Functional Silane-Based Nanohybrid Materials for the Development of Hydrophobic and Water-Based Stain Resistant Cotton Fabrics Coatings
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Fabric
2.2. Chemicals
2.3. Preparation of the Nanosol Solution
2.4. Sol–Gel Treatment of Cotton Fabrics
2.5. Characterization and Functional Properties of Treated Fabrics
3. Results
3.1. Nanosol Synthesis and Application on Cotton Fabrics
3.2. Wettability Measurement
3.2.1. Aqueous Liquid Repellency: Water/Alcohol Solution Test
3.2.2. Sessile Drop Method
3.2.3. Spray Test
3.2.4. Self-Cleaning Ability Measurement
3.3. Oil/Water Separation Ability
3.4. Morphological Characterization
3.4.1. Optical Microscopy (MO)
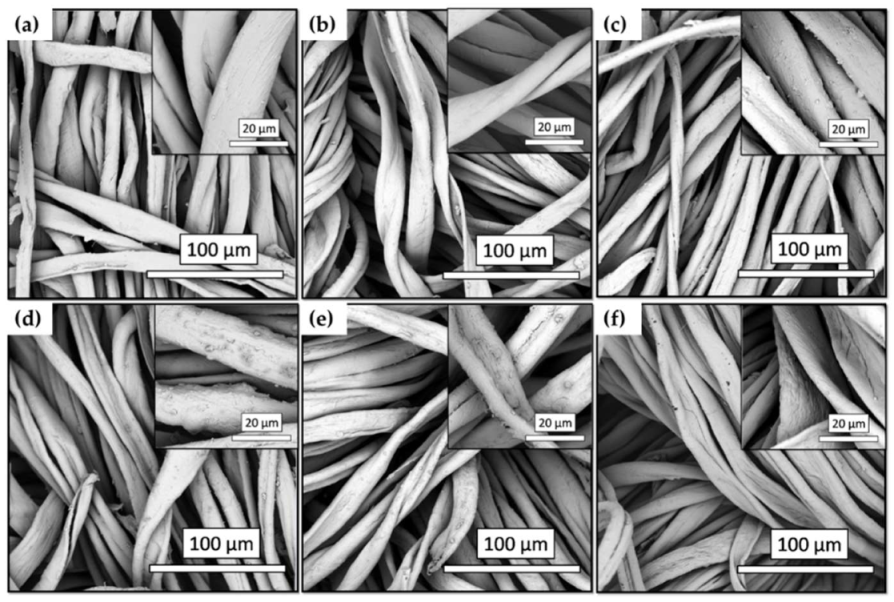
3.4.2. Morphological Characterization by SEM Analysis
3.5. Moisture-Adsorption Analysis
3.6. Air-Permeability Measurement
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Toprak, T.; Anis, P. Textile industry’s environmental effects and approaching cleaner production and sustainability, an overview. J. Text. Eng. Fash. Technol. 2017, 2, 429–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schindler, W.D.; Hauser, P.J. Chemical Finishing of Textiles; Woodhead Publishing: Cambridge, UK, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Hasanbeigi, A.; Price, L. A technical review of emerging technologies for energy and water efficiency and pollution reduction in the textile industry. J. Clean. Prod. 2015, 95, 30–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trovato, V.; Sfameni, S.; Rando, G.; Rosace, G.; Libertino, S.; Ferri, A.; Plutino, M.R. A review on stimuli-responsive smart materials for wearable health technology: Retrospective, perspective and prospective. Molecules 2022, 27, 5709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sobha, K.; Surendranath, K.; Meena, V.; Jwala, T.K.; Swetha, N.; Latha, K.S.M. Emerging trends in nanobiotechnology. Biotechnol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 2010, 5, 1–12. [Google Scholar]
- Ahmad, S.; Fatma, A.; Manal, E.; Ghada, A.M. Applications of Nanotechnology and Advancements in Smart Wearable Textiles: An Overview. Egypt. J. Chem. 2020, 63, 2177–2184. [Google Scholar]
- Sanchez, C.; Julián, B.; Belleville, P.; Popall, M. Applications of hybrid organic–inorganic nanocomposites. J. Mater. Chem. 2005, 15, 3559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Lan, T.; Pinnavaia, T. Hybrid organic-inorganic nanocomposites formed from an epoxy polymer and a layered silicic acid (magadiite). Chem. Mater. 1996, 8, 2200–2204. [Google Scholar]
- Mahltig, B.; Textor, T. Nanosols and Textiles; World Scientific: Singapore, 2008; ISBN 978-981-283-350-1. [Google Scholar]
- Mahltig, B.; Haufe, H.; Böttcher, H. Functionalisation of textiles by inorganic sol–gel coatings. J. Mater. Chem. 2005, 15, 4385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ismail, W.N.W. Sol–gel technology for innovative fabric finishing—A Review. J. Sol-Gel Sci. Technol. 2016, 78, 698–707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ielo, I.; Giacobello, F.; Sfameni, S.; Rando, G.; Galletta, M.; Trovato, V.; Rosace, G.; Plutino, M.R. Nanostructured Surface Finishing and Coatings: Functional Properties and Applications. Materials 2021, 14, 2733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trovato, V.; Rosace, G.; Colleoni, C.; Sfameni, S.; Migani, V.; Plutino, M.R. Sol-gel based coatings for the protection of cultural heritage textiles. IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2020, 777, 12007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giacobello, F.; Ielo, I.; Belhamdi, H.; Plutino, M.R. Geopolymers and Functionalization Strategies for the Development of Sustainable Materials in Construction Industry and Cultural Heritage Applications: A Review. Materials 2022, 15, 1725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trovato, V.; Mezzi, A.; Brucale, M.; Abdeh, H.; Drommi, D.; Rosace, G.; Plutino, M.R. Sol-Gel Assisted