Development of Eggshell-Based Orange Peel Activated Carbon Film for Synergetic Adsorption of Cadmium (II) Ion
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Preparation of Eggshell Powder (ESP) and Orange Peel Activated Carbon (OPAC)
2.3. Preparation of Cd (II) Ions and Methylene Blue
2.4. Fabrication of CS/ESP/OPAC and CS/ESP/CAC Composite Film
2.5. Physical Characterization of Composite Films
2.5.1. Thickness (e), Density (ρ)
2.5.2. Moisture Content (MC), Water Solubility (WS), Water Absorption (WA), Swelling Degree (SD)
2.5.3. Water Vapor Permeability (WVP)
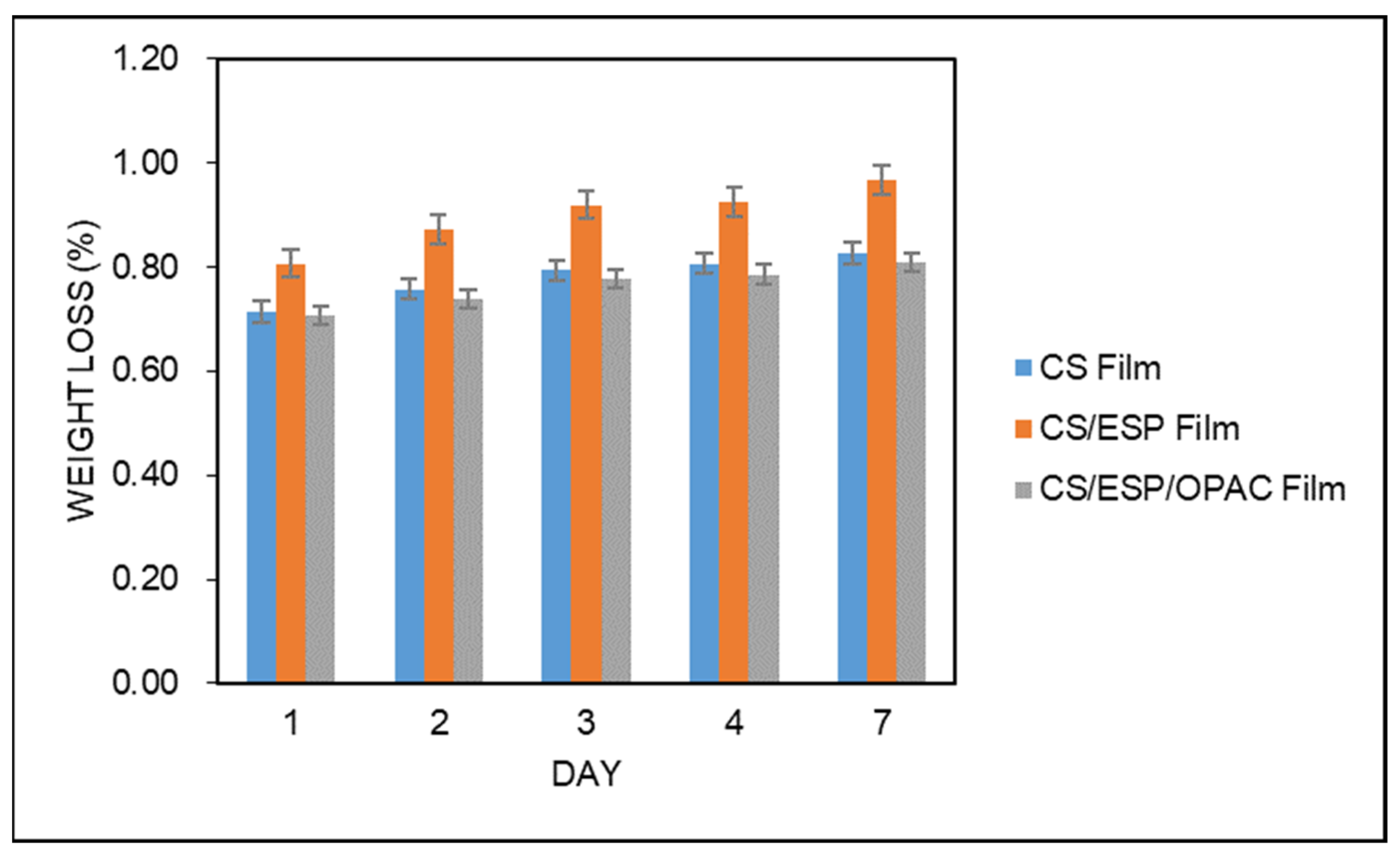
2.5.4. Biodegradation Test
2.6. Morphological Characterization of Films
2.6.1. Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM)
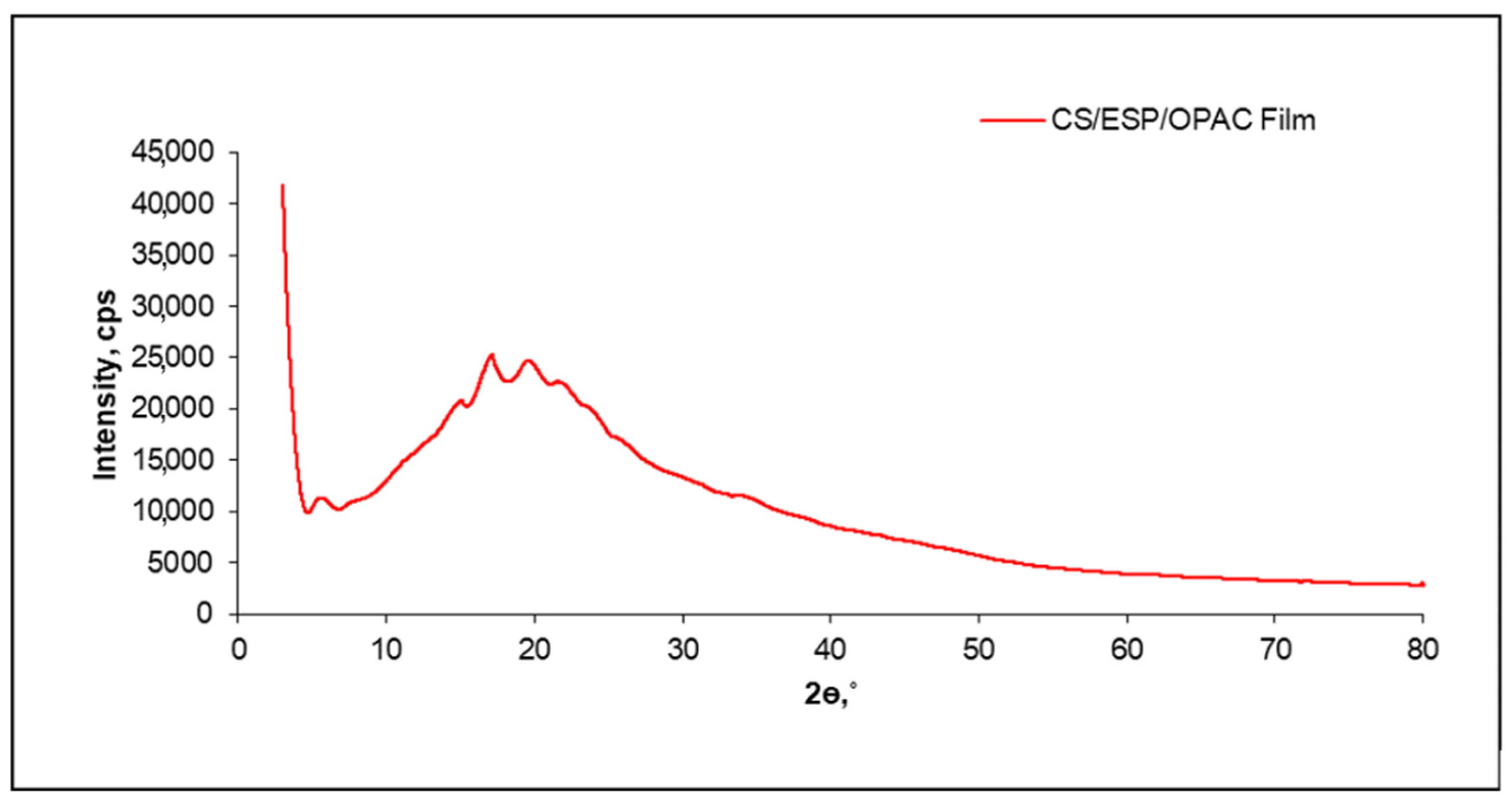
2.6.2. X-ray Diffraction (XRD)
2.7. Adsorption Studies
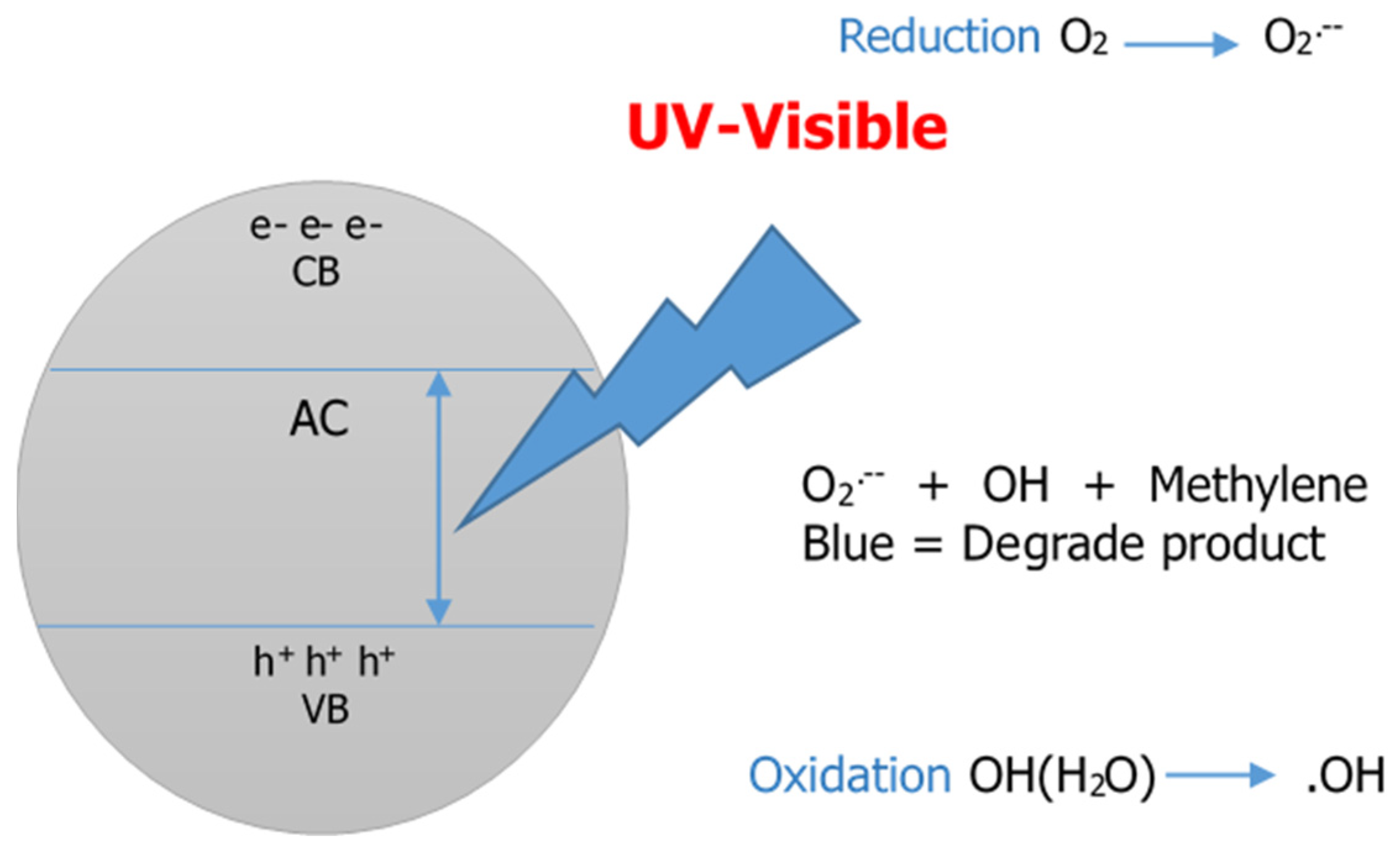
2.7.1. Photocatalytic Activity
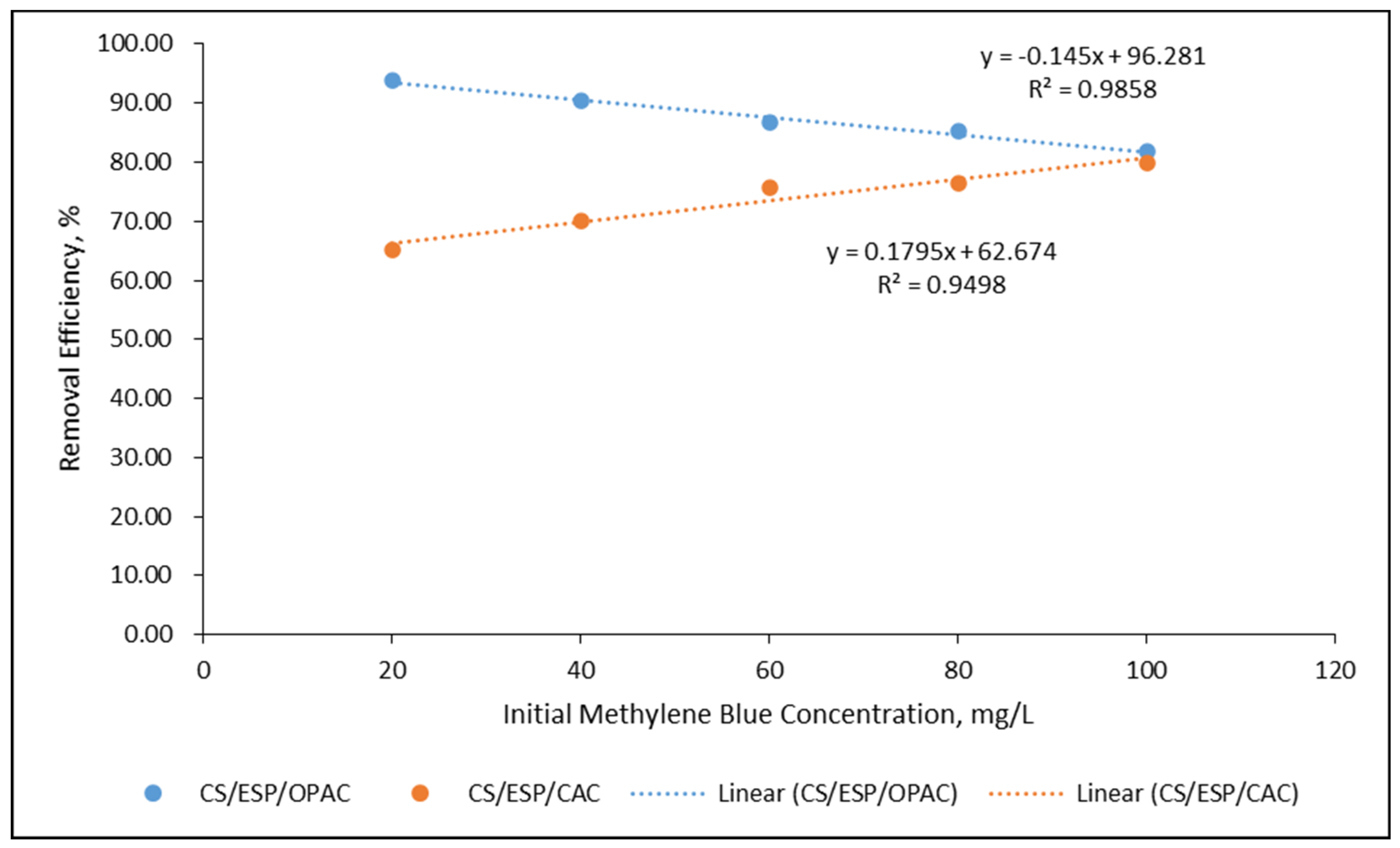
2.7.2. Effect of Metal Ion Concentration on Adsorption of Cd2+ Ion
2.8. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Characterization of Different Types of Film
3.2. Morphological Characterization
3.2.1. SEM
3.2.2. XRD
3.3. Adsorption Studies
3.3.1. Photocatalytic Activity
| Carbon + hv → H+ + e− |
| H+ + O–H → OH− |
| e− + O2 → O2− |
| Methylene Blue + Reactive Oxygen Species → CO2 + H2O |
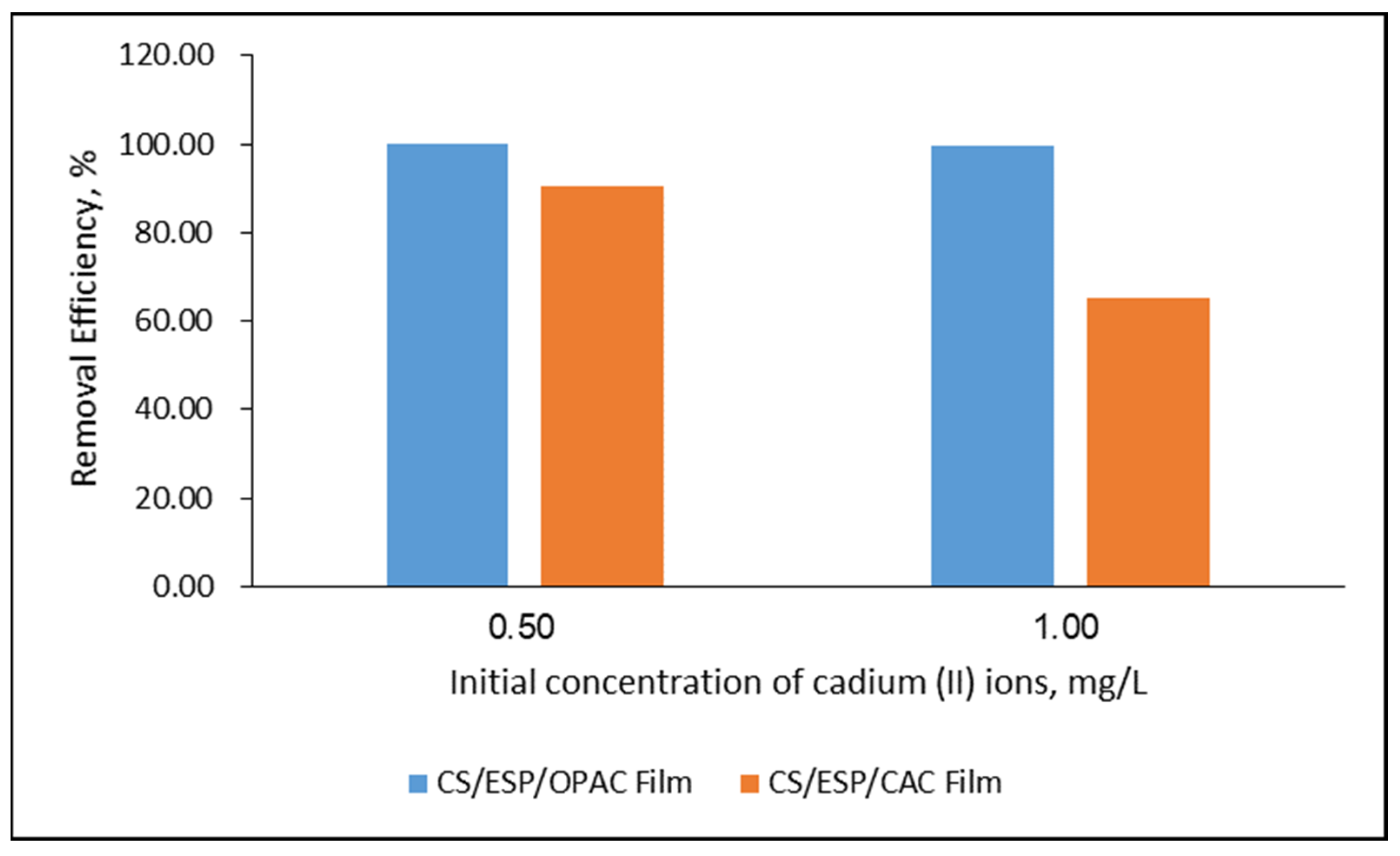
