Muon Irradiation of ZnO Rods: Superparamagnetic Nature Induced by Defects
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
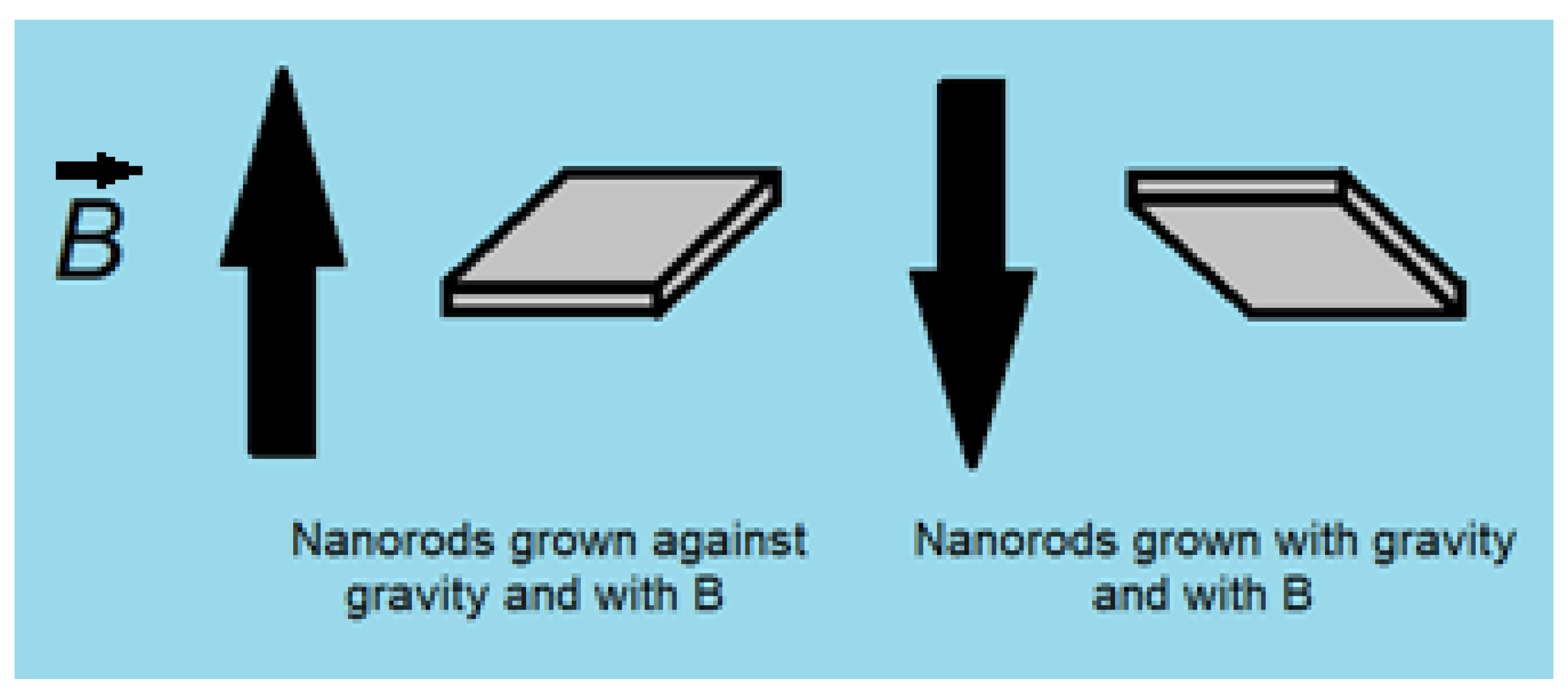
2.1. Synthesis
2.2. Conventional Characterization Methods
2.3. μSR
3. Results and Discussion
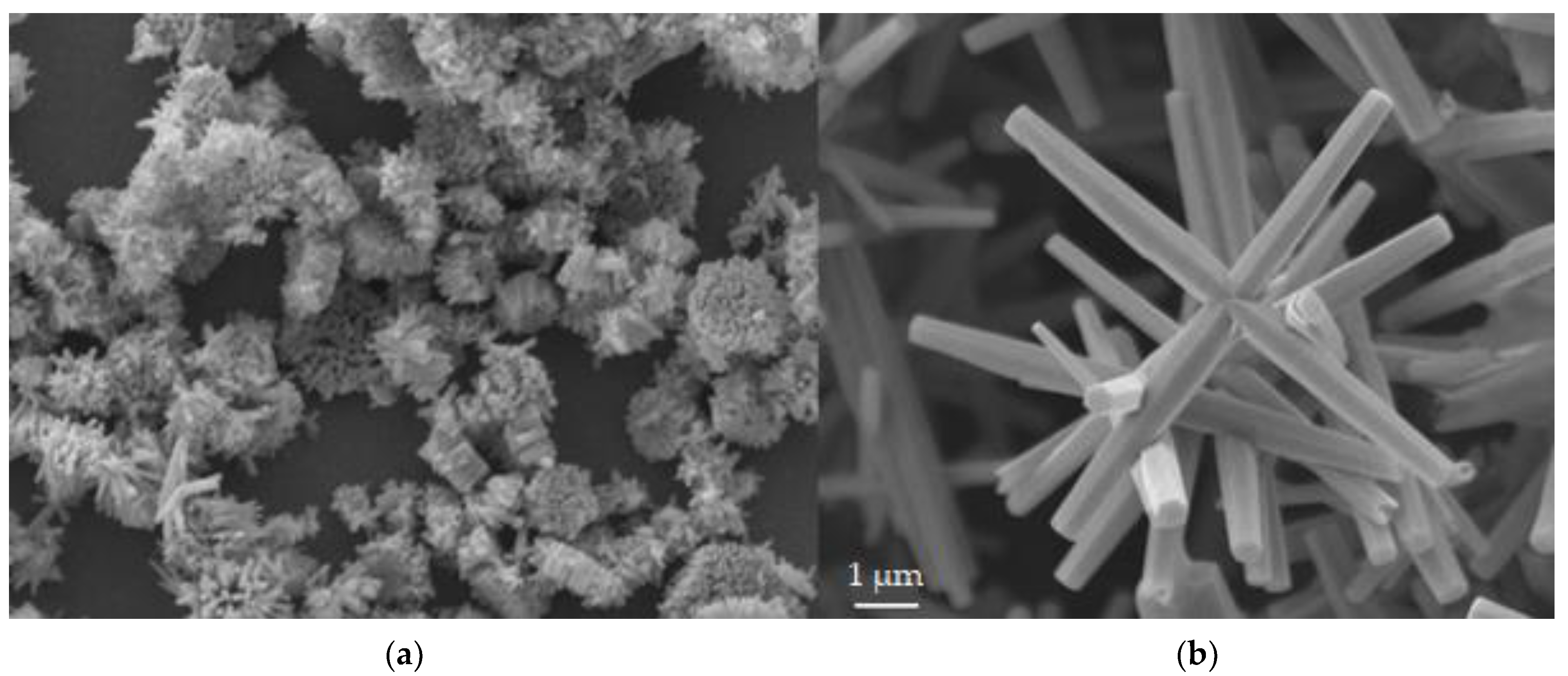
3.1. Morphology
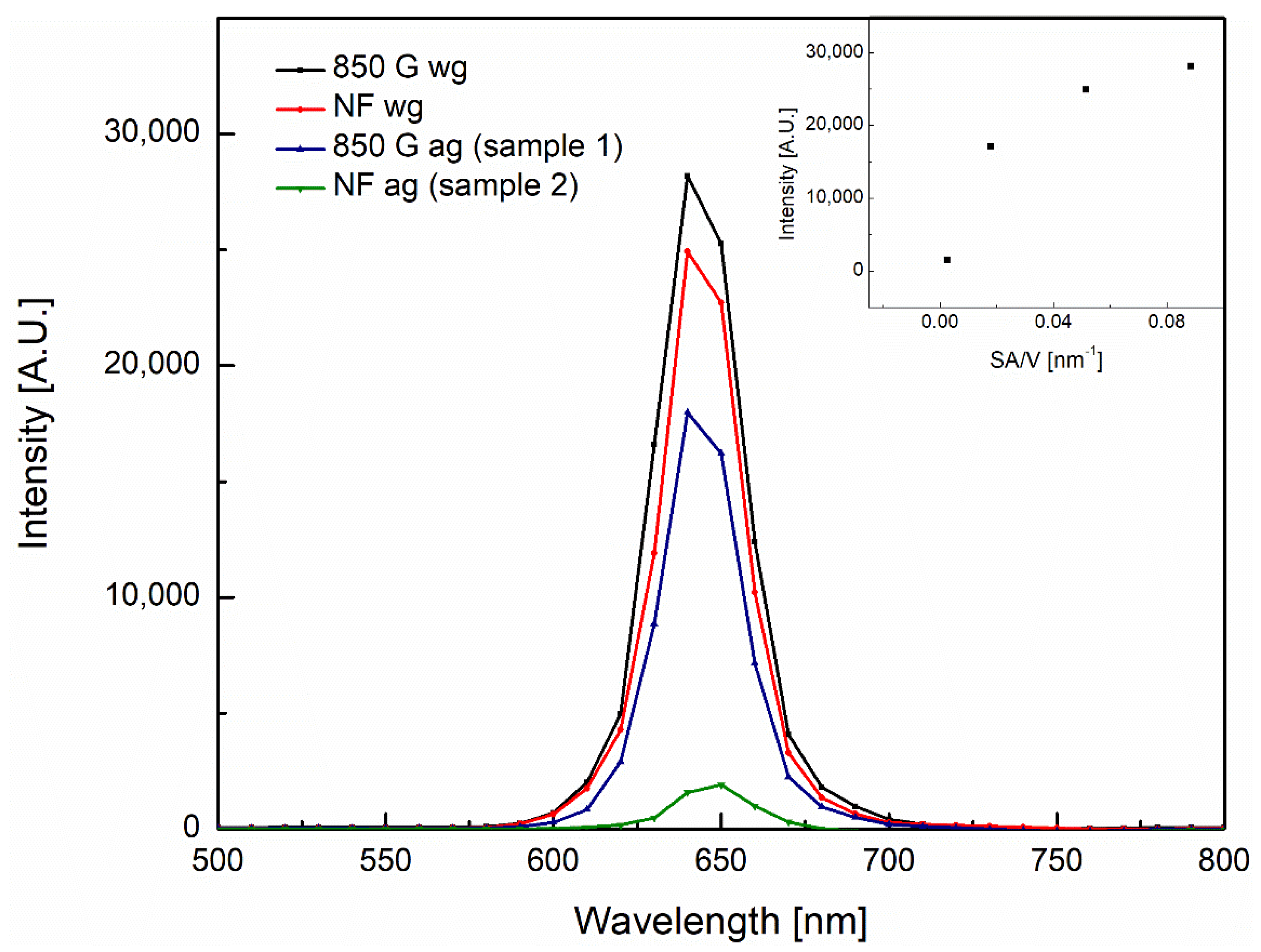
3.2. Photoluminescence/X-Ray Photoelectron Spectroscopy
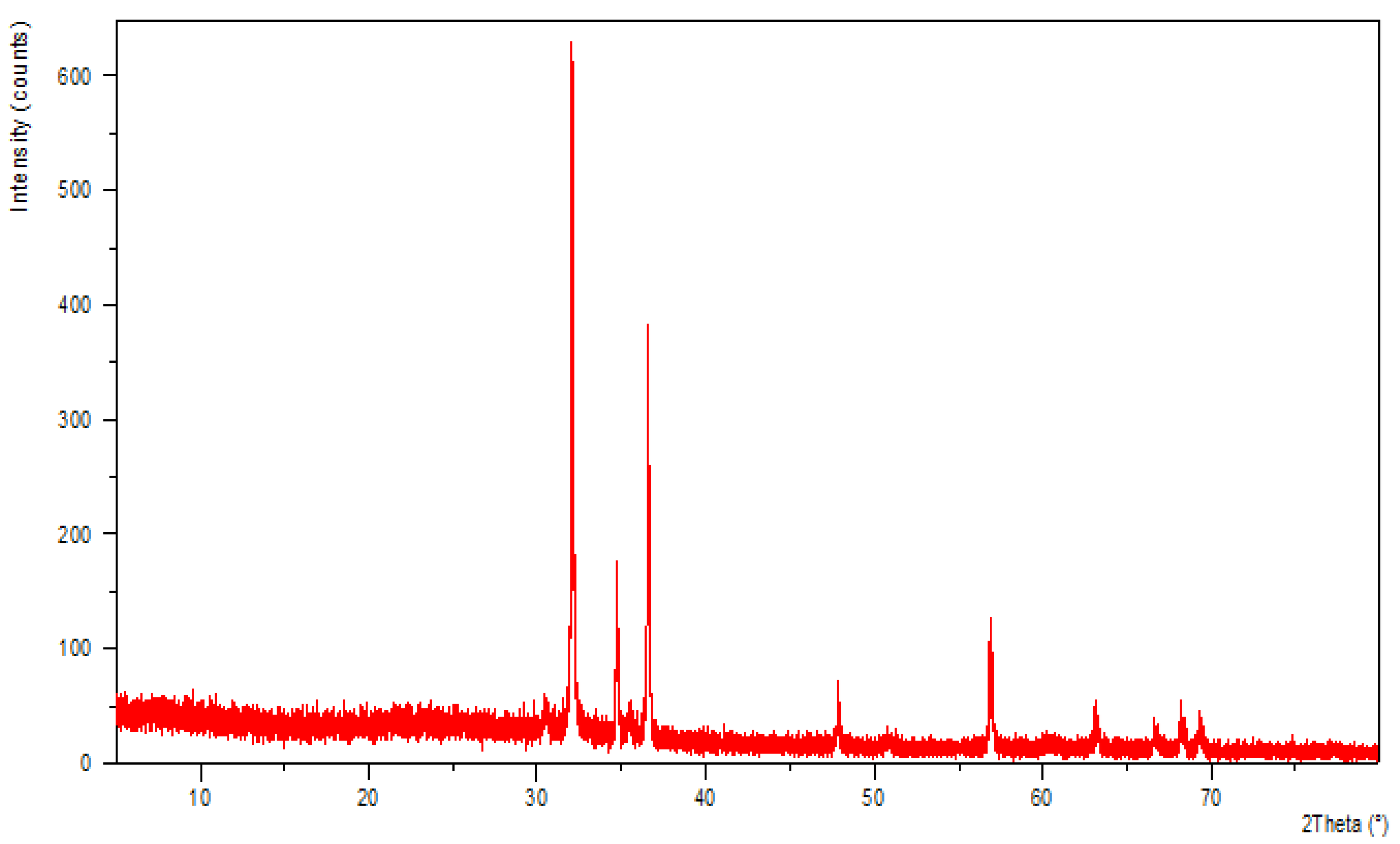
3.3. X-ray Diffraction
3.4. Magnetic Susceptibility
3.5. Zero-Field μSR
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Decan, M.R.; Impellizeri, S.; Marin, M.; Scaiano, J.C. Copper nanoparticle heterogeneous catalytic ‘click’ cycloaddition confirmed by single-molecule spectroscopy. Nat. Commun. 2014, 5, 4612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Khamarui, S.; Saima, Y.; Laha, R.M.; Ghosh, S.; Maiti, D. Functionalized MnVI-nanoparticles: An advanced high-valent magnetic catalyst. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 8636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.; Jang, J.; Choi, J.; Moon, S.H.; Noh, S.; Kim, J.; Kim, J.; Kim, I.; Park, K.I.; Cheon, J. Exchange-coupled magnetic nanoparticles for efficient heat induction. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2011, 6, 418–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reiss, G.; Hutten, A. Magnetic nanoparticles: Applications beyond data storage. Nat. Mater. 2005, 4, 725–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Landry, C.J.; Burns, F.P.; Baerlocher, F.; Ghandi, K. Novel Solid-State Microbial Sensors Based on ZnO Nanorod Arrays. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2018, 28, 1706309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torres-Díaz, I.; Rinaldi, C. Recent progress in ferrofluids research: Novel applications of magnetically controllable and tunable fluids. Soft Matter 2014, 10, 8584–8602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lahooti, A.; Sarkar, S.; Laurent, S.; Shanehsazzadeh, S. Dual nano-sized contrast agents in PET/MRI: A systematic review. Contrast Media Mol. Imaging 2016, 11, 428–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, Y.; Chen, D.; Shang, P.; Yin, D. A review of magnet systems for targeted drug delivery. J. Control. Release 2019, 302, 90–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yazyev, O.V.; Helm, L. Defect-induced magnetism in graphene. Phys. Rev. B 2007, 75, 125408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bean, C.P.; Livingston, J.D. Superparamagnetism. J. Appl. Phys. 1959, 30, S120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramazanov, S.; Sobola, D.; Orudzhev, F.; Knápek, A.; Polčák, J.; Potoček, M.; Kaspar, P.; Dallaev, R. Surface Modification and Enhancement of Ferromagnetism in BiFeO3 Nanofilms Deposited on HOPG. Nanomaterials 2020, 10, 1990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bedanta, S.; Kleemann, W. Supermagnetism. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 2009, 42, 013001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbasalipourkabir, R.; Moradi, H.; Zarei, S.; Asadi, S.; Salehzadeh, A.; Ghafourikhosroshahi, A.; Mortazavi, M.; Ziamajidi, N. Toxicity of zinc oxide nanoparticles on adult male Wistar rats. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2015, 84, 154–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koshy, O.; Khadar, M. Superparamagnetism in undoped ZnO nanorods. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2015, 346, 528–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, C.; Sun, S. New forms of superparamagnetic nanoparticles for biomedical applications. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2013, 65, 732–743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghosha, B.; Sardarb, M.; Banerjeea, S. Cooperative ordering of superparamagnetic ZnO nanograins. arXiv 2010, arXiv:1010.2381. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, Q.; Zhou, S.; Schmidt, H. Magnetic properties of ZnO nanopowders. J. Alloys Compd. 2009, 487, 665–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuo, X.; Yoon, S.; Yang, A.; Duan, W.; Vittoria, C.; Harris, V.G. Ferromagnetism in pure wurtzite zinc oxide. J. Appl. Phys. 2009, 105, 07C508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Botello-Mendez, A.R.; Lopez-Urias, F.; Terrones, M.; Terrones, H. Magnetic behavior in zinc oxide zigzag nanoribbons. Nano Lett. 2008, 8, 1562–1565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tietze, T.; Audehm, P.; Chen, Y.C.; Schütz, G.; Straumal, B.B.; Protasova, S.G.; Mazilkin, A.A.; Straumal, P.B.; Prokscha, T.; Luetkens, H.; et al. Interfacial dominated ferromagnetism in nanograined ZnO: A μSR and DFT study. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 8871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yun, J.; Zhang, Z.; Yin, T. Effect of Intrinsic Point Defect on the Magnetic Properties of ZnO Nanowire. Sci. World J. 2013, 2013, 541496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Djurisic, A.B.; Leung, Y.H.; Tam, K.H.; Hsu, Y.F.; Ding, L.; Ge, W.K.; Zhong, Y.C.; Wong, K.S.; Chan, W.K.; Tam, H.L.; et