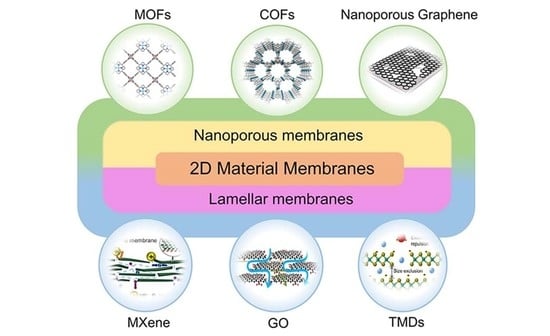
A Review of Advancing Two-Dimensional Material Membranes for Ultrafast and Highly Selective Liquid Separation
Abstract
:1. Introduction
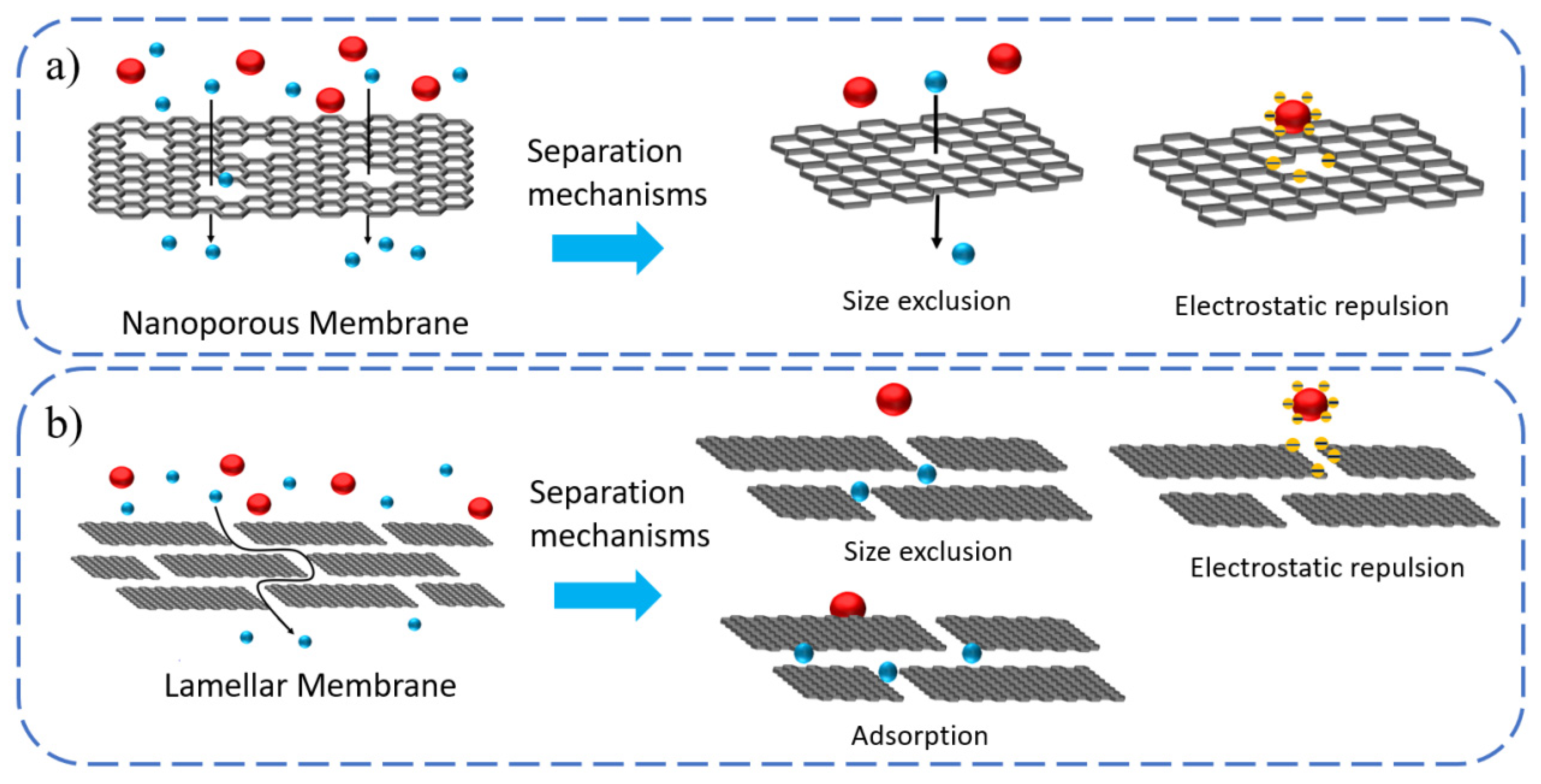
2. Separation Mechanisms of 2DNM Membranes
3. 2D Nanosheet Membranes (Porous Membranes)
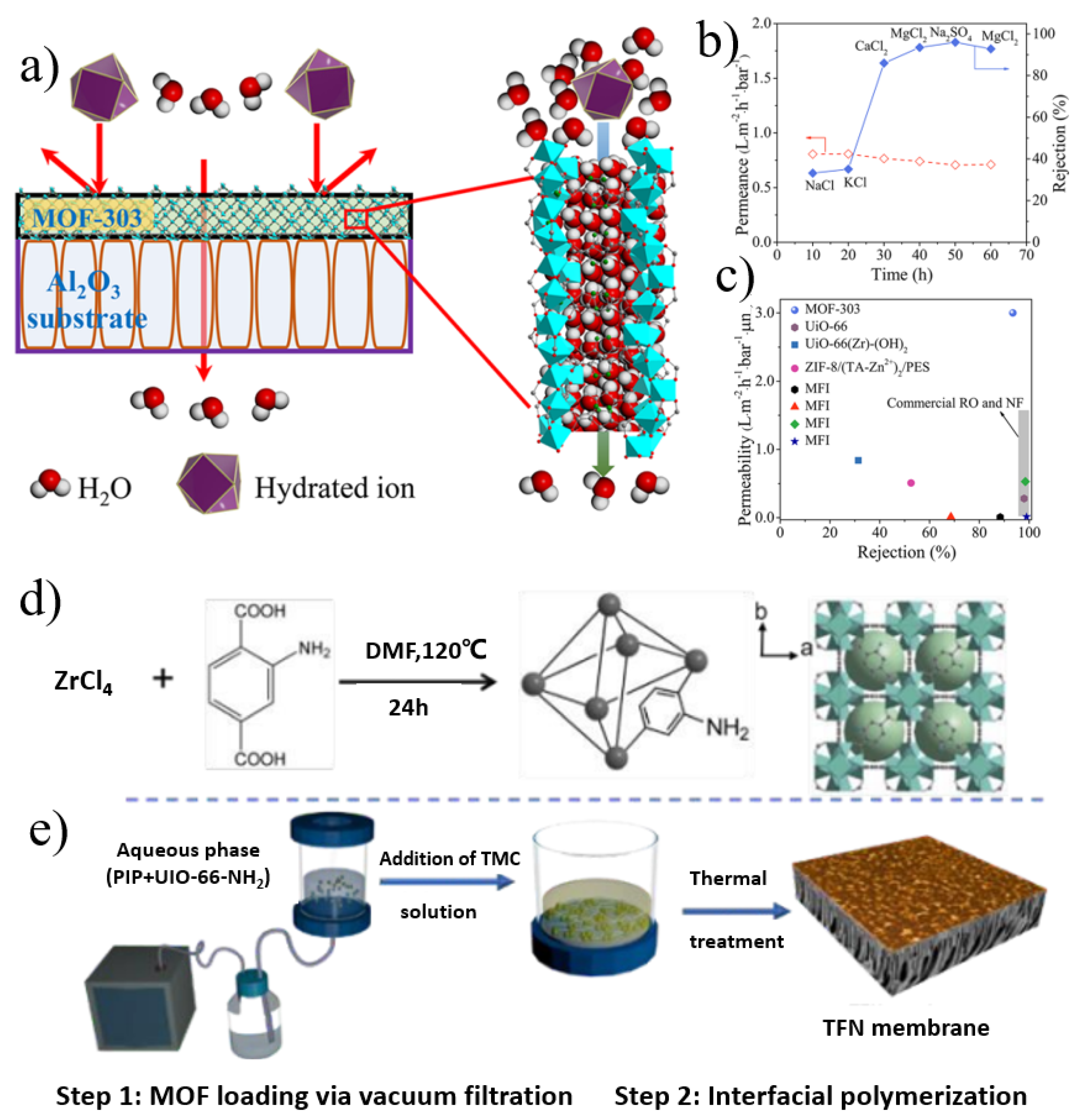
3.1. MOF
3.2. COF
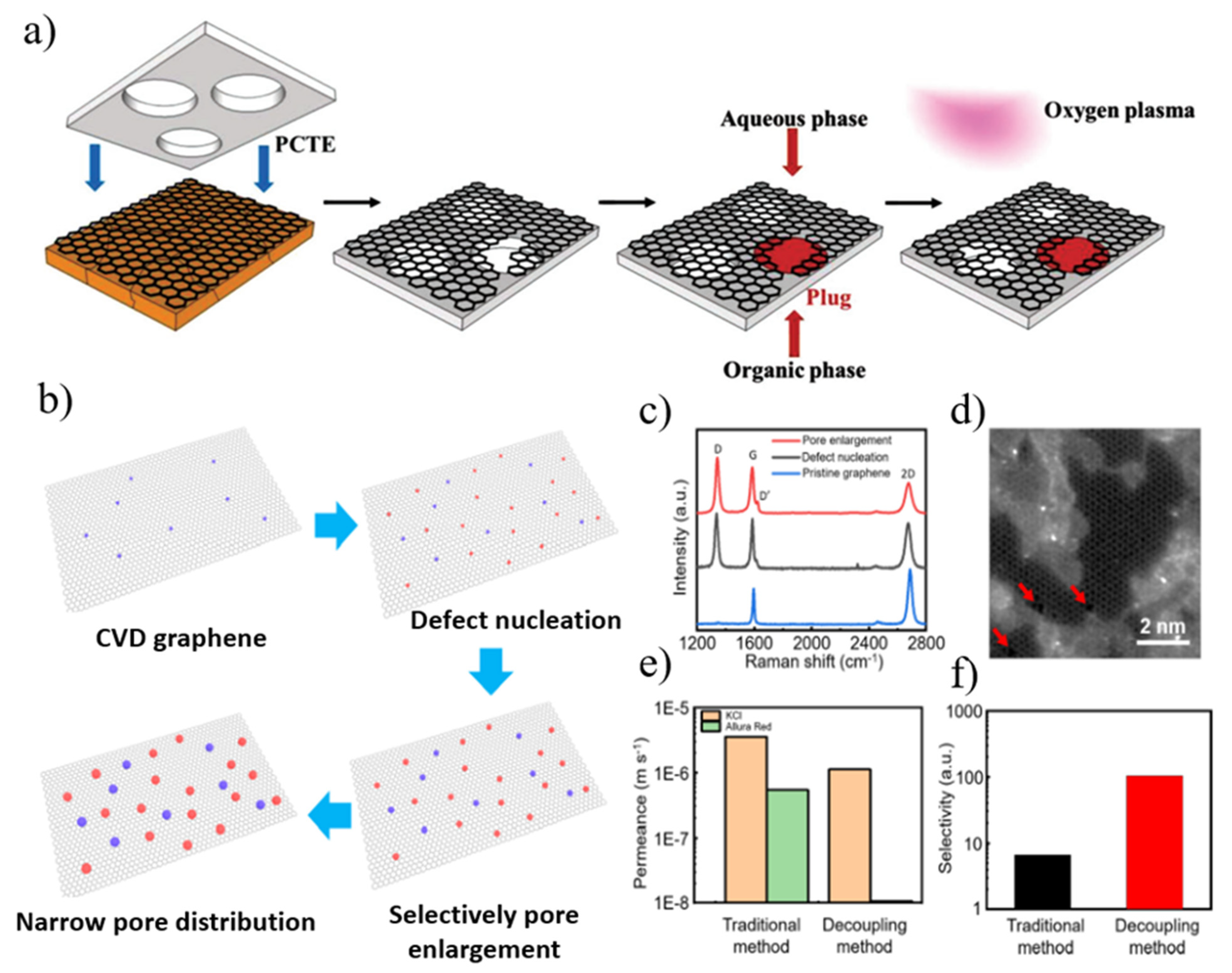
3.3. Nanoporous Graphene Membranes
3.4. Others Nanoporous Membrane
4. 2D Lamellar Membranes (Layered Stacks)
4.1. Graphene Oxide Membranes

4.2. RGO Membrane
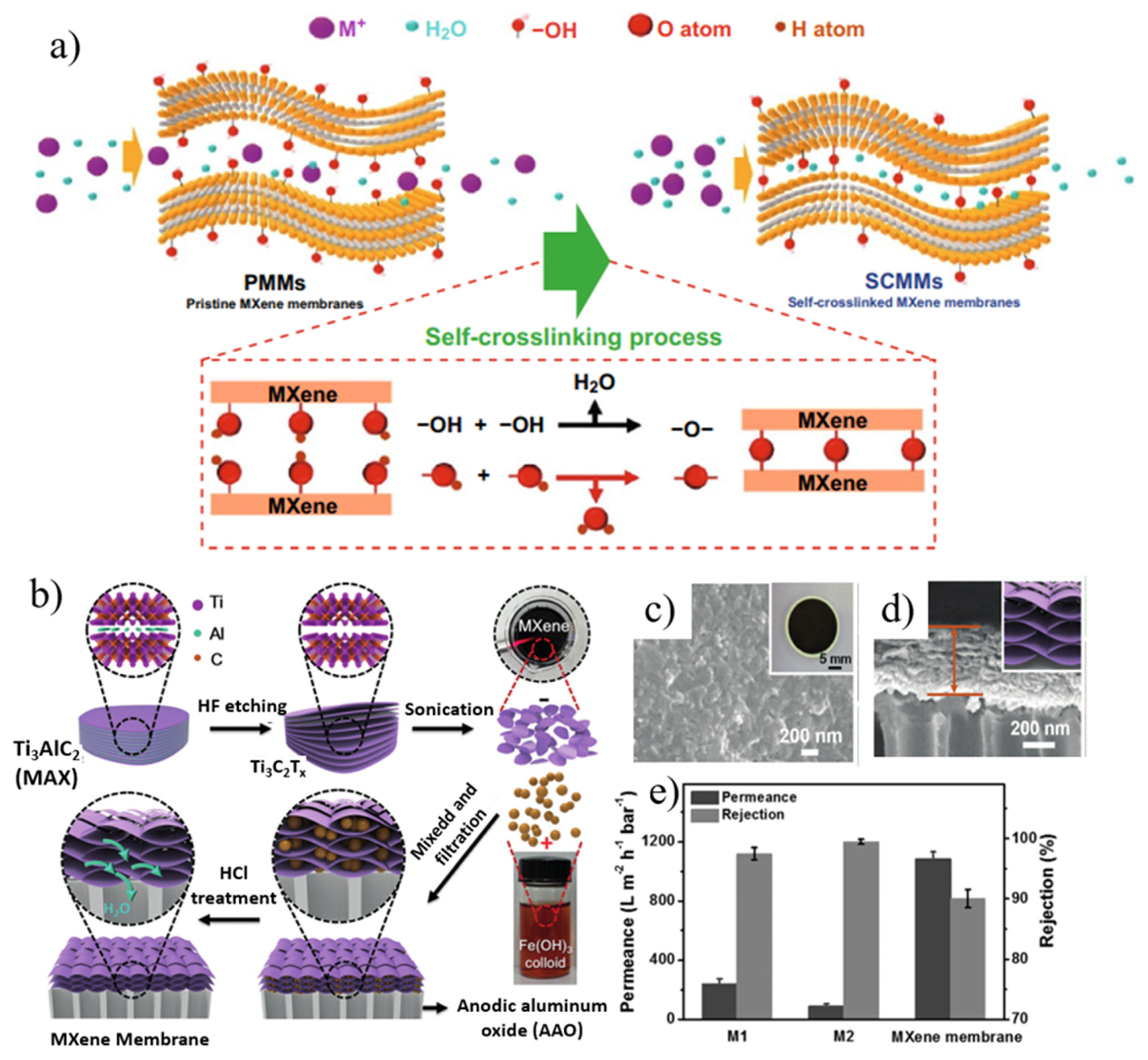
4.3. MXene Membranes
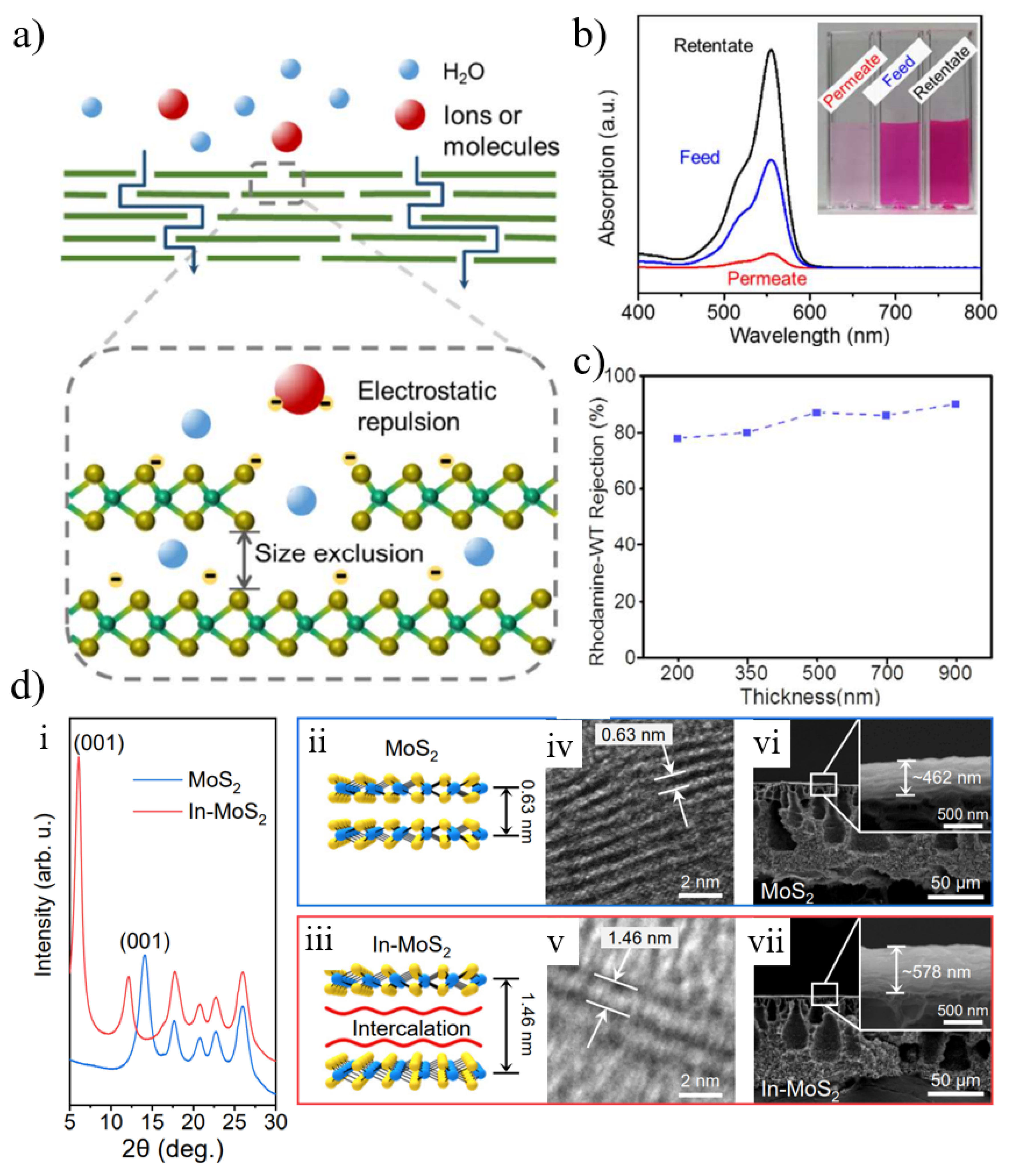
4.4. Transition Metal Dichalcogenide (TMD) Membranes
4.5. g-C3N4 Membrane
4.6. Others
5. Conclusions and Future Outlook
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhao, P.; Jian, M.; Zhang, Q.; Xu, R.; Liu, R.; Zhang, X.; Liu, H. A new paradigm of ultrathin 2D nanomaterial adsorbents in aqueous media: Graphene and GO, MoS2, MXenes, and 2D MOFs. J. Mater. Chem. A 2019, 7, 16598–16621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, J.; Li, J.; Xu, Z.; Liu, Y.; Cheng, F. Simultaneous anti-fouling and flux-enhanced membrane distillation via incorporating graphene oxide on PTFE membrane for coking wastewater treatment. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2020, 531, 147349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van der Bruggen, B. Sustainable implementation of innovative technologies for water purification. Nat. Rev. Chem. 2021, 5, 217–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Wei, Y.; Fan, J.; Cai, J.; Lu, Z.; Ding, L.; Wang, H. Recent progress of two-dimensional nanosheet membranes and composite membranes for separation applications. Front. Chem. Sci. Eng. 2021, 15, 793–819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwon, O.; Choi, Y.; Choi, E.; Kim, M.; Woo, Y.C.; Kim, D.W. Fabrication techniques for graphene oxide-based molecular separation membranes: Towards industrial application. Nanomaterials 2021, 11, 757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, H.B.; Kamcev, J.; Robeson, L.M.; Elimelech, M.; Freeman, B.D. Maximizing the right stuff: The trade-off between membrane permeability and selectivity. Science 2017, 356, 6343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, J.; Cheng, Y.; Pu, Y.; Zhao, D. Two-Dimensional Membranes: New Paradigms for High-Performance Separation Membranes. Chem.-Asian J. 2020, 15, 2241–2270. [Google Scholar]
- Perreault, F.; Faria, A.F.; Elimelech, M. Environmental applications of graphene-based nanomaterials. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2015, 44, 5861–5896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rasool, K.; Pandey, R.P.; Rasheed, P.A.; Buczek, S.; Gogotsi, Y.; Mahmoud, K.A. Water treatment and environmental remediation applications of two-dimensional metal carbides (MXenes). Mater. Today 2019, 30, 80–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Wu, A.; Ciacchi, L.C.; Wei, G. Recent advances in nanoporous membranes for water purification. Nanomaterials 2018, 8, 65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, H.; Ko, T.-J.; Lee, M.; Chung, H.-S.; Han, S.S.; Oh, K.H.; Sadmani, A.; Kang, H.; Jung, Y. Experimental realization of few layer two-dimensional MoS2 membranes of near atomic thickness for high efficiency water desalination. Nano Lett. 2019, 19, 5194–5204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tetteh, E.K.; Rathilal, S.; Asante-Sackey, D.; Chollom, M.N. Prospects of synthesized magnetic TiO2-based membranes for wastewater treatment: A review. Materials 2021, 14, 3524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, Y.; Chen, D.; Li, N.; Xu, Q.; Li, H.; He, J.; Lu, J. A self-cleaning heterostructured membrane for efficient oil-in-water emulsion separation with stable flux. Adv. Mater. 2020, 32, 2001265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, G.; Jin, W.; Xu, N. Two-Dimensional-Material Membranes: A new family of high-performance separation membranes. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2016, 55, 13384–13397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, Y.; Li, Y.; Ban, Y.; Jin, H.; Jiao, W.; Liu, X.; Yang, W. Metal-organic framework nanosheets as building blocks for molecular sieving membranes. Science 2014, 346, 1356–1359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Pan, Y.; Xu, J.; Wang, A.; Wu, S.; Shen, J. The carbonization of polyethyleneimine: Facile fabrication of N-doped graphene oxide and graphene quantum dots. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 105855–105861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, S.; Zhang, T.; Fan, S.; Jia, Z.; Yang, Y. Preparation of COF-TpPa1 membranes by chemical vapor deposition method for separation of dyes. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 421, 129750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Li, Z.; Wang, Z.; Yuan, S.; Li, Y.; Zhao, W.; Zhang, X. 2D material based thin-film nanocomposite membranes for water treatment. Adv. Mater. Technol. 2021, 6, 2000862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, P.; Hou, J.; Zhang, Y.; Li, L.; Lu, X.; Tang, Z. Two-dimensional material membranes for critical separations. Inorg. Chem. Front. 