3.3.2. Effect of Initial Cd2+ Concentration
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ali, H.; Khan, E.; Ilahi, I. Environmental chemistry and ecotoxicology of hazardous heavy metals: Environmental persistence, toxicity, and bioaccumulation. J. Chem. 2019, 2019, 6730305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peigneux, A.; Puentes-Pardo, J.D.; Rodríguez-Navarro, A.B.; Hincke, M.T.; Jimenez-Lopez, C. Development and characterization of magnetic eggshell membranes for lead removal from wastewater. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2020, 192, 110307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giraldo, L.; Moreno-Piraján, J.C. Study of adsorption of phenol on activated carbons obtained from eggshells. J. Anal. Appl. Pyrolysis 2014, 106, 41–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mensah, M.B.; Lewis, D.J.; Boadi, N.O.; Awudza, J.A. Heavy metal pollution and the role of inorganic nanomaterials in environmental remediation. R. Soc. Open Sci. 2021, 8, 201485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, S.; Sidhu, G.K.; Singh, H. Removal of methylene blue dye using activated carbon prepared from biowaste precursor. Indian Chem. Eng. 2019, 61, 28–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diao, Z.H.; Xu, X.R.; Chen, H.; Jiang, D.; Yang, Y.X.; Kong, L.J.; Sun, Y.X.; Hu, Y.X.; Hao, Q.W.; Liu, L. Simultaneous removal of Cr (VI) and phenol by persulfate activated with bentonite-supported nanoscale zero-valent iron: Reactivity and mechanism. J. Hazard Mater. 