Plasma-Modified PI Substrate for Highly Reliable Laser-Sintered Copper Films Using Cu2O Nanoparticles
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experimental Procedures
2.1. Plasma Modification of the Surface of a Polymeric Substrate
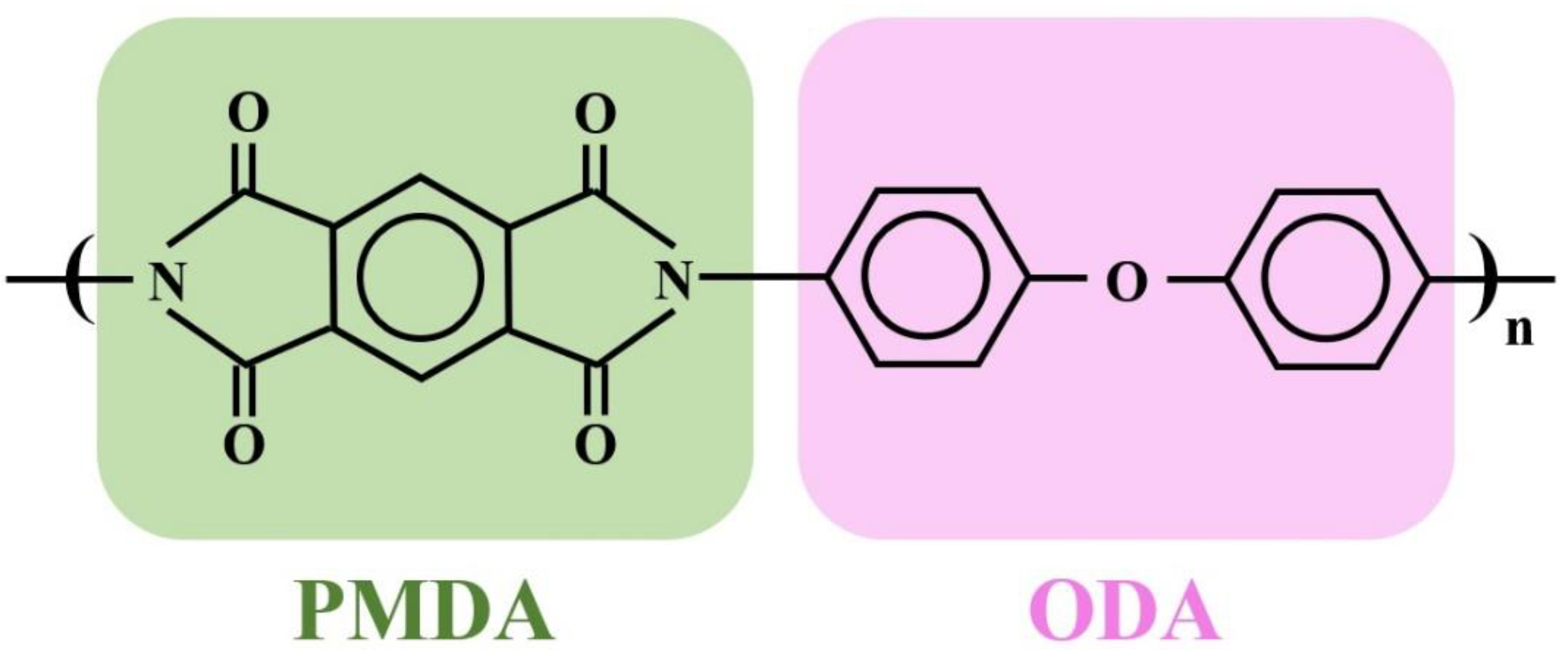
2.2. Preparation and Coating with Cuprous Oxide Composite Pastes
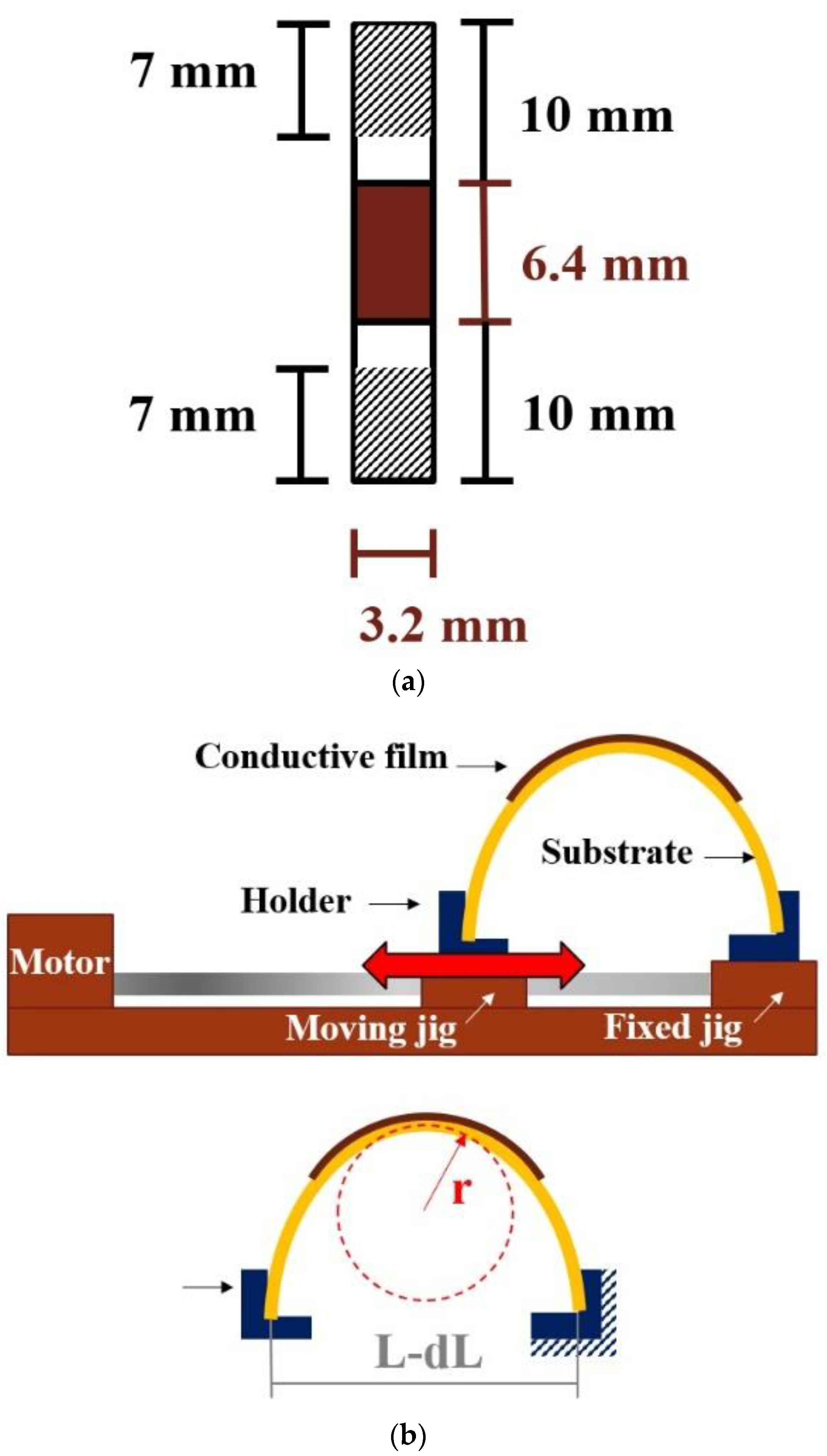
2.3. Laser Sintering and Reliability Testing
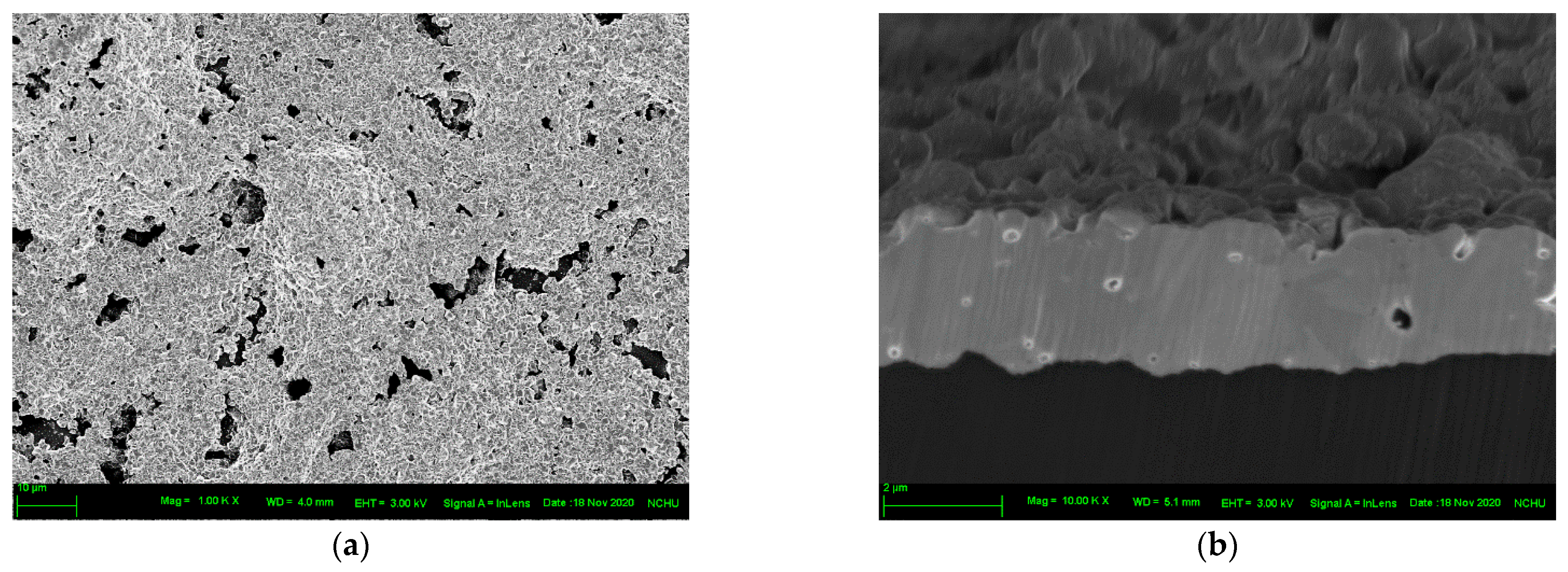
3. Results and Discussion
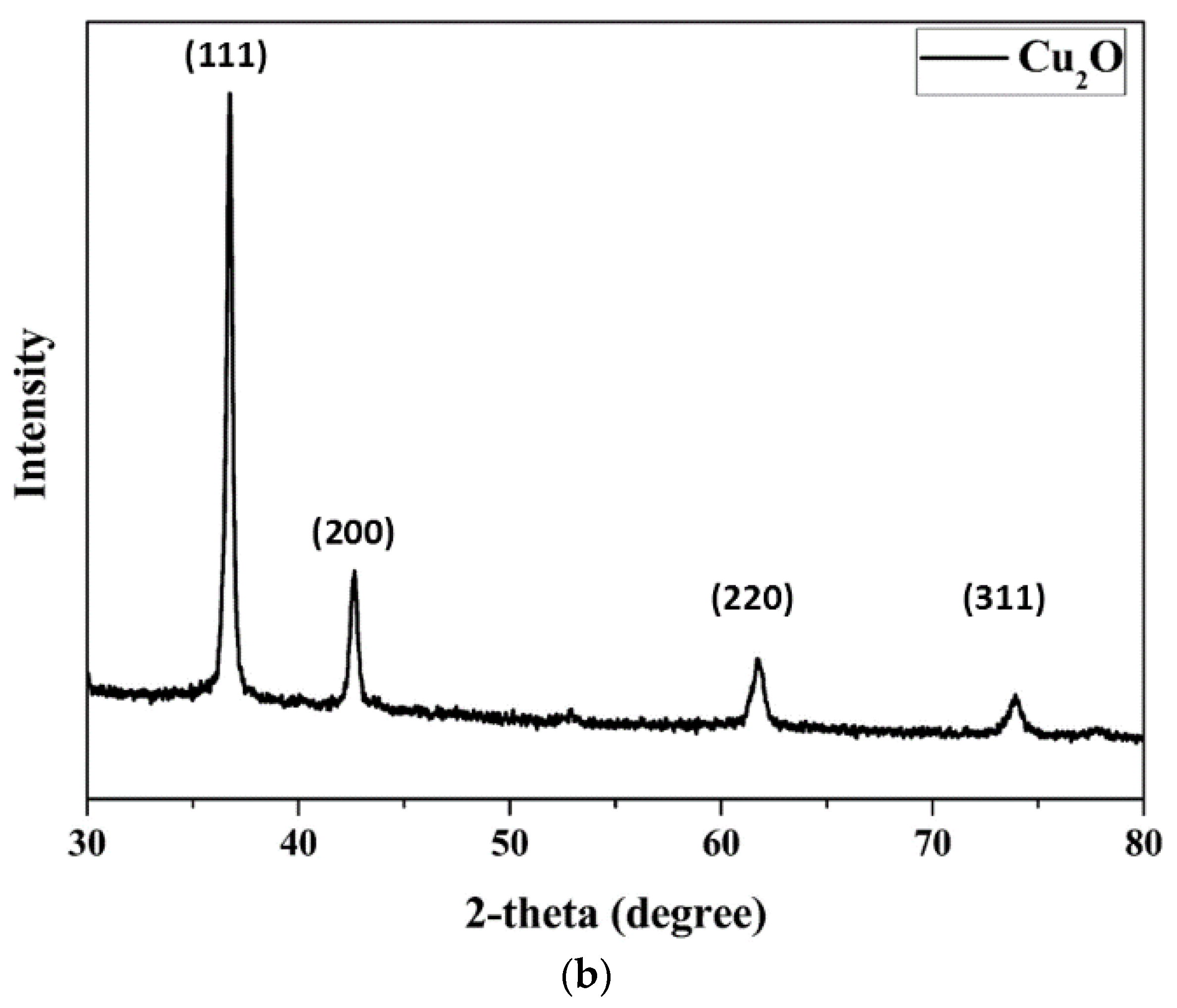
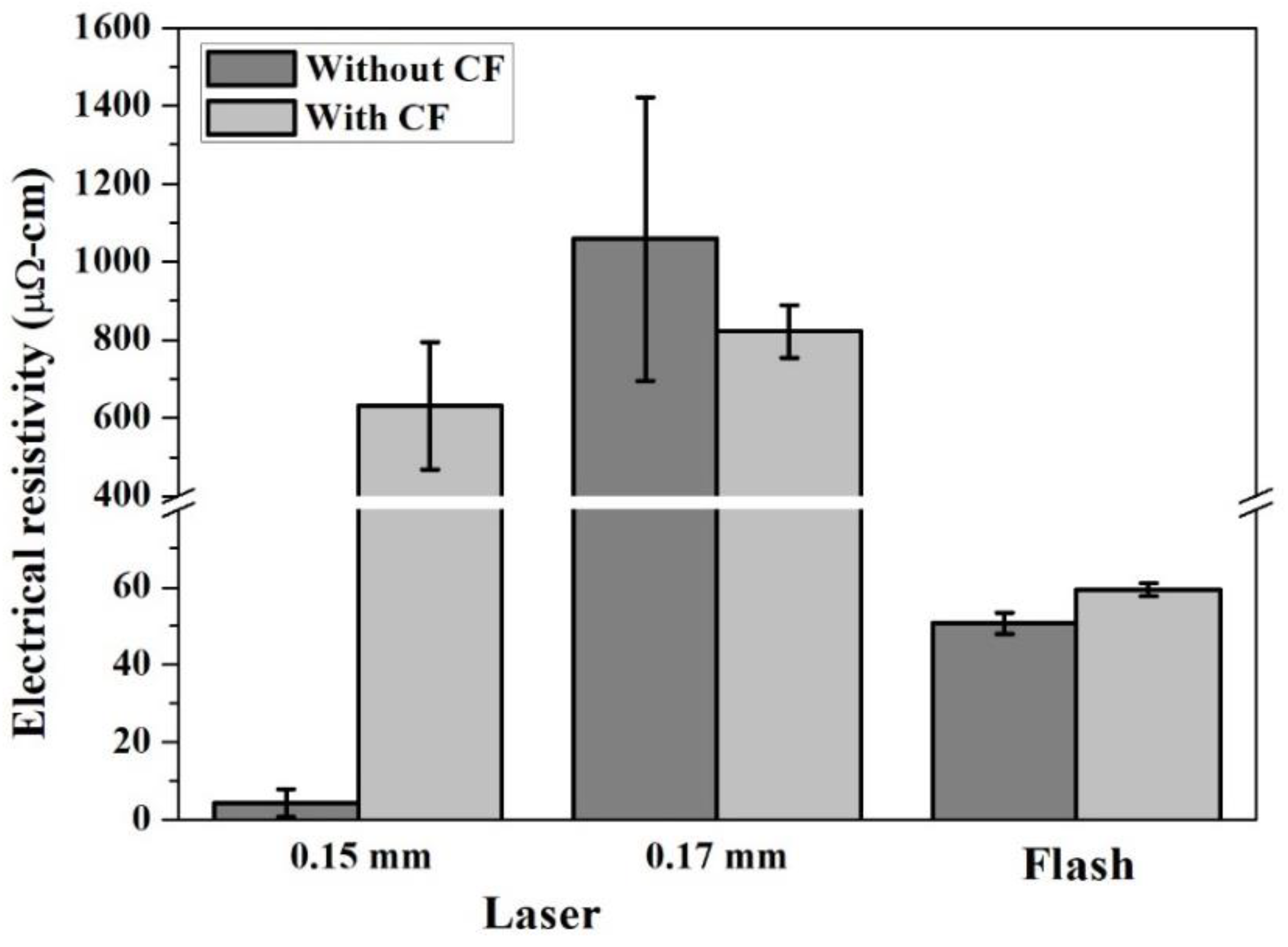
3.1. Optimal Sintering Conditions
3.2. Changes in the Resistivity of Sintered Copper Thin Films Caused by Bending Deformation
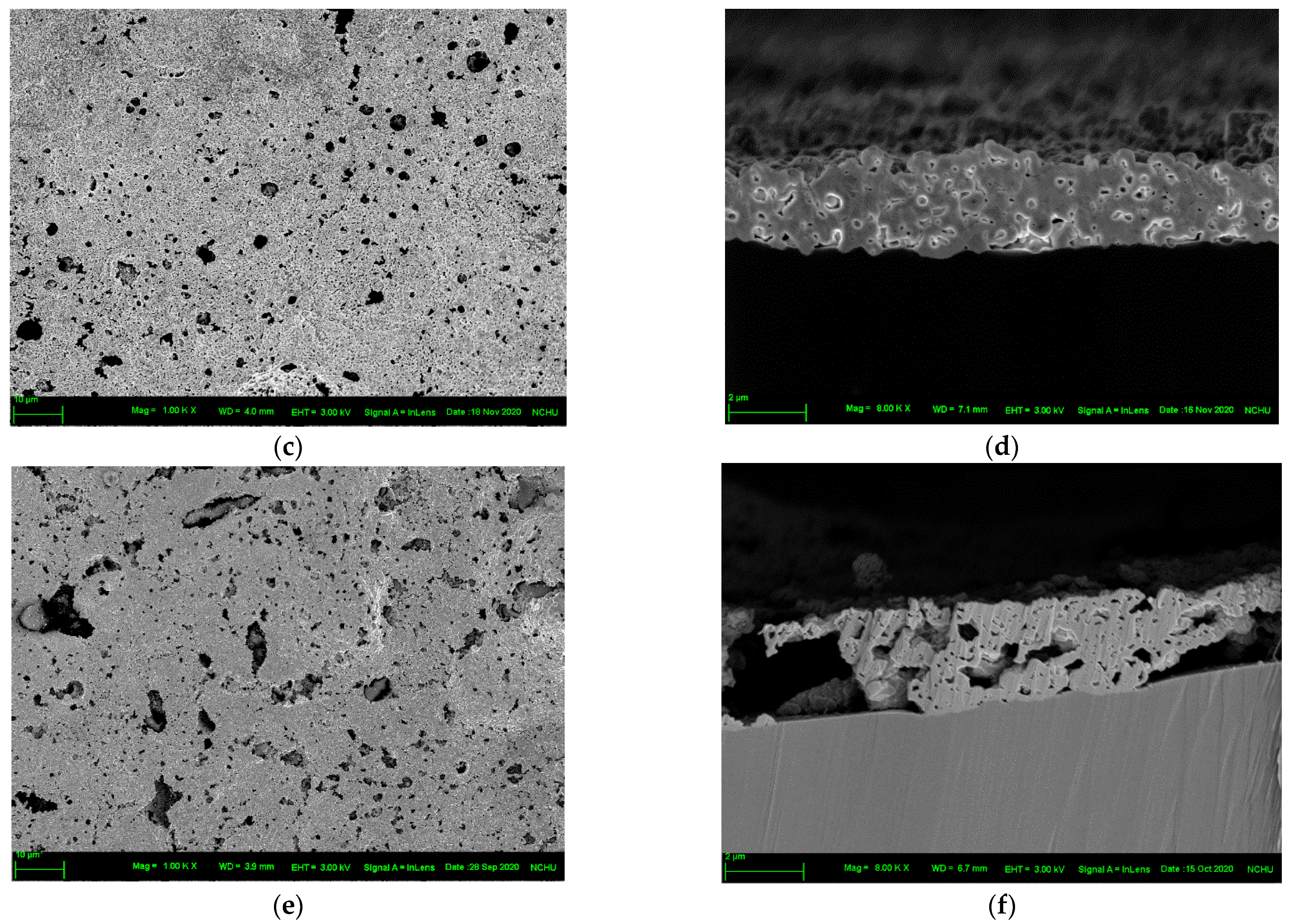
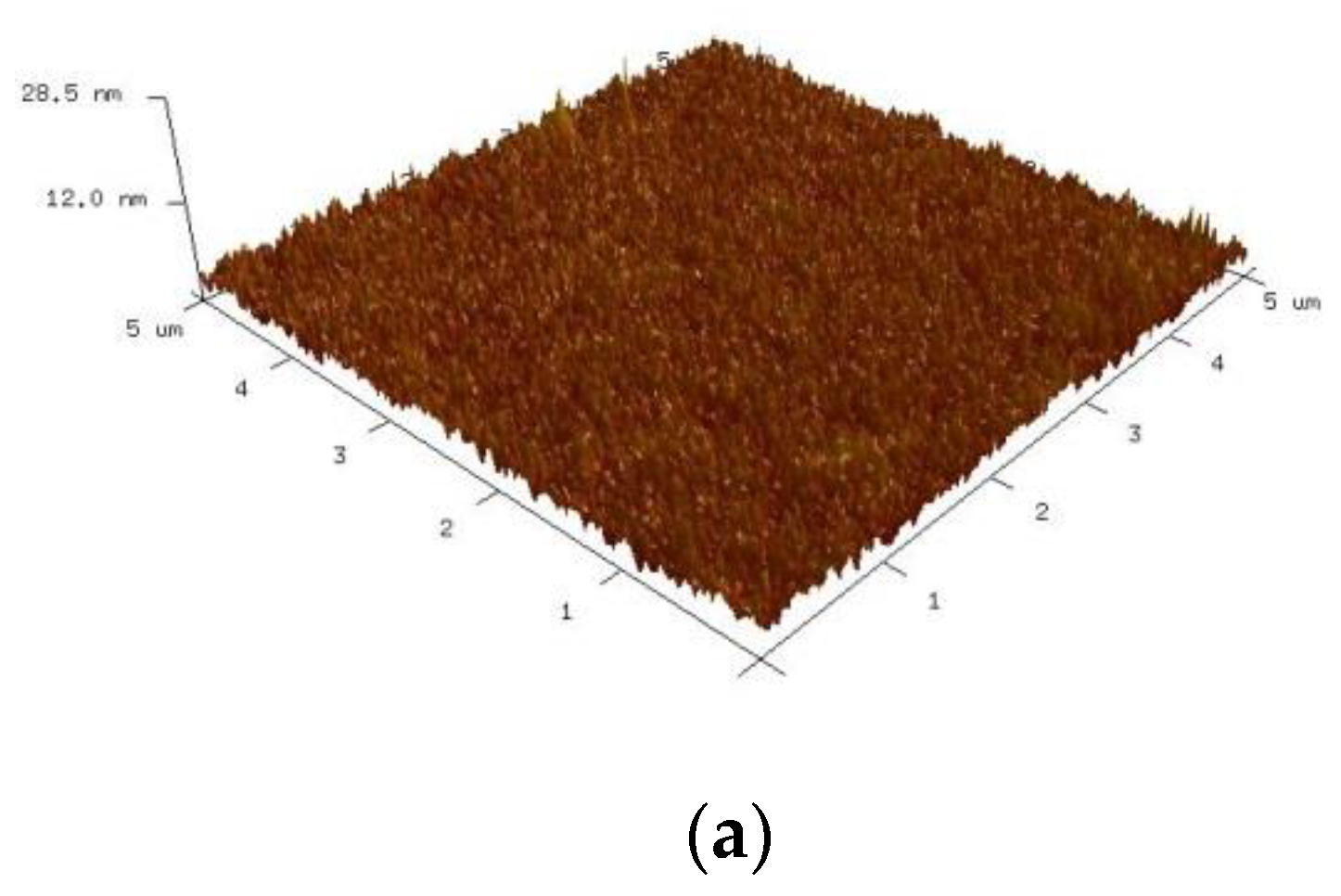
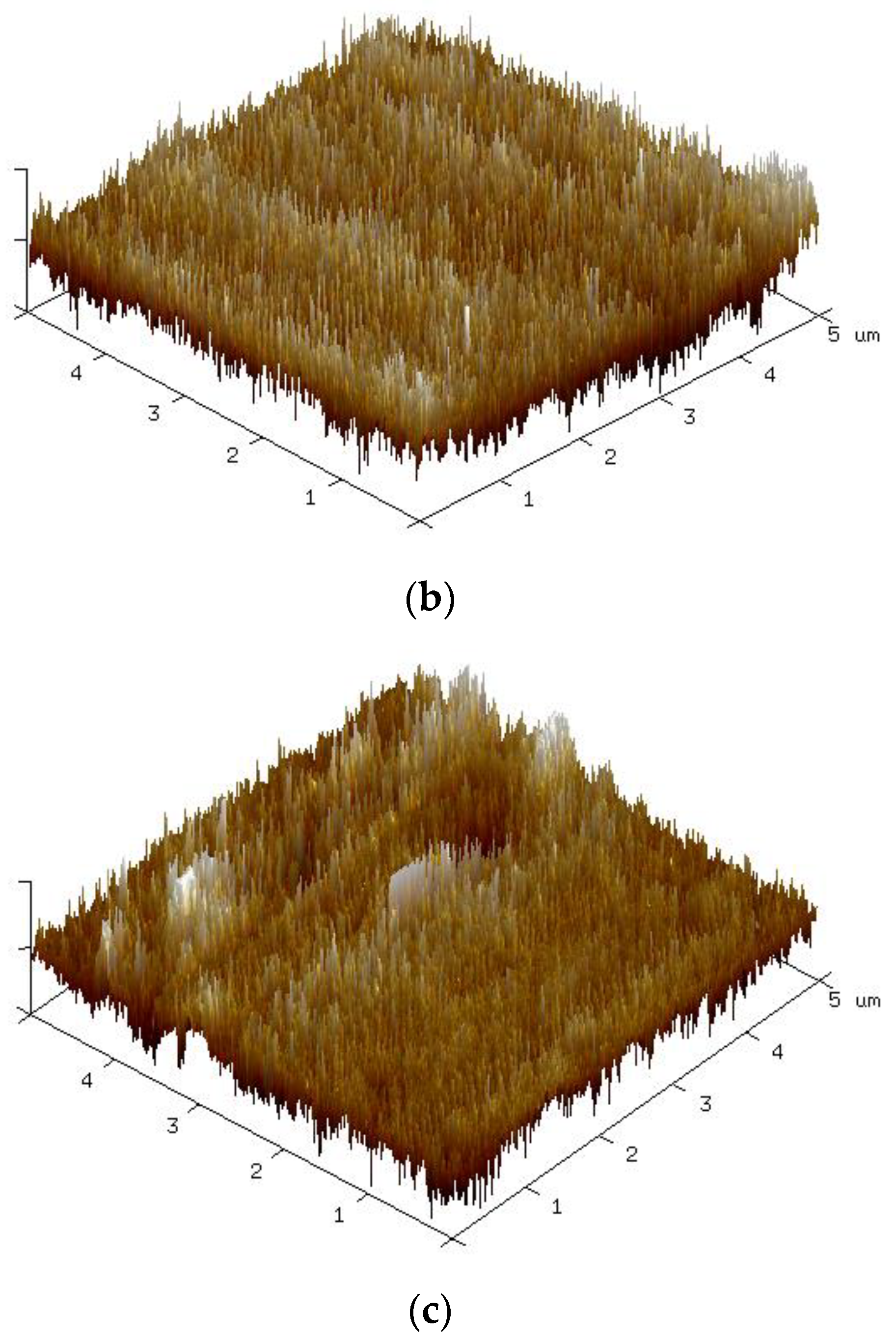
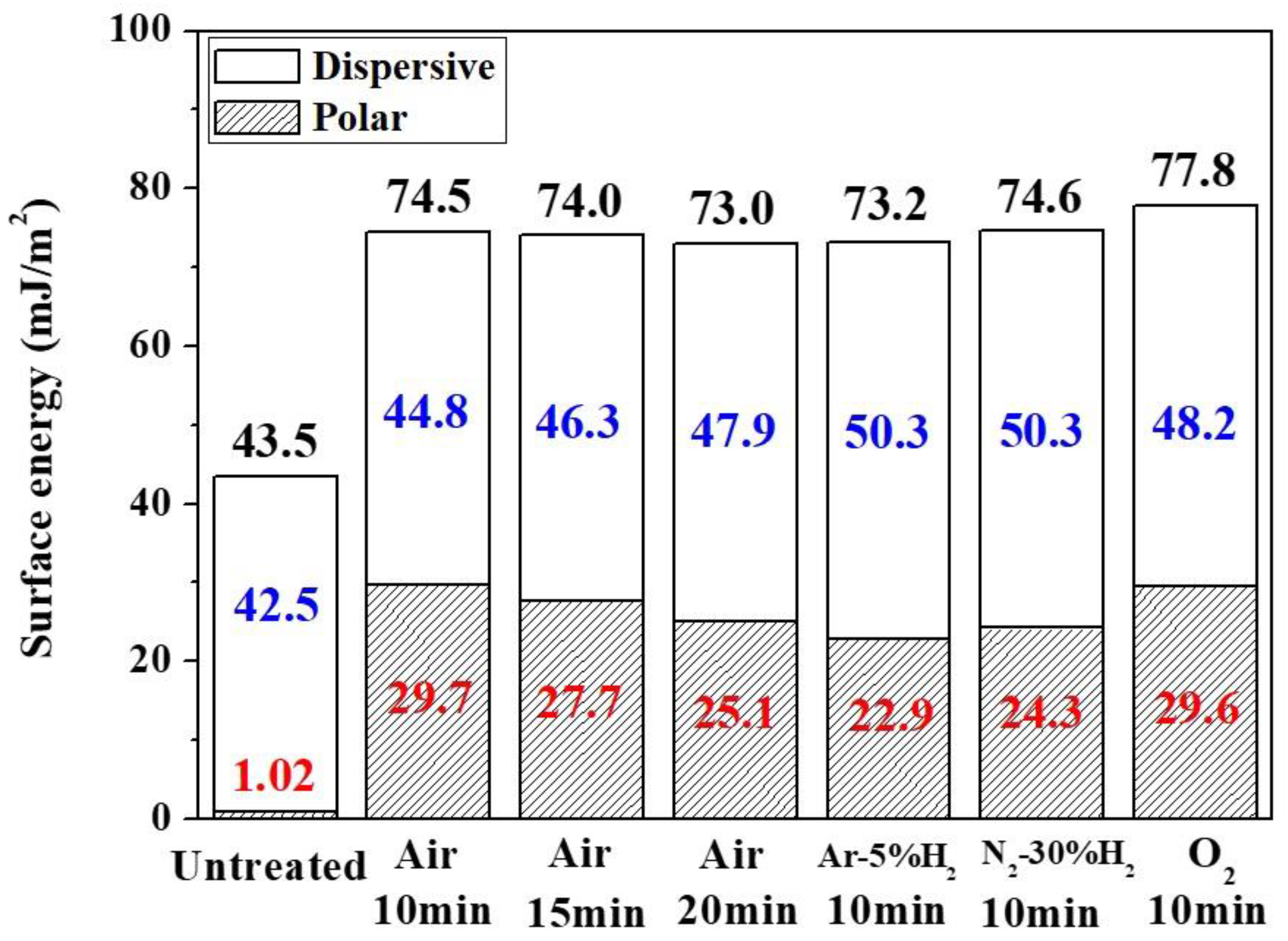
3.3. Surface Properties of PI Substrate after Plasma Modification
3.4. Surface Binding Analysis of Plasma-Modified PI Substrate
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Girotto, C.; Rand, B.P.; Steudel, S.; Genoe, J.; Heremans, P. Nanoparticle-based, spray-coated silver top contacts for efficient polymer solar cells. Org. Electron. 