al. Defect emissions in ZnO nanostructures. Nanotechnology 2007, 18, 095702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jackson, T.J.; Binns, C.; Forgan, E.M.; Morenzoni, E.; Niedermayer, C.; Gluckler, H.; Hofer, A.; Leutkens, H.; Prokscha, T.; Riseman, T.M.; et al. Superparamagnetic relaxation in iron nanoclusters measured by low energy muon spin rotation. J. Phys. Condens. Matter 2000, 12, 1399–1411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiarelli, R.; Novak, M.A.; Rassat, A.; Tholence, J.L. A ferromagnetic transition at 1.48 K in an organic nitroxide. Nature 1993, 363, 147–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chattopadhyay, M.K.; Roy, S.B.; Chaddah, P. Kinetic arrest of the first-order ferromagnetic-to-antiferromagnetic transition in Ce(Fe0.96Ru0.04)2: Formation of a magnetic glass. Phys. Rev. B 2005, 72, 180401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yoon, S.; Han, K.H.; Suh, B.J.; Jang, Z.H.; Kim, J.H.; Jung, D.Y. Magnetic properties of thiol-capped gold nanoparticles. J. Korean Phys. Soc. 2012, 60, 7–1078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bewley, R.I.; Cywinski, R. Muon spin relaxation in a superparamagnet: Field dynamics in Cu98Co2. Phys. Rev. B 1998, 58, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Gaashani, R.; Radiman, S.; Daud, A.R.; Tabet, N.; Al-Douri, Y. XPS and optical studies of different morphologies of ZnO nanostructures prepared by microwave methods. Ceram. Int. 2013, 39, 2283–2292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- West, A.R. Solid State Chemistry and Its Applications; Wiley: New York, NY, USA, 2014; pp. 26–28. [Google Scholar]
