Maximum Incorporation of Soft Microgel at Interfaces of Water in Oil Emulsion Droplets Stabilized by Solid Silica Spheres
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Silica Nanosphere Preparation
2.3. Microgel Synthesis and Characterization
2.4. Emulsion Preparation
2.5. Microscopy and Drop Size Distribution
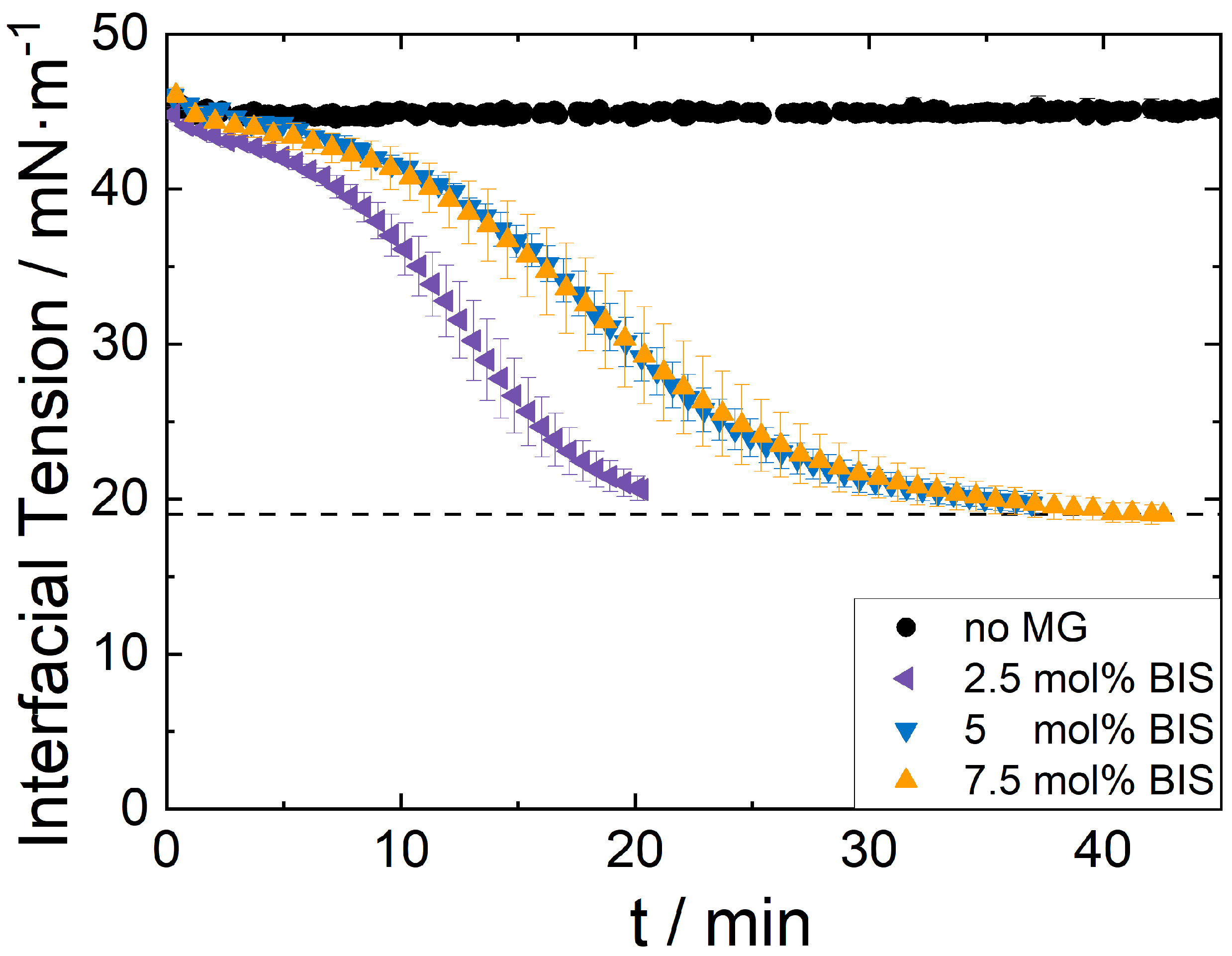
2.6. Interfacial Tension Measurements via Pendant Drop Shape Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Particle Characterization
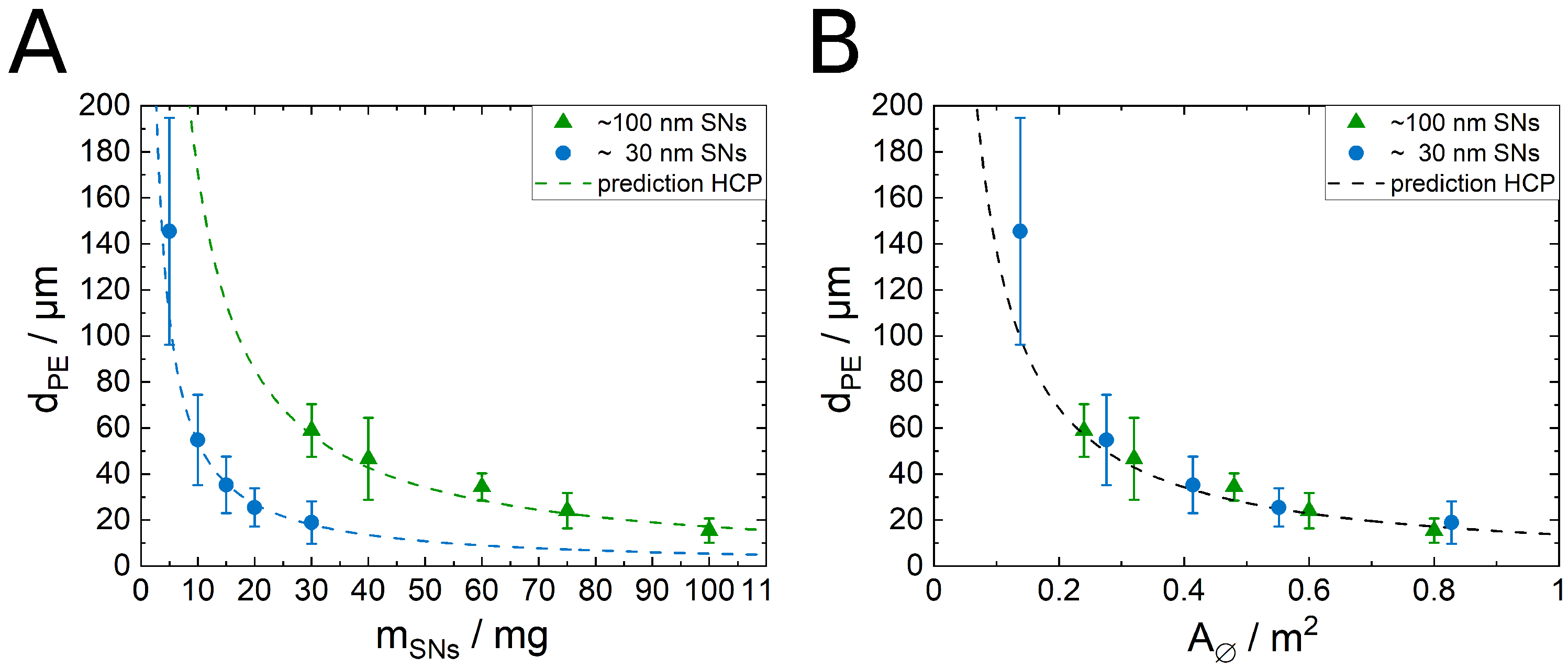
3.2. Droplet Size and Particle Coverage in PEs Stabilized by SNs Only
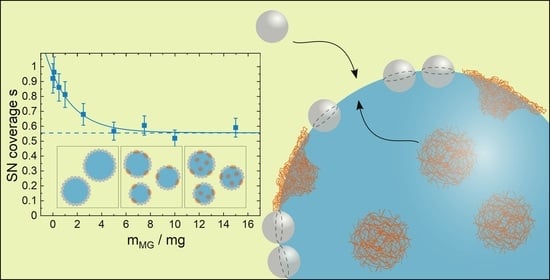
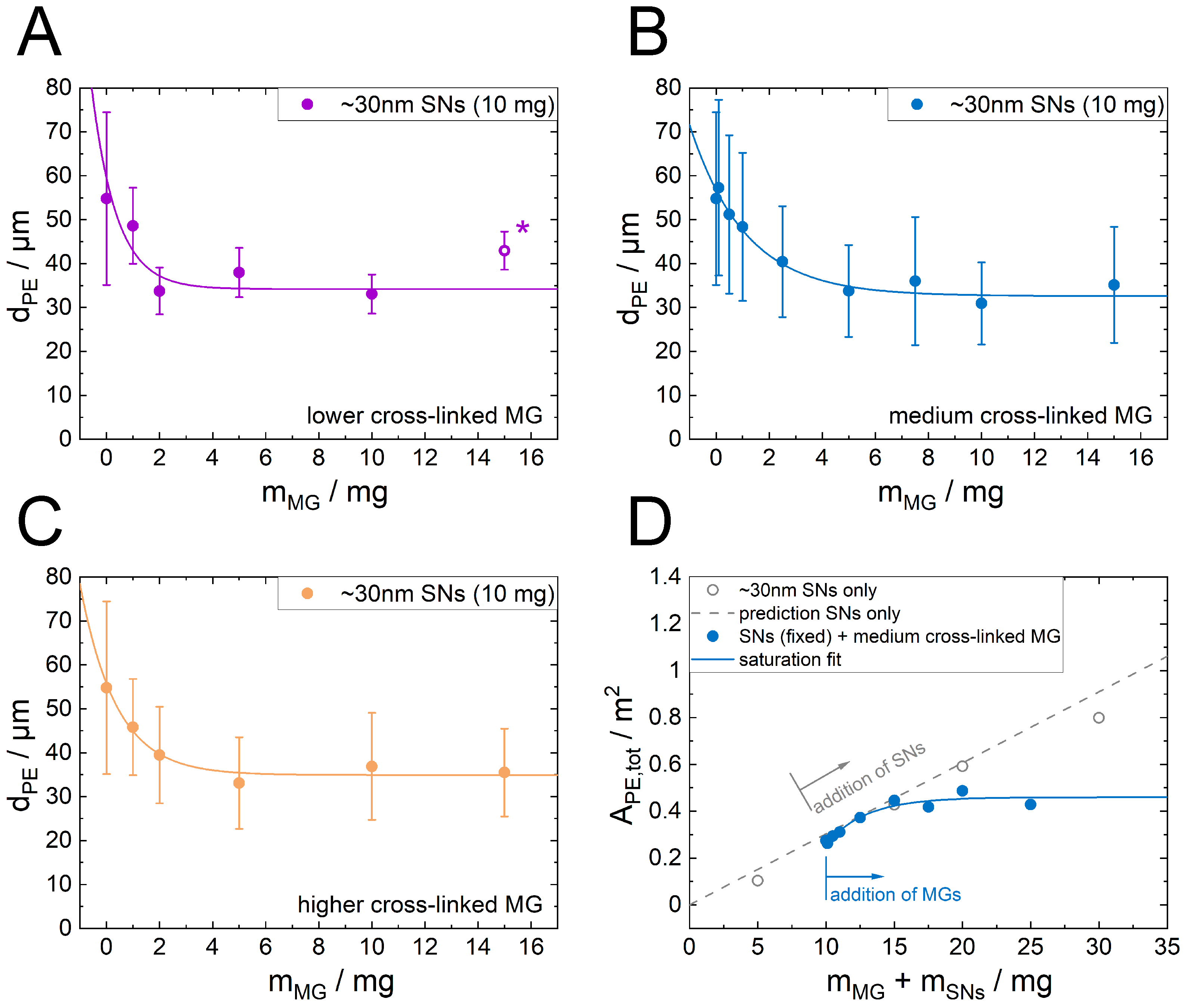
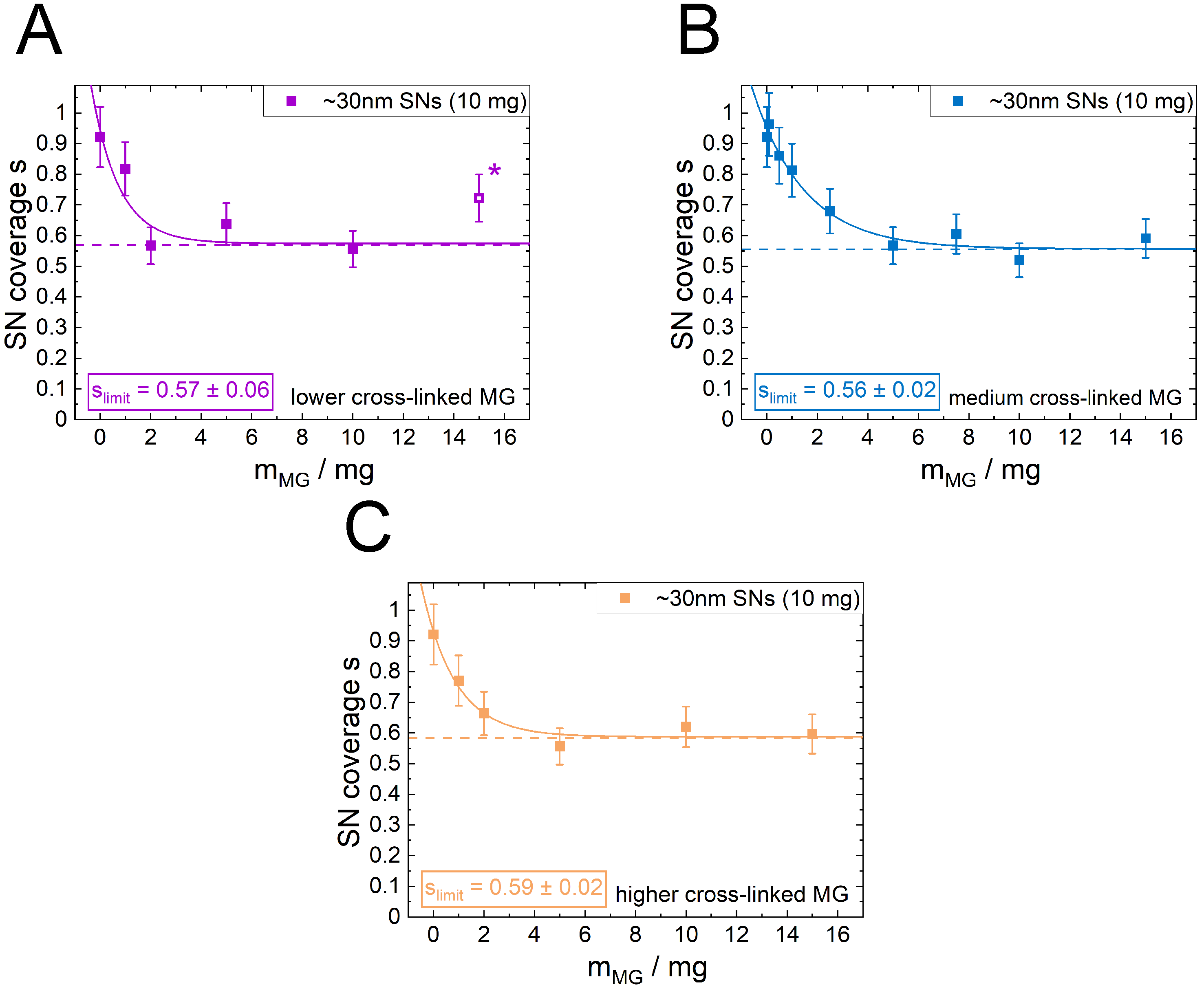
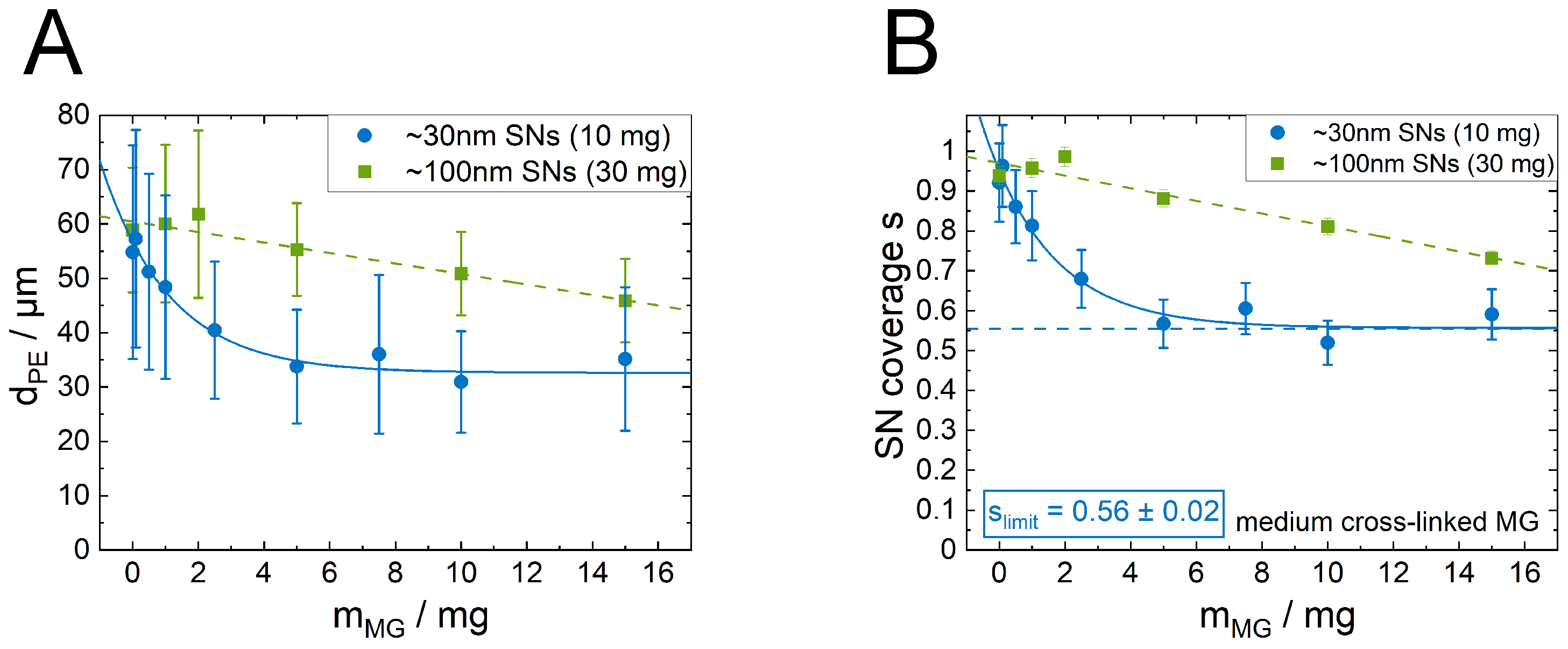
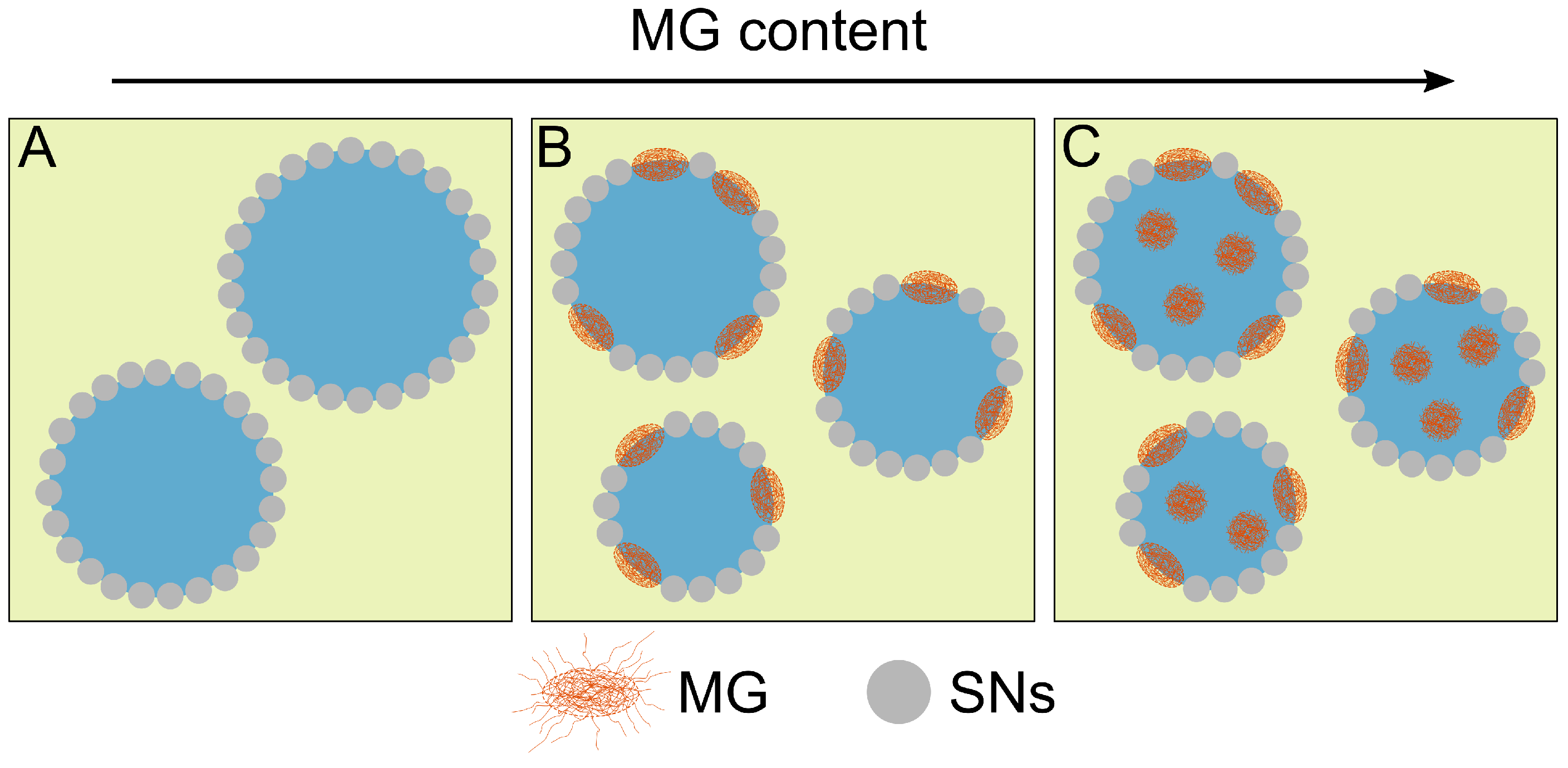
3.3. Influence of Microgel Softness on the PE Structure
3.4. Influence of the SN Size on the PE Structure
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AAPH | 2,2-azobis-2-methyl-propanimidamide dihydrochloride |
| total particle cross-section | |
| specific particle cross-section | |
| specific particle surface area | |
| total emulsion droplet interface | |
| strength of size loss per MG mass | |
| strength of silica nanosphere coverage loss per MG mass | |
| BIS | N,N’-methylenbisacrylamid |
| CA | contact angle |
| Sauter mean particle diameter | |
| maximum loss in droplet size | |
| minimal droplet size for high MG concentrations | |
| hydrodynamic microgel diameter | |
| Sauter mean droplet diameter | |
| volume water fraction | |
| total microgel particle mass | |
| MG | microgel particle |
| total silica nanosphere mass | |