2016, 316, 186–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaur, R.; Sharma, S.; Kaur, H. Heavy metals toxicity and the environment. In Molecular, Clinical and Environmental Toxicology; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2019; pp. 133–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuang, Y.; Zhang, X.; Zhou, S. Adsorption of methylene blue in water onto activated carbon by surfactant modification. Water 2020, 12, 587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shrestha, R.; Ban, S.; Devkota, S.; Sharma, S.; Joshi, R.; Tiwari, A.P.; Kim, H.Y.; Joshi, M.K. Technological trends in heavy metals removal from industrial wastewater: A review. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2021, 9, 105688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burakov, A.E.; Galunin, E.V.; Burakova, I.V.; Kucherova, A.E.; Agarwal, S.; Tkachev, A.G.; Gupta, V.K. Adsorption of heavy metals on conventional and nanostructured materials for wastewater treatment purposes: A review. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2018, 148, 702–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Danish, M.; Ahmad, T. A review on utilization of wood biomass as a sustainable precursor for activated carbon production and application. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2018, 87, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Gisi, S.; Lofrano, G.; Grassi, M.; Notarnicola, M. Characteristics and adsorption capacities of low-cost sorbents for wastewater treatment: A review. Sustain. Mater. Technol. 2016, 9, 10–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akinhanmi, T.F.; Ofudje, E.A.; Adeogun, A.I.; Aina, P.; Joseph, I.M. Orange peel as low-cost adsorbent in the elimination of Cd (II) ion: Kinetics, isotherm, thermodynamic and optimization evaluations. Bioresour. Bioprocess. 2020, 7, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lugo-Lugo, V.; Barrera-Díaz, C.; Ureña-Núñez, F.; Bilyeu, B.; Linares-Hernández, I. Biosorption of Cr (III) and Fe (III) in single and binary systems onto pretreated orange peel. J. Environ. Manag. 2012, 112, 120–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mora, B.P.; Bertoni, F.A.; Mangiameli, M.F.; González, J.C.; Bellú, S.E. Batch and fixed-bed column studies of selenite removal from contaminated water by orange peel-based sorbent. Water Sci. Eng. 2020, 13, 307–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abd-Talib, N.; Chuong, C.S.; Mohd-Setapar, S.H.; Asli, U.A.; Pa’ee, K.F.; Len, K.Y.T. Trends in adsorption mechanisms of fruit peel adsorbents to remove wastewater pollutants (Cu (II), Cd (II) and Pb (II)). J. Water Environ. Technol. 