Organic-Free Synthesis of Finned Mordenite Zeolite
Abstract
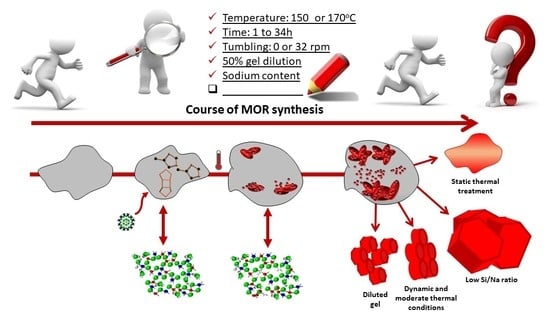
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Synthesis Procedure and Reference Synthesis
2.2. Influence of Hydrothermal Treatment Conditions
2.3. Influence of Temperature and Time of Synthesis
2.4. Influence of Gel Dilution
2.5. Influence of Sodium Content
2.6. Characterization
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Influence of Thermal Treatment Conditions: Agitation and Time
3.2. Influence of Temperature and Time of Synthesis
3.3. Influence of Gel Dilution
3.4. Influence of the Sodium Content
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A




References
- Narayanan, S.; Tamizhdurai, P.; Mangesh, V.L.; Ragupathi, C.; Santhana krishnan, P.; Ramesh, A. Recent Advances in the Synthesis and Applications of Mordenite Zeolite—Review. RSC Adv. 2020, 11, 250–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiang, H.; Bhan, A. Catalytic Consequences of Hydroxyl Group Location on the Rate and Mechanism of Parallel Dehydration Reactions of Ethanol over Acidic Zeolites. J. Catal. 2010, 271, 251–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez, C.; Corma, A. Inorganic Molecular Sieves: Preparation, Modification and Industrial Application in Catalytic Processes. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2011, 255, 1558–1580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Camblor, M.A.; Corma, A.; Martínez, A.; Mocholí, F.A.; Pariente, J.P. Catalytic Cracking of Gasoil. Benefits in Activity and Selectivity of Small Y Zeolite Crystallites Stabilized by a Higher Silicon-to-Aluminium Ratio by Synthesis. Appl. Catal. 1989, 55, 65–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Zhang, H.; Wang, P.; Zhao, Y.; Shi, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Tang, Y. Organic Template-Free Synthesis of Zeolite Mordenite Nanocrystals through Exotic Seed-Assisted Conversion. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 47623–47631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Xing, J.; Zhou, M.; Zhang, H.; Huang, H.; Zhang, C.; Song, L.; Li, X. Influence of Crystal Size of HZSM-5 on Hydrodeoxygenation of Eugenol in Aqueous Phase. Catal. Commun. 2014, 56, 123–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez, A.; López, C. The Influence of ZSM-5 Zeolite Composition and Crystal Size on the In Situ Conversion of Fischer-Tropsch Products over Hybrid Catalysts. Appl. Catal. A Gen. 2005, 294, 251–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Liu, M.; Tan, W.; Hou, K.; Zhang, A.; Wang, Y.; Guo, X. Effect of ZSM-5 Zeolite Morphology on the Catalytic Performance of the Alkylation of Toluene with Methanol. J. Energy Chem. 2014, 23, 491–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palčić, A.; Catizzone, E. Application of Nanosized Zeolites in Methanol Conversion Processes: A Short Review. Curr. Opin. Green Sustain. Chem. 2021, 27, 100393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hincapie, B.O.; Garces, L.J.; Zhang, Q.; Sacco, A.; Suib, S.L. Synthesis of Mordenite Nanocrystals. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2004, 67, 19–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.; Liu, Z.; Endo, A.; Yanaba, Y.; Yoshikawa, T.; Wakihara, T.; Okubo, T. Ultrafast, OSDA-Free Synthesis of Mordenite Zeolite. CrystEngComm 2017, 19, 632–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; va Laak, A.N.C.; Jongh, P.E.D.; Jong, K.P.D. Synthesis of Large Mordenite Crystals with Different Aspect Ratios. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2009, 126, 115–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valtchev, V.; Tosheva, L. Porous Nanosized Particles: Preparation, Properties, and Applications. Chem. Rev. 2013, 113, 6734–6760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dai, H.; Shen, Y.; Yang, T.; Lee, C.; Fu, D.; Agarwal, A.; Le, T.T.; Tsapatsis, M.; Palmer, J.C.; Weckhuysen, B.M.; et al. Finned Zeolite Catalysts. Nat. Mater. 2020, 19, 1074–1080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- International Zeolite Association. Verified Syntheses of Zeolitic Materials; Mintova, S., Barrier, N., Eds.; Synthesis Commission of the International Zeolite Association: Naples, Italy, 2016; Volume 1, ISBN 9780692685396. [Google Scholar]