| NIPAM | N-isopropylacrylamide |
| o/w | oil in water |
| PE | Pickering emulsion |
| PNIPAM | polyN-isopropylacrylamide |
| q | swelling ratio |
| average single particle density | |
| s | silica nanosphere coverage |
| maximum loss in silica nanosphere coverage | |
| final silica nanosphere coverage | |
| SN | silica nanosphere |
| total Pickering emulsion volume | |
| VPT | volume phase transition |
| VPTT | volume phase transition temperature |
| w/o | water in oil |
| -potential |
References
- Linke, C.; Drusch, S. Pickering emulsions in foods-opportunities and limitations. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2018, 58, 1971–1985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murray, B.S. Pickering emulsions for food and drinks. Curr. Opin. Food Sci. 2019, 27, 57–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, X.; Ma, C.; Cui, F.; McClements, D.J.; Liu, X.; Liu, F. Protein-stabilized Pickering emulsions: Formation, stability, properties, and applications in foods. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2020, 103, 293–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niroula, A.; Gamot, T.D.; Ooi, C.W.; Dhital, S. Biomolecule-based pickering food emulsions: Intrinsic components of food matrix, recent trends and prospects. Food Hydrocoll. 2021, 112, 106303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Fang, Z.; Chen, X.; Zhang, W.; Xie, Y.; Chen, Y.; Liu, Z.; Yuan, W. An Overview of Pickering Emulsions: Solid-Particle Materials, Classification, Morphology, and Applications. Front. Pharmacol. 