Nanocomposite Hydrogels Containing Few-Layer Graphene Sheets Prepared through Noncovalent Exfoliation Show Improved Mechanical Properties
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Preparation of PImQ/Graphene Suspensions
2.3. Preparation of NC Hydrogels Containing Exfoliated Graphene Sheets
2.4. Characterization
3. Results and Discussion
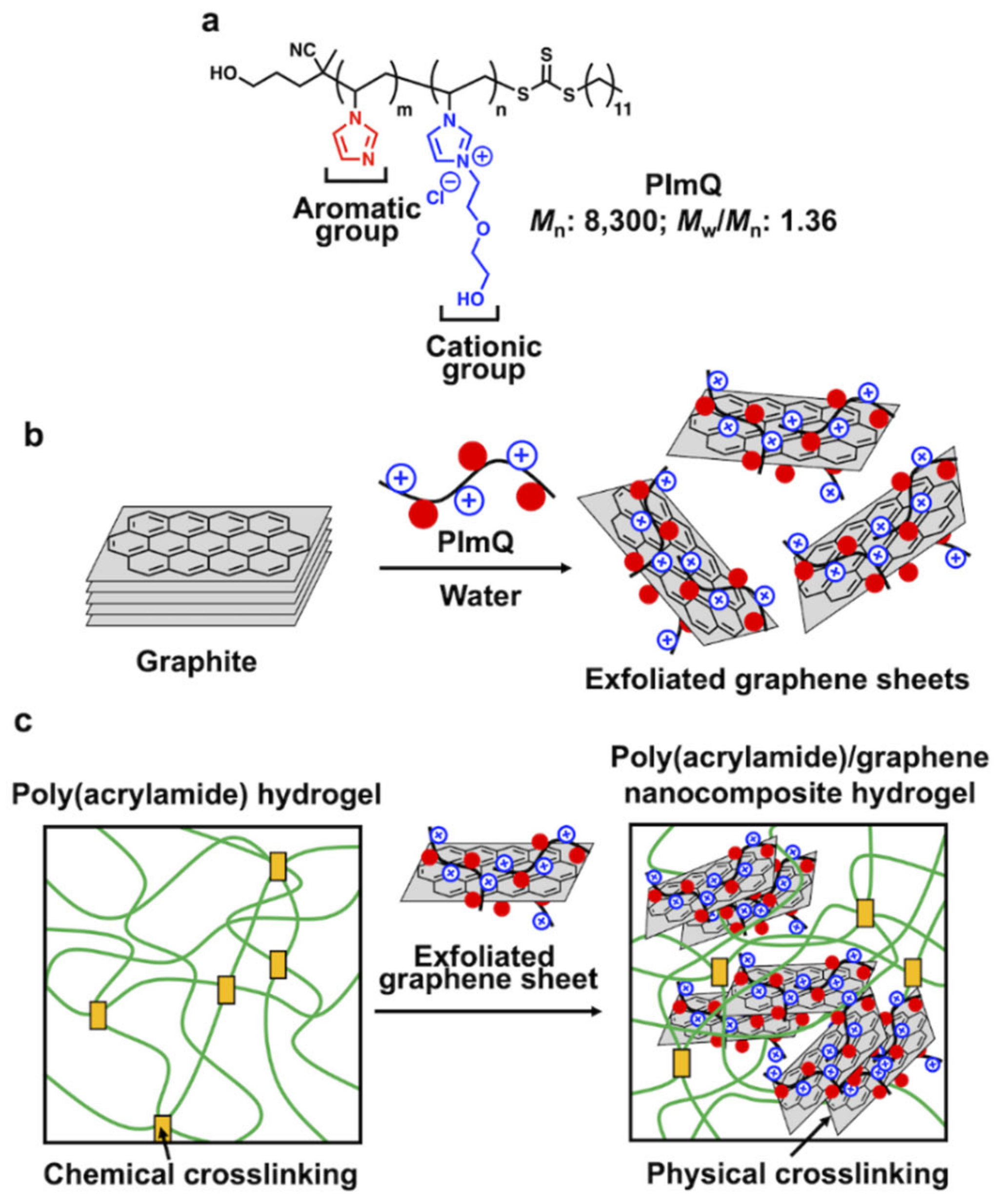
3.1. Noncovalent Exfoliation of Graphite to Graphene Using PImQ
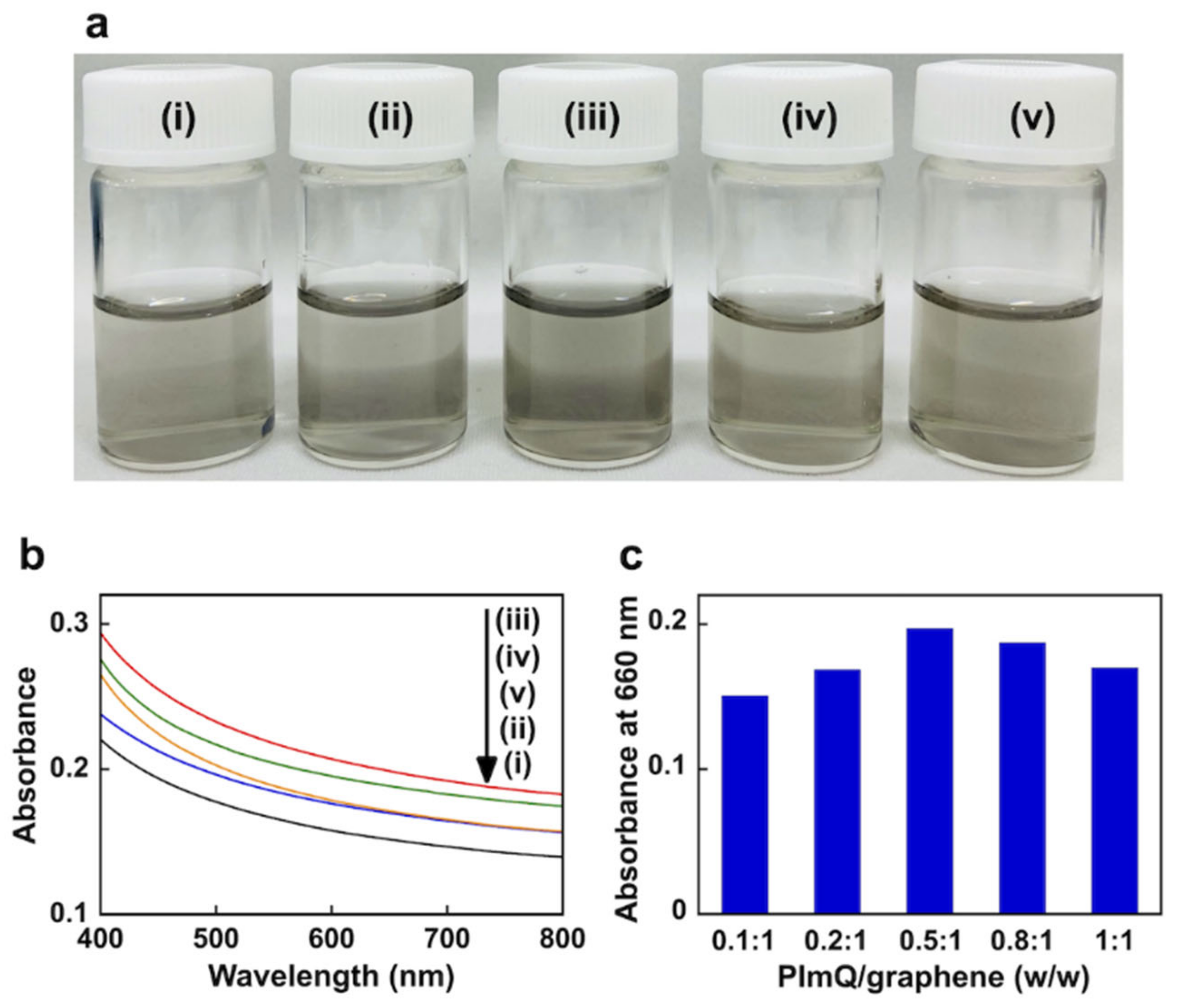
3.1.1. Aqueous Suspension of PImQ/Graphene
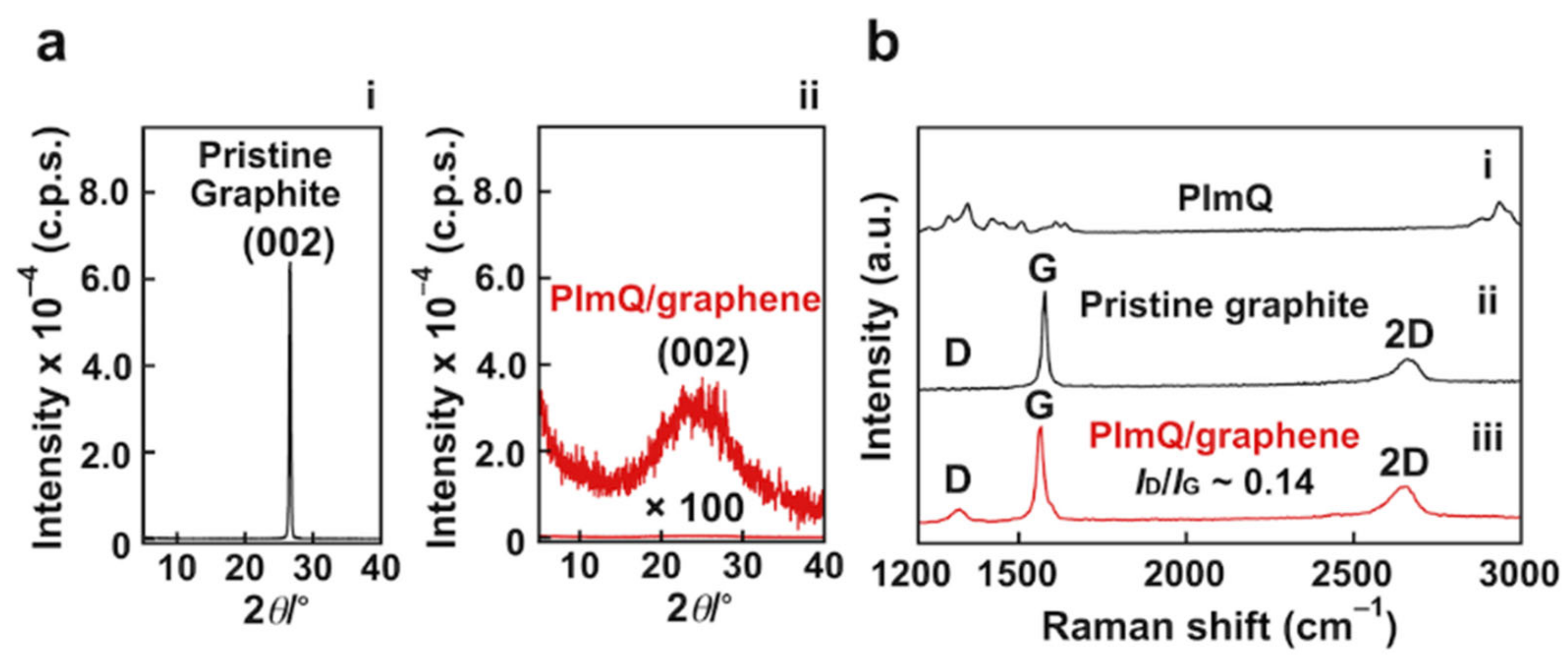
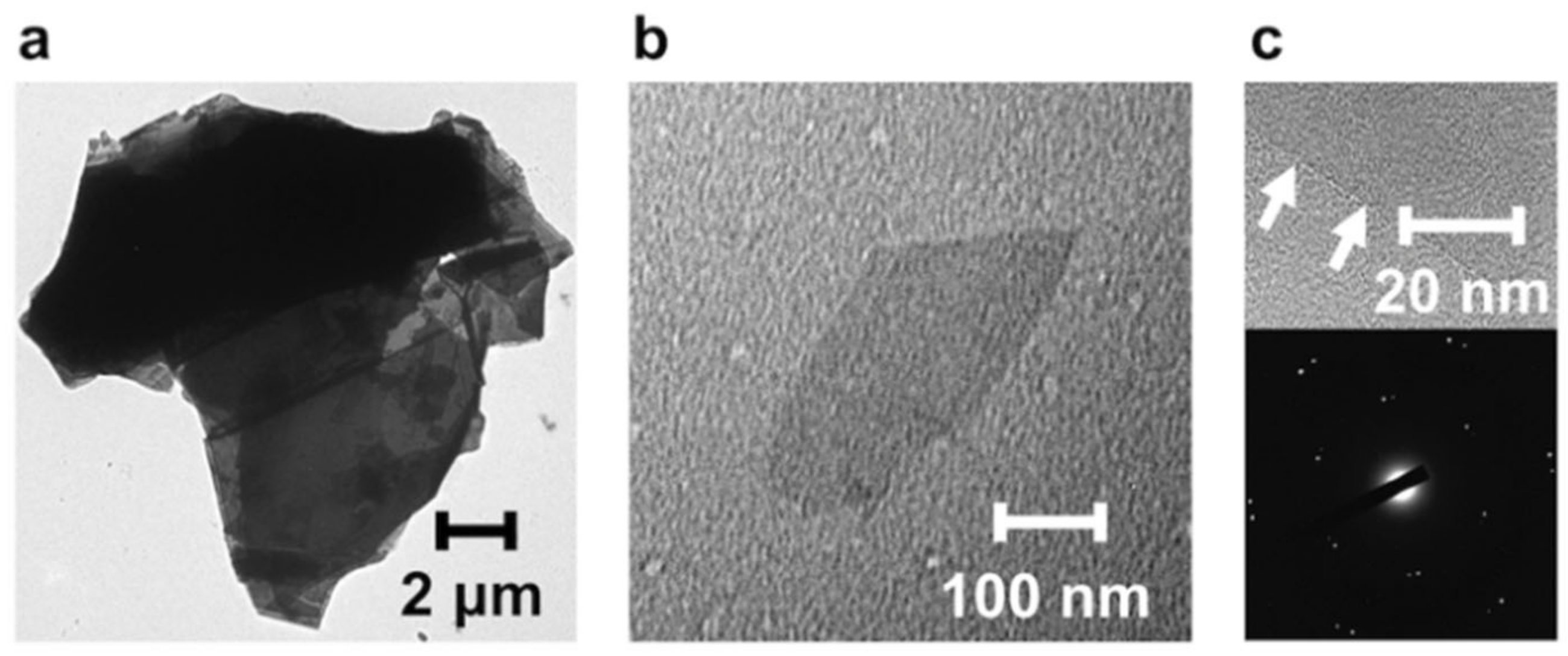
3.1.2. Exfoliation Behavior of the PImQ/Graphene Sheets
3.2. Mechanical Properties of NC Hydrogels Containing Exfoliated Graphene Sheets
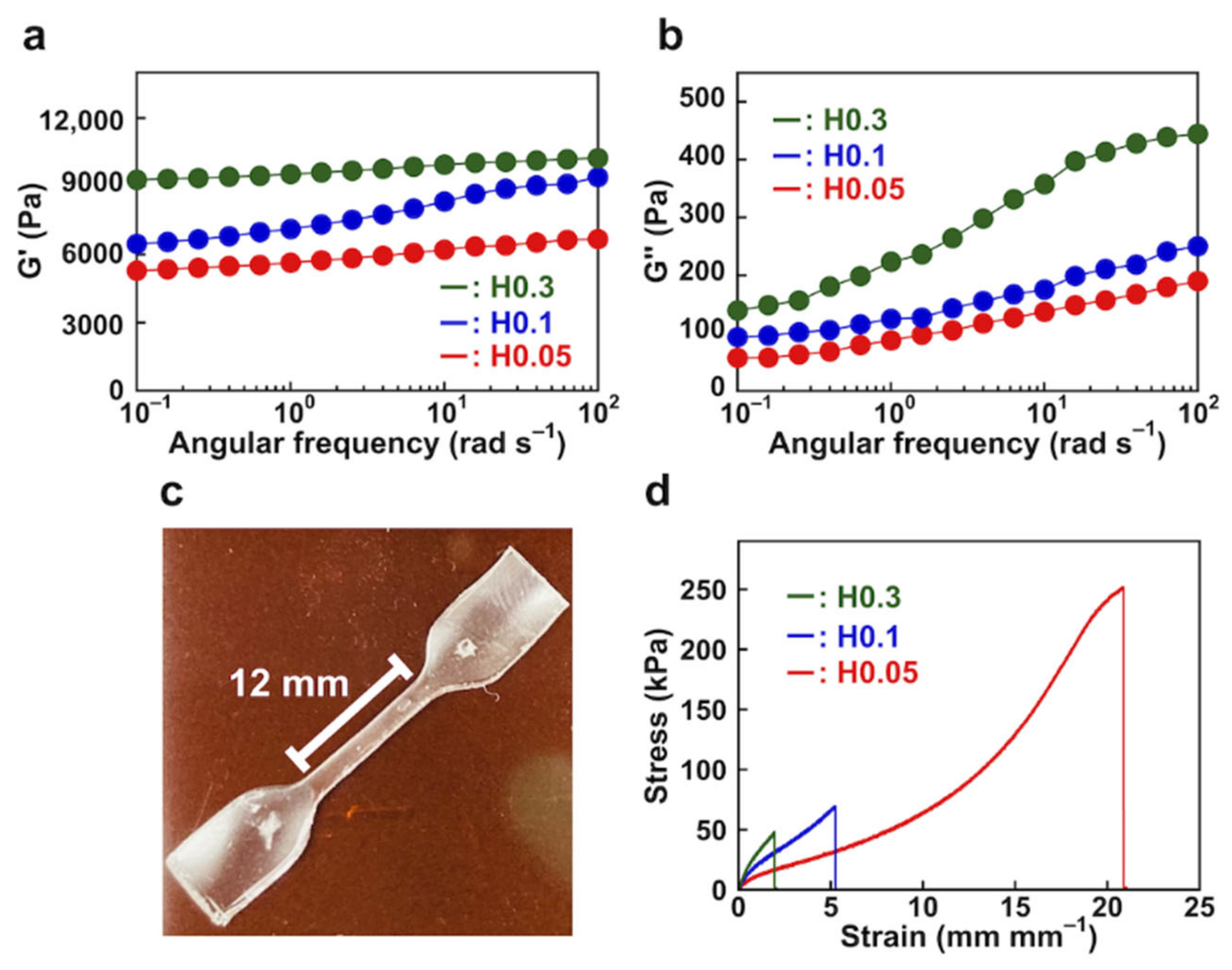
3.2.1. Rheological and Mechanical Behavior of PAAm Hydrogels
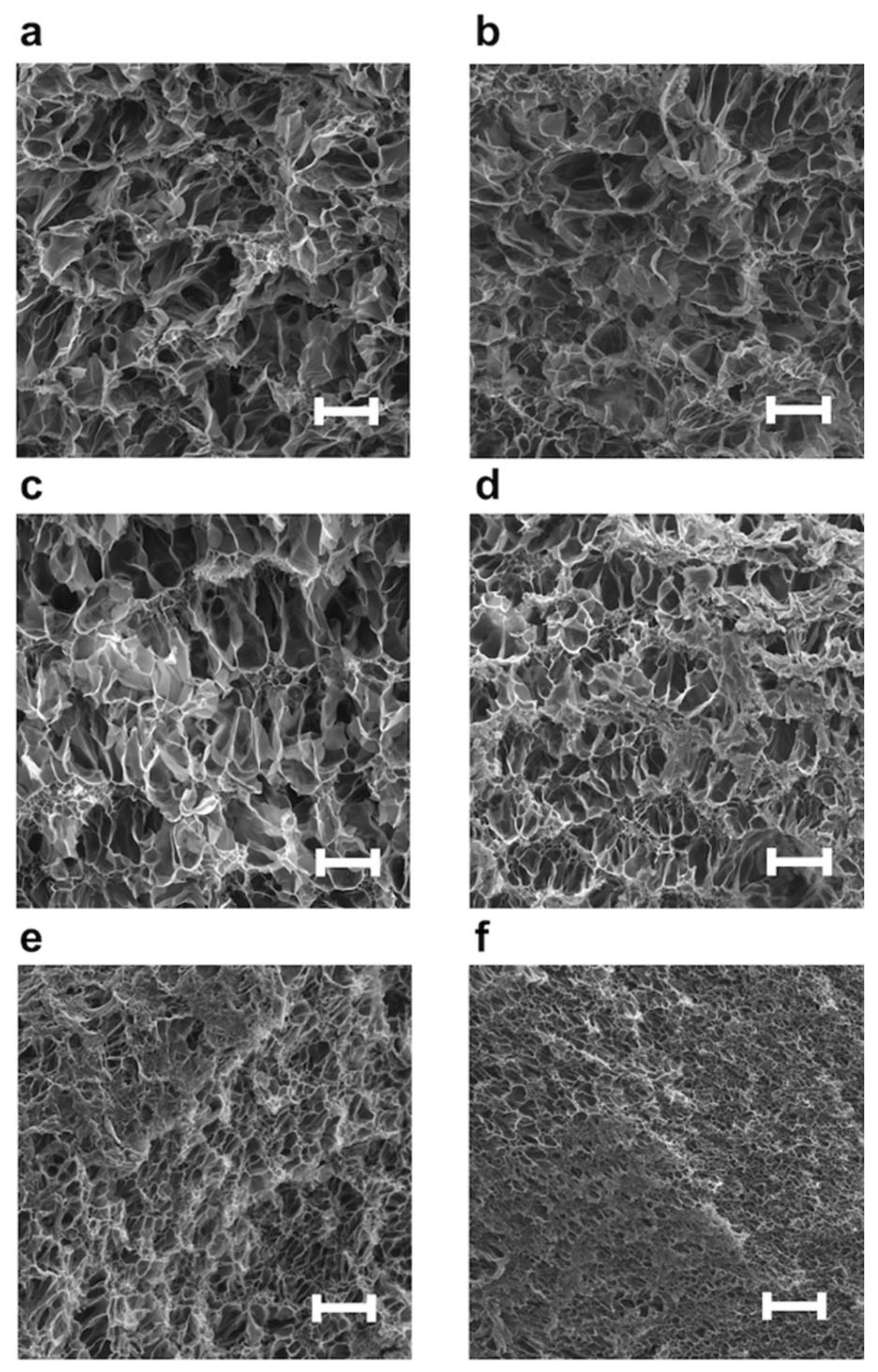
3.2.2. Surface Morphologies of NC Hydrogels Containing PImQ/Graphene Nanofillers
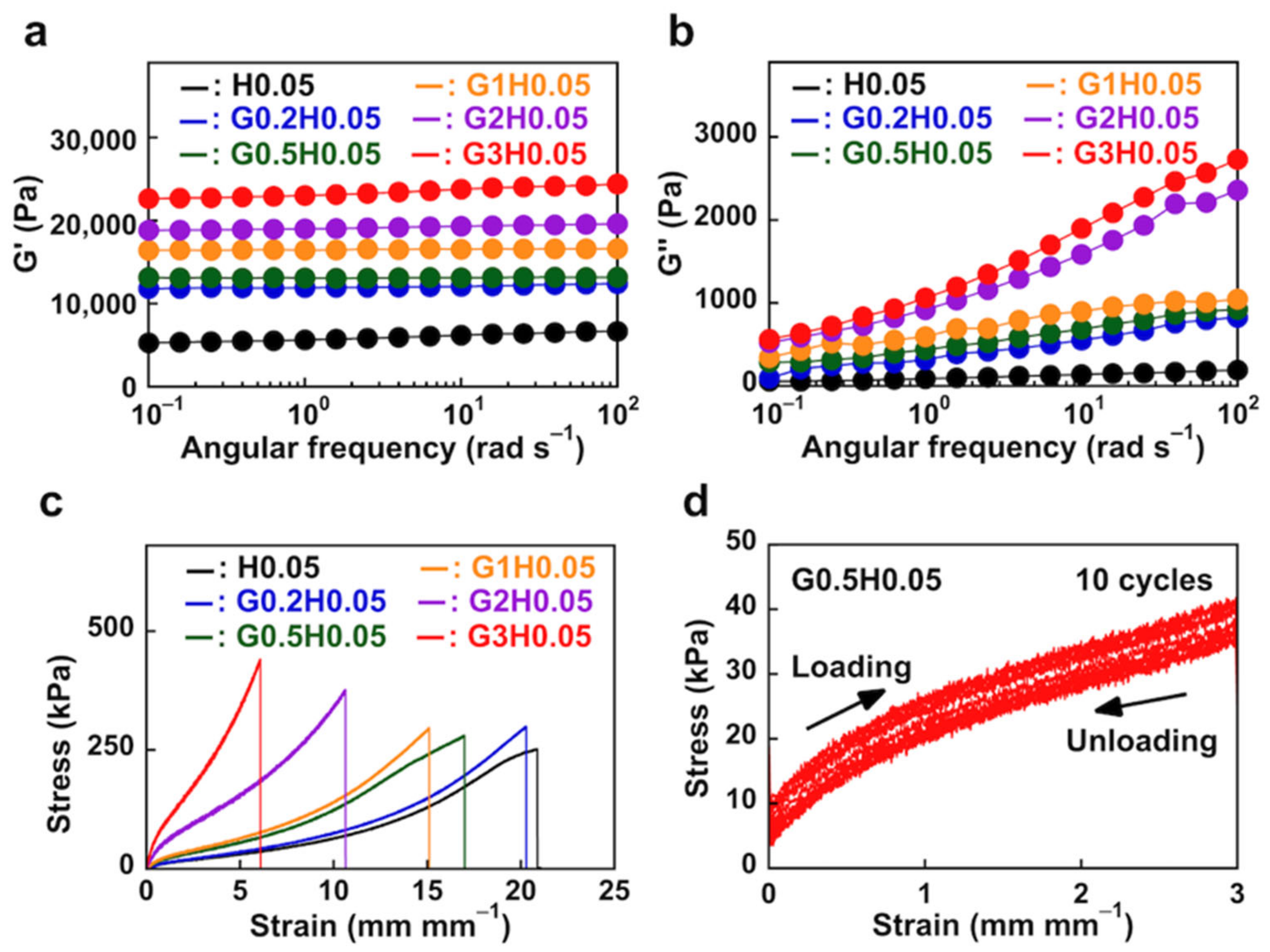
3.2.3. Mechanical Properties of NC Hydrogels
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Correa, S.; Grosskopf, A.K.; Lopez Hernandez, H.; Chan, D.; Yu, A.C.; Stapleton, L.M.; Appel, E.A. Translational applications of hydrogels. Chem. Rev. 2021, 121, 11385–11457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuk, H.; Lu, B.; Zhao, X. Hydrogel bioelectronics. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2019, 48, 1642–1667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mahinroosta, M.; Jomeh Farsangi, Z.; Allahverdi, A.; Shakoori, Z. Hydrogels as intelligent materials: A brief review of synthesis, properties and applications. Mater. Today Chem. 2018, 8, 42–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.; Agate, S.; Salem, K.S.; Lucia, L.; Pal, L. Hydrogel-based sensor networks: Compositions, properties, and applications—A review. ACS Appl. Bio Mater. 2021, 4, 140–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, F.-M.; Chen, H.-X.; Li, H.-D. Recent progress on hydrogel actuators. J. Mater. Chem. B 2021, 9, 1762–1780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.; Song, W.J.; Sun, J.Y. Hydrogel soft robotics. Mater. Today Phys. 2020, 15, 100258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.; Yao, F.; Li, J. Nanocomposite hydrogel-based strain and pressure sensors: A review. J. Mater. Chem. A 2020, 8, 18605–18623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thoniyot, P.; Tan, M.J.; Karim, A.A.; Young, D.J.; Loh, X.J. Nanoparticle–hydrogel composites: Concept, design, and applications of these promising, multi-functional materials. Adv. Sci. 2015, 2, 1400010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicolosi, V.; Chhowalla, M.; Kanatzidis, M.G.; Strano, M.S.; Coleman, J.N. Liquid exfoliation of layered materials. Science 2013, 340, 1226419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bandara, P.C.; Perez, J.V.D.; Nadres, E.T.; Nannapaneni, R.G.; Krakowiak, K.J.; Rodrigues, D.F. Graphene oxide nanocomposite hydrogel beads for removal of selenium in contaminated water. ACS Appl. Polym. Mater. 2019, 1, 2668–2679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olate-Moya, F.; Arens, L.; Wilhelm, M.; Mateos-Timoneda, M.A.; Engel, E.; Palza, H. Chondroinductive alginate-based hydrogels having graphene oxide for 3D printed scaffold fabrication. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2020, 12, 4343–4357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, Y.; Ye, L.; Coates, P.; Twigg, P. In situ cross-linking of poly(vinyl alcohol)/graphene oxide–polyethylene glycol nanocomposite hydrogels as artificial cartilage replacement: Intercalation structure, unconfined compressive behavior, and biotribological behaviors. J. Phys. Chem. C 2018, 122, 3157–3167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hummers, W.S.; Offeman, R.E. Preparation of graphitic oxide. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1958, 80, 1339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawamoto, M.; He, P.; Ito, Y. Green processing of carbon nanomaterials. Adv. Mater. 