Immobilization of Alizarin Red S on Polyester Fabrics for Developing Stimuli-Responsive Wearable Sensors. Polymers 2022, 14, 2788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filipic, J.; Glazar, D.; Jerebic, S.; Kenda, D.; Modic, A.; Roskar, B.; Vrhovski, I.; Stular, D.; Golja, B.; Smolej, S.; et al. Tailoring of antibacterial and UV protective cotton fabric by an in-situ synthesis of silver particles in the presence of a sol–gel matrix and sumac leaf extract. Tekstilec 2020, 63, 4–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puoci, F.; Saturnino, C.; Trovato, V.; Iacopetta, D.; Piperopoulos, E.; Triolo, C.; Bonomo, M.G.; Drommi, D.; Parisi, O.I.; Milone, C.; et al. Sol–Gel Treatment of Textiles for the Entrapping of an Antioxidant/Anti-Inflammatory Molecule: Functional Coating Morphological Characterization and Drug Release Evaluation. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 2287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.Y.; Xu, Q.B.; Fu, F.Y.; Liu, X.D. Durable antimicrobial cotton textiles modified with inorganic nanoparticles. Cellulose 2016, 23, 2791–2808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuk, N.; Sala, M.; Gorjanc, M. Development of antibacterial and UV protective cotton fabrics using plant food waste and alien invasive plant extracts as reducing agents for the in-situ synthesis of silver nanoparticles. Cellulose 2021, 28, 3215–3233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ielo, I.; Giacobello, F.; Castellano, A.; Sfameni, S.; Rando, G.; Plutino, M.R. Development of Antibacterial and Antifouling Innovative and Eco-Sustainable Sol–Gel Based Materials: From Marine Areas Protection to Healthcare Applications. Gels 2022, 8, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saleemi, S.; Naveed, T.; Riaz, T.; Memon, H.; Awan, J.A.; Siyal, M.I.; Xu, F.; Bae, J. Surface Functionalization of Cotton and PC Fabrics Using SiO2 and ZnO Nanoparticles for Durable Flame Retardant Properties. Coatings 2020, 10, 124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibrahim, H.M.; Zaghloul, S.; Hashem, M.; El-Shafei, A. A green approach to improve the antibacterial properties of cellulosebased fabrics using Moringa oleifera extract presence of silver nanoparticles. Cellulose 2021, 28, 549–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colleoni, C.; Massafra, M.R.; Rosace, G. Photocatalytic properties and optical characterization of cotton fabric coated via sol–gel with non-crystalline TiO2 modified with poly(ethylene glycol). Surf. Coat. Technol. 2012, 207, 79–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colleoni, C.; Guido, E.; Migani, V.; Rosace, G. Hydrophobic behaviour of non fluorinated sol-gel based cotton and polyester fabric coatings. J. Ind. Text. 2015, 44, 815–834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sfameni, S.; Rando, G.; Galletta, M.; Ielo, I.; Brucale, M.; De Leo, F.; Cardiano, P.; Cappello, S.; Visco, A.; Trovato, V.; et al. Design and Development of Fluorinated and Biocide-Free Sol–Gel Based Hybrid Functional Coatings for Anti-Biofouling/Foul-Release Activity. Gels 2022, 8, 538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Textor, T.; Mahltig, B. A sol–gel based surface treatment for preparation of water repellent antistatic textiles. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2010, 256, 1668–1674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alongi, J.; Colleoni, C.; Rosace, G.; Malucelli, G. The role of pre-hydrolysis on multi step sol-gel processes for enhancing the flame retardancy of cotton. Cellulose 2013, 20, 525–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, M.; Morshed, M.; Farjana, S.; Ana, S. Fabrication of new multifunctional cotton–modal–recycled aramid blended protective textiles through deposition of a 3D-polymer coating: High fire retardant, water repellent and antibacterial properties. New J. Chem. 2020, 44, 12122–12133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castellano, A.; Colleoni, C.; Iacono, G.; Mezzi, A.; Plutino, M.R.; Malucelli, G.; Rosace, G. Synthesis and characterization of a phosphorous/nitrogen based sol-gel coating as a novel halogen- and formaldehyde-free flame retardant finishing for cotton fabric. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2019, 162, 148–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caldara, M.; Colleoni, C.; Guido, E.; Rosace, G. Optical sensor development for smart textiles. In Proceedings of the 12th World Textile Conference AUTEX, Zadar, Croatia, 13–15 June 2012; pp. 1149–1452. [Google Scholar]
