Enhanced Electrical Properties of Copper Nitride Films Deposited via High Power Impulse Magnetron Sputtering
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Jhi, S.H.; Ihm, J.; Louie, S.G.; Cohen, M.L. Electronic mechanism of hardness enhancement in transition-metal carbonitrides. Nature 1999, 399, 132–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, J.; Xia, J.; Zhou, T.; Niu, Y.; Chen, Y.; Luo, J.; Liu, J.; Zhou, J.; Fan, J.; Wang, C. Mechanical reliability, thermal stability and thermoelectric performance of the transition-metal nitride CrN. Philos. Mag. Lett. 2020, 100, 128–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Navinsek, B.; Seal, S. Transition metal nitride functional coatings. JOM 2001, 53, 51–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gautam, G.S.; Kumar, K.H. Elastic, thermochemical and thermophysical properties of rock salt-type transition metal carbides and nitrides: A first principles study. J. Alloys Compd. 2014, 587, 380–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blaha, P.; Redinger, J.; Schwarz, K. Bonding study of TiC and TiN. II. theory. Phys. Rev. B 1985, 31, 2316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lambrecht, W.R. Electronic structure and optical spectra of the semimetal ScAs and of the indirect-band-gap semiconductors ScN and GdN. Phys. Rev. B 2000, 62, 13538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stampfl, C.; Mannstadt, W.; Asahi, R.; Freeman, A.J. Electronic structure and physical properties of early transition metal mononitrides: Density-functional theory LDA, GGA, and screened-exchange LDA FLAPW calculations. Phys. Rev. B 2001, 63, 155106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fallberg, A.; Ottosson, M.; Carlsson, J.O. CVD of copper (I) nitride. Chem. Vap. Depos. 