- Borysiewicz, M.A. ZnO as a functional material, a review. Crystals 2019, 9, 505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dellis, S.; Pliatsikas, N.; Kalfagiannis, N.; Lidor-Shalev, O.; Papaderakis, A.; Vourlias, G.; Sotiropoulos, S.; Koutsogeorgis, D.C.; Mastai, Y.; Patsalas, P. Broadband luminescence in defect-engineered electrochemically produced porous Si/ZnO nanostructures. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 6988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohite, R.S.; Roy, A. Significant enhancement in the conductivity of Al-doped zinc oxide thin films for TCO application. Int. J. Nanosci. 2016, 15, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raj, V.; Balaji, P.; Joshi, M.; Kumar, M. Ag Grafted ZnO nanoplates for photocatalytic applications. Mater. Focus 2014, 3, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le, L.P.; Luke, G.M.; Sternlieb, B.J.; Uemura, Y.J. Muon-spin-rotation studies in single-crystal Sr2CuO2Cl2. Phys. Rev. B 1990, 42, 2182–2187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dalmas de Reotier, P.; Yaouanc, A. Muon spin rotation and relaxation in magnetic materials. J. Phys Condens. Matter 1997, 9, 9113–9166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rodriguez, J.; Amato, A.; Pomjakushina, E. Muon diffusion in diluted paramagnetic systems. arXiv 2011, arXiv:1112.1618. [Google Scholar]
- Shimomura, K.; Nishiyama, K.; Kadono, R. Electronic Structure of the Muonium Center as a Shallow Donor in ZnO. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2002, 89, 255505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lord, J.S. Muon methods for studying nanomagnetism. J. Phys Conf. Ser. 2005, 17, 014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moscoso-Londoño, O.; Tancredi, P.; Muraca, D.; Mendoza Zélis, P.; Coral, D.; Fernández van Raap, M.B.; Wolff, U.; Neu, V.; Damm, C.; de Oliveira, C.L.P.; et al. Different approaches to analyze the dipolar interaction effects on diluted and concentrated granular superparamagnetic systems. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2017, 428, 105–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frandsen, B.A.; Read, C.; Stevens, J.; Walker, C.; Christiansen, M.; Harrison, R.G.; Chesnel, K. Superparamagnetic dynamics and blocking transition in Fe3O4 nanoparticles probed by vibrating sample magnetometry and muon spin relaxation. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2101.00258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, E.; Yu, H.; Kim, Y.; Yi, G.; Choi, Y.; Han, S. Local Structural and Optical Properties of ZnO Nanoparticles. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2010, 10, 3562–3565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Theerthagiri, J.; Salla, S.; Senthil, R.A.; Nithyadharseni, P.; Madankumar, A.; Arunachalam, P.; Maiyalagan, T.; Kim, H. A review on ZnO nanostructured materials: Energy, environmental and biological applications. Nanotechnology 2019, 30, 392001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nishad, K.K.; Pandey, R.K. Size dependent ferromagnetism in dodecyl amine capped ZnO nanoparticles. Mater. Sci. Eng. B 2013, 178, 1380–1389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zargar Shoushtari, M.; Poormoghadam, A.; Farbod, M. The size dependence of the magnetic properties of ZnO and Zn 1-x Ni x O nanoparticles. Mater. Res. Bull. 2017, 88, 