2020, 7, 2560–2581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, X.; Zheng, Q.; Kim, J.-K. Rational design of two-dimensional nanofillers for polymer nanocomposites toward multifunctional applications. Prog. Mater. Sci. 2021, 115, 100708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Liu, X.; Feng, Y.; Yin, J. Recent progress in polymer/two-dimensional nanosheets composites with novel performances. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2022, 126, 101505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Safaei, J.; Xiong, P.; Wang, G. Progress and prospects of two-dimensional materials for membrane-based water desalination. Mater. Today Adv. 2020, 8, 100108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Li, Y.; Goethem, C.V.; Wan, K.; Zhang, W.; Luo, J.; Vankelecom, I.F.J.; Fransaer, J. Electrochemically Assisted interfacial growth of MOF membranes. Matter 2019, 1, 1285–1292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yao, Y.; Wang, C.; Na, J.; Hossain, M.S.A.; Yan, X.; Zhang, H.; Amin, M.A.; Qi, J.; Yamauchi, Y.; Li, J. Macroscopic MOF architectures: Effective strategies for practical application in water treatment. Small 2021, 18, 2104387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Wang, H.; Yuan, X.; Zhang, J.; Chew, J.W. Metal-organic framework membranes for wastewater treatment and water regeneration. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2020, 404, 213116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.-L.; Chen, J.; Zhang, Y.; Yu, C.-X.; Du, W.; Sun, X.-Q.; Zhang, J.-L.; Hu, F.-L.; Mi, Y.; Ma, L.-F. Fabrication of ultrathin single-layer 2D metal-organic framework nanosheets with excellent adsorption performance via a facile exfoliation approach. J. Mater. Chem. A 2020, 5, 546–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, G.; Zhou, Z.; Zhao, X.; Zhang, W.; An, C. Ultrathin metal-organic framework nanosheets derived ultrathin Co3O4 nanomeshes with robust oxygen-evolving performance and asymmetric supercapacitors. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2018, 10, 23721–23730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cong, S.; Yuan, Y.; Wang, J.; Wang, Z.; Kapteijn, F.; Liu, X. Highly water-permeable metal−organic framework MOF-303 membranes for desalination. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2021, 143, 20055–20058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.; Hou, J.; Yuan, S.; Zhao, Y.; Li, Y.; Zhang, R.; Tian, M.; Li, J.; Wang, J.; Van der Bruggen, B. MOF-positioned polyamide membranes with a fishnet-like structure for elevated nanofiltration performance. J. Mater. Chem. A 2019, 7, 16313–16322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, Y.; Dai, R.; Li, X.; Zhang, X.; Cao, X.; Wu, Z.; Lin, S.; Tang, C.; Wang, Z. Metal-organic framework enables ultraselective polyamide membrane for desalination and water reuse. Sci. Adv. 2022, 8, 4149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Zhang, S.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Ma, S. Covalent organic frameworks for separation applications. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2020, 49, 708–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.; Lin, X. Fabricating compact covalent organic framework membranes with superior performance in dye separation. J. Membr. Sci. 2021, 637, 119667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Zhang, K.; Tsuru, T. Two-dimensional covalent organic framework (COF) membranes fabricated via the assembly of exfoliated COF nanosheets. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2017, 9, 8433–8436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Si, Z.; Cai, D.; Li, G.L.S.; Qin, P. Synthesis of stable COF-300 nanofiltration membrane via in-situ growth with ultrahigh flux for selective dye separation. J. Membr. Sci. 2020, 615, 118466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, H.; Gu, J.; Meng, H.; Knebel, A.; Caro, J. High-flux imine-linked covalent organic framework COF-LZU1 membranes on tubular alumina supports for highly selective dye separation by nanofiltration. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2018, 57, 4104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yang, H.; Wu, H.; Zhao, Y.; Wang, M.; Song, Y.; Cheng, X.; Wang, H.; Cao, X.; Pan, F.; Jiang, Z. Ultrathin heterostructured covalent organic framework membranes with interfacial molecular sieving capacity for fast water-selective permeation. J. Mater. Chem. A 2020, 8, 19328–19336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheng, F.; Li, X.; Li, Y.; Afsar, N.U.; Zhao, Z.; Ge, L.; Xu, T. Cationic covalent organic framework membranes for efficient dye/salt separation. J. Membr. Sci. 2022, 644, 120118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L.; Xu, J.; Shan, B.; Wang, X.; Gao, C. TpPa-2-incorporated mixed matrix membranes for efficient water purification. J. Membr. Sci. 2017, 526, 355–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, X.; Wang, R.; Xiao, A.; Jia, T.; Sun, S.-P.; Wang, Y. Layer-by-layer synthesis of covalent organic frameworks on porous substrates for fast molecular separations. ACS Appl. Nano Mater. 2018, 1, 6320–6326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dey, K.; Pal, M.; Rout, K.C.; Kunjattu, H.S.; Das, A.; Mukherjee, R.; Kharul, U.K.; Banerjee, R. Selective molecular separation by interfacially crystallized covalent organic framework thin films. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2017, 139, 13083–13091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, H.; Gu, J.; Meng, H.; Knebel, A.; Caro, J. High-flux membranes based on the covalent organic framework COF-LZU1 for selective dye separation by nanofiltration. Angew. Chem. 2018, 57, 4083–4087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, D.; Li, K.; Li, M.; Wang, Z.; Shan, M.; Zhang, Y. Moderately crystalline azine-linked covalent organic framework membrane for ultrafast molecular sieving. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2021, 13, 37775–37784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Yang, L.; Wang, H.; Xu, Z.; Zhao, Y.; Luo, Y.; Nasir, N.; Song, Y.; Wu, H.; Pan, F.; et al. Covalent organic framework membranes through a mixed-dimensional assembly for molecular separations. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 2101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sheng, F.; Wu, B.; Li, X.; Xu, T.; Shehzad, M.A.; Wang, X.; Ge, L.; Wang, H.; Xu, T. Efficient ion sieving in covalent organic framework membranes with sub-2-nanometer channels. Adv. Mater. 2021, 33, 2104404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, G.-R.; Xu, J.-M.; Su, H.-C.; Liu, X.-Y.; Li, L.; Zhao, H.-L.; Feng, H.-J.; Das, R. Two-dimensional (2D) nanoporous membranes with sub-nanopores in reverse osmosis desalination: Latest developments and future directions. Desalination 2017, 451, 18–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, G.; Jin, W.; Xu, N. Graphene-based membranes. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2015, 44, 5016–5030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, C.; Wen, B.; Bai, B. Recent advances in nanoporous graphene membrane for gas separation and water purification. Sci. Bull. 2015, 60, 1807–1823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bodzek, M.; Konieczny, K.; Kwiecińska-Mydlak, A. Nanotechnology in water and wastewater treatment. Graphene-the nanomaterial for next generation of semipermeable membranes. Crit. Rev. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2020, 50, 1515–1579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kidambi, P.R.; Chaturvedi, P.; Moehring, N.K. Subatomic species transport through atomically thin membranes: Present and future applications. Science 2021, 374, 6568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bunch, J.S.; Verbridge, S.S.; Alden, J.S.; van der Zande, A.M.; Parpia, J.M.; Craighead, H.G.; McEuen, P.L. Impermeable atomic membranes from graphene sheets. Nano Lett. 2008, 8, 2458–2462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Asif, M.B.; Iftekhar, S.; Maqbool, T.; Pramanik, B.K.; Tabraiz, S.; Sillanpää, M.; Zhang, Z. Two-dimensional nanoporous and lamellar membranes for water purification: Reality or a myth? Chem. Eng. J. 2022, 432, 134335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grasso, G.; Galiano, F.; Yoo, M.J.; Mancuso, R.; Park, H.B.; Gabriele, B.; Figoli, A.; Drioli, E. Development of graphene-PVDF composite membranes for membrane distillation. J. Membr. Sci. 2022, 604, 118017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen-Tanugi, D.; Grossman, J.C. Water desalination across nanoporous graphene. Nano Lett. 2012, 12, 3602–3608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, L.; Zhang, M.; Li, C.; Shi, G. Graphene-based membranes for molecular separation. J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 2015, 6, 2806–2815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konatham, D.; Yu, J.; Ho, T.A.; Striolo, A. Simulation insights for graphene-based water desalination membranes. Langmuir 2013, 29, 11884–11897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hegab, H.M.; Kallem, P.; Pandey, R.P.; Ouda, M.; Banat, F.; Hasan, S.W. Mechanistic insights into the selective mass-transport and fabrication of holey graphene-based membranes for water purification applications. Chem. Eng. J. 2022, 431, 134248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, C.; Ajay Iyengar, A.; Karnik, R. Molecular size-dependent subcontinuum solvent permeation and ultrafast nanofiltration across nanoporous graphene membranes. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2021, 16, 989–995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, Y.; Su, S.; Zhang, N.; Wang, Y.; Guo, X.; Xue, J. Dehydration-determined ion selectivity of graphene subnanopores. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2020, 12, 24281–24288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Zhang, S.; Hou, D.; Duan, H.; Deng, B.; Zeng, Z.; Liu, B.; Sun, L.; Song, R.; Du, J.; et al. Tunable pore size from sub-nanometer to a few nanometers in large-area graphene nanoporous atomically thin membranes. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2021, 13, 29926–29935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kidambi, P.R.; Jang, D.; Idrobo, J.-C.; Boutilier, M.S.H.; Wang, L.; Kong, J.; Karnik, R. Nanoporous atomically thin graphene membranes for desalting and dialysis applications. Adv. Mater. 2017, 29, 1700277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koh, D.-Y.; Lively, R.P. Nanoporous graphene: Membranes at the limit. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2015, 10, 385–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kidambi, P.R.; Nguyen, G.D.; Zhang, S.; Chen, Q.; Kong, J.; Warner, J.; Li, A.-P.; Karnik, R. Facile fabrication of large-area atomically thin membranes by direct synthesis of graphene with nanoscale porosity. Adv. Mater. 2018, 30, 1804977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, J.; Choi, Y.; Kim, J.P.; Kim, J.H.; Kim, J.Y.; Kwon, O.; Kim, D.I.; Kim, D.W. Thermally-induced pore size tuning of multilayer nanoporous graphene for organic solvent nanofiltration. J. Membr. Sci. 2021, 637, 119620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, D.; Idrobo, J.-C.; Laoui, T.; Karnik, R. Water and solute transport governed by tunable pore size distributions in nanoporous graphene membranes. ACS Nano 2017, 11, 10042–10052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heiranian, M.; Farimani, A.B.; Aluru, N.R. Water desalination with a single-layer MoS2 nanopore. Nat. Commun. 2015, 6, 8616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Thiruraman, J.P.; Fujisawa, K.; Danda, G.; Das, P.M.; Zhang, T.; Bolotsky, A.; Perea-López, N.; Nicolaï, A.; Senet, P.; Terrones, M.; et al. Angstrom-size defect creation and ionic transport through pores in single-layer MoS2. Nano Lett. 2018, 18, 1651–1659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jafarzadeh, R.; Azamat, J.; Erfan-Niya, H.; Hosseini, M. Molecular insights into effective water desalination through functionalized nanoporous boron nitride nanosheet membranes. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2018, 471, 921–928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Y.G.; Wang, W.S.; Li, W.; Loh, K.P.; Zhang, J. A graphene-like membrane with an ultrahigh water flux for desalination. Nanoscale 2017, 9, 18951–18958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yang, T.; Lin, H.; Loh, K.P.; Jia, B. Fundamental transport mechanisms and advancements of graphene oxide membranes for molecular separation. Chem. Mater. 2019, 31, 1829–1846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, G.; Jin, W. Graphene oxide membrane for molecular separation: Challenges and opportunities. Sci. China Mater. 2018, 61, 1021–1026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Homaeigohar, S.; Elbahri, M. Graphene membranes for water desalination. NPG Asia Mater. 2017, 9, e427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yulaev, A.; Lipatov, A.; Lu, A.X.; Sinitskii, A.; Leite, M.S.; Kolmakov, A. Imaging and analysis of encapsulated objects through self-assembled electron and optically transparent graphene oxide membranes. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2017, 4, 1600734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahalingam, D.K.; Falca, G.; Upadhya, L.; Abou-Hamad, E.; Batra, N.; Wang, S.; Musteata, V.; da Costa, P.M.; Nunes, S.P. Spray-Coated Graphene Oxide Hollow Fibers for Nanofiltration. J. Membr. Sci. 2020, 606, 118006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Shen, Q.; Hou, J.; Sutrisna, P.D.; Chen, V. Shear-aligned graphene oxide laminate/Pebax ultrathin composite hollow fiber membranes using a facile dip-coating approach. J. Mater. Chem. A 2017, 5, 7732–7737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Sun, N.; Xu, X.L.; Wang, S.; Kang, W.; Zhuang, X.; Yin, Y.; Cheng, B. Adenosine triphosphate@graphene oxide proton channels for proton exchange membranes constructed via electrostatic layer-by-layer deposition. J. Membr. Sci. 2020, 620, 118880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halakoo, E.; Feng, X. Layer-by-layer assembly of polyethyleneimine/graphene oxide membranes for desalination of high-salinity water via pervaporation. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2020, 234, 116077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, X.; Sun, S.; Zhou, L.; Miao, Z.; Zhang, X.; Su, Z.; Wei, G. Removing metal ions from water with graphene–bovine serum albumin hybrid membrane. Nanomaterials 2019, 9, 276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pedico, A.; Fontana, M.; Bianco, S.; Kara, S.; Periolatto, M.; Carminati, S.; Pirri, C.F.; Tresso, E.; Lamberti, A. Graphene oxide membranes for trace hydrocarbon contaminant removal from aqueous solution. Nanomaterials 2020, 10, 2242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, A.; Aamir, M.; Thebo, K.H.; Akhtar, J. Laminar graphene oxide membranes towards selective ionic and molecular separations: Challenges and progress. Chem. Rec. 2020, 20, 344–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, P.; Zhu, M.; Wang, K.; Zhong, M.; Wei, J.; Wu, D.; Xu, Z.; Zhu, H. Selective ion penetration of graphene oxide membranes. ACS Nano 2013, 7, 428–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nair, R.R.; Wu, H.A.; Jayaram, P.N.; Grigorieva, I.V.; Geim, A.K. Unimpeded permeation of water through helium-leak-tight graphene-based membranes. Science 2012, 335, 442–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Boretti, A.; Al-Zubaidy, S.; Vaclavikova, M.; Al-Abri, M.; Castelletto, S.; Mikhalovsky, S. Outlook for graphene-based desalination membranes. NPJ Clean Water 2018, 1, 2059–7037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumari, P.; Tripathi, K.M.; Jangir, L.K.; Gupta, R.; Awasthi, K. Recent advances in application of the graphene-based membrane for water purification. Mater. Today Chem. 2021, 22, 100597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, J.; Bao, H.; Zhang, Y.; Shen, X.; Kim, J.