2009, 10, 735–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gittins, D.I.; Bethell, D.; Schiffrin, D.J.; Nichols, R.J. A nanometre-scale electronic switch consisting of a metal cluster and redox-addressable groups. Nature 2000, 408, 67–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumpulainen, T.; Pekkanen, J.; Valkama, J.; Laakso, J.; Tuokko, R.; Mantysalo, M. Low temperature nanoparticle sintering with continuous wave and pulse lasers. Opt. Laser. Technol. 2010, 43, 570–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allen, M.; Alastalo, A.; Suhonen, M.; Mattila, T.; Leppaniemi, J.; Seppa, H. Contactless electrical sintering of silver nanoparticles on flexible substrates. IEEE Trans. Microw. Theory Tech. 2011, 59, 1419–1429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simchi, A. Direct laser sintering of metal powders: Mechnism, kinetics and microstructural features. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2006, 428, 148–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Govorov, A.O.; Richardson, H.H. Generating heat with metal nanoparticles. Nanotoday 2007, 2, 30–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fischer, P.; Romano, V.; Weber, H.P.; Karapatis, N.P.; Boillat, E.; Glardon, R. Sintering of commercially pure titanium powder with a Nd:YAG laser source. Acta Mater. 2003, 51, 1651–1662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fischer, P.; Romano, V.; Weber, H.P. Pulsed laser sintering of metal powders. Thin Solid Films 2004, 453–454, 139–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.S.; Dhage, S.R.; Shim, D.E.; Hahn, H.T. Intense pulsed light sintering of copper nanoink for printed electronics. Appl. Phys. A 2009, 97, 791–798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, G.H.; Hwang, H.J.; Kim, H.S. Effect of copper oxide shell thickness on flash light sintering of copper nanoparticle ink. RSC Adv. 2017, 7, 17724–17731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Niittynen, J.; Mäntysalo, M. Characterization of Laser Sintering of Copper Nanoparticle Ink by FEM and Experimental Testing. IEEE Trans. Compon. Packag. Manuf. Technol. 2014, 4, 2018–2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niittynen, J.; Sowade, E.; Kang, H.; Baumann, R.R.; Mäntysalo, M. Comparison of laser and intense pulsed light sintering (IPL) for inkjet-printed copper nanoparticle layers. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 8832. [Google Scholar]
- Kwon, J.; Cho, H.; Eom, H.; Lee, H.; Suh, Y.D.; Moon, H.; Shin, J.; Hong, S.; Ko, S.H. Low-temperature oxidation-free selective laser sintering of Cu nanoparticle paste on a polymer substrate for the flexible touch panel applications. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2016, 8, 11575–11582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rahman, M.K.; Lu, Z.; Kwon, K.S. Green laser sintering of copper oxide (CuO) nano particle (NP) film to form Cu conductive lines. AIP Adv. 2018, 8, 095008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paglia, F.; Vak, D.; van Embden, J.; Chesman, A.S.R.; Martucci, A.; Jasieniak, J.J.; Gaspera, E.D. Photonic Sintering of Copper through the Controlled Reduction of Printed CuO Nanocrystals. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2015, 7, 25473–25478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, B.; Han, S.; Kim, J.; Ko, S.; Yang, M. One-Step Fabrication of Copper Electrode by Laser-Induced Direct Local Reduction and Agglomeration of Copper Oxide Nanoparticle. J. Phys. Chem. C 2011, 115, 23664–23670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiu, P.H.; Cheng, W.H.; Lee, M.T.; Yasuda, K.; Song, J.M. Low-Thermal-Budget Photonic Sintering of Hybrid Pastes Containing Submicron/Nano CuO/Cu2O Particles. Nanomaterials 2021, 11, 1864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.S.; Liu, H.M.; Chen, C.-L. Plasma surface modification of polyimide films by air glow discharge for copper metallization on microelectronic flex substrates. Thin Solid Films 2006, 200, 3775–3785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akram, M.; Jansen, K.M.B.; Ernst, L.J.; Bhowmik, S. Atmospheric plasma modification of polyimide sheet for joining to titanium with high temperature adhesive. Int. J. Adhes. Adhes. 