Novel Magnetically Driven Superhydrophobic Sponges Coated with Asphaltene/Kaolin Nanoparticles for Effective Oil Spill Cleanup
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
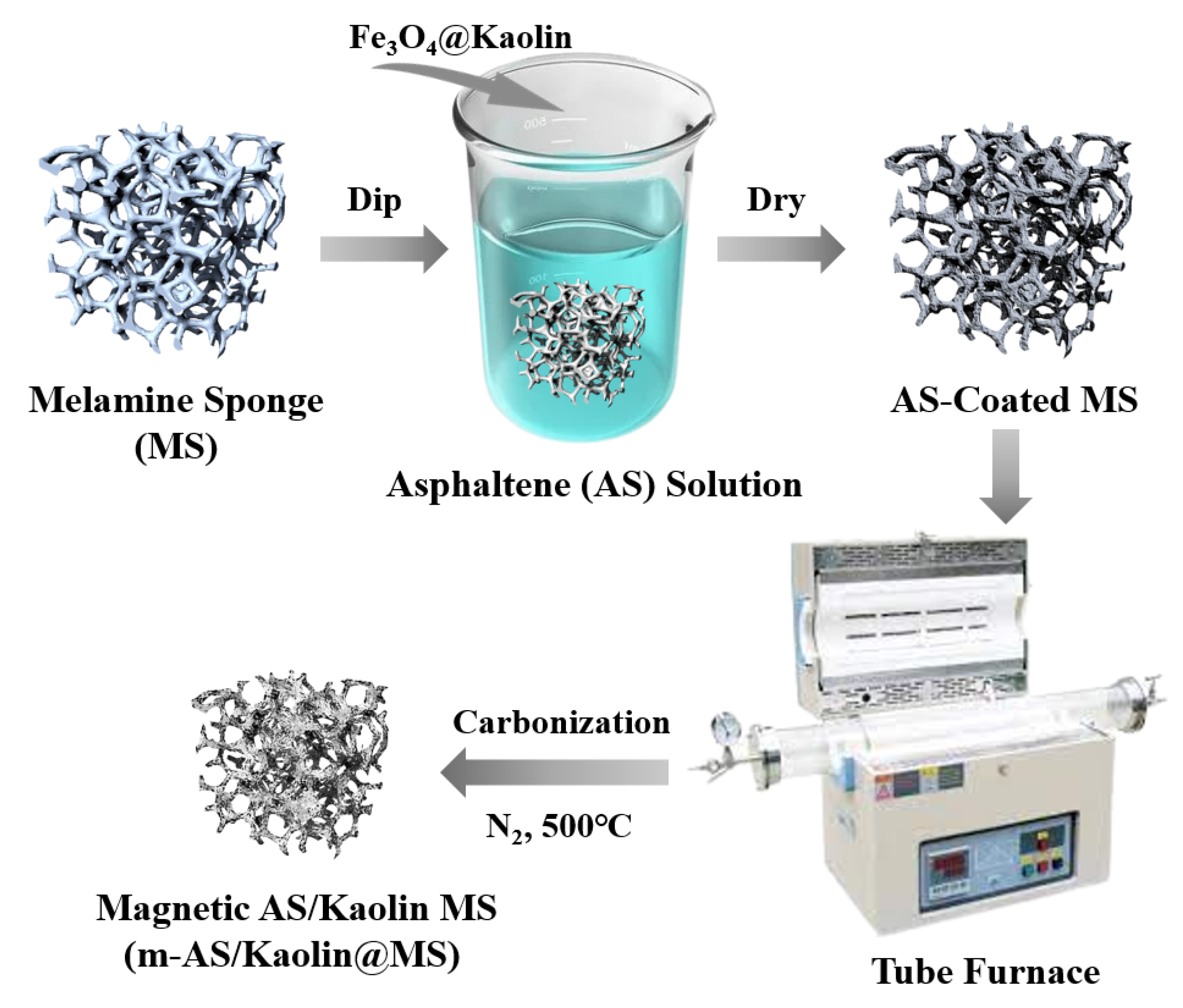
2.2. Preparation of Samples
2.3. Structural Characterization
2.4. Wettability and Absorption Tests
2.5. Demulsification and Burning Tests
3. Results and Discussion
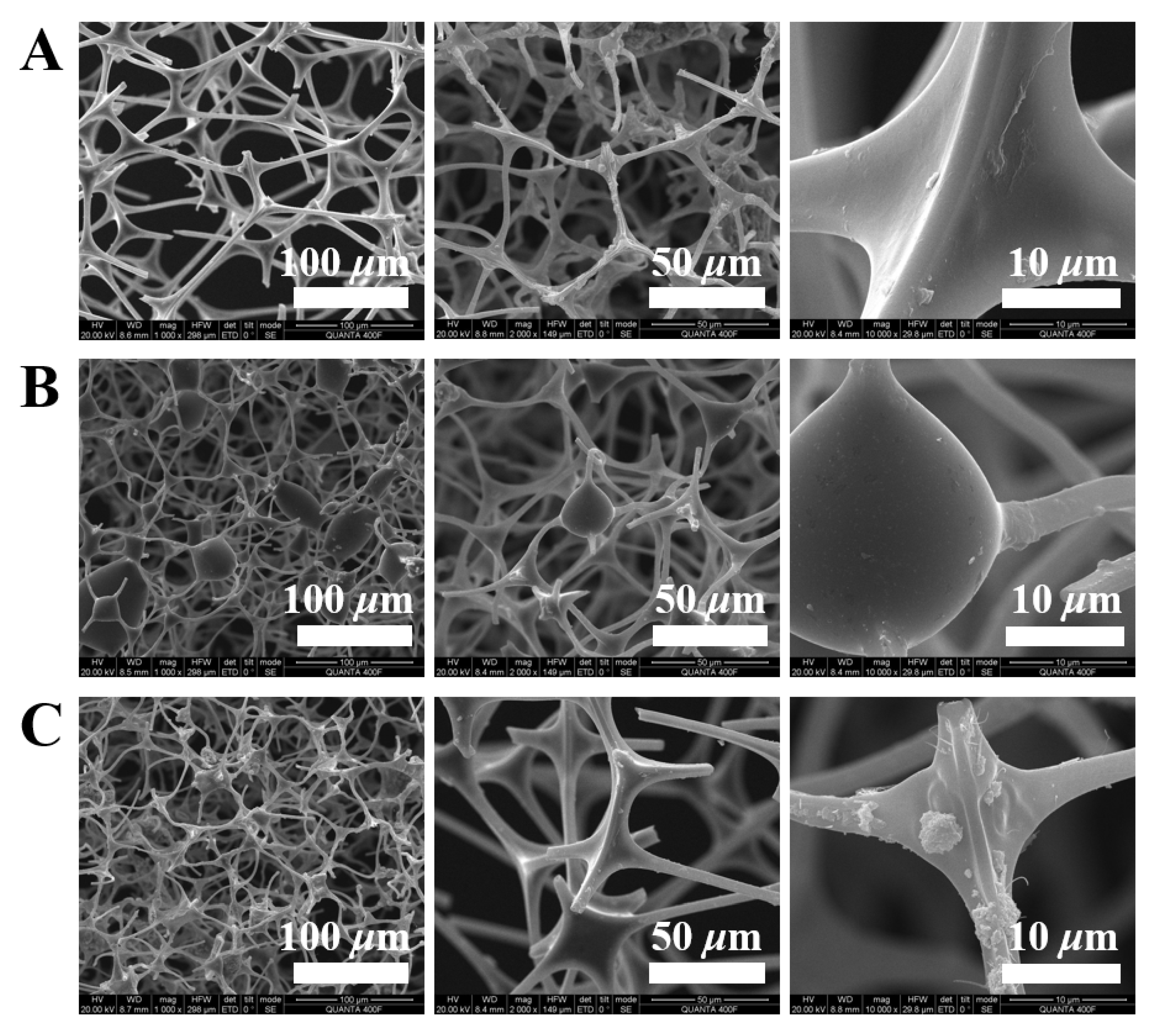
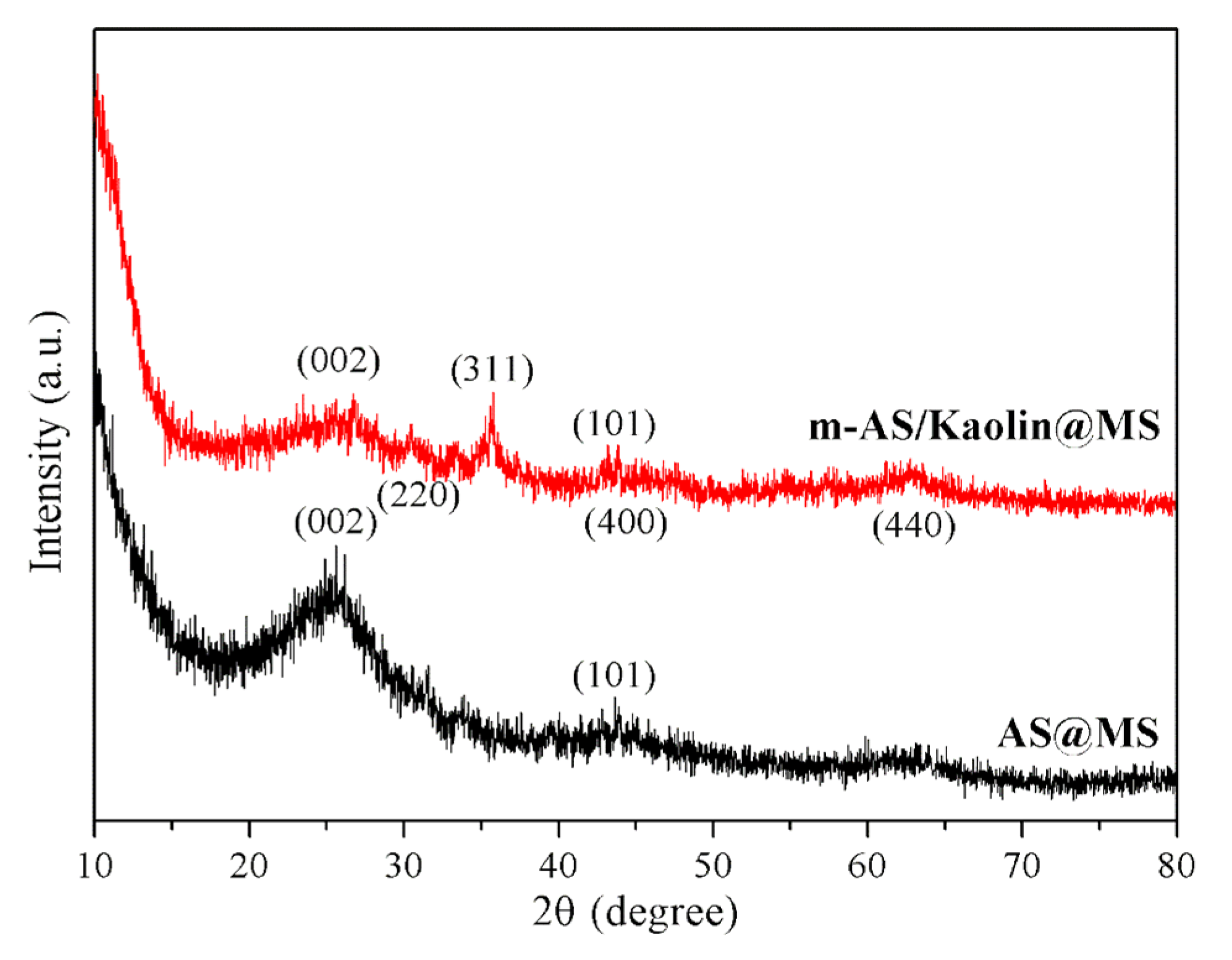
3.1. Structural Features of the Asphaltene-Melamine Sponges
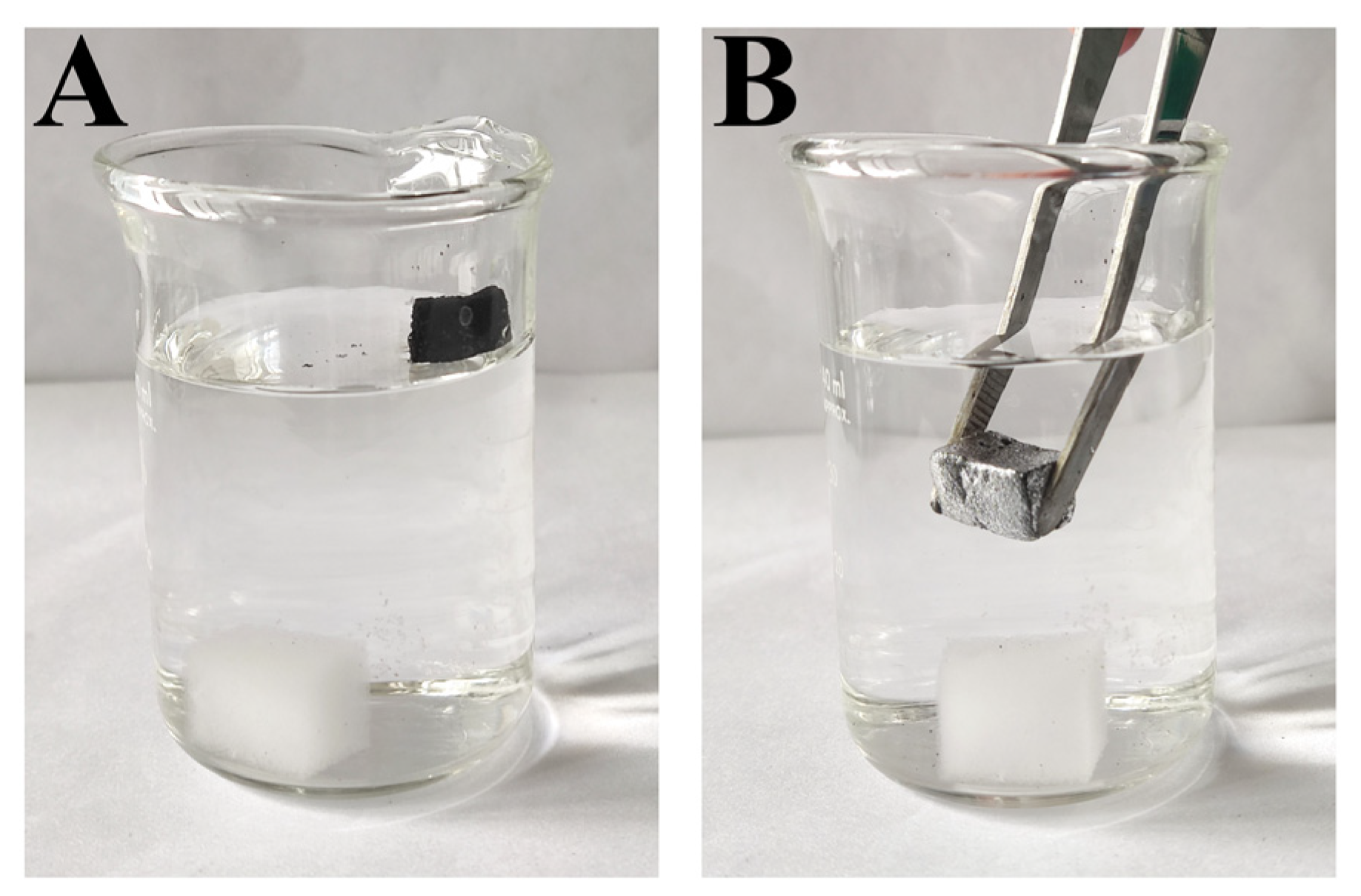
3.2. Wettability Characterization
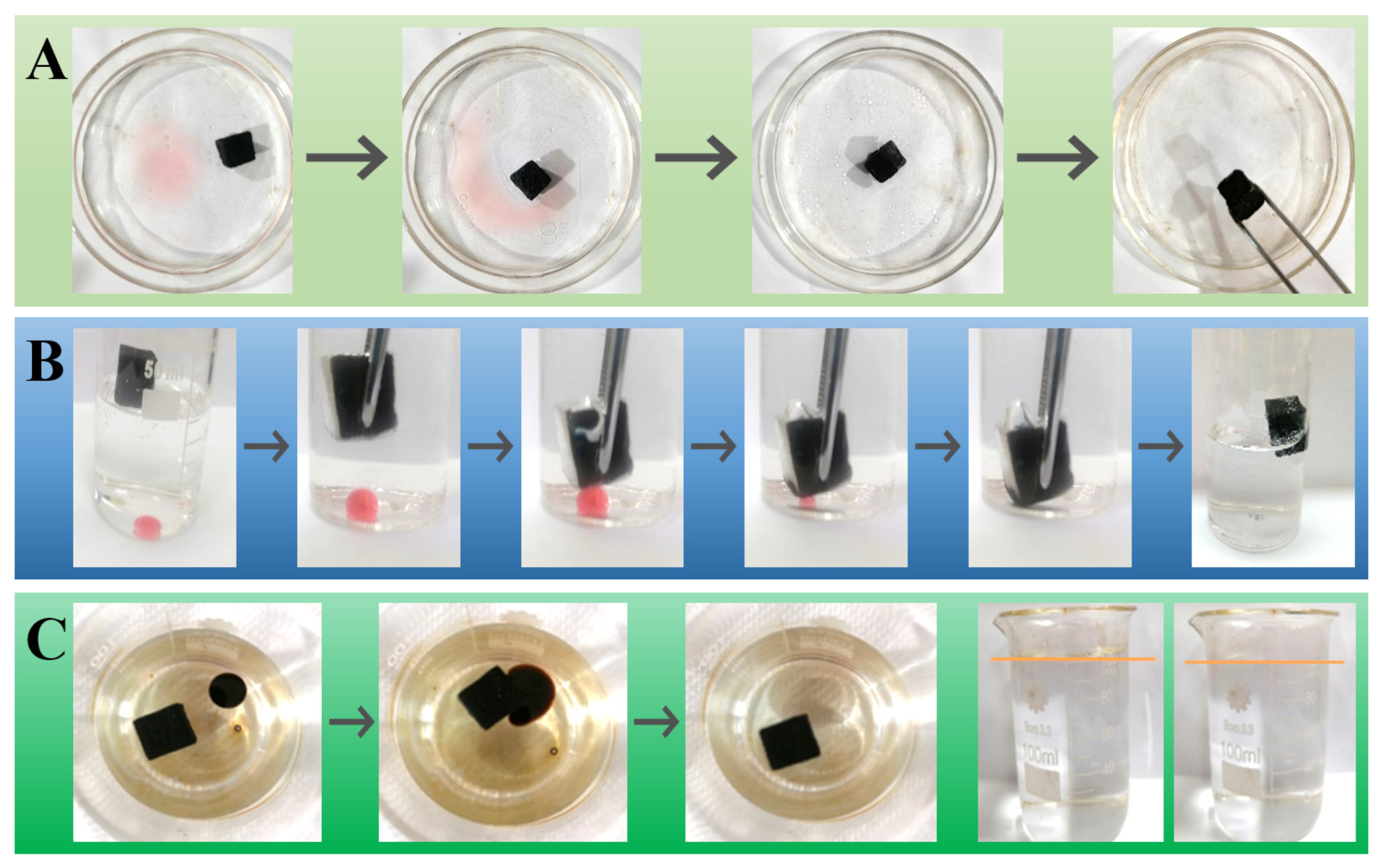
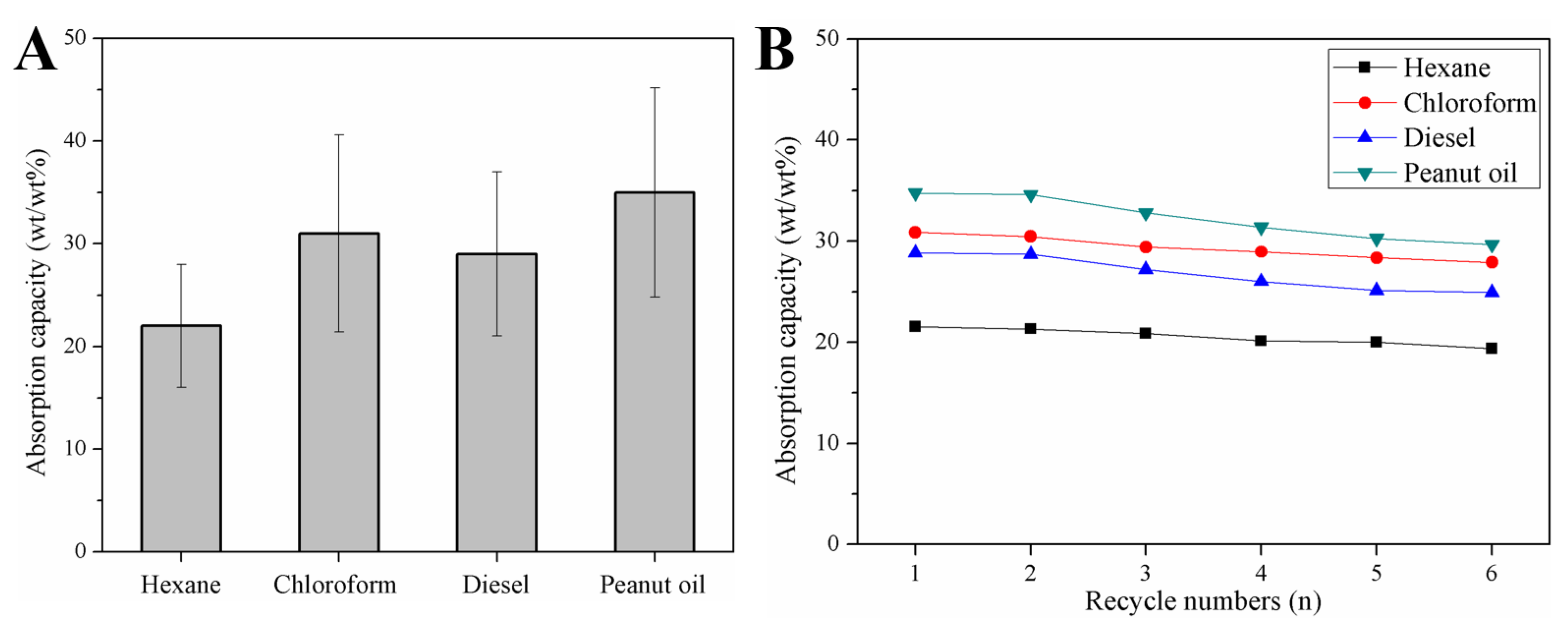
3.3. Absorption Capability
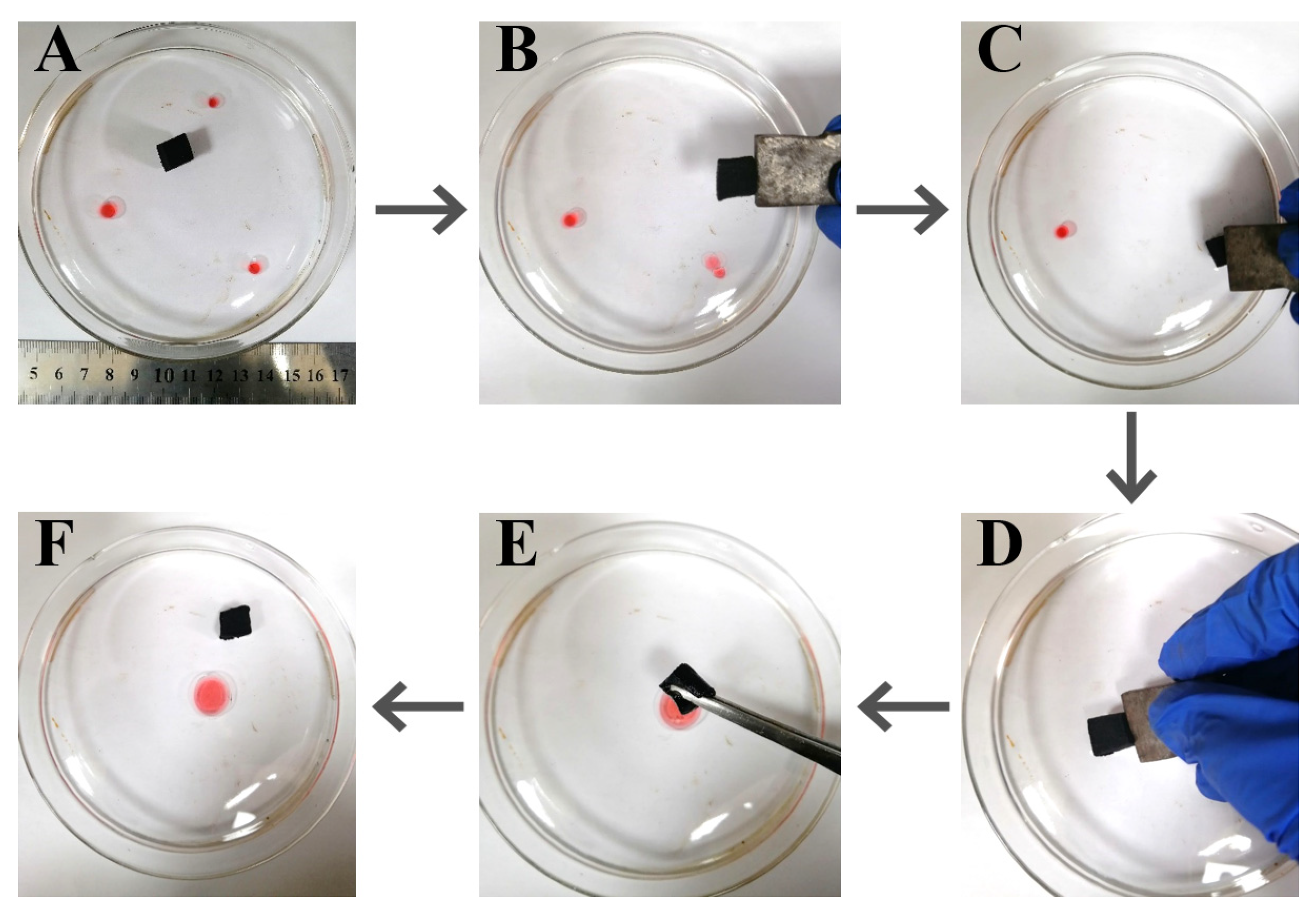
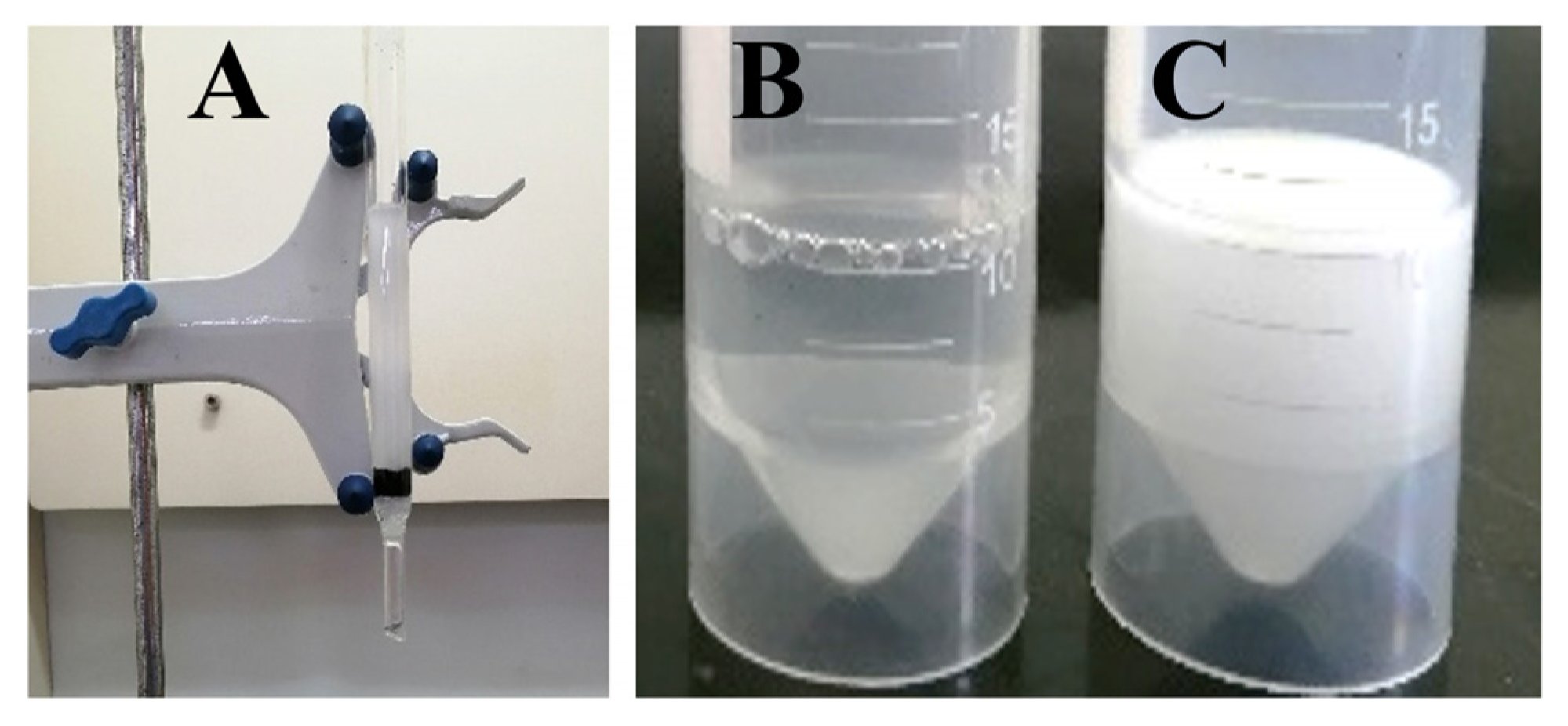
3.4. Oil–Water Demulsification
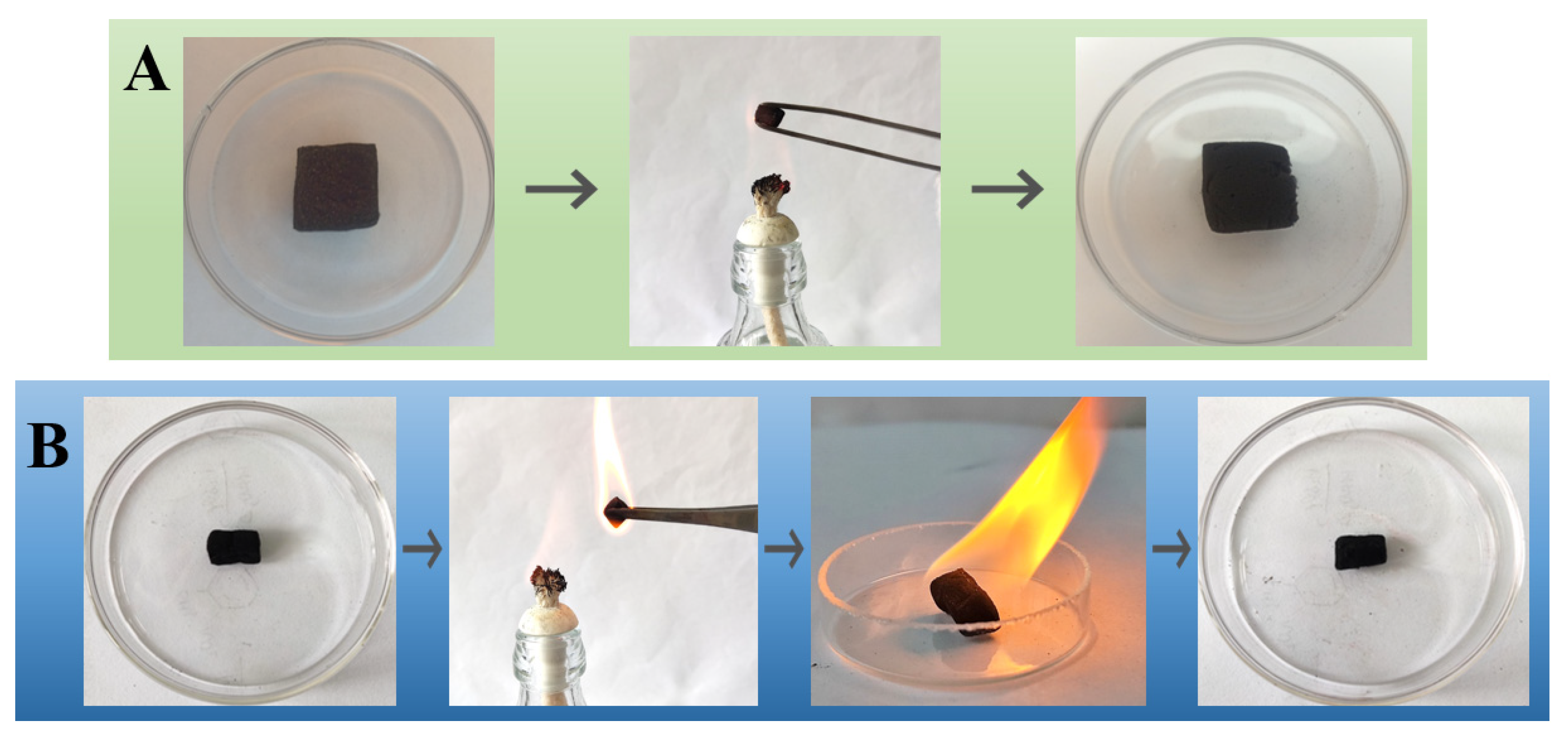
3.5. Refractory Property
3.6. Application Scenario in In Situ Burning of Oil Spills
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Abdullah, M.M.S.; Atta, A.M.; Al-Lohedan, H.A.; Alkhathlan, H.Z.; Khan, M.; Ezzat, A.O. Synthesis of green recyclable magnetic iron oxide nanomaterials coated by hydrophobic plant extracts for efficient collection of oil spills. Nanomaterials 2019, 9, 1505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Visco, A.; Quattrocchi, A.; Nocita, D.; Montanini, R.; Pistone, A. Polyurethane foams loaded with carbon nanofibers for oil spill recovery: Mechanical properties under fatigue conditions and selective absorption in oil/water mixtures. Nanomaterials 2021, 11, 735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mishra, S.; Chauhan, G.; Verma, S.; Singh, U. The emergence of nanotechnology in mitigating petroleum oil spills. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2022, 178, 113609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Asif, Z.; Chen, Z.; An, C.; Dong, J. Environmental impacts and challenges associated with oil spills on shorelines. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2022, 10, 762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Y.; Liu, Y.; Hu, C.; MacDonald, I.R.; Lu, Y. Chronic oiling in global oceans. Science 2022, 376, 1300–1304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, I.A.; Almeida, F.C.; Souza, T.C.; Bezerra, K.G.; Durval, I.J.; Converti, A.; Sarubbo, L.A. Oil spills: Impacts and perspectives of treatment technologies with focus on the use of green surfactants. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2022, 194, 143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, L.; Nedwed, T.; Daling, P.S.; Brandvik, P.J. Investigation of the spreading tendency of emulsified oil slicks on open systems. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2022, 180, 113739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Etkin, D.S.; Nedwed, T.J. Effectiveness of mechanical recovery for large offshore oil spills. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2021, 163, 111848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhaka, A.; Chattopadhyay, P. A review on physical remediation techniques for treatment of marine oil spills. J. Environ. Manag. 2021, 288, 112428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chapman, H.; Purnell, K.; Law, R.J.; Kirby, M.F. The use of chemical dispersants to combat oil spills at sea: A review of practice and research needs in Europe. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2007, 54, 827–838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Omer, A.M.; Eweida, B.Y.; Tamer, T.M.; Soliman, H.; Ali, S.M.; Zaatot, A.A.; Mohy-Eldin, M.S. Removal of oil spills by novel developed amphiphilic chitosan-g-citronellal schiff base polymer. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 19879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iturbe-Espinoza, P.; Bonte, M.; Gundlach, E.; Brandt, B.W.; Braster, M.; van Spanning, R.J. Adaptive changes of sediment microbial communities associated with cleanup of oil spills in Nigerian mangrove forests. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2022, 176, 113406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madhubashani, A.M.P.; Giannakoudakis, D.A.; Amarasinghe, B.M.W.P.K.; Rajapaksha, A.U.; Kumara, P.T.P.; Triantafyllidis, K.S.; Vithanage, M. Propensity and appraisal of biochar performance in removal of oil spills: A comprehensive review. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 288, 117676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wegeberg, S.; Fritt-Rasmussen, J.; Geertz-Hansen, O.; Wiktor Jr, J.; Bogø-Wilms, L.; Larsen, M.B.; Renvald, L.; Gustavson, K. Coastline in-situ burning of oil spills in the Arctic. Studies of the environmental impacts on the littoral zone community. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2021, 173, 113128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mullin, J.V.; Champ, M.A. Introduction/overview to in situ burning of oil spills. Spill Sci. Technol. Bull. 2003, 8, 323–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gatou, M.A.; Lagopati, N.; Tsoukleris, D.; Pavlatou, E.A. Commercial sponges as a novel technology for crude oil removal from seawater and industrial wastewater: A review. Biomed. J. Sci. Technol. Res. 2020, 25, 19426–19436. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Z.; An, C.; Lee, K.; Owens, E.; Boufadel, M.; Feng, Q. Dispersion modeling of particulate matter from the in-situ burning of spilled oil in the northwest Arctic area of Canada. J. Environ. Manag. 2022, 301, 113913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faksness, L.G.; Leirvik, F.; Taban, I.C.; Engen, F.; Jensen, H.V.; Holbu, J.W.; Dolva, H.; Bråtveit, M. Offshore field experiments with in-situ burning of oil: Emissions and burn efficiency. Environ. Res. 2022, 205, 112419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aurell, J.; Holder, A.; Gullett, B.; Lamie, N.; Arsava, K.; Conmy, R.; Sundaravadivelue, D.; Mitchell, W.; Stone, K. Analysis of emissions and residue from methods to improve efficiency of at—Sea, in situ oil spill burns. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2021, 173, 113016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dave, D.A.E.G.; Ghaly, A.E. Remediation technologies for marine oil spills: A critical review and comparative analysis. Am. J. Environ. Sci. 2011, 7, 423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, B.; Ye, X.; Zhang, B.; Jing, L.; Lee, K. Marine oil spills—Preparedness and countermeasures. World Seas Environ. Eval. 2019, 3, 407–426. [Google Scholar]
- Brussaard, C.P.; Peperzak, L.; Beggah, S.; Wick, L.Y.; Wuerz, B.; Weber, J.; Arey, J.S.; Burg, B.; Jonas, A.; Huisman, J.; et al. Immediate ecotoxicological effects of short-lived oil spills on marine biota. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 11206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Shi, L.A.; Ge, J.; Hu, B.C.; Ma, T.; Zhao, H.; Song, Y.H.; Li, C.; Yu, S.H. Joule-heated carbonized melamine sponge for high-speed absorption of viscous oil spills. Nano Res. 2021, 14, 2697–2702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kukkar, D.; Rani, A.; Kumar, V.; Younis, S.A.; Zhang, M.; Lee, S.S.; Tsang, C.W.; Kim, K.H. Recent advances in carbon nanotube sponge–based sorption technologies for mitigation of marine oil spills. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2020, 570, 411–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fang, Y.; Yan, L.; Liu, H. Facile preparation of hydrophobic melamine sponges using naturally derived urushiol for efficient oil/water separation. ACS Appl. Polym. Mater. 2020, 2, 3781–3788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shui, Y.; Xian, Y.; Chen, L.; Li, M.; Yao, Y.; Zhang, Q. High oil absorbable superhydrophobic melamine sponges and evaluation in oil spill clean-ups. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2020, 137, 49306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.T.; Wu, H.T.; Chen, W.Y.; He, F.A.; Li, D.H. Preparation of magnetic superhydrophobic melamine sponges for effective oil-water separation. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2019, 212, 40–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, W.; Wang, H. Magnetically driven motile superhydrophobic sponges for efficient oil removal. Appl. Mater. Today 2019, 15, 263–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, K.; Li, W.; Zhou, S.; Huang, G. Facile one-step fabrication of superhydrophobic melamine sponges by poly(phenol-amine) modification method for effective oil–water separation. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 429, 128348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, Y.; Yao, J. Design of melamine sponge-based three-dimensional porous materials toward applications. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2018, 57, 7322–7330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruan, C.; Ai, K.; Li, X.; Lu, L. A superhydrophobic sponge with excellent absorbency and flame retardancy. Angew. Chem. 2014, 126, 5662–5666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Weibel, J.A.; Garimella, S.V. Continuous oil–water separation using polydimethylsiloxane-functionalized melamine sponge. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2016, 55, 3596–3602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, M.; Men, X.; Xue, Q. One-pot fabrication of nanoporous polymer decorated materials: From oil-collecting devices to high-efficiency emulsion separation. J. Mater. Chem. A 2017, 5, 5077–5087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, Z.; Zhang, G.; Ouyang, Y.; Liang, Y.; Deng, Y.; Wang, C. Simple fabrication of multi-functional melamine sponges. Mater. Lett. 2017, 190, 119–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pomerantz, A.E.; Hammond, M.R.; Morrow, A.L.; Mullins, O.C.; Zare, R.N. Two-step laser mass spectrometry of asphaltenes. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2008, 130, 7216–7217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamkar, M.; Natale, G. A review on novel applications of asphaltenes: A valuable waste. Fuel 2021, 285, 119272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassanzadeh, M.; Abdouss, M. A comprehensive review on the significant tools