2017, 29, 1602423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, J.; Wu, J.; Wang, M.; Dong, P.; Xu, J.; Li, X.; Zhang, X.; Yuan, J.; Wang, X.; Ye, M.; et al. Surface tension components based selection of cosolvents for efficient liquid phase exfoliation of 2D materials. Small 2016, 12, 2741–2749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sampath, S.; Basuray, A.N.; Hartlieb, K.J.; Aytun, T.; Stupp, S.I.; Stoddart, J.F. Direct exfoliation of graphite to graphene in aqueous media with diazaperopyrenium dications. Adv. Mater. 2013, 25, 2740–2745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lotya, M.; Hernandez, Y.; King, P.J.; Smith, R.J.; Nicolosi, V.; Karlsson, L.S.; Blighe, F.M.; De, S.; Wang, Z.; McGovern, I.T.; et al. Liquid phase production of graphene by exfoliation of graphite in surfactant/water solutions. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2009, 131, 3611–3620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujigaya, T.; Kim, C.; Hamasaki, Y.; Nakashima, N. Growth and deposition of Au nanoclusters on polymer-wrapped graphene and their oxygen reduction activity. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 21314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van der Schueren, B.; El Marouazi, H.; Mohanty, A.; Lévêque, P.; Sutter, C.; Romero, T.; Janowska, I. Polyvinyl alcohol-few layer graphene composite films prepared from aqueous colloids. Investigations of mechanical, conductive and gas barrier properties. Nanomaterials 2020, 10, 858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ba, H.; Pham-Huu, C.; Luo, W.; Baaziz, W.; Romero, T.; Janowska, I. Colloid approach to the sustainable top-down synthesis of layered materials. ACS Omega 2017, 2, 8610–8617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Marouazi, H.; Van der Schueren, B.; Favier, D.; Bolley, A.; Dagorne, S.; Dintzer, T.; Janowska, I. Great enhancement of mechanical features in PLA based composites containing aligned few layer graphene (FLG), the effect of FLG loading, size, and dispersion on mechanical and thermal properties. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2021, 138, 51300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Georgakilas, V.; Tiwari, J.N.; Kemp, K.C.; Perman, J.A.; Bourlinos, A.B.; Kim, K.S.; Zboril, R. Noncovalent functionalization of graphene and graphene oxide for energy materials, biosensing, catalytic, and biomedical applications. Chem. Rev. 2016, 116, 5464–5519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernandez, Y.; Nicolosi, V.; Lotya, M.; Blighe, F.M.; Sun, Z.; De, S.; McGovern, I.T.; Holland, B.; Byrne, M.; Gun’Ko, Y.K.; et al. High-yield production of graphene by liquid-phase exfoliation of graphite. Nat. Nanotech. 