2016, 65, 63–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.H.; Na, S.W.; Lee, N.E.; Nam, Y.W.; Kim, Y.H. Effect of surface roughness on the adhesion properties of Cu/Cr films on polyimide substrate treated by inductively coupled oxygen plasma. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2005, 200, 2072–2079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Owens, D.K.; Wendt, R.C. Estimation of surface free energy of polymers. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 1969, 13, 1741–1747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.I.; Ahn, J.H.; Feng, X.; Wang, S.; Huang, Y.; Rogers, J.A. Theoretical and experimental studies of bending of inorganic electronic materials on plastic substrates. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2008, 18, 2673–2684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tam, S.K.; Ng, K.M. High-concentration copper nanoparticles synthesis process for screen-printing conductive paste on flexible substrate. J. Nanopart. Res. 2015, 17, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eun, K.; Chon, M.W.; Yoo, T.H.; Song, Y.W.; Choa, S.H. Electromechanical properties of printed copper ink film using a white flash light annealing process for flexible electronics. Microelectron. Reliab. 2015, 55, 838–845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naddaf, M.; Balasubramanian, C.; Alegaonkar, P.S.; Bhoraskar, V.N.; Mandle, A.B.; Ganeshan, V.; Bhoraskar, S.V. Surface interaction of polyimide with oxygen ECR plasma. Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res. B 2004, 222, 135–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bang, S.H. Improvement of NiMoNb to polyimide adhesion by inductively coupled nitrogen plasma treatment. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2016, 360B, 553–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pylypenko, S.; Artyushkova, K.; Fulghum, J.E. Application of XPS spectral subtraction and multivariate analysis for the characterization of Ar+ ion beam modified polyimide surfaces. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2010, 266, 3204–3210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


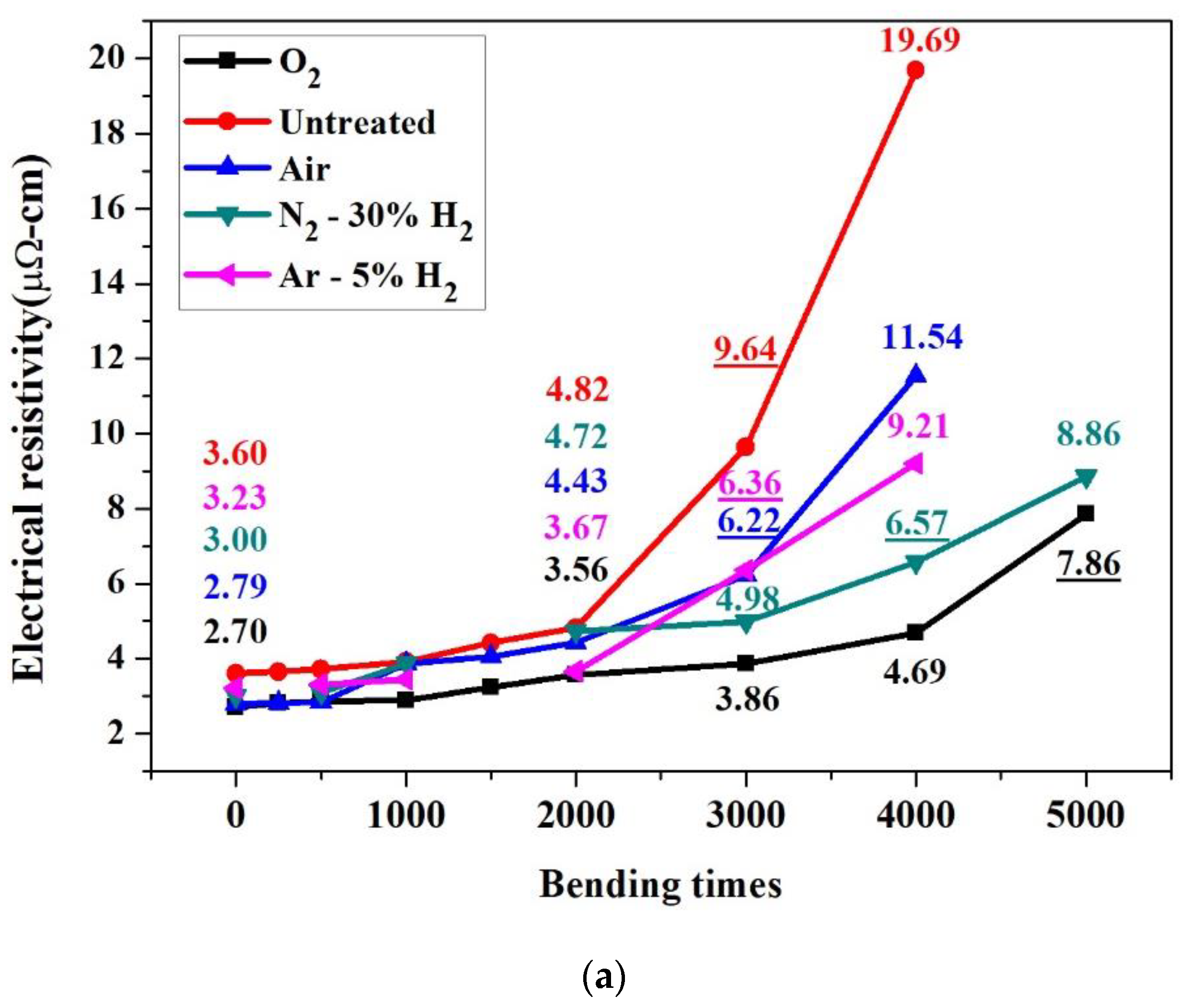
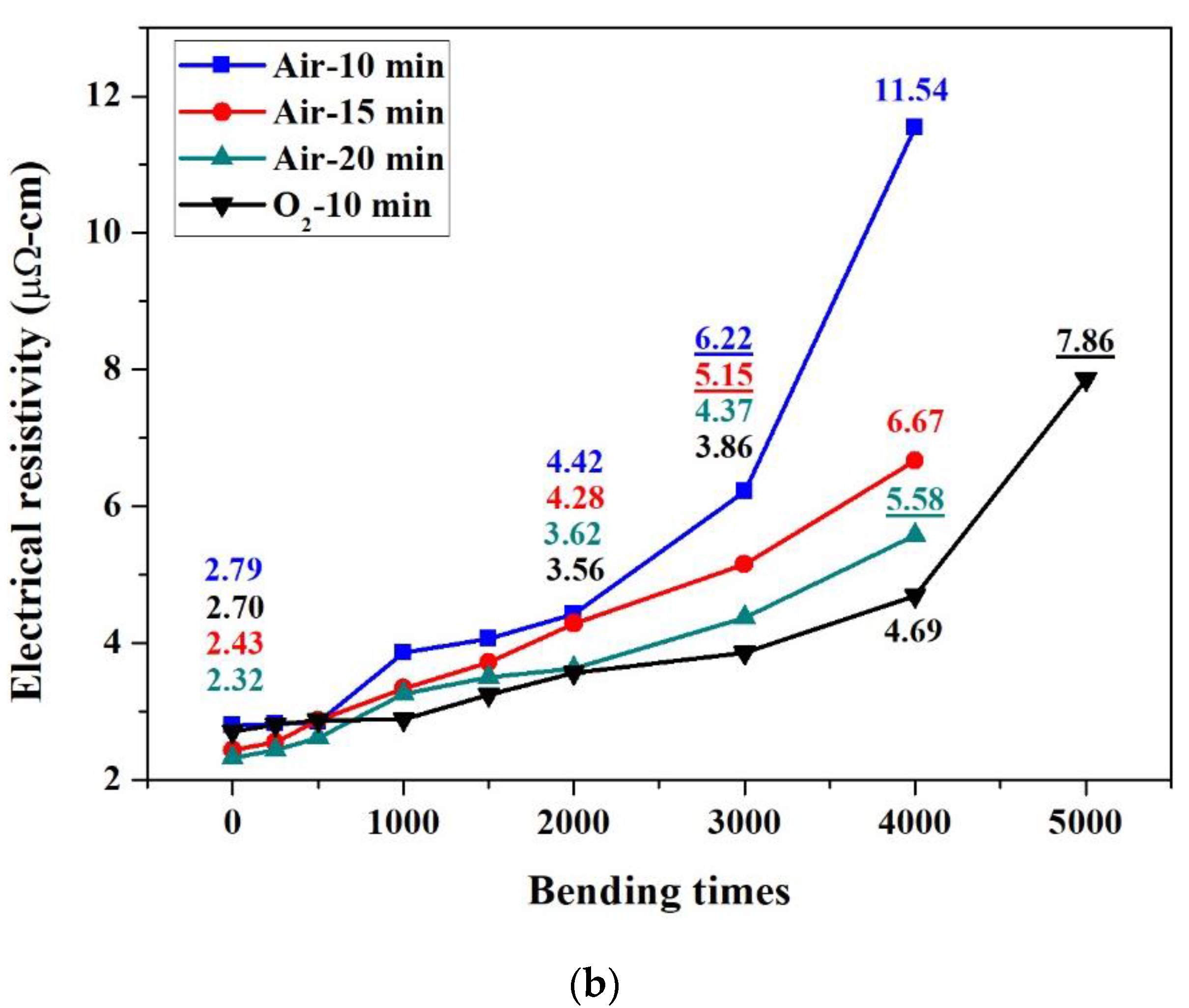




| Cycles | 0 | 1000 | 2000 | 3000 | 4000 | 5000 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Conditions | |||||||
| Untreated | 3.6 ± 0.4 | 3.9 ± 0.5 | 4.8 ± 0.5 | 9.6 ± 0.8 | 19.7 ± 0.6 | N/A | |
| Air | 2.8 ± 0.3 | 3.7 ± 0.4 | 4.4 ± 0.4 | 6.2 ± 0.5 | 11.5 ± 0.8 | N/A | |
| O2 | 2.7 ± 0.2 | 2.9 ± 0.3 | 3.6 ± 0.4 | 3.9 ± 0.1 | 4.7 ± 0.4 | 7.9 ± 0.7 | |
| N2-30%H2 | 3.0 ± 0.3 | 3.9 ± 0.3 | 4.7 ± 0.5 | 5.0 ± 0.4 | 6.6 ± 0.6 | 8.9 ± 0.3 | |
| Ar-5%H2 | 3.2 ± 0.3 | 3.4 ± 0.4 | 3.7 ± 0.3 | 6.4 ± 0.3 | 9.2 ± 0.3 | N/A | |