2017, 8, 287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Harman, C.L.; Patel, M.A.; Guldin, S.; Davies, G.L. Recent developments in Pickering emulsions for biomedical applications. Curr. Opin. Colloid Interface Sci. 2019, 39, 173–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez, A.M.B.; Binks, B.P. Catalysis in Pickering emulsions. Soft Matter 2020, 16, 10221–10243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, F.; Vis, C.M.; Ciptonugroho, W.; Bruijnincx, P.C.A. Recent developments in catalysis with Pickering Emulsions. Green Chem. 2021, 23, 2575–2594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiley, R. Limited coalescence of oil droplets in coarse oil-in-water emulsions. J. Colloid Sci. 1954, 9, 427–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kempin, M.V.; Stock, S.; von Klitzing, R.; Kraume, M.; Drews, A. Influence of particle type and concentration on the ultrafiltration behavior of nanoparticle stabilized Pickering emulsions and suspensions. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2020, 252, 117457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stock, S.; Schlander, A.; Kempin, M.; Geisler, R.; Stehl, D.; Spanheimer, K.; Hondow, N.; Micklethwaite, S.; Weber, A.; Schomäcker, R.; et al. The quantitative impact of fluid vs. solid interfaces on the catalytic performance of pickering emulsions. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. PCCP 2021, 23, 2355–2367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kempin, M.V.; Kraume, M.; Drews, A. W/O Pickering emulsion preparation using a batch rotor-stator mixer-Influence on rheology, drop size distribution and filtration behavior. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2020, 573, 135–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Binks, B.P. Particles as surfactants—Similarities and differences. Curr. Opin. Colloid Interface Sci. 2002, 7, 21–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Q.; Pan, Y.; Jia, X.; Li, J.; Zhang, M.; Yin, L. Review on the Stability Mechanism and Application of Water-in-Oil Emulsions Encapsulating Various Additives. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2019, 18, 1660–1675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zembyla, M.; Murray, B.S.; Sarkar, A. Water-in-oil emulsions stabilized by surfactants, biopolymers and/or particles: A review. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2020, 104, 49–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, H.; Liu, L.; Li, Y.; Yin, S.; Ngai, T. Inverse Pickering Emulsion Stabilized by Binary Particles with Contrasting Characteristics and Functionality for Interfacial Biocatalysis. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2020, 12, 4989–4997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eral, H.B.; López-Mejías, V.; O’Mahony, M.; Trout, B.L.; Myerson, A.S.; Doyle, P.S. Biocompatible Alginate Microgel Particles as Heteronucleants and Encapsulating Vehicles for Hydrophilic and Hydrophobic Drugs. Cryst. Growth Des. 2014, 14, 2073–2082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Zhang, R.; Zou, L.; McClements, D.J. Protein encapsulation in alginate hydrogel beads: Effect of pH on microgel stability, protein retention and protein release. Food Hydrocoll. 2016, 58, 308–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lopez, V.C.; Hadgraft, J.; Snowden, M.J. The use of colloidal microgels as a (trans)dermal drug delivery system. Int. J. Pharm. 