- Caldara, M.; Colleoni, C.; Guido, E.; Re, V.; Rosace, G. Optical monitoring of sweat pH by a textile fabric wearable sensor based on covalently bonded litmus-3-glycidoxypropyltrimethoxysilane coating. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2016, 222, 213–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trovato, V.; Rosace, G.; Colleoni, C.; Plutino, M.R. Synthesis and characterization of halochromic hybrid sol-gel for the development of a pH sensor fabric. IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2017, 254, 72027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ielo, I.; Rando, G.; Giacobello, F.; Sfameni, S.; Castellano, A.; Galletta, M.; Drommi, D.; Rosace, G.; Plutino, M.R. Synthesis, Chemical–Physical Characterization, and Biomedical Applications of Functional Gold Nanoparticles: A Review. Molecules 2021, 26, 5823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahltig, B.; Textor, T. Combination of silica sol and dyes on textiles. J. Sol-Gel Sci. Technol. 2006, 39, 111–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AbouElmaaty, T.; Abdeldayem, S.; Ramadan, S.; Sayed-Ahmed, K.; Plutino, M. Coloration and Multi-Functionalization of Polypropylene Fabrics with Selenium Nanoparticles. Polymers 2021, 13, 2483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibrahim, N.; Eid, B.; Abd El-Aziz, E.; AbouElmaaty, T.; Ramadan, S. Loading of chitosan Nano metal oxide hybrids ontocotton/polyester fabrics to impart permanent and effective multifunctions. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2017, 105, 769–776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aya, R.; Abdel Rahim, A.; Amr, H.; El-Amir, M. Improving Performance and Functional Properties of Different Cotton Fabrics by Silicon Dioxide Nanoparticles. J. Eng. Sci. 2019, 4, 1–17. [Google Scholar]
- AbouElmaaty, T.; Elsisi, H.G.; Elsayad, G.M.; Elhadad, H.H.; Sayed-Ahmed, K.; Plutino, M.R. Fabrication of New Multifunctional Cotton/Lycra Composites Protective Textiles through Deposition of Nano Silica Coating. Polymers 2021, 13, 2888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trovato, V.; Vitale, A.; Bongiovanni, R.; Ferri, A.; Rosace, G.; Plutino, M.R. Development of a Nitrazine Yellow-glycidyl methacrylate coating onto cotton fabric through thermal-induced radical polymerization reactions: A simple approach towards wearable pH sensors applications. Cellulose 2021, 28, 3847–3868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.M.; Reinhoudt, D.; Crego, C.M. What do we need for a superhydrophobic surface? A review on the recent progress in the preparation of superhydrophobic surfaces. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2007, 36, 1350–1368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richard, E.; Lakshmi, R.V.; Aruna, S.T.; Basu, B.J. A simple cost-effective and eco-friendly wet chemical process for the fabrication of superhydrophobic cotton fabrics. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2013, 277, 302–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, B.; Cai, Z.; Wang, W.; Ge, F. Preparation of superhydrophobic cotton fabrics based on SiO2 nanoparticles and ZnO nanorod arrays with subsequent hydrophobic modification. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2010, 204, 1556–1561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Shi, F.; Niu, J.; Jiang, Y.; Wang, Z. Superhydrophobic surfaces: From structural control to functional application. J. Mater. Chem 2008, 18, 621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patankar, N.A. Mimicking the Lotus Effect: Influence of Double Roughness Structures and Slender Pillars. Langmuir 2004, 20, 8209–8213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cassie, A.B.D.; Baxter, S. Wettability of porous surfaces. Trans. Faraday Soc. 1944, 40, 546–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balani, K.; Batista, R.G.; Lahiri, D.; Agarwal, A. The hydrophobicity of a lotus leaf: A nanomechanical and computational approach. Nanotechnology 2009, 20, 305707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heiman-Burstein, D.; Dotan, A.; Dodiuk, H.; Kenig, S. Hybrid Sol-Gel Superhydrophobic Coatings Based on Alkyl Silane-Modified Nanosilica. Polymers 2021, 13, 539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, C.H.; Jia, S.T.; Zhang, J.; Ma, J.Z. Large-area fabrication of superhydrophobic surfaces for practical applications: An overview. Sci. Technol. Adv. Mater. 2010, 11, 033002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Wang, S.; Wang, C.; Li, J. A facile method to fabric at superhydrophobic cotton fabrics. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2012, 261, 561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, W.Q.; Xing, Y.J.; Yu, Y.; Shang, S.M.; Dai, J.J. Enhanced washing durability of hydrophobic coating on cellulose fabric using polycarboxylic acids. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2011, 257, 4443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rando, G.; Sfameni, S.; Galletta, M.; Drommi, D.; Cappello, S.; Plutino, M.R. Functional Nanohybrids and Nanocomposites Development for the Removal of Environmental Pollutants and Bioremediation. Molecules 2022, 27, 4856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bae, G.Y.; Jeong, Y.G.; Min, B.G. Superhydrophobic PET fabrics achieved bysilica nanoparticles and water-repellent agent. Fibers Polym. 2010, 11, 976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bae, G.Y.; Geun, Y.; Min, B.G.; Jeong, Y.G.; Lee, S.C.; Jang, J.H.; Koo, G.H. Superhydrophobicity of cotton fabrics treated with silica nanoparticles and water-repellent agent. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2009, 337, 170–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lehocky, M.; Amaral, P.F.F.; St’ahel, P.; Coelho, M.A.Z.; Timmons, A.M.; Coutinho, J.A.P. Preparation and characterization of organosilicon thin films for selective adhesion of yarrowialipolytica yeast cells. J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol. 2007, 366, 360–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lakshmi, R.V.; Bera, P.; Anandan, C.; Basu, B. Effect of the size of silica nanoparticles on wettability and surface chemistry of sol–gel superhydrophobic and oleophobic nanocomposite coatings. J. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2014, 320, 780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, W.H.; Lin, C.S. Robust superhydrophobic transparent coatings fabricated by a low-temperature sol–gel process. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2014, 305, 702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shang, Q.; Zhou, Y.; Xiao, G. A simple method for the fabrication of silica-based superhydrophobic surfaces. Coat. Technol. Res. 2014, 11, 509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramezani, M.; Vaezi, M.R.; Kazemzadeh, A. Preparation of silane-functionalized silica films via two-step dip coating sol–gel and evaluation of their superhydrophobic properties. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2014, 317, 147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, H.; Lin, S.; Tu, Y.; Liu, G.; Hu, J.; Li, F.; Miao, L.; Zhang, G.; Luo, H.; Liu, F.; et al. Simple approach towards fabrication of highly durable and robust superhydrophobic cotton fabric from functional di block copolymer. J. Mat. Chem. A 2013, 1, 11246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Huang, Y.G.; Feng, S.J.; Gu, G.T.; Qing, F.L. Novel superhydrophobic and highly oleophobic PFPE-modified silica nanocomposite. J. Mater. Sci. 2010, 45, 460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guido, E.; Colleoni, C.; De Clerck, K.; Plutino, M.R.; Rosace, G. Influence of catalyst in the synthesis of a cellulose-based sensor: Kinetic study of 3-glycidoxypropyltrimethoxysilane epoxy ring opening by Lewis acid. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2014, 203, 213–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trovato, V.; Colleoni, C.; Castellano, A.; Plutino, M.R. The key role of 3-glycidoxypropyltrimethoxysilane sol–gel precursor in the development of wearable sensors for health monitoring. J. Sol-Gel Sci. Technol. 2018, 87, 27–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plutino, M.R.; Guido, E.; Colleoni, C.; Rosace, G. Effect of GPTMS functionalization on the improvement of the pH-sensitive methyl red photostability. Sens. Actuators B 2017, 238, 281–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosace, G.; Guido, E.; Colleoni, C.; Brucale, M.; Piperopoulos, E.; Milone, C.; Plutino, M.R. Halochromic resorufin-GPTMS hybrid sol-gel: Chemical-physical properties and use as pH sensor fabric coating. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2017, 241, 85–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plutino, M.R.; Colleoni, C.; Donelli, I.; Freddi, G.; Guido, E.; Maschi, O.; Mezzi, A.; Rosace, G. Sol-gel 3-glycidoxypropyltriethoxysilane finishing on different fabrics: The role of precursor concentration and catalyst on the textile performances and cytotoxic activity. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2017, 506, 504–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ielo, I.; Galletta, M.; Rando, G.; Sfameni, S.; Cardiano, P.; Sabatino, G.; Drommi, D.; Rosace, G.; Plutino, M.R. Design, synthesis and characterization of hybrid coatings suitable for geopolymeric-based supports for the restoration of cultural heritage. IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2020, 777, 012003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sfameni, S.; Rando, G.; Marchetta, A.; Scolaro, C.; Cappello, S.; Urzì, C.; Visco, A.; Plutino, M.R. Development of eco-friendly hydrophobic and fouling-release coatings for blue-growth environmental applications: Synthesis, mechanical characterization and biological activity. Gels 2022, 8, 528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, D.; Hu, N.; Schaefer, D.W. Chapter 1—Water-Based Sol–Gel Coatings for Military Coating Applications; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2020; pp. 1–27. [Google Scholar]
- Khatri, M.; Qureshi, U.A.; Ahmed, F.; Khatri, Z.; Kim, I.S. Dyeing of Electrospun Nanofibers BT. In Handbook of Nanofibers; Barhoum, A., Bechelany, M., Makhlouf, A.S.H., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2019; pp. 373–388. ISBN 978-3-319-53655-2. [Google Scholar]
- El-Ghazali, S.; Khatri, M.; Kobayashi, S.; Kim, I.S. 1—An overview of medical textile materials. In Medical Textiles from Natural Resources; The Textile Institute Book, Series; Mondal, M.I.H., Ed.; Woodhead Publishing: Sawston, UK, 2022; pp. 3–42. ISBN 978-0-323-90479-7. [Google Scholar]
- Basak, S.; Samanta, K.K.; Chattopadhyay, S.K. Fire retardant property of cotton fabric treated with herbal extract. J. Text. Inst. 2015, 106, 1338–1347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, T.-C.; Lee, D.-J. Cotton fabrics modified for use in oil/water separation: A perspective review. Cellulose 2021, 28, 4575–4594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, B.; Pu, H.; Sun, D.-W. Multifunctional cellulose based substrates for SERS smart sensing: Principles, applications and emerging trends for food safety detection. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2021, 110, 304–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malshe, P.; Mazloumpour, M.; El-Shafei, A.; Hauser, P. Multi-functional military textile: Plasma-induced graft polymerization of a C6 fluorocarbon for repellent treatment on nylon–cotton blend fabric. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2013, 217, 112–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marmur, A.A. Guide to the Equilibrium Contact Angles Maze. In Contact angle, Wettability and Adhesion; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2009; pp. 1–18. [Google Scholar]
