Significance of Hydroxyl Groups on the Optical Properties of ZnO Nanoparticles Combined with CNT and PEDOT:PSS
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Synthesis
2.1.1. ZnO
2.1.2. ZnO-CNT Hybrids
2.1.3. ZnO-PEDOT:PSS Hybrids
2.2. Characterization
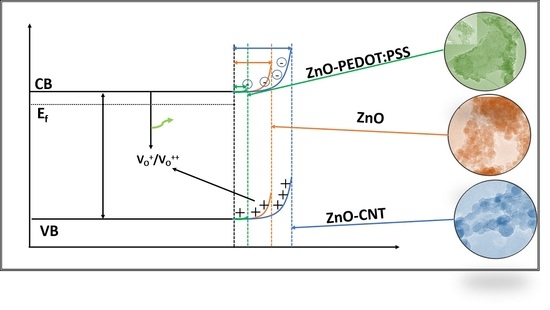
3. Results
3.1. Structure and Morphology
3.2. Optical Properties
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Huang, J.; Yin, Z.; Zheng, Q. Applications of ZnO in organic and hybrid solar cells. Energy Environ. Sci. 2011, 4, 3861–3877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Periyayya, U.; Kang, J.H.; Ryu, J.H.; Hong, C.-H. Synthesis and improved luminescence properties of OLED/ZnO hybrid materials. Vacuum 2011, 86, 254–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagpal, K.; Rauwel, E.; Ducroquet, F.; Rauwel, P. Assessment of the optical and electrical properties of light-emitting diodes containing carbon-based nanostructures and plasmonic nanoparticles: A review. Beilstein J. Nanotechnol. 2021, 12, 1078–1092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shirota, Y.; Kageyama, H. 1—Organic materials for optoelectronic applications: Overview. In Handbook of Organic Materials for Electronic and Photonic Devices, 2nd ed.; Ostroverkhova, O., Ed.; Woodhead Publishing: Sawston, UK, 2019; pp. 3–42. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, K.J.; Yan, Z.; Han, M.; Rogers, J.A. Inorganic semiconducting materials for flexible and stretchable electronics. NPJ Flex. Electron. 2017, 1, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Könenkamp, R.; Word, R.C.; Godinez, M. Ultraviolet Electroluminescence from ZnO/Polymer Heterojunction Light-Emitting Diodes. Nano Letters 2005, 5, 2005–2008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biju, V.; Itoh, T.; Anas, A.; Sujith, A.; Ishikawa, M. Semiconductor quantum dots and metal nanoparticles: Syntheses, optical properties, and biological applications. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2008, 391, 2469–2495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, P.; Yan, H.; Mao, S.; Russo, R.; Johnson, J.; Saykally, R.; Morris, N.; Pham, J.; He, R.; Choi, H.-J. Controlled Growth of ZnO Nanowires and Their Optical Properties. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2002, 12, 323–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huseynova, G.; Hyun Kim, Y.; Lee, J.-H.; Lee, J. Rising advancements in the application of PEDOT:PSS as a prosperous transparent and flexible electrode material for solution-processed organic electronics. J. Inf. Disp. 2020, 21, 71–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, K.; Zhang, S.; Li, P.; Xia, Y.; Zhang, X.; Du, D.; Isikgor, F.H.; Ouyang, J. Review on application of PEDOTs and PEDOT:PSS in energy conversion and storage devices. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 2015, 26, 4438–4462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, Y.; Müller-Meskamp, L.; Vandewal, K.; Leo, K. PEDOT:PSS with embedded TiO2 nanoparticles as light trapping electrode for organic photovoltaics. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2016, 108, 253302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, B.K.; Khare, N.; Ahmad, S. A ZnO/PEDOT:PSS based inorganic/organic hetrojunction. Solid State Commun. 2009, 149, 771–774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, B.; Fu, Z.; Jia, Y. Green luminescent center in undoped zinc oxide films deposited on silicon substrates. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2001, 79, 943–945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raji, R.; Gopchandran, K.G. ZnO nanostructures with tunable visible luminescence: Effects of kinetics of chemical reduction and annealing. J. Sci. Adv. Mater. Devices 2017, 2, 51–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polsongkram, D.; Chamninok, P.; Pukird, S.; Chow, L.; Lupan, O.; Chai, G.; Khallaf, H.; Park, S.; Schulte, A. Effect of synthesis conditions on the growth of ZnO nanorods via hydrothermal method. Phys. B Condens. Matter 2008, 403, 3713–3717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Chen, R.; Xiang, L.; Komarneni, S. Synthesis, properties and applications of ZnO nanomaterials with oxygen vacancies: A review. Ceram. Int. 2018, 44, 7357–7377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagpal, K.; Rapenne, L.; Wragg, D.S.; Rauwel, E.; Rauwel, P. The role of CNT in surface defect passivation and UV emission intensification of ZnO nanoparticles. Nanomater. Nanotechnol. 