2005, 292, 137–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, J.K.; Drumright, R.; Siegwart, D.J.; Matyjaszewski, K. The development of microgels/nanogels for drug delivery applications. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2008, 33, 448–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malmsten, M.; Bysell, H.; Hansson, P. Biomacromolecules in microgels—Opportunities and challenges for drug delivery. Curr. Opin. Colloid Interface Sci. 2010, 15, 435–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dirksen, M.; Dargel, C.; Meier, L.; Brändel, T.; Hellweg, T. Smart microgels as drug delivery vehicles for the natural drug aescin: Uptake, release and interactions. Colloid Polym. Sci. 2020, 298, 505–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lefroy, K.S.; Murray, B.S.; Ries, M.E. Advances in the use of microgels as emulsion stabilisers and as a strategy for cellulose functionalisation. Cellulose 2021, 28, 647–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiese, S.; Tsvetkova, Y.; Daleiden, N.J.; Spieß, A.C.; Richtering, W. Microgel stabilized emulsions: Breaking on demand. Colloids Surf. Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2016, 495, 193–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stock, S.; von Klitzing, R. Microgels at droplet interfaces of water-in-oil emulsions—Challenges and progress. Curr. Opin. Colloid Interface Sci. 2022, 58, 101561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stock, S.; Jakob, F.; Röhl, S.; Gräff, K.; Kühnhammer, M.; Hondow, N.S.; Micklethwaite, S.; Kraume, M.; von Klitzing, R. Exploring Water in Oil Emulsions simultaneously stabilized by solid hydrophobic Silica Nanospheres and hydrophilic soft PNIPAM Microgel. Soft Matter 2021, 17, 8258–8268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pelton, R. Temperature-sensitive aqueous microgels. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2000, 85, 1–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stöber, W.; Fink, A.; Bohn, E. Controlled growth of monodisperse silica spheres in the micron size range. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 1968, 26, 62–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Blaaderen, A.; van Geest, J.; Vrij, A. Monodisperse colloidal silica spheres from tetraalkoxysilanes: Particle formation and growth mechanism. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 1992, 154, 481–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graf, C.; van Blaaderen, A. Metallodielectric Colloidal Core–Shell Particles for Photonic Applications. Langmuir 2002, 18, 524–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pelton, R.H.; Chibante, P. Preparation of aqueous latices with N-isopropylacrylamide. Colloids Sur. 1986, 20, 247–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoare, T.; Pelton, R. Highly pH and Temperature Responsive Microgels Functionalized with Vinylacetic Acid. Macromolecules 2004, 37, 2544–2550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia, A.; Marquez, M.; Cai, T.; Rosario, R.; Hu, Z.; Gust, D.; Hayes, M.; Vail, S.A.; Park, C.D. Photo-, thermally, and pH-responsive microgels. Langmuir Acs J. Sur. Colloids 2007, 23, 224–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanson, N.; Rieger, J. Synthesis of nanogels/microgels by conventional and controlled radical crosslinking copolymerization. Polym. Chem. 2010, 1, 965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Senff, H.; Richtering, W. Influence of cross-link density on rheological properties of temperature-sensitive microgel suspensions. Colloid Polym. Sci. 2000, 278, 830–840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varga, I.; Gilányi, T.; Mészáros, R.; Filipcsei, G.; Zrínyi, M. Effect of Cross-Link Density on the Internal Structure of Poly( N -isopropylacrylamide) Microgels. J. Phys. Chem. B 2001, 105, 9071–9076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pelton, R.H.; Pelton, H.M.; Morphesis, A.; Rowell, R.L. Particle sizes and electrophoretic mobilities of poly(N-isopropylacrylamide) latex. Langmuir 1989, 5, 816–818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Utashiro, Y.; Takiguchi, M.; Satoh, M. Zeta potential of PNIPAM microgel particles dispersed in water—Effects of charged radical initiators vs. OH− ion adsorption. Colloid Polym. Sci. 2017, 295, 45–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wellert, S.; Richter, M.; Hellweg, T.; von Klitzing, R.; Hertle, Y. Responsive Microgels at Sur. and Interfaces. Z. Fur Phys. Chem. 2015, 229, 1225–1250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tatry, M.C.; Laurichesse, E.; Perro, A.; Ravaine, V.; Schmitt, V. Kinetics of spontaneous microgels adsorption and stabilization of emulsions produced using microfluidics. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2019, 548, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Destribats, M.; Lapeyre, V.; Wolfs, M.; Sellier, E.; Leal-Calderon, F.; Ravaine, V.; Schmitt, V. Soft microgels as Pickering emulsion stabilisers: Role of particle deformability. Soft Matter 2011, 7, 7689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| ∼30 nm SNs | ∼100 nm SNs | |