- Ubuo, E.E.; Udoetok, I.A.; Tyowua, A.T.; Ekwere, I.O.; Al-Shehri, H.S. The Direct Cause of Amplified Wettability: Roughness or Surface Chemistry? J. Compos. Sci. 2021, 5, 213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wenzel, R.N. Resistance of solid surfaces to wetting by water. Ind. Eng. Chem. 1936, 28, 988–994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glosz, K.; Stolarczyk, A.; Jarosz, T. Siloxanes—Versatile Materials for Surface Functionalisation and Graft Copolymers. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 6387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Y.; Hu, J.; Xin, Z. In-Situ Incorporation of Alkyl-Grafted Silica into Waterborne Polyurethane with High Solid Content for Enhanced Physical Properties of Coatings. Polymers 2018, 10, 514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez-Milla, M.; Gómez, R.; Pérez-Serrano, J.; Sánchez-Nieves, J.; de la Mata, F.J. Functionalization of silica with amine and ammonium alkyl chains, dendrons and dendrimers: Synthesis and antibacterial properties. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2020, 109, 110526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radhakrishnan, B.; Ranjan, R.; Brittain, W.J. Surface initiated polymerizations from silica nanoparticles. Soft Matter 2006, 2, 386–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donnini, J.; Corinaldesi, V.; Nanni, A. Mechanical properties of FRCM using carbon fabrics with different coating treatments. Compos. Part B Eng. 2016, 88, 220–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koo, K.; Park, Y. Characteristics of double-layer coated fabrics with and without phase change materials and nano-particles. Fibers Polym. 2014, 15, 1641–1647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazzon, G.; Zahid, M.; Heredia-Guerrero, J.A.; Balliana, E.; Zendri, E.; Athanassiou, A.; Bayer, I.S. Hydrophobic treatment of woven cotton fabrics with polyurethane modified aminosilicone emulsions. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2019, 490, 331–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, H.; Rosu, C.; Jiang, L.; Sundar, V.A.; Breedveld, V.; Hess, D.W. Nonfluorinated Superhydrophobic Chemical Coatings on Polyester Fabric Prepared with Kinetically Controlled Hydrolyzed Methyltrimethoxysilane. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2019, 58, 15368–15378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pavlidou, S.; Paul, R. 3—Soil repellency and stain resistance through hydrophobic and oleophobic treatments. In Waterproof and Water Repellent Textiles and Clothing; The Textile Institute Book, Series; Williams, J., Ed.; Woodhead Publishing: Sawston, UK, 2018; pp. 73–88. ISBN 978-0-08-101212-3. [Google Scholar]
- Peran, J.; Ercegović Ražić, S. Application of atmospheric pressure plasma technology for textile surface modification. Text. Res. J. 2019, 90, 1174–1197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Xin, J.H.; Choi, C.-H. Cotton Fabrics with Single-Faced Superhydrophobicity. Langmuir 2012, 28, 17426–17434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Yu, Q.; Yin, X.; Xu, J.; Cai, Y.; Han, L.; Huang, H.; Zhou, Y.; Tan, Y.; Wang, L.; et al. Fabrication of superhydrophobic and superoleophilic polybenzoxazine-based cotton fabric for oil–water separation. Cellulose 2018, 25, 6691–6704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.; Wan, M.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, X.; Zhao, Y.; Sun, L. Fabrication and characterization of degradable and durable fluoride-free super-hydrophobic cotton fabrics for oil/water separation. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2019, 378, 125079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, H.; Fu, Y.; Yang, C.; Zhu, D.; Yang, J. A UV-driven superhydrophilic/superoleophobic polyelectrolyte multilayer film on fabric and its application in oil/water separation. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 91301–91307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Chen, Y. Oil–water separation capability of superhydrophobic fabrics fabricated via combining polydopamine adhesion with lotus-leaf-like structure. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2015, 132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Liu, E.; Fan, J.; Chen, B.; Hu, X.; He, Y.; He, C. Superhydrophobic PDMS/wax coated polyester textiles with self-healing ability via inlaying method. Prog. Org. Coat. 2019, 132, 100–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, G.; Huo, L.; Jin, Y.; Yuan, S.; Zhao, R.; Zhao, J.; Li, Z.; Li, Y. Fluorine-free superhydrophobic PET fabric with high oil flux for oil–water separation. Prog. Org. Coat. 2022, 163, 106671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canal, L.P.; González, C.; Molina-Aldareguía, J.M.; Segurado, J.; LLorca, J. Application of digital image correlation at the microscale in fiber-reinforced composites. Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2012, 43, 1630–1638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghaffari, S.; Yousefzadeh, M.; Mousazadegan, F. Investigation of thermal comfort in nanofibrous three-layer fabric for cold weather protective clothing. Polym. Eng. Sci. 2019, 59, 2032–2040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, T.; Stylios, G.K. Effects of coating process on the surface roughness of coated fabrics. J. Text. Inst. 2017, 108, 712–719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsieh, C.-T.; Chen, W.-Y.; Wu, F.-L. Fabrication and superhydrophobicity of fluorinated carbon fabrics with micro/nanoscaled two-tier roughness. Carbon 2008, 46, 1218–1224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.; Kim, J.; Park, C.H. Influence of micro and nano-scale roughness on hydrophobicity of a plasma-treated woven fabric. Text. Res. J. 2016, 87, 193–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zarrinabadi, E.; Abghari, R.; Nazari, A.; Mirjalili, M. Environmental effects of enhancement of mechanical and hydrophobic properties of polyester fabrics using silica/kaolinite/silver nanocomposite: A facile technique for synthesis and RSM optimization. Eurasian J. Biosci. 2018, 12, 1–14. [Google Scholar]
- Forsman, N.; Lozhechnikova, A.; Khakalo, A.; Johansson, L.-S.; Vartiainen, J.; Österberg, M. Layer-by-layer assembled hydrophobic coatings for cellulose nanofibril films and textiles, made of polylysine and natural wax particles. Carbohydr. Polym. 2017, 173, 392–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glampedaki, P.; Jocic, D.; Warmoeskerken, M.M.C.G. Moisture absorption capacity of polyamide 6,6 fabrics surface functionalised by chitosan-based hydrogel finishes. Prog. Org. Coat. 2011, 72, 562–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tissera, N.D.; Wijesena, R.N.; Perera, J.R.; de Silva, K.M.N.; Amaratunge, G.A.J. Hydrophobic cotton textile surfaces using an amphiphilic graphene oxide (GO) coating. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2015, 324, 455–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zupin, Ž.; Hladnik, A.; Dimitrovski, K. Prediction of one-layer woven fabrics air permeability using porosity parameters. Text. Res. J. 2011, 82, 117–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, R.; Li, J.; Li, M.; Zhang, Q.; Shi, G.; Li, Y.; Hou, C.; Wang, H. MXene-Coated Air-Permeable Pressure-Sensing Fabric for Smart Wear. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2020, 12, 46446–46454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, J.; Shen, Y.; Yu, D.; Yang, T.; Wu, M.; Yang, L.; Petru, M. Porous Film Coating Enabled by Polyvinyl Pyrrolidone (PVP) for Enhanced Air Permeability of Fabrics: The Effect of PVP Molecule Weight and Dosage. Polymers 2020, 12, 2961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, J.-H.; Ko, T.-J.; Moon, M.-W.; Park, C.H. Nanostructured fabric with robust superhydrophobicity induced by a thermal hydrophobic ageing process. RSC Adv. 2017, 7, 25597–25604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]