2020, 18, 290–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pavithra, S.; Thandapani, G.; Sugashini, S.; Sudha, P.N.; Alkhamis, H.H.; Alrefaei, A.F.; Almutairi, M.H. Batch adsorption studies on surface tailored chitosan/orange peel hydrogel composite for the removal of Cr (VI) and Cu (II) ions from synthetic wastewater. Chemosphere 2021, 271, 129415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guiza, S. Biosorption of heavy metal from aqueous solution using cellulosic waste orange peel. Ecol. Eng. 2017, 99, 134–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mittal, A.; Teotia, M.; Soni, R.K.; Mittal, J. Applications of egg shell and egg shell membrane as adsorbents: A review. J. Mol. Liq. 2016, 223, 376–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, A.; Jini, D.; Aravind, M.; Parvathiraja, C.; Ali, R.; Kiyani, M.Z.; Alothman, A. A novel study on synthesis of egg shell based activated carbon for degradation of methylene blue via photocatalysis. Arab. J. Chem. 2020, 13, 8717–8722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ribeiro, A.; Graça, J.; Castro, F.; Vilarinho, C.; Carvalho, J. Development of a Process for Waste Eggshell Valorisation—Wasteeng Conference Series. 2012. Available online: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/258514905_Development_of_a_process_for_waste_eggshell_valorisation (accessed on 31 May 2022).