315–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tóthová, E.; Senna, M.; Yermakov, A.; Kováč, J.; Dutková, E.; Hegedüs, M.; Kaňuchová, M.; Baláž, M.; Bujňáková, Z.; Briančin, J.; et al. Zn source-dependent magnetic properties of undoped ZnO nanoparticles from mechanochemically derived hydrozincite. J. Alloys Compd. 2019, 787, 1249–1259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nair, S.; Sasidharan, A.; Divya Rani, V.V.; Menon, D.; Nair, S.; Manzoor, K.; Raina, S. Role of size scale of ZnO nanoparticles and microparticles on toxicity toward bacteria and osteoblast cancer cells. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Med. 2008, 20, 235–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olejnik, M.; Kersting, M.; Rosenkranz, N.; Loza, K.; Breisch, M.; Rostek, A.; Prymak, O.; Schürmeyer, L.; Westphal, G.; Köller, M.; et al. Cell-biological effects of zinc oxide spheres and rods from the nano- to the microscale at sub-toxic levels. Cell Biol. Toxicol. 2020, 37, 573–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pankhurst, Q.A.; Connolly, J.; Jones, S.K.; Dobson, J. Applications of magnetic nanoparticles in biomedicine. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 2003, 36, R167–R181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]

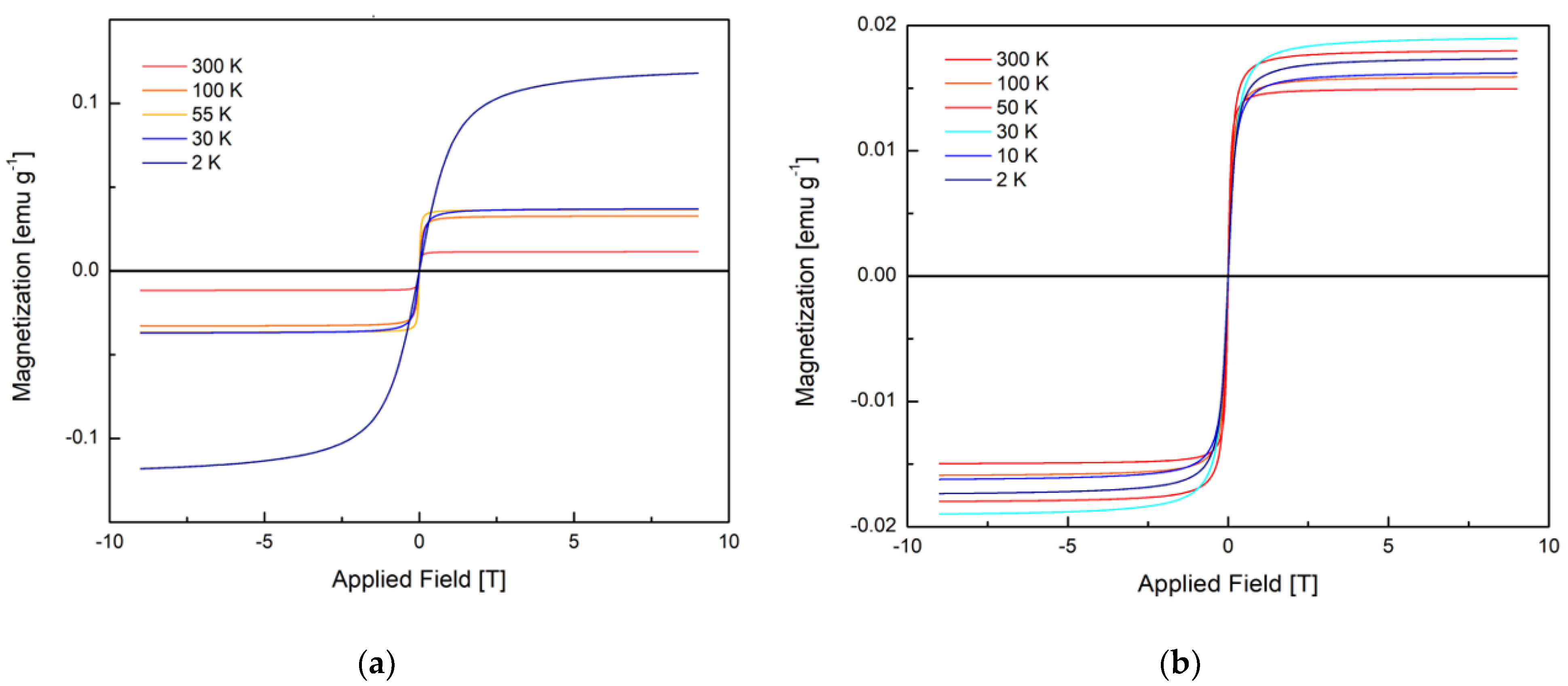
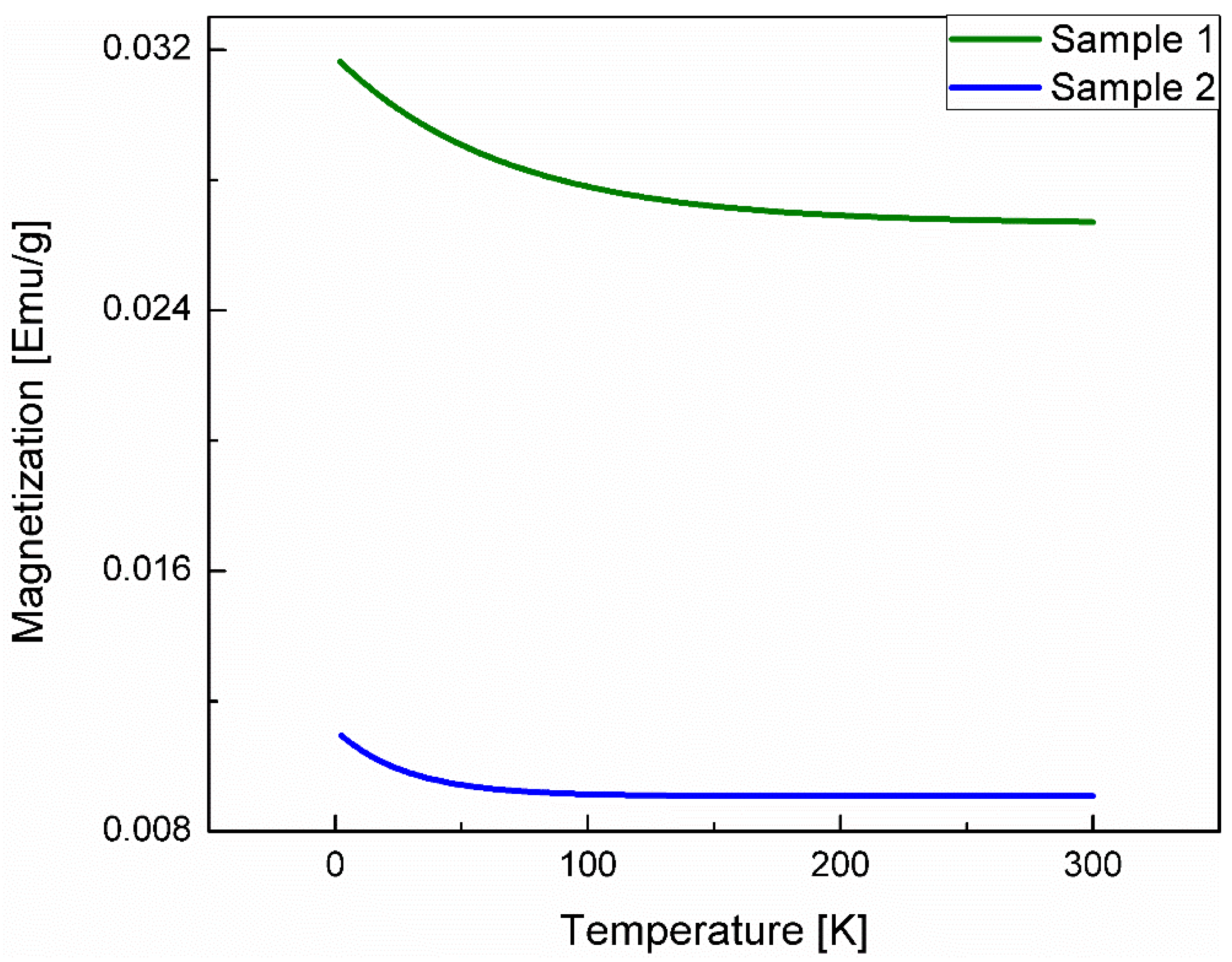
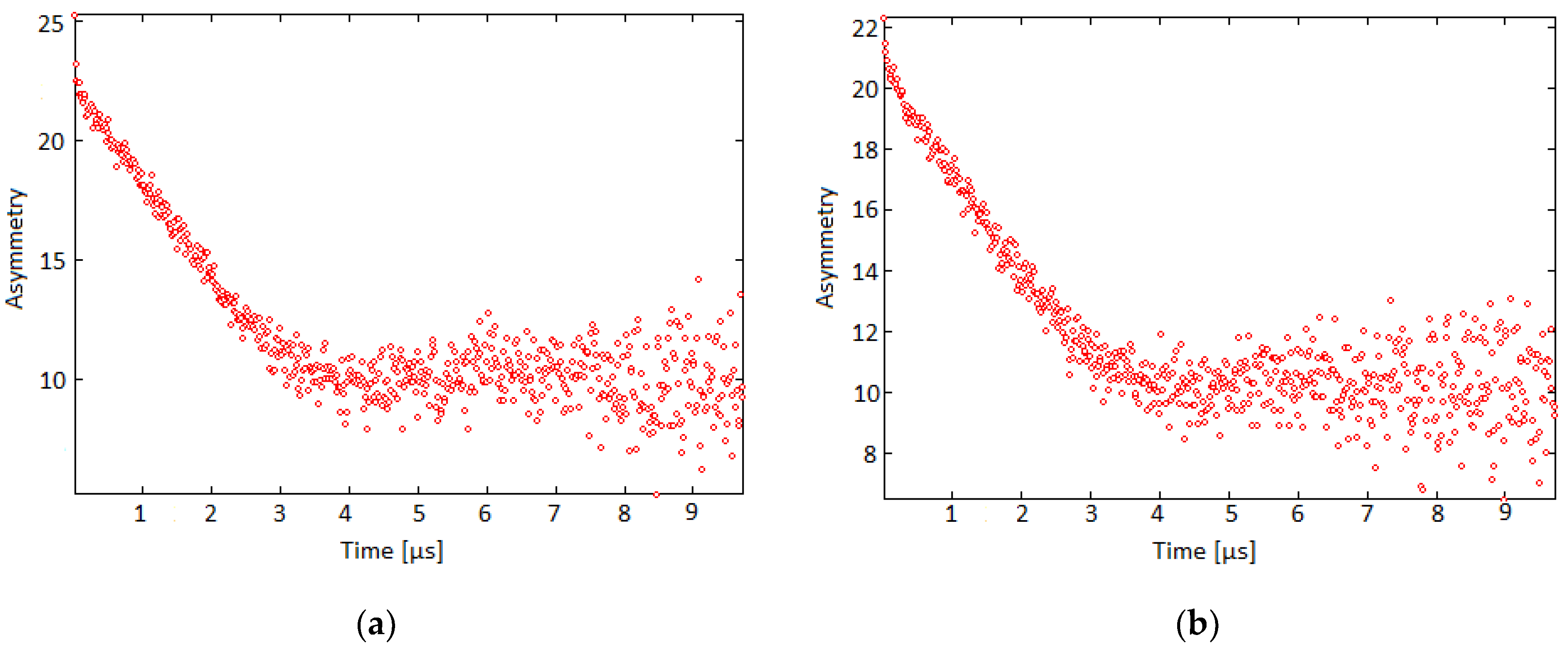

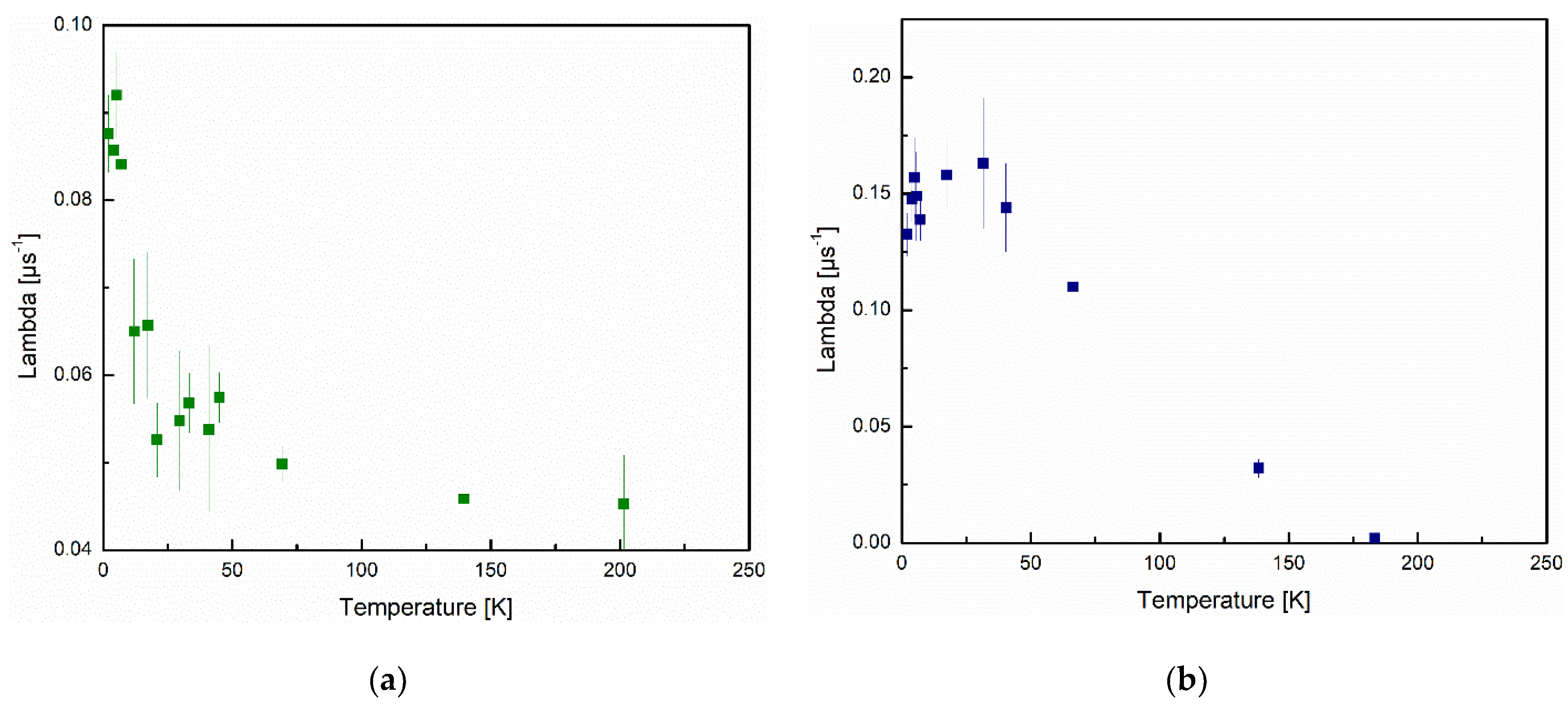
| Sample 1 | Sample 2 | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| T (K) | μ (J/T) | Ms (Emu/g) | χ2 | μ (J/T) | Ms (Emu/g) | χ2 |
| 2 | 6.5 × 10−23 | 0.124 | 0.08982983 | 2.8 × 10−22 | 0.019 | 0.01756598 |
| 10 | - | - | - | 3.7 × 10−21 | 0.018 | 0.04717651 |
