High-Efficiency Utilization of Waste Tobacco Stems to Synthesize Novel Biomass-Based Carbon Dots for Precise Detection of Tetracycline Antibiotic Residues
Abstract
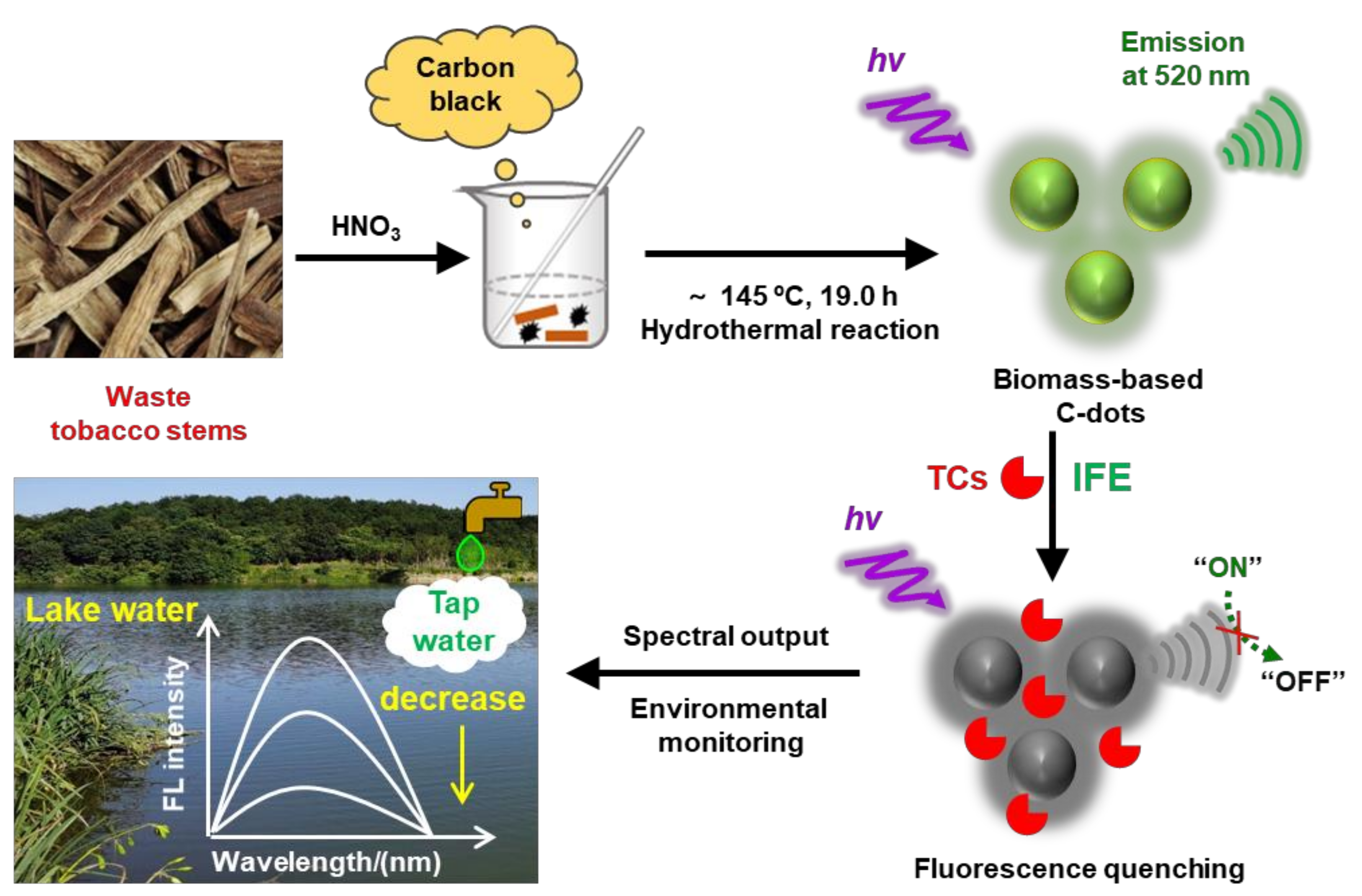
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Synthesis of Biomass-Based C−Dots
2.2. Detection of TCs with a Biomass-Based C−Dots Assay
2.3. Selectivity and Interference Experiments
2.4. Real Sample Analysis
3. Results and Discussions
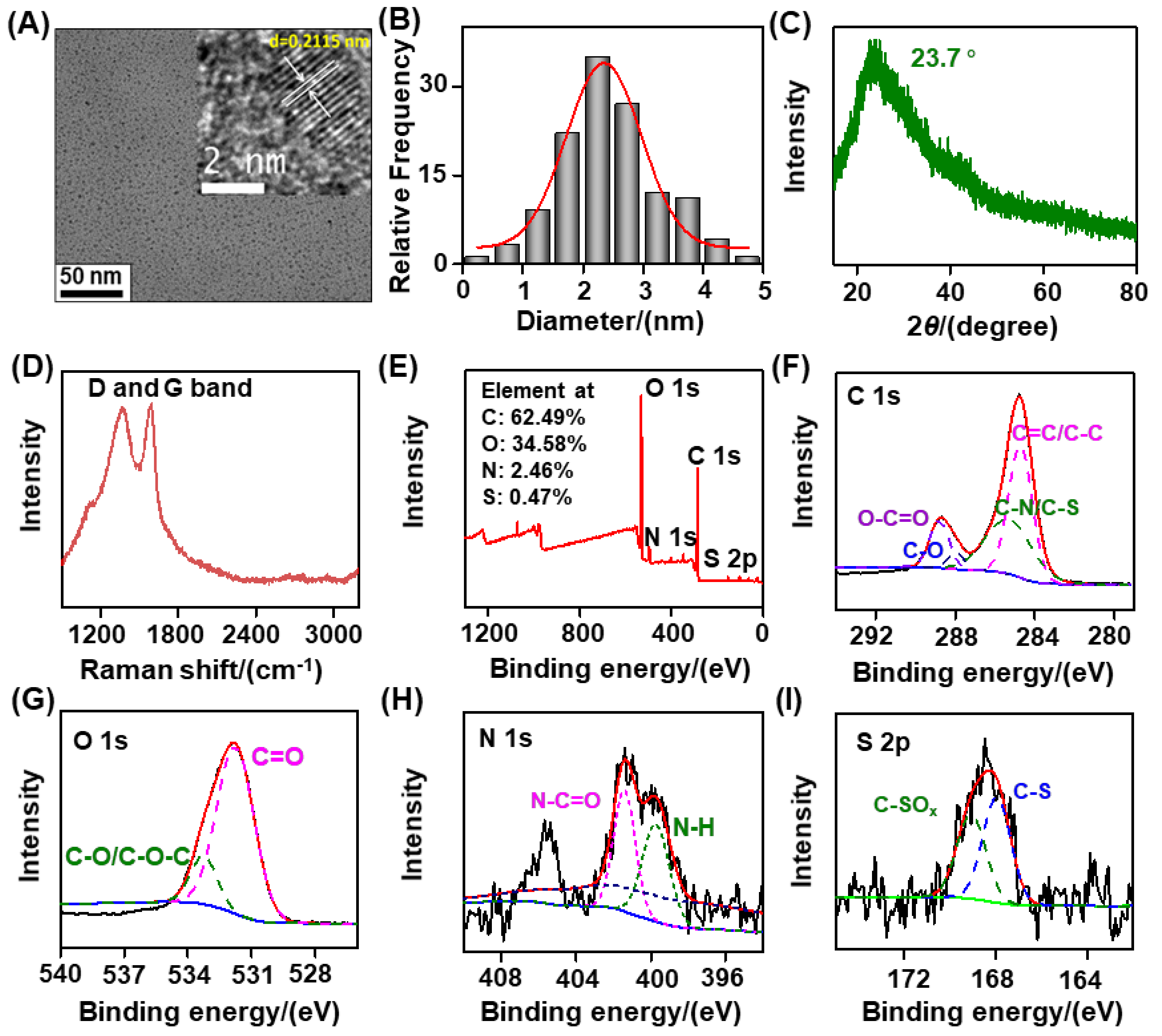
3.1. Synthesis and Characterization of Biomass−Based C−Dots
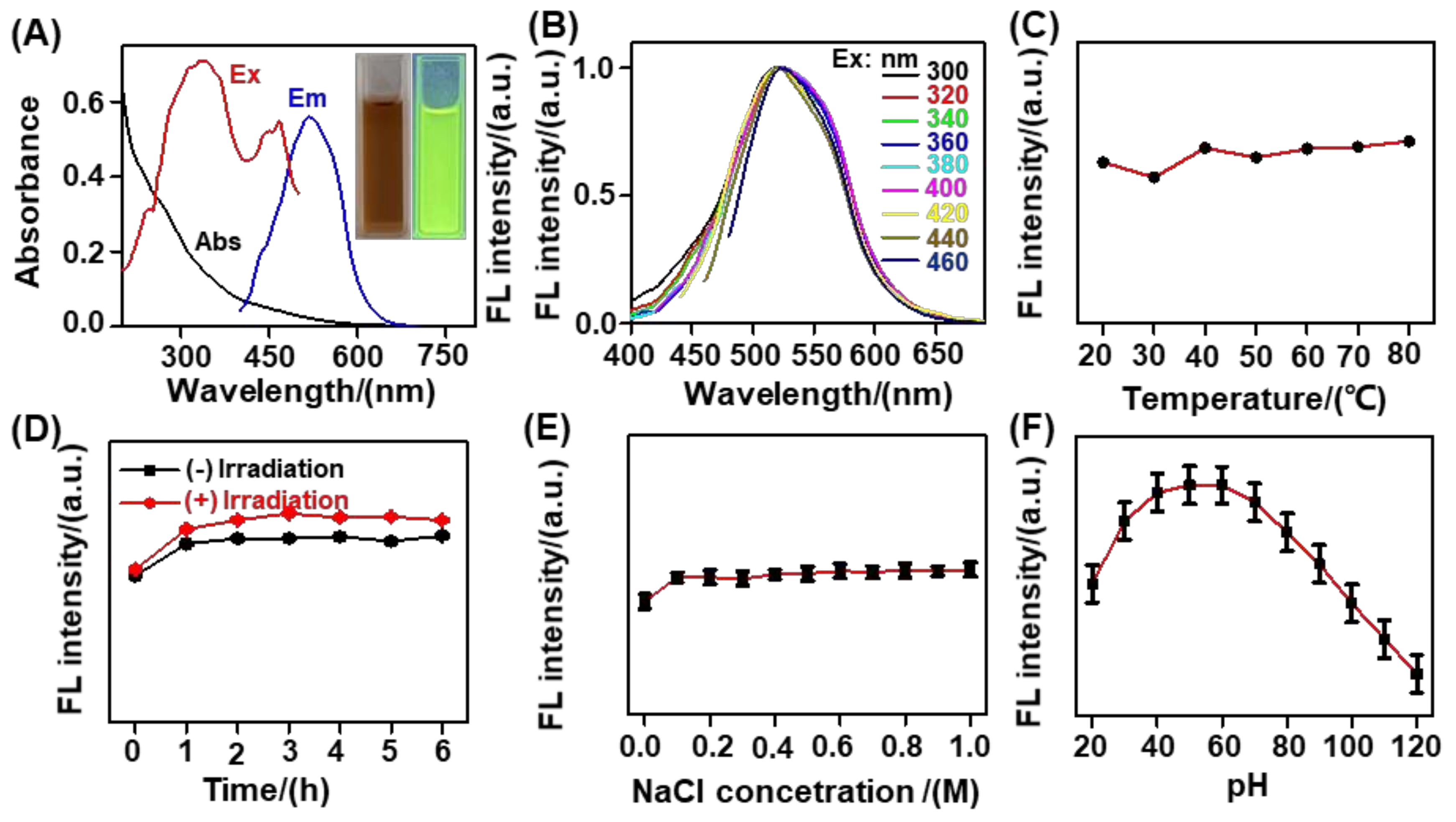
3.2. Optical Features of the Biomass-Based C−Dots
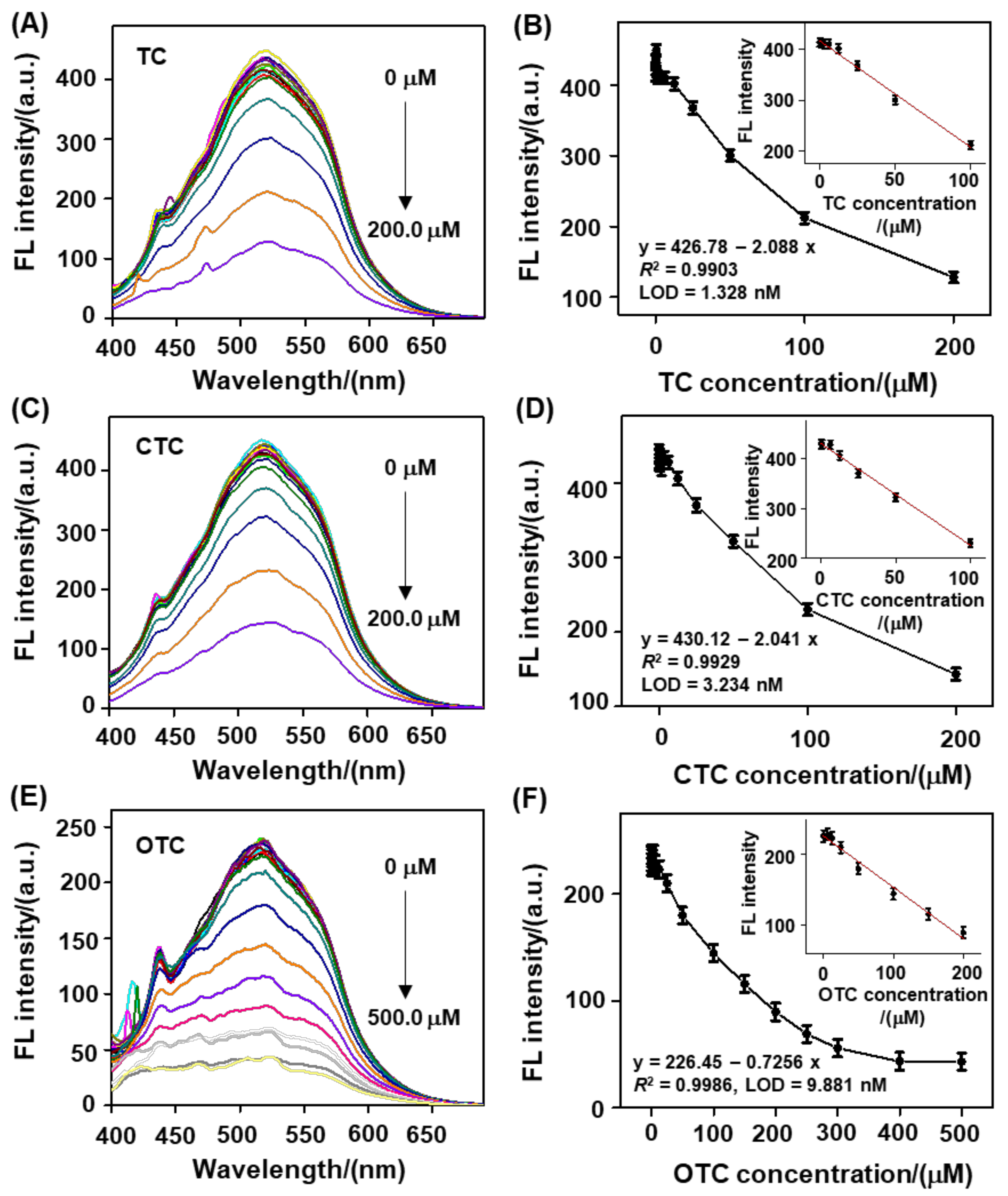
3.3. Fluorescence Response of this Biomass−Based C−Dots toward TCs Residues
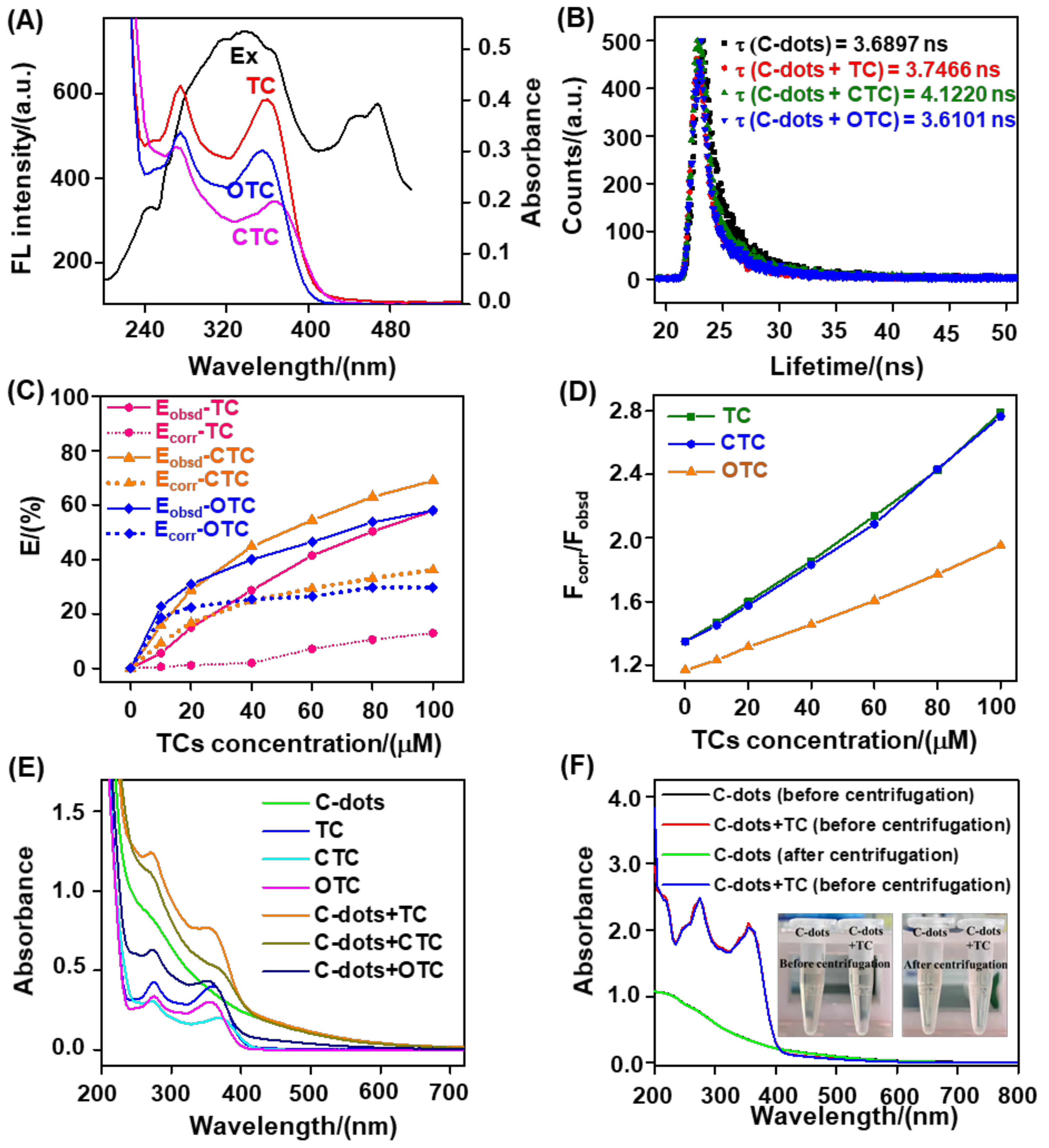
3.4. Response Mechanism of Biomass-Based C−Dots toward TC Residues
3.5. Analysis of TCs in Real Samples
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Baragau, I.-A.; Power, N.P.; Morgan, D.J.; Lobo, R.A.; Roberts, C.S.; Titirici, M.-M.; Middelkoop, V.; Diaz, Z.; Kellici, S. Efficient Continuous Hydrothermal Flow Synthesis of Carbon Quantum Dots from a Targeted Biomass Precursor for on-off Metal Ions Nanosensing. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2021, 9, 2559–2569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramanan, V.; Siddaiah, B.; Raji, K.; Ramamurthy, P. Green Synthesis of Multifunctionalized, Nitrogen-doped, Highly Fluorescent Carbon Dots from Waste Expanded Polystyrene and its Application in the Fluorimetric Detection of Au3+ Ions in Aqueous Media. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2018, 6, 1627–1638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samanta, S.K.; Dey, N.; Kumari, N.; Biswakarma, D.; Bhattacharya, S. Multimodal Ion Sensing by Structurally Simple Pyridine-end Oligo p-phenylenevinylenes for Sustainable Detection of Toxic Industrial Waste. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2019, 7, 12304–12314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, T.; Liu, L.; Li, Y.; Zhang, X.; Deng, Z.; Huo, L.; Gao, S. Highly Sensitive and Selective Detection of Long-chain Alcohol Vapors based on Keel-type ZnO Fibers Derived from Waste Cigarette Butts. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2021, 9, 5838–5848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Huang, M.; Zhang, L.; Zou, M.; Chen, D.; Huang, Y.; Zhao, S. Unique Approach to Develop Carbon Dot-based Nanohybrid Near-infrared Ratiometric Fluorescent Sensor for the Detection of Mercury Ions. Anal. Chem. 2017, 89, 8044–8049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zairov, R.R.; Dovzhenko, A.P.; Sarkanich, K.A.; Nizameev, I.R.; Luzhetskiy, A.V.; Sudakova, S.N.; Podyachev, S.N.; Burilov, V.A.; Vatsouro, I.M.; Vomiero, A.; et al. Single Excited Dual Band Luminescent Hybrid Carbon Dots-Terbium Chelate Nanothermometer. Nanomaterials 2021, 11, 3080–3095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamyshnikov, A.G.; Zaripov, A.T.; Beregovoy, A.N.; Ibatullin, R.R.; Zairov, R.R.; Dovzhenko, A.P. Carbon quantum dots used as tracers in ecological, hydrogeological monitoring and reservoir management. Neftyanoe Khozyaystvo Oil Ind. 2021, 2021, 44–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Liu, J.; Zhao, B.; Bai, Y.; Peng, Z.; Zhou, J.; Wang, C.; Zhao, X.; Han, S.; Zhang, C. One-step Synthesis of Biomass-based Carbon Dots for Detection of Metal Ions and Cell Imaging. Front. Energy Res. 2022, 10, 871617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, C.; Xie, X.; Zhang, D.; Feng, J.; Lu, S.; Shi, Q. Biomass Carbon Dots Derived from Wedelia Trilobata for the Direct Detection of Glutathione and Their Imaging Application in Living Cells. J. Mater. Chem. B 2021, 9, 5670–5681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wareing, T.C.; Gentile, P.; Phan, A.N. Biomass-based Carbon Dots: Current Development and Future Perspectives. ACS Nano 2021, 15, 15471–15501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chellasamy, G.; Arumugasamy, S.K.; Govindaraju, S.; Yun, K. Green Synthesized Carbon Quantum Dots from Maple Tree Leaves for Biosensing of Cesium and Electrocatalytic Oxidation of Glycerol. Chemosphere 2022, 287, 131915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yadav, P.K.; Singh, V.K.; Chandra, S.; Bano, D.; Kumar, V.; Talat, M.; Hasan, S.H. Green Synthesis of Fluorescent Carbon Quantum Dots from Azadirachta Indica Leaves and Their Peroxidase-mimetic Activity for the Detection of H2O2 and Ascorbic Acid in Common Fresh Fruits. ACS Biomater. Sci. Eng. 2019, 5, 623–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Z.; Wang, Q.; Zhou, Z.; Zhao, S.; Zhong, S.; Xu, L.; Gao, Y.; Cui, X. Green Synthesis of Carbon Quantum Dots from Corn Stalk Shell by Hydrothermal Approach in Near-critical Water and Applications in Detecting and Bioimaging. Microchem. J. 2021, 166, 106250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; He, Q.; Zhao, X.; Yuan, J.; Zhao, H.; Wang, G.; Li, M. Synthesis of Corn Straw-based Graphene Quantum Dots (GQDs) and Their Application in PO43- Detection. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2022, 10, 107150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, M.; Zhan, Z.; Zou, M.; Zhang, L.; Zhao, S. Green Synthesis of Stable and Biocompatible Fluorescent Carbon Dots from Peanut Shells for Multicolor Living Cell Imaging. New J. Chem. 2016, 40, 1698–1703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, L.; Zhao, M.-M.; Luo, Q.-W.; Zhang, Y.-C.; Liu, T.-T.; Yang, Z.; Zeng, K.-W. Carbon Quantum Dots-based Nanozyme from Coffee Induces Cancer Cell Ferroptosis to Activate Antitumor Immunity. ACS Nano 2022, 16, 9228–9239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, D.; Zhao, J.; Zhang, L.; Liu, R.; Huang, Y.; Lan, C.; Zhao, S. Capsicum-derived Biomass Quantum Dots Coupled with Alizarin Red S as An Inner-filter-mediated Illuminant Nanosystem for Imaging of Intracellular Calcium Ions. Anal. Chem. 2018, 90, 13059–13064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Sheng, Z.; Han, H.; Zou, M.; Li, C. Facile Synthesis of Fluorescent Carbon Dots Using Watermelon Peel as A Carbon Source. Mater. Lett. 2012, 66, 222–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuzzin, G.; Godinho, M.; Dettmer, A.; Zattera, A.J. Nanofibrillated Cellulose from Tobacco Industry Wastes. Carbohydr. Polym. 2016, 148, 69–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Zhu, C.; Chen, F.; Xu, J.; Jiang, X.; Wu, Z.; Ding, X.; Fan, G.-C.; Shen, Y.; Ye, Y. Profiling the Interaction of Al (III)-GFLX Complex, A Potential Pollution Risk, with Bovine Serum Albumin. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2020, 136, 111058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Y.; Wei, Y.; Zhu, C.; Cao, J.; Han, D.-M. Ratiometric Fluorescent Signals-driven Smartphone-based Portable Sensors for Onsite Visual Detection of Food Contaminants. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2022, 458, 214442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, Y.; Wu, T.; Jiang, X.; Cao, J.; Ling, X.; Mei, Q.; Chen, H.; Han, D.; Xu, J.