|---|---|---|
| /nm | ||
| /g · cm−3 | ||
| /m2 · g−1 | ||
| /m2 · g−1 | ||
| /mV | ||
| CA/° |
| Lower Cross-Linked MG | Medium Cross-Linked MG | Higher Cross-Linked MG | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 20 °C | 50 °C | 20 °C | 50 °C | 20 °C | 50 °C | |
| /nm | ||||||
| q | ||||||
| /mV | ||||||
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Stock, S.; Röhl, S.; Mirau, L.; Kraume, M.; von Klitzing, R. Maximum Incorporation of Soft Microgel at Interfaces of Water in Oil Emulsion Droplets Stabilized by Solid Silica Spheres. Nanomaterials 2022, 12, 2649. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano12152649
Stock S, Röhl S, Mirau L, Kraume M, von Klitzing R. Maximum Incorporation of Soft Microgel at Interfaces of Water in Oil Emulsion Droplets Stabilized by Solid Silica Spheres. Nanomaterials. 2022; 12(15):2649. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano12152649
Chicago/Turabian StyleStock, Sebastian, Susanne Röhl, Luca Mirau, Matthias Kraume, and Regine von Klitzing. 2022. "Maximum Incorporation of Soft Microgel at Interfaces of Water in Oil Emulsion Droplets Stabilized by Solid Silica Spheres" Nanomaterials 12, no. 15: 2649. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano12152649
APA StyleStock, S., Röhl, S., Mirau, L., Kraume, M., & von Klitzing, R. (2022). Maximum Incorporation of Soft Microgel at Interfaces of Water in Oil Emulsion Droplets Stabilized by Solid Silica Spheres. Nanomaterials, 12(15), 2649. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano12152649