- Brunauer, S.; Emmett, P.H.; Teller, E. Adsorption of Gases in Multimolecular Layers. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1938, 60, 309–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thommes, M.; Kaneko, K.; Neimark, A.V.; Olivier, J.P.; Rodriguez-Reinoso, F.; Rouquerol, J.; Sing, K.S.W. Physisorption of Gases, with Special Reference to the Evaluation of Surface Area and Pore Size Distribution (IUPAC Technical Report). Pure Appl. Chem. 2015, 87, 1051–1069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sing, K.S.W.; Williams, R.T. Empirical Procedures for the Analysis of Physisorption Isotherms. Adsorpt. Sci. Technol. 2005, 23, 839–853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kruk, M.; Jaroniec, M.; Sayari, A. Application of Large Pore MCM-41 Molecular Sieves to Improve Pore Size Analysis Using Nitrogen Adsorption Measurements. Langmuir 1997, 13, 6267–6273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gurvich, L.G. Physico-Chemical Attractive Force. II. J. Phys. Chem. Soc. Russ. 1915, 47, 805. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, G.J.; Ahn, W.S. Direct Synthesis and Characterization of High-SiO2-Content Mordenites. Zeolites 1991, 11, 745–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Derouane, E.G.; Determmerie, S.; Gabelica, Z.; Blom, N. Synthesis and Characterization of ZSM-5 Type Zeolites I. Physico-Chemical Properties of Precursors and Intermediates. Appl. Catal. 1981, 1, 201–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, L.; Xiong, Z.; Zhan, E.; Li, S.; Shen, W. Piperazine as a Versatile Organic Structure-Directing Agent for Zeolite Synthesis: Effect of SiO 2 /Al 2 O 3 Ratio on Phase Selectivity. J. Mater. Sci. 2019, 54, 7589–7602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simoncic, P.; Armbruster, T. Peculiarity and Defect Structure of the Natural and Synthetic Zeolite Mordenite: A Single-Crystal X-Ray Study. Am. Mineral. 2004, 89, 421–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cundy, C.S.; Cox, P.A. The Hydrothermal Synthesis of Zeolites: Precursors, Intermediates and Reaction Mechanism. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2005, 82, 1–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Xie, S.; Xin, W.; Li, X.; Liu, S.; Xu, L. Crystallization and Morphology of Mordenite Zeolite Influenced by Various Parameters in Organic-Free Synthesis. Mater. Res. Bull. 2011, 46, 894–900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shukla, D.B.; Pandya, V.P. Estimation of Crystalline Phase in ZSM-5 Zeolites by Infrared Spectroscopy. J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol. 1989, 44, 147–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flanigen, E.M.; Khatami, H. Infrared Structural Studies of Zeolite Frameworks. In Molecular Sieve Zeolites-I; American Chemical Society: Washington, DC, USA, 1974; pp. 201–229. ISBN 9780841201149. [Google Scholar]
- Mohamed, M.M.; Salama, T.M. Effect of Mordenite Dealumination on the Structure of Encapsulated Molybdenum Catalysts. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2002, 249, 104–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stojkovic, S.R.; Adnadjevic, B. Investigation of the NaA Zeolite Crystallization Mechanism by i.r. Spectroscopy. Zeolites 1988, 8, 523–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X. Infrared and Raman Spectroscopy. In Zeolite Characterization and Catalysis: A Tutorial; Chester, A.W., Derouane, E.G., Eds.; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2010; pp. 197–222. ISBN 9781402096778. [Google Scholar]