-J.; Shen, Y. Portable Smartphone-based QDs for the Visual Onsite Monitoring of Fluoroquinolone Antibiotics in Actual Food and Environmental Samples. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2020, 12, 14552–14562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, Y.; Wei, Y.; Chen, H.; Wu, Z.; Ye, Y.; Han, D.-M. Liposome-encapsulated Aggregation-induced Emission Fluorogen Assisted with Portable Smartphone for Dynamically on-site Imaging of Residual Tetracycline. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2022, 350, 130871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Y.; Wei, Y.; Liu, Z.; Nie, C.; Ye, Y. Engineering of 2D Artificial Nanozyme-based Blocking Effect-triggered Colorimetric Sensor for Onsite Visual Assay of Residual Tetracycline in Milk. Microchim. Acta 2022, 189, 233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moga, A.; Vergara-Barberán, M.; Lerma-García, M.J.; Carrasco-Correa, E.J.; Herrero-Martínez, J.M.; Simó-Alfonso, E.F. Determination of Antibiotics in Meat Samples using Analytical Methodologies: A review. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2021, 20, 1681–1716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Huang, D.; Lai, C.; Zeng, G.; Qin, L.; Zhang, C.; Yi, H.; Li, B.; Deng, R.; Liu, S.; et al. Recent Advances in Sensors for Tetracycline Antibiotics and Their Applications. Trends Anal. Chem. 2018, 109, 260–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zong, L.-P.; Li, J.; Shu, G.; Liu, X.; Marks, R.S.; Zhang, X.-J.; Cosnier, S.; Shan, D. Rational Design of a Highly Dispersed Fe-N-C Nanosheet with 1,10-Phenanthroline-2,9-Dicarboxylic Acid as A Preorganized Ligand: Boosted Electrochemiluminescence Detection of Tetracycline. Anal. Chem. 2021, 94, 1325–1332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Li, L.; Jiang, H.; Zhangsun, H.; Wang, Q.; Sun, X.; Wang, L. Highly Selective and Sensitive Fluorescence Detection of Tetracyclines based on Novel Tungsten Oxide Quantum Dots. Food Chem. 2022, 374, 131774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Wu, J.; Meng, F.; Li, A. Immunochromatographic Assay for the Detection of Antibiotics in Animal-derived Foods: A review. Food Control 2021, 130, 108356. [Google Scholar]