2008, 3, 563–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lotya, M.; King, P.J.; Khan, U.; De, S.; Coleman, J.N. High-concentration, surfactant-stabilized graphene dispersions. ACS Nano 2010, 4, 3155–3162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.; Zhang, Z.; He, C.; Dai, L.; Liu, J.; Wang, L. Rationally designed surfactants for few-layered graphene exfoliation: Ionic groups attached to electron-deficient π-conjugated unit through alkyl spacers. ACS Nano 2014, 8, 6663–6670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, M.; Wang, N.; Wang, L.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, Y.; Xie, Z.; Li, Z.; Pambou, E.; Li, R.; Chen, C.; et al. Direct exfoliation of graphite into graphene in aqueous solutions of amphiphilic peptides. J. Mater. Chem. B 2016, 4, 152–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zappacosta, R.; Di Giulio, M.; Ettorre, V.; Bosco, D.; Hadad, C.; Siani, G.; Di Bartolomeo, S.; Cataldi, A.; Cellini, L.; Fontana, A. Liposome-induced exfoliation of graphite to few-layer graphene dispersion with antibacterial activity. J. Mater. Chem. B 2015, 3, 6520–6527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katsyuba, S.A.; Dyson, P.J.; Vandyukova, E.E.; Chernova, A.V.; Vidiš, A. Molecular