| Sample Code | First Deposition | Second Deposition |
|---|---|---|
| G | G | G |
| G/C2_C′2 | G and C2 | C2 |
| G/C8 _C′8 | G and C8 | C8 |
| G/C16 _C′16 | G and C16 | C16 |
| G/C2_C′16 | G and C2 | C16 |
| G/C8_C′16 | G and C8 | C16 |
| Sample Code | Wi | Wf | Total Add-on wt.% (A) |
|---|---|---|---|
| COT + G | 2.140 g | 2.163 g | 1.06% |
| COT + G/C2_C′2 | 2.237 g | 2.292 g | 2.39% |
| COT + G/C8 _C′8 | 2.121 g | 2.201 g | 3.63% |
| COT + G/C16 _C′16 | 2.157 g | 2.217 g | 2.70% |
| COT + G/C2_C′16 | 2.210 g | 2.308 g | 4.24% |
| COT + G/C8_C′16 | 2.188 g | 2.196 g | 0.36% |
| Sample Code | Aqueous-Solution Repellency-Grade Number | Composition (by Volume) |
|---|---|---|
| Cot + G | 0 | 100% Water |
| Cot + GC2_C′2 | 1 | 98:2/water:isopropyl alcohol |
| Cot + GC8_C′8 | 3 | 90:10/water:isopropyl alcohol |
| Cot + GC16_C′16 | 3 | 90:10/water:isopropyl alcohol |
| Cot + GC2_C′16 | 3 | 90:10/water:isopropyl alcohol |
| Cot + GC8_C′16 | 4 | 80:20/water:isopropyl alcohol |
| Sample Code | Static Water Contact Angle θw [°] |
|---|---|
| Cot + G | 53.83 ± 0.82 |
| Cot + GC2_C′2 | 71.71 ± 0.33 |
| Cot + GC8_C′8 | 138.46 ± 0.40 |
| Cot + GC16_C′16 | 142.53 ± 0.34 |
| Cot + GC2_C′16 | 148.20 ± 0.80 |
| Cot + GC8_C′16 | 148.83 ± 0.29 |
| Sample Code | Wettability Level | Water-Stain Characteristics |
|---|---|---|
| Cot + G | 50 (ISO 1) | Complete wetting of the entire specimen face |
| Cot + GC2_ C′2 | 50 (ISO 1) | Complete wetting of the entire specimen face |
| Cot + GC8_ C′8 | 100 (ISO 5) | No wetting of the specimen face |
| Cot + GC16_ C′16 | 100 (ISO 5) | No wetting of the specimen face |
| Cot + GC2_ C′16 | 100 (ISO 5) | No wetting of the specimen face |
| Cot + GC8_ C′16 | 100 (ISO 5) | No wetting of the specimen face |
| Sample Code | Weight (g) | Drying Temperature (°C) | Drying Time (min) 1 | Humidity (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Untreated cotton | 2.156 | 130 | 5–6 | 4.31 |
| COT + G | 2.181 | 130 | 2 | 3.62 |
| COT + GC2_C′2 | 2.230 | 130 | 3 | 4.44 |
| COT+ GC8_C′8 | 2.198 | 130 | 2 | 3.55 |
| COT + GC16_C′16 | 2.209 | 130 | 3 | 4.07 |
| COT + GC2_C′16 | 2.280 | 130 | 2–3 | 3.90 |
| COT + GC8_C′16 | 2.206 | 130 | 3–4 | 4.12 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sfameni, S.; Lawnick, T.; Rando, G.; Visco, A.; Textor, T.; Plutino, M.R. Functional Silane-Based Nanohybrid Materials for the Development of Hydrophobic and Water-Based Stain Resistant Cotton Fabrics Coatings. Nanomaterials 2022, 12, 3404. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano12193404
Sfameni S, Lawnick T, Rando G, Visco A, Textor T, Plutino MR. Functional Silane-Based Nanohybrid Materials for the Development of Hydrophobic and Water-Based Stain Resistant Cotton Fabrics Coatings. Nanomaterials. 2022; 12(19):3404. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano12193404
Chicago/Turabian StyleSfameni, Silvia, Tim Lawnick, Giulia Rando, Annamaria Visco, Torsten Textor, and Maria Rosaria Plutino. 2022. "Functional Silane-Based Nanohybrid Materials for the Development of Hydrophobic and Water-Based Stain Resistant Cotton Fabrics Coatings" Nanomaterials 12, no. 19: 3404. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano12193404
APA StyleSfameni, S., Lawnick, T., Rando, G., Visco, A., Textor, T., & Plutino, M. R. (2022). Functional Silane-Based Nanohybrid Materials for the Development of Hydrophobic and Water-Based Stain Resistant Cotton Fabrics Coatings. Nanomaterials, 12(19), 3404. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano12193404









