Surface Oxidation of Cu2O Nanoparticles by Adsorbed Ammonia
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
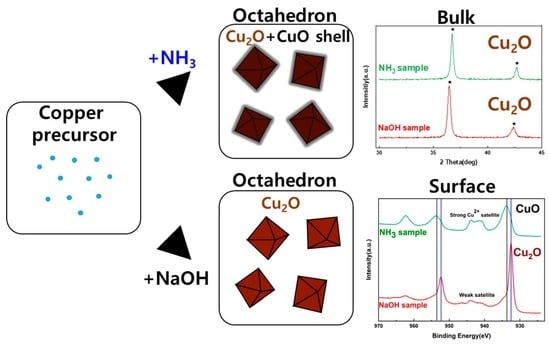
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Czubryt, M.P.; Stecy, T.; Popke, E.; Aitken, R.; Jabusch, K.; Pound, R.; Lawes, P.; Ramjiawan, B.; Pierce, G.N. N95 mask reuse in a major urban hospital: COVID-19 response process and procedure. J. Hosp. Infect. 2020, 106, 277–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seidi, F.; Deng, C.; Zhong, Y.; Liu, Y.; Huang, Y.; Li, C.; Xiao, H. Functionalized Masks: Powerful Materials against COVID-19 and Future Pandemics. Small 2021, 17, 2102453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- U.S. Food and Drug Administration. Nanotechnology Task Force Report 2020; U.S. Food and Drug Administration: VA, USA, 2020. Available online: https://www.fda.gov/media/140395/download (accessed on 1 November 2022).
- Vincent, M.; Duval, R.E.; Hartemann, P.; Engels-Deutsch, M. Contact killing and antimicrobial properties of copper. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2018, 124, 1032–1046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chatterjee, A.K.; Sarkar, R.K.; Chattopadhyay, A.P.; Aich, P.; Chakraborty, R.; Basu, T. A simple robust method for synthesis of metallic copper nanoparticles of high antibacterial potency against E. coli. Nanotechnology 2012, 23, 085103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jia, B.; Mei, Y.; Cheng, L.; Zhou, J.; Zhang, L. Preparation of copper nanoparticles coated cellulose films with antibacterial properties through one-step reduction. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2012, 4, 2897–2902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Longano, D.; Ditaranto, N.; Cioffi, N.; Di Niso, F.; Sibillano, T.; Ancona, A.; Conte, A.; Del Nobile, M.A.; Sabbatini, L.; Torsi, L. Analytical characterization of laser-generated copper nanoparticles for antibacterial composite food packaging. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2012, 403, 1179–1186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, H.-J.; Song, J.Y.; Kim, B.S. Biological synthesis of copper nanoparticles using Magnolia kobus leaf extract and their antibacterial activity. J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol. 2013, 88, 1971–1977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chatterjee, A.K.; Chakraborty, R.; Basu, T. Mechanism of antibacterial activity of copper nanoparticles. Nanotechnology 2014, 25, 135101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Din, M.I.; Arshad, F.; Hussain, Z.; Mukhtar, M. Green Adeptness in the Synthesis and Stabilization of Copper Nanoparticles: Catalytic, Antibacterial, Cytotoxicity, and Antioxidant Activities. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2017, 12, 638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Prabhu, Y.T.; Venkateswara Rao, K.; Sesha Sai, V.; Pavani, T. A facile biosynthesis of copper nanoparticles: A micro-structural and antibacterial activity investigation. J. Saudi Chem. Soc. 2017, 21, 180–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajeshkumar, S.; Menon, S.; Venkat Kumar, S.; Tambuwala, M.M.; Bakshi, H.A.; Mehta, M.; Satija, S.; Gupta, G.; Chellappan, D.K.; Thangavelu, L.; et al. Antibacterial and antioxidant potential of biosynthesized copper nanoparticles mediated through Cissus arnotiana plant extract. J. Photochem. Photobiol. B Biol. 2019, 197, 111531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bastos, C.A.P.; Faria, N.; Wills, J.; Malmberg, P.; Scheers, N.; Rees, P.; Powell, J.J. Copper nanoparticles have negligible direct antibacterial impact. NanoImpact 2020, 17, 100192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, P.; Zhu, L.; Yu, Y.; Wang, W.; Liu, G.; Lu, H. Effect of NaOH concentration on antibacterial activities of Cu nanoparticles and the antibacterial mechanism. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2020, 110, 110669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jayaramudu, T.; Varaprasad, K.; Pyarasani, R.D.; Reddy, K.K.; Akbari-Fakhrabadi, A.; Carrasco-Sánchez, V.; Amalraj, J. Hydroxypropyl methylcellulose-copper nanoparticle and its nanocomposite hydrogel films for antibacterial application. Carbohydr. Polym. 