| Air-15 min | 2.4 ± 0.2 | 3.3 ± 0.3 | 4.3 ± 0.3 | 5.2 ± 0.3 | 6.7 ± 0.5 | N/A | |
| Air-20 min | 2.3 ± 0.2 | 3.2 ± 0.3 | 3.6 ± 0.3 | 4.4 ± 0.3 | 5.6 ± 0.5 | N/A | |
| Untreated | Air-10 min | Air-15 min | Air-20 min | Ar-5%H2 | N2-30%H2 | O2 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Water (polar) | 83.7° ± 2.7° | 15.1° ± 1.2° | 19.0° ± 1.5° | 23.7° ± 1.5° | 26.2° ± 2.1° | 22.5° ± 2.5° | 3.6° ± 0.3° |
| CH2I2 (non-polar) | 34.0° ± 2.1° | 28.5° ± 1.7° | 24.6° ± 1.6° | 19.5° ± 1.3° | 8.16° ± 1.1° | 8.1° ± 0.9° | 18.5° ± 0.9° |
| Untreated | O2 | Air | N2-30%H2 | Ar-5%H2 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
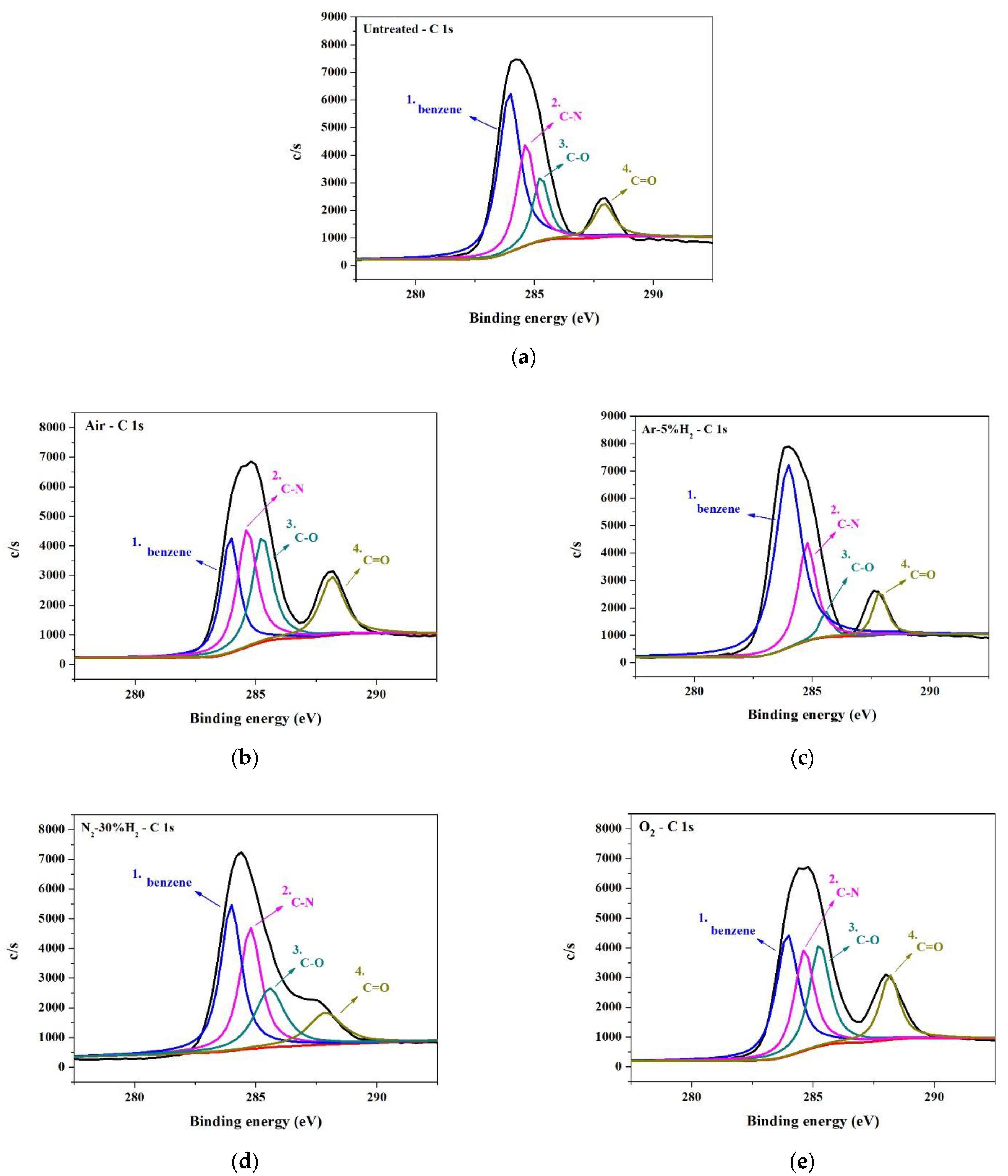
| Peak No. 1 (C=C, C-C, C-H) | 49.8% | 34.0% | 26.2% | 36.2% | 63.7% |
| Peak No. 2 (C=C, C-C, C-H C-N, C-N-C) | 26.0% | 24.8% | 29.1% | 30.5% | 23.8% |
| Peak No. 3 (C-O, C-O-C, C-OH) | 15.8% | 24.7% | 27.0% | 20.5% | 4.14% |
| Peak No. 4 (C=O) | 8.3% | 16.5% | 17.7% | 12.8% | 8.25% |
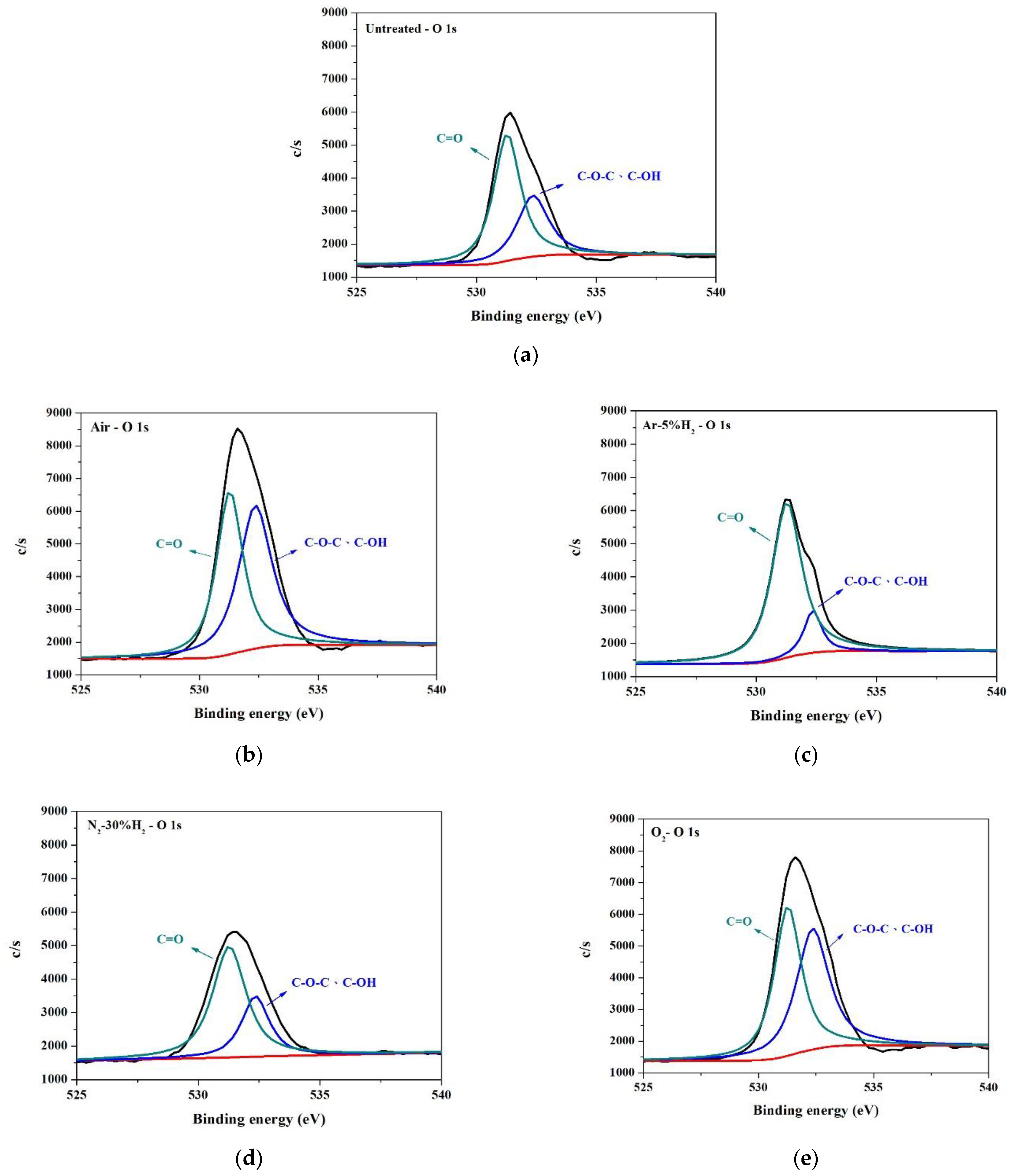
| Untreated | O2 | Air | N2-30%H2 | Ar-5%H2 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| C-O-C C-OH | 4231.4 (35.9%) | 9421.3 (49.4%) | 10730.3 (52.4%) | 3590.6 (31.2%) | 1613.6 (13.9%) |
| C=O | 7526.9 (64.1%) | 9636.5 (50.6%) | 9761.3 (47.6%) | 7930.2 (68.8%) | 9974.4 (86.1%) |
| Total | 11758.3 | 19057.8 | 20491.6 | 11520.8 | 11588.0 |
