, 1 × 1013 ion cm−2 | 1.74 | 51.13 |
| Sample | A2,5/A1,6 | θ (°) |
|---|---|---|
| CK021 | ||
| non-irradiated | 3.46 | 74.4 |
| µ = 2000 | ||
| CK021 | ||
| irradiated | ||
| 160 MeV 132Xe, 1 × 1013 ion cm−2 | 2.62 | 62.9 |
| CK022 | ||
| non-irradiated | 3.97 | 86.8 |
| µ = 8000 | ||
| CK022 | ||
| irradiated | ||
| 160 MeV 132Xe, 1 × 1013 ion cm−2 | 3.1 | 69.2 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kuzmann, E.; Stichleutner, S.; Machala, L.; Pechoušek, J.; Vondrášek, R.; Smrčka, D.; Kouřil, L.; Homonnay, Z.; Oshtrakh, M.I.; Mozzolai, A.; et al. Change in Magnetic Anisotropy at the Surface and in the Bulk of FINEMET Induced by Swift Heavy Ion Irradiation. Nanomaterials 2022, 12, 1962. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano12121962
Kuzmann E, Stichleutner S, Machala L, Pechoušek J, Vondrášek R, Smrčka D, Kouřil L, Homonnay Z, Oshtrakh MI, Mozzolai A, et al. Change in Magnetic Anisotropy at the Surface and in the Bulk of FINEMET Induced by Swift Heavy Ion Irradiation. Nanomaterials. 2022; 12(12):1962. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano12121962
Chicago/Turabian StyleKuzmann, Ernő, Sándor Stichleutner, Libor Machala, Jiří Pechoušek, René Vondrášek, David Smrčka, Lukáš Kouřil, Zoltán Homonnay, Michael I. Oshtrakh, András Mozzolai, and et al. 2022. "Change in Magnetic Anisotropy at the Surface and in the Bulk of FINEMET Induced by Swift Heavy Ion Irradiation" Nanomaterials 12, no. 12: 1962. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano12121962
APA StyleKuzmann, E., Stichleutner, S., Machala, L., Pechoušek, J., Vondrášek, R., Smrčka, D., Kouřil, L., Homonnay, Z., Oshtrakh, M. I., Mozzolai, A., Skuratov, V. A., Kudor, M., Herczeg, B., & Varga, L. K. (2022). Change in Magnetic Anisotropy at the Surface and in the Bulk of FINEMET Induced by Swift Heavy Ion Irradiation. Nanomaterials, 12(12), 1962. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano12121962