2009, 15, 300–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dorranian, D.; Dejam, L.; Mosayebian, G. Optical characterization of Cu3N thin film with Swanepoel method. J. Theor. Appl. Phys. 2012, 6, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Li, Y. Controllable synthesis of Cu-based nanocrystals in ODA solvent. Chem. Commun. 2011, 47, 3604–3606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahoo, G.; Meher, S.; Jain, M.K. Band gap variation in copper nitride thin films. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Advanced Nanomaterials & Emerging Engineering Technologies, IEEE, Chennai, India, 24–26 July 2013; pp. 540–542. [Google Scholar]
- Du, Y.; Ji, A.; Ma, L.; Wang, Y.; Cao, Z. Electrical conductivity and photoreflectance of nanocrystalline copper nitride thin films deposited at low temperature. J. Cryst. Growth 2005, 280, 490–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsuzaki, K.; Harada, K.; Kumagai, Y.; Koshiya, S.; Kimoto, K.; Ueda, S.; Sasase, M.; Maeda, A.; Susaki, T.; Kitano, M. High-Mobility p-Type and n-Type Copper Nitride Semiconductors by Direct Nitriding Synthesis and In Silico Doping Design. Adv. Mater. 2018, 30, 1801968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, A.; Hu, R.; Liu, W.; Zhang, R.; Zhang, J.; Pu, Y.; Chu, L.; Yang, J.; Li, X.a. Preparation and characterization of Mn doped copper nitride films with high photocurrent response. Curr. Appl. Phys. 2018, 18, 1306–1312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Zhao, J.; Yang, T.; Zhang, J.; Yang, J.; Li, X.a. Enhanced write-once optical storage capacity of Cu3N film by coupling with an Al2O3 protective layer. Ceram. Int. 2016, 42, 4486–4490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vega, C.G.; De la Cruz, W. Study of the structure and electrical properties of the copper nitride thin films deposited by pulsed laser deposition. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2006, 252, 8001–8004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, J.; Qi, M.; Cheng, Y.; Jiang, A.; Zeng, Y.; Ma, J. Influences of nitrogen partial pressure on the optical properties of copper nitride films. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 40895–40899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, W.; Zhang, X.; Fu, X.; Zhou, Y.; Luo, S.; Wu, X. Resistive-switching behavior and mechanism in copper-nitride thin films prepared by DC magnetron sputtering. Phys. Status Solidi A 2012, 209, 1996–2001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ebaid, M.; Larson, D.M.; Bustillo, K.C.; Turner, J.H.; Cooper, J.K. Saw-Tooth Heat-Cycling Nitridation of Metallic Cu Yields First Photoactive p-Cu3N for PEC Applications. ACS Appl. Energy Mater. 2020, 3, 10714–10721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Birkett, M.; Savory, C.N.; Fioretti, A.N.; Thompson, P.; Muryn, C.A.; Weerakkody, A.; Mitrovic, I.; Hall, S.; Treharne, R.; Dhanak, V.R. Atypically small temperature-dependence of the direct band gap in the metastable semiconductor copper nitride Cu3N. Phys. Rev. B 2017, 95, 115201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.C.; Huang, S.Y.; Sakalley, S.; Paliwal, A.; Chen, Y.H.; Liao, M.H.; Sun, H.; Biring, S. Optoelectronic properties of Cu3N thin films deposited by reactive magnetron sputtering and its diode rectification characteristics. J. Alloys Compd. 2019, 789, 428–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Zhang, H.; Yang, B.; Li, B.; Li, Z. Characterization of Cu3N/CuO thin films derived from annealed Cu3N for electrode application in Li-ion batteries. Thin Solid Film. 2019, 672, 157–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miura, A.; Takei, T.; Kumada, N. Synthesis