of asphaltene investigation. Analysis and characterization techniques and computational methods. J. Pet. Eng. 2022, 208, 109611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, P.; Yao, Q.; Zhou, G.; Yan, X.; Li, S.; Dou, X.; Yang, M. Green preparation of nonflammable carbonized asphalt-melamine sponges as recyclable oil absorbents. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2019, 226, 235–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, Q.; Zhao, P.; Li, R.; Li, C.; Luo, Y.; Zhou, G.; Yang, M. Fabrication of recyclable carbonized asphalt-melamine sponges with high oil-absorption capability. J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol. 2017, 92, 1415–1420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atta, A.M.; Abdullah, M.M.S.; Al-Lohedan, H.A.; Mohamed, N.H. Novel superhydrophobic sand and polyurethane sponge coated with silica/modified asphaltene nanoparticles for rapid oil spill cleanup. Nanomaterials 2019, 9, 187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Enayat, S.; Tran, M.K.; Salpekar, D.; Kabbani, M.A.; Babu, G.; Ajayan, P.M.; Vargas, F.M. From crude oil production nuisance to promising energy storage material: Development of high-performance asphaltene-derived supercapacitors. Fuel 2020, 263, 116641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Behnamfard, A.; Chegni, K.; Alaei, R.; Veglio, F. The effect of thermal and acid treatment of kaolin on its ability for cyanide removal from aqueous solutions. Environ. Earth Sci. 2019, 78, 408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Z.; Pan, Z.; Zhao, Y.; Qian, L.; Shen, J.; Xia, K.; Guo, Y.; Qu, Z. Removal of Hg2+ with polypyrrole-functionalized Fe3O4/kaolin: Synthesis, performance and optimization with response surface methodology. Nanomaterials 2020, 10, 1370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fadillah, G.; Yudha, S.P.; Sagadevan, S.; Fatimah, I.; Muraza, O. Magnetic iron oxide/clay nanocomposites for adsorption and catalytic oxidation in water treatment applications. Open Chem. 2020, 18, 