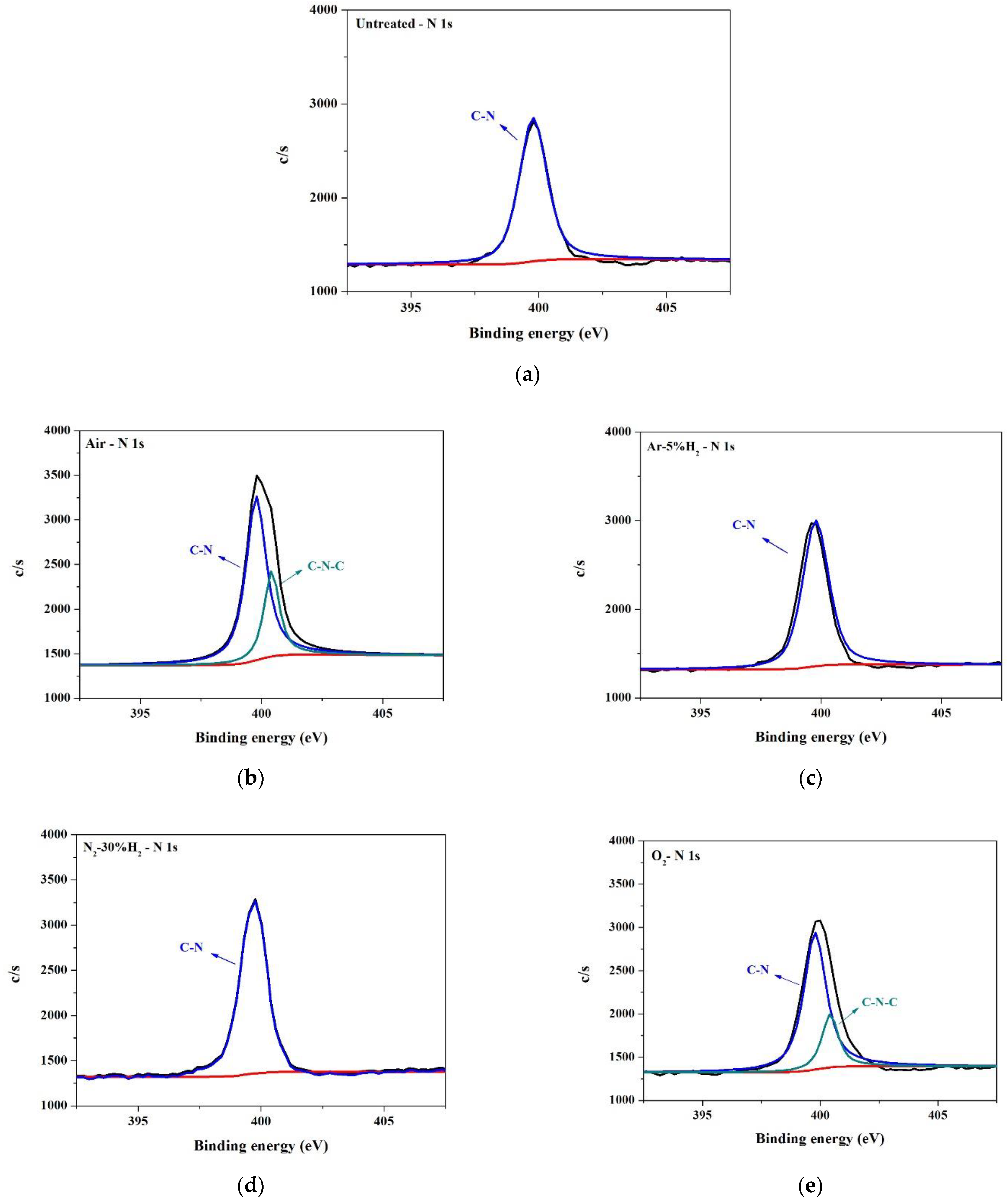
| Untreated | O2 | Air | N2-30%H2 | Ar-5%H2 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| C-N | 2625.4 (100%) | 2658.9 (78.2%) | 2706.2 (71.9%) | 2937 (100%) | 2820 (100%) |
| C-N-C | ND | 741.3 (21.8%) | 1059.7 (28.1%) | ND | ND |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cheng, W.-H.; Lee, M.-T.; Yasuda, K.; Song, J.-M. Plasma-Modified PI Substrate for Highly Reliable Laser-Sintered Copper Films Using Cu2O Nanoparticles. Nanomaterials 2022, 12, 3237. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano12183237
Cheng W-H, Lee M-T, Yasuda K, Song J-M. Plasma-Modified PI Substrate for Highly Reliable Laser-Sintered Copper Films Using Cu2O Nanoparticles. Nanomaterials. 2022; 12(18):3237. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano12183237
Chicago/Turabian StyleCheng, Wei-Han, Ming-Tsang Lee, Kiyokazu Yasuda, and Jenn-Ming Song. 2022. "Plasma-Modified PI Substrate for Highly Reliable Laser-Sintered Copper Films Using Cu2O Nanoparticles" Nanomaterials 12, no. 18: 3237. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano12183237
APA StyleCheng, W.-H., Lee, M.-T., Yasuda, K., & Song, J.-M. (2022). Plasma-Modified PI Substrate for Highly Reliable Laser-Sintered Copper Films Using Cu2O Nanoparticles. Nanomaterials, 12(18), 3237. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano12183237