2021, 254, 117302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crisan, M.C.; Teodora, M.; Lucian, M. Copper Nanoparticles: Synthesis and Characterization, Physiology, Toxicity and Antimicrobial Applications. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonçalves, R.A.; Ku, J.W.K.; Zhang, H.; Salim, T.; Oo, G.; Zinn, A.A.; Boothroyd, C.; Tang, R.M.Y.; Gan, C.L.; Gan, Y.-H.; et al. Copper-Nanoparticle-Coated Fabrics for Rapid and Sustained Antibacterial Activity Applications. ACS Appl. Nano Mater. 2022, 5, 12876–12886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sood, A.; Arora, V.; Shah, J.; Kotnala, R.K.; Jain, T.K. Ascorbic acid-mediated synthesis and characterisation of iron oxide/gold core–shell nanoparticles. J. Exp. Nanosci. 2015, 11, 370–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ong, H.R.; Rahman Khan, M.M.; Ramli, R.; Du, Y.; Xi, S.; Yunus, R.M. Facile synthesis of copper nanoparticles in glycerol at room temperature: Formation mechanism. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 24544–24549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Marković, D.; Ašanin, J.; Nunney, T.; Radovanović, Ž.; Radoičić, M.; Mitrić, M.; Mišić, D.; Radetić, M. Broad Spectrum of Antimicrobial Activity of Cotton Fabric Modified with Oxalic Acid and CuO/Cu2O Nanoparticles. Fibers Polym. 2019, 20, 2317–2325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tam, S.K.; Ng, K.M. High-concentration copper nanoparticles synthesis process for screen-printing conductive paste on flexible substrate. J. Nanopart. Res. 2015, 17, 466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sayed, M.; Zhang, L.; Yu, J. Plasmon-induced interfacial charge-transfer transition prompts enhanced CO2 photoreduction over Cu/Cu2O octahedrons. Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 397, 125390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, C.W.; Tai, W.P.; Lee, H.S. Characteristics of Zirconia Nanoparticles with Hydrothermal Synthesis Process. Appl. Chem. Eng. 2014, 25, 564–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sōmiya, S.; Roy, R. Hydrothermal synthesis of fine oxide powders. Bull. Mater. Sci. 2000, 23, 453–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gou, L.; Murphy, C.J. Controlling the size of Cu2O nanocubes from 200 to 25 nm. J. Mater. Chem. 2004, 14, 735–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilbertson, L.M.; Albalghiti, E.M.; Fishman, Z.S.; Perreault, F.; Corredor, C.; Posner, J.D.; Elimelech, M.; Pfefferle, L.D.; Zimmerman, J.B. Shape-Dependent Surface Reactivity and Antimicrobial Activity of Nano-Cupric Oxide. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2016, 50, 3975–3984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiong, L.; Yu, H.; Nie, C.; Xiao, Y.; Zeng, Q.; Wang, G.; Wang, B.; Lv, H.; Li, Q.; Chen, S. Size-controlled synthesis of Cu2O nanoparticles: Size effect on antibacterial activity and application as a photocatalyst for highly efficient H2O2 evolution. RSC Adv. 2017, 7, 51822–51830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jung, H.-Y.; Seo, Y.; Park, H.; Huh, Y.-D. Morphology-controlled Synthesis of Octahedral-to-Rhombic Dodecahedral Cu2O Microcrystals and Shape-dependent Antibacterial Activities. Bull. Korean Chem. Soc. 2015, 36, 1828–1833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Odnevall, I.; Leygraf, C. Atmospheric Corrosion of Copper in a Rural Atmosphere. J. Electrochem. Soc. 1995, 142, 3682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- FitzGerald, K.P.; Nairn, J.; Skennerton, G.; Atrens, A. Atmospheric corrosion of copper and the colour, structure and composition of natural patinas on copper. Corros. Sci. 2006, 48, 2480–2509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meghana, S.; Kabra, P.; Chakraborty, S.; Padmavathy, N. Understanding the pathway of antibacterial activity of copper oxide nanoparticles. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 12293–12299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Wang, W.; Zhu, W. Shape Evolution and Size-Controllable Synthesis of Cu2O Octahedra and Their Morphology-Dependent Photocatalytic Properties. J. Phys. Chem. B 2006, 110, 13829–13834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ren, J.; Wang, W.; Sun, S.; Zhang, L.; Wang, L.; Chang, J. Crystallography Facet-Dependent Antibacterial Activity: The Case of Cu2O. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2011, 50, 10366–10369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Wang, H.; Yu, Y.; Tian, L.; Zhao, W.; Zhang, B. Cu2O Nanocrystals: Surfactant-Free Room-Temperature Morphology-Modulated Synthesis and Shape-Dependent Heterogeneous Organic Catalytic Activities. J. Phys. Chem. C 2011, 115, 15288–15296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, K.; Xue, D. Chemoaffinity-mediated crystallization of Cu2O: A reaction effect on crystal growth and anode property. CrystEngComm 2013, 15, 1739–1746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, M.; Ullah, M.; Iqbal, T.; Mahmood, H.; Khan, A.A.; Shafique, M.; Majid, A.; Ahmed, A.; Khan, N.A. Surfactant assisted synthesis of cuprous oxide (Cu2O) nanoparticles via solvothermal process. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. Res. 2015, 3, 16–22. [Google Scholar]
- Ethiraj, A.S.; Kang, D.J. Synthesis and characterization of CuO nanowires by a simple wet chemical method. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2012, 7, 70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Elango, M.; Deepa, M.; Subramanian, R.; Mohamed Musthafa, A. Synthesis, Characterization, and Antibacterial Activity of Polyindole/Ag–Cuo Nanocomposites by Reflux Condensation Method. Polym.-Plast. Technol. Eng. 2018, 57, 1440–1451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramis, G.; Yi, L.; Busca, G.; Turco, M.; Kotur, E.; Willey, R.J. Adsorption, Activation, and Oxidation of Ammonia over SCR Catalysts. J. Catal. 1995, 157, 523–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Liu, Y.; Gong, T.; Wang, L.; Zhao, K.; Zhou, S. Use of intermolecular hydrogen bonding to synthesize triple-shape memory supermolecular composites. RSC Adv. 2013, 3, 7048–7056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strohmeier, B.R.; Levden, D.E.; Field, R.S.; Hercules, D.M. Surface spectroscopic characterization of CuAl2O3 catalysts. J. Catal. 1985, 94, 514–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chuang, C.-C.; Shiu, J.-S.; Lin, J.-L. Interaction of hydrazine and ammonia with TiO2. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2000, 2, 2629–2633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Wang, H.; Meng, L.; Nie, X.; Qu, Z. Investigation on Cu2O Surface Reconstruction and Catalytic Performance of NH3-SCO by Experimental and DFT Studies. ACS Appl. Energy Mater. 2020, 3, 3465–3476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Epron, F.; Gauthard, F.; Pinéda, C.; Barbier, J. Catalytic Reduction of Nitrate and Nitrite on Pt–Cu/Al2O3 Catalysts in Aqueous Solution: Role of the Interaction between Copper and Platinum in the Reaction. J. Catal. 2001, 198, 309–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, L.; Zhan, W.; Liang, X.; Zhang, W.; Huang, R.; Chen, R.; Ni, H. In-situ generation Cu2O/CuO core-shell heterostructure based on copper oxide nanowires with enhanced visible-light photocatalytic antibacterial activity. Ceram. Int. 2022, 48, 22018–22030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, D.; Xue, J.; Wu, L.; Zhou, W.; Zhang, Y.; Li, X. Photocatalytic performance enhancement of CuO/Cu2O heterostructures for photodegradation of organic dyes: Effects of CuO morphology. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2017, 211, 199–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]







| Sample | Control | NaOH | NH3 | NaOH 80 °C |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Colony count (average) | 706.8 | 54.3 | 466.3 | 465.5 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lee, S.; Jang, J.W.; Ryu, Y.B. Surface Oxidation of Cu2O Nanoparticles by Adsorbed Ammonia. Nanomaterials 2022, 12, 4242. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano12234242
Lee S, Jang JW, Ryu YB. Surface Oxidation of Cu2O Nanoparticles by Adsorbed Ammonia. Nanomaterials. 2022; 12(23):4242. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano12234242
Chicago/Turabian StyleLee, Siwoo, Ji Won Jang, and Young Bok Ryu. 2022. "Surface Oxidation of Cu2O Nanoparticles by Adsorbed Ammonia" Nanomaterials 12, no. 23: 4242. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano12234242
APA StyleLee, S., Jang, J. W., & Ryu, Y. B. (2022). Surface Oxidation of Cu2O Nanoparticles by Adsorbed Ammonia. Nanomaterials, 12(23), 4242. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano12234242