1148–1166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, W.; Zhang, S.; Sun, J.; Li, H.; Liu, X.; Gu, X. Effects of surface acid-activated kaolinite on the fire performance of polypropylene composite. Thermochim. Acta 2017, 648, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, W.; Zhao, S.; Wu, H.; Deligeer, W.; Asuha, S. Direct acid activation of kaolinite and its effects on the adsorption of methylene blue. Appl. Clay Sci. 2016, 126, 98–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, J.; Wang, F.; Yin, X.; Yu, J.; Ding, B. Polybenzoxazine-functionalized melamine sponges with enhanced selective capillarity for efficient oil spill cleanup. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2018, 10, 40274–40285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, R.; Liu, S.; Wang, R.; Fu, T.; Zhang, R.; Zhang, Q.; Zhou, Y. In situ modification of melamine sponge by MgAl-LDH with super-hydrophobicity and excellent harsh environment tolerance for high flux emulsion separation. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2022, 291, 120916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Chen, Z.; Zhang, J.; Ai, S.; Tang, H. Ultralight and thermal insulation carbon foam/SiO2 aerogel composites. J. Porous Mater. 2019, 26, 1305–1312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makoś-Chełstowska, P.; Słupek, E.; Małachowska, A. Superhydrophobic sponges based on green deep eutectic solvents for spill oil removal from water. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 425, 127972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kabataş, M.B.; Çetinkaya, S. Petroleum asphaltene-derived highly porous carbon for the efficient removal of pharmaceutical compounds in water. J. Porous Mater. 