| 30 | 6.5 × 10−21 | 0.038 | 0.00548285 | 1.5 × 10−21 | 0.017 | 0.01950495 |
| 55 | 4.6 × 10−20 | 0.037 | 0.00375101 | 2.2 × 10−20 | 0.016 | 0.00132365 |
| 100 | 3.7 × 10−20 | 0.033 | 0.00052324 | 1.1 × 10−20 | 0.016 | 0.06141114 |
| 300 | 2.1 × 10−19 | 0.011 | 0.00363221 | 1.2 × 10−19 | 0.015 | 0.00048272 |
| Material | v0 (GHz) | Ea/kB (K) | K (J M−3) | V (m3) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Present work | ZnO rods | 7.36, 6.40 (10−3) | 4.5, 20.8 | 153, 1235 | 4.05, 2.33 (10−25) |
| Bewley [26] | 2% Co-doped Cu | 0.7, 2.7 | 35.4, 48.4 | - | - |
| Jackson [22] | Iron nanoclusters | 833 | 51 | 2.3 × 105 | 1.2 × 10−26 |
| Frandsen [34] | Fe3O4 nanoparticle | 36 | 101, 1750 | 19, 6.1 (103) | - |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Landry, C.; Morrison, A.; Esmaeili, M.; Ghandi, K. Muon Irradiation of ZnO Rods: Superparamagnetic Nature Induced by Defects. Nanomaterials 2022, 12, 184. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano12020184
Landry C, Morrison A, Esmaeili M, Ghandi K. Muon Irradiation of ZnO Rods: Superparamagnetic Nature Induced by Defects. Nanomaterials. 2022; 12(2):184. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano12020184
Chicago/Turabian StyleLandry, Cody, Alexander Morrison, Mehdi Esmaeili, and Khashayar Ghandi. 2022. "Muon Irradiation of ZnO Rods: Superparamagnetic Nature Induced by Defects" Nanomaterials 12, no. 2: 184. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano12020184
APA StyleLandry, C., Morrison, A., Esmaeili, M., & Ghandi, K. (2022). Muon Irradiation of ZnO Rods: Superparamagnetic Nature Induced by Defects. Nanomaterials, 12(2), 184. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano12020184