-K.; Ma, J.; Shao, L. Unravelling intercalation-regulated nanoconfinement for durably ultrafast sieving graphene oxide membranes. J. Membr. Sci. 2021, 619, 118791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, D.; Liang, H.; Zhu, X.; Yang, L.; Luo, X.; Guo, Y.; Liu, Y.; Bai, L.; Li, G.; Tang, X. Metal-polyphenol dual crosslinked graphene oxide membrane for desalination of textile wastewater. Desalination 2020, 487, 114503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Wang, H. Graphene oxide patchwork membranes. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2021, 16, 226–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Fu, C.-F.; Huang, Q.; Zhang, P.; Cui, P.; Ran, J.; Yang, J.; Xu, T. 2D Heterostructured nanofluidic channels for enhanced desalination performance of graphene oxide membranes. ACS Nano 2021, 15, 7586–7595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Z.; Fang, Q.; Xu, X.; Raj, D.; Zhou, X.; Liu, Z. Attapulgite nanofibers and graphene oxide composite membrane for high-performance molecular separation. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2019, 545, 276–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Qian, X.; Wang, Z.; Zeng, F.; Bai, H.; Li, N. Tailoring the microstructure of poly(vinyl alcohol)-intercalated graphene oxide membranes for enhanced desalination performance of high-salinity water by pervaporation. J. Membr. Sci. 2020, 599, 117838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.-H.; Yin, M.-J.; Zhao, Q.; Jin, C.-G.; Wang, N.; Ji, S.; Ritt, C.L.; Elimelech, M.; An, Q.-F. Graphene oxide membranes with stable porous structure for ultrafast water transport. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2021, 16, 337–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Y.; Pastuovic, Z.; Shen, C.; Murphy, T.; Gore, D.B. Ion beam engineered graphene oxide membranes for mono-/di-valent metal ions separation. Carbon 2020, 158, 598–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mi, B. Scaling up nanoporous graphene membranes. Science 2019, 364, 1033–1034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cohen-Tanugi, D.; Lin, L.-C.; Grossman, J.C. Multilayer nanoporous graphene membranes for water desalination. Nano Lett. 2016, 16, 1027–1033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kang, J.; Choi, Y.; Kim, J.H.; Choi, E.; Choi, S.E.; Kwon, O.; Kim, D.W. Functionalized nanoporous graphene membrane with ultrafast and stable nanofiltration. J. Membr. Sci. 2021, 618, 118635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.; Tian, M.; Hou, J.; Wang, J.; Lin, J.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, J.; Van der Bruggen, B. Surface zwitterionic functionalized graphene oxide for a novel loose nanofiltration membrane. J. Mater. Chem. A 2016, 4, 1980–1990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarcan, R.; Todor-Boer, O.; Petrovai, I.; Leordean, C.; Astilean, S.; Botiz, I. Reduced graphene oxide today. J. Mater. Chem. C 2020, 8, 1198–1224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, A.; Bai, J.; Hong, W.; Bai, H. Electrochemically reduced graphene oxide: Preparation, composites, and applications. Carbon 2022, 191, 301–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Wang, J.; Zhang, Y.; Zhu, J.; Yang, J.; Wang, J.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, Y. Leaf-veins-inspired nickel phosphate nanotubes-reduced graphene oxide composite membranes for ultrafast organic solvent nanofiltration. J. Membr. Sci. 2022, 649, 120401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, S.; Li, Y.; Xia, Y.; Selomulya, C.; Zhang, X. Stable cation-controlled reduced graphene oxide membranes for improved NaCl rejection. J. Membr. Sci. 2021, 621, 118995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, R.; Gu, Y.; Zhao, J.; Zhou, H.; Jiang, H.; Li, J.; Zhang, B. Engineering robust RGO/PVA composite membrane for acid recovery via electron beam irradiation. Carbon 2022, 191, 243–254. [Google Scholar]
- Straub, A.P.; Bergsman, D.S.; Getachew, B.A.; Leahy, L.M.; Patil, J.J.; Ferralis, N.; Grossman, J.C. Highly conductive and permeable nanocomposite ultrafiltration membranes using laser-reduced graphene oxide. Nano Lett. 2021, 21, 2429–2435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Q.; Qian, X.T.; Thebo, K.H.; Cheng, H.-M.; Ren, W. Controlling reduction degree of graphene oxide membranes for improved water permeance. Sci. Bull. 2018, 63, 788–794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yang, R.; Fan, Y.; Yu, R.; Dai, F.; Lan, J.; Wang, Z.; Chen, J.; Chen, L. Robust reduced graphene oxide membranes with high water permeance enhanced by K+ modification. J. Membr. Sci. 2021, 635, 119437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, H.; Wang, G.; Xu, Z.; Dong, X.; Zhang, X. Confining peroxymonosulfate activation in carbon nanotube intercalated nitrogen doped reduced graphene oxide membrane for enhanced water treatment: The role of nanoconfinement effect. J. Colloid. Interface Sci. 2021, 608, 2740–2751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Yue, M.; Yuan, F.; Yang, L.; Chen, C.; Sun, D. Bio-inspired fabrication of highly permeable and anti-fouling ultrafiltration membranes based on bacterial cellulose for efficient removal of soluble dyes and insoluble oils. J. Membr. Sci. 2021, 621, 118982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Xu, H.; Xie, F.; Ma, X.; Niu, B.; Chen, M.