- Shamsutdinova, N.; Zairov, R.; Mustafina, A.; Podyachev, S.; Sudakova, S.; Nizameev, I.; Kadirov, M.; Amirov, R. Interfacial interactions of hard polyelectrolyte-stabilized luminescent colloids with substrates. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2015, 482, 231–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ehrat, F.; Bhattacharyya, S.; Schneider, J.; Löf, A.; Wyrwich, R.; Rogach, A.L.; Stolarczy, J.K.; Urban, A.S.; Feldmann, J. Tracking the Source of Carbon Dot Photoluminescence: Aromatic Domains versus Molecular Fluorophores. Nano Lett. 2017, 17, 7710–7716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mao, Y.-N.; Wang, J.; Gao, Y.-H.; Zhao, T.-T.; Xu, S.-H.; Luo, X.-L. Progress in Synthesis and Sensing Imaging of Biomass-based Carbon Quantum dots. Chinese J. Anal. Chem. 2021, 49, 1076–1088. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, G.; Guo, Q.; Chen, D.; Liu, Z.; Zheng, X.; Xu, A.; Yang, S.; Ding, G. Facile and Highly Effective Synthesis of Controllable Lattice Sulfur-doped Graphene Quantum Dots via Hydrothermal Treatment of Durian. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2018, 10, 5750–5759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Huang, H.; Liu, J.; Liu, Y.; Kang, Z. Carbon Quantum Dots Serving as Spectral Converters Through Broadband Upconversion of Near-infrared Photons for Photoelectrochemical Hydrogen Generation. J. Mater. Chem. A 2013, 1, 11529–11533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, J.; Wang, W.; Hai, X.; Yu, Y.L.; Wang, J.H. Green preparation of nitrogen doped carbon dots derived from silkworm chrysalis for cell imaging. J. Mater. Chem. B 2016, 4, 387–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, R.; Wu, D.; Feng, X.; Müllen, K. Bottom-up fabrication of photoluminescent graphene quantum dots with uniform morphology. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2011, 133, 15221–15223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Y.; Wu, T.; Zhang, Y.; Ling, N.; Zheng, L.; Zhang, S.-L.; Xu, J.-J.; Ye, Y. Engineering of A Dual-recognition Ratiometric Fluorescent Nanosensor with A Remarkably Large stokes Shift for Accurate Tracking of Pathogenic Bacteria at the Single-cell Level. Anal. Chem. 2020, 92, 13396–13404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Gao, Z. Yellow Emissive Se,N-codoped Carbon Dots toward Sensitive Fluorescence Assay of Crystal Violet. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 388, 122073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miao, H.; Wang, Y.; Yang, X. Carbon dots derived from Tobacco for Visually Distinguishing and Detecting Three Kinds of Tetracyclines. Nanoscale 2018, 10, 8139–8145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.; Wang, C.; Li, P.; Shao, Z.; Xia, J.; Liu, Q.; Shen, F.; Fang, Y. The Facile Synthesis of Nitrogen and Sulfur Co-doped Carbon Dots for Developing a Powerful “On-off-on” Fluorescence Probe to Detect Glutathione in Vegetables. Food Chem. 2022, 372, 131142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, W.; Guo, F.; Han, M.; Yuan, S.; Guan, W.; Li, H.; Huang, H.; Liu., Y.; Kang, Z. N,S co-doped Carbon Dots as A Stable Bio-imaging Probe for Detection of Intracellular Temperature and Tetracycline. J. Mater. Chem. B 2017, 5, 3293–3299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.; Wei, Q.; Zou, T.; Kong, Y.; Su, L.; Ma, D.; Wang, Y. Dual-emission Ratiometric Fluorescent Detection of Dinotefuran based on Sulfur-doped Carbon Quantum Dots and Copper Nanocluster Hybrid. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2020, 321, 128534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gan, Z.; Xu, H.; Hao, Y. Mechanism for excitation-dependent photoluminescence from graphene quantum dots and other graphene oxide derivates: Consensus, debates and challenges. Nanoscale 2016, 8, 7794–7807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Long, Y.; Zhou, C.; Zhang, Z. Shifting and non-shifting fluorescence emitted by carbon nanodots. J. Mater. Chem. 2012, 22, 5917–5920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Wang, Z.; Shao, H.; Jiang, X. Hydrothermal Synthesis of Highly Fluorescent Carbon Nanoparticles from Sodium Citrate and Their Use for the Detection of Mercury Ions. Carbon 2013, 52, 583–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ti, M.; Li, Y.; Li, Z.; Zhao, D.; Wu, L.; Yuan, L.; He, Y. A Ratiometric Nanoprobe based on Carboxylated Graphitic Carbon Nitride Nanosheets and Eu3+ for the Detection of Tetracyclines. Analyst 2021, 146, 1065–1073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhai, W.; Wang, C.; Yu, P.; Wang, Y.; Mao, L. Single-layer MnO2 Nanosheets Suppressed Fluorescence of 7-Hydroxycoumarin: Mechanistic Study and Application for Sensitive Sensing of Ascorbic Acid in Vivo. Anal. Chem. 2014, 86, 12206–12213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Y.; Sun, Y.; Yan, R.; Chen, E.; Wang, H.; Ye, D.; Xu, J.-J.; Chen, H.