of Cu3N from CuO and NaNH2. J. Asian Ceram. Soc. 2014, 2, 326–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Yuk, L.F.L.; Yan, Z.; Hu, X. Fabrication of copper (I) nitride nanorods within SBA-15 by metal organic chemical vapor deposition. Sci. China Ser. E Technol. Sci. 2009, 52, 352–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, C.; Luo, G.; Xu, Z.; Yan, S.; Zhang, J.; Chen, M.; Qian, L.; Wei, W.; Han, Q.; Zheng, G. Lithiation-Enabled High-Density Nitrogen Vacancies Electrocatalyze CO2 to C2 Products. Adv. Mater. 2021, 33, e2103150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yue, G.; Yan, P.; Liu, J.; Wang, M.; Li, M.; Yuan, X. Copper nitride thin film prepared by reactive radio-frequency magnetron sputtering. J. Appl. Phys. 2005, 98, 103506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsuzaki, K.; Okazaki, T.; Lee, Y.S.; Hosono, H.; Susaki, T. Controlled bipolar doping in Cu3N (100) thin films. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2014, 105, 222102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahmati, A. Reactive DC magnetron sputter deposited Ti–Cu–N nano-composite thin films at nitrogen ambient. Vacuum 2011, 85, 853–860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, H.; Yazdi, M.A.P.; Briois, P.; Pierson, J.F.; Sanchette, F.; Billard, A. Towards delafossite structure of Cu–Cr–O thin films deposited by reactive magnetron sputtering: Influence of substrate temperature on optoelectronics properties. Vacuum 2015, 114, 101–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christou, C.; Barber, Z. Ionization of sputtered material in a planar magnetron discharge. J. Vac. Sci. Technol. A 2000, 18, 2897–2907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.C.; Kuo, T.Y.; Lin, H.C.; Chen, R.Z.; Sun, H. Optoelectronic properties of p-type NiO films deposited by direct current magnetron sputtering versus high power impulse magnetron sputtering. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2020, 508, 145106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, H.; Kuo, T.Y.; Chen, S.C.; Chen, Y.H.; Lin, H.C.; Yazdi, M.A.P.; Billard, A. Contribution of enhanced ionization to the optoelectronic properties of p-type NiO films deposited by high power impulse magnetron sputtering. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 2019, 39, 5285–5291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, H.; Chen, S.C.; Wen, C.K.; Chuang, T.H.; Yazdi, M.A.P.; Sanchette, F.; Billard, A. p-type cuprous oxide thin films with high conductivity deposited by high power impulse magnetron sputtering. Ceram. Int. 2017, 43, 6214–6220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antonin, O.; Tiron, V.; Costin, C.; Popa, G.; Minea, T. On the HiPIMS benefits of multi-pulse operating mode. J. Phys. D 2014, 48, 015202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganesan, R.; Akhavan, B.; Dong, X.; McKenzie, D.; Bilek, M. External magnetic field increases both plasma generation and deposition rate in HiPIMS. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2018, 352, 671–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kouznetsov, V.; Macak, K.; Schneider, J.M.; Helmersson, U.; Petrov, I. A novel pulsed magnetron sputter technique utilizing very high target power densities. Surf. Coat. Technol. 1999, 122, 290–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.y.; Nakamine, N.; Hayashi, Y. Properties of various sputter-deposited Cu–N thin films. J. Vac. Sci. Technol. A 1998, 16, 2084–2092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pierson, J. Structure and properties of copper nitride films formed by