2022, 12, 18479804221079419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rauwel, E.; Galeckas, A.; Rauwel, P.; Sunding, M.F.; Fjellvåg, H. Precursor-Dependent Blue-Green Photoluminescence Emission of ZnO Nanoparticles. J. Phys. Chem. C 2011, 115, 25227–25233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niederberger, M. Nonaqueous Sol–Gel Routes to Metal Oxide Nanoparticles. Acc. Chem. Res. 2007, 40, 793–800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.; Somaratne, R.M.D.S.; Whitten, J.E. Effect of Adsorption on the Photoluminescence of Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles. J. Phys. Chem. C 2018, 122, 18982–18994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, A.; Singh, B.P.; Dhar, S.; Gondorf, A.; Spasova, M. Effect of surface groups on the luminescence property of ZnO nanoparticles synthesized by sol–gel route. Surf. Sci. 2012, 606, L13–L17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahai, A.; Goswami, N. Probing the dominance of interstitial oxygen defects in ZnO nanoparticles through structural and optical characterizations. Ceram. Int. 2014, 40, 14569–14578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Šarić, A.; Gotić, M.; Štefanić, G.; Dražić, G. Synthesis of ZnO particles using water molecules generated in esterification reaction. J. Mol. Struct. 2017, 1140, 12–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leitão Muniz, F.; Miranda, M.; Morilla-Santos, C.; Sasaki, J. The Scherrer equation and the dynamical theory of X-ray diffraction. Acta Crystallogr. Sect. A Found. Adv. 2016, 72, 385–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hosseini Largani, S.; Akbarzadeh Pasha, M. The effect of concentration ratio and type of functional group on synthesis of CNT–ZnO hybrid nanomaterial by an in situ sol–gel process. Int. Nano Lett. 2017, 7, 25–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Wang, X.; Fang, D. A review on C1s XPS-spectra for some kinds of carbon materials. Fuller. Nanotub. Carbon Nanostructures 2020, 28, 1048–1058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aïssa, B.; Fauteux, C.; El Khakani, M.A.; Daniel, T. Structural and photoluminescence properties of laser processed ZnO/carbon nanotube nanohybrids. J. Mater. Res. 2009, 24, 3313–3320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossell, M.D.; Kuebel, C.; Ilari, G.; Rechberger, F.; Heiligtag, F.J.; Niederberger, M.; Koziej, D.; Erni, R. Impact of sonication pretreatment on carbon nanotubes: A transmission electron microscopy study. Carbon 2013, 61, 404–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mengistie, D.A.; Ibrahem, M.A.; Wang, P.-C.; Chu, C.-W. Highly Conductive PEDOT:PSS Treated with Formic Acid for ITO-Free Polymer Solar Cells. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2014, 6, 2292–2299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeferino, R.S.; Flores, M.B.; Pal, U. Photoluminescence and Raman Scattering in Ag-doped ZnO Nanoparticles. J. Appl. Phys. 2011, 109, 014308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Q.; Dai, Y.; Li, C.; Yang, L.; Li, X.; Cui, C. Correlation between oxygen vacancies and dopant concentration in Mn-doped ZnO nanoparticles synthesized by co-precipitation technique. J. Alloys Compd. 2016, 684, 669–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naeem, M.; Qaseem, S.; Gul, I.H.; Maqsood, A. Study of active surface defects in Ti doped ZnO nanoparticles. J. Appl. Phys. 2010, 107, 124303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khachadorian, S.; Gillen, R.; Choi, S.; Ton-That, C.; Kliem, A.; Maultzsch, J.; Phillips, M.R.; Hoffmann, A. Effects of annealing on optical and structural properties of zinc oxide nanocrystals. Phys. Status Solidi B 2015, 252, 2620–2625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.B.; Huang, G.J.; Zhong, X.L.; Sun, L.Z.; Zhou, Y.C.; Liu, E.H. Raman scattering and high temperature ferromagnetism of Mn-doped ZnO nanoparticles. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2006, 88, 252502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gluba, M.A.; Nickel, N.H.; Karpensky, N. Interstitial zinc clusters in zinc oxide. Phys. Rev. B 2013, 88, 245201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montanheiro, T.L.d.A.; de Menezes, B.R.C.; Ribas, R.G.; Montagna, L.S.; Campos, T.M.B.; Schatkoski, V.M.; Righetti, V.A.N.; Passador, F.R.; Thim, G.P. Covalently γ-aminobutyric acid-functionalized carbon nanotubes: Improved compatibility with PHBV matrix. SN Appl. Sci. 2019, 1, 1177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsyganenko, A.A.; Lamotte, J.; Saussey, J.; Lavalley, J.C. Bending vibrations of OH groups resulting from H2 dissociation on ZnO. J. Chem. Soc. Faraday Trans. 