- Isa, Y.M.; Harripersadth, C.; Musonge, P.; Sayago, A.; Morales, M.G. The application of eggshells and sugarcane bagasse as potential biomaterials in the removal of heavy metals from aqueous solutions. S. Afr. J. Chem. Eng. 2020, 34, 142–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdel-Khalek, M.A.; Rahman, M.A.; Francis, A.A. Exploring the adsorption behavior of cationic and anionic dyes on industrial waste shells of egg. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2017, 5, 319–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shukla, S.K.; Al Mushaiqri, N.R.; Al Subhi, H.M.; Yoo, K.; Al Sadeq, H. Low-cost activated carbon production from organic waste and its utilization for wastewater treatment. Appl. Water Sci. 2020, 10, 166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Xiao, D.; Lu, J.; Li, T.; Jiao, C.; Li, S.; Lu, P.; Zhang, Z. Preparation and properties of biocomposite films based on poly (vinyl alcohol) incorporated with eggshell powder as a biological Filler. J. Polym. Environ. 2020, 28, 2020–2028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashtaputrey, P.D.; Ashtaputrey, S.D. Preparation and Characterization of Activated Charcoal derived from Wood Apple Fruit Shell. J. Sci. Res. 2020, 64, 236–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elsherif, K.M.; Ewlad-Ahmed, A.M.; Treban, A. Removal of Fe (III), Cu (II), and Co (II) from aqueous solutions by orange peels powder: Equilibrium study. J. Biochem. Mol. Biol. Res. 2017, 2, 46–51. [Google Scholar]
- Senthil Kumar, P.; Fernando, P.S.; Ahmed, R.T.; Srinath, R.; Priyadharshini, M.; Vignesh, A.M.; Thanjiappan, A. Effect of temperature on the adsorption of methylene blue dye onto sulfuric acid–treated orange peel. Chem. Eng. Commun. 2014, 201, 1526–1547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, B.; Li, S.; Wu, Y.; Song, J.; Chen, S.; Li, X.; Sun, H. Preparation and characterization of natural corn starch-based composite films reinforced by eggshell powder. CyTA-J. Food 2018, 16, 1045–1054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chavoshizadeh, S.; Pirsa, S.; Mohtarami, F. Conducting/smart color film based on wheat gluten/chlorophyll/polypyrrole nanocomposite. Food Packag. Shelf Life 2020, 24, 100501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herniou, C.; Mendieta, J.R.; Gutiérrez, T.J. Characterization of biodegradable/non-compostable films made from cellulose acetate/corn starch blends processed under reactive extrusion conditions. Food Hydrocoll. 2019, 89, 67–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.; Li, X.; Liu, L.; Chen, W.; Bai, J.; Ma, F.; Liu, X.; Kang, W. Preparation and characterization of edible films composed of Dioscorea opposita Thunb. mucilage and starch. Polym. Test 2020, 90, 106708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cazón, P.; Vázquez, M.; Velazquez, G. Novel composite films based on cellulose reinforced with chitosan and polyvinyl alcohol: Effect on mechanical properties and water vapour permeability. Polym. Test 2018, 69, 536–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gutiérrez, T.J. Are modified pumpkin flour/plum flour nanocomposite films biodegradable and compostable? Food Hydrocoll. 2018, 83, 397–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammadi, R.; Mohammadifar, M.A.; Rouhi, M.; Kariminejad, M.; Mortazavian, A.M.; Sadeghi, E.; Hasanvand, S. Physico-mechanical and structural properties of eggshell membrane gelatin-chitosan blend edible films. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 107, 406–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ibrahim, M.I.; Sapuan, S.M.; Zainudin, E.S.; Zuhri, M.Y. Physical, thermal, morphological, and tensile properties of cornstarch-based films as affected by different plasticizers. Int. J. Food Prop. 2019, 22, 925–941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amin, M.T.; Alazba, A.A.; Shafiq, M. Comparative study for adsorption of methylene blue dye on biochar derived from orange peel and banana biomass in aqueous solutions. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2019, 191, 735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jha, P. Effect of plasticizer and antimicrobial agents on functional properties of bionanocomposite films based on corn starch-chitosan for food packaging applications. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 160, 571–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Araújo, A.; Galvão, A.; Silva Filho, C.; Mendes, F.; Oliveira, M.; Barbosa, F.; Sousa Filho, M.; Bastos, M. Okra mucilage and corn starch bio-based film to be applied in food. Polym. Test 2018, 71, 352–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Q.; Du, L.; Yang, Y.; Wang, L. Rheology of film-forming solutions and physical properties of tara gum film reinforced with polyvinyl alcohol (PVA). Food Hydrocoll. 2017, 63, 677–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarifuddin, N.; Azhar, A.Z.A.; Zaki, H.H.M. Biodegradation of mango seed starch films in soil. IIUM Eng. J. 2022, 23, 258–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Husain, H.; Senawi, N.; Rahman, A.Y.; Kuthiah, Y.; Nadarajah, T.; Ya’cob, S.S.; Khairudin, S. Development of mushroom-based film from waste and its role in mycoremediation. J. Adv. Res. Mater. Sci. 2017, 28, 9–15. [Google Scholar]