reactive magnetron sputtering. Vacuum 2002, 66, 59–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dorranian, D.; Dejam, L.; Sari, A.H.; Hojabri, A. Structural and optical properties of copper nitride thin films in a reactive Ar/N2 magnetron sputtering system. EPJ Appl. Phys. 2010, 50, 20503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, X.; Li, Z.; Meng, A.; Li, C.; Wu, Z.; Yan, P. Improving the Thermal Stability of Cu3N Films by Addition of Mn. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2015, 31, 822–827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, X.M.; Li, H.J.; Wei, Y.; Zhang, Q. Copper nitride films prepared by reactive radio-frequency magnetron sputtering. In Advanced Materials Research; Trans Tech Publ.: Zurich, Switzerland, 2012; pp. 1515–1518. [Google Scholar]
- Li, X.A.; Yang, J.P.; Li, Y.T.; Wang, L.X.; Wang, H.Y. Study on copper nitride thin films prepared by reactive DC magnetron sputtering. In Materials Science Forum; Trans Tech Publ.: Zurich, Switzerland, 2011; pp. 706–710. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, Y.; Li, X.; Liu, Y.; Sun, W.; Dong, C. Preparation and characterization of CuN-based ternary alloy films using Cr or Zr for stabilizing N. J. Mater. Res. 2017, 32, 1333–1342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, T.; Cao, Z.; Ji, A. Lattice extension in Cu3NMgx thin films and the induced effect. J. Alloys Compd. 2016, 685, 423–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, A.; Lu, N.; Gao, L.; Zhang, W.; Liao, L.; Cao, Z. Electrical properties and thermal stability of Pd-doped copper nitride films. J. Appl. Phys. 2013, 113, 043705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fioretti, A.N.; Schwartz, C.P.; Vinson, J.; Nordlund, D.; Prendergast, D.; Tamboli, A.C.; Caskey, C.M.; Tuomisto, F.; Linez, F.; Christensen, S.T. Understanding