1 Phys. Chem. Condens. Phases 1989, 85, 2397–2403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scarano, D.; Bertarione, S.; Cesano, F.; Vitillo, J.G.; Zecchina, A. Plate-like zinc oxide microcrystals: Synthesis and characterization of a material active toward hydrogen adsorption. Catal. Today 2006, 116, 433–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dent, A.L.; Kokes, R.J. Hydrogenation of ethylene by zinc oxide. I. Role of slow hydrogen chemisorption. J. Phys. Chem. 1969, 73, 3772–3780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, S.H.; Chiang, C.H.; Kao, F.S.; Tien, C.L.; Wu, C.G. Unraveling the Enhanced Electrical Conductivity of PEDOT:PSS Thin Films for ITO-Free Organic Photovoltaics. IEEE Photonics J. 2014, 6, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.; Kim, Y.; Cho, H.; Lee, J.-g.; Kim, J.H. Improvement of PEDOT:PSS linearity via controlled addition process. RSC Adv. 2019, 9, 17318–17324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Sun, K.; Fu, J.; Chen, R.; Li, M.; Zang, Z.; Liu, X.; Li, B.; Gong, H.; Ouyang, J. Enhancement of Conductivity and Thermoelectric Property of PEDOT:PSS via Acid Doping and Single Post-Treatment for Flexible Power Generator. Adv. Sustain. Syst. 2018, 2, 1800085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, K.; Yarbrough, R.; Froeschle, M.; White, J.; Rathnayake, H. Band gap engineered zinc oxide nanostructures via a sol–gel synthesis of solvent driven shape-controlled crystal growth. RSC Adv. 2019, 9, 14638–14648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rauwel, P.; Galeckas, A.; Salumaa, M.; Ducroquet, F.; Rauwel, E. Photocurrent generation in carbon nanotube/cubic-phase HfO2 nanoparticle hybrid nanocomposites. Beilstein J. Nanotechnol. 2016, 7, 1075–1085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar Jangir, L.; Kumari, Y.; Kumar, A.; Kumar, M.; Awasthi, K. Investigation of luminescence and structural properties of ZnO nanoparticles, synthesized with different precursors. Mater. Chem. Front. 2017, 1, 1413–1421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oudhia, A.; Choudhary, A.; Sharma, S.; Aggrawal, S.; Dhoble, S.J. Study of defect generated visible photoluminescence in zinc oxide nano-particles prepared using PVA templates. J. Lumin. 2014, 154, 211–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vanheusden, K.; Warren, W.L.; Seager, C.H.; Tallant, D.R.; Voigt, J.A.; Gnade, B.E. Mechanisms behind green photoluminescence in ZnO phosphor powders. J. Appl. Phys. 1996, 79, 7983–7990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rauwel, P.; Galeckas, A.; Rauwel, E. Enhancing the UV Emission in ZnO–CNT Hybrid Nanostructures via the Surface Plasmon Resonance of Ag Nanoparticles. Nanomaterials 2021, 11, 452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Przezdziecka, E.; Guziewicz, E.; Jarosz, D.; Snigurenko, D.; Sulich, A.; Sybilski, P.; Jakiela, R.; Paszkowicz, W. Influence of oxygen-rich and zinc-rich conditions on donor and acceptor states and conductivity mechanism of ZnO films grown by ALD—Experimental studies. J. Appl. Phys. 2020, 127, 075104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]







| Sample Name | CNT (wt%) | PEDOT:PSS (wt%) |
|---|---|---|
| ZnO-D-CNT | ~1 | - |
| ZnO-A-CNT | ~1 | - |
| ZnO-D-PEDOT:PSS | - | ~95 |
| ZnO-A-PEDOT:PSS | - | ~95 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Nagpal, K.; Rauwel, E.; Estephan, E.; Soares, M.R.; Rauwel, P. Significance of Hydroxyl Groups on the Optical Properties of ZnO Nanoparticles Combined with CNT and PEDOT:PSS. Nanomaterials 2022, 12, 3546. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano12193546
Nagpal K, Rauwel E, Estephan E, Soares MR, Rauwel P. Significance of Hydroxyl Groups on the Optical Properties of ZnO Nanoparticles Combined with CNT and PEDOT:PSS. Nanomaterials. 2022; 12(19):3546. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano12193546
Chicago/Turabian StyleNagpal, Keshav, Erwan Rauwel, Elias Estephan, Maria Rosario Soares, and Protima Rauwel. 2022. "Significance of Hydroxyl Groups on the Optical Properties of ZnO Nanoparticles Combined with CNT and PEDOT:PSS" Nanomaterials 12, no. 19: 3546. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano12193546
APA StyleNagpal, K., Rauwel, E., Estephan, E., Soares, M. R., & Rauwel, P. (2022). Significance of Hydroxyl Groups on the Optical Properties of ZnO Nanoparticles Combined with CNT and PEDOT:PSS. Nanomaterials, 12(19), 3546. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano12193546