-Y. Rational Engineering of Semiconductor QDs Enabling Remarkable O-1(2) Production for Tumor-targeted Photodynamic Therapy. Biomaterials 2017, 148, 31–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Y.; Liu, S.; Wang, J.; Li, D.; Wang, X.; He, Y. A Sensitive Assay of Chelerythrine Using a Fluorescence Quenching Approach with Glutathione Capped CdTe/CdS Quantum Dots as A Probe. Anal. Methods 2013, 5, 5309–5316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magde, D.; Wong, R.; Seybold, P.G. Fluorescence quantum yields and their relation to lifetimes of rhodamine 6G and fluorescein in nine solvents: Improved absolute standards for quantum yields. Photochem. Photobiol. 2002, 75, 327–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Y.J.; Su, M.; Shi, Y.E.; Liu, X.T.; Shen, S.G.; Dong, J.X. A ratiometric fluorescent sensor for tetracyclines detection in meat based on pH-dependence of targets with lanthanum-doped carbon dots as probes. Anal. Bioanal.Chem. 2022, 414, 2597–2606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Yang, W.; Zhang, Y.; Tang, W.; Yue, T.; Li, Z. A 3D hierarchical dual-metal–organic framework heterostructure up-regulating the pre-concentration effect for ultrasensitive fluorescence detection of tetracycline antibiotics. J. Mater. Chem. C 2020, 8, 2054–2064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, K.; Jia, P.; Hou, J.; Bu, T.; Sun, X.; Liu, Y.; Wang, L. Innovative dual-emitting ratiometric fluorescence sensor for tetracyclines detection based on boron nitride quantum dots and europium ions. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2020, 8, 17185–17193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, X.; Zhao, Y.; Dong, J.; Liu, C.; Qi, Y.; Fang, G.; Wang, S. A strong blue fluorescent nanoprobe based on Mg/N co-doped carbon dots coupled with molecularly imprinted polymer for ultrasensitive and highly selective detection of tetracycline in animal-derived foods. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2021, 338, 129809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Zeng, C.; Chen, Z.; Jiang, Y.; Yao, H.; Yang, Y.; Wong, W.T. Luminescent lanthanide metal-organic framework test strip for immediate detection of tetracycline antibiotics in water. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 384, 121498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, R.; Wang, W.; El-Sayed, E.S.M.; Su, K.; He, P.; Yuan, D. Ratiometric fluorescence detection of tetracycline antibiotic based on a polynuclear lanthanide metal–organic framework. Sens. Actuators B Chemical 2021, 330, 129314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Samples | TCs | Spiked (μM) | Found (μM) | Recovery (%, n = 5) | R.S.D. (%, n = 5) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tap water | 20.00 | 19.37 | 96.86 | 5.67 | |
| TC | 60.00 | 60.23 | 100.39 | 2.60 | |
| 80.00 | 78.61 | 98.27 | 1.56 | ||
| 20.00 | 21.23 | 106.16 | 4.58 | ||
| CTC | 60.00 | 61.84 | 103.58 | 4.22 | |
| 80.00 | 81.60 | 101.99 | 1.81 | ||
| 60.00 | 60.51 | 100.86 | 4.04 | ||
| OTC | 120.00 | 117.71 | 98.09 | 0.91 | |
| 180.00 | 179.52 | 99.73 | 0.79 | ||
| Lake water | 10.00 | 9.68 | 96.89 | 6.12 | |
| TC | 20.00 | 17.79 | 88.95 | 3.02 | |
| 30.00 | 31.95 | 106.48 | 4.66 | ||
| 10.00 | 9.12 | 91.22 | 1.47 | ||
| CTC | 20.00 | 20.33 | 101.64 | 3.18 | |
| 30.00 | 33.62 | 112.07 | 3.43 | ||
| 20.00 | 18.97 | 94.86 | 4.40 | ||
| OTC | 30.00 | 32.57 | 108.58 | 4.73 | |
| 50.00 | 53.11 | 106.22 | 1.57 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yang, H.; Wei, Y.; Yan, X.; Nie, C.; Sun, Z.; Hao, L.; Su, X. High-Efficiency Utilization of Waste Tobacco Stems to Synthesize Novel Biomass-Based Carbon Dots for Precise Detection of Tetracycline Antibiotic Residues. Nanomaterials 2022, 12, 3241. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano12183241
Yang H, Wei Y, Yan X, Nie C, Sun Z, Hao L, Su X. High-Efficiency Utilization of Waste Tobacco Stems to Synthesize Novel Biomass-Based Carbon Dots for Precise Detection of Tetracycline Antibiotic Residues. Nanomaterials. 2022; 12(18):3241. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano12183241
Chicago/Turabian StyleYang, Hui, Yunlong Wei, Xiufang Yan, Chao Nie, Zhenchun Sun, Likai Hao, and Xiankun Su. 2022. "High-Efficiency Utilization of Waste Tobacco Stems to Synthesize Novel Biomass-Based Carbon Dots for Precise Detection of Tetracycline Antibiotic Residues" Nanomaterials 12, no. 18: 3241. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano12183241
APA StyleYang, H., Wei, Y., Yan, X., Nie, C., Sun, Z., Hao, L., & Su, X. (2022). High-Efficiency Utilization of Waste Tobacco Stems to Synthesize Novel Biomass-Based Carbon Dots for Precise Detection of Tetracycline Antibiotic Residues. Nanomaterials, 12(18), 3241. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano12183241