- Obasi, H.C.; Igwe, I.O.; Madufor, I.C. Effect of soil burial on tensile properties of polypropylene/plasticized cassava starch blends. Adv. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2013, 2013, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ranaweera, C.K.; Kahol, P.K.; Ghimire, M.; Mishra, S.R.; Gupta, R.K. Orange-peel-derived carbon: Designing sustainable and high-performance supercapacitor electrodes. C J. Carbon Res. 2017, 3, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Somsesta, N.; Sricharoenchaikul, V.; Aht-Ong, D. Adsorption removal of methylene blue onto activated carbon/cellulose biocomposite films: Equilibrium and kinetic studies. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2020, 240, 122221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Talat, M.; Mohan, S.; Dixit, V.; Singh, D.K.; Hasan, S.H.; Srivastava, O.N. Effective removal of fluoride from water by coconut husk activated carbon in fixed bed column: Experimental and breakthrough curves analysis. Ground Sustain. Dev. 2018, 7, 48–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afolabi, I.C.; Popoola, S.I.; Bello, O.S. Modeling pseudo-second-order kinetics of orange peel-paracetamol adsorption process using artificial neural network. Chemom. Intell. Lab. Syst. 2020, 203, 104053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruthiraan, M.; Abdullah, E.C.; Mubarak, N.M.; Noraini, M.N. A promising route of magnetic based materials for removal of cadmium and methylene blue from waste water. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2017, 5, 1447–1455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fonseca-García, A.; Jiménez-Regalado, E.J.; Aguirre-Loredo, R.Y. Preparation of a novel biodegradable packaging film based on corn starch-chitosan and poloxamers. Carbohydr. Polym. 2021, 251, 117009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Z.; Guan, W.; Ji, F.; Song, Z.; Zhao, Y. Production of biologically activated carbon from orange peel and landfill leachate subsequent treatment technology. J. Chem. 2014, 2014, 491912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.; Han, J.; Ro, H.M. Mechanistic insights into Cd (II) and As (V) sorption on Miscanthus biochar at different pH values and pyrolysis temperatures. Chemosphere 2022, 287, 132179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zoumaki, M.; Tzetzis, D.; Mansour, G. Development and characterization of starch-based nanocomposite materials. IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2019, 564, 012037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, R.; Wang, J.; Cheng, M.; Lu, W.; Chen, M.; Zhang, R.; Wang, X. Development and characterization of corn starch/PVA active films incorporated with carvacrol nanoemulsions. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 164, 1631–1639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eshaghi, A.; Moradi, H. Optical and photocatalytic properties of the Fe-doped TiO2 nanoparticles loaded on the activated carbon. Adv. Powder Technol. 2018, 29, 1879–1885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jayakumar, G.; Irudayaraj, A.A.; Raj, A.D. Photocatalytic degradation of methylene blue by nickel oxide nanoparticles. Mater. Today Proc. 2017, 4, 11690–11695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muzarpar, M.S.; Leman, A.M.; Rahman, K.A.; Shayfull, Z.; Irfan, A.R. Exploration Sustainable Base Material for Activated Carbon Production Using Agriculture Waste as Raw Materials: A Review. IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2020, 864, 012022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hameed, A.M. Synthesis of Si/Cu amorphous adsorbent for efficient removal of methylene blue dye from aqueous media. J. Inorg. Organomet. Polym. Mater. 2020, 30, 2881–2889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mandal, S.; Calderon, J.; Marpu, S.B.; Omary, M.A.; Shi, S.Q. Mesoporous activated carbon as a green adsorbent for the removal of heavy metals and Congo red: Characterization, adsorption kinetics, and isotherm studies. J. Contam. Hydrol. 2021, 243, 103869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sherugar, P.; Padaki, M.; Naik, N.S.; George, S.D.; Murthy, D.H. Biomass-derived versatile activated carbon removes both heavy metals and dye molecules from wastewater with near-unity efficiency: Mechanism and kinetics. Chemosphere 2022, 287, 132085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, V.K.; Kumar, E.A. Comparative studies on CO2 adsorption kinetics by solid adsorbents. Energy Procedia 2016, 90, 316–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.H.; Li, J.; Luo, J.H.; Jin, Y.; Zheng, D. Removal of cadmium (II) from aqueous solution by a new adsorbent of fluor-hydroxyapatite composites. J. Taiwan Inst. Chem. Eng. 2017, 70, 200–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmadi, M.; Niari, M.H.; Kakavandi, B. Development of maghemite nanoparticles supported on cross-linked chitosan (γ-Fe2O3@CS) as a recoverable mesoporous magnetic composite for effective heavy metals removal. J. Mol. Liq. 2017, 248, 184–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jafari, A.J.; Kakavandi, B.; Kalantary, R.R.; Gharibi, H.; Asadi, A.; Azari, A.; Babaei, A.A.; Takdastan, A. Application of mesoporous magnetic carbon composite for reactive dyes removal: Process optimization using response surface methodology. Korean J. Chem. Eng. 2016, 33, 2878–2890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hiew, B.Y.Z.; Lee, L.Y.; Lee, X.J.; Thangalazhy-Gopakumar, S.; Gan, S. Utilisation of environmentally friendly okara-based biosorbent for cadmium (II) removal. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 40608–40622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ayouch, I.; Kassem, I.; Kassab, Z.; Barrak, I.; Barhoun, A.; Jacquemin, J.; Draoui, K.; El Achaby, M. Crosslinked carboxymethyl cellulose-hydroxyethyl cellulose hydrogel films for adsorption of cadmium and methylene blue from aqueous solutions. Surf. Interfaces 2021, 24, 101124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jayakumar, V.; Govindaradjane, S.; Kumar, P.S.; Rajamohan, N.; Rajasimman, M. Sustainable removal of cadmium from contaminated water using green alga–Optimization, characterization and modeling studies. Environ. Res. 2021, 199, 111364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, X.; Yan, X.; Yao, J.; Zheng, S.; Wei, Q. Feasibility and comparative analysis of cadmium biosorption by living Scenedesmus obliquus FACHB-12 biofilms. Chemosphere 2021, 275, 130125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brandes, R.; Belosinschi, D.; Brouillette, F.; Chabot, B. A new electrospun chitosan/phosphorylated nanocellulose biosorbent for the removal of cadmium ions from aqueous solutions. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2019, 7, 103477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmoud, A.E.D.; Fawzy, M.; Radwan, A. Optimization of Cadmium (CD2+) removal from aqueous solutions by novel biosorbent. Int. J. Phytoremediation 2016, 18, 619–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, L.; Chen, Y.; Wang, Y.; Lv, J.; Dai, P.; Zhang, J.; Huang, Y.; Lv, W. Contributions of Various Cd (II) Adsorption Mechanisms by Phragmites australis-Activated Carbon Modified with Mannitol. ACS Omega 2022, 7, 10502–10515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hevira, L.; Ighalo, J.O.; Aziz, H.; Zein, R. Terminalia catappa shell as low-cost biosorbent for the removal of methylene blue from aqueous solutions. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2021, 97, 188–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mathivanan, M.; Syed Abdul Rahman, S.; Vedachalam, R.; Karuppiah, S. Ipomoea carnea: A novel biosorbent for the removal of methylene blue (MB) from aqueous dye solution: Kinetic, equilibrium and statistical approach. Int. J. Phytoremediation 2021, 23, 982–1000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parlayıcı, Ş.; Pehlivan, E. Biosorption of methylene blue and malachite green on biodegradable magnetic Cortaderia selloana flower spikes: Modeling and equilibrium study. Int. J. Phytoremediation 2021, 1, 26–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, Y.; Zeng, C.; Lü, Q.F.; Yu, Y. Efficient adsorption of methylene blue and lead ions in aqueous solutions by 5-sulfosalicylic acid modified lignin. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 123, 50–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Parameters | CS Film | CS/ESP Film | CS/ESP/OPAC Film |
|---|---|---|---|
| e (mm) | 0.01 | 0.02 | 0.03 |
| ρ (g/cm3) | 0.9387 ± 0.07 b | 0.4587 ± 0.02 a | 0.4053 ± 0.06 a |
| MC (%) | 17.56 ± 0.26 b | 14.24 ± 0.44 a | 15.15 ± 0.93 a |
| WS (%) | 21.77 ± 1.21 b | 18.67 ± 1.15 a | 18.08 ± 1.09 a |
| WA (%) | 231.96 ± 1.56 b | 269.74 ± 1.70 c | 197.44 ± 1.78 a |
| SD (%) | 238.28 ± 1.48 a | 290.96 ± 1.57 c | 249.40 ± 2.58 b |
| WVP (gs−1 m Pa) (×10−9) | 315.69 ± 9.00 a | 664.62 ± 6.90 b | 1007.1 ± 12.63 c |
| Biodegradability (%) | 0.83 ± 0.06 a | 0.97 ± 0.17 a | 0.81 ± 0.19 a |
| Surface color measurements | |||
| L* | 99.15 ± 0.01 b | 99.43 ± 0.02 b | 24.76 ± 0.69 a |
| a* | 4.07 ± 0.03 b | 4.24 ± 0.03 c | 1.37 ± 0.05 a |
| b* | 2.95 ± 0.09 c | 2.73 ± 0.07 b | 1.97 ± 0.08 a |
| ΔE | - | 0.39 ± 0.04 | 81.45 ± 0.69 |
| Adsorbents | Removal Efficiency (%) | References |
|---|---|---|
| Okara waste | 77.07 | [64] |
| Carboxymethyl cellulose-hydroxyethyl cellulose hydrogel films | 91.99 | [65] |
| Green algae | 80.87 | [66] |
| Microalgal biofilm | 90.35 | [67] |
| Chitosan/phosphorylated nanocellulose | 85.00 | [68] |
| Dracaena draca | 79.60 | [69] |
| Phragmites australis-Activated Carbon Modified with Mannitol | 76.62 | [70] |
| CS/ESP/OPAC film | 99.70 | This work |
| Adsorbents | Removal Efficiency (%) | References |
|---|---|---|
| Eggshell and eggshell membrane | 94.9 | [23] |
| Terminalia catappa shell | 90.56 | [71] |
| Ipomoea carnea | 79.74 | [72] |
| Magnetic Cortaderia selloana flower spikes | 94.69 | [73] |
| 5-solfosalycilic acid modified lignin | 83.2 | [74] |
| CS/ESP/OPAC film | 93.75 | This work |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Vonnie, J.M.; Li, C.S.; Erna, K.H.; Yin, K.W.; Felicia, W.X.L.; Aqilah, M.N.N.; Rovina, K. Development of Eggshell-Based Orange Peel Activated Carbon Film for Synergetic Adsorption of Cadmium (II) Ion. Nanomaterials 2022, 12, 2750. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano12162750
Vonnie JM, Li CS, Erna KH, Yin KW, Felicia WXL, Aqilah MNN, Rovina K. Development of Eggshell-Based Orange Peel Activated Carbon Film for Synergetic Adsorption of Cadmium (II) Ion. Nanomaterials. 2022; 12(16):2750. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano12162750
Chicago/Turabian StyleVonnie, Joseph Merillyn, Chua Shek Li, Kana Husna Erna, Koh Wee Yin, Wen Xia Ling Felicia, Md Nasir Nur’ Aqilah, and Kobun Rovina. 2022. "Development of Eggshell-Based Orange Peel Activated Carbon Film for Synergetic Adsorption of Cadmium (II) Ion" Nanomaterials 12, no. 16: 2750. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano12162750
APA StyleVonnie, J. M., Li, C. S., Erna, K. H., Yin, K. W., Felicia, W. X. L., Aqilah, M. N. N., & Rovina, K. (2022). Development of Eggshell-Based Orange Peel Activated Carbon Film for Synergetic Adsorption of Cadmium (II) Ion. Nanomaterials, 12(16), 2750. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano12162750