- Sharma, P.; Tomar, R. Sorption Behaviour of Nanocrystalline MOR Type Zeolite for Th(IV) and Eu(III) Removal from Aqueous Waste by Batch Treatment. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2011, 362, 144–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narayanan, S.; Vijaya, J.J.; Sivasanker, S.; Alam, M.; Tamizhdurai, P.; Kennedy, L.J. Characterization and Catalytic Reactivity of Mordenite—Investigation of Selective Oxidation of Benzyl Alcohol. Polyhedron 2015, 89, 289–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szostak, R. Molecular Sieves: Principles of Synthesis and Identification, 1st ed.; Springer Science: New York, NY, USA, 1989; ISBN 9789401095310. [Google Scholar]
- Bodart, P.; Nagy, J.B.; Debras, G.; Gabelica, Z.; Jacobs, P.A. Aluminum Siting in Mordenite and Dealumination Mechanism. J. Phys. Chem. 1986, 90, 5183–5190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, L.; Zheng, Y. Effect of Template Concentration and Gel Dilution on Crystallization and Particle Size of Zeolite Beta in the Absence of Alkali Cations. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2007, 103, 94–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yakimov, A.V.; Kolyagin, Y.G.; Tolborg, S.; Vennestrøm, P.N.R.; Ivanova, I.I. Accelerated Synthesis of Sn-BEA in Fluoride Media: Effect of H2O Content in the Gel. N. J. Chem. 2016, 40, 4367–4374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kurniawan, T.; Muraza, O.; Hakeem, A.S.; Al-Amer, A.M. Mechanochemical Route and Recrystallization Strategy to Fabricate MOR Nanoparticles from Natural Zeolites. Cryst. Growth Des. 2017, 17, 3313–3320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, N.; Subotić, B.; Bronić, J.; Tang, Y.; Dutour Sikirić, M.; Mišić, T.; Svetličić, V.; Bosnar, S.; Antonić Jelić, T. Unusual Pathway of Crystallization of Zeolite ZSM-5 in a Heterogeneous System: Phenomenology and Starting Considerations. Chem. Mater. 2012, 24, 1726–1737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Do, M.H.; Wang, T.; Cheng, D.G.; Chen, F.; Zhan, X.; Gong, J. Zeolite Growth by Synergy between Solution-Mediated and Solid-Phase Transformations. J. Mater. Chem. A 2014, 2, 14360–14370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]







| Entry | T (°C) | Time | Condition | SBET (M2/G) | VμP (CM3/G) | VTP (CM3/G) | SEXT (M2/G) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 170 | 8 h 15 a | 32 rpm | 70 | 0.02 | 0.04 | 12 |
| 2 | 170 | 8 h 30 a | 32 rpm | 170 | 0.05 | 0.08 | 26 |
| 3 | 170 | 10 h | 32 rpm | 240 | 0.08 | 0.10 | 28 |
| 4 | 170 | 24 h | 32 rpm | 470 | 0.16 | 0.17 | 50 |
| 5 | 170 | 10 h | Static | 3 | 0 | 0 | 3 |
| 6 | 150 | 20 h | 32 rpm | 50 | 0.02 | 0.02 | 6 |
| 7 | 150 | 24 h | 32 rpm | 470 | 0.15 | 0.23 | 70 |
| 8 | 150 | 28 h | 32 rpm D b | 15 | 0 | 0.03 | 12 |
| 9 | 150 | 32 h | 32 rpm D | 34 | 0.01 | 0.04 | 14 |
| 10 | 150 | 34 h | 32 rpm D | 390 | 0.12 | 0.21 | 66 |
| 11 | 170 | 12 h | 32 rpm D | 11 | 0 | 0.02 | 9 |
| 12 | 170 | 24 h | 32 rpm D | 470 | 0.15 | 0.19 | 58 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lima, R.C.; Lopes, C.W.; Villarroel-Rocha, J.; Bieseki, L.; Sapag, K.; Pergher, S.B.C. Organic-Free Synthesis of Finned Mordenite Zeolite. Nanomaterials 2022, 12, 2623. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano12152623
Lima RC, Lopes CW, Villarroel-Rocha J, Bieseki L, Sapag K, Pergher SBC. Organic-Free Synthesis of Finned Mordenite Zeolite. Nanomaterials. 2022; 12(15):2623. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano12152623
Chicago/Turabian StyleLima, Rafael C., Christian W. Lopes, Jhonny Villarroel-Rocha, Lindiane Bieseki, Karim Sapag, and Sibele B. C. Pergher. 2022. "Organic-Free Synthesis of Finned Mordenite Zeolite" Nanomaterials 12, no. 15: 2623. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano12152623
APA StyleLima, R. C., Lopes, C. W., Villarroel-Rocha, J., Bieseki, L., Sapag, K., & Pergher, S. B. C. (2022). Organic-Free Synthesis of Finned Mordenite Zeolite. Nanomaterials, 12(15), 2623. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano12152623