structure, vibrational spectra, and hydrogen bonding of the ionic liquid 1-ethyl-3-methyl-1H-imidazolium tetrafluoroborate. Helv. Chim. Acta 2004, 87, 2556–2565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohanty, N.; Nagaraja, A.; Armesto, J.; Berry, V. High-throughput, ultrafast synthesis of solution-dispersed graphene via a facile hydride chemistry. Small 2010, 6, 226–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tung, V.C.; Allen, M.J.; Yang, Y.; Kaner, R.B. High-throughput solution processing of large-scale graphene. Nat. Nanotech. 2009, 4, 25–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, S.-H.; Lee, O.-J.; Lee, K.-H.; Oh, S.H.; Park, C.-G. Preparation of aligned carbon nanotubes with prescribed dimensions: template synthesis and sonication cutting approach. Chem. Mater. 2002, 14, 1859–1862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meyer, J.C.; Geim, A.K.; Katsnelson, M.I.; Novoselov, K.S.; Booth, T.J.; Roth, S. The structure of suspended graphene sheets. Nature 2007, 446, 60–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warner, J.H.; Rümmeli, M.H.; Gemming, T.; Büchner, B.; Briggs, G.A.D. Direct imaging of rotational stacking faults in few layer graphene. Nano Lett. 2009, 9, 102–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haraguchi, K.; Takehisa, T. Nanocomposite hydrogels: A unique organic–inorganic network structure with extraordinary mechanical, optical, and swelling/de-swelling properties. Adv. Mater. 2002, 14, 1120–1124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
El-Refaey, A.; Ito, Y.; Kawamoto, M. Nanocomposite Hydrogels Containing Few-Layer Graphene Sheets Prepared through Noncovalent Exfoliation Show Improved Mechanical Properties. Nanomaterials 2022, 12, 3129. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano12183129
El-Refaey A, Ito Y, Kawamoto M. Nanocomposite Hydrogels Containing Few-Layer Graphene Sheets Prepared through Noncovalent Exfoliation Show Improved Mechanical Properties. Nanomaterials. 2022; 12(18):3129. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano12183129
Chicago/Turabian StyleEl-Refaey, Ahmed, Yoshihiro Ito, and Masuki Kawamoto. 2022. "Nanocomposite Hydrogels Containing Few-Layer Graphene Sheets Prepared through Noncovalent Exfoliation Show Improved Mechanical Properties" Nanomaterials 12, no. 18: 3129. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano12183129
APA StyleEl-Refaey, A., Ito, Y., & Kawamoto, M. (2022). Nanocomposite Hydrogels Containing Few-Layer Graphene Sheets Prepared through Noncovalent Exfoliation Show Improved Mechanical Properties. Nanomaterials, 12(18), 3129. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano12183129