and control of bipolar self-doping in copper nitride. J. Appl. Phys. 2016, 119, 181508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamada, N.; Maruya, K.; Yamaguchi, Y.; Cao, X.; Ninomiya, Y. P-to n-type conversion and nonmetal–metal transition of lithium-inserted Cu3N Films. Chem. Mater. 2015, 27, 8076–8083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nandy, S.; Saha, B.; Mitra, M.K.; Chattopadhyay, K.K. Effect of oxygen partial pressure on the electrical and optical properties of highly (200) oriented p-type Ni1− xO films by DC sputtering. J. Mater. Sci. 2007, 42, 5766–5772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, H.; Chen, S.C.; Hsu, S.W.; Wen, C.K.; Chuang, T.H.; Wang, X. Microstructures and optoelectronic properties of nickel oxide films deposited by reactive magnetron sputtering at various working pressures of pure oxygen environment. Ceram. Int. 2017, 43, S369–S375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakalley, S.; Saravanan, A.; Cheng, W.C.; Chen, S.C.; Sun, H.; Hsu, C.L.; Huang, B.R. High Power Impulse Magnetron Sputtering Growth Processes for Copper Nitride Thin Film and its highly enhanced UV-Visible Photodetection Properties. J. Alloys Compd. 2021, 896, 162924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

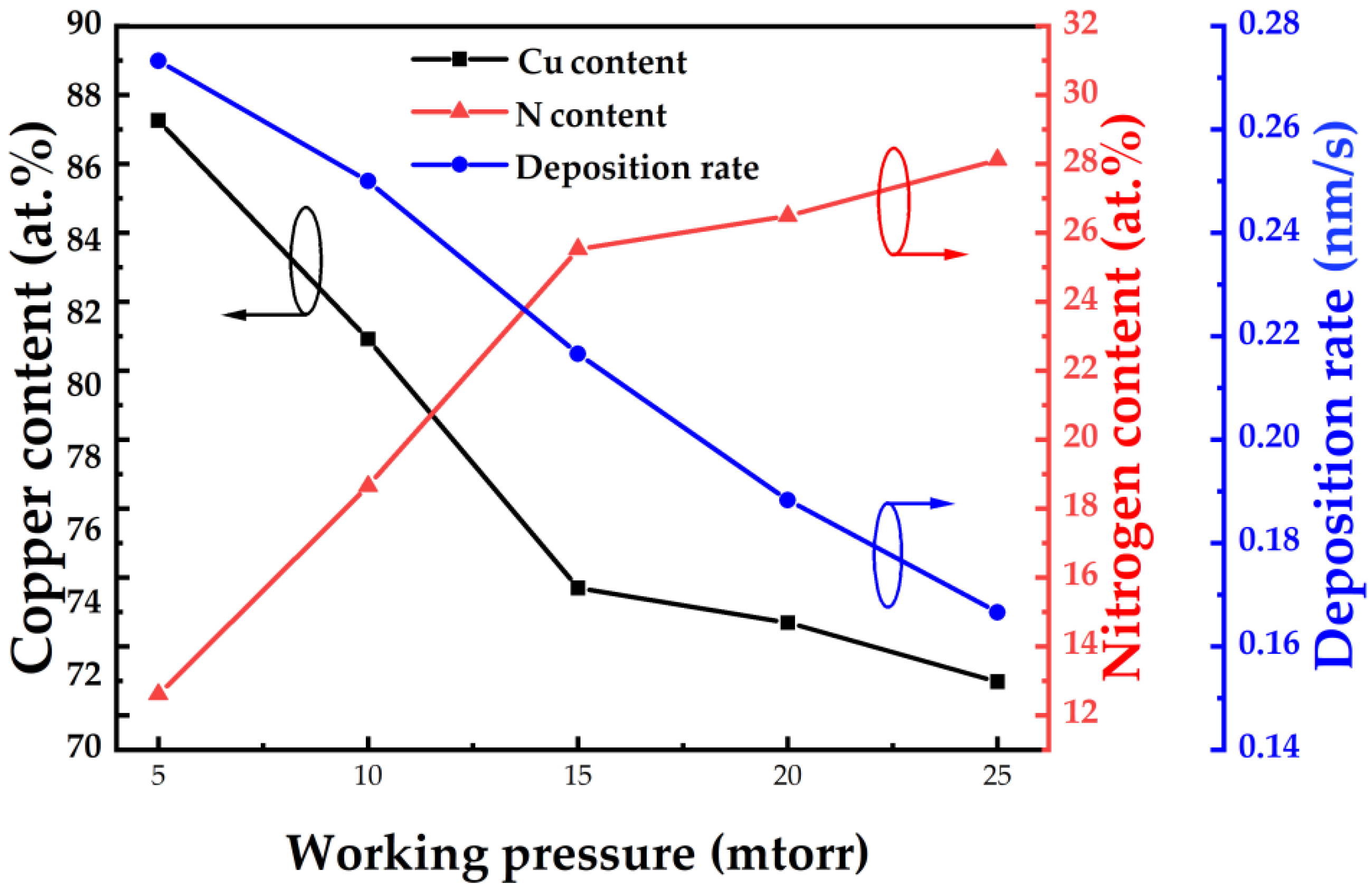
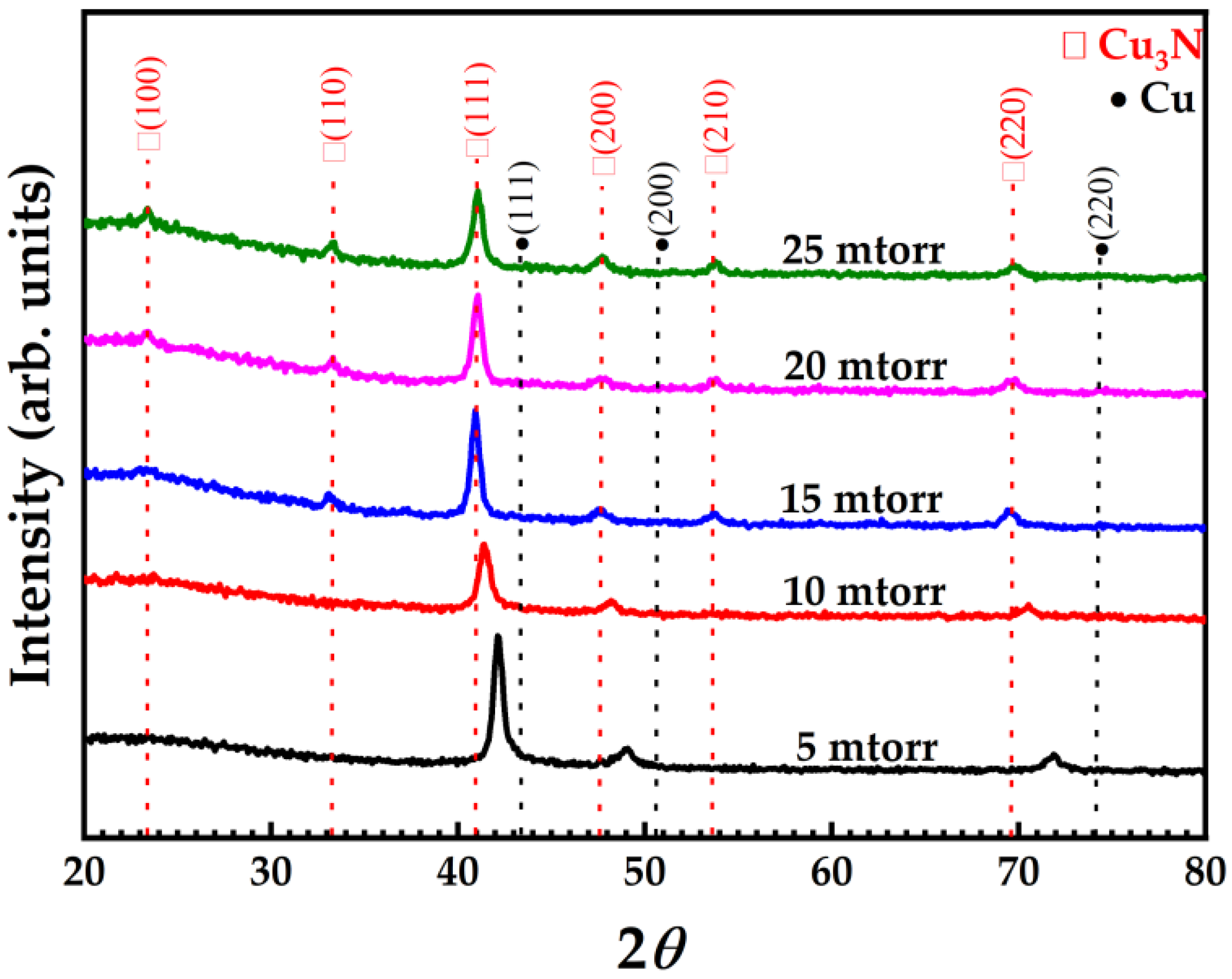
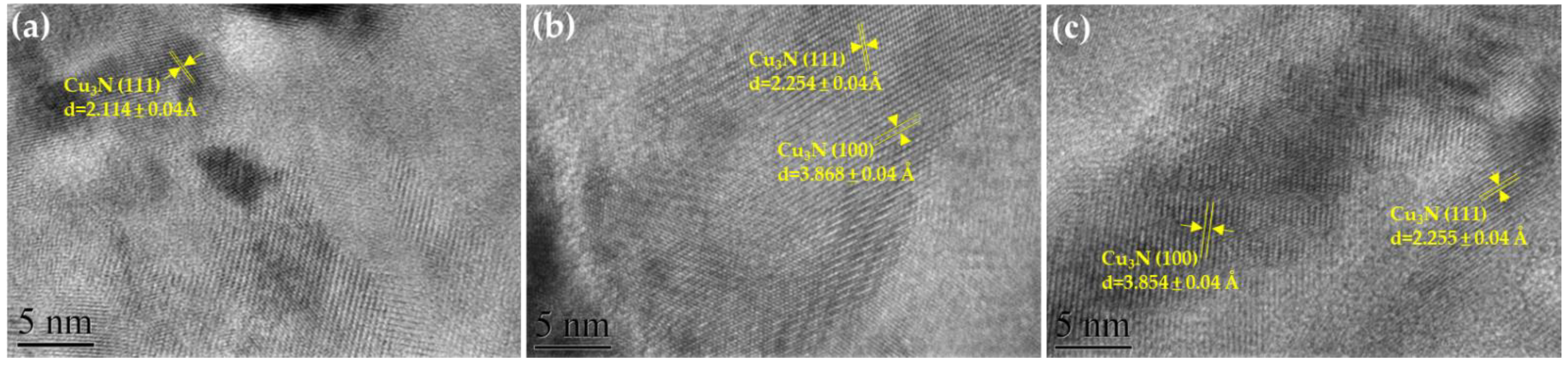
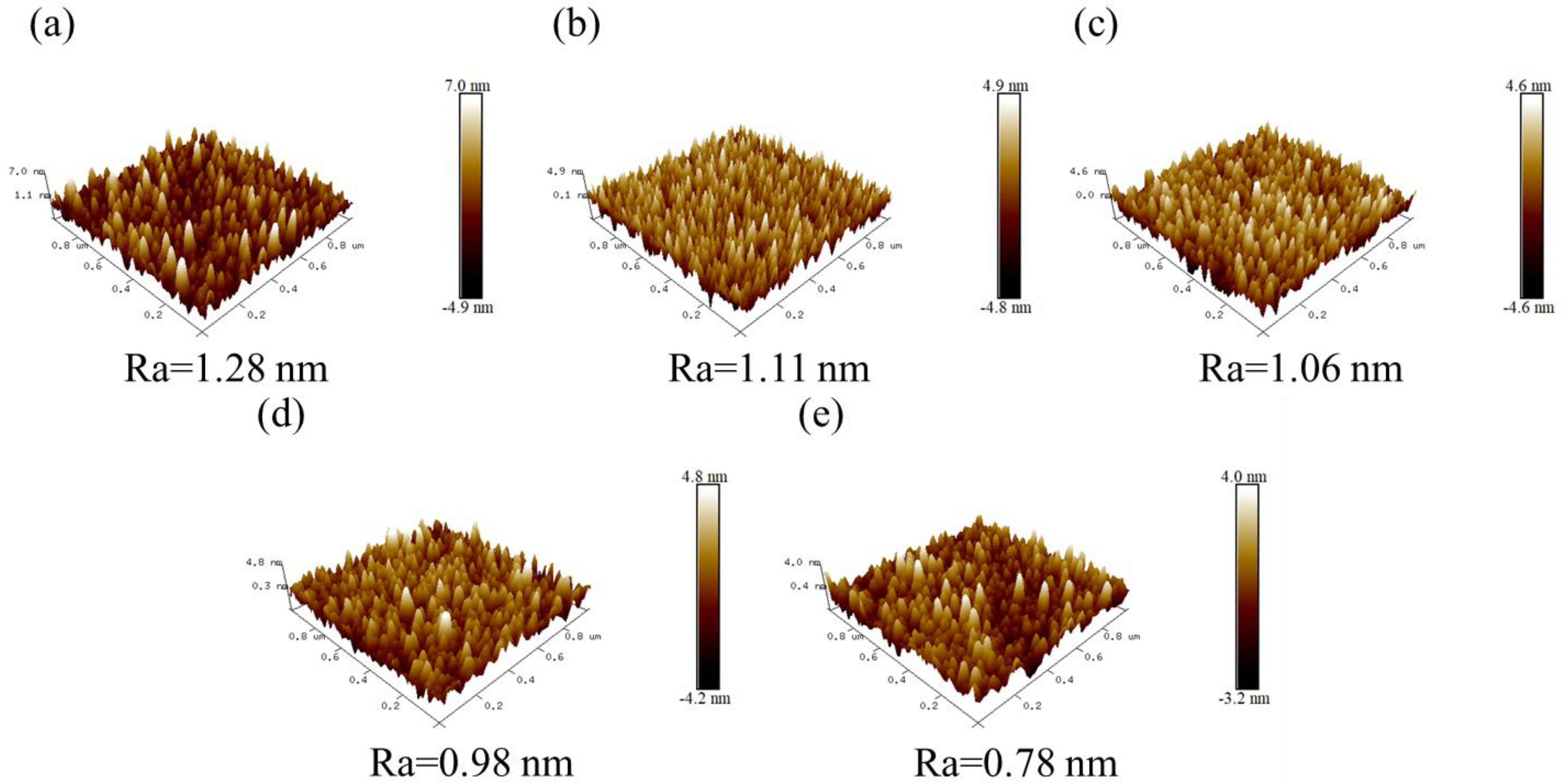
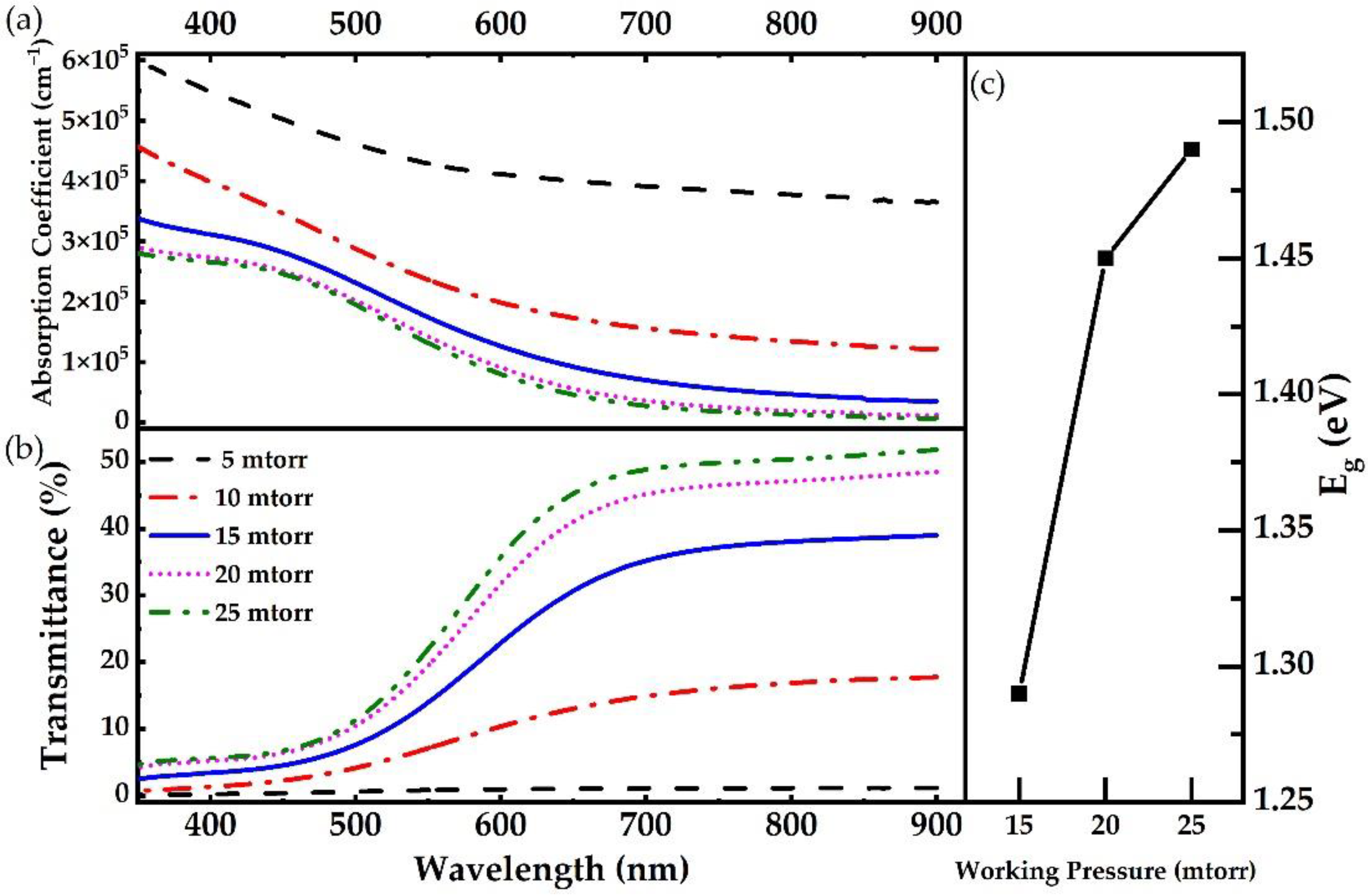
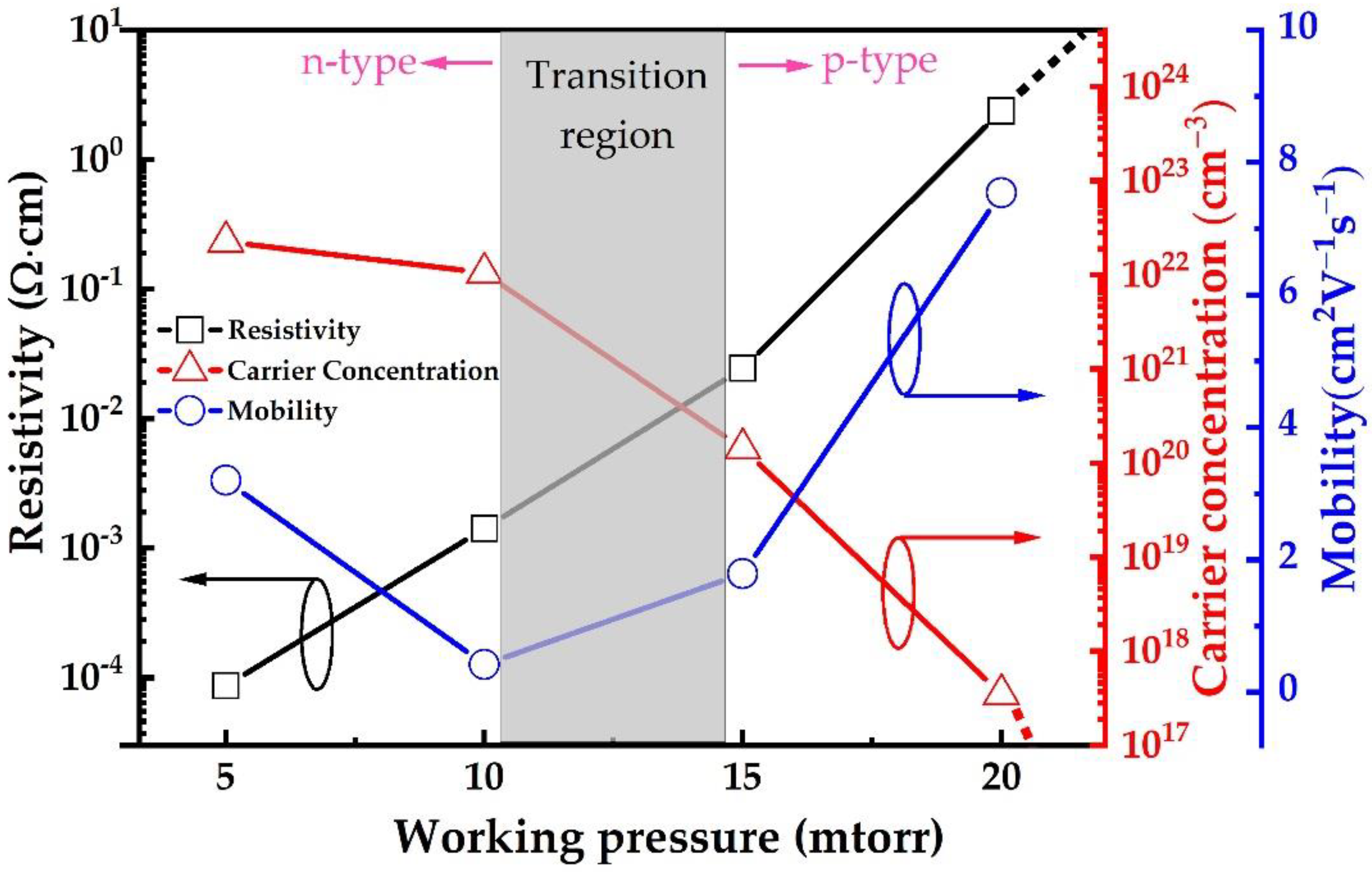
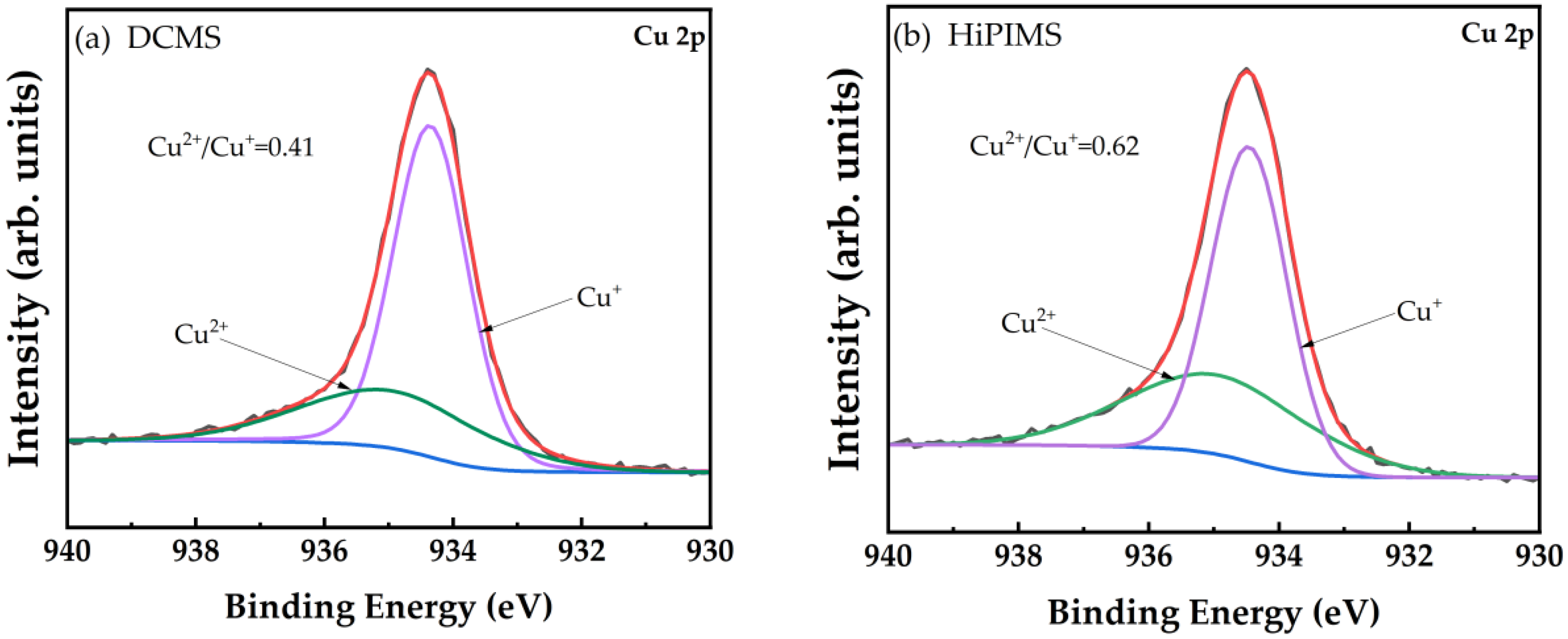
| Material | Growth Method | Resistivity (Ω cm) | Carrier Concentration (cm−3) | Mobility (cm2V−1s−1) | Type | Year | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cu3N | RF-Sputter | 1.1 × 103 | - | - | n | 2012 | [41] |