2022, 29, 1211–1224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AlHumaidan, F.S.; Rana, M.S.; Lababidi, H.M.S.; Hauser, A. Pyrolysis of asphaltenes derived from residual oils and their thermally treated pitch. ACS Omega 2020, 5, 24412–24421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.; Deng, Y.; Tong, Z.; Wang, C. Multifunctional foams derived from poly(melamine formaldehyde) as recyclable oil absorbents. J. Mater. Chem. A 2014, 2, 9994–9999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avila, A.F.; Munhoz, V.C.; de Oliveira, A.M.; Santos, M.C.; Lacerda, G.R.; Gonçalves, C.P. Nano-based systems for oil spills control and cleanup. J. Hazard. Mater. 2014, 272, 20–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, L.; Zhu, H.; Wu, W.; Lin, D.; Yang, K. A durable superhydrophobic porous polymer coated sponge for efficient separation of immiscible oil/water mixtures and oil-in-water emulsions. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 425, 127980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| AS@MS | m-AS/Kaolin@MS | |
|---|---|---|
| weight loss (wt%) | 82 | 67 |
| volume loss (vol%) | 86 | 78 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chen, Q.; Zhang, L.; Shan, Y.; Liu, Y.; Zhao, D. Novel Magnetically Driven Superhydrophobic Sponges Coated with Asphaltene/Kaolin Nanoparticles for Effective Oil Spill Cleanup. Nanomaterials 2022, 12, 3527. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano12193527
Chen Q, Zhang L, Shan Y, Liu Y, Zhao D. Novel Magnetically Driven Superhydrophobic Sponges Coated with Asphaltene/Kaolin Nanoparticles for Effective Oil Spill Cleanup. Nanomaterials. 2022; 12(19):3527. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano12193527
Chicago/Turabian StyleChen, Qiang, Lingling Zhang, Yuanhang Shan, Yindong Liu, and Dongfeng Zhao. 2022. "Novel Magnetically Driven Superhydrophobic Sponges Coated with Asphaltene/Kaolin Nanoparticles for Effective Oil Spill Cleanup" Nanomaterials 12, no. 19: 3527. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano12193527
APA StyleChen, Q., Zhang, L., Shan, Y., Liu, Y., & Zhao, D. (2022). Novel Magnetically Driven Superhydrophobic Sponges Coated with Asphaltene/Kaolin Nanoparticles for Effective Oil Spill Cleanup. Nanomaterials, 12(19), 3527. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano12193527