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, Y.; Long, D. General synthesis of ultrafine metal oxide/reduced graphene oxide nanocomposites for ultrahigh-flux nanofiltration membrane. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Zhao, W.; Weyland, M.; Yuan, S.; Xia, Y.; Liu, H.; Jian, M.; Yang, J.; Easton, C.D.; Selomulya, C.; et al. Thermally reduced nanoporous graphene oxide membrane for desalination. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2019, 53, 8314–8323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.-H.; Joshi, R.K.; Silva, K.K.H.D.; Badam, R.; Yoshimura, M. Fabrication of reduced graphene oxide membranes for water desalination. J. Membr. Sci. 2019, 572, 12–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Liang, S.; Chen, L.; Fang, H. Realizing ultrahigh nanofiltration performance based on small flake reduced graphene oxide membranes. Desalination 2022, 528, 115601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, R.; Xia, X.; Yang, R.; Yu, R.; Dai, F.; Chen, J.; Liu, W.; Wu, M.; Xu, J.; Chen, L. Selective reduction of epoxy groups in graphene oxide membrane for ultrahigh water permeation. Carbon 2020, 172, 228–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ihsanullah, I. Potential of MXenes in Water Desalination: Current Status and Perspectives. Nanomicro. Lett. 2020, 12, 74–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pogorielov, M.; Smyrnova, K.; Kyrylenko, S.; Gogotsi, O.; Zahorodna, V.; Pogrebnjak, A. MXenes-a new class of two-dimensional materials: Structure, properties and potential applications. Nanomaterials 2021, 11, 3412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dixit, F.; Zimmermann, K.; Dutta, R.; Prakash, N.J.; Barbeau, B.; Mohseni, M.; Kandasubramanian, B. Application of MXenes for water treatment and energy-efficient desalination: A review. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 423, 127050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, N.; Yang, W.; Zhang, C. Perspectives on preparation of two-dimensional MXenes. Sci. Technol. Adv. Mater. 2021, 22, 917–930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- VahidMohammadi, A.; Rosen, J.; Gogotsi, Y. The world of two-dimensional carbides and nitrides (MXenes). Science 2021, 372, 6547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ren, C.E.; Hatzell, K.B.; Alhabeb, M.; Ling, Z.; Mahmoud, K.A.; Gogotsi, Y. Charge- and size-selective ion sieving through Ti3C2Tx MXene Membranes. J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 2015, 6, 4026–4031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, Z.; Wei, Y.; Deng, J.; Ding, L.; Li, Z.-K.; Wang, H. Self-crosslinked MXene (Ti3C2Tx) membranes with good anti-swelling property for monovalent metal ions exclusion. ACS Nano 2019, 13, 10535–10544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, L.; Li, L.; Liu, Y.; Wu, Y.; Lu, Z.; Deng, J.; Wei, Y.; Caro, J.; Wang, H. Effective ion sieving with Ti3C2Tx MXene membranes for production of drinking water from seawater. Nat. Sustain. 2020, 3, 296–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Li, S.; Huang, R.; Sun, J.H.Y.; Qin, Y.; Shen, L. Stabilizing MXene-based nanofiltration membrane by forming analogous semi-interpenetrating network architecture using flexible poly(acrylic acid) for effective wastewater treatment. J. Membr. Sci. 2022, 648, 120360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Xu, D.; Li, S.; Cui, L.; Zhuang, Y.; Xing, W.; Jing, W. Assembly of multidimensional MXene-carbon nanotube ultrathin membranes with an enhanced anti-swelling property for water purification. J. Membr. Sci. 2021, 623, 119075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Wei, Y.; Wang, Y.; Chen, H.; Caro, J.; Wang, H. A two-dimensional lamellar membrane: MXene nanosheet stacks. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2017, 56, 1825–1829. [Google Scholar]
- Liao, F.; Xu, Z.; Fan, Z.; Meng, Q.; Lv, B.; Ye, X.; Shenb, C.; Zhang, G. Confined assembly of ultrathin dual-functionalized Z-MXene nanosheet intercalated GO nanofilms with controlled structure for size-selective permeation. J. Mater. Chem. A 2021, 9, 12236–12243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, K.M.; Kim, D.W.; Ren, C.E.; Cho, K.M.; Kim, S.J.; Choi, J.H.; Nam, Y.T.; Gogotsi, Y.; Jung, H.-T. Selective molecular separation on Ti3C2Tx-graphene oxide membranes during pressure-driven filtration: Comparison with graphene oxide and MXenes. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2017, 9, 44687–44694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, Z.; Sun, Y.; Zhuang, Y.; Jing, W.; Ye, H.; Cui, Z. Assembly of 2D MXene nanosheets and TiO2 nanoparticles for fabricating mesoporous TiO2-MXene membranes. J. Membr. Sci. 2018, 564, 35–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Z.; Wu, Y.; Ding, L.; Wei, Y.; Wang, H. A lamellar MXene (Ti3C2Tx)/PSS composite membrane for fast and selective lithium-ion separation. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2021, 60, 22265–22269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.; Zhang, L.; Shi, L.; Wang, P. MXene Ti3C2: An effective 2D light-to-heat conversion material. ACS Nano 2017, 11, 3752–3759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rasool, K.; Helal, M.; Ali, A.; Ren, C.E.; Gogotsi, Y.; Mahmoud, K.A. Antibacterial activity of Ti3C2Tx MXene. ACS Nano 2016, 10, 3674–3684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pandey, R.P.; Rasool, K.; Madhavan, V.E.; Aïssa, B.; Gogotsi, Y.; Mahmoud, K.A. Ultrahigh-flux and fouling-resistant membranes based on layered silver/MXene (Ti3C2Tx) nanosheets. J. Mater. Chem. A 2018, 6, 3522–3533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Q.; Zeng, G.; Yan, G.; Luo, J.; Cheng, X.; Zhao, Z.; Li, H. Self-cleaning photocatalytic MXene composite membrane for synergistically enhanced water treatment: Oil/water separation and dyes removal. Chem. Eng. J. 2022, 427, 131668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Natu, V.; Hart, J.L.; Sokol, M.; Chiang, H.; Taheri, M.L.; Barsoum, M.W. Edge Capping of 2D-MXene sheets with polyanionic salts to mitigate oxidation in aqueous colloidal suspensions. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2019, 58, 12655–12660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, S.; Ke, T.; Rajavel, K.; Yang, K.; Lin, D. Dispersibility and photochemical stability of delaminated MXene flakes in water. Small 2020, 16, 2002433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mathis, T.S.; Maleski, K.; Goad, A.; Sarycheva, A.; Anayee, M.; Foucher, A.C.; Hantanasirisakul, K.; Shuck, C.E.; Stach, E.A.; Gogotsi, Y. Modified MAX phase synthesis for environmentally stable and highly conductive Ti3C2 MXene. ACS Nano 2021, 15, 6420–6429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Monga, D.; Sharma, S.; Shetti, N.P.; Basu, S.; Reddy, K.R.; Aminabhavi, T.M. Advances in transition metal dichalcogenide-based two-dimensional nanomaterials. Mater. Today Chem. 2021, 19, 100399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Zhang, X.; Huang, X.; Liao, W.; Zhao, Y. MoS2-based membranes in water treatment and purification. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 422, 130082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Tu, Q.; Zheng, S.; Urban, J.J.; Li, S.; Mi, B. Understanding the aqueous stability and filtration capability of MoS2 membranes. Nano Lett. 2017, 17, 7289–7298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, X.; Gabinet, U.R.; Ritt, C.L.; Feng, X.; Deshmukh, A.; Kawabata, K.; Kaneda, M.; Hashmi, S.M.; Osuji, C.O.; Elimelech, M. Relating selectivity and separation performance of lamellar two-dimensional molybdenum disulfide (MoS2) membranes to nanosheet stacking behavior. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2020, 54, 9640–9651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirunpinyopas, W.; Prestat, E.; Worrall, S.D.; Haigh, S.J.; Dryfe, R.A.W.; Bissett, M.A. Desalination and nanofiltration through functionalized laminar MoS2 membranes. ACS Nano 2017, 11, 11082–11090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Zhang, K. Few-layers MoS2 nanosheets modified thin film composite nanofiltration membranes with improved separation performance. J. Membr. Sci. 2020, 595, 117526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, M.-Q.; Zhang, C.; Zhu, C.-Y.; Huang, S.; Yang, J.; Xu, Z.-K. Nanocomposite membranes embedded with functionalized MoS2 nanosheets for enhanced interfacial compatibility and nanofiltration performance. J. Membr. Sci. 2019, 591, 117316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Taymazov, D.; Li, M.-P.; Huang, Z.-H.; Liu, W.-L.; Zhang, X.; Ma, X.-H.; Xu, Z.-L. Construction of MoS2 composite membranes on ceramic hollow fibers for efficient water desalination. J. Membr. Sci. 2019, 592, 117369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Yang, Y.; An, X.; Hou, L.-A. A critical review of g-C3N4-based photocatalytic membrane for water purification. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 412, 128663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, Y.; An, X.; Zhang, S.; Tang, Q.; Lan, H.; Liu, H.; Qu, J. Emerging graphitic carbon nitride-based membranes for water purification. Water Res. 2021, 200, 117207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Gao, B.; Yue, Q.; Wang, Z. Graphitic carbon nitride (g-C3N4)-based membranes for advanced separation. J. Mater. Chem. A 2020, 8, 19133–19155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Li, L.; Wei, Y.; Xue, J.; Chen, H.; Ding, L.; Caro, J.; Wang, H. Water transport with ultralow friction through partially exfoliated g-C3N4 nanosheet membranes with self-supporting spacers. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2017, 56, 8974–8980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Ho, W.; Wang, X. Metal-free disinfection effects induced by graphitic carbon nitride polymers under visible light illumination. Chem. Commun. 2014, 50, 4338–4340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Su, Y.; Guan, J.; Cao, J.; Zhang, R.; He, M.; Gao, K.; Zhou, L. 2D heterostructure membranes with sunlight-driven self-cleaning ability for highly efficient oil–water separation. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2018, 28, 1706545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.; Yu, Z.; Shi, H.; Yang, Q.; Chen, Q.; Pan, Y.; Zeng, G.; Yan, L. A Mussel-inspired method to fabricate reduced graphene oxide/g-C3N4 composites membranes for catalytic decomposition and oil-in-water emulsion separation. Chem. Eng. J. 2017, 322, 33–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, F.; Li, J.; Dong, C.; Bi, Y.; Han, X. Plasmonic Ag decorated graphitic carbon nitride sheets with enhanced visible-light response for photocatalytic water disinfection and organic pollutant removal. Chemosphere 2020, 242, 125201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, X.; Zhang, T.; Yang, D.; Qiu, F.; Li, Z.; Zhu, Y.; Yu, H. Oil removal from oily water by a low-cost and durable flexible membrane made of layered double hydroxide nanosheet on cellulose support. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 180, 307–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Song, P.; Yang, Y.; Li, Y.; Wang, N.; An, Q. CNTs intercalated LDH composite membrane for water purification with high permeance. Nanomaterials 2021, 12, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Wang, J.M.; Liu, D.; Yang, C.; Liu, Y.; Ruoff, R.S.; Lei, W. Functionalized boron nitride membranes with ultrafast solvent transport performance for molecular separation. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 1902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Doménech, N.G.; Purcell-Milton, F.; Arjona, A.S.; García, M.-L.C.; Ward, M.; Cabré, M.B.; Rafferty, A.; McKelvey, K.; Dunne, P.; Gun’ko, Y.K. High-performance boron nitride-based membranes for water purification. Nanomaterials 2022, 12, 473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, G.; Zhang, D.; Wang, C.; Liu, H.; Qu, L.; Li, H. A novel nanocomposite membrane combining BN nanosheets and GO for effective removal of antibiotic in water. Nanomaterials 2019, 9, 986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Peng, F.B.; Huang, X.; Jawor, A.; Hoek, E.M.V. Transport, structural, and interfacial properties of poly (vinyl alcohol)-polysulfone composite nanofiltration membranes. J. Membr. Sci. 2010, 353, 169–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Liu, F.; Wang, Y.; Lin, H.; Han, L. A tight nanofiltration membrane with multi-charged nanofilms for high rejection to concentrated salts. J. Membr. Sci. 2017, 537, 407–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, S.; Zhou, Q.; Shuai, S.; Yao, G.; Ma, M.; Gao, C. Thin-film composite nanofiltration membranes with improved acid stability prepared from naphthalene-1,3,6-trisulfonylchloride (NTSC) and trimesoyl chloride (TMC). Desalination 2013, 315, 164–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| 2DNM Membranes | Interlayer Spacing/Pore Size (nm) | Zeta Potential (mV) | Surface Area (m2/g) | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| GO | 0.85 | −24 to −46 | 90 |
|
|
| rGO | 0.7–1.2 nm | −24 | 130 |
|
|
| MXene (Ti3C2Tx) | 0.35 nm | −35 | 108 |
|
|
| MoS2 | 0.65 nm | −45 | 165 |
|
|
| MOF | <2 nm | - | - |
|
|
| COF | 1–3 nm | - | - |
|
|
| Membrane | Permeability (L m−2 h−1 bar−1) | Rejection (%) | Feed Concentration (g L−1) | Operating Pressure (bar) | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NF-270 (polyamide) | 11.6 | Na2SO4: 94.0 | 2 | 10 | [154] |
| NF-PDA/PEI/PAA | 5.5 | Na2SO4: 98.3 | 1 | 5 | [155] |
| PIP-TMC/NTSC | 10.6 | Na2SO4: 97.8 | 0.5 | 5 | [156] |
| MOF-303 | 0.74 | Na2SO4: 96.0 | 1 | 5 | [28] |
| UiO-66-NH2/TFN | 30.8 | Na2SO4: 97.5 | 1 | 4 | [29] |
| TpTGCl@CNFs | 42.8 | Na2SO4: 96.8 | 1 | 2 | [43] |
| ACOF-1/HPAN | 142 | CR: 99.2 | 0.2 | 4 | [42] |
| FNG/PES | 131 | MR > 90 | 0.01 | 1 | [93] |
| GO/g-C3N4 | 33.5 | Na2SO4: 92.5 | 2.8 | 1–5 | [88] |
| ZIF-8@f-GOm | 49.8 | Na2SO4: 52.9 | 1 | 2 | [90] |
| ZnO/rGO | 225 | MB: 98 | 0.025 | 1 | [106] |
| rNPGO | 63.06 | Na2SO4: 92.9 | 2.8 | 6 | [109] |
| Fe(OH)3/MXene | 1084 | EB: 90 | - | 1 | [121] |
| GO/AA-Ti3C2Tx | 115.5 | CR: 99.1 | 0.01 | 1 | [122] |
| Ag@MXene | 387.05 | RhB: 79.93 | 0.05 | 1 | [128] |
| MoS2/PVDF | 24.7 | MB: 82.17 | 0.37 | 1.38 | [136] |
| g-C3N4/AAO | 29.5 | EB: 87.2 | 0.2 | - | [144] |
| MWCNTs/BNNSs/GO | 30.2 | TCH: 96.1 | 0.03 | 0.9 | [153] |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, H.; Zheng, Y.; Yu, S.; Chen, W.; Yang, J. A Review of Advancing Two-Dimensional Material Membranes for Ultrafast and Highly Selective Liquid Separation. Nanomaterials 2022, 12, 2103. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano12122103
Zhang H, Zheng Y, Yu S, Chen W, Yang J. A Review of Advancing Two-Dimensional Material Membranes for Ultrafast and Highly Selective Liquid Separation. Nanomaterials. 2022; 12(12):2103. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano12122103
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Hongli, Yiling Zheng, Shuwen Yu, Weixing Chen, and Jie Yang. 2022. "A Review of Advancing Two-Dimensional Material Membranes for Ultrafast and Highly Selective Liquid Separation" Nanomaterials 12, no. 12: 2103. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano12122103
APA StyleZhang, H., Zheng, Y., Yu, S., Chen, W., & Yang, J. (2022). A Review of Advancing Two-Dimensional Material Membranes for Ultrafast and Highly Selective Liquid Separation. Nanomaterials, 12(12), 2103. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano12122103