| Cu3N | DC-Sputter | 20 | - | - | n | 2011 | [42] |
| Cu3N-(Zr, Cr) | RF-Sputter | 1.65 × 10−4 | - | - | n | 2017 | [43] |
| Cu3N-Mg | RF-Sputter | 1 | 6.8 × 1018 | 6 | n | 2016 | [44] |
| Cu3N-Pd | RF-Sputter | 1.08 × 10−3 | 1021 | 18.9 | n | 2013 | [45] |
| Cu3N | RF-Sputter | 100 | 1015 | 1 | p | 2016 | [46] |
| Cu3N | RF-Sputter | 120 | - | - | p | 2015 | [47] |
| Cu3N | DC-Sputter | 0.33 | 1.29 × 1019 | 1.45 | p | 2019 | [21] |
| Cu3N | DCMS | 18.82 | - | - | p | 2022 | This Study |
| Cu3N | HiPIMS | 0.024 | 1.43 × 1020 | 1.79 | p | 2022 | This Study |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chen, Y.-H.; Lee, P.-I.; Sakalley, S.; Wen, C.-K.; Cheng, W.-C.; Sun, H.; Chen, S.-C. Enhanced Electrical Properties of Copper Nitride Films Deposited via High Power Impulse Magnetron Sputtering. Nanomaterials 2022, 12, 2814. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano12162814
Chen Y-H, Lee P-I, Sakalley S, Wen C-K, Cheng W-C, Sun H, Chen S-C. Enhanced Electrical Properties of Copper Nitride Films Deposited via High Power Impulse Magnetron Sputtering. Nanomaterials. 2022; 12(16):2814. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano12162814
Chicago/Turabian StyleChen, Yin-Hung, Pei-Ing Lee, Shikha Sakalley, Chao-Kuang Wen, Wei-Chun Cheng, Hui Sun, and Sheng-Chi Chen. 2022. "Enhanced Electrical Properties of Copper Nitride Films Deposited via High Power Impulse Magnetron Sputtering" Nanomaterials 12, no. 16: 2814. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano12162814
APA StyleChen, Y.-H., Lee, P.-I., Sakalley, S., Wen, C.-K., Cheng, W.-C., Sun, H., & Chen, S.-C. (2022). Enhanced Electrical Properties of Copper Nitride Films Deposited via High Power Impulse Magnetron Sputtering. Nanomaterials, 12(16), 2814. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano12162814






